Preparation of Monoclonal Antibodies
|
|
|
- Amice Shaw
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C H A P T E R 57 Preparation of Monoclonal Antibodies Peter J. Macardle and Sheree Bailey I. INTRODUCTION In 1975 Kohler and Milstein reported the outcome of fusing antibody-producing mouse spleen cells with a mouse myeloma cell line. The monoclonal antibodies produced were of the specificity dictated by the spleen cells but in the quantity characterized by the myeloma cell line. From this beginning the preparation of monoclonal antibodies has become an important tool in almost every scientific discipline. No longer restricted to the immunology laboratory, monoclonal antibodies are used in a variety of experimental techniques and diagnostic assays and now, with improvements in molecular engineering techniques, are realizing their potential in therapeutic applications (Grillo-Lopez, 2000). When the need arises to produce monoclonal antibodies to a particular antigen, the decision to establish the technology, use commercial enterprises, or approach private groups to produce them has to be made. For laboratories that decide to establish the technology, this article describes a method that has evolved in our laboratory since the mid-1980s. The method is robust, in routine use, and has produced hundreds of monoclonal antibodies to a wide variety of antigens. The method uses commercial high-quality reagents, including cloning supplements that replace the messy and wasteful use of in vivo-derived feeder cells. The reagents detailed are the ones used in our laboratory but other manufacturers make equivalent reagents. The intention of this article is to describe the reagents, equipment, and techniques used to prepare monoclonal antibodies. Full reviews of monoclonal antibody production, including methods for charac- terization, purification, use of monoclonal antibodies, and antibody engineering applications, are available in a number of monographs, including Campbell (1991), Donohoe et al. (1994) and Goding (1986). Sterile culture technique and accurate record keeping are essential for success in monoclonal antibody preparation. The sterile culture technique is not difficult to learn, with attention to detail paramount for success. There are many excellent texts on basic and advanced tissue culture techniques, including Freshney (2002) and Harrison and Rae (2003). II. MATERIALS AND INSTRUMENTATION A. Essential Equipment Sterile laminar flow hood, benchtop centrifuge, liquid nitrogen storage or equivalent, 37~ water bath, and a 37~ 5% CO2 gassed tissue culture incubator. An inverted microscope to view cell growth is also useful. B. Cell Culture Reagents RPMI 1640 (10 x 500ml) (Cat. No ), penicillin (10,000 U) / streptomycin (10,000 ~tg), L-glutamine (29.2 mg) (PSGxl00, Cat. No ), 10 mm sodium hypoxanthine, 40~tM aminopterin, 1.6mM thymidine (HATxl00, Cat. No ), 10mM sodium hypoxanthine, and 1.6mM thymidine (HTxl00, Cat. No ) are from GIBCO Invitrogen Corporation. Fetal bovine serum (FBS, Cat. No M) is from JRH Biosciences; select batches of FBS that have been screened for hybridoma produc- Cell Biology 475 Copyright 2006, Elsevier Science (USA). All rights reserved.
2 476 ANTIBODIES tion. Complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA, Cat. No ) and incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA, Cat. No ) are from Pierce Biotechnology Inc. Hybridoma fusion cloning supplement (HFCS, Cat. No ) and polyethylene glycol 1500 in 75 mm HEPES, sterile and fusion tested (PEG, Cat. No ), are from Roche Diagnostics. Red blood cell lysing buffer (8.3g/liter NH4C1 in 0.01M Tris-HC1) (Cat. No. R-7757) and trypan blue solution (Cat. No. T- 8154) are from Sigma. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Cat. No ) is from Merck. ELISA-based isotyping kits are available from a number of manufacturers, including Roche Diagnostics (Cat. No ) and Pierce Biotechnology Inc (Cat. No ). Store all stock reagents as recommended by the manufacturer. C. Cell Culture Materials Tissue culture plates, 24-well (Cat. No ) and 96-well (Cat. No ) flat-bottom plates with lids, 25-cm 2 (Cat. No ) and 80-cm 2 (Cat. No ) tissue culture flasks, cryotubes (Cat. No ), 10-ml disposable pipettes (Cat. No ) and petri dishes (Cat. No ) are from Nalge Nunc Int. V-bottom 30-ml tubes (Cat. No. 128A) and wide-bore graduated transfer pipettes (Cat. No. PP88SA) are from Bibby-Sterilin Ltd. A container (Cat. No Nalgene Nunc) or a foam box with walls of about 1 cm thick is required for the control rate freezing of cells. In addition, we use Gilson Pipetman 5- to 20- and 20- to 200-~tl pipettes and a Gilson Distriman repeating pipette for cloning, all with sterile tips. Hamilton 500-~tl glass luer lock syringes are used for immunization (Cat. No Hamilton, Reno. Nev). Sterile forceps and scissors are also required. D. Myeloma Cell Line Several myeloma cell lines are commonly used for fusion with murine spleen cells; most have been derived from the P3X63Ag8.653 murine myeloma line (Kearney et al., 1979). The myeloma clones SP2/0 (Shulman et al., 1978) and FO (de St Groth and Scheidegger, 1980), derived from P3X63Ag8.65, are commonly used. These cell lines are available from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) ( as CRL1580, CRL1581, and CRL1646, respectively. We use P3X63Ag8.653 cells that have been maintained in our laboratory for many years, which are screened regularly for mycoplasma, and we select batches that have been previously successful in hybridoma production. A. General III. PROCEDURES The preparation of monoclonal antibodies depends on a series of steps that require attention to detail and careful laboratory management. The major requirement is time; Table I gives an approximate time frame for monoclonal antibody preparation. Phase I is largely taken up by the immunization protocol, ensuring that the screening method is working, growing the myeloma cells, and finally performing the fusion. Phase 2 encompasses testing, cloning, and freezing and is more labor-intensive. However, the workload is variable and unless the screening method is cumbersome or many fusions are carried out, it is not a fulltime occupation. In our experience the secret to success in monoclonal antibody preparation is the screening method. Ideally the method should be in place before the animals are immunized. The method needs to be robust and reliable and, as there may be 30 to 50 samples to screen a day, reagents and equipment need to be readily available. The method should be appropriate to the intended use of the monoclonal antibod- TABLE I Time Frame for Monoclonal Antibody Preparation Phase One Light workload Prepare antigen and develop screening assay Immunize animals Test bleed Thaw myeloma line Fuse spleen and myeloma line HAT selection medium Feed with HT medium Feed with HT medium Colonies become visible, screening begins Phase Two Heavy workload Screen wells as required Clone, freeze, feed, test Reclone, freeze, feed, test Third clone cycle Keep extensive records Phase Three Variable workload Isotype and scale up Characterization. Antibody purification, labeling, etc. Maintenance of frozen stock 4-8 weeks Week 7 Fourth or 8th week Day 1 Day 7 Day 14 Day 14 to about day 32 About 21-day cycle About 21-day cycle About 21-day cycle
