ICF CORE SETS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS
|
|
|
- Beatrix Austin
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Rehabil Med 2004; Suppl. 44: ICF CORE SETS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS Karsten Dreinhöfer, 1 Gerold Stucki, 2,3 Thomas Ewert, 2 Erika Huber, 5 Gerold Ebenbichler, 6 Christoph Gutenbrunner, 7 Nenad Kostanjsek 4 and Alarcos Cieza 3 From the 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Rehabilitationskrankenhaus, Ulm University, 2 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich, 3 ICF Research Branch, WHO FIC Collaborating Center (DIMDI), IMBK, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich, Germany, 4 Classification, Assessment, Surveys and Terminology Team, World Health Organization, Geneva, 5 Swiss Association of Physical Therapy, Sursee, Switzerland, 6 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, University of Vienna, Austria 7 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Medical School Hannover, Germany Objective: To report on the results of the consensus process integrating evidence from preliminary studies to develop the first version of a Comprehensive ICF Core Set and a Brief ICF Core Set for osteoarthritis. Methods: A formal decision-making and consensus process integrating evidence gathered from preliminary studies was followed. Preliminary studies included a Delphi exercise, a systematic review, and an empirical data collection. After training in the ICF and based on these preliminary studies relevant ICF categories were identified in a formal consensus process by international experts from different backgrounds. Results: The preliminary studies identified a set of 388 ICF categories at the second, third, and fourth ICF levels with 144 categories on body functions, 49onbody structures; 165 on activities and participation, and 43 on environmental factors. Seventeen experts from 7 different countries attended the consensus conference on osteoarthritis. Altogether 55 second-level categories were included in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set with 13 categories from the component body functions, 6 from body structures, 19 from activities and participation, and 17 from environmental factors. The Brief ICF Core Set included a total of 13 second-level categories (3 on body functions, 3 on body structures, 3onactivities and participation, and 4 on environmental factors). Conclusion: A formal consensus process integrating evidence and expert opinion based on the ICF framework and classification led to the definition of ICF Core Sets for osteoarthritis. Both the Comprehensive ICF Core Set and the Brief ICF Core Set were defined. Key words: osteoarthritis, musculoskeletal diseases, outcome assessment, quality of life, ICF. J Rehabil Med 2004; suppl. 44: Correspondence address: Gerold Stucki, Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, University of Munich, DE Munich, Germany. Tel: Fax: [email protected] INTRODUCTION Osteoarthritis (OA) is amongst the 3 most disabling conditions having a remarkable public health impact of disability adjusted life years (DALYs) in the developed countries in 1990 (1). In 2001, the prevalence of self-reported arthritis or chronic joint symptoms among US adults was 33%, of physician-diagnosed arthritis 22.4% (2). Because of its high prevalence in the increasing population of elderly people an increase up to DALYs is estimated under the present conditions for 2020 (3). Direct and indirect costs for OA of the knee and hip in the US in 1994 were 12.9 billion US dollars (4). OA can occur in all joints, but most frequently in the interphalangeal joints, the knee and hip joints. Relatively little is known of the natural history of OA. The disease progress might remain static for a period of time or progress rapidly. A variety of symptomatic conservative therapies are available for OA, including drugs and physical therapy, but they only achieve modest improvements in pain and other further limitations in functioning. In advanced disease, surgery is the only effective intervention and especially total hip and knee replacement has shown its ability to restore function and quality of life (5). Research and clinical management of patients with OA relies on the sound measurement of pain and functional limitations. The OMERACT (Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials) group has recommended 4 domains to be evaluated: pain, physical function, joint imaging, and patient global assessment (6). Previous studies showed that hip joint space narrowing was most predictive of hip pain. Progression of hip OA could be defined by a change in joint space narrowing, and narrowing correlated with changes in clinical status (7). There is, however, discordance between radiographs and reports on pain (8). Ten percent of patients with normal radiographs report pain, while only 40 70% of those with advanced radiographic abnormalities complain about pain (9). Therefore, the OMERACT group advised to always include the domains pain and physical function in phase-iii clinical trials and described stiffness as an important optional domain (6). The OMERACT and the 5th WHO/ILAR Task Force (World Health Organisation/International League Against Rheumatism) (10, 11) recommended the use of condition-specific health-status 2004 Taylor & Francis. ISSN DOI /
2 76 K. Dreinhöfer et al. measures including the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) (12) and the Lequesne- Algofunctional Index (13) to measure these domains in clinical research and practice. In the measurement of outcomes in OA it is desirable to include both a generic instrument and a condition-specific instrument (14, 15). These generic health status instruments (SF-36, EQ5D, NHP, MFA) assess domains relevant to patients with OA including dimensions of social function, emotional function, role function, pain and physical function. Condition-specific measures typically cover only selected aspects of the entire patient experience associated with OA. These measures also vary in the concepts included (2, 16). However, the patient experience of functioning and health goes beyond pain, stiffness and functional limitation with a focus on physical function. Also in contrast to the OMERACT perspective, which focuses on functioning and health as an outcome of the disease process to be evaluated in phase-iii trials, functioning and health is not merely an outcome, but the starting point for assessing functioning and health of patients, e.g. in the context of rehabilitation. With the approval of the new International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF, formerly ICIDH-2 (17, 18) we can now rely on a globally agreed framework and classification to define the typical spectrum of problems in functioning of patients with OA. For practical purposes and in line with the concept of conditionspecific health status measures it would thus seem most helpful to link specific conditions or diseases to salient ICF categories of functioning (19). Such generally-agreed-on lists of ICF categories can serve as Brief ICF Core Set to be rated in all patients included in a clinical study with OA or as Comprehensive ICF Core Set to guide multidisciplinary assessments in patients with OA. The objective of this paper is to report on the results of the consensus process integrating evidence from preliminary studies to develop the first version of the ICF Core Sets for OA, the Comprehensive ICF Core Set and the Brief ICF Core Set. METHODS The development of the ICF Core Sets for OA involved a formal decision-making and consensus process integrating evidence gathered from preliminary studies including a Delphi exercise (20), a systematic review (21) and an empirical data collection, using the ICF checklist (22). After training in the ICF and based on these preliminary studies relevant ICF categories were identified in a formal consensus process by international experts from different backgrounds. Seventeen experts from 7 different countries attended the consensus process for OA. The professional background of the experts (13 physicians with various sub-specializations and 4 physical therapists) covered the wide spectrum of limitations in functioning that occurs in patients with OA. The decision-making process for OA involved 3 working groups with 5 6 experts each. The process was facilitated by the condition co-ordinator for OA (KD) and the 3 working-group leaders (EH, GE, CG). The tables on the preliminary studies presented to the participants included 388 (144 on body functions, 49 on body structures, 165 on activities and participation, and 43 on environmental factors) ICF categories at the second, third, and fourth levels. Table I. