The isopod Asellus aquaticus: A novel arthropod model organism to study evolution of segment identity and patterning 1
|
|
|
- Marian Dixon
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Palaeodiversity 3, Supplement: 89 97; Stuttgart 30 December The isopod Asellus aquaticus: A novel arthropod model organism to study evolution of segment identity and patterning 1 PHILIPP VICK & MARTIN BLUM Abstract Hox genes have been recognized as widely conserved metazoan genes relevant for patterning of embryonic axes. In insects, Hox genes display more or less strict tagmata-related expression patterns. For example, activity of abdominal-a (abd-a) correlates with the legless abdomen. In crustaceans, in contrast, expression domains are more divers. In the branchiopod Artemia franciscana, expression domains of posterior Hox genes display overlapping patterns. In the more modern malacostracan isopod Porcellio scaber however, abd-a is restricted to the developing pleon. Here we present the partial cloning and expression patterns of the Hox genes abd-a and Antennapedia from the freshwater crustacean Asellus aquaticus. In contrast to Porcellio this isopod shows a slightly different regulation of posterior segment patterning. The obtained abd-a signal points to a conserved early role in the pleon as well as to an anteriorly extended function in the pereon and pleon in later stages. In addition, we detected an as yet unknown endodermal expression domain of abd-a in the epithelium of the early developing digestive gland, which indicates a diverse role of this gene. The waterlouse Asellus aquaticus thus may provide a relevant and novel crustacean model organism for the study of evolutionary changes of segment identity and patterning. K e y w o r d s : EvoDevo, Asellus aquaticus, Hox, Antp, abd-a, dll, evolution, segment identity, segment patterning. Zusammenfassung Hox-Gene sind stark konservierte Gene der Metazoa, die für die Musterbildung embryonaler Achsen von Bedeutung sind. In Insekten zeigen Hox-Gene mehr oder weniger streng an Tagmata gebundene Expressionsmuster. Die Aktivität von abdominal-a (abd-a) korreliert zum Beispiel mit dem beinlosen Abdomen. In den Krebstieren sind die Expressionsdomänen dagegen unterschiedlicher. In dem Kiemenfußkrebs Artemia franciscana zeigen die posterioren Hox-Expressionsdomänen überlappende Muster. In dem modernen Isopoden Porcellio scaber ist abd-a jedoch auf das entstehende Pleon beschränkt. Wir berichten hier von der partiellen Klonierung und den Expressionsmustern der Hox-Gene abd-a und Antennapedia des Süßwasserkrebses Asellus aquaticus. Im Gegensatz zu Porcellio zeigt dieser Isopode eine leicht unterschiedliche Regulierung der posterioren Segmente. Das erhaltene abd-a-signal deutet sowohl auf eine konservierte frühe Rolle im Pleon als auch auf eine in späteren Stadien nach anterior hin erweiterte Funktion in Pereon und Pleon hin. Zusätzlich entdeckten wir eine bislang unbekannte endodermale Expression von abd-a im entstehenden Mitteldarmdrüsenepithel, was auf eine vielfältige Rolle für dieses Gen hindeutet. Die Wasserassel Asellus aquaticus könnte damit einen neuen und relevanten Modellorganismus zur Studie von evolutionären Änderungen von Segmentidentität und -musterbildung darstellen. Contents 1. Introduction Results and discussion Adult morphology of Asellus aquaticus Embryonic development of Asellus aquaticus Early expression patterns of abdominal-a in embryos of Asellus aquaticus Late expression pattern of abd-a Late expression pattern of Antp in Asellus aquaticus Distal-less (dll) expression in developing appendages of Asellus aquaticus embryos Summary and outlook: comparison of Hox expression patterns in Asellus and Porcellio References Contribution to the WILLI-HENNIG-Symposium on Phylogenetics and Evolution, University of Hohenheim, 29 September 2 October 2009.
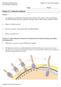
2 90 PALAEODIVERSITY 3, SUPPLEMENT, Introduction The Hox genes have been recognized as widely conserved metazoan genes relevant for patterning of the em- bryonic axes (TABIN 1992; K RUMLAUF 1993; AKAM et al. 1994; RUDDLE et al. 1994; AKAM 1995; HOLLAND & GARCIAFERNANDEZ 1996; AVEROF 1997; WOLPERT 2000; POPODI & R AFF 2001; VERVOORT 2002; DEUTSCH & MOUCHEL-VIELH Fig. 1. Asellus aquaticus: adult female morphology. A. Dorsal view of an adult female displaying the cephalothorax (ct) with a pair of antennules (an) and antennae (at), seven free thoracic segments (T2 T8), two free pleonic segments and the pleotelson (pt) bearing the uropods (u). B. Lateral view of same specimen displaying the seven pairs of pereopods (walking legs), marsupium and operculum. Please note the absence of the 5th pereopod (marked by an asterisk). C. Ventral view of a female with the marsupium in high magnification. The breeding room is filled with developing embryos. For some embryos the body shape is outlined by dotted lines. Eyes have developed and are visible as pigmented dots (e), and the green yolk inside the paired digestive glands is clearly discernable. Anterior to the left. m, marsupium; op, operculum; T2 T8, thoracomer 2 8; y, yolk; zc, Zenker cells (ZENKER 1854; DOHRN 1867).
3 VICK & BLUM, THE ISOPOD ASELLUS AQUATICUS 2003; GARCIA-FERNANDEZ 2005; HOEGG & MEYER 2005; PEARSON et al. 2005; DUBOULE 2007; HUEBER & LOHMANN 2008; WELLIK 2009). In particular, they act as selector genes for segment identity throughout the animal kingdom. In insects, Hox genes display more or less strict tagmata-related expression patterns. For example, activity of abdominal-a (abd-a) correlates with the legless abdomen. In crustaceans, in contrast, expression domains are more divers. In the branchiopod brine shrimp Artemia franciscana, for example, expression domains of the posterior Hox genes follow the insect-type overlapping pattern (AVEROF & A KAM 1995). In the more modern malacostracan isopod Porcellio scaber however, abd-a is restricted to the developing pleon (ABZHANOV & KAUFMAN 2000a). Here we present the partial cloning and expression patterns of the Hox genes abd-a and Antennapedia (Antp), 91 and the homeobox gene distal-less (dll) from the freshwater crustacean Asellus aquaticus. In contrast to Porcellio this isopod shows a similar but slightly different regulation of posterior segment patterning. The abd-a signal obtained by whole-mount in situ hybridization points to a more anterior extended function in the posterior pereon as well as to a conserved role in the pleon. In addition, we detected an as yet unknown endodermal expression domain of abd-a in the epithelium of the early developing digestive gland, which indicates a diverse role of this gene. Furthermore, we analyzed the expression of Asellus Antp, a Hox gene known to be expressed in the crustacean trunk, and of distal-less (dll), a gene expressed specifically in body appendages. Both expression domains are conserved in Asellus, underlining the significance of the derived expression patterns of abd-a. The waterlouse Fig. 2. Embryonic development of Asellus aquaticus. A. Lateral view of an embryo at about 40 % of development, still inside the chorion. The starting point of the dorsal curvature between head and posterior end of the pleon is indicated by a dotted line. B. Lateral view of an embryo at about 60 % of development. B. Ventral view of the embryo shown in B. Lateral organs can be seen at the level of the first thoracomer. C. Lateral view of an embryo at about 70 % of development. Anteriorly, the yolk begins to be incorporated into the paired digestive glands (arrowhead). Appendages are well developed and dorsal bending is nearly fully retracted. D. Dorsal view of an embryo just before the end of embryonic development (first molt). The yolk now is fully incorporated into the glands and thoracomers are clearly distinguishable. Please note the greenish color of the yolk. Staging of embryos according to WHITINGTON et al. (1993). Anterior to the left. White arrows mark approximate border between pereon/thorax and pleon. at, antenna; ct, cephalothorax; e, eye; h, head; lo, lateral organ; pl, pleon; pt, pleotelson; T2 T8, thoracomer 2 8; u, uropod; y, yolk.
