Hearing Screenings in Arkansas Schools. Education for School Nurses in Arkansas Updated Summer 2012
|
|
|
- Jonathan Rice
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hearing Screenings in Arkansas Schools Education for School Nurses in Arkansas Updated Summer 2012
2 The planning committee & faculty attest that NO relevant financial, professional or personal conflict of interest exists, nor was sponsorship of commercial support obtained, in the preparation or presentation of this educational activity.
3 Objectives 1. Explain the importance of hearing screening for the school-aged child 2. Identify the components of a hearing screening and the pass/fail criteria for each 3. Apply age appropriate screening techniques and procedures 4. Demonstrate the use of an audiometer 5. Identify the steps of the recording, referral and reporting process
4 Outline for Training Why are hearing screenings performed in Arkansas schools? What is needed to perform appropriate hearing screenings? How is a pure-tone hearing screening performed? What should happen when a student doesn't pass the hearing screening protocol? Do s and Don ts of hearing screenings
5 Why are hearing screenings performed in Arkansas schools?
6 It s the Law! Arkansas Code Annotated states that each school district shall employ a physician or nurse to make such physical examinations. The exam shall be only such as to detect contagious or infectious diseases or any defect of sight, hearing or condition that would prevent a pupil from the benefits of school work.
7 It s Important! Approximately 15% of children in the U.S. have hearing loss in one or both ears. Hearing loss can seriously impede learning Early identification and treatment can prevent or at least alleviate the consequences of many hearing problems
8 Purpose of Hearing Screening To identify those children likely to have hearing problems from those not likely to have hearing problems To screen a large number of children in a short amount of time To refer those children who do not pass the screening or who are suspect for hearing problems
9 What is needed to perform appropriate hearing screenings?
10 Background Knowledge
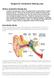
11 Ear Anatomy
12 Outer Ear Labels 27 = Pinna or auricle 29 = External auditory meatus or ear canal 31 = Tympanic membrane or eardrum
13 Microtia and Atresia
14 Wax Impaction
15 Middle Ear Malleus Incus Stapes Eustachian Tube
16 Ossicles
17 Inner Ear
18 Sound & Sound Measurement Frequency: Measured in Hertz (Hz) Human Range is 20 to 20,000 Hz Psychological correlate = Pitch Intensity: Measured in decibels (db) Normal conversation = db HL Psychological correlate = Loudness
19 Normal Hearing
20 Speech Sounds
21 Types of Hearing Loss
22 Conductive Hearing Loss (CHL) Conductive hearing loss (CHL) occurs when there is a decrease in sound transmission before the sound reaches the inner ear CHL occurs because of a problem in the outer or middle ear (as previously discussed) USUALLY (but not always), CHL can be treated medically or repaired Examples of issues causing CHL and possible treatments: Problem contributing to CHL: Wax blockage Fluid in middle ear (otitis media) Ossicular chain abnormality Possible treatment: Have wax removed by physician or audiologist Physician prescribes antibiotic treatment Otologist performs partial or total ossicular chain replacement with prothesis
23 Otitis Media Middle Ear Infections 24.5 million visits to doctors offices yearly Most frequently cited reason for taking child to the emergency room Most common surgery for children is a Tympanostomy, 110,000 per year Health care costs are reported between $3 and $5 billion/year
24 Secondhand Smoke More ear infections and hearing problems More upper respiratory infections More bronchitis and pneumonia Higher rate of SIDS More cases of asthma More severe symptoms in children who already have asthma
25 Secondhand Smoke Children living in households where more than three packs of cigarettes were smoked per day were more than four times as likely to be hospitalized for placement of PE tubes.
26 Conductive Hearing Loss
27 Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL) Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) usually occurs because of a problem in the inner ear (as previously discussed) USUALLY (but not always), SNHL is permanent and cannot be repaired to a normal state Examples of issues causing SNHL and possible treatments: Problem causing SNHL: Damage to the inner hair cells of the inner ear Hearing loss due to noise exposure Hearing loss due to ototoxic drugs Possible treatment: May require amplification May require amplification May require amplification
28 Sensorineural Hearing Loss
29 Mixed Hearing Loss Mixed hearing loss occurs when there is both a conductive component and a sensorineural component to the hearing loss There are many ways that this can happen, however, the best example of a mixed hearing loss is when a child who is known to have sensorineural hearing loss also has an ear infection. The conductive component of this hearing loss is temporary and can be treated medically.