3 PREPARATION OF MONOGLONAL ANTIBODIES 477 ies. Although many antibodies do perform in alternative protocols, there is no guarantee unless they have been screened appropriately. Some suggestions for screening methods are included in Table II, but detailed descriptions are outside the scope of this article. B. Antigen Preparation and Immunization A number of protocols that we have used to immunize mice to a variety of antigens are shown in Table II. Animals can make antibodies to a wide range of molecular structures with two important general exceptions: animals will not usually make antibodies to self-antigen (see Section V) and will not usually recognize small molecules. Small molecules need to be conjugated to a carrier protein. Selection of the carrier protein appears to be largely personal, but the ease of and position of conjugation are important criteria. When linking peptides to carrier proteins, Landsteiner's principle (Landsteiner, 1945) should be taken into account, that antibody specificity tends to be directed to epitopes of the hapten furthest removed from the functional group linked to the carrier protein. Commonly used carrier proteins include keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) and bovine serum albumin (BSA). If you are going to screen for monoclonal antibodies by ELISA, make both peptide-klh and peptide-bsa combinations; immunize with one and screen against the other. There are a number of methods for the conjugation of peptides to carrier proteins and the protocol selected will depend on the amino acid sequence of the peptide and the epitope of interest. However, if you are having a peptide synthesized, consider adding a biotin tag; a streptavidinconjugated carrier protein can then make a convenient carrier. If high-affinity IgG monoclonal antibodies are required, the immunization protocol needs to invoke T-cell help. Hence, adjuvant and several booster injections may be needed and test bleeds should be examined for the presence of antigen-specific IgG. If IgG isotype monoclonal antibodies are essential, they should be screened for specifically. The protein antigen immunization schedule used in our laboratory is shown in Table III. Most protocols require antigen in adjuvant for immunization. Complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) is highly effective but may cause toxic side effects. A number of new adjuvants are becoming available, including Hunter's TiterMax ( titermax, com), Pierce' s AdjuPrime Immune Modulator ( piercenet.com), and RIBI adjuvant systems ( among others. Advice from the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee should be taken on which adjuvants are recommended. If CFA is used, it should only ever be used subcutaneously for the primary immunization and Freund's incomplete used for subsequent boosts. Complete Freund's adjuvant causes inflammation and granuloma formation in mice and will cause severe injury in humans. Take suitable precautions to prevent self-injection and employ eye protection. Six-week-old female BALB/c mice are preferred for immunization as the myeloma lines used for fusion were derived from that strain. Routinely, we immunize six animals, in batches of two, with a 2-week interval between immunizing the next two animals. TABLE III Immunization Schedule for Protein Antigens Primary immunization Day 0 First boost Day 14 Second boost Day 28 Test bleed Day 35 Third boost Day 42 Fusion Day 45 TABLE II Suggested Immunization and Screening Protocols Immunogen Concentration Route of injection Screening assay Cells, bacteria, virus, nematodes Plasmid DNA Glycoprotein peptides / carrier Proteins 5 x X ~tg plasmid 2-50~tg Intraperitoneal (200 ~tl saline) Intramuscular (50 ~tl / site, both rear legs) a Subcutaneous b (100 ~tl / site, CFA, IFA) or intraperitoneal (200~tl saline) Flow cytometry Dot blot, ELISA Immunohistochemistry ELISA Western blot ELISA a Anesthesia is essential or muscle contraction will eject the immunogen. b Typically at the nape of the neck and at the base of the tail.
4 478 ANTIBODIES Wear eye protection. 1. Draw an equal volume of antigen in saline and CFA into two separate Hamilton 500-~tl glass luer lock syringes. 2. Connect the syringes with a three-way stopcock and emulsify the mixture slowly by passing material from one syringe to the other. 3. Check that an emulsion has been formed by taking a drop of the mixture from the stopcock and placing on water, an emulsion will float and not dissipate. 4. Using the Hamilton syringe and a 21-gauge needle, immunize the animals with 100~1 of emulsion subcutaneously at the base of the tail and nape of the neck. C. Test Bleeds Analysis of a test bleed can allow the fusion to be postponed and the animals reimmunized if the antibody titer is low or nonexistent. Test bleeds should only be carried out by experienced personnel. Test bleeds should preferably be from the lateral tail vein using a 26-gauge needle and syringe. A maximum of 1% of the body weight of the animal should be collected, about ~tl. Larger volumes of blood can be collected at the time of euthanasia and can provide a valuable positive control sample for the screening protocol. D. Myeloma Cell Preparation About 1 week before the fusion, thaw a vial of the myeloma cell line from the liquid nitrogen stock (see Section IV, B). The myeloma cells should be of known pedigree; it is vital to maintain the myeloma line carefully. Mycoplasma-contaminated stock or stock that has been overgrown will result in poor production of hybridomas. 1. Transfer the cells into 24-well plates at about 2 x 105 per well, check cell numbers daily, and scale up as they double in number into 25-cm 2 flasks and then into 80-cm 2 flasks containing 50ml of RF Maintain vigorous growth rates during the scaleup period. The day prior to the fusion the myeloma cells should be given a one-to-one split so that the cells are in an exponential growth phase at the time of fusion. 3. The number of myeloma cells required depends on how many spleen cells are to be fused. Typically, we use a spleen to myeloma cell fusion ratio of 10:1. Normal BALB/c mice produce about 108 leukocytes per spleen, hence 107 myeloma cells are required for each spleen. 