4 92 PALAEODIVERSITY 3, SUPPLEMENT, 2010 Asellus aquaticus thus may provide a relevant and novel crustacean model organism for the study of evolutionary changes of segment identity and patterning. 2. Results and discussion 2.1. Adult morphology of Asellus aquaticus Fig. 1 shows the adult morphology of Asellus aquaticus, both as a reference point and to correlate embryonic expression patterns shown below. In the genus Asellus the head and the first trunk segment are fused to form a cephalothorax, followed by seven free thoracic segments (the so-called pereomers), two small free pleonic segments and a pleotelson, in which four pleon segments are fused with the telson (Fig. 1A, B). Females temporarily develop a marsupium on the ventral side, representing an isopodcharacteristic breeding room, in which the whole embryonic development takes place (Fig. 1C). The marsupium is bordered by the anterior pereonic sternites and the specialized, flattened epipodites of the same segments. Embryos are visible through the marsupium and may easily be obtained (GRUNER 1965; VICK et al. 2009) Embryonic development of Asellus aquaticus For a comparative analysis of embryonic development of Asellus aquaticus in relation to other crustacean species, staging of embryos was adapted to WHITINGTON et al. (1993). Asellus develops no ventral groove and is thus characterized by a dorsal curvature, which separates head and pleon early during development (Fig. 2A, B). This represents a typical feature of isopods and a few other crustacean orders, which all lack development of a ventral groove (GRUNER 1965). Another typical characteris- Fig. 3. Early embryonic expression patterns of abd-a in Asellus aquaticus embryos. A A. Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WMISH) of an embryo at ~50 % of development showing abd-a mrna expression mainly in the pleon and in the paired endodermal anlagen of the digestive glands (e). A. Only the posterior expression domain can bee seen. A. Ventral view displaying lateral organs (lo) and endodermal primordia, which are visible through the translucent ectoderm (dotted rings). A. A sagittal section (plane indicated in A ) highlights expression domains. B B. Control embryo at ~50 % of development hybridized with a sense probe showing no expression in any tissue. A, A, B, B lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal to the top; A, B ventral views, anterior to the left. an, antennule; h, head; y, yolk. Black arrowheads indicate approximate anterior and posterior expression boundaries.
5 VICK & BLUM, THE ISOPOD ASELLUS AQUATICUS 93 tic of this species are the so-called lateral organs (WEY- GOLDT 1959). These arise very early in development and persist until the first ecdysis, i. e. they mark embryonic development (Fig. 2B, D). During development, appendages arise from all segments formed. Parallel to the stretching of the anterior-posterior axis, through which the dorsal curvature disappears, the yolk is consumed or incorporated into the digestive glands (Fig. 2B D). Before the first molt, which transforms the embryo into a juvenile isopod, the embryo is fully stretched, bears developed appendages, eye spots, and a continuous gut, and thus roughly resembles an adult specimen (Fig. 2D). However, this late embryo as well as the following juvenile (or manca) stage still lack the eighth thoracic appendages, i. e. the last pair of walking legs Early expression patterns of abdominal-a in embryos of Asellus aquaticus Following partial cloning of the Asellus aquaticus abd-a gene (VICK et al. 2009; accession number ACG63499), an expression analysis was performed by whole-mount in situ hybridization using an antisense-specific riboprobe. At about 50 % of development, mrna transcription could be detected in the developing pleon, excluding the very posterior part, i. e. the telson (Fig. 3A A ). Most remarkably, an additional expression domain was detected in the epithelial lining of the two endodermal anlagen of the digestive glands in the anterior thorax (Fig. 3A, A ). A sense control probe revealed no staining, underscoring the specificity of the obtained mrna signals (Fig. 3B B ). Fig. 4. Late expression patterns of abd-a in embryos of Asellus aquaticus. A A. abd-a mrna expression in a ~75 % embryo. Expression was seen between the 5 th pereonic segment and the anterior pleon. Transversal sections (A, A ) showed strong expression in the ventral nerve cord (vnc) and weaker signals in the proximal limbs and the remainder of the mesodermal and ectodermal trunk tissue, which gradually faded towards the dorsal side. B, B. Expression of abd-a in an embryo at ~90 % of development. The signal was clearly restricted to a region between T5 and pleonic segment 3, with strongest expression in T7 and T8 (B ), the developing 7 th pereopod (* in B), and the proximal limbs of the anterior pleonic segments (B). A and B, lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal to the top; B, dorsal view, anterior to the left; A and A, transversal sections, dorsal to the top. White arrows mark tagmata boundary between pereon and pleon. Black arrowheads indicate approximate anterior and posterior expression boundaries. Dashed lines indicate approximate planes of section. h, head; lo, lateral organ; pt pleotelson; T2 T8, thoracomers 2 8; y, yolk.
6 94 PALAEODIVERSITY 3, SUPPLEMENT, Late expression pattern of abd-a A careful expression analysis of the final stages of embryonic development of Asellus aquaticus revealed a striking change of abd-a transcript distribution. From 75 % of embryonic development onwards, abd-a was active more anteriorly in the embryo. abd-a was found to be expressed in the anterior-most pleon (pleomeres 1 and 2) and most strongly in the posterior thoracic segments (T5 T8; Fig. 4A, B). Transversal histological sections revealed strong staining of the ventral nerve cord and of the surrounding ventral ectodermal and mesodermal tissues (Fig. 4A, A ). The appendages of these segments showed positive abd-a signals only in the very proximal parts (asterisk in Fig. 4B). Interestingly, this positive staining of the pleonic ventral nerve cord was not found in Porcellio scaber (ABZHANOV & KAUFMAN 2000a) Late expression pattern of Antp in Asellus aquaticus To learn more about the significance of this derived expression pattern of abd-a, Antennapedia (Antp), another trunk Hox gene, was cloned (accession number Fig. 5. Late embryonic expression patterns of Antp in embryos of Asellus aquaticus. A. Lateral view of an embryo at about 90 % of development after WMISH. A strong signal was detectable in T2 T8 and in the proximal appendages. Weak expression was seen in T1 and the ventral pleonic segments. A. Transverse histological section through the pereon. Besides weak ventral and lateral expression patterns, a strong signal was detected in the ventral nerve cord (vnc). B. Lateral view of a sense control embryo of the same stage, in which no staining could be detected besides an artificial signal at the base of the lateral organ. B, B. Higher magnification of the lateral organ region to visualize artificial staining at its basis. Dorsal to the top in A, A, B. Anterior to the top in B, B. Black arrowheads indicate approximate anterior and posterior expression boundaries. White arrow marks tagmata boundary between pereon/thorax and pleon. Dashed line in (A) indicates approximate plane of section. h, head; lo, lateral organ; T2 T8, thoracomers 2 8; y, yolk.