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)-categories of the component body functions included in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set for osteoarthritis ICF code b130 b134 b152 b280 b710 b715 b720 b730 b735 b740 b760 b770 b780 Energy and drive functions Sleep functions Emotional functions Sensation of pain Mobility of joint functions Stability of joint functions Mobility of bone functions Muscle power functions Muscle tone functions Muscle endurance functions Control of voluntary movement functions Gait pattern functions Sensations related to muscles and movement functions RESULTS Tables I IV show the second-level ICF categories included in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set. Table V shows the secondlevel ICF categories included in the Brief ICF Core Set, as well as the rank order by component allotted to the selected ICF categories. The total number of categories in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set is 55 and the total number of categories included in the Brief ICF Core Set is 13. No categories at the third and fourth levels were included in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set or in the Brief ICF Core Set. Table VI summarizes the number and percentage of selected categories on the second level in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set and the Brief ICF Core Set. Comprehensive ICF Core Set The 55 categories of the Comprehensive ICF Core Set are made up of 13 categories from the component body functions, 6 from the component body structures, 19 from the component activities and participation, and 17 from the component environmental factors. The 13 categories of the component body functions represent 11% of the total number of ICF categories at the second level in this component. Most of the body-functions categories belong to chapter 7 neuromusculoskeletal and movement-related functions (9 categories). Chapter 1 mental functions is represented by 3 categories, and chapter 2 sensory functions and pain by 1 category. Table II. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)-categories of the component body structures included in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set for osteoarthritis ICF code s720 s730 s740 s750 s770 s799 Structure of shoulder region Structure of upper extremity Structure of pelvic region Structure of lower extremity Additional musculoskeletal structures related to movement Structures related to movement, unspecified
3 ICF Core Sets for osteoarthritis 77 Table III. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)-categories of the component activities and participation included in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set for osteoarthritis Table IV. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)-categories of the component environmental factors included in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set for osteoarthritis ICF code d410 d415 d430 d440 d445 d450 d455 d470 d475 d510 d530 d540 d620 d640 d660 d770 d850 d910 d920 Changing basic body position Maintaining a body position Lifting and carrying objects Fine hand use Hand and arm use Walking Moving around Using transportation Driving Washing oneself Toileting Dressing Acquisition of goods and services Doing housework Assisting others Intimate relationships Remunerative employment Community Life Recreation and leisure ICF code e110 e115 e120 e135 e150 e155 e225 e310 e320 e340 e355 e410 e450 e460 e540 e575 e580 Products or substances for personal consumption Products and technology for personal use in daily living Products and technology for personal indoor and outdoor mobility and transportation Products and technology for employment Design, construction and building products and technology of buildings for public use Design, construction and building products and technology of buildings for private use Climate Immediate family Friends Personal care providers and personal assistants Health professionals Individual attitudes of immediate family members Individual attitudes of health professionals Societal attitudes Transportation services, systems and policies General social support services, systems and policies Health services, systems and policies The 6 categories of the component body structures represent 11% of the total number of ICF categories at the second level in this component. All of them belong to chapter 7 structures related to movement. The 19 categories of the component activities and participation represent 16% of the total number of ICF categories at the second level in this component. Most of the activities and participation categories belong to chapter 4 mobility (9 categories). Chapter 5 self care as well as chapter 6 domestic life are represented by 3 categories, chapter 9 community, social and civic life by 2 categories, chapter 7 interpersonal interactions and relationships, and chapter 8 major life areas by 1 category, respectively. All 5 chapters of the component environmental factors are represented in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set for OA. The 17 categories represent 23% of the total number of ICF categories at the second level in this component. Most of the environmental-factors categories belong to chapter 1 products and technology (6 categories) and chapter 3 support and relationships (4 categories). Chapter 4 attitudes and chapter 5 services, systems and policies are represented by 3 categories, respectively. Chapter 2 natural environment and human-made changes to environment is represented by the category e225 climate. Brief ICF Core Set The Brief ICF Core Set includes a total of 13 second-level categories representing 23% of all categories that were chosen for the Comprehensive ICF Core Set. Three categories from the component body functions were selected, representing 21% of the Comprehensive ICF Core Set, in addition 3 (50%) from body structures, 3 (16%) from activities and participation, and 4 (24%) from environmental factors. DISCUSSION The formal consensus process integrating evidence from preliminary studies and expert knowledge at the third ICF Core Sets conference led to the definition of the Brief ICF Core Set and the Comprehensive ICF Core Set for multidisciplinary assessment. One challenge during the experts discussion and consensus process was to comprehensively cover the wide spectrum of OA-related functional limitations, body structure changes, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. During the selection process of the categories, the experts were strongly encouraged to identify additional ICF categories of importance not provided in the data from the preliminary studies. Another challenge was to focus on the diagnosis OA and not to pay attention to the related co-morbidities and complications under consideration at all possible stages during the disease. In the consensus process the varying spectrum of limitations in functioning in OA was addressed. In the early stage of the condition the burden may be limited to minor and only sporadic symptoms. In the later stages patients may experience a wide spectrum of functional impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions in addition to now often more severe symptoms. Since ICF Core Sets need to capture the experience of all patients with OA independent of the stage, the joint involved or age, the participants included all categories that were considered relevant for patients with OA at some point. This will allow us to follow patients over time and to detect changes in the pattern of problems over time. If patients are scheduled for hip or knee replacement surgery the disease is already in a late stage. At that time nearly all patients suffer from pain. More then two-third have severe