30 Mixed Hearing Loss
31 Other Hearing Disorders
32 Auditory Neuropathy A hearing disorder in which sound enters the INNER ear normally but the transmission of the signals from the inner ear to the brain is impaired May exhibit normal hearing sensitivity to pure tones or hearing loss ranging from mild to severe Usually have poor speech-perception abilities Diagnosis is usually made with several tests including auditory brainstem response and otoacoustic emissions Can be very complex and confusing diagnosis
33 (Central) Auditory Processing Disorders These children will usually pass the hearing screening administered by the nurse Difficulty understanding speech in noise most common symptom Maturation is a factor (most audiologists agree that a child needs to be 7 years or older for appropriate diagnosis) Normal or near-normal hearing sensitivity Diagnosis should be made by an audiologist
34 Audiometers
35 Portable Audiometer A portable audiometer is needed Conduct a biological (or listening) check everyday that it is used Calibrate the audiometer on a yearly basis (see list for sources of calibration services) Use extreme caution when moving audiometer around from school to school be gentle
36 EXAMPLES OF APPROPRIATE AUDIOMETERS
37 Earscan 3M
38 Maico 27
39 Maico 39
40 Maico Pilot Audiometer (*this is MORE than you need)
41 EXAMPLES OF AUDIOMETERS THAT ARE NOT APPROPRIATE
42 Welch Allyn AudioScope 3 Screening Audiometer (not appropriate for school screening)
43 OtoScreen I by Handtronix (not appropriate for school screenings)
44 How is a pure-tone hearing screening performed?
45 Protocol Summary Pure Tone Screening Rescreening (if did not pass 1 st screen) Referral Follow-up Annual summary
46 Who to screen Students in grades Pre-K, K, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 & transfer students Special education students & teacher referrals NOTE: Students who wear hearing aids, who have cochlear implants or have documented hearing loss (by an audiologist/md) should NOT be screened
47 FYI: Example of Hearing Aids
48 FYI: Example of Bone Anchored A BAI uses a titanium implant, which is placed in the skull bone behind the ear. An abutment connects the sound processor with the implant in the bone, creating direct bone conduction. Direct bone conduction, provided by a BAI, gives improved access to sound when compared to traditional bone conductors since sound is not weakened when passing through the skin. Can be worn on a headband Implant
49 Built-in multi-function LED status indicator FYI: Example of Cochlear Implant (Advanced Bionics) Processor: holds 3 listening programs that can be used for FM and/or different listening environments Head piece/coil Additional external microphone & Rechargeable Battery Designed withstand rain, sweat and moisture
50 When to Screen NOT the first week of school Children entering school for the first time Need time to adjust to school environment BUT you do not want to wait too long if a child DOES have hearing loss Don t wait too long Cold and Flu season Need time for follow-up
51 Audiometer Controls Power (on/off) Ear indicator (right/left) Intensity selector (db; e.g. 40 db HL) Frequency selector (Hz; e.g Hz) Signal selector (use continuous or pulsed tone only) Presentation function (how do you present the tone)
52 Headphone Placement Place the headphones on student (red on right ear; blue on left ear) Hair behind ears Remove large earrings May want to remove glasses Diaphragm of headphones over ear canal Adjust head band for snug, even fit Head band on top of head is preferred
53 How to screen Instruct student for the task (e.g. raise hand when they hear the beep) Condition the student to the task (i.e. present a tone in one ear at one frequency ABOVE the screening level example: 50 db) Once the student is conditioned start the screening protocol
54 Screening Protocol Right Ear 1000 Hz 20 db 2000 Hz 20 db 4000 Hz 20 db Left Ear 1000 Hz 20 db 2000 Hz 20 db 4000 Hz 20 db NOTE: Need to obtain 2 responses in each ear at each frequency for a pass
55 Pass/Fail Criteria Student must pass all frequencies in an ear for that ear to be classified as a pass If a student does not pass ALL frequencies in each ear, he/she should be re-screened in 2-4 weeks
56 Rescreening Protocol Right Ear 1000 Hz 20 db 2000 Hz 20 db 4000 Hz 20 db Left Ear 1000 Hz 20 db 2000 Hz 20 db 4000 Hz 20 db NOTE: Need to obtain 2 responses in each ear at each frequency for a pass
57 Tips and Tricks to Perform Hearing Screenings
58 Play Audiometry Use with students who are difficult-to-test, who are developmentally delayed, or who are non-english speaking Use a play task (drop blocks in a bucket) Teach child the task at an elevated intensity level (e.g. 50 db HL) Make sure child can do on his own before you attempt screening at 20 db HL
