). The multiple regression analysis, adjusted by sex and other variables, showed that children with DMFT > 1 presented 2.
|
|
|
- Britton Maxwell
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Braz Oral Res 2004;18(2): Epidemiology Dental pain prevalence and association with dental caries and socioeconomic status in schoolchildren, Southern Brazil, 2002 Prevalência de dor de dente e associação com cárie e condições socioeconômicas em escolares, sul do Brasil, 2002 Lincon Hideo Nomura* João Luiz Dornelles Bastos** Marco Aurélio Peres*** ABSTRACT: The objective of this study was to assess the relation between dental pain, dental caries and socioeconomic status among 12- and 13-year-old schoolchildren enrolled in a public school in Florianópolis, SC, Brazil in This study was a cross-sectional study involving 181 schoolchildren. Dental pain experience was the dependend variable analyzed. Socioeconomic data of the children s families were obtained through a questionnaire. Dental caries experience was registered according to the DMFT index (WHO, 1997). The field workteam consisted of an examiner and a recorder. The statistical analysis was performed using the chi-square test and the non-conditional multiple logistic regression. The response rate was 93.4%. The intraexaminer agreement measured on a tooth by tooth basis was high (kappa 0.73). Dental pain prevalence was 33.7% (CI 95% ). The multiple regression analysis, adjusted by sex and other variables, showed that children with DMFT > 1 presented 2.9 (OR CI 95% , p < 0.01) more chances of having dental pain when compared with those with DMFT 1. Children whose mother s schooling level was equal or less than 4 years presented 2.5 (OR CI 95% , p = 0.02) more chances of having dental pain when compared with others whose mothers had more than 5 years of schooling and, finally, children whose family income was up to U$ showed 3.2 (OR CI 95% , p = 0.02) more chances of having dental pain when compared with the ones whose families had higher income. High levels of caries attack, low mother schooling level and low family income were associated to dental pain. DESCRIPTORS: Toothache; Epidemiology; Prevalence; Socioeconomic factors. RESUMO: O objetivo deste estudo foi investigar as relações entre dor de dente, cárie dentária e condições socioeconômicas em escolares de 12 e 13 anos de idade de uma escola estadual de Florianópolis, SC, Brasil em Tratou-se de um estudo transversal que envolveu 181 escolares. Episódio de dor de dente foi a variável dependente investigada. Através de um questionário, foram obtidas informações socioeconômicas das famílias. Cárie dentária foi aferida através do índice CPOD. A equipe consistiu de um examinador e um anotador. A análise estatística compreendeu o teste qui-quadrado e a análise de regressão logística múltipla não condicional. A taxa de resposta foi de 93,4%. A concordância intra-examinador para diagnóstico de cárie dentária, medida dente a dente, foi alta (kappa 0,73). A prevalência de dor de dente foi de 33,7% (IC 95% 26,0-42,0). A análise de regressão revelou, após o ajuste pelo sexo e demais variáveis, que crianças com índice CPOD > 1 apresentaram uma chance 2,9 (OR IC 95% 1,4-6,1, p < 0,01) maior de ter dor de dente em relação àquelas com índice CPOD 1. Crianças cujas mães tinham até 4 anos de estudo relataram 2,5 (OR IC 95% 1,2-5,6, p = 0,02) mais a chance de dor de dente comparadas às demais que tinham mais de 5 anos de estudo e, finalmente, àquelas de famílias com renda menor que R$ 200,00 mensais apresentaram 3,2 (OR IC 95% 1,2-8,4, p = 0,02) vezes mais a chance de apresentarem dor em relação às com renda maior. Alto ataque de cárie dentária, baixa escolaridade materna e baixa renda familiar estiveram associados, independentemente, à dor de dente na população estudada. DESCRITORES: Odontalgia; Epidemiologia; Prevalência; Fatores socioeconômicos. INTRODUCTION Pain experience, normally conceived as a consequence of the disorders of the human body organs/systems, is considered a major public health problem 17. From an oral health perspective, untreated dental caries usually lead to a specific kind of pain, dental pain 22. * Undergraduate Student; **Scholarship Holder of the Scientific Initiation Institutional Scholarship Program of the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) 2002/3; ***PhD, Professor, Department of Public Health, Center of Health Sciences Graduation Course in Dentistry, Federal University of Santa Catarina. 134
2 Current neurophysiological concepts of pain recognize that a specific pathological process, such as dental caries, is neither necessary nor sufficient to cause dental pain 22. The additional finding that individuals pain perception can be affected by cognitive factors, such as knowledge, beliefs and expectations, all these being influenced by social and cultural environments, give pain a multifactorial aetiology 6,7,22. A few epidemiological studies on the dental health of the population inquired about toothache 22. However, it is known that such phenomenon can affect people s daily lives, causing an impact on their quality of life 21. Disturbance of sleep, decreased work effectiveness, school absences and avoidance of certain types of food are events frequently related to orofacial pain, particularly dental pain 15,21,22. Dental pain has been associated with many factors, such as low socioeconomic status, high levels of dental caries and restricted access to dental services*. The association between socioeconomic status and dental pain prevalence still remains unclear. Some findings point to a higher prevalence of dental pain among low socioeconomic groups 1,4,9,11,16,19,25, *. On the other hand, some studies point to a lack of association between these two factors 2,14,20,26. Caries experience has been consistently associated in some studies with dental pain. However, these studies did not control potential confounding factors, such as the pattern of dental care 4,5,12,23,24,27. Toothache has also been associated with patterns of dental care. Individuals with restricted access to dental services tend to report dental pain and seek emergency service more frequently. Some authors consider dental pain experience as a predictor of dental services utilization 8. Dental caries could also be used as a predictor to identify those at greatest risk for dental pain and elucidate possible risk factors involved in the aetiology of dental pain 22. The objective of this study was to assess dental pain prevalence and its association with dental caries and socioeconomic status among 12- and 13-year-old schoolchildren enrolled in a public school in Southern Brazil in MATERIAL AND METHODS A cross-sectional study was carried out involving 12- and 13-year-old schoolchildren (n = 181) enrolled in a public school, named Padre Anchieta Basic School, in Florianópolis, Santa Catarina, Brazil, in The dental caries status of this population was assessed in 1971 and and later, in All non-clinical and clinical data were collected between August and December, Prevalence of dental caries was measured through DMFT Index (decayed, missing, filled teeth) according to the WHO (World Health Organization) criteria 28. The field workteam consisted of an examiner and a recorder. The examiner had previous calibration training 18. One in every 10 children was re-examined to test intraexaminer agreement. The kappa test was adopted on a tooth by tooth basis in order to check the intraexaminer agreement in caries diagnosis. Non-clinical data such as behavioral and socioeconomic information, as well as access to dental service and fluoride sources were collected through a questionnaire applied to the families at the children s houses. The questionnaire was pre-tested at the Pediatric Dental Clinic, Federal University of Santa Catarina. Eighteen 12- or 13-year-old children who agreed to participate in the pre-test procedure were interviewed, as well as their parents. As a result, language adaptations were made to the questionnaire. Dental pain experience reported up to twelve months before this study was the dependent variable analyzed. A letter was sent to the parents of the selected children explaining the aims, characteristics and importance of the study and asking for their participation. Data were processed for analysis using a statistical software (Statistical Package for Social Sciences - SPSS 10.0 for Windows, Chicago, USA). Confidence intervals (95%) were calculated for prevalence of dental pain and for caries experience. The chi-square test was used to evaluate the relationship between non-clinical/clinical data and dental pain prevalence. Variables with p val- * Goes PSA, Watt R, Hardy R, Sheiham A. Factors associated with the prevalence and severity of dental pain in years old Brazilian schoolchildren. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol (in press). 135