4. On the day of the fusion and before the animals are euthanized, examine the myeloma cells carefully to check that the culture is not contaminated. Solutions IV. CELL FUSION PROCEDURE 1. RFIO medium: To 500 ml of RPMI 1640 add 50 ml of FBS and 5ml of PSGxl00. Store at 4~ for up to 14 days; after 14 days replace the PSG. Warm to 37~ in a water bath before use. 2. HAT selection medium: Reconstitute 100x lyophilized HAT supplement with 10ml of sterile distilled water and store 1-ml aliquots at 4~ protected from light. Add I ml HAT and 2ml of HFCS to 100ml of RF10 medium. Make only as much as required for the fusion. Warm to 37~ in a water bath before use. 3. HT medium: To 500ml of RF10 medium add 5 ml of HT supplement. Warm to 37~ in a water bath before use. 4. HT medium +2% HFCS: Add 2ml of HFCS to 100 ml HT medium. Warm to 37~ in a water bath before use. A. Background Notes HAT medium is used to selectively grow hybrids following fusion. Aminopterin selects against unfused myeloma cells and myeloma:myeloma-fused cells by blocking the main synthetic pathway for DNA. Unfused spleen cells do not have the capacity to survive for more than a few days. In hybridomas, hypoxanthine and thymidine supply purines and pyrimidines for DNA synthesis via HGPRTase salvage pathways derived from the spleen cells. The HT medium acts as a rescue medium while the aminopterin is being diluted out. Although the HT medium can be withdrawn once the nucleoside biosynthesis pathways are re-established, in our experience it is rarely worth the effort. Cells under pressure often require "supplements" to maintain growth. In many monoclonal antibody preparation methods, these are supplied by feeder cells, usually mouse thymocytes or peritoneal washout cells. In the method described, feeder cells are replaced with hybridoma fusion cloning supplement HFCS, which in addition to being preferred for reasons of
5 PREPARATION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES 47 9 animal ethics, is more convenient and, in our experience, more effective. B. Fusion Protocol 1. For each spleen to be fused, place a 1-ml aliquot of PEG mixture and a 3- and a 7-ml aliquot of RF10 in a 37~ water bath. 2. After euthanasia, submerge the mouse in 70% alcohol for a few minutes; this prevents hair and bedding material from contaminating the laminar flow hood. 3. Place the animal on its right-hand side, grasp the skin posterior to the rib cage with sterile forceps, and make a small incision to cut the skin but not to penetrate the subcutaneous fascia. With two pairs of forceps, grasp the skin at either side of the incision and pull. The skin should peel away, revealing the subcutaneous fascia. Flush the area with 70% alcohol to remove any stray hair. Using forceps and scissors, cut through the subcutaneous fascia into the peritoneal cavity and locate the spleen and remove by cutting away the connective tissue. 4. Place the spleen into a petri dish containing about 15ml of RF10. At this point, blood can be collected by opening the thoracic cavity, quickly puncturing the heart, and collecting blood; this can be useful as a positive control. 5. Half-fill two 10-ml syringes with RF10 from the petri dish and, using 21-gauge needles, gently disrupt the spleen by injecting the medium. Inject the media slowly, a little at a time; you should see clouds of cells going into the medium and the spleen turning lighter in color. Finally, when the spleen looks like a limp sack, gently tease apart the spleen with the needle and flat tweezers to remove any remaining cells. Discard the spleen connective tissue. 6. Gently pipette the cell suspension to break up clumps and transfer into a 30-ml V-bottom tube, ignoring large clumps and the remains of the spleen connective tissue; let the tube stand for about 5 min. 7. Remove cells from the tube and transfer into another 30-ml V-bottom tube, leaving behind the debris and connective tissue that has settled to the bottom. 8. Pellet the spleen cells at 400g for 5 min. 9. Resuspend the cell pellet in 5ml of red cell lysing solution, leave for 5 min, and then fill the tube with media and pellet at 400g for 5 min. 10. Resuspend the spleen cells in 5 ml of media and perform a cell count. The number of leucocytes derived from a single spleen should be approximately 108 cells total. 11. Wash and count the myeloma cells; for 108 spleen cells, 10 7 myeloma cells will be required. 12. Add the myeloma cells to the spleen cell suspension to give a spleen/myeloma cell ratio of 10:1. Note: This is the critical bit, for the next 20min you will be committed to fusing the cells. 13. Pellet the cells (400g for 5 rain) and remove all of the supernatant; this is best done with a Pasteur pipette attached to a vacuum line. 14. Tap the pellet to loosen the cells. 15. With a wide-bore transfer pipette, add I ml of PEG solution per spleen. Gently mix with the pipette for 10s and then continue to mix the cells gently by tapping the tube for a further 50 s. 16. Retrieve the 3-ml RF10 sample and slowly add dropwise over a 10-rain period continually mixing the cells gently by tapping the tube. This can be accomplished (for a right-handed person) by holding the tube in the left hand between thumb and forefinger, tapping the tube with the second or third finger, depending on comfort and reach, and adding the medium with a transfer pipette held in the right hand. With a little practice a steady rhythm can be produced. 17. After the first 3 ml, retrieve the 7-ml aliquot and add over the next 10-min period. 18. Pellet the cells at 400g for 5 rain and resuspend in about 10 ml of RF10; loosen the tube cap to allow for CO2 transfer and place the cells in the tissue culture incubator for about I h. 19. Pellet the cells at 400g for 5 min. 20. Gently resuspend the cell pellet in a small volume of the HAT selection medium. 21. Add this suspension back into HAT selection medium; 50ml of HAT selection medium will be needed for every 107 myeloma cells used in the fusion. 22. Add about lml of the cell suspension to each well of the 24-well plates. This is the equivalent of 2 x 105 myeloma cells per well. We prefer plating the fusion into 24-well plates, as evaporation is less of a problem. The larger volume also provides enough supernatant for any screening assay. 23. Label and place the plates in the tissue culture incubator. With the exception of the 1-h incubation period, the entire fusion protocol should take no more then 2 to 3h. C. Maintaining Hybridomas Examine the wells using the inverted microscope on days following the fusion. Do not keep the plates out of the incubator for more than about 10min, as media
