Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0: Survey Results from Brunei Tracking a Future Path in E-Health Research
|
|
|
- Angel Booker
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Forum Südostasien / Forum South-East Asia Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0: Survey Results from Brunei Tracking a Future Path in E-Health Research Muhammad Anshari 1, Mohammad N. Almunawar 2, Patrick K. C. Low 3 & Zaw Wint 4 Citation Anshari, M., Almunawar, M. N., Low, P. K. C., & Wint, Z. (2012). Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0: Survey Results from Brunei Tracking a Future Path in E-Health Research. ASEAS - Austrian Journal of South-East Asian Studies, 5(1), Introduction The idea of customers empowerment in healthcare emerged in response to the rising concern that customers or patients should be able to play a critical role in improving their own health. In traditional healthcare practices, a patient is the recipient of care as well as medical decisions. However, a paradigm shift has taken place that is, a change from patients who merely receive care to those who actively participate in their healthcare. This change emerged in the 1960s and has spread throughout the entire healthcare industry as a social movement characterised by the right to act based on informed choice, active participation, a self-help perspective, and full engagement in critical processes (Kieffer, 1984). Traditionally, healthcare providers have made most of the decisions on treatments. Indeed, the lack of participation of patients in healthcare processes was the main obstacle to the empowerment of patients as customers. Nevertheless, there doi /10.ASEAS will always be circumstances in which patients choose to hand over responsibility for 1 Muhammad Anshari is a PhD candidate at the Faculty of Business, Economics, and Policy Studies, Universiti Brunei Darussalam. Contact: anshari@yahoo.com (Corresponding author) 2 Mohammad N. Almunawar is a Senior Lecturer and a Deputy Dean of Faculty of Business, Economics, and Policy Studies, Universiti Brunei Darussalam. Contact: nabil.almunawar@ubd.edu.bn 3 Patrick K. C. Low is is a Professor and an Associate at the University of South Australia. Contact: patrick_low2003@yahoo.com 4 Zaw Wint is a Senior Lecturer at the PAPRSB Institute of Health and the Acting Director of Graduate Studies and Research Office, Universiti Brunei Darussalam, Brunei Darusssalam. Contact: zaw.wint@ubd.edu.bn 139
2 ASEAS 5(1) decisions about their healthcare to providers due to the difficulty in selecting available options or the time needed to understand the health problem and the options. However, this does not undermine the proposition that customers empowerment will promote efficiency and that decisions should also be made from the perspective of customers (Segal, 1998). The utilisation of information and communications technology (ICT), especially the Internet, in the healthcare sector is frequently referred to as electronic health or e-health. The main purpose of e-health is to improve healthcare management for the mutual benefit of patients and healthcare providers. One important aspect of e-health is how to manage relationships between a healthcare provider and its customers (patients) in order to create greater mutual understanding, trust, and patient involvement in decision making. Therefore, healthcare organisations are implementing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) as a strategy for managing interactions with their patients (Anshari & Almunawar, 2012). The recent Web technology (Web 2.0) facilitates customers to generate contents to accommodate both patienthealth provider and patient-patient interactions. CRM enriched with the Web 2.0 (also called CRM 2.0) provides the capability for the intensive interactions mentioned above (Anshari, Almunawar, & Low, 2012). Besides, it can be considered a technology and strategy at the same time, raising hope for the advancement of e-health initiatives around the world. The main goal of this paper is to introduce a promising future research direction which may shape the future of e-health systems. In this paper, we examine customers expectations concerning the process of empowerment through CRM 2.0 to make customers more proficient in dealing with their own healthcare issues. A preliminary survey regarding empowerment in e-health services was conducted in Brunei Darussalam (Brunei). The Internet density in Brunei is high with over 75 percent of the population having access to the Internet, and there is a very narrow digital divide in Brunei (AITI, 2010). Internet literacy in Brunei is high, and so are people s expectations to be empowered through e-health. However, it has to be noted that the development of e-health in Brunei is still in its infancy. The future developments within the scope of e-health services in Brunei should therefore significantly focus on patients empowerment as one of the important features required by the people. The rest of this paper is organised as follows: the following section presents the background of 140