3 ues 0.20 under the chi-square test were included in the non-conditional multiple logistic regression analysis, using the stepwise forward procedure. Such variables entered this model according to their significance under the chi-square test. Formal ethical approval for this project was granted by the Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Santa Catarina. RESULTS Of a total of 181 schoolchildren, 169 participated in the study (93.4% response rate). Half of the lack of responses was due to refusal in taking part of the study and the other half was due to children s transference to other schools. Examiner agreement was high. Kappa values were calculated on a tooth by tooth basis. The minimum value obtained was 0.73, but the great majority of values were equal to one. DMFT index values are presented in Table 1, with means, percentages and confidence intervals. Caries prevalence was 57.40% (CI 95% ), the mean value was 1.39 and the median was Dental pain prevalence was 33.7% (CI 95% ). Socioeconomic data collected are displayed in Table 2. Only 21 (12.4%) parents could not be interviewed due to incomplete address information or relocation to another neighborhood or city. Father average years of study was 5.3 years, while mother average years of study was 5.4 years. Mean family income was R$ per month, which corresponded to 3.46 Brazilian minimum wages in December All children confirmed the habit of toothbrushing with fluoridated dentifrice. A hundred and twenty seven children (75.10%) did not have the habit of flossing (Table 2). Almost 65% of the children reported having experience with school-based fluoride mouthrinse (Table 2). When asked about professionally applied fluoride compounds at a private service, fewer children answered affirmatively (32.50%) (Table 2). Only 19 children (11.20%) reported having no contact with any kind of dental services in their whole life (Table 2). A significant association between dental pain prevalence and higher caries experience (p = 0.01), low father schooling level (p = 0.01, considering 8-year cut-off point), low mother schooling level (p 0.01, considering both 4- and 8-year cut-off point), low family income (p = 0.02), positive fluoride mouthrinse experience (p = 0.03) and professionally applied fluoride compounds at a private service (p = 0.03) was identified using the chisquare test (Table 3). Low father schooling level (8-year cut-off point), low mother schooling level (8-year cut-off pont), experience with fluoride mouthrinse and experience with professionally applied fluoride compounds were no longer significant when the non-conditional multiple logistic regression was performed (Table 4). The multiple regression analysis showed that children with DMFT > 1 presented 2.9 (OR CI 95% , p < 0.01) more chances to have dental pain when compared with those with DMFT 1. Children whose mother schooling level was lower than 4 years of study presented 2.5 (OR CI 95% , p = 0.02) more chances of dental pain when compared with others whose mothers had 4 years or more of schooling and, finally, children whose family income was up to U$ presented 3.2 (OR CI 95% , p = 0.02) more chances of having dental pain when compared with the ones whose families had higher income. DISCUSSION Dental pain prevalence observed in the schoolchildren during the last twelve months before this study was 33.7% (CI 95% ). A higher prevalence of dental pain was registered, in the city of Harrow (England), among 8-year-old schoolchildren (47.5%, CI 95% ) 21. Another study, which involved 14- and 15-year-old schoolchildren TABLE 1 - Caries experience, according to the DMFT index, in 12- and 13-year-old schoolchildren enrolled in the Padre Anchieta Basic School. Florianópolis, Southern Brazil, Age n D M F DMFT 12 and Mean % CI 95%
4 TABLE 2 - Socioeconomic and behavioral data of 12- and 13-year-old schoolchildren enrolled in the Padre Anchieta Basic School and their families. Florianópolis, Southern Brazil, Variables n % Gender Male Female Father schooling (years of study) < Father schooling (years of study) < Mother schooling (years of study) < Mother schooling (years of study) < Number of family members < Family income (Brazilian currency) R$ < R$ Dwelling conditions Masonry Another type of material Frequency of toothbrushing 2 times a day < 2 times a day Frequency of flossing once a day Variables n % < once a day Presence of sugar in breakfast Yes No Presence of sugar in lunch Yes No Presence of sugar in dinner Yes No Experience with fluoride mouthrinse at school Yes No Ignored Previous exposure to fluoride gel at school Yes No Ignored Exposure to fluoride gel at a private dental office Yes No Ignored Have you ever been to the dentist at least once before? Yes No from Recife (Brazil), showed a dental pain prevalence of 33.6% (CI 95% )* - findings very similar to those presented in this study. High levels of caries attack were strongly associated with dental pain, which corroborates the findings presented by Goes et al.*. This ascertainment reveals that dental caries and their severe and cumulative consequences still need more adequate approaches/interventions in order to reduce and/or control them. Low family income and low mother schooling levels were associated with dental pain prevalence even after adjusting possible confounding fac- tors. Goes et al.* also reported strong association between dental pain prevalence and low socioeconomic position. Hypothetically, variable pain thresholds, according to the socioeconomic status and also influenced by other socio-cultural factors, could, to some extent, explain these findings 3. Contrary to some other studies 8,11, no association between restricted access to dental services and higher prevalence of dental pain were found in this study, while analizing these variables under the non-conditional multiple logistic regression. Although the female sex was not associated with a higher prevalence of dental pain in this study, 137
5 TABLE 3 - Association between dental pain experience and socioeconomic factors, dental caries, behavioral variables and dental service in 12- and 13-year-old schoolchildren enrolled in the Padre Anchieta Basic School. Florianópolis, Southern Brazil, Gender DMFT DMFT Father schooling (years study) Father schooling (years study) Mother schooling (years of study) Mother schooling (years of study) Number of family members Family income (Brazilian currency) Type of housing Frequency of toothbrushing Presence of sugar in breakfast Presence of sugar in lunch Presence of sugar in dinner Experience with fluoride mouthrinse at school Previous exposure to fluoride gel at school Exposure to fluoride gel at a private dental office Have you ever been to the dentist before? Variables Yes Dental pain No n % n % Male Female > < < < < < R$ < R$ Masonry Another type of material times a day < 2 times a day Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No χ 2 p
6 TABLE 4 - Risk factors associated with dental pain in 12- and 13-year-old schoolchildren enrolled in the Padre Anchieta Basic School. Florianópolis, Southern Brazil, Multiple logistic regression analysis. Variables Mother schooling (years of study) OR (CI 95% ) it was used as a control variable. This study presents some limitations. Some cross-sectional epidemiologic studies describe their results as odds ratio but use the definition of prevalence ratio (PR). However, when prevalence is high, differences are found between estimators and confidence intervals, although all the measures maintained statistical significance. In addition, analyses based on PR, particularly those examining the effects of more than one exposure variable, as in the present study, can cause computational problems and are difficult to interpret 13. Moreover, all results showed cannot be inferred to all 12- p OR a (CI 95% ) p < 4 Family income (Brazilian currency) 2.5 ( ) 2.5 ( ) R$ < R$ ( ) 3.2 ( ) DMFT 0.02 < > ( ) 2.9 ( ) OR = odds ratio; OR a = odds ratio adjusted by gender and the other variables. and 13-year-old schoolchildren from Florianópolis. Furthermore, subjects may have failed to identify their pain as of dental origin or may have included other conditions in their reporting of dental pain. However, the strong association found between higher levels of caries attack and prevalence of dental pain indicates that these biases may not have occurred. A high response rate (of almost 94%) and a high intraexaminer agreement (kappa minimum value of 0.73) reinforce the internal validity of this study. Some important findings emerge from our analyses. First, dental pain prevalence was high in the studied population. Second, dental caries is one of the major pathological causes of dental pain. Third, low family income and low mother schooling are factors involved in the aetiology of dental pain. Moreover, a borderline interaction association with dental pain between income and DMFT was found (0.44). However, interaction between mother schooling and DMFT, and income and DMFT was not associated with dental pain (p = 0.20). This last finding is unexpected and may have occurred due to the small size of the sample of this study. Slade 22 (2001) showed evidences about the role of social class on dental pain. Deprivation and stress caused by poverty may alter the hypothalamic adrenal axis and modulate pain thresholds. Finally, services and strategies focusing this population may not have been adequately applied, especially for those at worse socioeconomic and oral health conditions. These findings help us elucidate the aetiology of dental pain and call our attention to the necessity of more specific studies about the subject. Precise questionnaires, capable of isolating the type of dental pain, need to be developed to be used in epidemiological studies 22. REFERENCES 1. Bailit HL. The prevalence of dental pain and anxiety: their relationship to quality of life. NY State Dent J 1987;53: Bassols A, Bosch F, Campillo M, Canellas M, Banos JE. An epidemiological comparison of pain complaints in the general population of Catalonia (Spain). Pain 1999;83: Brunner E, Marmot M. Social organization, stress and health. In: Marmot M, Wilkinson RG. Social determinants of health. Oxford: Oxford University Press; Carmichael C, French A, Rugg-Gunn A, Furness JA. The relationship between social class and caries experience in five-year-old children in Newcastle and Northumberland after twelve years fluoridation. Community Dent Health 1984;1: Cushing AM, Sheiham A, Maizels J. Developing socio-dental indicators the social impact of dental disease. Community Dent Health 1986;3: Dworkin SF, Chen CAN, Schubert MM, Clark DW. Cognitive modification of pain: information in combination with N 2 Ο. Pain 1984;19: Ekanayake L, Mendis R. Self reported use of dental services among employed adults in Sri Lanka. Int Dent J 2002;52(3):