7 VICK & BLUM, THE ISOPOD ASELLUS AQUATICUS 95 HM044765). Antp is known to be expressed in the crustacean thorax (AVEROF & AKAM 1995; ABZHANOV & KAUFMAN 2000a) and therefore served as a probe to compare conservation of expression patterns among different crustacean species. In contrast to abd-a, expression of Antp was found to be conserved as compared to other crustacean and isopod species. Expression was detected in all thorax segments (including T1) as well as in the ventral parts of the anterior pleon and some proximal pleonic appendages (Fig. 5A). The domain in the pleonic appendages represented the sole difference to Porcellio Antp (ABZHANOV & KAUFMAN, 2000a). Histological sections revealed intense signals in the ventral nerve cords (Fig. 5A ). Sense control riboprobes showed no specific staining (Fig. 5B). dll as a further example (accession number HM044766). In all arthropod species analyzed so far, dll is expressed in developing appendages (PANGANIBAN et al. 1994, 1995, 1997; ABZHANOV & KAUFMAN 2000b; PANGANIBAN & RU- BENSTEIN 2002). Expression of Asellus aquaticus dll was found in most developing appendages in embryos developed to 60 % and 70 % of embryogenesis (Fig. 6A, B), while sense control riboprobes were negative in all cases (cf. inset in Fig. 6A). In accordance with their very early occurrence and origin, the lateral organs showed no expression ( WEYGOLDT 1959). Histological sections verified specific staining of the appendages (Fig. 6A, B, B ). Therefore, Asellus aquaticus represents another example of conserved dll expression in developing appendages Distal-less (dll) expression in developing appendages of Asellus aquaticus embryos To verify conservation of expression patterns of major developmental genes in Asellus aquaticus, we analyzed 2.7. Summary and outlook: comparison of Hox expression patterns in Asellus and Porcellio In summary, the expression patterns of the developmental genes were largely conserved, particularly with Fig. 6. Expression of dll in appendages but not in the lateral organs of Asellus aquaticus embryos. A. Ventral view of an embryo at about 60 % of development showed expression specifically in developing appendages (arrows). Sense control (inset) was free of staining. A. Lateral view of the same specimen showed strong expression in the antenna. Lateral staining at the posterior thorax and pleon represents an artifact. A. Transversal section as indicated in (A) and (A ) revealed staining in the appendages. B. Lateral view of an embryo at about 70 % exhibited expression in the mouth parts and appendages. B. Ventral view of the same embryo showed distinct domains of dll expression in the pleonic and posterior thoracic appendages. B, B. Sagittal sections of the specimen as depicted in (B ) underlined appendage-specific dll mrna transcription in the proximal and distal parts. Anterior to the left in A, A and B B. In A B, B and B dorsal is to the top. an, antennula; at, antenna; h, head; lo, lateral organ; pp, pleopod; pr, pereopod; y, yolk.
8 96 PALAEODIVERSITY 3, SUPPLEMENT, 2010 respect to Antp and dll. In this light, the divergent patterns of abd-a deserve all the more attention (Fig. 7). Asellus aquaticus displayed strong expression patterns of abd-a in P6, P7 and the free pleonic segments 1 and 2, and weaker levels in P5 and pleonic segment 3. In contrast, strong expression in Porcellio was restricted to the pleonic segments. In P6 and P7 a weak expression was reported (ABZHANOV & KAUFMAN 2000a). Our abd-a expression analysis in Asellus aquaticus thus demonstrated a clear correlation of expression domains with distinct morphogenetic units in two cases: pleotelson fusion (absence of abd-a transcription; cf. Fig. 4B ) and pereonic limb orientation (strong abd-a expression during the process of posterior bending in late stages; cf. Fig. 4A). Compared to abd-a expression in Porcellio, the adult morphology divergence is mimicked by a corresponding change in gene expression, i. e. abd-a activity throughout the pleonic segments (which do not fuse), and lack of activity in posterior pereopods (which do hardly orient posteriorly; VON H AFFNER 1937; GRUNER 1965). Thus, even between highly related crustaceans, shifts of Hox gene expression boundaries correlate with adult morphological variations. We thus hypothesize that temporal-spatial changes in abd-a gene expression are responsible for morphogenetic variations in adult morphologies of Asellus aquaticus and Porcellio scaber. Direct testing of this proposal might become possible in the future, provided that techniques for genetic manipulation of embryos become available. 3. References ABZHANOV, A. & KAUFMAN, T. C. (2000a): Crustacean (malacostracan) Hox genes and the evolution of the arthropod trunk. Development, 127: ABZHANOV, A. & KAUFMAN, T. C. (2000b): Homologs of Drosophila appendage genes in the patterning of arthropod limbs. Developmental Biololgy, 227: AKAM, M. (1995): Hox genes and the diversification of insect and crustacean body plans. Nature, 376: AKAM, M., AVEROF, M., CASTELLI-GAIR, J., DAWES, R., FALCIANI, F., & FERRIER, D. (1994): The evolving role of Hox genes in arthropods. Development, Supplement: AVEROF, M. (1997): Arthropod evolution: same Hox genes, different body plans. Current Biology, 7: R634 R636. AVEROF, M. & AKAM, M. (1995): Hox genes and the diversification of insect and crustacean body plans. Nature, 376: DEUTSCH, J. S. & MOUCHEL-VIELH, E. (2003): Hox genes and the crustacean body plan. Bioessays, 25: DOHRN, A. (1867): Die embryonale Entwicklung des Asellus aquaticus. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 17: DUBOULE, D. (2007): The rise and fall of Hox gene clusters. Development, 134: Fig. 7. Expression domains of abd-a mrna in Asellus aquaticus (left) and Porcellio scaber (right). The experimentally derived embryonic patterns are shown in relation to the adult morphology. Dark blue coloring indicates strong gene activities, while a light blue color refers to weaker expression domains. at, antennae; an, antennule; ct, cephalothorax; pl, pleon; pt, pleotelson.
9 VICK & BLUM, THE ISOPOD ASELLUS AQUATICUS 97 GARCIA-FERNANDEZ, J. (2005): The genesis and evolution of homeobox gene clusters. Nature Review Genetics, 6: GRUNER, H.-E. (1965): Krebstiere oder Crustacea, V. Isopoda. In: DAHL, M. & PEUS, F. (eds.): Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der angenzenden Meeresteile, 51: VIII pp.; Jena (Gustav Fischer Verlag). HOEGG, S. & MEYER, A. (2005): Hox clusters as models for vertebrate genome evolution. Trends in Genetics, 21: HOLLAND, P. W. & GARCIA-FERNANDEZ, J. (1996): Hox genes and chordate evolution. Developmental Biololgy, 173: HUEBER, S. D. & LOHMANN, I. (2008): Shaping segments: Hox gene function in the genomic age. Bioessays, 30: KRUMLAUF, R. (1993): Hox genes and pattern formation in the branchial region of the vertebrate head. Trends in Genetics, 9: PANGANIBAN, G. & RUBENSTEIN, J. L. (2002): Developmental functions of the Distal-less/Dlx homeobox genes. Development, 129: PANGANIBAN, G., NAGY, L. & CARROLL, S. B. (1994): The role of the Distal-less gene in the development and evolution of insect limbs. Current Biology, 4: PANGANIBAN, G., SEBRING, A., NAGY, L. & CARROLL, S. (1995): The development of crustacean limbs and the evolution of arthropods. Science, 270: PANGANIBAN, G., IRVINE, S. M., LOWE, C., ROEHL, H., CORLEY, L. S., SHERBON, B., GRENIER, J. K., FALLON, J. F., KIMBLE, J., WALKER, M., WRAY, G. A., SWALLA, B. J., MARTINDALE, M. Q. & CARROLL, S. B. (1997): The origin and evolution of animal appendages. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 94: PEARSON, J. C., LEMONS, D. & MCGINNIS, W. (2005): Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning. Nature Review Genetics, 6: POPODI, E. & RAFF, R. A. (2001): Hox genes in a pentameral animal. Bioessays, 23: RUDDLE, F. H., BARTELS, J. L., BENTLEY, K. L., KAPPEN, C., MURTHA, M. T. & PENDLETON, J. W. (1994): Evolution of Hox genes. Annual Review of Genetics, 28: TABIN, C. J. (1992): Why we have (only) five fingers per hand: hox genes and the evolution of paired limbs. Development, 116: VERVOORT, M. (2002): Functional evolution of Hox proteins in arthropods. Bioessays, 24: VICK, P., SCHWEICKERT, A. & BLUM, M. (2009). Cloning and expression analysis of the homeobox gene abdominal-a in the isopod Asellus aquaticus. In: KURZFIELD, N. C. (ed.): Development Gene Expression Regulation: ; Hauppauge (Nova Science Publishers). VON HAFFNER, K. (1937): Untersuchungen über die ursprüngliche und abgeleitete Stellung der Beine bei den Isopoden. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 149: WELLIK, D. M. (2009): Hox genes and vertebrate axial pattern. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 88: WEYGOLDT, P. (1959): Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Malakostrakenentwicklung. Die Keimblätterbildung bei Asellus aquaticus (L.). Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 163: WHITINGTON, P. M., LEACH, D. & SANDEMAN, R. (1993): Evolutionary change in neural development within the arthropods: axonogenesis in the embryos of two crustaceans. Development, 118: WOLPERT, L. (2000): What is evolutionary developmental biology? Novartis Foundation Symposium, 228: 1 14, discussion ZENKER, D. (1854): Über Asellus aquaticus. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 20: Addresses of the authors: PHILIPP VICK, MARTIN BLUM, Institute of Zoology, University of Hohenheim, Garbenstr. 30, Stuttgart, Germany Present address of P. VICK: HHMI, University of California, Los Angeles, CA , USA of corresponding author: martin.blum@uni-hohenheim.de Manuscript received 15 April 2010, accepted 15 June 2010.