6 480 ANTIBODIES in the wells will cool and the ph may also change. Large numbers of dead cells may be seen, this is normal. You may also see some small moving particles; this is due to Brownian movement of debris and does not indicate bacterial infection. After 7 days, media needs to be replenished, this is also the beginning of diluting out the aminopterin from the HAT selection medium. To each well add 1 ml of HT medium +2% HFCS. Add the medium slowly so as not to break up any colonies; this is not critical, but it is easier to judge when to test a well if you can see the size of intact colonies. From now on it is a matter of observing colony growth and changes in the ph of the medium. Screen for antibody from wells in which the medium is yellow (acidic) and colonies are about 25% confluent. Keep feeding wells on a 7-day cycle for slow growers and as needed for fast growers. For the second and subsequent feeds we use HT medium +1% HFCS. D. Testing and Cloning When testing for antibody, ensure that appropriate negative controls are used. A positive control can be a dilution of the test bleed or of serum collected when the spleen was removed. If screening by ELISA, falsepositive "antiplastic responses" can be a nuisance. The use of antigen-negative wells as a control can help screen these out. It is a waste of time cloning cells from wells that display an antiplastic response. Cells from wells that are positive in the screening assay need to be cloned and stored in liquid nitrogen as soon as possible. Cloning is performed not only to produce a monoclonal population, but also to stabilize cell growth and eliminate antibody nonproducers. Nonproducers often grow faster than cells producing antibody and can quickly outgrow the antibodyproducing population. We routinely clone at 3 cells per well and observe about two-thirds of the wells with cell growth. This approximates to Poisson's distribution of a probable cell cloning number of I cell per well. If you find more wells with cell growth, clone at a lower cell number per well, 1 or even 0.5 cells per well. E. Cloning Solutions 1. HT medium +2% HFCS: Add 2ml of HFCS to 100 ml of HT medium. Store at 4~ Warm to 37~ in a water bath before use. 2. Trypan blue solution (Cat. No. T8154 Sigma) 1. Gently resuspend the cells in a positive well of the 24-well plate using a sterile transfer pipette; avoid creating air bubbles. Transfer the cells to a new 24-well plate. 2. Perform a viable cell count at a 1:2 dilution in trypan blue solution. In this example we will work from a viable cell count of 6 x 105 cells / ml 3. To obtain 3 cells/well, perform a series of dilutions: 1/1000 dilution = 600 cells/ml; add 10btl cells into 10 ml of HT medium. From this make a 1/20 dilution = 30 cells/ml or 3 cells/100btl. 4. Conveniently make this dilution by taking 500 btl of cells from the 1/1000 dilution and place into 9.5 ml of HT medium +2% HFCS. This gives 10ml of cells, which is sufficient for one cloning plate at 100btl per well. 5. Using a Gilson Distriman, add 100btl of cell suspension to each well of a flat-bottomed 96-well plate. Label the new plate with the date and code of the original well and plate that it came from, e.g., P1D3 means plate 1 row D well Examine the cloning plates regularly and replenish with HT medium +2% HFCS on at least day 7 but beforehand if noticeable evaporation of media occurs. Some methods suggest wrapping 96-well plates with plastic film to slow down evaporation. This can be successful but makes viewing the wells difficult and can also give a false sense of security, care also needs to be taken when removing the film so as not to contaminate the plate. 7. Test wells that display cell growth as required, reclone, and freeze cells from positive wells using the same procedure. We clone a minimum of three times in order to achieve monoclonality. When storing positive wells in liquid nitrogen, we routinely store two vials from the initial positive 24- well plate. From subsequent 96-well cloning plates we keep no more than three or four positive wells and store about two cryotubes of each and the same at each subsequent cloning step. F. lsotyping and Scaling up of Hybridomas Isotyping of the monoclonal antibody can be performed with a commercial ELISA kit, this can help confirm monoclonality and determine the strategy for antibody purification from the culture supernatant. Care should be taken in scaling up the cultures from wells to flasks, ensure that cell growth is stable, and split cells into a number of wells of the 24-well plate;
7 PREPARATION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES 481 we establish confluent growth in at least four wells before transferring the cells to a 25-cm 2 flask. V. LIQUID NITROGEN STORAGE PROCEDURE The only means by which long-term survival of hybridomas can be achieved is by storing cells in liquid nitrogen. It is essential that an up-to-date catalogue of stocks is maintained. Valuable hybridoma stocks should be kept in more than one freezer, preferably at separate sites. A. Cell Freezing Protocol Solutions 1. Solution A: Gently mix 10 ml of RF10 and 10 ml FBS. This solution may be stored at 4~ indefinitely if kept sterile. Warm to 37~ in a water bath before use. 2. Solution B: Add 6ml of DMSO to 14ml of RF10. This mixture causes an exothermic reaction and may be stored at 4~ for several days if kept sterile. Warm to 37~ in a water bath before use. 1. Resuspend cells in solution A. 2. To this add an equal volume of solution B. Mix the suspension gently and dispense into labeled sterile cryotubes. 3. After sealing the tubes, place them into a Nunc freezing container or a foam box. 4. Put the container into a -80~ freezer for 24 h, after which the tubes should be transferred into a liquid nitrogen store. The location and contents of the tubes have to be catalogued carefully. B. Cell Thawing Protocol We strongly recommend that full-face protection be worn when retrieving cells from liquid nitrogen. 1. Remove vials using cryogloves and forceps. 2. Transfer vials immediately to a shatter-proof container. 3. Using a beaker, transfer warm water from the 37~ water bath into the container. 4. The lid of the container need only be partially removed to allow access with the beaker and replaced as soon as water is added. The use of the shatter-proof container prevents injury from tubes that explode on contact with warm water. This is a comparatively rare event but has caused severe injury. 5. After a few minutes when the contents have thawed, remove and wash the vials in alcohol. 6. Remove the cells with a transfer pipette and place in a sterile 30-ml tube. 7. Slowly add an equal volume of RF10 medium dropwise. 8. Let stand for 5 min. 9. Add 10ml of RF10 and let stand for a further 5 min. 10. Centrifuge at 400g for 5min and resuspend in HT medium for hybridomas and in RF10 for myeloma. 11. We routinely start cells growing at about 2 x 105 cells/well in a 24-well plate. The addition of 1% HFCS will speed up cell growth. Do not let cells overgrow and scale up to other wells and flasks as required. 12. The first priority is to maintain frozen stock, so ensure that more tubes are stored in liquid nitrogen. V. COMMENTS We have overcome tolerance to self-antigen by linking the conserved peptide to a fusion protein and using the construct as the immunogen. Using this strategy, we have been successful in making antibodies to a human peptide with 95% homology to the murine protein (Cavill et al., 1999). If purchasing a tissue culture incubator, ensure that it can be cleaned easily, has readily accessible filters that are changed easily, and does not have "hidden" tubing that cannot be cleaned and acts as a harbor for infections. VI. PITFALLS 1. Make sure that the marker pen ink used to label the cryotubes tubes is resistant to alcohol. 2. We cannot overemphasize the importance of storing positive hybridomas in liquid nitrogen for subsequent retrieval. References Campbell, A. M. (1991). Monoclonal antibody and immunosensor technology. In "Laboratory Techniques in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology" (van der Vliet, P. C., ed.) Elsevier, Amsterdam. Cavill, D., Macardle, P. J., Beroukas, D., Kinoshita, G., Stahl, J., McCluskey, J., and Gordon, T. P. (1999). Generation of a monoclonal antibody against human calreticulin by immunization with a recombinant calreticulin fusion protein: Application in