7 8. Eli I. Oral psychophysiology: stress, pain and behavior in dental care. Boca Raton: CRC Press; Evans DJ, Rugg-Gunn A, Tabari ED, Butler T. The effect of fluoridation and social class on caries experience in 5-year-old Newcastle children in 1994 compared with results over the previous 18 years. Community Dent Health 1996;13: Freysleben GR, Peres MA, Marcenes W. Prevalência de cárie e CPO-D médio em escolares de doze a treze anos de idade de 1971 e 1997, região Sul, Brasil. Rev Saúde Pública 2000;34(3): Gilbert GH, Duncan RP, Vogel WB. Determinants of dental care use in dentate adults: six-montly use during a 24-month period in the Florida Dental Care Study. Soc Sci Med 1998;47(6): Jaafar N. Evaluation of the outcome of dental services among Malaysian secondary school children [PhD thesis]. Malaysia: School of Dentistry of the University of Malaysia; Kirkwood BR, Sterne JAC. Medical statistics. 2 nd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; Lipton JA, Ship JA, Larach-Robinson D. Estimated prevalence and distribution of reported orofacial pain in the United States. J Am Dent Assoc 1993;124: Macfarlane TV, Blinkhorn AS, Davies RM, Kincey J, Worthington HV. Oro-facial pain in the community: prevalence and associated impact. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2002;30: Miller J, Swallow JN. Dental pain and health. Public Health 1970;85: Osterweis M, Kleinman A, Mechanic D. Pain and disability clinical, behavioral, and public policy perspectives. Washington: National Academy Press; Peres MA, Traebert J, Marcenes W. Calibração de examinadores para estudos epidemiológicos de cárie dentária. Cad Saúde Pública 2001;17: Prendergast MJ, Beal JF, Williams SA. The relationship between deprivation, ethnicity and dental health in 5-year-old children in Leeds, UK. Community Dent Health 1997;14: Richards W, Scourfield S. Oral ill-health in a general dental practice in South Wales. Prim Dent Care 1996;3: Shepherd MA, Nadanovsky P, Sheiham A. The prevalence and impact of dental pain in 8-year-old school children in Harrow, England. Br Dent J 1999;187(1): Slade GD. Epidemiology of dental pain and dental caries among children and adolescents. Community Dent Health 2001;18: Slade GD, Spencer AJ, Davies MJ, Burrow D. Intra-oral distribution and impact of caries experience among South Australian school children. Aust Dent J 1996;41: Treasure ET, Dever JG. The prevalence of caries in 5- year-old children living in fluoridated and non-fluoridated communities in New Zealand. N Z Dent J 1992;88: Unell L, Soderfeldt B, Halling A, Birkhed D. Explanatory models for clinically determined and symptom-reported caries indicators in an adult population. Acta Odontol Scand 1999;57: Vigild M, Petersen PE, Hadi R. Oral health behaviour of 12-year-old children in Kuwait. Int J Paediatr Dent 1999;9: Whittle J, Whittle K. Five-year-old children: changes in their decay experience and dental health related behaviours over four years. Community Dent Health 1995;12: WHO (World Health Organization). Oral health surveys: basic methods. Geneve: WHO; Received for publication on Sep 12, 2003 Sent for alterations on Jan 21, 2004 Accepted for publication on Apr 05,
Household income modifies the association of insurance and
 1 Household income modifies the association of insurance and dental visiting Olga Anikeeva, David Brennan, Dana Teusner Corresponding author: Dr Olga Anikeeva Australian Research Centre for Population
1 Household income modifies the association of insurance and dental visiting Olga Anikeeva, David Brennan, Dana Teusner Corresponding author: Dr Olga Anikeeva Australian Research Centre for Population
Evaluation of the National Program of Oral Health Promotion (NPOHP) at schools in Castelo Branco, Portugal
 Evaluation of the National Program of Oral Health Promotion (NPOHP) at schools in Castelo Branco, Portugal Avaliação do Programa Nacional de Promoção em Saúde Oral (NPOHP) em escolares de Castelo Branco,
Evaluation of the National Program of Oral Health Promotion (NPOHP) at schools in Castelo Branco, Portugal Avaliação do Programa Nacional de Promoção em Saúde Oral (NPOHP) em escolares de Castelo Branco,
DMFT index of 12 year-old students of public schools participating in the Project of Education for Working for Health
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2013 Jul-Sep;10(3):245-51 Original Research Article DMFT index of 12 year-old students of public schools participating in the Project of Education for Working
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2013 Jul-Sep;10(3):245-51 Original Research Article DMFT index of 12 year-old students of public schools participating in the Project of Education for Working
Household income modifies the association of insurance and dental visiting
 Anikeeva et al. BMC Health Services Research 2013, 13:432 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Household income modifies the association of insurance and dental visiting Olga Anikeeva 1*, David S Brennan 2 and
Anikeeva et al. BMC Health Services Research 2013, 13:432 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Household income modifies the association of insurance and dental visiting Olga Anikeeva 1*, David S Brennan 2 and
Australian Dental Journal
 Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association DATA WATCH Australian Dental Journal 2012; 57: 1 5 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2012.01697.x The avoidance and delaying of
Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association DATA WATCH Australian Dental Journal 2012; 57: 1 5 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2012.01697.x The avoidance and delaying of
Determinants of dental care utilization by the adult population in Buenos Aires
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.15.e316 Determinants of dental care utilization by the adult population in Buenos Aires Gustavo H Marin 1,2,
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.15.e316 Determinants of dental care utilization by the adult population in Buenos Aires Gustavo H Marin 1,2,
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme
 The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
The Queen Mary Cavity Free Incremental Children s Programme Programme Overview Oral diseases are preventable and treatable, yet national oral health surveys clearly show that children s oral health is
Post-graduate Program in Dentistry, Piracicaba School of Dentistry, Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP), Piracicaba, SP, Brazil 2
 ISSNe 2178-1990 10.7308/ aodontol/2012.48.3.02 Accuracy and reproducibility of dental caries risk classification in São Paulo, Brazil Acurácia e reprodutibilidade da classificação de risco de cárie dentária
ISSNe 2178-1990 10.7308/ aodontol/2012.48.3.02 Accuracy and reproducibility of dental caries risk classification in São Paulo, Brazil Acurácia e reprodutibilidade da classificação de risco de cárie dentária
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada ISSN: 1519-0501 apesb@terra.com.br Universidade Federal da Paraíba Brasil
 Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada ISSN: 1519-0501 apesb@terra.com.br Universidade Federal da Paraíba Brasil TANGADE, Pradeep S.; JAIN, Manish; MATHUR, Anmol; PRASAD, Sumanth; Natashekara,
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada ISSN: 1519-0501 apesb@terra.com.br Universidade Federal da Paraíba Brasil TANGADE, Pradeep S.; JAIN, Manish; MATHUR, Anmol; PRASAD, Sumanth; Natashekara,
Longitudinal behavioral analysis during dental care of children aged 0 to 3 years
 Pediatric Dentistry Pediatric Dentistry Longitudinal behavioral analysis during dental care of children aged 0 to 3 years Robson Frederico Cunha (a) Ana Carolina Soares Fraga Zaze (b) Ana Elisa de Mello
Pediatric Dentistry Pediatric Dentistry Longitudinal behavioral analysis during dental care of children aged 0 to 3 years Robson Frederico Cunha (a) Ana Carolina Soares Fraga Zaze (b) Ana Elisa de Mello
Non-carious dental conditions
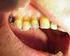 Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
Caries experience associated to social and preventive factors in children of a pastoral community from Limeira-SP
 Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2011 - Volume 10, Number 2 Caries experience associated to social and preventive factors in children of a pastoral community from Limeira-SP Maria Julia Pereira
Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2011 - Volume 10, Number 2 Caries experience associated to social and preventive factors in children of a pastoral community from Limeira-SP Maria Julia Pereira
relatively slow process; it takes about 2 years from the initial attack of caries to be clinically evident and be counted as D in the DMFT index.
