FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING (FE) EXAMINATION REVIEW
|
|
|
- Nigel Mosley
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-1 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING (FE) EXAMINATION REIEW ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Charles A. Gross, Professor Emeritus Electrical and Comp Engineering Auburn University Broun FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-2 1
2 EE Review Problems 1. dc Circuits 2. Complex Numbers 3. ac Circuits 4. 3-phase Circuits 1 st Order Transients Control Signal Processing Electronics Digital Systems We will discuss these. We may discuss these as time permits FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE dc Circuits: Find all voltages, currents, and powers. FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-4 2
3 Solution The 8 and 7 resistors are in series: R18715 R1 and 1 are in parallel: 1 R R1 1R1 6 1 R1 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-5 Solution 4 and R2 are in series: 4 R21 Rab L : ab 1 Ia 1 A R 1 ab 4 4Ia 4 ( L) KL FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-6 3
4 Solution 1 6 Ic 6A L 1 1 KCL: I I I 1 6 4A b a c 8 8Ib 32 ( L) 7 7Ib 28 ( L) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-7 Absorbed Powers... 2 R I W 2 4 a R I W 2 1 c R I W 2 7 b R I W 2 8 b Total Absorbed Power 1W Power Delivered by Source I 1 1 1W s a In General: P ABS = P DE (Tellegen's Theorem) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-8 4
5 2. Complex Numbers 2 Consider x 2x5 x ( 2) 4(1)(5) 2 16 The numbers "1 2 1" are called complex numbers 9 Summer 28 The I (j) operator Math Department... Define i 1 x 12i ECE Department Define j 1 x 1 j2 We choose ECE notation! Terminology Rectangular Form... Z X jy a complex number X e Z real part of Z Y Im Z imaginary part of Z 1 Summer 28 5
6 Polar Form Math Department... Z i Re a complex number R Z modulus of Z Z Z arg argument of radians ECE Department... Z Z a complex number Z Z magnitude of Z Z Z ang angle of degrees 11 The Argand Diagram It is useful to plot complex numbers in a 2-D cartesian space, creating the so-called Argand Diagram (Jean Argand ( )). imaginary axis (Y) 2 Z X jy 1 j2 1 real axis (X) 12 Summer 28 6
7 Conversions Retangular Polar Z X Y tan 2 2 Y X 1 Y Z Polar Retangular... X Zcos Y Zsin X 13 Summer 28 Example: Z 3 j4 X e Z 3 Y Im Z Rect Polar... Z Summer tan.9273 rad
8 Conjugate Z X jy Z Z* conjugate of Z X jy Z Example... (3 j4)* 3 j Summer 28 Addition (think rectangular) Aa jb A 3 j Bc jd B 5 j A B( a jb) ( c jd) ( ac) j( bd) A B (3 j4) (5 j12) (3 5) j(4 12) 8 j8 16 Summer 28 8
9 Multiplication (think polar) Aa jb A 3 j Bc jd B 5 j AB( A ) ( B ) AB( ) AB ( ) ( ) (5) (13) ( ) Summer 28 Division (think polar) Aa jb A 3 j Bc jd B 5 j A A A ( ) B B B A B Summer 28 9
10 Multiplication (rectangular) ( ) ac bd j ad bc A B a jb c jd AB(3 j4) (5 j12) (15 48) j( 36 2) 63 j Summer 28 EL EC 38 1 Addition (polar) Complex number addition is the same as "vector addition"! Summer EL EC
11 3. ac Circuits v(t) - i(t) mf mh Find "everything" in the given circuit. vt ( ) 141.4cos(377 t) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-21 Frequency, period vt ( ) 141.4cos(377 t) (radian) frequency 377 rad / s (cyclic) frequency f 6 Hz Period ms f 6 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
12 The ac Circuit To solve the problem, we convert the circuit into an "ac circuit": RLC,, elements Z(impedance) vi, sources, I(phasors) R : Z R j8 j R L: ZL j L j(.377)(26.53) j1 C: 1 1 ZC j j4 jc.377(.663) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-23 The Phasor vt () cos( t ) MAX To convert to a phasor... For example.. MAX 2 vt ( ) 141.4cos(377 t) MAX 1 2 o FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
13 The "ac circuit" 1 I R C L( ac): I Z 1 8 j1 j o L o it ( ) cos(377t 36.9 ) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-25 Solving for voltages o o Z I (8)(136.9 ) R R o v ( t) 113.1cos(377t 36.9 ) R o o Z I ( j4)(136.9 ) C C o v ( t) cos(377t ) C o o Z I ( j1)(136.9 ) L L o v ( t) cos(377t 53.1 ) L FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
14 Absorbed powers S I* P jq o o S I* (136.9 )* 8 j R R o o S I* (136.9 )* j4 C C o o S I* (136.9 )* j1 L L S S S S 8 j6 P TOT R C L TOT 8 watts; Q 6 vars; S S 1A TOT TOT TOT FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-27 Delivered power o o S I* 1 (136.9 )* 8 j6 S S S S 8 j6 P Q S S S P Q TOT TOT TOT 8 watts 6 vars In General: P ABS = P DE Q ABS = Q DE (Tellegen's Theorem) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
15 The Power Triangle S 8 j6 S = 1 A = 36.9 Q = 6 var 1 o P = 8 W I o P power factor pf cos( ).8 lagging S FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-29 Leading, Lagging Concepts Leading Case I Lagging Case I Q < Q > FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-3 15
16 A Lagging pf Example 7.2 k R jx R jx j43.2 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-31 Currents I R I I R I L R jx A R IL j166.7 A jx j43.2 I I I R I j166.7 I L A FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
17 Powers pf cos cos I R I R jx S * 5 R IR kw j I L 13 ka 12 k var S I * j12 kvar S I* S S S L L S R L S 5 j kw FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-33 Add Capacitance I I R I L jx C IC j125 I C I R 7.2 I C j125 A jx j57.6 I I I I R L C I j166.7 j A IL j166.7 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