Evolution of new appendage types by gradual changes in Hox gene expression the case of crustacean maxillipeds 1
 Palaeodiversity 3, Supplement: 141 145; Stuttgart 30 December 2010. 141 Evolution of new appendage types by gradual changes in Hox gene expression the case of crustacean maxillipeds 1 MICHALIS AVEROF,
Palaeodiversity 3, Supplement: 141 145; Stuttgart 30 December 2010. 141 Evolution of new appendage types by gradual changes in Hox gene expression the case of crustacean maxillipeds 1 MICHALIS AVEROF,
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Chapter 47: Animal Development
 Name Period Overview 1. An organism s development is controlled by the genome of the zygote as well as by molecules from the mother that are in the cytoplasm of the egg. What are these proteins and RNAs
Name Period Overview 1. An organism s development is controlled by the genome of the zygote as well as by molecules from the mother that are in the cytoplasm of the egg. What are these proteins and RNAs
Chapter 32: An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Name Period Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 1. Like the fungi, animals are multicellular heterotrophs. How do they feed?
Name Period Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 1. Like the fungi, animals are multicellular heterotrophs. How do they feed?
ALLEN Mouse Brain Atlas
 TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER: QUALITY CONTROL STANDARDS FOR HIGH-THROUGHPUT RNA IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION DATA GENERATION Consistent data quality and internal reproducibility are critical concerns for high-throughput
TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER: QUALITY CONTROL STANDARDS FOR HIGH-THROUGHPUT RNA IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION DATA GENERATION Consistent data quality and internal reproducibility are critical concerns for high-throughput
Origin of insect metamorphosis based on designby-contract: larval stages as an atavism
 Origin of insect metamorphosis based on designby-contract: larval stages as an atavism Albert D.G. de Roos, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Abstract The steps leading to the insertion of a larval stage during
Origin of insect metamorphosis based on designby-contract: larval stages as an atavism Albert D.G. de Roos, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Abstract The steps leading to the insertion of a larval stage during
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Fossils, genes and the evolution of animal limbs
 Fossils, genes and the evolution of animal limbs Neil Shubin, Cliff Tabin & Sean Carroll... The morphological and functional evolution of appendages has played a crucial role in the adaptive radiation
Fossils, genes and the evolution of animal limbs Neil Shubin, Cliff Tabin & Sean Carroll... The morphological and functional evolution of appendages has played a crucial role in the adaptive radiation
The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology 2. Cleavage, Gastrulation, Neurulation and Organogenesis
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lectures 4 and 5 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology 2 Cleavage, Gastrulation, Neurulation and Organogenesis Early animal development
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lectures 4 and 5 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology 2 Cleavage, Gastrulation, Neurulation and Organogenesis Early animal development
In developmental genomic regulatory interactions among genes, encoding transcription factors
 JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY Volume 20, Number 6, 2013 # Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 419 423 DOI: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0297 Research Articles A New Software Package for Predictive Gene Regulatory Network
JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY Volume 20, Number 6, 2013 # Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 419 423 DOI: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0297 Research Articles A New Software Package for Predictive Gene Regulatory Network
II. Germ Layers Ontogeny can reveal a great deal about evolutionary relationships. Answer and discuss the following:
 Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia by Dana Krempels Perhaps even more than the other Eukarya, Animalia is characterized by a distinct progression of complexity in form and function as one moves from the
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia by Dana Krempels Perhaps even more than the other Eukarya, Animalia is characterized by a distinct progression of complexity in form and function as one moves from the
Biological kinds and the causal theory of reference
 Biological kinds and the causal theory of reference Ingo Brigandt Department of History and Philosophy of Science 1017 Cathedral of Learning University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA 15260 E-mail: inb1@pitt.edu
Biological kinds and the causal theory of reference Ingo Brigandt Department of History and Philosophy of Science 1017 Cathedral of Learning University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA 15260 E-mail: inb1@pitt.edu
Macroevolution: Change above the species level NABT 2006 Evolution Symposium
 Introduction Macroevolution: Change above the species level NABT 2006 Evolution Symposium The basic concept of evolution change over time can be examined in two different time frames. The first, which
Introduction Macroevolution: Change above the species level NABT 2006 Evolution Symposium The basic concept of evolution change over time can be examined in two different time frames. The first, which
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Letter to the Student... 5 Letter to the Family... 6 Ohio Academic Content Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Investigation 1... 11
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 Ohio Academic Content Standards Correlation Chart...........
Table of Contents Letter to the Student...................................... 5 Letter to the Family....................................... 6 Ohio Academic Content Standards Correlation Chart...........
FIELD RECOGNITION OF THE LARVAE OF NATIVE COCCINELLIDAE, COMMON TO THE POTATO FIELDS OF AROOSTOOK COUNTY
 FIELD RECOGNITION OF THE LARVAE OF NATIVE COCCINELLIDAE, COMMON TO THE POTATO FIELDS OF AROOSTOOK COUNTY R. H. Storch Department of Entomolgy, University of Maine TECHNICAL BULLETIN 43 MAINE AGRICULTURAL
FIELD RECOGNITION OF THE LARVAE OF NATIVE COCCINELLIDAE, COMMON TO THE POTATO FIELDS OF AROOSTOOK COUNTY R. H. Storch Department of Entomolgy, University of Maine TECHNICAL BULLETIN 43 MAINE AGRICULTURAL
The Making of the Fittest: Evolving Switches, Evolving Bodies
 OVERVIEW MODELING THE REGULATORY SWITCHES OF THE PITX1 GENE IN STICKLEBACK FISH This hands-on activity supports the short film, The Making of the Fittest:, and aims to help students understand eukaryotic
OVERVIEW MODELING THE REGULATORY SWITCHES OF THE PITX1 GENE IN STICKLEBACK FISH This hands-on activity supports the short film, The Making of the Fittest:, and aims to help students understand eukaryotic
AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Note: At least 1 point must be earned from each of parts (a), (b), (c), and (d) in order to earn a maximum score of 10. The ability to reproduce is a characteristic
AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Note: At least 1 point must be earned from each of parts (a), (b), (c), and (d) in order to earn a maximum score of 10. The ability to reproduce is a characteristic
Mit einem Auge auf den mathema/schen Horizont: Was der Lehrer braucht für die Zukun= seiner Schüler
 Mit einem Auge auf den mathema/schen Horizont: Was der Lehrer braucht für die Zukun= seiner Schüler Deborah Löwenberg Ball und Hyman Bass University of Michigan U.S.A. 43. Jahrestagung für DidakEk der
Mit einem Auge auf den mathema/schen Horizont: Was der Lehrer braucht für die Zukun= seiner Schüler Deborah Löwenberg Ball und Hyman Bass University of Michigan U.S.A. 43. Jahrestagung für DidakEk der
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
A Process Flow for Classification and Clustering of Fruit Fly Gene Expression Patterns
 A Process Flow for Classification and Clustering of Fruit Fly Gene Expression Patterns Andreas Heffel, Peter F. Stadler, Sonja J. Prohaska, Gerhard Kauer, Jens-Peer Kuska Santa Fe Institute Department
A Process Flow for Classification and Clustering of Fruit Fly Gene Expression Patterns Andreas Heffel, Peter F. Stadler, Sonja J. Prohaska, Gerhard Kauer, Jens-Peer Kuska Santa Fe Institute Department
Biological Sciences Initiative. Human Genome
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Interphase (A) and mitotic (B) D16 cells were plated on concanavalin A and processed for
 E07-10-1069 Rogers SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplemental Figure 1. Interphase day-7 control and γ-tubulin23c RNAi-treated S2 cells stained for MTs (green), γ-tubulin (red), and DNA (blue). Scale, 5μm. Supplemental
E07-10-1069 Rogers SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplemental Figure 1. Interphase day-7 control and γ-tubulin23c RNAi-treated S2 cells stained for MTs (green), γ-tubulin (red), and DNA (blue). Scale, 5μm. Supplemental
Preparing RTF and MS Word Files with Untranslatable Content for SDL Trados TagEditor & Déjà Vu
 Preparing RTF and MS Word Files with Untranslatable Content for SDL Trados TagEditor & Déjà Vu Categories of jobs with text to skip...1 Multilingual tables...1 Documents using text properties to mark sections...4
Preparing RTF and MS Word Files with Untranslatable Content for SDL Trados TagEditor & Déjà Vu Categories of jobs with text to skip...1 Multilingual tables...1 Documents using text properties to mark sections...4
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression
 13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression Lesson Objectives Describe gene regulation in prokaryotes. Explain how most eukaryotic genes are regulated. Relate gene regulation to development in multicellular organisms.