8 482 ANTIBODIES paraffin-embedded sections. App. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 1, de St Groth, S. E, and Scheidegger, D. (1980). Production of monoclonal antibodies: Strategy and tactics. J. Immunol. Methods 35, Donohoe, P. J., Macardle, P. J., and Zola, H. (1994). Making and using conventional mouse monoclonal antibodies. In "Monoclonal Antibodies: The Second Generation" (H. Zola, ed.), Biological Sciences, Coronet Books, Philadelphia, PA. Freshney, R. I. (2002). "Culture of Animal Cells: A Manual of Basic Technique," 4th Ed. Wiley-Liss, New York. Goding, J. W. (1986). "Monoclonal Antibodies: Principles and Practice," 2nd Ed. Academic Press, London. Grillo-Lopez, A. J. (2000). Rituximab: An insider's historical perspective. Semin. Oncol. 27(Suppl. 12), Harrison, M. A., and Rae, I. E (2003). General Techniques of Cell Culture. In Handbooks in Practical Animal Cell Biology (M. Harrison, I. E. Roe, A. Harris, Series Eds.) Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, U.K. Kearney, J., Radbruch, A., Liesegang, B., and Rajewsky, K. (1979). A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting cell lines. J. Immunol. 123, Kohler, G., and Milstein, C. (1975). Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256, Landsteiner, K. (1945). "The Specificity of Serological Reactions." Harvard Univ. Press, Boston, MA. Shulman, M., Wilde, C. D., and Kohler, G. (1978). A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature 276,
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Antibody Production at Strategic Diagnostics Inc. SOP#: M-119 Version #: 1 Date Approved: August 6, 2009 Author: Strategic Diagnostic Inc. Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Antibody Production at Strategic Diagnostics Inc. SOP#: M-119 Version #: 1 Date Approved: August 6, 2009 Author: Strategic Diagnostic Inc. Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE
HARVESTING AND CRYOPRESERVATION OF HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS (hescs)
 HARVESTING AND CRYOPRESERVATION OF HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS (hescs) OBJECTIVE: can be cryopreserved in a liquid nitrogen (LN 2 ) freezer for long-term storage. This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
HARVESTING AND CRYOPRESERVATION OF HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS (hescs) OBJECTIVE: can be cryopreserved in a liquid nitrogen (LN 2 ) freezer for long-term storage. This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
Custom Antibodies Services. GeneCust Europe. GeneCust Europe
 GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 6 rue Dominique Lang L-3505 Dudelange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com
GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 6 rue Dominique Lang L-3505 Dudelange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com
Dot Blot Analysis. Teacher s Guidebook. (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences www.gbiosciences.com
 PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service
 KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
From Biology to Discovery
 POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION SERVICES Abbiotec offers custom polyclonal antibody production services to the scientific community to accelerate a project From Biology to Discovery. When the antibody for
POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION SERVICES Abbiotec offers custom polyclonal antibody production services to the scientific community to accelerate a project From Biology to Discovery. When the antibody for
SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract Monoclonal Antibody Production
 A Technical Publication of SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Volume 1 Number 4 9336 Abraham Way Santee, CA 92071 USA (619) 258-9300 fax (619) 258-9366 www.scantibodies.com SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract
A Technical Publication of SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Volume 1 Number 4 9336 Abraham Way Santee, CA 92071 USA (619) 258-9300 fax (619) 258-9366 www.scantibodies.com SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract
Production of Monoclonal Antibodies
 UNIT 2.5 Production of Highly specific antibodies can be obtained by fusing immune B cells from the spleen with tumor cells to produce hybridomas, each of which will then secrete a single antibody. The
UNIT 2.5 Production of Highly specific antibodies can be obtained by fusing immune B cells from the spleen with tumor cells to produce hybridomas, each of which will then secrete a single antibody. The
Aviva Systems Biology
 Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA)
 STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual
 Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
Human Adult Mesothelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0025.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Mesothelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders are shipped
Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal
 198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
How To Use An Antibody
 GUIDELINES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF ANTIBODIES IN LABORATORY ANIMALS Table of Contents 1. Purpose 2. Choice of Species and Strain 3. Immunizing Antigen 4. Procedures for Polyclonal Antibody Production 5.
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF ANTIBODIES IN LABORATORY ANIMALS Table of Contents 1. Purpose 2. Choice of Species and Strain 3. Immunizing Antigen 4. Procedures for Polyclonal Antibody Production 5.
CUSTOM ANTIBODIES. Fully customised services: rat and murine monoclonals, rat and rabbit polyclonals, antibody characterisation, antigen preparation
 CUSTOM ANTIBODIES Highly competitive pricing without compromising quality. Rat monoclonal antibodies for the study of gene expression and proteomics in mice and in mouse models of human diseases available.
CUSTOM ANTIBODIES Highly competitive pricing without compromising quality. Rat monoclonal antibodies for the study of gene expression and proteomics in mice and in mouse models of human diseases available.