18 Powers pf cos cos kvar 12 kvar S * 9kvar C IC j S I* S S S SS 5 j12 j9 S ka S R L C S ka 5 kw FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-35 Observations By adding capacitance to a lagging pf (inductive) load, we have significantly reduced the source current., without changing P! Before After Note that: I 18.6 A; pf.3845 I 81 A; pf.8575 low pf, high current; high pf, low current; If we consider the source in the example to represent an Electric Utility, this reduction in current is of major practical importance, since the utility losses are proportional to the square of the current. FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
19 Observations That is, by adding capacitance the utility losses have been reduced by almost a factor of 5! Since this results in significant savings to the utility, it has an incentive to induce its customers to operate at high pf. This leads to the Power Factor Correction problem, which is a classic in electric power engineering and is extremely likely to be on the FE exam. We will be using the same numerical data as we did in the previous example. Pretty clever, eh what? FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-37 The Power Factor Correction problem Utility Load pf correcting capacitance An Electric Utility supplies 7.2 k to a customer whose load is 7.2 k 13 pf =.3845 lagging. The utility offers the customer a reduced rate if he will correct ( improve or raise ) his pf to Determine the requisite capacitance. FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
20 PF Correction: the solution 1. Draw the load power triangle. 13 pf =.3845 lagging. S S pf.3845 cos LOAD LOAD S j12 12 kvar Because the pf is lagging, the load is inductive, and Q is positive. Therefore we must add negative Q to reduce the total, which means we must add capacitance kw FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-39 PF Correction: the solution 2. We need to modify the source complex power so that the pf rises to.8575 lagging. pf.8575 cos 31 Closing the switch (inserting the capacitors) S 5 j12 jq 5 j 12 Q S C C Let QX 12 QC Therefore 5 31 SS jqx SS ka Q X Tan Then Tan FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-4 2
21 PF Correction: the solution Q X.6 Q 3 kvar X 5 Q C 12 Q 9 kvar The new source power triangle Install 9 kvar of 7.2 k Capacitors X 9 kvar 3 kvar 12 kvar 5 kw FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE Three-phase ac Circuits Although essentially all types of EE s use ac circuit analysis to some degree, the overwhelming majority of applications are in the high energy ( power ) field. It happens that if power levels are above about 1 kw, it is more practical and efficient to arrange ac circuits in a polyphase configuration. Although any number of phases are possible, 3-phase is almost exclusively used in high power applications, since it is the simplest case that achieves most of the advantage of polyphase. It is virtually certain that some 3-phase problems will appear on the FE and PE examinations, which is why 3-phase merits our attention. 21
22 A single-phase ac circuit a n Generator Line Load a is the phase conductor n is the neutral conductor For a given load, the phase a conductor must have a crosssectional area A, large enough to carry the requisite current. Since the neutral carries the return current, we need a total of 2A worth of conductors. Tripling the capacity I a I b I c I n If I I I I then I 3I a b c n We need a total of A A A 3A = 6A conductors. 22
23 But what if the currents are not in phase? Suppose I I I I12 I I12 Then a b c I I I I I I12 I12 n a b c In I j j j In I ) j( I( j) Now we only need a total of A A A = 3A conductors! A 5% savings! The 3-Phase Situation FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
24 "Balanced" voltage means equal in magnitude, 12 o separated in phase v ( t) cos( t) 2 cos( t) an max v t t t bn( ) max cos( 12 ) 2 cos( 12 ) v t t t cn ( ) max cos( 12 ) 2 cos( 12 ) an bn cn FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-47 The Line oltages By KL ab an bn 1 3 ab 12 1 j j bc ca ab bc ca L 3 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
25 An Example When a power engineer says the primary distribution voltage is 12 k he/she means k ab bc ca L ab bc ca k k k L an bn cn 7.2 k 3 an bn cn 7.2 k k k FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-49 bc An Important Insight. All balanced three-phase problems can be solved by focusing on a-phase, solving the single-phase (a-n) problem, and using 3-phase symmetry to deal with b-n and c-n values! This involves judicious use of the factors 3, 3, and 12! To demonstrate FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-5 bc 25
26 Recall the pf Correction Problem An Electric Utility supplies 7.2 k to a single-phase customer whose load is 7.2 k 13 pf =.3845 lagging. 7.2 k 14 j43.2 I IR IL A 13 ka 12 kvar 5 kw FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-51 bc The pf Correction Problem in the 3-phase case An Electric Utility supplies k to a 3-phase customer whose load is k 39 pf =.3845 lagging. an I a 7.2 k A 14 j ka 3 times bigger! 36 kvar 15 kw FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