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression Lesson Objectives Describe gene regulation in prokaryotes. Explain how most eukaryotic genes are regulated. Relate gene regulation to development in multicellular organisms.
Lab #10 Invertebrates 2 and Vertebrates 1 (Exercises 39, 40)
 Name Bio 182-General Biology Lab #10 Invertebrates 2 and Vertebrates 1 (Exercises 39, 40) Answer the questions in the space provided. You need to turn this sheet at the end of the lab. In general know
Name Bio 182-General Biology Lab #10 Invertebrates 2 and Vertebrates 1 (Exercises 39, 40) Answer the questions in the space provided. You need to turn this sheet at the end of the lab. In general know
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
BIOLOGY REDISCOVERING. Genes and Development. Molecular to Global Perspectives. Differentiation and Genetic Cascades
 REDISCOVERING BIOLOGY Molecular to Global Perspectives Animals that look nothing like each other develop by using much the same basic toolkit of molecules and often in much the same ways. M. PALOPOLI AND
REDISCOVERING BIOLOGY Molecular to Global Perspectives Animals that look nothing like each other develop by using much the same basic toolkit of molecules and often in much the same ways. M. PALOPOLI AND
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
How To Ensure A Kreditierung Austria Is A Successful
 Akkreditierungserfordernisse an Stellen, die Managementsysteme nach EN 9100 bzw. EN 9110 (EN 9120) auditieren und zertifizieren - Änderungen zur Vorgängerversion sind gelb hinterlegt. Der Leitfaden wurde
Akkreditierungserfordernisse an Stellen, die Managementsysteme nach EN 9100 bzw. EN 9110 (EN 9120) auditieren und zertifizieren - Änderungen zur Vorgängerversion sind gelb hinterlegt. Der Leitfaden wurde
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Embryo Clay Model Embryogenesis and Stem Cell Development
 Embryo Clay Model Embryogenesis and Stem Cell Development Objective: To identify stages and locations of early embryonic development To see at what point stem cells are totipotent, pluripotent, and multipotent
Embryo Clay Model Embryogenesis and Stem Cell Development Objective: To identify stages and locations of early embryonic development To see at what point stem cells are totipotent, pluripotent, and multipotent
Mitotic Membrane Turnover Coordinates Differential Induction of the Heart Progenitor Lineage
 Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Mitotic Membrane Turnover Coordinates Differential Induction of the Heart Progenitor Lineage Christina D. Cota and Brad Davidson Supplemental Figures S1-S7 S1.
Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Mitotic Membrane Turnover Coordinates Differential Induction of the Heart Progenitor Lineage Christina D. Cota and Brad Davidson Supplemental Figures S1-S7 S1.
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112)
 Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
Fig. S1. Identification of CRMs with activity in Ci-Tbx2/3 expression domains outside the notochord. B-F
 Fig. S1. Identification of CRMs with activity in Ci-Tbx2/3 expression domains outside the notochord. (A) Top: map of the Ci- Tbx2/3 locus. Teal rectangles and lines denote exons and introns, respectively.
Fig. S1. Identification of CRMs with activity in Ci-Tbx2/3 expression domains outside the notochord. (A) Top: map of the Ci- Tbx2/3 locus. Teal rectangles and lines denote exons and introns, respectively.
Upgrading Your Skills to MCSA Windows Server 2012 MOC 20417
 Upgrading Your Skills to MCSA Windows Server 2012 MOC 20417 In dieser Schulung lernen Sie neue Features und Funktionalitäten in Windows Server 2012 in Bezug auf das Management, die Netzwerkinfrastruktur,
Upgrading Your Skills to MCSA Windows Server 2012 MOC 20417 In dieser Schulung lernen Sie neue Features und Funktionalitäten in Windows Server 2012 in Bezug auf das Management, die Netzwerkinfrastruktur,
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
eaged salmon and trout in Chile 1
 Revta bras. Zoot 1 R (~linl 1 \.?I':Q _?71':?nn~ Ani/oera montti sp. n. (Isopoda, Cymothoidae) a parasite of eaged salmon and trout in Chile 1 Vernon E. Thatcher 2 Carlos Lobos Blumenfeldt 3 ABSTRACT.
Revta bras. Zoot 1 R (~linl 1 \.?I':Q _?71':?nn~ Ani/oera montti sp. n. (Isopoda, Cymothoidae) a parasite of eaged salmon and trout in Chile 1 Vernon E. Thatcher 2 Carlos Lobos Blumenfeldt 3 ABSTRACT.