59
60 What should happen when a student doesn t pass the hearing screening protocol?
61 REMEMBER: Pass/Fail Criteria Student must pass all frequencies in an ear for that ear to be classified as a pass If a student does not pass ALL frequencies in each ear, he/she should be re-screened in 2-4 weeks
62 Referral Refer immediately if you observe physical abnormalities that are not documented in the student s file May immediately refer if child does not pass and there is serious concern regarding hearing or speech/language development Refer to MD or Audiologist if fails rescreen Refer to MD or Audiologist if child passes, but there is concern regarding hearing
63 Follow-up Send letter, referral form, financial assistance information and list of appropriate professionals to the parent/guardian (make sure school nurse contact info is on referral form) If no response from parent/guardian in 2 weeks, follow-up with a phone call or personal contact Review information received from examining professional Rescreen after medical treatment if indicated Collaborate with special education personnel if indicated
64 Do s DO find a quiet room DO screen at 20 db HL DO present tone for at least 3 seconds DO use pulsed tones if possible
65 Don ts Don t require students to raise right or left hand Don t get into a pattern with your presentation of the tone Don t give visual cues-position audiometer controls out of view
66 Don ts Don t screen ear with known hearing loss Don t switch the headphones from one audiometer to another. This changes the calibration for your machine. If you have to get your headphones repaired or replaced, your audiometer has to be re-calibrated
67 Forms Forms are available on the Arkansas Coordinated School Health Website Referral Form (which has been re-formatted) HS Record Form Rescreen Record Form Summary Form
68 Documentation Data entry will be in APSCN (or use the summary form if APSCN not available) eschool+ will be the data entry software for public and charter schools in the future You may need to get more training/information on APSCN data entry in your coop area
69 Resources Parent and Student Education Childhood Hearing Loss Loss-Childhood.pdf Recreational Firearm Noise Exposure Recreational-Firearm-Noise-Exposure.pdf
70
71 How to contact the EARS ACH Donna Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A Coordinator/Audiologist smileydf@archildrens.org
72 Committee Members Donna Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A (Audiologist) Nancy Green, RN, BSN (CHNS Supervisor, North) Nancy Marsh, RN, BSN (CHNS) Cheryl Byrd, RN, BSN (CHNS) Laura Cook, RN, BSN (CHNS) Juanita Buckmaster, RN, BSN (CHNS) Kimberly Hooks, RN, BSN, MPH (CHNS Supervisor, South) Paula Smith, RNP, MNSc (State School Nurse Consultant)
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884. www.childrensent.com
 Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Questions and Answers for Parents
 Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Questions and Answers for Parents There are simple, inexpensive tests available to detect hearing impairment in infants during the first days of life. In the past, most hearing deficits in children were
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video. IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
 Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
HEARING SCREENING (May 2006)
 HEARING SCREENING (May 2006) Definition Procedures for Hearing Screening Student with hearing loss School Nurse Role Referral Criteria Resources Definition: Hearing is the perception of sound. The normal
HEARING SCREENING (May 2006) Definition Procedures for Hearing Screening Student with hearing loss School Nurse Role Referral Criteria Resources Definition: Hearing is the perception of sound. The normal
HEARING SCREENING: PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY
 HEARING SCREENING: PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY QUALIFIED SCREENERS 7-005.01 For the purposes of the school officials verifying that a qualified screener is carrying out the required screening activity, the qualified
HEARING SCREENING: PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY QUALIFIED SCREENERS 7-005.01 For the purposes of the school officials verifying that a qualified screener is carrying out the required screening activity, the qualified
Section 4. Hearing loss and hearing tests
 Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
SEMI-IMPLANTABLE AND FULLY IMPLANTABLE MIDDLE EAR HEARING AIDS
 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
STATE OF AL ASK A. Hearing Screening Guidelines for the Pre-school/School Population
 STATE OF AL ASK A Hearing Screening Guidelines for the Pre-school/School Population DIVISION OF PUBLIC HEALTH APRIL, 2016 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Prepared by: Mary Bell, BSN, RN, NCSN Mindy Galyon, MA, CCC-A
STATE OF AL ASK A Hearing Screening Guidelines for the Pre-school/School Population DIVISION OF PUBLIC HEALTH APRIL, 2016 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Prepared by: Mary Bell, BSN, RN, NCSN Mindy Galyon, MA, CCC-A
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan
 Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
Learners Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing Kalie Carlisle, Lauren Nash, and Allison Gallahan Definition Deaf A deaf person is one whose hearing disability precludes successful processing of linguistic information
What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who has a hearing loss? How does hearing work?
 This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System
 Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
HEARING SCREENING FOR CHILDREN
 PURPOSE Audiologic (hearing) screening identifies those persons who are likely to have hearing impairments or disorders that may interfere with body function/structure and/or activity/participation as
PURPOSE Audiologic (hearing) screening identifies those persons who are likely to have hearing impairments or disorders that may interfere with body function/structure and/or activity/participation as
Once your baby has good head control and can turn towards something interesting, a more advanced behavioural procedure can be used.
 How do we test the hearing of babies and children? An audiologist will select from a range of different tests to evaluate your child s hearing. The choice of test depends on the information that is needed
How do we test the hearing of babies and children? An audiologist will select from a range of different tests to evaluate your child s hearing. The choice of test depends on the information that is needed
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS
 CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
Getting Started Kei Te Timata
 Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
GUIDELINES FOR HEARING SCREENING In the School Setting
 GUIDELINES FOR HEARING SCREENING In the School Setting SEPTEMBER 2014 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Contributors This manual was reviewed and revised based on valuable input from the following individuals: Karen Bauer,
GUIDELINES FOR HEARING SCREENING In the School Setting SEPTEMBER 2014 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Contributors This manual was reviewed and revised based on valuable input from the following individuals: Karen Bauer,
Hearing Aids. What Is a Hearing Aid? How Common Is Hearing Loss and What Causes It? How Do We Hear?
 Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance
 Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Unilateral (Hearing Loss in One Ear) Hearing Loss Guidance Indiana s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program Before universal newborn hearing screening, most children with unilateral hearing loss
Presbycusis. What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis?
 Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Audiology Services. Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS
 Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Chapter 8. Hearing and Ear Abnormalities in Fanconi Anemia. Introduction. Anatomy and Function of the Ear
 Chapter 8 Hearing and Ear Abnormalities in Fanconi Anemia H. Jeffrey Kim, MD, FACS, Christopher Zalewski, MA, and Carmen C. Brewer, PhD Introduction In 1927, Guido Fanconi, MD, noticed an association between
Chapter 8 Hearing and Ear Abnormalities in Fanconi Anemia H. Jeffrey Kim, MD, FACS, Christopher Zalewski, MA, and Carmen C. Brewer, PhD Introduction In 1927, Guido Fanconi, MD, noticed an association between
Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD
 Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD Q: In my office practice, I screen for hearing loss with A Level of difficulty in office conversation Questionnaire Hand held hldaudiometer
Hearing Loss in Geriatric Primary Care Mary Ann Forciea MD Josh Uy MD Q: In my office practice, I screen for hearing loss with A Level of difficulty in office conversation Questionnaire Hand held hldaudiometer
Children s Hearing Aid Clinic
 Children s Hearing Aid Clinic Enclosed are a number of information sheets. Each has a separate heading. Don t feel that you have to read them all at one go. These sheets are not intended to be the answer
Children s Hearing Aid Clinic Enclosed are a number of information sheets. Each has a separate heading. Don t feel that you have to read them all at one go. These sheets are not intended to be the answer
Veterans UK Leaflet 10. Notes about War Pension claims for deafness
 Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
Information for parents. Deafness
 About this publication This is a guide for parents with young children who have recently been told that their child is deaf, or who are in the process of getting a diagnosis. It was developed by the Early
About this publication This is a guide for parents with young children who have recently been told that their child is deaf, or who are in the process of getting a diagnosis. It was developed by the Early
My child has a hearing loss
 My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents Content You are not alone 3 Hearing impairment 5 Methods of testing hearing 6 Audiogram 7 Types and causes of hearing loss 8 Degree of hearing loss 10 Where
My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents Content You are not alone 3 Hearing impairment 5 Methods of testing hearing 6 Audiogram 7 Types and causes of hearing loss 8 Degree of hearing loss 10 Where
8.Audiological Evaluation
 8. A U D I O L O G I C A L E V A L U A T I O N 8.Audiological Evaluation The external ear of the child with Progeria Behavioral testing for assessing hearing thresholds Objective electrophysiologic tests
8. A U D I O L O G I C A L E V A L U A T I O N 8.Audiological Evaluation The external ear of the child with Progeria Behavioral testing for assessing hearing thresholds Objective electrophysiologic tests
GUIDELINES FOR THE SCHOOL HEARING SCREENING PROGRAM FOR PENNSYLVANIA S SCHOOL AGE POPULATION
 08/2011- Under Review GUIDELINES FOR THE SCHOOL HEARING SCREENING PROGRAM FOR PENNSYLVANIA S SCHOOL AGE POPULATION ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Department of Health, Division of School Health appreciates the
08/2011- Under Review GUIDELINES FOR THE SCHOOL HEARING SCREENING PROGRAM FOR PENNSYLVANIA S SCHOOL AGE POPULATION ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Department of Health, Division of School Health appreciates the
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Hearing Aids (BAHA) Amended Date: October 1, 2015.
 Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Conductive Hearing Loss... 1 1.2 Sensorineural Hearing Loss...
Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Conductive Hearing Loss... 1 1.2 Sensorineural Hearing Loss...
PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD
 PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD Pure tone audiometry is the standard behavioral assessment of an individual s hearing. The results of pure tone audiometry are recorded on a chart or form called
PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD Pure tone audiometry is the standard behavioral assessment of an individual s hearing. The results of pure tone audiometry are recorded on a chart or form called
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
Department of Developmental Services Terrence W. Macy, Ph.D., Commissioner Linda Goodman, System Director
 Acknowledgments This guideline was revised and updated in July 2012 to add more current information and resources. The Connecticut Birth to Three System would like to thank the following people who worked
Acknowledgments This guideline was revised and updated in July 2012 to add more current information and resources. The Connecticut Birth to Three System would like to thank the following people who worked
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology])
![REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology]) REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology])](/thumbs/27/10327872.jpg) 224 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to
224 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN AUDIOLOGY (MSc[Audiology]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to
Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
 Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received for such services is a
S-822. Noise and Hearing Conservation RISK MANAGEMENT
 RISK MANAGEMENT Noise and Hearing Conservation Resources and information for developing Patient handling programs in health care Employers with workplaces that have excessive levels of noise need to implement
RISK MANAGEMENT Noise and Hearing Conservation Resources and information for developing Patient handling programs in health care Employers with workplaces that have excessive levels of noise need to implement
Hearing Aids - Adult HEARING AIDS - ADULT HS-159. Policy Number: HS-159. Original Effective Date: 3/18/2010. Revised Date(s): 3/18/2011; 3/1/2012
 Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Guidelines: Hearing and Middle-Ear Screening
 Guidelines: Hearing and Middle-Ear Screening Screening, Special Services and SoonerStart Oklahoma State Department of Health 1000 NE 10 th Street Oklahoma City, OK 73117-1299 405-271-6617 January 2006
Guidelines: Hearing and Middle-Ear Screening Screening, Special Services and SoonerStart Oklahoma State Department of Health 1000 NE 10 th Street Oklahoma City, OK 73117-1299 405-271-6617 January 2006
Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
www.complexchild.com Hearing Tests for Children with Multiple or Developmental Disabilities by Susan Agrawal Hearing impairment is a common problem in children with developmental disabilities or who have
Vision and Hearing Screening Training 2014-2015
 Vision and Hearing Screening Training 2014-2015 Kimberly H Bass, MA, CCC-A Educational Audiologist Bibb PEC 3600 Brookdale Ave. Macon, GA 31204 (478) 779-2771 Kimberly.bass@bcsdk12.net Meeting Norms Begin
Vision and Hearing Screening Training 2014-2015 Kimberly H Bass, MA, CCC-A Educational Audiologist Bibb PEC 3600 Brookdale Ave. Macon, GA 31204 (478) 779-2771 Kimberly.bass@bcsdk12.net Meeting Norms Begin
A Guide to Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs) for Physicians
 A Guide to Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs) for Physicians Introduction Hearing loss is not uncommon in children and adults. According to recent estimates, 31.5 million people in the United States report difficulty
A Guide to Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs) for Physicians Introduction Hearing loss is not uncommon in children and adults. According to recent estimates, 31.5 million people in the United States report difficulty
Hearing Conservation Procedures
 Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Table of Contents SOUND STEPS SOUND STEPS. Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss
 Table of Contents SOUND STEPS SOUND STEPS Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Department
Table of Contents SOUND STEPS SOUND STEPS Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Resource Guide for Families of Children with Hearing Loss Hawaii State Department
Hearing Devices Policy and Administration Manual
 Hearing Devices Policy and Administration Manual Assistive Devices Program, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Table of Amendments This page will list all substantive changes to policies and procedures
Hearing Devices Policy and Administration Manual Assistive Devices Program, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Table of Amendments This page will list all substantive changes to policies and procedures
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED
 Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
Learning Objective. To learn about current technological interventions that allow children with hearing loss to access auditory information
 Learning Objective To learn about current technological interventions that allow children with hearing loss to access auditory information in the educational environment. Module Outline Goal: To improve
Learning Objective To learn about current technological interventions that allow children with hearing loss to access auditory information in the educational environment. Module Outline Goal: To improve
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians
 1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
1/1/2015 Hearing Testing Coding Fact Sheet Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians While coding for hearing screening is relatively straightforward, ensuring that appropriate payment is received
Sound Perception. Sensitivity to Sound. Sensitivity to Sound 1/9/11. Not physically sensitive to all possible sound frequencies Range
 Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING GUIDELINES for Audiology
 DIAGNOSTIC TESTING GUIDELINES for Audiology In 1999, the Illinois legislature passed the Hearing Screening for Newborns Act. By December 31, 2002, hospitals delivering babies were required to provide hearing
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING GUIDELINES for Audiology In 1999, the Illinois legislature passed the Hearing Screening for Newborns Act. By December 31, 2002, hospitals delivering babies were required to provide hearing
Audiology as a School Based Service. Purpose. Audiology (IDEA 2004) Arkansas SPED Regulations. IDEA 2004 Part B
 Audiology as a School Based Service 2008 Medicaid in the Schools (MITS) Summit January 24, 2008 Donna Fisher Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A Audiologist Arkansas Children s Hospital and Conway Public Schools Purpose
Audiology as a School Based Service 2008 Medicaid in the Schools (MITS) Summit January 24, 2008 Donna Fisher Smiley, Ph.D., CCC-A Audiologist Arkansas Children s Hospital and Conway Public Schools Purpose
Pediatric Hearing Assessment
 Pediatric Hearing Assessment Stanton Jones Key Points This chapter outlines the methods of hearing assessment that are appropriate for children from birth to adolescence. The importance of timely referral
Pediatric Hearing Assessment Stanton Jones Key Points This chapter outlines the methods of hearing assessment that are appropriate for children from birth to adolescence. The importance of timely referral
Hearing Loss after Treatment for Childhood Cancer
 after Treatment for Childhood Cancer Some chemotherapy drugs, other medications, or radiation needed for treatment of childhood cancer can damage hearing. Hearing loss interferes with daily living. If
after Treatment for Childhood Cancer Some chemotherapy drugs, other medications, or radiation needed for treatment of childhood cancer can damage hearing. Hearing loss interferes with daily living. If
Audio Examination. Place of Exam:
 Audio Examination Name: Date of Exam: SSN: C-number: Place of Exam: The Handbook of Standard Procedures and Best Practices for Audiology Compensation and Pension Exams is available online. ( This is a
Audio Examination Name: Date of Exam: SSN: C-number: Place of Exam: The Handbook of Standard Procedures and Best Practices for Audiology Compensation and Pension Exams is available online. ( This is a
1/26/2011. 50% of deafness and hearing impairment is avoidable through prevention, early diagnosis, and management.
 Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Hearing Impairment Roseann Mulligan, DDS, MS Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of the University of Southern California 1 JAMA, July 4, 2007 Vol 298, No. 1 2 278 million - moderate to profound bilateral
Middle Ear. Inner Ear. Ossicles Semicircular canals. Auditory nerve. Cochlea. Eardrum Eustachian tube
 2007 Middle Ear Inner Ear } } Ossicles Semicircular canals Auditory nerve Cochlea Eardrum Eustachian tube Table of Contents Requirements and Guidelines...page 3 I. Introduction to Hearing Screening Policies
2007 Middle Ear Inner Ear } } Ossicles Semicircular canals Auditory nerve Cochlea Eardrum Eustachian tube Table of Contents Requirements and Guidelines...page 3 I. Introduction to Hearing Screening Policies
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents WHAT S NEW FOR THE 2016 MANUAL? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents WHAT S NEW FOR THE 2016 MANUAL? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
Intermediate School District 917 CLASSIFICATION DESCRIPTION Educational Audiologist Department: Special Education
 Title of Immediate Supervisor: Assistant Director of Special Education Intermediate School District 917 Department: Special Education FLSA Status: Exempt Accountable For (Job Titles): None Pay Grade Assignment:
Title of Immediate Supervisor: Assistant Director of Special Education Intermediate School District 917 Department: Special Education FLSA Status: Exempt Accountable For (Job Titles): None Pay Grade Assignment:
HEARING & HEARING LOSS. Dr I Butler 2015
 HEARING & HEARING LOSS Dr I Butler 2015 DISCLOSURE Sponsorship to attend local and international workshops Cochlear (Southern ENT) Med el TOPICS Anatomy Classification of hearing loss Congenital hearing
HEARING & HEARING LOSS Dr I Butler 2015 DISCLOSURE Sponsorship to attend local and international workshops Cochlear (Southern ENT) Med el TOPICS Anatomy Classification of hearing loss Congenital hearing
My child has a hearing loss. A guide for parents
 My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents 2 Donna S. Wayner, Ph.D., author of Hearing and Learning: A Guide for Helping Children, prepared the material in this booklet. Copies of her various books
My child has a hearing loss A guide for parents 2 Donna S. Wayner, Ph.D., author of Hearing and Learning: A Guide for Helping Children, prepared the material in this booklet. Copies of her various books
Light wear for a powerful hearing. Bone Conduction Headset
 Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
DAILY BIOLOGIC CHECK OF AUDIOMETERS
 DAILY BIOLOGIC CHECK OF AUDIOMETERS An audiometer must be checked before each day of use or if a problem is suspected with the equipment during use. After the audiometer is turned on, the operator should
DAILY BIOLOGIC CHECK OF AUDIOMETERS An audiometer must be checked before each day of use or if a problem is suspected with the equipment during use. After the audiometer is turned on, the operator should
Middle Ear Implants for the Treatment of Hearing Loss
 Middle Ear Implants for the Treatment of Hearing Loss FINAL STE REPORT December 2011 Submitted to: The Alberta Health Technologies Decision Process Health Technologies and Services Policy Unit Clinical
Middle Ear Implants for the Treatment of Hearing Loss FINAL STE REPORT December 2011 Submitted to: The Alberta Health Technologies Decision Process Health Technologies and Services Policy Unit Clinical
MODEL SUPERBILL for AUDIOLOGY
 MODEL SUPERBILL for AUDIOLOGY The following is a model of a superbill which could be used by an audiology practice when billing private health plans. This sample is not meant to dictate which services
MODEL SUPERBILL for AUDIOLOGY The following is a model of a superbill which could be used by an audiology practice when billing private health plans. This sample is not meant to dictate which services
HEARING LOSS AND LANGUAGE DELAY IN LITTLE CHILDREN. Prepared by Jane H. LeBlanc, M.S., M.S.P. Audiologist, CCC-A Speech Language Pathologist, CCC-SLP
 HEARING LOSS AND LANGUAGE DELAY IN LITTLE CHILDREN Prepared by Jane H. LeBlanc, M.S., M.S.P. Audiologist, CCC-A Speech Language Pathologist, CCC-SLP This is being written to provide information to concerned
HEARING LOSS AND LANGUAGE DELAY IN LITTLE CHILDREN Prepared by Jane H. LeBlanc, M.S., M.S.P. Audiologist, CCC-A Speech Language Pathologist, CCC-SLP This is being written to provide information to concerned
Audiometry and Hearing Loss Examples
 Audiometry and Hearing Loss Examples An audiogram shows the quietest sounds you can just hear. The red circles represent the right ear and the blue crosses represent the left ear. Across the top, there