3 Anshari, Almunawar, Low, & Wint - Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0 the study, followed by the research methodology. We then discuss the results of the study in relation to a CRM 2.0 model we propose based on this investigation. Study Background Many researchers have discussed the issue of empowerment in healthcare organisations. For instance, empowerment can be analysed from the perspective of patienthealthcare provider interactions (Dijkstra, Braspenning, & Grol, 2002; Paterson, 2001; Skelton, 1997; van Dam, van der Horst, van den Borne, Ryckman, & Crebolder, 2003), or from the point of view of the patient alone (Anderson et al., 1995; Davison & Degner, 1997;; Desbiens et al., 1998; McCann & Weinman, 1996), or analysis can encompass both above mentioned perspectives (Golant, Altman, & Martin, 2003; Maliski, Clerkin, & Letwin, 2004; McWilliam et al., 1997). However, research that specifically discusses the issue of empowerment through CRM, and particularly CRM 2.0, is still very limited in the domain of e-health. Australia, a pioneer on this matter, has adopted a Personally Controlled Electronic Health Record (PCEHR) system, which stands out as an example for empowerment through e-health services (NEHTA, 2012). A significant element of patients empowerment was achieved by allowing them to view their medical information electronically. However, PCEHR only enables patients to view their Electronic Health Record (EHR); it has not utilised features of CRM 2.0, which allow collaboration and conversation among patients or between patients and their healthcare providers. Therefore, our research primarily aims to develop a system that utilises features of CRM 2.0 in order to meet significant challenges in patients empowerment in the domain of healthcare. Customer Relationship Management The fact that customer expectations in healthcare services are high poses a serious challenge to healthcare organisations as they have to meet customers requirements and make an exceptional impression on every customer (Anshari & Almunawar, 2011). CRM can be used by healthcare organisations both as a tool and a strategy to meet their customers expectations. The terms of Social CRM and CRM 2.0 are used inter- 141
4 ASEAS 5(1) changeably; both signify a new approach in CRM by allowing intensive interaction between customers and organisations and among customers by utilising Web 2.0. Hence, both share new distinct capabilities of social media and social networks that provide new approaches and potential which surpass the scope of traditional CRM. Cipriani (2008) described the fundamental changes offered by CRM 2.0 in terms of relationship, connection, and generated value. The most significant feature of CRM 2.0 for e-health is the extensive network among customers and healthcare providers. This network is beneficial for customers as it provides multiple ways of interactive communication that enables sharing experience and knowledge electronically. Furthermore, it accommodates both the interaction between provider and patient, and between patient and patient. It also enables patients to generate contents of their personal health records. With regard to these new features, Table 1 summarises the difference between CRM 2.0 and the precedent CRM 1.0 based on the type of relationship, connection, and generated value. CRM 1.0 mainly focuses on the individual one-way relationship, either customer to customer (C2C) or customer to business (C2B), whereas CRM 2.0 offers a collaborative relationship and thus supports the engagement in a more complex relationship network. Consequentially, CRM 2.0 enables customers to take a greater role in forming relationships. The connection types in CRM 1.0 present a limited view of the customer which has an adverse effect on their narrow information. On the other hand, CRM 2.0 enables multiple connections which allow customers to gain additional knowledge. In terms of generated value, CRM 1.0 is restricted to targeted messages, whereas CRM 2.0 offers more diverse value generation resulting from informal conversations of customers within social networks. A healthcare provider must consider the essential role of the conversation among patients as recent ICT enables them to share experiences without barriers. For example, the conversation that takes place among patients on a social network on healthcare services may influence the image of the healthcare provider. Shared experience of unprofessional treatments or services to patients can easily lead to distrust (Almunawar et al., 2012). With all its features and benefits, CRM 2.0 can enhance the sense of control, improve self-care practices, and increase the scope of utilisations of healthcare services. The role of CRM 2.0 in empowering customers within healthcare organisations is further explored in the next section. 142