DNA Fingerprinting. Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA
 DNA Fingerprinting Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA DNA fingerprinting The name used for the unambiguous identifying technique that takes advantage of differences in DNA sequence
DNA Fingerprinting Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA DNA fingerprinting The name used for the unambiguous identifying technique that takes advantage of differences in DNA sequence
Fig. S1. Visualizing and manipulating peripheral MEs and SAs in zebrafish. (A) Lateral wholemount view of peripheral MEs (magenta: TgNBT:dsRed) and
 Fig. S1. Visualizing and manipulating peripheral MEs and SAs in zebrafish. (A) Lateral wholemount view of peripheral MEs (magenta: TgNBT:dsRed) and SAs (yellow: Tg- 8.4neurog1:GFP) in 72 hpf zebrafish
Fig. S1. Visualizing and manipulating peripheral MEs and SAs in zebrafish. (A) Lateral wholemount view of peripheral MEs (magenta: TgNBT:dsRed) and SAs (yellow: Tg- 8.4neurog1:GFP) in 72 hpf zebrafish
BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN. Third Examination April 2, 2009
 BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Third Examination April 2, 2009 Please put your name at the top of each page. Read each question carefully before answering- i.e. read the instructions. Be
BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Third Examination April 2, 2009 Please put your name at the top of each page. Read each question carefully before answering- i.e. read the instructions. Be
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
A new araneid genus from the Galapagos Islands (Araneae: Araneidae)
 A new araneid genus from the Galapagos Islands (Araneae: Araneidae) Herbert W. Levi ABSTRACT Contrib. Nat. Hist. 12: 893 898. A new araneid, Galaporella thaleri sp. nov., similar to species of the genus
A new araneid genus from the Galapagos Islands (Araneae: Araneidae) Herbert W. Levi ABSTRACT Contrib. Nat. Hist. 12: 893 898. A new araneid, Galaporella thaleri sp. nov., similar to species of the genus
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Vertebrate Development Chapter 60
 Vertebrate Development Chapter 60 Copyright McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display Raven - Johnson - Biology: 6th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies Stages
Vertebrate Development Chapter 60 Copyright McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display Raven - Johnson - Biology: 6th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies Stages
Leitfaden für die Antragstellung zur Förderung einer nationalen Biomaterialbankeninitiative
 Seite 1 von 8 Leitfaden für die Antragstellung zur Förderung einer nationalen Biomaterialbankeninitiative Anträge zu Biomaterialbanken sind entsprechend den Vorgaben dieses Leitfadens zu erstellen (DIN
Seite 1 von 8 Leitfaden für die Antragstellung zur Förderung einer nationalen Biomaterialbankeninitiative Anträge zu Biomaterialbanken sind entsprechend den Vorgaben dieses Leitfadens zu erstellen (DIN
Matthias Kistler, Urs Marti, Jérôme Ray, Christian Baumann and Adrian Wiget (Federal Office of Topography swisstopo - Switzerland)
 Towards a Distortion Free National Spatial Data Infrastructure in Switzerland: Approach, Developed Tools and Internet Services for the Change of the Reference Frame Matthias Kistler, Urs Marti, Jérôme
Towards a Distortion Free National Spatial Data Infrastructure in Switzerland: Approach, Developed Tools and Internet Services for the Change of the Reference Frame Matthias Kistler, Urs Marti, Jérôme
Microsoft Certified IT Professional (MCITP) MCTS: Windows 7, Configuration (070-680)
 Microsoft Office Specialist Office 2010 Specialist Expert Master Eines dieser Examen/One of these exams: Eines dieser Examen/One of these exams: Pflichtexamen/Compulsory exam: Word Core (Exam 077-881)
Microsoft Office Specialist Office 2010 Specialist Expert Master Eines dieser Examen/One of these exams: Eines dieser Examen/One of these exams: Pflichtexamen/Compulsory exam: Word Core (Exam 077-881)
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Class Insecta - The insects
 A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
Mechanosensitive Neurons on the Internal Reproductive Tract Contribute to Egg-Laying- Induced Acetic Acid Attraction in Drosophila
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information Mechanosensitive Neurons on the Internal Reproductive Tract Contribute to Egg-Laying- Induced Acetic Acid Attraction in Drosophila Bin Gou, Ying Liu, Ananya
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information Mechanosensitive Neurons on the Internal Reproductive Tract Contribute to Egg-Laying- Induced Acetic Acid Attraction in Drosophila Bin Gou, Ying Liu, Ananya
Kapitel 2 Unternehmensarchitektur III
 Kapitel 2 Unternehmensarchitektur III Software Architecture, Quality, and Testing FS 2015 Prof. Dr. Jana Köhler jana.koehler@hslu.ch IT Strategie Entwicklung "Foundation for Execution" "Because experts
Kapitel 2 Unternehmensarchitektur III Software Architecture, Quality, and Testing FS 2015 Prof. Dr. Jana Köhler jana.koehler@hslu.ch IT Strategie Entwicklung "Foundation for Execution" "Because experts
Developments in the Austrian Surveying Education
 Gert STEINKELLNER, Austria Key words: University Curriculum, Advanced Technical College, Civil Engineer, Assistant Surveyor. ABSTRACT In Austria was a substantial change of surveying education during the
Gert STEINKELLNER, Austria Key words: University Curriculum, Advanced Technical College, Civil Engineer, Assistant Surveyor. ABSTRACT In Austria was a substantial change of surveying education during the
Businessmodelle des SaaS Eco-Systems Chancen, Risiken und kritische Erfolgsfaktoren
 Businessmodelle des SaaS Eco-Systems Chancen, Risiken und kritische Erfolgsfaktoren Partnering for the Cloud 14 th of Mai, 2013 Ulrich Hubert und Klaus Kaufmann Fujitsu Enabling Software Technology 0 Copyright
Businessmodelle des SaaS Eco-Systems Chancen, Risiken und kritische Erfolgsfaktoren Partnering for the Cloud 14 th of Mai, 2013 Ulrich Hubert und Klaus Kaufmann Fujitsu Enabling Software Technology 0 Copyright
SPICE auf der Überholspur. Vergleich von ISO (TR) 15504 und Automotive SPICE
 SPICE auf der Überholspur Vergleich von ISO (TR) 15504 und Automotive SPICE Historie Software Process Improvement and Capability determination 1994 1995 ISO 15504 Draft SPICE wird als Projekt der ISO zur
SPICE auf der Überholspur Vergleich von ISO (TR) 15504 und Automotive SPICE Historie Software Process Improvement and Capability determination 1994 1995 ISO 15504 Draft SPICE wird als Projekt der ISO zur
Problems With Programmable self-assembly in a thousand-robot swarm
 Problems With Programmable self-assembly in a thousand-robot swarm Affiliations: Department of Computer Science, COMSATS Institute of IT, Islamabad, Pakistan Author: Muaz A. Niazi* ǂ *Correspondence to:
Problems With Programmable self-assembly in a thousand-robot swarm Affiliations: Department of Computer Science, COMSATS Institute of IT, Islamabad, Pakistan Author: Muaz A. Niazi* ǂ *Correspondence to:
Limb Development. Limb Development. Limb Axes. Limb Development. Clinical Terms
 Limb Development Overview of Limb Formation Initiation of Limb Development Limb Field Outgrowth of the Mesoderm Morphogenetic Signaling Development of Limb Tissues Skeleton Musculature Innervation Vasculature
Limb Development Overview of Limb Formation Initiation of Limb Development Limb Field Outgrowth of the Mesoderm Morphogenetic Signaling Development of Limb Tissues Skeleton Musculature Innervation Vasculature
Gene Switches A Model
 Gene Switches A Model Abstract Conceptually, how genetic switches function and their role in the process of evolution, can be difficult for students to visualize. Gene Switches A Model attempts to make
Gene Switches A Model Abstract Conceptually, how genetic switches function and their role in the process of evolution, can be difficult for students to visualize. Gene Switches A Model attempts to make
The exhibition brought together three aspects of Reiner Maria Matysik s multi-layered oeuvre in a new synthesis: in the museum s lecture hall ruins
 Curating Life In the last decade we have seen a number of artists questioning our concept of life while moving beyond the boundaries of art and science. Debates about changing the face of our planet through
Curating Life In the last decade we have seen a number of artists questioning our concept of life while moving beyond the boundaries of art and science. Debates about changing the face of our planet through
Human Embryonic Development. Human fetal development
 Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
How To Analyse A Flugzeugflugfl\U00Fcgels In 3D Cda
 cfd analyse eines flugzeugflügels bei mach 7 Zum Start der Entwicklung unseres Entwurfswerkzeuges werden wir die Ergebnisse des Workshops Speculative Patterns aus dem Entwurfsprojekt 51,9 N mit der Software
cfd analyse eines flugzeugflügels bei mach 7 Zum Start der Entwicklung unseres Entwurfswerkzeuges werden wir die Ergebnisse des Workshops Speculative Patterns aus dem Entwurfsprojekt 51,9 N mit der Software
Martin Krus, Klaus Sedlbauer, Herbert Sinnesbichler
 Martin Krus, Klaus Sedlbauer, Herbert Sinnesbichler Artificial thermal bridge with a dew point switch to accomplish an appropriate control of the ventilation for the prevention of mould growth in buildings
Martin Krus, Klaus Sedlbauer, Herbert Sinnesbichler Artificial thermal bridge with a dew point switch to accomplish an appropriate control of the ventilation for the prevention of mould growth in buildings
9. PHARYNGEAL ARCHES. READING ASSIGNMENT: Larsen 3 rd Edition. Chapter 12: pp. 352; 358-365; 405-412 SUMMARY: LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 9. PHARYNGEAL ARCHES Letty Moss-Salentijn DDS, PhD Dr. Edwin S. Robinson Professor of Dentistry (in Anatomy and Cell Biology) E-mail: lm23@columbia.edu READING ASSIGNMENT: Larsen 3 rd Edition. Chapter
9. PHARYNGEAL ARCHES Letty Moss-Salentijn DDS, PhD Dr. Edwin S. Robinson Professor of Dentistry (in Anatomy and Cell Biology) E-mail: lm23@columbia.edu READING ASSIGNMENT: Larsen 3 rd Edition. Chapter
Guide for Data Visualization and Analysis using ACSN
 Guide for Data Visualization and Analysis using ACSN ACSN contains the NaviCell tool box, the intuitive and user- friendly environment for data visualization and analysis. The tool is accessible from the
Guide for Data Visualization and Analysis using ACSN ACSN contains the NaviCell tool box, the intuitive and user- friendly environment for data visualization and analysis. The tool is accessible from the
Distinguishing characters of Niphargus gebhardti Schellenberg, 1934 and Niphargus molnari Mehely, 1927 (Crustacea: Amphipoda): a clarification
 Opusc. Zool. Budapest, 2013, 44(1): 3 8 Distinguishing characters of Niphargus gebhardti Schellenberg, 1934 and Niphargus molnari Mehely, 1927 (Crustacea: Amphipoda): a clarification D. ANGYAL 1 and G.