4 78 K. Dreinhöfer et al. Table V. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)-categories included in the Brief ICF Core Set for osteoarthritis. The categories per component are listed according to the conceded rank order ICF component Rank order ICF code Body functions 1 b280 Sensation of pain 2 b710 Mobility of joint functions 3 b730 Muscle power functions Body structures 1 s750 Structure of lower extremity 2 s730 Structure of upper extremity 3 s770 Additional musculoskeletal structures related to movement Activities and participation 1 d450 Walking 2 d540 Dressing 4 d445 Hand and arm use Environmental factors 1 e310 Immediate family 2 e115 Products and technology for personal use in daily living 4 e580 Health services, systems and policies 5 e150 Design, construction and building products and technology of buildings for public use Table VI. Number of relevant International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)-categories on the second level for osteoarthritis in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set and the Brief ICF Core Set and percentage of the overall ICF categories Components Second level ICF categories Comprehensive ICF Core Set Brief ICF Core Set Body functions (11%) 3 (3%) Body structures 56 6 (11%) 3 (5%) Activities and (16%) 3 (3%) participation Environmental (23%) 4 (5%) factors Total pain when walking. Many patients in this advanced stage report pain at night (23), 1 out of 3 arthritis patients suffers from sleep disturbances (24). Half of the patients have walked in the past 2 weeks less then 1 block, every fourth is only walking in the room. Every second patient needs assistance with walking, about one-third needs assistance with housework or shopping (23). In addition, depression is common in persons with OA (25). All these aspects are represented in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set. In the Brief ICF Core Set sensation of pain and walking but not emotional functions, sleep, doing housework, and acquisition of goods and services are included. Also, according to 1 study, patients may have a high preference regarding the importance of certain problems. For example, public transportation, unequal limb length, concerns about falling, the need to use walking aids, and difficulty with recreational activities may be as important as the problems mentioned above (26). Again, these aspects are represented in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set but not in the Brief ICF Core Set. Two main concerns, concerns about falling and the loss of independence, are only represented indirectly by categories reflecting limitations in moving around, using transportation and the environmental factors, personal care providers and personal assistants, individual attitudes of immediate family members, individual attitudes of health professionals, and societal attitudes. This clearly indicates the need to use the Comprehensive ICF Core Set in the assessment and follow-up of patients considering or undergoing joint replacement surgery. As could be expected for a musculoskeletal condition, neuromusculoskeletal- and movement-related functions are covered in great depth at the body-functions level. This is reflected by the fact that 9 of the 11 top-ranked categories in this component belong to chapter 7 neuromusculoskeletal and movement-related functions. Consistent with the results of the Delphi (20) and the checklist study (22), sensation of pain, mobility of joint functions, and muscle power functions were considered the most important categories and were included in the Brief ICF Core Set. Consistent with the definition of OA and their task to focus on the disease and not on the co-morbidity, the experts selected at the body-structures level only categories belonging to structures related to movement. All second-level categories of this domain, except 2 related to the vertebra, were selected for the comprehensive assessment. Since degenerative, changes in OA also occur in the spine, some experts opted for including structures of head and neck region and structure of trunk. However, it was decided to limit the definition of OA to joints of the extremities. Limitations and restrictions in activity and participation may indeed be most relevant to patients with OA. This is reflected by the fact that this component is represented by 19 categories, as compared with the 13 body functions considered relevant. The areas that are covered represent key issues for patients with OA, including 9 categories of the domain mobility. These comprise active changes of body position, but also using transportation and driving. Beside the commonly reflected activities such as lifting and carrying objects, walking, doing housework and selfcare (washing oneself, toileting, dressing), recreation and leisure, intimate relationships and remunerative employment
5 ICF Core Sets for osteoarthritis 79 were included. While these last categories have not been addressed in most of the prior assessments, they are of great importance at least for a subgroup of patients (27). Three of the 5 highest ranked categories in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set belong to the domain self-care. However, the experts decided to include only 1 of these in the Brief ICF Core Set, and so they selected hand and arm use since this category is necessary for most of self-care and domestic life-activities. It is significant that 17 categories representing 31% of the categories of the Comprehensive ICF Core Set belong to the component environmental factors. Products and technology as well as support and relationships and attitudes are highly important to patients with OA because they can serve as either a barrier or a facilitator. While products and technology for personal use in daily living (walking aids, etc.) are seen as the latter, design, construction and building products and technology of buildings for public use often impress as the former; immediate family, friends, and societal attitudes can also be either. Cultural differences will have a serious impact on the applicability of some of the individual categories in different countries. The wide variety in total hip replacement rates, even in OECD countries (28), reflects the different health services, systems and policies. However, as the developing world will account for a huge amount of the expected increase in OA prevalence globally, activities for improvement of OA-related health services in the individual countries are disparately required. While the category health professionals obtained rank 3, it was still not included in the Brief ICF Core Set. The experts discussed the greater importance of the health services, systems and policies as compared with the individual health professional. In addition, the importance of products and technology as well as support and relationships was expressed by the selection. The breadth of ICF chapters contained in the Comprehensive ICF Core Set reflects the important and complex impairments, limitations and restrictions of activity and participation involved, as well as the numerous interactions