Audiometry and Hearing Loss Examples An audiogram shows the quietest sounds you can just hear. The red circles represent the right ear and the blue crosses represent the left ear. Across the top, there
Understanding Childhood Hearing Loss. Information Booklet for Families of Children Newly Diagnosed with a Hearing Loss
 Understanding Childhood Hearing Loss Information Booklet for Families of Children Newly Diagnosed with a Hearing Loss 2 Understanding Childhood Hearing Loss This booklet is published by DeafHear in collaboration
Understanding Childhood Hearing Loss Information Booklet for Families of Children Newly Diagnosed with a Hearing Loss 2 Understanding Childhood Hearing Loss This booklet is published by DeafHear in collaboration
NIHL - understanding audiograms and medical causation
 NIHL - understanding audiograms and medical causation Darrell Smith Partner, BLM Manchester Birmingham Cardiff Leeds Liverpool London Manchester Southampton Stockton-on-Tees How the ear works The human
NIHL - understanding audiograms and medical causation Darrell Smith Partner, BLM Manchester Birmingham Cardiff Leeds Liverpool London Manchester Southampton Stockton-on-Tees How the ear works The human
Cochlear Implants: A Communication Choice. Cochlear Implants: A Communication Tool. www.cochlear.com
 Cochlear Ltd ABN 96 002 618 073 14 Mars Road, PO Box 629 Lane Cove NSW 2066 Australia Tel: 61 2 9428 6555 Fax: 61 2 9428 6353 Cochlear Americas 400 Inverness Parkway Suite 400 Englewood CO 80112 USA Tel:
Cochlear Ltd ABN 96 002 618 073 14 Mars Road, PO Box 629 Lane Cove NSW 2066 Australia Tel: 61 2 9428 6555 Fax: 61 2 9428 6353 Cochlear Americas 400 Inverness Parkway Suite 400 Englewood CO 80112 USA Tel:
USER GUIDE. Thank you for choosing Ovation Hearing and congratulations on taking control of your hearing health.
 Ovation Lift USER GUIDE Thank you for choosing Ovation Hearing and congratulations on taking control of your hearing health. While no hearing device can restore normal hearing health or prevent or improve
Ovation Lift USER GUIDE Thank you for choosing Ovation Hearing and congratulations on taking control of your hearing health. While no hearing device can restore normal hearing health or prevent or improve
SCHOOL HEARING SCREENING GUIDELINES
 SCHOOL HEARING SCREENING GUIDELINES The University of the State of New York THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT Student Support Services Team Albany, New York 12234 April 2008 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF
SCHOOL HEARING SCREENING GUIDELINES The University of the State of New York THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT Student Support Services Team Albany, New York 12234 April 2008 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF
More information >>> HERE <<<
 More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
More information >>> HERE http://urlzz.org/hearloss/pdx/dcli864/ Tags: ## best way to get cheapest natural methods to
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction:
 The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
The Role of the Educational Audiologist 2014. Introduction: As the current CHAIR of the BAEA I felt that it was time for the Role of the Educational Audiologist to be updated. There has been a period of
Ototoxicity Monitoring
 Ototoxicity Monitoring Aaron Jones, Au.D., M.S. Doctor of Audiology May 12, 2011 Agenda Background Antineoplastic ototoxicity monitoring Case study Company overview Gross Anatomy of the Ear Image: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:anatomy_of_the_human_ear.svg
Ototoxicity Monitoring Aaron Jones, Au.D., M.S. Doctor of Audiology May 12, 2011 Agenda Background Antineoplastic ototoxicity monitoring Case study Company overview Gross Anatomy of the Ear Image: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:anatomy_of_the_human_ear.svg
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
Where kids come first. Your Child and Ear Infections
 17 Where kids come first Your Child and Ear Infections How common are ear infections? Infection of the middle ear, or otitis media, is the most common affliction requiring medical therapy for children
17 Where kids come first Your Child and Ear Infections How common are ear infections? Infection of the middle ear, or otitis media, is the most common affliction requiring medical therapy for children
Middle ear conditions
 Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
OAE hearing screening at your fingertips OAE+
 OAE hearing screening at your fingertips OAE+ Periodic hearing screening leads to early detection of hearing loss 6-7 per 1000 children will be identified with permanent hearing loss in early childhood.
OAE hearing screening at your fingertips OAE+ Periodic hearing screening leads to early detection of hearing loss 6-7 per 1000 children will be identified with permanent hearing loss in early childhood.