 Most childhood tooth decay could be avoided through simple preventive measures such as screening, monitoring, combined use of fluorides and dental sealants and regular professional care. These measures
Most childhood tooth decay could be avoided through simple preventive measures such as screening, monitoring, combined use of fluorides and dental sealants and regular professional care. These measures
Dental fluorosis KEY POINTS. There are some 90 different causes of markings on the enamel surfaces of teeth. These are known as enamel defects.
 One in a Million: the facts about water fluoridation Dental fluorosis KEY POINTS There are some 90 different causes of markings on the enamel surfaces of teeth. These are known as enamel defects. One of
One in a Million: the facts about water fluoridation Dental fluorosis KEY POINTS There are some 90 different causes of markings on the enamel surfaces of teeth. These are known as enamel defects. One of
The psychosocial effects of severe caries in 4-year-old children in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil
 1550 ARTIGO ARTICLE The psychosocial effects of severe caries in 4-year-old children in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil As repercussões psicossociais da cárie severa em crianças aos quatro anos de idade em
1550 ARTIGO ARTICLE The psychosocial effects of severe caries in 4-year-old children in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil As repercussões psicossociais da cárie severa em crianças aos quatro anos de idade em
Dental Health Services in Canada
 Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
Dental Health Services in Canada Facts and Figures 2010 Canadian Dental Association Number of Dentists In January 2010, there were 19,563 licensed dentists in Canada. Approximately 89% were in general
A population-based cohort study of oral health in South Brazil: The Porto Alegre Study
 DOI: 10.1590/1980-5497201500020018 NOTES AND INFORMATIONS / NOTAS E INFORMAÇÕES A population-based cohort study of oral health in South Brazil: The Porto Alegre Study Um estudo de coorte de base populacional
DOI: 10.1590/1980-5497201500020018 NOTES AND INFORMATIONS / NOTAS E INFORMAÇÕES A population-based cohort study of oral health in South Brazil: The Porto Alegre Study Um estudo de coorte de base populacional
Epidemiological pattern of severe malocclusions in Brazilian adolescents
 Original Articles DOI:10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047004366 Karen Glazer Peres I,II Paulo Frazão III Angelo Giuseppe Roncalli IV Epidemiological pattern of severe malocclusions in Brazilian adolescents ABSTRACT
Original Articles DOI:10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047004366 Karen Glazer Peres I,II Paulo Frazão III Angelo Giuseppe Roncalli IV Epidemiological pattern of severe malocclusions in Brazilian adolescents ABSTRACT
Clinical oral health measures have been used as the
 DENTAL AND ORAL HEALTH Relationship Between Oral Health Related Quality of Life, Oral Health, Socioeconomic, and General Health Factors in Elderly Brazilians Fabíola Bof de Andrade, PhD, * Maria Lúcia
DENTAL AND ORAL HEALTH Relationship Between Oral Health Related Quality of Life, Oral Health, Socioeconomic, and General Health Factors in Elderly Brazilians Fabíola Bof de Andrade, PhD, * Maria Lúcia
Fluoride Products for Oral Health: Professional Information
 Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Laura Duncan, MA; Ashley Bonner, MSc
 l Association dentaire nadienne Professional Applied Research Issues Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2014;80:e6 Effects of Income and Dental Insurance Coverage on Need for Dental Care in Canada
l Association dentaire nadienne Professional Applied Research Issues Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2014;80:e6 Effects of Income and Dental Insurance Coverage on Need for Dental Care in Canada
A SCHOOL-BASED ORAL HEALTH EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM: THE EXPERIENCE OF MARINGA- PR, BRAZIL
 J Appl Oral Sci 2004; 12(1): 2733 A SCHOOLBASED ORAL HEALTH EDUCATIOAL PROGRAM: THE EXPERIECE OF MARIGA PR, BRAZIL PROGRAMA EDUCACIOAL EM SAÚDE BUCAL BASEADO EM ESCOLAS: A EXPERIÊCIA DE MARIGÁ PR, BRASIL
J Appl Oral Sci 2004; 12(1): 2733 A SCHOOLBASED ORAL HEALTH EDUCATIOAL PROGRAM: THE EXPERIECE OF MARIGA PR, BRAZIL PROGRAMA EDUCACIOAL EM SAÚDE BUCAL BASEADO EM ESCOLAS: A EXPERIÊCIA DE MARIGÁ PR, BRASIL
Concepts of risk in dental public health
 Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2005; 33: 240 7 All rights reserved Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Concepts of risk in dental public health Brian A. Burt Department of Epidemiology, School of Public
Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2005; 33: 240 7 All rights reserved Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Concepts of risk in dental public health Brian A. Burt Department of Epidemiology, School of Public
Index of clinical consequences of untreated dental caries (pufa) in primary dentition of children from north-east Poland
 Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 58(2) 2013 pp 442-447 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-012-0075-x Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Index of clinical consequences of untreated dental caries (pufa) in primary
Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 58(2) 2013 pp 442-447 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-012-0075-x Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Index of clinical consequences of untreated dental caries (pufa) in primary
MeSH Key Words: Canada/epidemiology; dental health services; emigration and immigration/statistics & numerical data; insurance, dental
 Professional ISSUES Use of Dental Services by Immigrant Canadians K. Bruce Newbold, PhD; Amish Patel, BSc Contact Author Dr. Newbold Email: newbold@mcmaster.ca ABSTRACT Although the health status and health
Professional ISSUES Use of Dental Services by Immigrant Canadians K. Bruce Newbold, PhD; Amish Patel, BSc Contact Author Dr. Newbold Email: newbold@mcmaster.ca ABSTRACT Although the health status and health
The state of children s oral health in England
 The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
The state of children s oral health in England Contents Overview 3 The impact of poor oral health 4 The prevalence of children s tooth decay in England 4 Regional inequalities 5 Hospital admission 5 What
Provision of Oral Health Care in Turkey
 Provision of Oral Health Care in Turkey PROF. DR. BETÜL KARGÜL DEPTARMENT of PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY DENTAL SCHOOL MARMARA UNIVERSITY - TURKEY TURKEY Since the formation of the Turkish Republic in 1923,
Provision of Oral Health Care in Turkey PROF. DR. BETÜL KARGÜL DEPTARMENT of PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY DENTAL SCHOOL MARMARA UNIVERSITY - TURKEY TURKEY Since the formation of the Turkish Republic in 1923,
Fluoridation Position Statement
 Fluoridation Position Statement Part B of the Oral Health Strategy relates to a separate document on a detailed Oral Health Strategy for the CDHB 1 PART A Fluoridation position statement 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Fluoridation Position Statement Part B of the Oral Health Strategy relates to a separate document on a detailed Oral Health Strategy for the CDHB 1 PART A Fluoridation position statement 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
research report 53 Dental decay among Australian children This report provides information on the dental decay experience of Australian Main findings
 AIHW Dental Statistics and Research Unit Research report 53 July 2011 Dental decay among Australian children This report provides information on the dental decay experience of Australian children from
AIHW Dental Statistics and Research Unit Research report 53 July 2011 Dental decay among Australian children This report provides information on the dental decay experience of Australian children from
Comparison of Association of Dental Caries in Relation with Body Mass Index (BMI) in Government and Private School Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Association of Dental Caries in Relation with Body Mass Index (BMI) in Government and Private School Children 1 1 1 1 Prashanth S.T, Venkatesh Babu, Vivek Dhruv Kumar, Amitha
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Association of Dental Caries in Relation with Body Mass Index (BMI) in Government and Private School Children 1 1 1 1 Prashanth S.T, Venkatesh Babu, Vivek Dhruv Kumar, Amitha
North Carolina Maternal and Perinatal Substance Abuse Initiative Study: Social Support and DSS Investigation Risk for Child Abuse or Neglect