with environmental factors. Although the participants were provided with the option to define the categories not only on the second, but possibly also on the third or fourth levels of the classification, it was decided to keep the definition on the second level. This allowed us to limit the ICF Core Sets to a certain number. However, the need for further specification of some second-level categories at least for subsets of patients may be necessary. Also, the ICF may not represent into enough detail some aspects of body functions considered relevant in OA. For example, problems in muscle activation, in muscle co-ordination, and automatic muscle responses are not adequately represented, e.g. muscle power functions. Similarly, a differentiation of pain to specifically address pain at night instead of referring to pain and sleep functions to represent this problem would be useful. It is important to note that the ICF does not generally address the issue of time (e.g. rest pain, night pain, pain with activity, etc.). The time perspective needs to be addressed in the measurement of a specific category such as pain. One limitation of this study is the representation of the experts. The results of any consensus process may differ with different groups of experts. Since most members of the panels live in the Western world, some cultural aspects might have been overlooked or might be under-represented in the ICF Core Sets. As an example, OA of the hip and knee might severely affect the ability to participate in religious ceremonies in some parts of the world. However, the experts did not prioritise this category. This emphasizes the importance of the extensive validation of this first version of the ICF Core Sets from the perspective of different professions and in different countries. The first version of the ICF Core Sets will also be tested in the view of patients and in different clinical settings. It is important to note that this first version of the ICF Core Sets is only recommended for validation or pilot studies. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank the Bone and Joint Decade, the European League against Rheumatism (EULAR), and the EU Health Monitor Project Group for their support of the project. We are most grateful for the contributions made by the following experts attending the conference: Michael Berliner, Abdulla Eyadah, Balint Geza, Juan Manuel G. Guzman, Michael Harder, Khelaf Kerkour, Otto Knüsel, Hannelore Kremser-Rüssel, Lajos Kullmann, Marta Roa, Hans Schwarz, Walter Swoboda, Edina Sziraki and Beat Wunderlin. REFERENCES 1. Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global health statistics. Global Burden of Disease and Injury Series Vol II. Harvard School of Public Health, World Bank, and World Health Organization. Geneva, Prevalence of self-reported arthritis or chronic joint symptoms among adults United States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2002; 51: Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause : Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 1997; 349: Yelin E. The economics of osteoarthritis. New York: Oxford University Press; 1998, p Murray D. Surgery and joint replacement for joint disease. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 1998; 281: Bellamy N, Kirwan J, Boers M, Brooks P, Strand V, Tugwell P, et al. Recommendations for a core set of outcome measures for future phase III clinical trials in knee, hip, and hand osteoarthritis. Consensus development at OMERACT III. J Rheumatol 1997; 24: Dougados M, Gueguen A, Nguyen M, Berdah L, Lequesne M, Mazieres B, et al. Radiological progression of hip osteoarthritis: definition, risk factors and correlations with clinical status. Ann Rheum Dis 1996; 55: Nilsdotter AK, Aurell Y, Siosteen AK, Lohmander LS, Roos HP. Radiographic stage of osteoarthritis or sex of the patient does not predict one year outcome after total hip arthroplasty. Ann Rheum Dis 2001; 60: Creamer P, Hochberg MC. Why does osteoarthritis of the knee hurt sometimes? Br J Rheumatol 1997; 36 37: Lequesne M. ILAR guidelines for testing slow acting drugs in osteoarthritis (SYSADOAs). Rev Esp Rheumatol 1993; 20: Bellamy N. Outcome measurement in osteoarthritis clinical trials. J Rheumatol Suppl 1995; 43: Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to anti-
6 80 K. Dreinhöfer et al. rheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 1988; 15: Lequesne MG. The algofunctional indices for hip and knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 1997; 24 24: Dieppe PA. Recommended methodology for assessing the progression of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee joints. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1995; 3 2: Hawker G, Melfi C, Paul J, Green R, Bombardier C. Comparison of a generic (SF-36) and a disease specific (WOMAC) (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) instrument in the measurement of outcomes after knee replacement surgery. J Rheumatol 1995; 22: Weigl M, Cieza A, Harder M, Geyh S, Amann E, Kostanjsek N, Stucki G. Linking osteoarthritis-specific health-status measures to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF). Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2003; 11: ICF formerly ICIDH World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: ICF. Geneva: WHO; Stucki G, Cieza A, Ewert T, Kostanjsek N, Chatterji S, Bedirhan Uestuen T. Application of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) in clinical practice. Disabil Rehabil 2002; 24: Weigl M, Cieza A, Andersen A, Kollerits B, Amann E, Füssl M, Stucki G. Identification of the most relevant ICF categories in patients with chronic health conditions: a Delphi exercise. J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: (suppl 44): Brockow T, Cieza A, Kuhlow H, Sigl T, Franke T, Harder M, Stucki G. Identifying the concepts contained in outcome measures of clinical trials on musculoskeletal disorders and chronic widespread pain Using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health as a reference. J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: (suppl 44): Ewert T, Fuessl M, Cieza A, Andersen A, Chatterji S, Kostanjsek N, Stucki G. Indentification of the most common patient problems in patients with chronic conditions using the ICF checklist. J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: (suppl 44): Holtzman J, Saleh K, Kane R. Gender differences in functional status and pain in a Medicare population undergoing elective total hip arthroplasty. Med Care 2002; 40: Jordan JM, Bernard SL, Callahan LF, Kincade JE, Konrad TR, DeFriese GH. Self-reported arthritis-related disruptions in sleep and daily life and the use of medical, complementary, and self-care strategies for arthritis: the National Survey of Self-care and Aging. Arch Fam Med 2000; 9: Frank RG HK. Mood disorders. Atlanta, Georgia: American College of Rheumatology; Wright JG, Young NL. The patient-specific index: asking patients what they want. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1997; 79: Wright JG, Rudicel S, Feinstein AR. Ask patients what they want. Evaluation of individual complaints before total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1994; 76: Merx H, Dreinhofer K, Schrader P, Sturmer T, Puhl W, Gunther KP, Brenner H. International variation in hip replacement rates. Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62:
The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Core Sets for rheumatoid arthritis: a way to specify functioning
 ii40 REPORT The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Core Sets for rheumatoid arthritis: a way to specify functioning G Stucki, A Cieza... Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63(Suppl
ii40 REPORT The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Core Sets for rheumatoid arthritis: a way to specify functioning G Stucki, A Cieza... Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63(Suppl