Opusc. Zool. Budapest, 2013, 44(1): 3 8 Distinguishing characters of Niphargus gebhardti Schellenberg, 1934 and Niphargus molnari Mehely, 1927 (Crustacea: Amphipoda): a clarification D. ANGYAL 1 and G.
Conference Paper Computer model for agricultural holdings: Useful tool in the evaluation and implementation of a high performance management
 econstor www.econstor.eu Der Open-Access-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtschaft The Open Access Publication Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Economics Berevoianu,
econstor www.econstor.eu Der Open-Access-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtschaft The Open Access Publication Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Economics Berevoianu,
INSRUCTION MANUAL AND GUARANTEE POLICY
 INSRUCTION MANUAL AND GUARANTEE POLICY FRACTOMETER II made in Germany by: IML- Instrumenta Mechanik Labor GmbH Großer Stadtacker 2 69168 Wiesloch Germany Phone: (+49) 6222 / 6797-0 Fax: (+49) 6222-6797-
INSRUCTION MANUAL AND GUARANTEE POLICY FRACTOMETER II made in Germany by: IML- Instrumenta Mechanik Labor GmbH Großer Stadtacker 2 69168 Wiesloch Germany Phone: (+49) 6222 / 6797-0 Fax: (+49) 6222-6797-
Carnivore, omnivore or herbivore?
 Carnivore, omnivore or herbivore? Physical adaptations of the giant panda Student booklet (ST) October 2010 panda_st_student.doc Context The Giant Panda is a species that is faced with extinction. It is
Carnivore, omnivore or herbivore? Physical adaptations of the giant panda Student booklet (ST) October 2010 panda_st_student.doc Context The Giant Panda is a species that is faced with extinction. It is
Search Engines Chapter 2 Architecture. 14.4.2011 Felix Naumann
 Search Engines Chapter 2 Architecture 14.4.2011 Felix Naumann Overview 2 Basic Building Blocks Indexing Text Acquisition Text Transformation Index Creation Querying User Interaction Ranking Evaluation
Search Engines Chapter 2 Architecture 14.4.2011 Felix Naumann Overview 2 Basic Building Blocks Indexing Text Acquisition Text Transformation Index Creation Querying User Interaction Ranking Evaluation
CARO The Common Anatomy Reference Ontology
 16 CARO The Common Anatomy Reference Ontology Melissa A. Haendel, Fabian Neuhaus, David Osumi-Sutherland, Paula M. Mabee, José L.V. Mejino Jr., Chris J. Mungall, and Barry Smith Summary. The Common Anatomy
16 CARO The Common Anatomy Reference Ontology Melissa A. Haendel, Fabian Neuhaus, David Osumi-Sutherland, Paula M. Mabee, José L.V. Mejino Jr., Chris J. Mungall, and Barry Smith Summary. The Common Anatomy
HYPO TIROL BANK AG. EUR 5,750,000,000 Debt Issuance Programme (the "Programme")
 Third Supplement dated 29 December 2015 to the Prospectus dated 9 June 2015 This document constitutes a supplement (the "Third Supplement") within the meaning of Article 16 of the Directive 2003/71/EC
Third Supplement dated 29 December 2015 to the Prospectus dated 9 June 2015 This document constitutes a supplement (the "Third Supplement") within the meaning of Article 16 of the Directive 2003/71/EC
Trasposable elements: P elements
 Trasposable elements: P elements In 1938 Marcus Rhodes provided the first genetic description of an unstable mutation, an allele of a gene required for the production of pigment in maize. This instability
Trasposable elements: P elements In 1938 Marcus Rhodes provided the first genetic description of an unstable mutation, an allele of a gene required for the production of pigment in maize. This instability
CobraNet TM User s Manual
 CobraNet TM User s Manual 19201 Cook Street, Foothill Ranch, CA 92610-3501 USA Phone: (949) 588-9997 Fax: (949) 588-9514 Email: sales@renkus-heinz.com Web: www.renkus-heinz.com CobraNet TM is a registered
CobraNet TM User s Manual 19201 Cook Street, Foothill Ranch, CA 92610-3501 USA Phone: (949) 588-9997 Fax: (949) 588-9514 Email: sales@renkus-heinz.com Web: www.renkus-heinz.com CobraNet TM is a registered
30 August 1985. PROC. BIOL. SOC. WASH. 98(3), 1985, pp. 615-621
 30 August 1985 PROC. BIOL. SOC. WASH. 98(3), 1985, pp. 615-621 FRESHWATER SHRIMPS FROM VENEZUELA III: MACROBRACHIUM QUELCHI (DE MAN) AND EURYRHYNCHUS PEMONI, N. SP.; (CRUSTACEA: DECAPODA: PALAEMONIDAE)
30 August 1985 PROC. BIOL. SOC. WASH. 98(3), 1985, pp. 615-621 FRESHWATER SHRIMPS FROM VENEZUELA III: MACROBRACHIUM QUELCHI (DE MAN) AND EURYRHYNCHUS PEMONI, N. SP.; (CRUSTACEA: DECAPODA: PALAEMONIDAE)
Services supply chain management and organisational performance
 Services supply chain management and organisational performance Irène Kilubi Services supply chain management and organisational performance An exploratory mixed-method investigation of service and manufacturing
Services supply chain management and organisational performance Irène Kilubi Services supply chain management and organisational performance An exploratory mixed-method investigation of service and manufacturing
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Implementing Data Models and Reports with Microsoft SQL Server
 Implementing Data Models and Reports with Microsoft SQL Server Dauer: 5 Tage Kursnummer: M20466 Überblick: Business Intelligence (BI) wird für Unternehmen von verschiedenen Größen aufgrund des dadurch
Implementing Data Models and Reports with Microsoft SQL Server Dauer: 5 Tage Kursnummer: M20466 Überblick: Business Intelligence (BI) wird für Unternehmen von verschiedenen Größen aufgrund des dadurch
CCR Biology - Chapter 10 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 10 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term for a feature
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 10 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term for a feature
The shape of things to come: Young researchers in Germany
 The shape of things to come: Young researchers in Germany Universitätsverband zur Qualifizierung des wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchses in Deutschland German University Association of Advanced Graduate Training
The shape of things to come: Young researchers in Germany Universitätsverband zur Qualifizierung des wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchses in Deutschland German University Association of Advanced Graduate Training
How To Teach A Software Engineer
 Corporate Technology Social Skills für Experten Erfahrungsbericht vom Siemens Curriculum für Senior Architekten / Architekten Matthias Singer Siemens AG Learning Campus Copyright 2010. All rights reserved.