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Cellartis Protocol Culturing of hes Cells
 Cellartis Protocol Culturing of hes Cells This material was cultured and frozen using Cellartis protocols. WiCell recommends that stem cells should be thawed and established in the conditions in which
Cellartis Protocol Culturing of hes Cells This material was cultured and frozen using Cellartis protocols. WiCell recommends that stem cells should be thawed and established in the conditions in which
MAB Solut. MABSolys Génopole Campus 1 5 rue Henri Desbruères 91030 Evry Cedex. www.mabsolut.com. is involved at each stage of your project
 Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
Transformation Protocol
 To make Glycerol Stocks of Plasmids ** To be done in the hood and use RNase/DNase free tips** 1. In a 10 ml sterile tube add 3 ml autoclaved LB broth and 1.5 ul antibiotic (@ 100 ug/ul) or 3 ul antibiotic
To make Glycerol Stocks of Plasmids ** To be done in the hood and use RNase/DNase free tips** 1. In a 10 ml sterile tube add 3 ml autoclaved LB broth and 1.5 ul antibiotic (@ 100 ug/ul) or 3 ul antibiotic
RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method)
 Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL
 GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
GASTRIC ORGANOID CULTURE PROTOCOL THIS PROTOCOL PROVIDES THE PROCEDURE FOR SUBCULTURING NORMAL HUMAN GASTRIC ORGANOIDS WHICH WAS DERIVED FROM THE SUBMERGED METHOD AS DESCRIBED IN BARKER N, ET AL. LGR5+VE
Classic Immunoprecipitation
 292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
Antibody Services. Best Guarantees in the Industry! Monoclonal Antibody Services. Polyclonal Antibody Services. Express Antibody TM Services
 Antibody Services Best Guarantees in the Industry! Monoclonal Antibody Services Polyclonal Antibody Services Express Antibody TM Services Guaranteed Antibody Services Antibody Purification Services Your
Antibody Services Best Guarantees in the Industry! Monoclonal Antibody Services Polyclonal Antibody Services Express Antibody TM Services Guaranteed Antibody Services Antibody Purification Services Your
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Work Package 8. Sample Collection and Storage
 Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Work Package 8 Sample Collection and Storage May 2008 SOP WP 8 - Sample collection Table of Contents 1 SAMPLE COLLECTION... 3 1.1 Sample collection -summary... 3 1.2
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Work Package 8 Sample Collection and Storage May 2008 SOP WP 8 - Sample collection Table of Contents 1 SAMPLE COLLECTION... 3 1.1 Sample collection -summary... 3 1.2
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse
 THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit
 Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit
 Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit Catalog No. MBS702810 (96 tests) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro semi-quantitative determination of mouse KLH(IgM)antibody concentrations
Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit Catalog No. MBS702810 (96 tests) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro semi-quantitative determination of mouse KLH(IgM)antibody concentrations
Applications of Ab Molecules. Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128)
 Applications of Ab Molecules Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128) Monoclonal Antibodies Clonal Selection of B Lymphocytes Hybridoma Köhler and Milsten (1975) - continuous
Applications of Ab Molecules Chapter 4 Monoclonal Ab (p.99) Chapter 5 Ab genes and Ab Engineering (p.128) Monoclonal Antibodies Clonal Selection of B Lymphocytes Hybridoma Köhler and Milsten (1975) - continuous
EdU Flow Cytometry Kit. User Manual
 User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
Chapter 2 Antibodies. Contents. Introduction
 Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
SOP 001: POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION IN RABBITS
 SOP 001: POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION IN RABBITS PURPOSE: To describe the proper procedure to follow when injecting adjuvants into rabbits for the production of polyclonal antibodies. POLICY: The improper
SOP 001: POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION IN RABBITS PURPOSE: To describe the proper procedure to follow when injecting adjuvants into rabbits for the production of polyclonal antibodies. POLICY: The improper
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a
 Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
QED Bioscience Inc. Revision 05/04/11 ADVANCED ANTIBODY TECHNOLOGIES
 CUSTOM POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY DEVELOPMENT QED is committed to excellence across all facets of our operations, and to responding to the ever-changing needs of our customers. We have been developing monoclonal
CUSTOM POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY DEVELOPMENT QED is committed to excellence across all facets of our operations, and to responding to the ever-changing needs of our customers. We have been developing monoclonal
Frozen-EZ Yeast Transformation II Catalog No. T2001
 INSTRUCTIONS Frozen-EZ Yeast Transformation II Catalog No. T2001 Highlights High transformation efficiency that yields approximately 10 5-10 6 transformants per μg plasmid DNA (circular). Frozen storage
INSTRUCTIONS Frozen-EZ Yeast Transformation II Catalog No. T2001 Highlights High transformation efficiency that yields approximately 10 5-10 6 transformants per μg plasmid DNA (circular). Frozen storage
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit
 ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
NCL Method ITA-6. Leukocyte Proliferation Assay
 NCL Method ITA-6 Leukocyte Proliferation Assay Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory National Cancer Institute-Frederick SAIC-Frederick Frederick, MD 21702 (301) 846-6939 ncl@mail.nih.gov December
NCL Method ITA-6 Leukocyte Proliferation Assay Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory National Cancer Institute-Frederick SAIC-Frederick Frederick, MD 21702 (301) 846-6939 ncl@mail.nih.gov December
3 months 1.5 months 1.5 months. 1 month
 Rabbit monoclonal antibody (Mab) is secreted by the plasma B-cell of the rabbit. Traditional generation of rabbit Mab relies on a rabbit myeloma for B- cell fusion (
Rabbit monoclonal antibody (Mab) is secreted by the plasma B-cell of the rabbit. Traditional generation of rabbit Mab relies on a rabbit myeloma for B- cell fusion (
STEMCELL Quality Control Kits
 STEMCELL Quality Control Kits i Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction...1 2.0 Thawing Cells, Plating and Colony Enumeration...2 2.1 Supplies and reagents included in the QC kit...2 2.2 Additional reagents
STEMCELL Quality Control Kits i Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction...1 2.0 Thawing Cells, Plating and Colony Enumeration...2 2.1 Supplies and reagents included in the QC kit...2 2.2 Additional reagents
Elabscience Biotechnology Co.,Ltd
 Biotechnology Co.,Ltd Your one-stop custom antibody service Antibody is a kind of protein that is the most widely used in the fields of biology and medicine. Antibodies, as the preparations for disease
Biotechnology Co.,Ltd Your one-stop custom antibody service Antibody is a kind of protein that is the most widely used in the fields of biology and medicine. Antibodies, as the preparations for disease
Production of Monoclonal Catalytic Antibodies: Principles and Practice Diane Kubitz, Ehud Keinan
 489 18 Production of Monoclonal Catalytic Antibodies: Principles and Practice Diane Kubitz, Ehud Keinan 18.1 Introduction Antibody catalysis is an experimental science. Although success in this field is
489 18 Production of Monoclonal Catalytic Antibodies: Principles and Practice Diane Kubitz, Ehud Keinan 18.1 Introduction Antibody catalysis is an experimental science. Although success in this field is
Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA
 KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse CKMB in serum, plasma, cell culture fluid and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-57681
KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse CKMB in serum, plasma, cell culture fluid and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-57681
OBTAINING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES TO EPITOPES OF IVERMECTIN
 С.Сейфуллин атындағы Қазақ агротехникалық университетінің Ғылым жаршысы / Вестник науки Казахского агротехнического университета им. С. Сейфуллина. 2013. - 4 (79). C.8-14 OBTAINING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
С.Сейфуллин атындағы Қазақ агротехникалық университетінің Ғылым жаршысы / Вестник науки Казахского агротехнического университета им. С. Сейфуллина. 2013. - 4 (79). C.8-14 OBTAINING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
How To Make A Hybridoma
 Heddy Zola, Child Health Research Institute, Adelaide, Australia Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies with a unique specificity, generally made by cloning cells containing a particular antibody gene to
Heddy Zola, Child Health Research Institute, Adelaide, Australia Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies with a unique specificity, generally made by cloning cells containing a particular antibody gene to
Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348. Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins
 Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348 Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins Biocode Limited November 1992 R&D 348/04/A ENVIRONMENT AGENCY 135357 CONTENTS SUMMARY KEYWORDS
Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348 Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins Biocode Limited November 1992 R&D 348/04/A ENVIRONMENT AGENCY 135357 CONTENTS SUMMARY KEYWORDS
Bio-manufacturing of antigens, antibodies and bioresearch materials