 North Carolina Maternal and Perinatal Substance Abuse Initiative Study: Social Support and DSS Investigation Risk for Child Abuse or Neglect Sherri L. Green, MSW, LCSW Governor s Institute for Alcohol
North Carolina Maternal and Perinatal Substance Abuse Initiative Study: Social Support and DSS Investigation Risk for Child Abuse or Neglect Sherri L. Green, MSW, LCSW Governor s Institute for Alcohol
Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India Thanveer K* Ajith Krishnan** Sudheer Hongal*** *M.D.S,
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India Thanveer K* Ajith Krishnan** Sudheer Hongal*** *M.D.S,
Objectives: Autism is a lifelong neurodevelopmental disorder. The aims of this study
 www.scielo.br/jaos Dental caries experience, oral health status and treatment needs of dental patients with autism Mohamed Abdullah JABER 1 1- BDS, MSc, FDSRCS, FDSRCSE, PhD, Dental School, Ajman University
www.scielo.br/jaos Dental caries experience, oral health status and treatment needs of dental patients with autism Mohamed Abdullah JABER 1 1- BDS, MSc, FDSRCS, FDSRCSE, PhD, Dental School, Ajman University
A Simple Method for Estimating Relative Risk using Logistic Regression. Fredi Alexander Diaz-Quijano
 1 A Simple Method for Estimating Relative Risk using Logistic Regression. Fredi Alexander Diaz-Quijano Grupo Latinoamericano de Investigaciones Epidemiológicas, Organización Latinoamericana para el Fomento
1 A Simple Method for Estimating Relative Risk using Logistic Regression. Fredi Alexander Diaz-Quijano Grupo Latinoamericano de Investigaciones Epidemiológicas, Organización Latinoamericana para el Fomento
Published online 2014 March 30. Research Article. Traumatic Dental Injuries Among 12-15-Year-Old-School Children in Panchkula
 Arch Trauma Res. 2014 March; 3(1): e18127. Published online 2014 March 30. DOI: 10.5812/atr.18127 Research Article Traumatic Dental Injuries Among 12-15-Year-Old-School Children in Panchkula Amandeep Chopra
Arch Trauma Res. 2014 March; 3(1): e18127. Published online 2014 March 30. DOI: 10.5812/atr.18127 Research Article Traumatic Dental Injuries Among 12-15-Year-Old-School Children in Panchkula Amandeep Chopra
Is the degree of cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer s disease related to their capacity to appoint an enduring power of attorney?
 Age and Ageing 2007; 36: 527 531 doi:10.1093/ageing/afm104 The Author 2007. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please
Age and Ageing 2007; 36: 527 531 doi:10.1093/ageing/afm104 The Author 2007. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please
Water Fluoridation: A briefing on the York University Systematic Review and Subsequent Research Developments
 Water Fluoridation: A briefing on the York University Systematic Review and Subsequent Research Developments The York University Systematic Review 1. This systematic review, subsequently referred to as
Water Fluoridation: A briefing on the York University Systematic Review and Subsequent Research Developments The York University Systematic Review 1. This systematic review, subsequently referred to as
Oral health in Iran. Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran
 International Dental Journal (2004) 54, 367 372 Oral health in Iran Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran The health network in the Islamic Republic (I.R.) of Iran is an integrated public health system with
International Dental Journal (2004) 54, 367 372 Oral health in Iran Hamid Reza Pakshir Shiraz, Iran The health network in the Islamic Republic (I.R.) of Iran is an integrated public health system with
Parent s Perception on the Importance of their Children s First Dental Visit (A cross-sectional Pilot Study in Malaysia)
 Parent s Perception on the Importance of their Children s First Dental Visit (A cross-sectional Pilot Study in Malaysia) 1 Alaa S. Hussein, M.Sc; 2 Mohamed I. Abu-Hassan, PhD; 3 Robert J. Schroth, PhD;
Parent s Perception on the Importance of their Children s First Dental Visit (A cross-sectional Pilot Study in Malaysia) 1 Alaa S. Hussein, M.Sc; 2 Mohamed I. Abu-Hassan, PhD; 3 Robert J. Schroth, PhD;
Rev Saúde Pública 2003;37(5):603-8 www.fsp.usp.br/rsp
 Rev Saúde Pública 2003;37(5):603-8 603 Association between child-care and acute diarrhea: a study in Portuguese children Associação entre cuidados infantis e diarréia aguda em crianças portuguesas Henrique
Rev Saúde Pública 2003;37(5):603-8 603 Association between child-care and acute diarrhea: a study in Portuguese children Associação entre cuidados infantis e diarréia aguda em crianças portuguesas Henrique
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS: ORAL HEALTH IN NEW ZEALAND
 ORAL HEALTH IN NEW ZEALAND What is the oral health status of New Zealand? There are two measures of oral health in New Zealand: The percentage of five-year-olds that are free of dental decay ( caries free
ORAL HEALTH IN NEW ZEALAND What is the oral health status of New Zealand? There are two measures of oral health in New Zealand: The percentage of five-year-olds that are free of dental decay ( caries free
Oral hygiene practices among paramedical staff of a private dental institution in India
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2013 Jul-Sep;10(3):205-10 Original Research Article Oral hygiene practices among paramedical staff of a private dental institution in India Amith Holenarasipur
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2013 Jul-Sep;10(3):205-10 Original Research Article Oral hygiene practices among paramedical staff of a private dental institution in India Amith Holenarasipur
Dental caries in Uruguayan adults and elders: findings from the first Uruguayan National Oral Health Survey
 ARTIGO ARTICLE 1663 Dental caries in Uruguayan adults and elders: findings from the first Uruguayan National Oral Health Survey Caries dental en adultos y adultos mayores uruguayos: resultados del primer
ARTIGO ARTICLE 1663 Dental caries in Uruguayan adults and elders: findings from the first Uruguayan National Oral Health Survey Caries dental en adultos y adultos mayores uruguayos: resultados del primer
Adult oral health and dental visiting in Australia
 Adult oral health and dental visiting in Australia Results from the National Dental Telephone Interview Survey 2010 JE Harford and S Islam Dental statistics and research series No. 65 DENTAL STATISTICS
Adult oral health and dental visiting in Australia Results from the National Dental Telephone Interview Survey 2010 JE Harford and S Islam Dental statistics and research series No. 65 DENTAL STATISTICS
Assessment of prevalence of dental caries among 5 and 12-year-old schoolchildren in Chandigarh (U.T.), India
 ISSN 2236-8035 Archives of Oral Research, v. 8, n. 1, p. 39-45, Jan./Apr. 2012 Licensed under a Creative Commons License [T] Assessment of prevalence of dental caries among 5 and 12-year-old schoolchildren
ISSN 2236-8035 Archives of Oral Research, v. 8, n. 1, p. 39-45, Jan./Apr. 2012 Licensed under a Creative Commons License [T] Assessment of prevalence of dental caries among 5 and 12-year-old schoolchildren
Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows
 Issue Brief PROJECT Children s NAME Dental Campaign Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows Dental decay remains the most common chronic childhood disease in the United States. 1 More
Issue Brief PROJECT Children s NAME Dental Campaign Dental Therapists in New Zealand: What the Evidence Shows Dental decay remains the most common chronic childhood disease in the United States. 1 More
Disparities in Realized Access: Patterns of Health Services Utilization by Insurance Status among Children with Asthma in Puerto Rico
 Disparities in Realized Access: Patterns of Health Services Utilization by Insurance Status among Children with Asthma in Puerto Rico Ruth Ríos-Motta, PhD, José A. Capriles-Quirós, MD, MPH, MHSA, Mario
Disparities in Realized Access: Patterns of Health Services Utilization by Insurance Status among Children with Asthma in Puerto Rico Ruth Ríos-Motta, PhD, José A. Capriles-Quirós, MD, MPH, MHSA, Mario
ADEA Survey of Dental School Seniors, 2014 Graduating Class Tables Report
 ADEA Survey of Dental School Seniors, 2014 Graduating Class Tables Report Published February 2015 Suggested Citation American Dental Education Association. (February 2015). ADEA Survey of Dental School
ADEA Survey of Dental School Seniors, 2014 Graduating Class Tables Report Published February 2015 Suggested Citation American Dental Education Association. (February 2015). ADEA Survey of Dental School
Prevalence of dental caries among school-going children in South India
 Research Article Prevalence of dental caries among school-going children in South India Rajesh SS, Venkatesh P Department of Community Medicine, Sri Siddhartha Medical College, Tumkur, Karnataka, India.