27 If we want all the s, I s, and S s an bn cn I I I a b c 7.2 k k k A A A ab bc ca k k k S 5 j12 ka a S 5 j12 ka b S 5 j12 ka c FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1- PF Correction: the 3ph solution Install 27 kvar of Capacitance. The circuitry in the 3- phase case is a bit more complicated. There are two possibilities. 15 kw 27 kvar 9 kvar 36 kvar FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
28 The wye connection. S O U R C E a b c n L O A D Install three 9 kvar 7.2 k wye-connected Capacitors. FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-55 The delta connection. S O U R C E a b c n L O A D Install three 9 kvar k delta-connected Capacitors. FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
29 wye-delta connections Z 3 ZY wye case 27 Qan 9 kvar 3 I a Z C Qan A 7.2 an Y an an ZY 57.6 I 1 Z Y a 46.5 F I Z C delta case 27 Qan 9 kvar 3 ab ab Qab A ab Z F Z FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE st Order Transients.. Network A contains dc sources, resistors, one switch it v t Network B contains one energy storage element (L or C) The problem.(1) solve for v and/or t < ; (2) switch is t = ; (3) solve for v and/or i for t > FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
30 The inductive case di L vl L dt L's are SHORTS to dc i L (t) cannot change in zero time i ( ) i () i ( ) L L L FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-59 An Example di L vl L dt i ( ) i () i ( ) L L L FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-6 3
31 Solution... t : v ( t) v () constant C t : v ( t) v ( ) constant C C C t : vc( t) vc( ) vc() vc( ) e R C ab Our job is to determine v (); v ( ); and R C C C ab t / FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-61 Solution... For a capacitor: dv C ic C dt C's are OPENS to dc v C (t) cannot change in zero time Therefore, if the circuit is switched at t = : v ( ) v () v ( ) C C C FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
32 Solution: T < ; switch and "C" OPEN a vc 12 - A v C b FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-63 Solution: T > ; switch CLOSED vc 12 - A a v C - b i C R ab.2 F RabC 4(.2).8 s FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
33 Solution... v C () 48 v ( ) 8 C 1.25t 1.25 t : v ( t) e C v () t 832e C t FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE st Order Transients: RL.4 H b. The switch is closed at t =. Find and plot i L (t). FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
34 Solution... t : i ( t) i () L L t / t : i ( t) i ( ) i () i ( ) e L R ab L L L L Our job is to determine i (); i ( ); and L/ R L L ab FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-67 Solution... For an inductor: di L vl L dt L's are SHORTS to dc i L (t) cannot change in zero time i ( ) i () i ( ) L L L FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
35 Solution: T < ; switch OPEN; L SHORT a i L 12 - A il A v C - b FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-69 Solution: T > ; switch CLOSED a i L R ab A il 12 2 A 6 v L - b.4 H L R ab.1 s.4 4 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-7 35
36 Solution... t : i ( t) L t / t : i ( t) e L i ( t) e L 1t FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE Control Given the following feedback control system: R(s) - G(s) H(s) Gs 1 () () ( s 1)( s 4) Hs K C(s) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
37 a. Write the closed loop transfer function in rational form 1 C G ( s1)( s4) R 1 GH K 1 ( s 1)( s 4) C 1 1 R s s K s s K 2 ( 1)( 4) 3 ( 4) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-73 b. Write the characteristic equation 2 s s K 3 ( 4) c. What is the system order? 2 d. For K =, where are the poles located? 2 s 3s4 s1 s4 s = 1; s = - 4 e. For K =, is the system stable? NO FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
38 f. Complete the table 2 s s K 3 ( 4) Roots of the CE are poles of the CLTF K poles damping 4., 1. unstable 4 3.,. over ,.382 over , 1.5 critical j2, 1.5 j2 under FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-75 f. Sketch the root locus -4 j 1 g. Find the range on K for system stability. If K = 4: 2 s 3s s s3 Poles at s = ; s = - 3 Therefore for K>4, poles are in LH s-plane and system is stable. K 4 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
39 h. Find K for critical damping CE s s K 2 : 3 ( 4) 3 9 4( K 4) Solving the CE: s 2 Critical damping occurs when the poles are real and equal 9 4( K 4) K 49/4; K FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE Signal Processing a. periodic time-domain functions have continuous discrete frequency spectra. (circle the correct adjective) b. aperiodic time-domain functions have continuous discrete frequency spectra. (circle the correct adjective) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
40 c. Matching d. Laplace Transform Fourier Series Inverse FT t b. yt ( ) x( ) ht ( ) d st d. X( s) x( t) e dt d a e Fourier Transform c Convolution integral b N a. x( t) Dn exp( jn t) nn jt c. X( j) x( t) e dt 1 jt e. x( t) X( j) e d 2 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-79 c. Matching d. Z-Transform d Inverse ZT a Inverse DFT e d. X( z) x[ n] z k b. y[ k] x[ n] h[ n k] n n n DFT c Discrete Convolution b a. X( j) x[ n] e N 1 n n c. X x[ n] e k N 1 1 e. xn [ ] Xk e N k jn j2 kn/ N j2 kn/ N FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-8 4