ICF CORE SETS FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 J Rehabil Med 2004; Suppl. 44: 87 93 ICF CORE SETS FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Gerold Stucki, 1,2 Alarcos Cieza, 2 Szilvia Geyh, 2 Linamara Battistella, 4,5 Jill Lloyd, 6 Deborah Symmons, 7 Nenad Kostanjsek
J Rehabil Med 2004; Suppl. 44: 87 93 ICF CORE SETS FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Gerold Stucki, 1,2 Alarcos Cieza, 2 Szilvia Geyh, 2 Linamara Battistella, 4,5 Jill Lloyd, 6 Deborah Symmons, 7 Nenad Kostanjsek
Body Functions and Organisational Success - The ICF Core Set
 J Rehabil Med 2004; Suppl. 44: 81 86 ICF CORE SETS FOR OSTEOPOROSIS Alarcos Cieza, 1 Susanne R. Schwarzkopf, 2 Tanja Sigl, 2 Gerold Stucki, 1,2 John Melvin, 3 Thomas Stoll, 4 Anthony D. Woolf, 5 Nenad
J Rehabil Med 2004; Suppl. 44: 81 86 ICF CORE SETS FOR OSTEOPOROSIS Alarcos Cieza, 1 Susanne R. Schwarzkopf, 2 Tanja Sigl, 2 Gerold Stucki, 1,2 John Melvin, 3 Thomas Stoll, 4 Anthony D. Woolf, 5 Nenad
A User's Guide to: Rheumatoid and Arthritis Outcome Score RAOS
 RAOS User's Guide 2004 A User's Guide to: Rheumatoid and Arthritis Outcome Score RAOS RAOS is developed as an instrument to assess the patients opinion about their hips/knees and/or feet and associated
RAOS User's Guide 2004 A User's Guide to: Rheumatoid and Arthritis Outcome Score RAOS RAOS is developed as an instrument to assess the patients opinion about their hips/knees and/or feet and associated
LINKING HEALTH-STATUS MEASUREMENTS TO THE INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF FUNCTIONING, DISABILITY AND HEALTH
 J Rehabil Med 2002; 34: 205 210 SPECIAL REPORT LINKING HEALTH-STATUS MEASUREMENTS TO THE INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF FUNCTIONING, DISABILITY AND HEALTH Alarcos Cieza, 1 Thomas Brockow, 2 Thomas Ewert,
J Rehabil Med 2002; 34: 205 210 SPECIAL REPORT LINKING HEALTH-STATUS MEASUREMENTS TO THE INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF FUNCTIONING, DISABILITY AND HEALTH Alarcos Cieza, 1 Thomas Brockow, 2 Thomas Ewert,
MINERVA MEDICA COPYRIGHT
 EUR J PHYS REHABIL MED 2008;44:329-42 How to apply the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) for rehabilitation management in clinical practice Rehabilitation aims to
EUR J PHYS REHABIL MED 2008;44:329-42 How to apply the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) for rehabilitation management in clinical practice Rehabilitation aims to
Knee Pain/Osteoarthritis: Occupational Therapy Approaches
 Knee Pain/Osteoarthritis: Occupational Therapy Approaches Susan Murphy ScD OTR Associate Professor, Physical Medicine & Rehab Dept, University of Michigan Research Health Science Specialist VA Ann Arbor
Knee Pain/Osteoarthritis: Occupational Therapy Approaches Susan Murphy ScD OTR Associate Professor, Physical Medicine & Rehab Dept, University of Michigan Research Health Science Specialist VA Ann Arbor
A pilot study of the primary care management of knee osteoarthritis in the Northern States of Malaysia.
 A pilot study of the primary care management of knee osteoarthritis in the Northern States of Malaysia. Arshad A and Rashid R Putra Specialist Centre, Alor Setar, Kedah, Malaysia ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A pilot study of the primary care management of knee osteoarthritis in the Northern States of Malaysia. Arshad A and Rashid R Putra Specialist Centre, Alor Setar, Kedah, Malaysia ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE
THE ICF: AN OVERVIEW INTRODUCING THE ICF. Aims. Underlying principles
 THE ICF: AN OVERVIEW INTRODUCING THE ICF The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) is a framework for describing and organising information on functioning and disability.
THE ICF: AN OVERVIEW INTRODUCING THE ICF The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) is a framework for describing and organising information on functioning and disability.
ICF CORE SETS FOR OBESITY
 J Rehabil Med 2004; Suppl. 44: 107 113 ICF CORE SETS FOR OBESITY Armin Stucki, 1 Peter Daansen, 2 Michaela Fuessl, 3,4 Alarcos Cieza, 4 Erika Huber, 5 Richard Atkinson, 6 Nenad Kostanjsek, 7 Gerold Stucki
J Rehabil Med 2004; Suppl. 44: 107 113 ICF CORE SETS FOR OBESITY Armin Stucki, 1 Peter Daansen, 2 Michaela Fuessl, 3,4 Alarcos Cieza, 4 Erika Huber, 5 Richard Atkinson, 6 Nenad Kostanjsek, 7 Gerold Stucki
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
PT, OT, and SLP Services and the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) Mapping Therapy Goals to the ICF
 PT, OT, and SLP Services and the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) Mapping Therapy Goals to the ICF Disclaimer Contents of this presentation are for educational
PT, OT, and SLP Services and the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) Mapping Therapy Goals to the ICF Disclaimer Contents of this presentation are for educational
HEALTH CARE COSTS 11
 2 Health Care Costs Chronic health problems account for a substantial part of health care costs. Annually, three diseases, cardiovascular disease (including stroke), cancer, and diabetes, make up about
2 Health Care Costs Chronic health problems account for a substantial part of health care costs. Annually, three diseases, cardiovascular disease (including stroke), cancer, and diabetes, make up about
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS
 16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
Focus on the ICF. Creating an Interface Between the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health and Physical Therapist Practice
 Focus on the ICF Creating an Interface Between the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health and Physical Therapist Practice Reuben Escorpizo, Gerold Stucki, Alarcos Cieza, Kandace
Focus on the ICF Creating an Interface Between the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health and Physical Therapist Practice Reuben Escorpizo, Gerold Stucki, Alarcos Cieza, Kandace
MN Community Measurement Total Knee Replacement Impact and Recommendation Document June 2010
 MN Community Measurement Total Knee Replacement Impact and Recommendation Document June 2010 Degree of Impact Relevance to Consumers, Employers and Payers Annually there are over 500,000 total knee replacement
MN Community Measurement Total Knee Replacement Impact and Recommendation Document June 2010 Degree of Impact Relevance to Consumers, Employers and Payers Annually there are over 500,000 total knee replacement
ICF CHECKLIST Version 2.1a, Clinician Form for International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health
 ICF CHECKLIST Version 2.1a, Clinician Form for International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health This is a checklist of major categories of the International Classification of Functioning,
ICF CHECKLIST Version 2.1a, Clinician Form for International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health This is a checklist of major categories of the International Classification of Functioning,
Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis
 Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis Arthritis Foundation Pacific Region, Nevada Office Presented by: Crystal Schulz, MPH Community Development Manager Arthritis Foundation Improving lives through leadership
Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis Arthritis Foundation Pacific Region, Nevada Office Presented by: Crystal Schulz, MPH Community Development Manager Arthritis Foundation Improving lives through leadership
How To Cover Occupational Therapy
 Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
Integra. MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Address: Orthopaedic Specialty Clinics located at First Clinic, Etoile Center, King Road, North of Jeddah. Tel: 02-6922298, Fax: 02-6925387.