Research Article Prevalence of dental caries among school-going children in South India Rajesh SS, Venkatesh P Department of Community Medicine, Sri Siddhartha Medical College, Tumkur, Karnataka, India.
Oral health and dental care in Australia
 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures 2011 Sergio Chrisopoulos Research Associate Katie Beckwith Research Officer Jane Harford Research Fellow Australian Research Centre for Population
Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures 2011 Sergio Chrisopoulos Research Associate Katie Beckwith Research Officer Jane Harford Research Fellow Australian Research Centre for Population
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003
 Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
Big data size isn t enough! Irene Petersen, PhD Primary Care & Population Health
 Big data size isn t enough! Irene Petersen, PhD Primary Care & Population Health Introduction Reader (Statistics and Epidemiology) Research team epidemiologists/statisticians/phd students Primary care
Big data size isn t enough! Irene Petersen, PhD Primary Care & Population Health Introduction Reader (Statistics and Epidemiology) Research team epidemiologists/statisticians/phd students Primary care
Question ID: 6 Question type: Intervention Question: Does treatment of overactive bladder symptoms prevent falls in the elderly?
 PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation projects. QUESTION
Dental attendance patterns and oral health status
 DENTAL STATISTICS AND RESEARCH SERIES Number 57 Dental attendance patterns and oral health status AC Ellershaw Research Officer Australian Research Centre for Population Oral Health The University of Adelaide
DENTAL STATISTICS AND RESEARCH SERIES Number 57 Dental attendance patterns and oral health status AC Ellershaw Research Officer Australian Research Centre for Population Oral Health The University of Adelaide
Dental Fluosis and the Photographic Method
 ARTIGO ARTICLE 1017 Agreement in the diagnosis of dental fluorosis in central incisors performed by a standardized photographic method and clinical examination Concordância no diagnóstico da fluorose dentária
ARTIGO ARTICLE 1017 Agreement in the diagnosis of dental fluorosis in central incisors performed by a standardized photographic method and clinical examination Concordância no diagnóstico da fluorose dentária
Dental caries and related factors in Brazilian children from fluoridated and non-fluoridated areas
 Original Article Dental caries and related factors in Brazilian children from fluoridated and non-fluoridated areas Cárie dentária e fatores relacionados em crianças brasileiras de região com água fluoretada
Original Article Dental caries and related factors in Brazilian children from fluoridated and non-fluoridated areas Cárie dentária e fatores relacionados em crianças brasileiras de região com água fluoretada
INTRODUCTION. Community Dentistry. Community Dentistry
 Community Dentistry Braz Oral Res 2006;20(3):263-8 Community Dentistry Translation into Brazilian portuguese, cultural adaptation and validation of the oral health impact profile (ohip-49) Tradução para
Community Dentistry Braz Oral Res 2006;20(3):263-8 Community Dentistry Translation into Brazilian portuguese, cultural adaptation and validation of the oral health impact profile (ohip-49) Tradução para
VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO!
 VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO! 2012-2013 Annual Report The Varnish! Michigan Babies Too! Program was developed as an incentive for medical providers to have oral health training and begin an oral health
VARNISH! MICHIGAN BABIES TOO! 2012-2013 Annual Report The Varnish! Michigan Babies Too! Program was developed as an incentive for medical providers to have oral health training and begin an oral health
IMPROVING DENTAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH A CALL TO ACTION EVIDENCE RESOURCE PACK
 IMPROVING DENTAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH A CALL TO ACTION EVIDENCE RESOURCE PACK NHS England Dental Analytical Team February 2013/14 Gateway reference: 01173 Introduction to this pack This data pack has been
IMPROVING DENTAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH A CALL TO ACTION EVIDENCE RESOURCE PACK NHS England Dental Analytical Team February 2013/14 Gateway reference: 01173 Introduction to this pack This data pack has been
Caries diagnosis under the focus of the. Diagnóstico de cárie sob o enfoque da Odontologia baseada em evidências. Abstract
 ISSN 1806-7727 Caries diagnosis under the focus of the evidence-based dentistry Diagnóstico de cárie sob o enfoque da Odontologia baseada em evidências Ana Paula Pires dos SANTOS* Diana Ribeiro do Espírito
ISSN 1806-7727 Caries diagnosis under the focus of the evidence-based dentistry Diagnóstico de cárie sob o enfoque da Odontologia baseada em evidências Ana Paula Pires dos SANTOS* Diana Ribeiro do Espírito
original article KEY-WORDS Traumatic Dental injuries, Prevalence, Ellis and Davey classification, Fall, School Dental Health Program.
 Prevalence and Factors Associated with Traumatic Dental Injuries (TDI) to Anterior Teeth of 11-13 Year Old School Going Children of Maduravoyal, Chennai Navin Anand Ingle, Naveen Baratam, Zohara Charania
Prevalence and Factors Associated with Traumatic Dental Injuries (TDI) to Anterior Teeth of 11-13 Year Old School Going Children of Maduravoyal, Chennai Navin Anand Ingle, Naveen Baratam, Zohara Charania
4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009
 4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
Dental caries and treatment needs among indigenous people of the Potiguara Indian reservation in Brazil
 Investigación original / Original research Dental caries and treatment needs among indigenous people of the Potiguara Indian reservation in Brazil Fábio Correia Sampaio, 1 Cláudia Helena Soares de Morais
Investigación original / Original research Dental caries and treatment needs among indigenous people of the Potiguara Indian reservation in Brazil Fábio Correia Sampaio, 1 Cláudia Helena Soares de Morais
Executive Summary: Adult Dental Health Survey 2009
 Executive Summary: Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England s central, authoritative source
Executive Summary: Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England s central, authoritative source
Stomatos ISSN: 1519-4442 ppgpediatria@ulbra.br Universidade Luterana do Brasil Brasil
 Stomatos ISSN: 1519-4442 ppgpediatria@ulbra.br Universidade Luterana do Brasil Brasil Londero Pagliarin, Claudia; Londero Zenkner, Clacir; Branco Barletta, Fernando Knowledge of physical education teachers
Stomatos ISSN: 1519-4442 ppgpediatria@ulbra.br Universidade Luterana do Brasil Brasil Londero Pagliarin, Claudia; Londero Zenkner, Clacir; Branco Barletta, Fernando Knowledge of physical education teachers
A one-year survey of dental malpractice claims in Riyadh Wafa Al Ammar*, BDS E. Ernest Guile*, DMD, MPH
 95 A one-year survey of dental malpractice claims in Riyadh Wafa Al Ammar*, BDS E. Ernest Guile*, DMD, MPH Malpractice is an increasing problem related to dental treatment around the world. The present
95 A one-year survey of dental malpractice claims in Riyadh Wafa Al Ammar*, BDS E. Ernest Guile*, DMD, MPH Malpractice is an increasing problem related to dental treatment around the world. The present
Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample of Children Ages 6-8
 Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample of Children Ages 6-8 Area of Technology and Health Services Delivery Health Services Organization Regional Oral Health Program July 2004 Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample
Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample of Children Ages 6-8 Area of Technology and Health Services Delivery Health Services Organization Regional Oral Health Program July 2004 Nevis Oral Health Survey: Sample
The Oral Health Status and Behavior of Middle School Students According to Fluoridation Area
 , pp.279-286 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijbsbt.2016.8.2.26 The Oral Health Status and Behavior of Middle School Students According to Fluoridation Area Hye-Jung Jin, Min-Kyung Lee, Jung Hwa Lee * Department
, pp.279-286 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijbsbt.2016.8.2.26 The Oral Health Status and Behavior of Middle School Students According to Fluoridation Area Hye-Jung Jin, Min-Kyung Lee, Jung Hwa Lee * Department
Oral health and dental care in Australia
 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia: Key facts
Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia Key facts and figures trends 2014 Oral health and dental care in Australia: Key facts
DERBYSHIRE COUNTY COUNCIL CABINET. 06 May 2014. Report of the Director of Public Health. DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH IN DERBYSHIRE (Health and Communities)
 PUBLIC Author: Alison Pritchard Agenda Item No.7 (g) DERBYSHIRE COUNTY COUNCIL CABINET 06 May 2014 Report of the Director of Public Health DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH IN DERBYSHIRE (Health and Communities) 1.