41 7. Electronics et () v v e et ( ) sin( t) T a. Darken the conducting diodes at time T FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-81 b. Given the "OP Amp" circuit Ideal OpAmp... infinite input resistance zero input voltage infinite gain zero output resistance FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
42 Find the output voltage. v v 5 i R 1 k R i f KCL v 5 k v R i : R f Ri i v R v i f FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-83 c. Find the output voltage. 5 4k 2k 1k KCL : v v v v R R R R f 5 1k - v o LOAD - FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
43 Solution: "SUMMER" 5 5 4k 2k 1k 1k - v o 5 5 v v LOAD v FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE Digital Systems Logic Gates FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
44 a. Complete the Truth Table A C AND Half Adder (HA) B S XOR A B C S A B = CS = = = = 1 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-87 b. Complete the indicated row in the TT C 1 A 1 B 1 C 2 S A C A1 1 1 HA S 1 B OR C C HA 1C 1 Full Adder (FA) S 1 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
45 c. Indicate the inputs and outputs to perform the given sum in a 4-bit adder A 3 B 3 C 2 A 2 B 2 C 1 A 1 B 1 C A B FA FA FA HA C 3 S 3 S 2 S 1 S 1 1 FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-89 d. Design a D/A Converter to accomodate 3-bit digital inputs (5 volt logic) Resolution: 3-bits (2 3 = 8 levels; 1 scale) Example... Convert "11" to analog Digital Analog () Binary Word: ABC (A msb; C lsb) FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-9 45
46 d. Finished Design ABC = 11 5 C B 4k 2k 1k v A 1k - v o LOAD - FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE1-91 Good Luck on the Exam! If I can help with any ECE material, come see me (7:3-11:; 1:15-2:3) Charles A. Gross, Professor Emeritus Electrical and Comp Engineering Auburn University Broun gross@eng.auburn.edu Good Evening... FE: Electric Circuits C.A. Gross EE
Lecture Notes ELE A6
 ecture Notes EE A6 Ramadan El-Shatshat Three Phase circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 1 Three-phase Circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 2 Advantages of Three-phase Circuits Smooth
ecture Notes EE A6 Ramadan El-Shatshat Three Phase circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 1 Three-phase Circuits 9/12/2006 EE A6 Three-phase Circuits 2 Advantages of Three-phase Circuits Smooth
Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement. 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits. Experiment no 1
 Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Three phase circuits
 Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits
 Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
BALANCED THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS
 BALANCED THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS The voltages in the three-phase power system are produced by a synchronous generator (Chapter 6). In a balanced system, each of the three instantaneous voltages have equal
BALANCED THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS The voltages in the three-phase power system are produced by a synchronous generator (Chapter 6). In a balanced system, each of the three instantaneous voltages have equal
Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4
 Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4 Hello everybody. So, in the last class we have been
Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4 Hello everybody. So, in the last class we have been
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 10 - Balanced Three-Phase Networks Overview: Three-phase networks can be connected either in a
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 10 - Balanced Three-Phase Networks Overview: Three-phase networks can be connected either in a
Chapter 24. Three-Phase Voltage Generation
 Chapter 24 Three-Phase Systems Three-Phase Voltage Generation Three-phase generators Three sets of windings and produce three ac voltages Windings are placed 120 apart Voltages are three identical sinusoidal
Chapter 24 Three-Phase Systems Three-Phase Voltage Generation Three-phase generators Three sets of windings and produce three ac voltages Windings are placed 120 apart Voltages are three identical sinusoidal
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
Three Phase Circuits. Three Phase Circuits
 Three Phase Circuits 1 Three Phase Circuits Chater Objectives: Be familiar with different three-hase configurations and how to analyze them. Know the difference between balanced and unbalanced circuits
Three Phase Circuits 1 Three Phase Circuits Chater Objectives: Be familiar with different three-hase configurations and how to analyze them. Know the difference between balanced and unbalanced circuits
Phasors. Phasors. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department. ^ V cos (wt + θ) ^ V sin (wt + θ)
 V cos (wt θ) V sin (wt θ) by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Vector
V cos (wt θ) V sin (wt θ) by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Vector
Diodes have an arrow showing the direction of the flow.