DURATION OF HEARING LOSS
 When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
CALIFORNIA CHILDREN S SERVICES MANUAL OF PROCEDURES 3.42 STANDARDS FOR INFANT HEARING SCREENING SERVICES
 3.42 STANDARDS FOR 3.42.1 INPATIENT INFANT HEARING SCREENING PROVIDER A. Definition An Inpatient Infant Hearing Screening Provider shall be a general acute care hospital with licensed perinatal services
3.42 STANDARDS FOR 3.42.1 INPATIENT INFANT HEARING SCREENING PROVIDER A. Definition An Inpatient Infant Hearing Screening Provider shall be a general acute care hospital with licensed perinatal services
Down s syndrome and childhood deafness
 Information for families Down s syndrome and childhood deafness D O W N S SYNDROME ASSOCIATION Our vision is of a world without barriers for every deaf child. Down s syndrome and childhood deafness Information
Information for families Down s syndrome and childhood deafness D O W N S SYNDROME ASSOCIATION Our vision is of a world without barriers for every deaf child. Down s syndrome and childhood deafness Information
Counseling parents for the use of hearing aids
 Counseling parents for the use of hearing aids AUTHORS NACHIKETA ROUT ANIKET PANDIT (Under Revision) Kindly Post your Suggestions/ comments which can be incorporated for necessary modification at nachiketa_raut@yahoo.com
Counseling parents for the use of hearing aids AUTHORS NACHIKETA ROUT ANIKET PANDIT (Under Revision) Kindly Post your Suggestions/ comments which can be incorporated for necessary modification at nachiketa_raut@yahoo.com
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology
 Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS----------------------------------------------- 2 A. DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM HEARING AID/ AUDIOLOGY SERVICES PROCEDURE CODES Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS----------------------------------------------- 2 A. DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES
PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR SPEECH, LANGUAGE AND HEARING PROFESSIONS STANDARDS OF PRACTICE IN AUDIOLOGY
 The Health Professions Council of South Africa PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR SPEECH, LANGUAGE AND HEARING PROFESSIONS STANDARDS OF PRACTICE IN AUDIOLOGY December 2002 The following are considered to be standard
The Health Professions Council of South Africa PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR SPEECH, LANGUAGE AND HEARING PROFESSIONS STANDARDS OF PRACTICE IN AUDIOLOGY December 2002 The following are considered to be standard
Audiology (0340) Test at a Glance. About this test. Test Guide Available. See Inside Back Cover. Test Code 0340
 Audiology (0340) Test Guide Available See Inside Back Cover Test at a Glance Test Name Audiology Test Code 0340 Time 2 hours Number of Questions 150 Format Multiple-choice questions Approximate Approximate
Audiology (0340) Test Guide Available See Inside Back Cover Test at a Glance Test Name Audiology Test Code 0340 Time 2 hours Number of Questions 150 Format Multiple-choice questions Approximate Approximate
Introduction Noise and Occupational Hearing Loss
 Introduction Noise and Occupational Hearing Loss Dr Steven Sadhra Senior Lecturer & Director of Education for Occupational Medicine PhD, MIOSH, MFOM, FFOM (Hon.) Institute of Occupational and Environmental
Introduction Noise and Occupational Hearing Loss Dr Steven Sadhra Senior Lecturer & Director of Education for Occupational Medicine PhD, MIOSH, MFOM, FFOM (Hon.) Institute of Occupational and Environmental
Treatment Guide Understanding Hearing Loss. Cleveland Clinic Hearing Specialists. Choosing Care for Hearing Loss
 Treatment Guide Understanding Hearing Loss Good hearing is part of a full and active life. Let us help you achieve a world of better hearing and improve your quality of life. Choosing Care for Hearing
Treatment Guide Understanding Hearing Loss Good hearing is part of a full and active life. Let us help you achieve a world of better hearing and improve your quality of life. Choosing Care for Hearing
Noice induced hearing loss, Ototoxic drugs, Meniers disease, Rotataory vertigo, Sensorineural hearing loss, Tinnitis, Infections, Acoustic neuroma,
 Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
Disorders of hearing and balance LEARNING OBJECTIVE At the end of lecture student must be able to know, Hearing disorders, Types of hearing disorders, Functional classification, Causes, Middle ear disorders,
A PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE PROFILE
 A PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE PROFILE FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS The International Hearing Society has adopted the following practice profile as a comprehensive declaration of dispensing characteristics
A PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE PROFILE FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS The International Hearing Society has adopted the following practice profile as a comprehensive declaration of dispensing characteristics
Getting a Cochlear Implant
 Cochlear Implants Getting a Cochlear Implant the journey to better hearing 1 All of life s journeys depend on taking the first step determining how to get from where you are to where you want to go. This
Cochlear Implants Getting a Cochlear Implant the journey to better hearing 1 All of life s journeys depend on taking the first step determining how to get from where you are to where you want to go. This
Are there any differences of speech and language development in children with sensorineural hearing loss vs. conductive hearing loss?
 Are there any differences of speech and language development in children with sensorineural hearing loss vs. conductive hearing loss? Annette Limberger annette.limberger@htw-aalen.de Contents Types of
Are there any differences of speech and language development in children with sensorineural hearing loss vs. conductive hearing loss? Annette Limberger annette.limberger@htw-aalen.de Contents Types of
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