 Orthopaedic Specialty Clinics Group Practice Group Practice: is the practice of health care by an association of medical professionals who share premises and other resources. Our Orthopaedic Group Practice
Orthopaedic Specialty Clinics Group Practice Group Practice: is the practice of health care by an association of medical professionals who share premises and other resources. Our Orthopaedic Group Practice
X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating
X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating
A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course
 2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard.
 world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
The type of cancer Your specific treatment Your pre training levels before diagnose (your current strength and fitness levels)
 Exercise and Breast Cancer: Things you can do! Cancer within the fire service is one of the most dangerous threats to our firefighter s health & wellness. According to the latest studies firefighters are
Exercise and Breast Cancer: Things you can do! Cancer within the fire service is one of the most dangerous threats to our firefighter s health & wellness. According to the latest studies firefighters are
Extended Abstract. Evaluation of satisfaction with treatment for chronic pain in Canada. Marguerite L. Sagna, Ph.D. and Donald Schopflocher, Ph.D.
 Extended Abstract Evaluation of satisfaction with treatment for chronic pain in Canada Marguerite L. Sagna, Ph.D. and Donald Schopflocher, Ph.D. University of Alberta Introduction For millions of people
Extended Abstract Evaluation of satisfaction with treatment for chronic pain in Canada Marguerite L. Sagna, Ph.D. and Donald Schopflocher, Ph.D. University of Alberta Introduction For millions of people
THE TESTING AND VALIDATION OF THE ICF CORE SETS FOR THE ACUTE HOSPITAL AND POST-ACUTE REHABILITATION FACILITIES TOWARDS BRIEF VERSIONS
 J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 81 180 THE TESTING AND VALIDATION OF THE ICF CORE SETS FOR THE ACUTE HOSPITAL AND POST-ACUTE REHABILITATION FACILITIES TOWARDS BRIEF VERSIONS Eva Grill 1,2, Gunnar Grimby 3 and
J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 81 180 THE TESTING AND VALIDATION OF THE ICF CORE SETS FOR THE ACUTE HOSPITAL AND POST-ACUTE REHABILITATION FACILITIES TOWARDS BRIEF VERSIONS Eva Grill 1,2, Gunnar Grimby 3 and
Enhanced recovery programme after TKA through multi-disciplinary collaboration
 Enhanced recovery programme after TKA through multi-disciplinary collaboration ChanPK(1), ChiuKY(1), FungYK(6), YeungSS(7), NgT(8), ChanMT(5), LamR(4), WongNY(3), ChoiYY(3), ChanCW(2), NgFY(1), YanCH(1)
Enhanced recovery programme after TKA through multi-disciplinary collaboration ChanPK(1), ChiuKY(1), FungYK(6), YeungSS(7), NgT(8), ChanMT(5), LamR(4), WongNY(3), ChoiYY(3), ChanCW(2), NgFY(1), YanCH(1)
Keywords: ICF, Core sets, Occupational Therapy Published reference:
 Keywords: ICF, Core sets, Occupational Therapy Published reference: McIntyre A, Tempest S (2007) Disease specific core sets of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF):
Keywords: ICF, Core sets, Occupational Therapy Published reference: McIntyre A, Tempest S (2007) Disease specific core sets of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF):
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Physical Therapy Perspective on Ataxia. Roger Fong, MPT University of Chicago Medical Center March, 2010
 Physical Therapy Perspective on Ataxia Roger Fong, MPT University of Chicago Medical Center March, 2010 Definition: Physical Therapist Physical therapy dynamic profession with an established theoretical
Physical Therapy Perspective on Ataxia Roger Fong, MPT University of Chicago Medical Center March, 2010 Definition: Physical Therapist Physical therapy dynamic profession with an established theoretical
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol
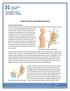 Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
Lumbar Disc Herniation/Bulge Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The lumbar spine is made up of 5 load transferring bones called vertebrae. They are stacked in a column with an intervertebral disc sandwiched
Updates into Therapeutic Exercise Programs for Patients with LBP. Maximizing Patient Motivation and Outcomes Alice M.
 Updates into Therapeutic Exercise Programs for Patients with LBP Maximizing Patient Motivation and Outcomes Alice M. Davis, PT, DPT Objectives Review Statistics on LBP Discuss current research findings
Updates into Therapeutic Exercise Programs for Patients with LBP Maximizing Patient Motivation and Outcomes Alice M. Davis, PT, DPT Objectives Review Statistics on LBP Discuss current research findings
(Intro to Arthritis with a. Arthritis) Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society
 Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Arthritis 101 (Intro to Arthritis with a Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis) by Cari Taylor by Cari Taylor Manager of Education & Services for the Vancouver Island Region of The Arthritis Society What You Will
Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
 A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
First Year. PT7040- Clinical Skills and Examination II
 First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
Total Knee Replacement Specifications 2014 (01/01/2012 to 12/31/2012 Dates of Procedure)
 Summary of Changes Removed following ICD-9 Procedure s: 81.54 Total Knee Replacement (Bicompartmental, Partial Knee Replacement, Tricompartmental, Unicompartmental (hemijoint)). 81.55 Revision of Knee
Summary of Changes Removed following ICD-9 Procedure s: 81.54 Total Knee Replacement (Bicompartmental, Partial Knee Replacement, Tricompartmental, Unicompartmental (hemijoint)). 81.55 Revision of Knee
The Chiropractic Profession s Role in Helping to Meet Vermont's Health Care Reform Goals. Better care Better health Lower costs
 The Chiropractic Profession s Role in Helping to Meet Vermont's Health Care Reform Goals Better care Better health Lower costs Chiropractic Abstract: Chiropractic is now more than a century old, and it
The Chiropractic Profession s Role in Helping to Meet Vermont's Health Care Reform Goals Better care Better health Lower costs Chiropractic Abstract: Chiropractic is now more than a century old, and it
W40 Total prosthetic replacement of knee joint using cement
 Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire Priorities Forum statement Number: 33 Subject: Referral criteria for patients from primary care presenting with knee pain due to ostoarthritis, and clinical threshold for
Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire Priorities Forum statement Number: 33 Subject: Referral criteria for patients from primary care presenting with knee pain due to ostoarthritis, and clinical threshold for
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury. Canadian Family Physician
 Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Tai Chi: : A Mind-body Exercise for Pain Relief and Well-being
 Tai Chi: : A Mind-body Exercise for Pain Relief and Well-being Chenchen Wang, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Center for Integrative Medicine Tufts Medical Center/Tufts University School