 Bio-manufacturing of antigens, antibodies and bioresearch materials Foetal Bovine Serum (FBS) Human AB Serum Chick Embryo Extract (CEE) Custom polyclonal antibody production Custom monoclonal antibody
Bio-manufacturing of antigens, antibodies and bioresearch materials Foetal Bovine Serum (FBS) Human AB Serum Chick Embryo Extract (CEE) Custom polyclonal antibody production Custom monoclonal antibody
Custom Antibody Services
 Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit
 Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Monoclonal Antibody Supernatant and Ascites Fluid Production
 Monoclonal Antibody Supernatant and Ascites Fluid Production UNIT 2.6 A major advantage of using monoclonal antibodies over polyclonal antisera is the potential availability of large quantities of the
Monoclonal Antibody Supernatant and Ascites Fluid Production UNIT 2.6 A major advantage of using monoclonal antibodies over polyclonal antisera is the potential availability of large quantities of the
POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY DEVELOPMENT
 POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY DEVELOPMENT Abcore is committed to excellence, and to responding to the changing needs of our customers. We have developed polyclonal antibodies for biotechnology and pharmaceutical
POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY DEVELOPMENT Abcore is committed to excellence, and to responding to the changing needs of our customers. We have developed polyclonal antibodies for biotechnology and pharmaceutical
Day -1 RETRIEVAL OF OVARIES AND OOCYTE COLLECTION AND MATURATION
 Day -1 RETRIEVAL OF OVARIES AND OOCYTE COLLECTION AND MATURATION OVARY COLLECTION Materials and Equipment Needed Thermos with 2 containers with 0.5 L of transport saline in each. Appropriate attire as
Day -1 RETRIEVAL OF OVARIES AND OOCYTE COLLECTION AND MATURATION OVARY COLLECTION Materials and Equipment Needed Thermos with 2 containers with 0.5 L of transport saline in each. Appropriate attire as
1.Gene Synthesis. 2.Peptide & Phospho-P. Assembly PCR. Design & Synthesis. Advantages. Specifications. Advantages
 1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
Inc. Wuhan. Quantity Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate 1 Plate sealer for 96 wells 4 Standard (liquid) 2
 Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: uscnk@uscnk.com ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: uscnk@uscnk.com ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal antibody development
 DELFIA DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal development INTRODUCTION The DELFIA system provides a method of discovering specific, high-affinity monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) even in low concentrations
DELFIA DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal development INTRODUCTION The DELFIA system provides a method of discovering specific, high-affinity monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) even in low concentrations
Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells
 METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Peptide Antibody Production
 Peptide Antibody Production A) Peptide BioSynthesis (http://www.biosyn.com, 800-227-0627) B) Conjugation of peptide to KLH (Imject Maleimide Activated KLH, PIERCE=Thermo #77605, 10 mg) C) Peptide affinity
Peptide Antibody Production A) Peptide BioSynthesis (http://www.biosyn.com, 800-227-0627) B) Conjugation of peptide to KLH (Imject Maleimide Activated KLH, PIERCE=Thermo #77605, 10 mg) C) Peptide affinity
Antigens & Antibodies II. Polyclonal antibodies vs Monoclonal antibodies
 A Brief Review of Antibody Structure A Brief Review of Antibody Structure The basic antibody is a dimer of dimer (2 heavy chain-light chain pairs) composed of repeats of a single structural unit known
A Brief Review of Antibody Structure A Brief Review of Antibody Structure The basic antibody is a dimer of dimer (2 heavy chain-light chain pairs) composed of repeats of a single structural unit known
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit
 Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
QIAGEN Supplementary Protocol
 QIAGEN Supplementary Protocol Isolation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) and Purification of Total RNA from PBMC Using the RNeasy Micro or Mini Kit This protocol describes how to isolate PBMC
QIAGEN Supplementary Protocol Isolation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) and Purification of Total RNA from PBMC Using the RNeasy Micro or Mini Kit This protocol describes how to isolate PBMC
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 Title: Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay (LPA) Using 3 H- Thymidine Incorporation Assay Core Name: Lloyd Mayer, Mount Sinai Medical Center Effective Date: 02/16/2012 Trial Number: ITN047AI SOP # ITN2800 SOP
Title: Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay (LPA) Using 3 H- Thymidine Incorporation Assay Core Name: Lloyd Mayer, Mount Sinai Medical Center Effective Date: 02/16/2012 Trial Number: ITN047AI SOP # ITN2800 SOP
Geniron. Custom Antibody Services. Serum services Antibody Monoclonal. Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody
 Geniron Custom Antibody Services Serum services Antibody Monoclonal Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody Geniron Poly Y WE PROVIDE OUR SERVICES TO With Expertise
Geniron Custom Antibody Services Serum services Antibody Monoclonal Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody Geniron Poly Y WE PROVIDE OUR SERVICES TO With Expertise
MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit
 Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0479r 96 Tests Operating instructions www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0479r 96 Tests Operating instructions www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein. Table of Contents Fall 2012
 Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
Aviva Systems Biology
 Aviva Custom Antibody Services and Prices Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Polyclonal package 1 (From protein to antiserum) Polyclonal package 2
Aviva Custom Antibody Services and Prices Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Polyclonal package 1 (From protein to antiserum) Polyclonal package 2
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions. Antibody Overview. by Advanced BioDesign. Project Start. Immunogenicity. Selecting Your Antigen
 Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions by Advanced BioDesign Antibody Overview Launching an immunisation programme is an important experimental step that needs care. With Advanced BioDesign, you may develop
Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions by Advanced BioDesign Antibody Overview Launching an immunisation programme is an important experimental step that needs care. With Advanced BioDesign, you may develop
Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual
 Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0065.03 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34+ Progenitor Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human umbilical
Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34 + Progenitor Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0065.03 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34+ Progenitor Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human umbilical
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit
 ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit ABE5487 100 assays; Store at -20 C
 Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit ABE5487 100 assays; Store at -20 C I. Introduction: Creatine Kinase (CK) also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and ATP: creatine N- phosphotransferase
Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit ABE5487 100 assays; Store at -20 C I. Introduction: Creatine Kinase (CK) also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and ATP: creatine N- phosphotransferase
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit
 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
CMP Antibody Production Service
 CMP Antibody Production Service Polyclonal antibody production has become an essential part of many research projects at Texas A&M. Standardization of production procedures and the performance of the procedures
CMP Antibody Production Service Polyclonal antibody production has become an essential part of many research projects at Texas A&M. Standardization of production procedures and the performance of the procedures
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual
 Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies
 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies 23 2 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies Mary A. Ritter 1. Introduction The breadth of repertoire yet beautiful specificity of the antibody response is the key to
Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies 23 2 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies Mary A. Ritter 1. Introduction The breadth of repertoire yet beautiful specificity of the antibody response is the key to
Custom Antibody Services
 prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
Mouse Insulin ELISA. For the quantitative determination of insulin in mouse serum and plasma
 Mouse Insulin ELISA For the quantitative determination of insulin in mouse serum and plasma Please read carefully due to Critical Changes, e.g., Calculation of Results. For Research Use Only. Not For Use
Mouse Insulin ELISA For the quantitative determination of insulin in mouse serum and plasma Please read carefully due to Critical Changes, e.g., Calculation of Results. For Research Use Only. Not For Use
HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit
 Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
How Does a Doctor Test for AIDS?