 The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
BALANCED THREE-PHASE AC CIRCUIT
 BAANCED THREE-PHASE AC CRCUT Balanced Three-Phase oltage Sources Delta Connection Star Connection Balanced 3-hase oad Delta Connection Star Connection Power in a Balanced Phase Circuit ntroduction Three
BAANCED THREE-PHASE AC CRCUT Balanced Three-Phase oltage Sources Delta Connection Star Connection Balanced 3-hase oad Delta Connection Star Connection Power in a Balanced Phase Circuit ntroduction Three
Chapter 11 Balanced Three-Phase Circuits
 Chapter 11 Balanced Three-Phase Circuits 11.1-2 Three-Phase Systems 11.3 Analysis of the Y-Y Circuit 11.4 Analysis of the Y- Circuit 11.5 Power Calculations in Balanced Three-Phase Circuits 11.6 Measuring
Chapter 11 Balanced Three-Phase Circuits 11.1-2 Three-Phase Systems 11.3 Analysis of the Y-Y Circuit 11.4 Analysis of the Y- Circuit 11.5 Power Calculations in Balanced Three-Phase Circuits 11.6 Measuring
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents. Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49
 Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
ES250: Electrical Science. HW7: Energy Storage Elements
 ES250: Electrical Science HW7: Energy Storage Elements Introduction This chapter introduces two more circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor whose elements laws involve integration or differentiation;
ES250: Electrical Science HW7: Energy Storage Elements Introduction This chapter introduces two more circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor whose elements laws involve integration or differentiation;
W03 Analysis of DC Circuits. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 W03 Analysis of DC Circuits Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors and
W03 Analysis of DC Circuits Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors and
(3 )Three Phase Alternating Voltage and Current
 EEE 2015 EECTRCS (3) Monophase 1 Three phase Three phase electric power is a common method of alternating current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. t is a type of polyphase system
EEE 2015 EECTRCS (3) Monophase 1 Three phase Three phase electric power is a common method of alternating current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. t is a type of polyphase system
Chapter 11. Inductors ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Topic Suggested Teaching Suggested Resources
 Lesson 1 & 2: DC Networks Learning Outcome: Be able to apply electrical theorems to solve DC network problems Electrical theorems and DC network problems Introduction into the unit contents, aims & objectives
Lesson 1 & 2: DC Networks Learning Outcome: Be able to apply electrical theorems to solve DC network problems Electrical theorems and DC network problems Introduction into the unit contents, aims & objectives
How To Understand And Understand The Theory Of Electricity
 DIRECT CURRENT AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SYSTEMS N. Rajkumar, Research Fellow, Energy Systems Group, City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK Keywords: Electrical energy, direct current, alternating
DIRECT CURRENT AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SYSTEMS N. Rajkumar, Research Fellow, Energy Systems Group, City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK Keywords: Electrical energy, direct current, alternating
First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering)
 Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA
 PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
Three-phase AC circuits
 Three-phase AC circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Three-phase AC circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
AC Power. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department
 by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Voltage Waveform Consider the
by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Voltage Waveform Consider the
Frequency Response of FIR Filters
 Frequency Response of FIR Filters Chapter 6 This chapter continues the study of FIR filters from Chapter 5, but the emphasis is frequency response, which relates to how the filter responds to an input
Frequency Response of FIR Filters Chapter 6 This chapter continues the study of FIR filters from Chapter 5, but the emphasis is frequency response, which relates to how the filter responds to an input
3-Phase AC Calculations Revisited
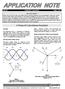 AN110 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 6 DID YOU KNOW? Nikola Tesla (1856-1943) came to the United States in 1884 from Yugosiavia. He arrived during the battle of the currents between Thomas Edison, who
AN110 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 6 DID YOU KNOW? Nikola Tesla (1856-1943) came to the United States in 1884 from Yugosiavia. He arrived during the battle of the currents between Thomas Edison, who
Network Theory Question Bank
 Network Theory Question Bank Unit-I JNTU SYLLABUS: Three Phase Circuits Three phase circuits: Phase sequence Star and delta connection Relation between line and phase voltages and currents in balanced
Network Theory Question Bank Unit-I JNTU SYLLABUS: Three Phase Circuits Three phase circuits: Phase sequence Star and delta connection Relation between line and phase voltages and currents in balanced
ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
 UNIT 1: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS A/601/1401 OUTCOME - TRIGONOMETRIC METHODS TUTORIAL 1 SINUSOIDAL FUNCTION Be able to analyse and model engineering situations
UNIT 1: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS A/601/1401 OUTCOME - TRIGONOMETRIC METHODS TUTORIAL 1 SINUSOIDAL FUNCTION Be able to analyse and model engineering situations
Equipment: Power Supply, DAI, Variable resistance (8311), Variable inductance (8321)
 Lab 4: 3-phase circuits. Objective: to study voltage-current relationships in 3-phase circuits; to learn to make delta and Y connections; to calculate and measure real, apparent, and reactive powers. Equipment:
Lab 4: 3-phase circuits. Objective: to study voltage-current relationships in 3-phase circuits; to learn to make delta and Y connections; to calculate and measure real, apparent, and reactive powers. Equipment:
ε: Voltage output of Signal Generator (also called the Source voltage or Applied
 Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
ECE 431. Experiment #1. Three-Phase ac Measurements. PERFORMED: 26 January 2005 WRITTEN: 28 January 2005. Jason Wells
 ECE 41 Experiment #1 Three- ac Measurements PERFORMED: 6 January 005 WRTTEN: 8 January 005 Jason Wells LEADER: Jason Wells RECORDER: Nathaniel Hakes 1 ntroduction The primary objectives of the experiment
ECE 41 Experiment #1 Three- ac Measurements PERFORMED: 6 January 005 WRTTEN: 8 January 005 Jason Wells LEADER: Jason Wells RECORDER: Nathaniel Hakes 1 ntroduction The primary objectives of the experiment
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure 2. R. Figure 1.
 Examples of Transient and RL Circuits. The Series RLC Circuit Impulse response of Circuit. Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure.
Examples of Transient and RL Circuits. The Series RLC Circuit Impulse response of Circuit. Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure.