PUBLIC Author: Alison Pritchard Agenda Item No.7 (g) DERBYSHIRE COUNTY COUNCIL CABINET 06 May 2014 Report of the Director of Public Health DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH IN DERBYSHIRE (Health and Communities) 1.
Child Oral Health in Hounslow
 Child Oral Health in Hounslow Introduction With the 2012 Health and Social Care Act the responsibilities for commissioning programmes to improve children s oral health changed and the commissioning of
Child Oral Health in Hounslow Introduction With the 2012 Health and Social Care Act the responsibilities for commissioning programmes to improve children s oral health changed and the commissioning of
Effect of IMC of toothpastes on Oral Hygiene Behavior among the School Children of Dhaka City
 Effect of IMC of toothpastes on Oral Hygiene Behavior among the School Children of Dhaka City Kashfia Ahmed Correspondence Author Senior Lecturer Department of Business Administration East West University
Effect of IMC of toothpastes on Oral Hygiene Behavior among the School Children of Dhaka City Kashfia Ahmed Correspondence Author Senior Lecturer Department of Business Administration East West University
REPORT ON THE COCHRANE TOPICAL FLUORIDE REVIEWS INFORMING ABOUT THE IMPORTANCE OF EFFECTIVE USE OF TOPICAL FLUORIDES
 6 May 2004 REPORT ON THE COCHRANE TOPICAL FLUORIDE REVIEWS INFORMING ABOUT THE IMPORTANCE OF EFFECTIVE USE OF TOPICAL FLUORIDES Prepared by the WHO Oral Health Programme with technical assistance from
6 May 2004 REPORT ON THE COCHRANE TOPICAL FLUORIDE REVIEWS INFORMING ABOUT THE IMPORTANCE OF EFFECTIVE USE OF TOPICAL FLUORIDES Prepared by the WHO Oral Health Programme with technical assistance from
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
A Review of Indonesia s Dental Health - Past, Present and Future
 Review Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2014;10(3):121-126ㆍhttp://dx.doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2014.10.3.121 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546ㆍISSN (Online) 2287-6197 A Review of Indonesia s Dental Health - Past, Present
Review Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2014;10(3):121-126ㆍhttp://dx.doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2014.10.3.121 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546ㆍISSN (Online) 2287-6197 A Review of Indonesia s Dental Health - Past, Present
In the mid-1960s, the need for greater patient access to primary care. Physician Assistants in Primary Care: Trends and Characteristics
 Physician Assistants in Primary Care: Trends and Characteristics Bettie Coplan, MPAS, PA-C 1 James Cawley, MPH, PA-C 2 James Stoehr, PhD 1 1 Physician Assistant Program, College of Health Sciences, Midwestern
Physician Assistants in Primary Care: Trends and Characteristics Bettie Coplan, MPAS, PA-C 1 James Cawley, MPH, PA-C 2 James Stoehr, PhD 1 1 Physician Assistant Program, College of Health Sciences, Midwestern
8: Access and barriers to care - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009
 8: Access and barriers to care - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
8: Access and barriers to care - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
ENTREPRENEURIAL INTENTION AMONG MALAYSIAN ENGINEERING GRADUATES: MALE VERSUS FEMALE
 ENTREPRENEURIAL INTENTION AMONG MALAYSIAN ENGINEERING GRADUATES: MALE VERSUS FEMALE Abbas, L. N. Faculty of Technical and Vocational Education, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Malaysia lutfiah@uthm.edu.my
ENTREPRENEURIAL INTENTION AMONG MALAYSIAN ENGINEERING GRADUATES: MALE VERSUS FEMALE Abbas, L. N. Faculty of Technical and Vocational Education, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Malaysia lutfiah@uthm.edu.my
Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians
 Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians Approved CDA Board of Directors May 2010 Preamble A daily regimen of brushing and flossing is an important part of good oral health while equitable
Position Paper on Access to Oral Health Care for Canadians Approved CDA Board of Directors May 2010 Preamble A daily regimen of brushing and flossing is an important part of good oral health while equitable
Module 223 Major A: Concepts, methods and design in Epidemiology
 Module 223 Major A: Concepts, methods and design in Epidemiology Module : 223 UE coordinator Concepts, methods and design in Epidemiology Dates December 15 th to 19 th, 2014 Credits/ECTS UE description
Module 223 Major A: Concepts, methods and design in Epidemiology Module : 223 UE coordinator Concepts, methods and design in Epidemiology Dates December 15 th to 19 th, 2014 Credits/ECTS UE description
Dental anxiety in an emergency dental service
 Revista de Saúde Pública ISSN 0034-8910 versão impressa Rev Saúde Pública 2003; 37(6) Dental anxiety in an emergency dental service Kazue Kanegane, Sibele Sarti Penha, Maria Aparecida Borsatti and Rodney
Revista de Saúde Pública ISSN 0034-8910 versão impressa Rev Saúde Pública 2003; 37(6) Dental anxiety in an emergency dental service Kazue Kanegane, Sibele Sarti Penha, Maria Aparecida Borsatti and Rodney
QUESTIONÁRIOS DE AVALIAÇÃO: QUE INFORMAÇÕES ELES REALMENTE NOS FORNECEM?