Corporate Technology Social Skills für Experten Erfahrungsbericht vom Siemens Curriculum für Senior Architekten / Architekten Matthias Singer Siemens AG Learning Campus Copyright 2010. All rights reserved.
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
The Olympus stereology system. The Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox
 The Olympus stereology system The Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox CAST is a Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox for PCs running Microsoft Windows TM. CAST is an interactive, user-friendly,
The Olympus stereology system The Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox CAST is a Computer Assisted Stereological Toolbox for PCs running Microsoft Windows TM. CAST is an interactive, user-friendly,
The transcription factor FoxH1 (FAST) mediates Nodal signaling during anterior-posterior patterning and node formation in the mouse
 The transcription factor FoxH1 (FAST) mediates Nodal signaling during anterior-posterior patterning and node formation in the mouse Masamichi Yamamoto, Chikara Meno, Yasuo Sakai, Hidetaka Shiratori, Kyoko
The transcription factor FoxH1 (FAST) mediates Nodal signaling during anterior-posterior patterning and node formation in the mouse Masamichi Yamamoto, Chikara Meno, Yasuo Sakai, Hidetaka Shiratori, Kyoko
Supply Chain and Logistics in National, International and Governmental Environment
 Contributions to Management Science Supply Chain and Logistics in National, International and Governmental Environment Concepts and Models Bearbeitet von Reza Zanjirani Farahani, Nasrin Asgari, Hoda Davarzani
Contributions to Management Science Supply Chain and Logistics in National, International and Governmental Environment Concepts and Models Bearbeitet von Reza Zanjirani Farahani, Nasrin Asgari, Hoda Davarzani
Development of a Topographical Transcription Method. Introduction
 Development of a Topographical Transcription Method Introduction In the past years, digitization was about transforming analog documents into a digital representation. Problems in respect of color management,
Development of a Topographical Transcription Method Introduction In the past years, digitization was about transforming analog documents into a digital representation. Problems in respect of color management,
Update to V10. Automic Support: Best Practices Josef Scharl. Please ask your questions here http://innovate.automic.com/q&a Event code 6262
 Update to V10 Automic Support: Best Practices Josef Scharl Please ask your questions here http://innovate.automic.com/q&a Event code 6262 Agenda Update to Automation Engine Version 10 Innovations in Version
Update to V10 Automic Support: Best Practices Josef Scharl Please ask your questions here http://innovate.automic.com/q&a Event code 6262 Agenda Update to Automation Engine Version 10 Innovations in Version
A new species of Myrmarachne from Kenya (Araneae: Salticidae)
 Genus Vol. 13 (3): 409-415 Wroc³aw, 30 IX 2002 A new species of Myrmarachne from Kenya (Araneae: Salticidae) WANDA WESO OWSKA 1 and KATHRYN SALM 2 1 Zoological Institute, Wroc³aw University, Sienkiewicza
Genus Vol. 13 (3): 409-415 Wroc³aw, 30 IX 2002 A new species of Myrmarachne from Kenya (Araneae: Salticidae) WANDA WESO OWSKA 1 and KATHRYN SALM 2 1 Zoological Institute, Wroc³aw University, Sienkiewicza
Vergleich der Versionen von Kapitel 1 des EU-GMP-Leitfaden (Oktober 2012) 01 July 2008 18 November 2009 31 Januar 2013 Kommentar Maas & Peither
 Chapter 1 Quality Management Chapter 1 Quality Management System Chapter 1 Pharmaceutical Quality System Principle The holder of a Manufacturing Authorisation must manufacture medicinal products so as
Chapter 1 Quality Management Chapter 1 Quality Management System Chapter 1 Pharmaceutical Quality System Principle The holder of a Manufacturing Authorisation must manufacture medicinal products so as
Big Data Vendor Benchmark 2015 A Comparison of Hardware Vendors, Software Vendors and Service Providers
 A Comparison of Hardware Vendors, Software Vendors and Service Providers The digital world is becoming a reality. Mit jedem Tag ein bisschen mehr. ECommerce, Online- Werbung, mobile Applikationen und soziale
A Comparison of Hardware Vendors, Software Vendors and Service Providers The digital world is becoming a reality. Mit jedem Tag ein bisschen mehr. ECommerce, Online- Werbung, mobile Applikationen und soziale
Proceedings of the 8 th Euro-Asia Conference on Environment and CSR: Tourism, MICE, Hospitality Management and Education Session (Part II)
 Proceedings of the 8 th Euro-Asia Conference on Environment and CSR: Tourism, MICE, Hospitality Management and Education Session (Part II) Yanling Zhang (Ed.) Proceedings of the 8 th Euro-Asia Conference
Proceedings of the 8 th Euro-Asia Conference on Environment and CSR: Tourism, MICE, Hospitality Management and Education Session (Part II) Yanling Zhang (Ed.) Proceedings of the 8 th Euro-Asia Conference
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Animal Models of Human Behavioral and Social Processes: What is a Good Animal Model? Dario Maestripieri
 Animal Models of Human Behavioral and Social Processes: What is a Good Animal Model? Dario Maestripieri Criteria for assessing the validity of animal models of human behavioral research Face validity:
Animal Models of Human Behavioral and Social Processes: What is a Good Animal Model? Dario Maestripieri Criteria for assessing the validity of animal models of human behavioral research Face validity:
Problems. Knowing. back of the
 Introduction Welcome to BodyZone Physiotherapy patient resource about Cervical Spine Problems. Knowing the main parts of your neck and how these parts work is important as you learn to care for your neck
Introduction Welcome to BodyZone Physiotherapy patient resource about Cervical Spine Problems. Knowing the main parts of your neck and how these parts work is important as you learn to care for your neck
Supplementary Information accompanying with the manuscript titled:
 Supplementary Information accompanying with the manuscript titled: Tethering preferences of domain families cooccurring in multi domain proteins Smita Mohanty, Mansi Purvar, Naryanswamy Srinivasan* and
Supplementary Information accompanying with the manuscript titled: Tethering preferences of domain families cooccurring in multi domain proteins Smita Mohanty, Mansi Purvar, Naryanswamy Srinivasan* and
LEARNING AGREEMENT FOR STUDIES
 LEARNING AGREEMENT FOR STUDIES The Student Last name (s) First name (s) Date of birth Nationality 1 Sex [M/F] Academic year 20../20.. Study cycle EQF level 6 Subject area, Code Phone E-mail 0421 The Sending
LEARNING AGREEMENT FOR STUDIES The Student Last name (s) First name (s) Date of birth Nationality 1 Sex [M/F] Academic year 20../20.. Study cycle EQF level 6 Subject area, Code Phone E-mail 0421 The Sending
Timebox Planning View der agile Ansatz für die visuelle Planung von System Engineering Projekt Portfolios
 Agile Leadership Day 2015 Markus Giacomuzzi - Siemens Building Technologies Headquarters Zug Timebox Planning View der agile Ansatz für die visuelle Planung von System Engineering Projekt Portfolios structure
Agile Leadership Day 2015 Markus Giacomuzzi - Siemens Building Technologies Headquarters Zug Timebox Planning View der agile Ansatz für die visuelle Planung von System Engineering Projekt Portfolios structure
Genetomic Promototypes
 Genetomic Promototypes Mirkó Palla and Dana Pe er Department of Mechanical Engineering Clarkson University Potsdam, New York and Department of Genetics Harvard Medical School 77 Avenue Louis Pasteur Boston,
Genetomic Promototypes Mirkó Palla and Dana Pe er Department of Mechanical Engineering Clarkson University Potsdam, New York and Department of Genetics Harvard Medical School 77 Avenue Louis Pasteur Boston,