Chapter 9: Controller design
 Chapter 9. Controller Design 9.1. Introduction 9.2. Effect of negative feedback on the network transfer functions 9.2.1. Feedback reduces the transfer function from disturbances to the output 9.2.2. Feedback
Chapter 9. Controller Design 9.1. Introduction 9.2. Effect of negative feedback on the network transfer functions 9.2.1. Feedback reduces the transfer function from disturbances to the output 9.2.2. Feedback
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 00 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
MT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 00 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
Understanding Power Factor and How it Affects Your Electric Bill. Presented by Scott Peele PE
 Understanding Power Factor and How it Affects Your Electric Bill Presented by Scott Peele PE Understanding Power Factor Definitions kva, kvar, kw, Apparent Power vs. True Power Calculations Measurements
Understanding Power Factor and How it Affects Your Electric Bill Presented by Scott Peele PE Understanding Power Factor Definitions kva, kvar, kw, Apparent Power vs. True Power Calculations Measurements
Motor Efficiency and Power Factor ME 416/516
 Motor Efficiency and Power Factor Motivation More than half of all electric energy generated goes to power electric motors. Electric motor converts electric power into shaft power. In thermodynamics terms,
Motor Efficiency and Power Factor Motivation More than half of all electric energy generated goes to power electric motors. Electric motor converts electric power into shaft power. In thermodynamics terms,
Introduction to Complex Numbers in Physics/Engineering
 Introduction to Complex Numbers in Physics/Engineering ference: Mary L. Boas, Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences Chapter 2 & 14 George Arfken, Mathematical Methods for Physicists Chapter 6 The
Introduction to Complex Numbers in Physics/Engineering ference: Mary L. Boas, Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences Chapter 2 & 14 George Arfken, Mathematical Methods for Physicists Chapter 6 The
Positive Feedback and Oscillators
 Physics 3330 Experiment #6 Fall 1999 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Physics 3330 Experiment #6 Fall 1999 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Section 3. Sensor to ADC Design Example
 Section 3 Sensor to ADC Design Example 3-1 This section describes the design of a sensor to ADC system. The sensor measures temperature, and the measurement is interfaced into an ADC selected by the systems
Section 3 Sensor to ADC Design Example 3-1 This section describes the design of a sensor to ADC system. The sensor measures temperature, and the measurement is interfaced into an ADC selected by the systems
SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES, COMERCIAL LTDA.
 Pocket book of Electrical Engineering Formulas Content 1. Elementary Algebra and Geometry 1. Fundamental Properties (real numbers) 1 2. Exponents 2 3. Fractional Exponents 2 4. Irrational Exponents 2 5.
Pocket book of Electrical Engineering Formulas Content 1. Elementary Algebra and Geometry 1. Fundamental Properties (real numbers) 1 2. Exponents 2 3. Fractional Exponents 2 4. Irrational Exponents 2 5.
Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2010, 2011 and 2012
 1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4
 DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
Low Pass Filter Rise Time vs Bandwidth
 AN121 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 7 DID YOU KNOW? The number googol is ten raised to the hundredth power or 1 followed by 100 zeros. Edward Kasner (1878-1955) a noted mathematician is best remembered
AN121 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 7 DID YOU KNOW? The number googol is ten raised to the hundredth power or 1 followed by 100 zeros. Edward Kasner (1878-1955) a noted mathematician is best remembered
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform
 S. Boyd EE12 Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform analysis of general LRC circuits impedance and admittance descriptions natural and forced response circuit analysis with impedances natural
S. Boyd EE12 Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform analysis of general LRC circuits impedance and admittance descriptions natural and forced response circuit analysis with impedances natural
Physics 6C, Summer 2006 Homework 2 Solutions
 Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
Lecturer: James Grimbleby URL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email: j.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk
 AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1.
 File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
Chapter 12 Driven RLC Circuits
 hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
DEFINITION 5.1.1 A complex number is a matrix of the form. x y. , y x
 Chapter 5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 5.1 Constructing the complex numbers One way of introducing the field C of complex numbers is via the arithmetic of matrices. DEFINITION 5.1.1 A complex number is a matrix of
Chapter 5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 5.1 Constructing the complex numbers One way of introducing the field C of complex numbers is via the arithmetic of matrices. DEFINITION 5.1.1 A complex number is a matrix of
VOLTAGE REGULATOR AND PARALLEL OPERATION
 VOLTAGE REGULATOR AND PARALLEL OPERATION Generator sets are operated in parallel to improve fuel economy and reliability of the power supply. Economy is improved with multiple paralleled generators by
VOLTAGE REGULATOR AND PARALLEL OPERATION Generator sets are operated in parallel to improve fuel economy and reliability of the power supply. Economy is improved with multiple paralleled generators by
THREE-PHASE POWER SYSTEMS ECE 454/554: Power Systems Laboratory
 THREE-PHSE POER SYSTEMS ECE 5/55: Power Systems Laboratory Contributors: Dr... El-Keib Mr. Clifton Black Dr. Tim. Haskew Mr. Johnny Carlisle Mr. Neil Hutchins Objectives Learn how to perform measurements
THREE-PHSE POER SYSTEMS ECE 5/55: Power Systems Laboratory Contributors: Dr... El-Keib Mr. Clifton Black Dr. Tim. Haskew Mr. Johnny Carlisle Mr. Neil Hutchins Objectives Learn how to perform measurements
Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits
 EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits 1. Introduction and Goal: Exploring transient behavior due to inductors and capacitors in DC circuits; gaining experience with lab instruments.
EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits 1. Introduction and Goal: Exploring transient behavior due to inductors and capacitors in DC circuits; gaining experience with lab instruments.