 Edvo-Kit #S-70 How Does a Doctor Test for AIDS? S-70 Experiment Objective: The Human Immunodefi ciency Virus (HIV) is an infectious agent that causes Acquired Immunodefi ciency Syndrome (AIDS) in humans.
Edvo-Kit #S-70 How Does a Doctor Test for AIDS? S-70 Experiment Objective: The Human Immunodefi ciency Virus (HIV) is an infectious agent that causes Acquired Immunodefi ciency Syndrome (AIDS) in humans.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for the production and testing of embryonic stem cell lines in Taiwan Stem Cell Bank
 Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for the production and testing of embryonic stem cell lines in Taiwan Stem Cell Bank Bioresource Collection and Research Centre (BCRC) at Food Industry Research and
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for the production and testing of embryonic stem cell lines in Taiwan Stem Cell Bank Bioresource Collection and Research Centre (BCRC) at Food Industry Research and
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual
 Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Taqman TCID50 for AAV Vector Infectious Titer Determination
 Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To determine the concentration of infectious particles in an AAV vector sample. This process involves serial dilution of the vector in a TCID50 format and endpoint determination through
Page 1 of 8 Purpose: To determine the concentration of infectious particles in an AAV vector sample. This process involves serial dilution of the vector in a TCID50 format and endpoint determination through
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION
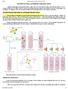 MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION Antibodies having single specificity produced from a single clone of B cell are referred as Mono clonal antibodies (MAbs). In 1975, Georges Köhler and Cesar Milstein devised
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION Antibodies having single specificity produced from a single clone of B cell are referred as Mono clonal antibodies (MAbs). In 1975, Georges Köhler and Cesar Milstein devised
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies
 Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies Authors: Adapted by Prof M van Vuuren. Originally compiled by Dr RW Worthington. (Retired) Licensed under a Creative
Serology: Fluorescent antibody tests and other tests employing conjugated antibodies Authors: Adapted by Prof M van Vuuren. Originally compiled by Dr RW Worthington. (Retired) Licensed under a Creative
Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies for aflatoxin B1
 Letters in Applied Microbiology 1999, 29, 284 288 Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies for aflatoxin B1 K. T. Devi 1, M.A. Mayo 2, K.L.N. Reddy 2, P. Delfosse 1, G. Reddy 3, S.V. Reddy
Letters in Applied Microbiology 1999, 29, 284 288 Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies for aflatoxin B1 K. T. Devi 1, M.A. Mayo 2, K.L.N. Reddy 2, P. Delfosse 1, G. Reddy 3, S.V. Reddy
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Day 1 A) DNA shearing 1. Samples Dissect tissue (One Mouse OBs) of interest and transfer to an eppendorf containing 0.5 ml of dissecting media (on ice) or PBS but without
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Day 1 A) DNA shearing 1. Samples Dissect tissue (One Mouse OBs) of interest and transfer to an eppendorf containing 0.5 ml of dissecting media (on ice) or PBS but without
PROTOCOL. Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry. Background. Materials and equipment required.
 PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
Proto col. GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells. Tech support: 877-994-8240. Luciferase Assay System
 Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
Benchtop Mitochondria Isolation Protocol
 Benchtop Mitochondria Isolation Protocol Note: Specific protocols are available for the following products: MS850 Mitochondria Isolation Kit for Rodent Tissue MS851 Mitochondria Isolation Kit for Rodent
Benchtop Mitochondria Isolation Protocol Note: Specific protocols are available for the following products: MS850 Mitochondria Isolation Kit for Rodent Tissue MS851 Mitochondria Isolation Kit for Rodent
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials Giving a subcutaneous injection
 NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
NCL Method ITA-14. Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro
 NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling
 Protocol Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-97893-117 Order per fax: +49-30-97893-299 Or e-mail: peptide@jpt.com www: www.jpt.com
Protocol Protease Peptide Microarrays Ready-to-use microarrays for protease profiling Contact us: InfoLine: +49-30-97893-117 Order per fax: +49-30-97893-299 Or e-mail: peptide@jpt.com www: www.jpt.com
Human Adult Stem Cell Manual Differentiation protocols for human adipose-derived adult stem cells
 Human Adult Stem Cell Manual Differentiation protocols for human adipose-derived adult stem cells INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0015.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Stem Cells (ASC) Orders are delivered via
Human Adult Stem Cell Manual Differentiation protocols for human adipose-derived adult stem cells INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0015.01 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult Stem Cells (ASC) Orders are delivered via
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
Item 2 Guidelines for the Production of Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies in Rodents and Rabbits
 Antibody Production/Neoplasia Item 2 Guidelines for the Production of Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies in Rodents and Rabbits Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are important reagents utilized in
Antibody Production/Neoplasia Item 2 Guidelines for the Production of Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies in Rodents and Rabbits Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are important reagents utilized in
Production of Monoclonal Antibody Supernatant and Ascites Fluid
 Production of Monoclonal Antibody Supernatant and Ascites Fluid Wayne M. Yokoyama 1 UNIT 11.10 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri ABSTRACT
Production of Monoclonal Antibody Supernatant and Ascites Fluid Wayne M. Yokoyama 1 UNIT 11.10 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri ABSTRACT
Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension
![Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Amaxa 4D-Nucleofector Protocol for Mouse Embryonic Stem [ES] Cells For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension](/thumbs/30/14702458.jpg) For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Cells derived from mouse blastocysts; round cells, growing in clumps s 1. This protocol is meant to provide an outline for the handling and the Nucleofection
For 4D-Nucleofector X Unit Transfection in suspension Cells derived from mouse blastocysts; round cells, growing in clumps s 1. This protocol is meant to provide an outline for the handling and the Nucleofection
Measuring Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity: Cell Counting Kit-F
 Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