 QUESTIONÁRIOS DE AVALIAÇÃO: QUE INFORMAÇÕES ELES REALMENTE NOS FORNECEM? Grizendi, J. C. M grizendi@acessa.com Universidade Estácio de Sá Av. Presidente João Goulart, 600 - Cruzeiro do Sul Juiz de Fora
QUESTIONÁRIOS DE AVALIAÇÃO: QUE INFORMAÇÕES ELES REALMENTE NOS FORNECEM? Grizendi, J. C. M grizendi@acessa.com Universidade Estácio de Sá Av. Presidente João Goulart, 600 - Cruzeiro do Sul Juiz de Fora
Variations in Children s Dental Service Use Based on Four National Health Surveys
 Variations in Children s Dental Service Use Based on Four National Health Surveys WHAT S KNOWN ON THIS SUBJECT: Oral health researchers and policy makers primarily use 4 national surveys to examine use
Variations in Children s Dental Service Use Based on Four National Health Surveys WHAT S KNOWN ON THIS SUBJECT: Oral health researchers and policy makers primarily use 4 national surveys to examine use
General practitioners psychosocial resources, distress, and sickness absence: a study comparing the UK and Finland
 Family Practice, 2014, Vol. 31, No. 3, 319 324 doi:10.1093/fampra/cmt086 Advance Access publication 30 January 2014 General practitioners psychosocial resources, distress, and sickness absence: a study
Family Practice, 2014, Vol. 31, No. 3, 319 324 doi:10.1093/fampra/cmt086 Advance Access publication 30 January 2014 General practitioners psychosocial resources, distress, and sickness absence: a study
Dental / Oral Health Services by Gina R. Lombardi
 M o n o g r a p h s e r i e s M i g r a n t H e a l t h I s s u e s Dental / Oral Health Services by Gina R. Lombardi Monograph no. 1 This Page Has Been Left Intentionally Blank. D ENTAL / O RAL H EALTH
M o n o g r a p h s e r i e s M i g r a n t H e a l t h I s s u e s Dental / Oral Health Services by Gina R. Lombardi Monograph no. 1 This Page Has Been Left Intentionally Blank. D ENTAL / O RAL H EALTH
AÓ ÛÎfiappleËÛË ÙˆÓ appleúfiûê ÙˆÓ ÂÍÂÏ ÍˆÓ. Basic Research of periodontal diseases: A review of recent developments
 BÈ ÏÈÔÁÚ ÊÈÎ AÓ ÛÎfiappleËÛË B ÛÈÎ ŒÚÂ Ó ÙˆÓ appleâúèô ÔÓÙÈÎÒÓ ÓÔÛËÌ ÙˆÓ: AÓ ÛÎfiappleËÛË ÙˆÓ appleúfiûê ÙˆÓ ÂÍÂÏ ÍˆÓ. KˆÙÛÔ ÏË * Basic Research of periodontal diseases: A review of recent developments
BÈ ÏÈÔÁÚ ÊÈÎ AÓ ÛÎfiappleËÛË B ÛÈÎ ŒÚÂ Ó ÙˆÓ appleâúèô ÔÓÙÈÎÒÓ ÓÔÛËÌ ÙˆÓ: AÓ ÛÎfiappleËÛË ÙˆÓ appleúfiûê ÙˆÓ ÂÍÂÏ ÍˆÓ. KˆÙÛÔ ÏË * Basic Research of periodontal diseases: A review of recent developments
Challenges in assessing disease latency for cancer in environmental epidemiology
 Challenges in assessing disease latency for cancer in environmental epidemiology Peggy Reynolds, Ph.D. Case-only Clustering in Mobile Populations Workshop - November 11-12, 2010 Ann Arbor, Michigan Outline
Challenges in assessing disease latency for cancer in environmental epidemiology Peggy Reynolds, Ph.D. Case-only Clustering in Mobile Populations Workshop - November 11-12, 2010 Ann Arbor, Michigan Outline
AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
Long-term Outcomes of a Dental Post-baccalaureate Program
 Long-term Outcomes of a Dental Post-baccalaureate Program Wides, Cynthia D., MA Brody, Harvey, DDS, M.Ed. Alexander, Charles J., Ph.D. Gansky, Stuart A., Dr.P.H. Mertz, Elizabeth, Ph.D., MA National Oral
Long-term Outcomes of a Dental Post-baccalaureate Program Wides, Cynthia D., MA Brody, Harvey, DDS, M.Ed. Alexander, Charles J., Ph.D. Gansky, Stuart A., Dr.P.H. Mertz, Elizabeth, Ph.D., MA National Oral
Traumatic dental injuries and associated factors among Brazilian preschool children
 Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2005.00413.x All rights reserved Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2006 DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Traumatic dental injuries and associated factors among Brazilian
Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2005.00413.x All rights reserved Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2006 DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Traumatic dental injuries and associated factors among Brazilian
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology
 Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
Caries Process and Prevention Strategies: Epidemiology Edward Lo, BDS, MDS, PhD, FHKAM Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Online Course: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/dental-education/continuing-education/ce368/ce368.aspx
The role of pediatrician in promoting oral health
 Braz J Oral Sci. 4(14):783-786 Braz J Effects Oral Sci. of ozonated October-December water on Candida 00 - albicans Vol. 4 - oral Number isolates 1 The role of pediatrician in promoting oral health Karina
Braz J Oral Sci. 4(14):783-786 Braz J Effects Oral Sci. of ozonated October-December water on Candida 00 - albicans Vol. 4 - oral Number isolates 1 The role of pediatrician in promoting oral health Karina
Children s Dental Health Survey 2013. Report 1: Attitudes, Behaviours and Children s Dental Health England, Wales and Northern Ireland, 2013
 Children s Dental Health Survey 2013 Report 1: Attitudes, Behaviours and Children s Dental Health, 2013 Published 19 March 2015 We are the trusted national provider of high-quality information, data and
Children s Dental Health Survey 2013 Report 1: Attitudes, Behaviours and Children s Dental Health, 2013 Published 19 March 2015 We are the trusted national provider of high-quality information, data and
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS. brought to you by:
 CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
CHILDREN S ORAL HEALTH RECENT RESEARCH & BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS brought to you by: February 2015 ABOUT COHAT: This toolkit is brought to you by the Children s Oral Health Action Team (COHAT), created
Healthy People (HP) 2010
 The military oral health care system as a model for eliminating disparities in oral health Jeffrey J. Hyman, DDS, PhD; Britt C. Reid, DDS, PhD; Susan W. Mongeau, DDS, MPH; Andrew K. York, DMD, MPH Healthy
The military oral health care system as a model for eliminating disparities in oral health Jeffrey J. Hyman, DDS, PhD; Britt C. Reid, DDS, PhD; Susan W. Mongeau, DDS, MPH; Andrew K. York, DMD, MPH Healthy
Variation in Urban and Rural Water Fluoride Levels in Ontario
 Professional I s s u e s Variation in Urban and Rural Water Fluoride Levels in Ontario James Yarmolinsky; Savithiri Ratnapalan, MBBS, MRCP, FAAP, FRCPC, MEd; David J. Kenny, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) Contact Author
Professional I s s u e s Variation in Urban and Rural Water Fluoride Levels in Ontario James Yarmolinsky; Savithiri Ratnapalan, MBBS, MRCP, FAAP, FRCPC, MEd; David J. Kenny, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) Contact Author
Attitudes of the Victorian oral health workforce to the employment and scope of practice of dental hygienists
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2008; 53: 67 73 doi:10.1111/j.1834-7819.2007.00012.x Attitudes of the Victorian oral health workforce to the employment and scope of practice of dental hygienists
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2008; 53: 67 73 doi:10.1111/j.1834-7819.2007.00012.x Attitudes of the Victorian oral health workforce to the employment and scope of practice of dental hygienists
C A LIFORNIA HEALTHCARE FOUNDATION. s n a p s h o t Haves and Have-Nots: A Look at Children s Use of Dental Care in California
 C A LIFORNIA HEALTHCARE FOUNDATION s n a p s h o t Haves and Have-Nots: A Look at Children s Use of Dental Care in California 2008 Introduction Public health efforts to promote community water fluoridation
C A LIFORNIA HEALTHCARE FOUNDATION s n a p s h o t Haves and Have-Nots: A Look at Children s Use of Dental Care in California 2008 Introduction Public health efforts to promote community water fluoridation
UMEÅ INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL
 UMEÅ INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PUBLIC HEALTH Master Programme in Public Health - Programme and Courses Academic year 2015-2016 Public Health and Clinical Medicine Umeå International School of Public Health
UMEÅ INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PUBLIC HEALTH Master Programme in Public Health - Programme and Courses Academic year 2015-2016 Public Health and Clinical Medicine Umeå International School of Public Health
Predisposing factors for traumatic dental injuries in brazilian preschool children
 C. M. Viegas, A. C. Scarpelli, A. C. Carvalho, F. M. Ferreira, I. A. Pordeus, S. M. Paiva Department of Paediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Federal University of Minas Gerais,
C. M. Viegas, A. C. Scarpelli, A. C. Carvalho, F. M. Ferreira, I. A. Pordeus, S. M. Paiva Department of Paediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Federal University of Minas Gerais,