Elementary Functions
 Chapter Three Elementary Functions 31 Introduction Complex functions are, of course, quite easy to come by they are simply ordered pairs of real-valued functions of two variables We have, however, already
Chapter Three Elementary Functions 31 Introduction Complex functions are, of course, quite easy to come by they are simply ordered pairs of real-valued functions of two variables We have, however, already
BSEE Degree Plan Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering: 2015-16
 BSEE Degree Plan Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering: 2015-16 Freshman Year ENG 1003 Composition I 3 ENG 1013 Composition II 3 ENGR 1402 Concepts of Engineering 2 PHYS 2034 University Physics
BSEE Degree Plan Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering: 2015-16 Freshman Year ENG 1003 Composition I 3 ENG 1013 Composition II 3 ENGR 1402 Concepts of Engineering 2 PHYS 2034 University Physics
REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO)
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO) Copyright 2008 Caribbean
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO) Copyright 2008 Caribbean
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL
 Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide necessary direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator.
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide necessary direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator.
AC Generators. Basic Generator
 AC Generators Basic Generator A basic generator consists of a magnetic field, an armature, slip rings, brushes and a resistive load. The magnetic field is usually an electromagnet. An armature is any number
AC Generators Basic Generator A basic generator consists of a magnetic field, an armature, slip rings, brushes and a resistive load. The magnetic field is usually an electromagnet. An armature is any number
2. A conductor of length 2m moves at 4m/s at 30 to a uniform magnetic field of 0.1T. Which one of the following gives the e.m.f. generated?
 Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3. AC Circuit Analysis
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3 AC Circuit Analysis 3.1 Introduction The steady-state behavior of circuits energized by sinusoidal sources is an important area of study for several reasons. First, the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3 AC Circuit Analysis 3.1 Introduction The steady-state behavior of circuits energized by sinusoidal sources is an important area of study for several reasons. First, the
BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. December 2011
 AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
30. Bode Plots. Introduction
 0. Bode Plots Introduction Each of the circuits in this problem set is represented by a magnitude Bode plot. The network function provides a connection between the Bode plot and the circuit. To solve these
0. Bode Plots Introduction Each of the circuits in this problem set is represented by a magnitude Bode plot. The network function provides a connection between the Bode plot and the circuit. To solve these
First Order Circuits. EENG223 Circuit Theory I
 First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH005/105)
 CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS MATHEMATICS AND ASTRONOMY DIVISION Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH5/15) Analog Electronics Active Filters Copyright c Virgínio de Oliveira Sannibale, 23 (Revision
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS MATHEMATICS AND ASTRONOMY DIVISION Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH5/15) Analog Electronics Active Filters Copyright c Virgínio de Oliveira Sannibale, 23 (Revision
Basic Op Amp Circuits
 Basic Op Amp ircuits Manuel Toledo INEL 5205 Instrumentation August 3, 2008 Introduction The operational amplifier (op amp or OA for short) is perhaps the most important building block for the design of
Basic Op Amp ircuits Manuel Toledo INEL 5205 Instrumentation August 3, 2008 Introduction The operational amplifier (op amp or OA for short) is perhaps the most important building block for the design of
Measurement of Power in single and 3-Phase Circuits. by : N.K.Bhati
 Measurement of Power in single and 3-Phase Circuits by : N.K.Bhati A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module 1. Power in
Measurement of Power in single and 3-Phase Circuits by : N.K.Bhati A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module 1. Power in
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND PHASORS
 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND PHASORS 1 Professor Andrew E. Yagle, EECS 206 Instructor, Fall 2005 Dept. of EECS, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2122 I. Abstract The purpose of this document is to
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND PHASORS 1 Professor Andrew E. Yagle, EECS 206 Instructor, Fall 2005 Dept. of EECS, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2122 I. Abstract The purpose of this document is to
Capacitors in Circuits
 apacitors in ircuits apacitors store energy in the electric field E field created by the stored charge In circuit apacitor may be absorbing energy Thus causes circuit current to be reduced Effectively
apacitors in ircuits apacitors store energy in the electric field E field created by the stored charge In circuit apacitor may be absorbing energy Thus causes circuit current to be reduced Effectively
3.4 - BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS
 BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
A few words about imaginary numbers (and electronics) Mark Cohen mscohen@g.ucla.edu
 A few words about imaginary numbers (and electronics) Mark Cohen mscohen@guclaedu While most of us have seen imaginary numbers in high school algebra, the topic is ordinarily taught in abstraction without
A few words about imaginary numbers (and electronics) Mark Cohen mscohen@guclaedu While most of us have seen imaginary numbers in high school algebra, the topic is ordinarily taught in abstraction without
Module 5. Three-phase AC Circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Three-hase AC Circuits ersion EE T, Kharagur esson 9 Three-hase Delta- Connected Balanced oad ersion EE T, Kharagur n the revious (first) lesson of this module, the two tyes of connections (star
Module 5 Three-hase AC Circuits ersion EE T, Kharagur esson 9 Three-hase Delta- Connected Balanced oad ersion EE T, Kharagur n the revious (first) lesson of this module, the two tyes of connections (star
Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation
 Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
Understanding Poles and Zeros
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 2.14 Analysis and Design of Feedback Control Systems Understanding Poles and Zeros 1 System Poles and Zeros The transfer function
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 2.14 Analysis and Design of Feedback Control Systems Understanding Poles and Zeros 1 System Poles and Zeros The transfer function
Chapter 35 Alternating Current Circuits
 hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
Content Map For Career & Technology
 Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
L and C connected together. To be able: To analyse some basic circuits.
 circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
13 ELECTRIC MOTORS. 13.1 Basic Relations
 13 ELECTRIC MOTORS Modern underwater vehicles and surface vessels are making increased use of electrical actuators, for all range of tasks including weaponry, control surfaces, and main propulsion. This
13 ELECTRIC MOTORS Modern underwater vehicles and surface vessels are making increased use of electrical actuators, for all range of tasks including weaponry, control surfaces, and main propulsion. This
Chapter 8 - Power Density Spectrum
 EE385 Class Notes 8/8/03 John Stensby Chapter 8 - Power Density Spectrum Let X(t) be a WSS random process. X(t) has an average power, given in watts, of E[X(t) ], a constant. his total average power is
EE385 Class Notes 8/8/03 John Stensby Chapter 8 - Power Density Spectrum Let X(t) be a WSS random process. X(t) has an average power, given in watts, of E[X(t) ], a constant. his total average power is
Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday s Law
 Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday s Law concept #1, 4, 5, 8, 13 Problem # 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13, 15, 24, 23, 25, 31, 32a, 34, 37, 41, 43, 51, 61 Last chapter we saw that a current produces a magnetic
Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday s Law concept #1, 4, 5, 8, 13 Problem # 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13, 15, 24, 23, 25, 31, 32a, 34, 37, 41, 43, 51, 61 Last chapter we saw that a current produces a magnetic
1 Introduction. 2 Two Phases. J.L. Kirtley Jr.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.061 Introduction to Power Systems Class otes Chapter 3 Polyphase etworks J.L. Kirtley Jr. 1 Introduction
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.061 Introduction to Power Systems Class otes Chapter 3 Polyphase etworks J.L. Kirtley Jr. 1 Introduction
Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive in Speed Control Of Induction Motor
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 78-7461, p-issn: 319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 5 (December 013) PP: 36-41 Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 78-7461, p-issn: 319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 5 (December 013) PP: 36-41 Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive
TRANSFORMER: THREE PHASE
 CONTENTS Transformer : Three Phase 1211 C H A P T E R 33 Learning Objectives Three-phase Transformers Three-phase Transformer Connections Star/Star or Y/Y Connection Delta-Delta or Connection Wye/Delta
CONTENTS Transformer : Three Phase 1211 C H A P T E R 33 Learning Objectives Three-phase Transformers Three-phase Transformer Connections Star/Star or Y/Y Connection Delta-Delta or Connection Wye/Delta
Impedance Matching. Using transformers Using matching networks
 Impedance Matching The plasma industry uses process power over a wide range of frequencies: from DC to several gigahertz. A variety of methods are used to couple the process power into the plasma load,
Impedance Matching The plasma industry uses process power over a wide range of frequencies: from DC to several gigahertz. A variety of methods are used to couple the process power into the plasma load,
Chapter 1. Fundamental Electrical Concepts
 Chapter 1 Fundamental Electrical Concepts Charge, current, voltage, power circuits, nodes, branches Branch and node voltages, Kirchhoff Laws Basic circuit elements, combinations 01 fundamental 1 1.3 Electrical
Chapter 1 Fundamental Electrical Concepts Charge, current, voltage, power circuits, nodes, branches Branch and node voltages, Kirchhoff Laws Basic circuit elements, combinations 01 fundamental 1 1.3 Electrical
PHY114 S11 Term Exam 3
 PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
Chapter 10. RC Circuits ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
Chapter 11 Current Programmed Control
 Chapter 11 Current Programmed Control Buck converter v g i s Q 1 D 1 L i L C v R The peak transistor current replaces the duty cycle as the converter control input. Measure switch current R f i s Clock
Chapter 11 Current Programmed Control Buck converter v g i s Q 1 D 1 L i L C v R The peak transistor current replaces the duty cycle as the converter control input. Measure switch current R f i s Clock
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks. Valentin Todorow, December, 2009
 Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra
 Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Radial Distribution Test Feeders
 Radial Distribution Test Feeders Distribution System Analysis Subcommittee Report Abstract: Many computer programs are available for the analysis of radial distribution feeders. In 1992 a paper was published
Radial Distribution Test Feeders Distribution System Analysis Subcommittee Report Abstract: Many computer programs are available for the analysis of radial distribution feeders. In 1992 a paper was published
EE 221 Circuits II. Chapter 13 Magnetically Coupled Circuits
 EE Circuits II Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits 3. What is a transformer? 3. Mutual Inductance 3.3 Energy in a Coupled Circuit 3.4 inear Transformers 3.5 Ideal Transformers
EE Circuits II Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits 3. What is a transformer? 3. Mutual Inductance 3.3 Energy in a Coupled Circuit 3.4 inear Transformers 3.5 Ideal Transformers
ECE 3510 Final given: Spring 11
 ECE 50 Final given: Spring This part of the exam is Closed book, Closed notes, No Calculator.. ( pts) For each of the time-domain signals shown, draw the poles of the signal's Laplace transform on the
ECE 50 Final given: Spring This part of the exam is Closed book, Closed notes, No Calculator.. ( pts) For each of the time-domain signals shown, draw the poles of the signal's Laplace transform on the