Tai Chi: : A Mind-body Exercise for Pain Relief and Well-being Chenchen Wang, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Center for Integrative Medicine Tufts Medical Center/Tufts University School
III STEP Series. Toward a Common Language for Function, Disability, and Health
 III STEP Series Toward a Common Language for Function, Disability, and Health Within physical therapy, the disablement model has proven useful as a language to delineate the consequences of disease and
III STEP Series Toward a Common Language for Function, Disability, and Health Within physical therapy, the disablement model has proven useful as a language to delineate the consequences of disease and
Rehabilitation Where You Recover. Inpatient Rehabilitation Services at Albany Medical Center
 Rehabilitation Where You Recover Inpatient Rehabilitation Services at Albany Medical Center You're Here and So Are We As the region s only academic medical center, Albany Medical Center offers a number
Rehabilitation Where You Recover Inpatient Rehabilitation Services at Albany Medical Center You're Here and So Are We As the region s only academic medical center, Albany Medical Center offers a number
SAM KARAS ACUTE REHABILITATION CENTER
 SAM KARAS ACUTE REHABILITATION CENTER 1 MEDICAL CARE Sam Karas Acute Rehabilitation The Sam Karas Acute Rehabilitation Center is a comprehensive and interdisciplinary inpatient unit. Medical care is directed
SAM KARAS ACUTE REHABILITATION CENTER 1 MEDICAL CARE Sam Karas Acute Rehabilitation The Sam Karas Acute Rehabilitation Center is a comprehensive and interdisciplinary inpatient unit. Medical care is directed
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors
 1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
it s time for rubber to meet the road
 your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
Structures and organization of services for medical rehabilitation in Germany* Wilfried Mau. Halle (Saale), Germany
 Structures and organization of services for medical rehabilitation in Germany* Wilfried Mau Halle (Saale), Germany Address for Correspondence: Professor Wilfried Mau, MD Director of the Institute for Rehabilitation
Structures and organization of services for medical rehabilitation in Germany* Wilfried Mau Halle (Saale), Germany Address for Correspondence: Professor Wilfried Mau, MD Director of the Institute for Rehabilitation
Introduction: Anatomy of the spine and lower back:
 Castleknock GAA club member and Chartered Physiotherapist, James Sherry MISCP, has prepared an informative article on the common causes of back pain and how best it can be treated. To book a physiotherapy
Castleknock GAA club member and Chartered Physiotherapist, James Sherry MISCP, has prepared an informative article on the common causes of back pain and how best it can be treated. To book a physiotherapy
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURE FOLLOWING TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 1 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURE FOLLOWING TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT László Sólyom ( ), András Vajda & József Lakatos Orthopaedic Department, Semmelweis University, Medical Faculty, Budapest, Hungary Correspondence:
1 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURE FOLLOWING TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT László Sólyom ( ), András Vajda & József Lakatos Orthopaedic Department, Semmelweis University, Medical Faculty, Budapest, Hungary Correspondence:
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery
 Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Get Back to the Life You Love! The MedStar Spine Center in Chevy Chase
 Get Back to the Life You Love! The MedStar Spine Center in Chevy Chase The MedStar Spine Center in Chevy Chase Relief from Pain, Restoration of Function Non-surgical, Minimally Invasive and Complex Surgical
Get Back to the Life You Love! The MedStar Spine Center in Chevy Chase The MedStar Spine Center in Chevy Chase Relief from Pain, Restoration of Function Non-surgical, Minimally Invasive and Complex Surgical
Massage Therapy Helps Back Pain By Susan Jackson Grubb, NCMT, CNMT
 1 By Susan Jackson Grubb, NCMT, CNMT Absenteeism, lost wages and reduced productivity due to low back pain are costly to people, companies, and corporations. It is estimated that eighty percent of Americans
1 By Susan Jackson Grubb, NCMT, CNMT Absenteeism, lost wages and reduced productivity due to low back pain are costly to people, companies, and corporations. It is estimated that eighty percent of Americans
Saskatchewan Workers Compensation Act Committee of Review
 Submission to the Saskatchewan Workers Compensation Act Committee of Review Submitted by the 3420A Hill Avenue Regina, SK S4S 0W9 Phone: (306) 585-1411 - Fax: (306) 585-0685 E-mail: [email protected]
Submission to the Saskatchewan Workers Compensation Act Committee of Review Submitted by the 3420A Hill Avenue Regina, SK S4S 0W9 Phone: (306) 585-1411 - Fax: (306) 585-0685 E-mail: [email protected]
Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice
 Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice PROBLEM: Neck Pain and Cervicogenic Headache 66% Proportion of individuals
Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice PROBLEM: Neck Pain and Cervicogenic Headache 66% Proportion of individuals
Therapeutic Canine Massage
 Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
Osteoporosis and Arthritis: Two Common but Different Conditions
 and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Medical Report Prepared for The Court on
 Medical Report Prepared for The Court on Mr Sample Report Claimant's Address Claimant's Date of Birth Instructing Party Instructing Party Address Instructing Party Ref Solicitors Ref Corex Ref 1 The Lane
Medical Report Prepared for The Court on Mr Sample Report Claimant's Address Claimant's Date of Birth Instructing Party Instructing Party Address Instructing Party Ref Solicitors Ref Corex Ref 1 The Lane
Occupational Therapy
 Occupational Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.09.003 07/15/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; EUTF; HSTA; QUEST; Federal Plan 87 02/01/2012 Line(s) of Business
Occupational Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.09.003 07/15/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; EUTF; HSTA; QUEST; Federal Plan 87 02/01/2012 Line(s) of Business
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals. RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014
 Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
Understanding and improving communications between people with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthcare professionals RCUKCOMM00116w February 2014 This project has been funded by Roche Products Ltd &
LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B
 1 Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your BACK/LEG (SCIATIC) PAIN has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
1 Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your BACK/LEG (SCIATIC) PAIN has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT:
 UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 2 Causes of Hip Pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 2 Causes of Hip Pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that
MAJOR DYSFUNCTION OF JOINTS TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET
 MAJOR DYSFUNCTION OF JOINTS TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET Long form FOR REPRESENTATIVE USE ONLY REPRESENTATIVE S NAME AND ADDRESS REPRESENTATIVE S TELEPHONE REPRESENTATIVE S EMAIL PHYSICIAN S NAME AND
MAJOR DYSFUNCTION OF JOINTS TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET Long form FOR REPRESENTATIVE USE ONLY REPRESENTATIVE S NAME AND ADDRESS REPRESENTATIVE S TELEPHONE REPRESENTATIVE S EMAIL PHYSICIAN S NAME AND
Occupational Therapy
 Occupational Therapy I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for occupational therapy when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria guidelines
Occupational Therapy I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for occupational therapy when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria guidelines
Alberta s chiropractors: Spine care experts Patient satisfaction and research synopsis
 www.albertachiro.com 11203 70 Street NW Edmonton, AB T5B 1T1 Telephone: 780.420.0932 Fax: 780.425.6583 Alberta s chiropractors: Spine care experts Patient satisfaction and research synopsis Chiropractic
www.albertachiro.com 11203 70 Street NW Edmonton, AB T5B 1T1 Telephone: 780.420.0932 Fax: 780.425.6583 Alberta s chiropractors: Spine care experts Patient satisfaction and research synopsis Chiropractic
Manual Physical Therapy Certificate Program. Curriculum
 Manual Physical Therapy Certificate Program Curriculum Effective: January 2014 MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY CERTIFICATE PROGRAM Program Director: Dr. Robert Boyles The EIM Manual Therapy Certificate Program
Manual Physical Therapy Certificate Program Curriculum Effective: January 2014 MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY CERTIFICATE PROGRAM Program Director: Dr. Robert Boyles The EIM Manual Therapy Certificate Program
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Major Joint Replacement in Otago, New Zealand
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Quantifying the demand for hip and knee replacement in Otago, New Zealand David Gwynne-Jones Abstract Aim The purpose of this
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Quantifying the demand for hip and knee replacement in Otago, New Zealand David Gwynne-Jones Abstract Aim The purpose of this
International Postprofessional Doctoral of Physical Therapy (DPT) in Musculoskeletal Management Program (non US/Canada) Curriculum
 International Postprofessional Doctoral of Physical Therapy (DPT) in Musculoskeletal Management Program (non US/Canada) Curriculum Effective: July 2015 INTERNATIONAL POSTPROFESSIONAL DOCTORAL OF PHYSICAL
International Postprofessional Doctoral of Physical Therapy (DPT) in Musculoskeletal Management Program (non US/Canada) Curriculum Effective: July 2015 INTERNATIONAL POSTPROFESSIONAL DOCTORAL OF PHYSICAL
Clinical Medical Policy Outpatient Rehab Therapies (PT & OT) for Members With Special Needs
 Benefit Coverage Rehabilitative services, (PT, OT,) are covered for members with neurodevelopmental disorders when recommended by a medical provider to address a specific condition, deficit, or dysfunction,
Benefit Coverage Rehabilitative services, (PT, OT,) are covered for members with neurodevelopmental disorders when recommended by a medical provider to address a specific condition, deficit, or dysfunction,
Document Author: Frances Hunt Date 03/03/2008. 1. Purpose of this document To standardise the treatment of whiplash associated disorder.
 Guideline Title: WHIPLASH ASSOCIATED DISORDER Document Author: Frances Hunt Date 03/03/2008 Ratified by: Frances Hunt, Head of Physiotherapy Date: 16.09.15 Review date: 16.09.17 Links to policies: All
Guideline Title: WHIPLASH ASSOCIATED DISORDER Document Author: Frances Hunt Date 03/03/2008 Ratified by: Frances Hunt, Head of Physiotherapy Date: 16.09.15 Review date: 16.09.17 Links to policies: All
frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology
 frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology Recently, you may have seen advertisements from legal companies
frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology frequently asked questions Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Technology Recently, you may have seen advertisements from legal companies
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Position Statement: The Use of Total Ankle Replacement for the Treatment of Arthritic Conditions of the Ankle
 Position Statement: The Use of Total Ankle Replacement for the Treatment of Arthritic Conditions of the Ankle Position Statement The (AOFAS) endorses the use of total ankle replacement surgery for treatment
Position Statement: The Use of Total Ankle Replacement for the Treatment of Arthritic Conditions of the Ankle Position Statement The (AOFAS) endorses the use of total ankle replacement surgery for treatment
Importance, Selection and Use of Outcome Measures. Carolyn Baum, PhD, OTR, FAOTA Allen Heinemann, PhD, ABPP (RP), FACRM
 Importance, Selection and Use of Outcome Measures Carolyn Baum, PhD, OTR, FAOTA Allen Heinemann, PhD, ABPP (RP), FACRM Objectives 1. Understand the Changing Medical System and the Changing Focus of Assessments
Importance, Selection and Use of Outcome Measures Carolyn Baum, PhD, OTR, FAOTA Allen Heinemann, PhD, ABPP (RP), FACRM Objectives 1. Understand the Changing Medical System and the Changing Focus of Assessments
.org. Rotator Cuff Tears. Anatomy. Description
 Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Facts About Aging and Bone Health
 Facts About Aging and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well Being with the compliments of Division of Health Services Diocese of Camden Exercise as treatment Along with medication, proper
Facts About Aging and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well Being with the compliments of Division of Health Services Diocese of Camden Exercise as treatment Along with medication, proper
Competency Based Goals and Objectives:
 PEDIATRIC SPORTS MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES & OVERALL EDUCATIONAL GOALS Competency Based Goals and Objectives: Mission: Train fellows to become sports medicine physicians
PEDIATRIC SPORTS MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES & OVERALL EDUCATIONAL GOALS Competency Based Goals and Objectives: Mission: Train fellows to become sports medicine physicians
SUBMISSION TO THE MEDICARE BENEFITS SCHEDULE REVIEW TASKFORCE
 SUBMISSION November 2015 SUBMISSION TO THE MEDICARE BENEFITS SCHEDULE REVIEW TASKFORCE Submission by the Chiropractors Association of Australia Page 1 of 10 About the Chiropractors Association of Australia
SUBMISSION November 2015 SUBMISSION TO THE MEDICARE BENEFITS SCHEDULE REVIEW TASKFORCE Submission by the Chiropractors Association of Australia Page 1 of 10 About the Chiropractors Association of Australia
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW
 BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