5 Anshari, Almunawar, Low, & Wint - Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0 Table 1: Comparison CRM 1.0 and CRM 2.0 Type Relationship Connection Generated Value CRM 1.0 Focus on individual relationship (C2C, C2B) Limited view of the customer & his/her community preferences, habits, etc. Targeted messages generate value CRM 2.0 Focus on collaborative relationship (engaging a more complex relationship network) Multiple connections allow better understanding of the customer and his/her community Conversation generates value Source: Cipriani, 2008 Empowering Customers Empowerment is well supported in the healthcare literature and related to customers and healthcare services over the past decade (Dijkstra et al., 2002; Paterson, 2001; Skelton, 1997; van Dam et al., 2003). In the organisation, empowerment implies the provision of necessary tools to staff in order to be able to resolve, on the spot, most problems or questions faced by customers. Besides, staff can deal with customers directly and so reduce the number of dissatisfied customers who would otherwise have complained, but now simply switch brands (Low, 2002). According to McWilliam et al. (1997), empowerment is a result of both interactive and personal processes, where caring relationships facilitate the emergence of power (or potential). Empowerment as an interactive process suggests that power is transferred by one person to another, whereas empowerment as a personal process suggests that power is created by and within the person. Although the expected outcome is the same, i.e. the gain of more power over one s life, the nature of the two processes is very different (Aujoulat et al, 2006). The first case entails that power can emerge through active co-creation and collaboration in an empowering relationship. Since CRM 2.0 facilitates interactions and collaborations, it can be used as a tool to implement empowerment. In the second case, when the process of empowerment is perceived from the point of view of the customers, it is considered as a process of personal transformation. 143
6 ASEAS 5(1) Online Social Networks Improve Health Literacy Figure 1 presents three features of CRM 2.0 that can be embedded in e-health systems: online social networks, empowerment of electronic medical object (EMO), and online health educators. Online social networks present a facility for patient to patient interaction; EMO entails the ability of patients to access their specific medical record, which is empowered by healthcare organisations; online health educators are provided by a healthcare provider to facilitate the interaction between healthcare organisations and patients. Details of each component will be highlighted in the model discussion. Figure 1: CRM 2.0 Features Empowerment (EMO) CRM 2.0 in e-health Online Health Educator Improve Customer Satisfaction Source: Authors Compilation Methodology With all the promises and benefits offered by empowerment, the research attempts to utilise CRM 2.0 as both a tool and a strategy to empower customers in healthcare scenarios. For this purpose we single out potential features offered by CRM 2.0 to support customers empowerment and prove these features in a survey. We use the purposive sampling methods in which respondents were intentionally selected from patients, patients family, or medical staff from hospitals and homecare centres across the country. Questionnaires were developed based on the extracted features of CRM 2.0 (see Figure 1). There were 366 respondents participating in the survey which was conducted from February to March Attributes of empowerment through CRM 2.0 were interrogated and analysed in order to gain preliminary responds from the potential users in Brunei. Data gathered from the survey was examined, interpreted and eventually converted in requirements to develop a prototype of CRM 2.0 for healthcare as shown in Figure 3. The prototype will be tested for the development of a system and for future recommendations. 144
7 Anshari, Almunawar, Low, & Wint - Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0 Table 2: Demographic Characteristics of Sample Analysis and Discussion 42% 58% 46% 54% 13% 38% 19% 18% 12% 10% 31% 59% 63% 18% 9% Employment Private Government Gender Male Female Age 20 years or younger years or older Education Did not complete high school Completed high school only Completed more than high school Internet Usage At least daily Daily to weekly Weekly to monthly Table 3: Empowerment Features in CRM 2.0 To analyse the reliability of the questionnaire items used in this study, Cronbach s alpha is used to measure internal consistency (1). Cronbach s Alpha 5 measured 0.80 for 363 items which indicates a relatively high internal consistency and therefore reliability of the study. Table 2 shows the demographic characteristics of the samples. Important to note here is that respondents between the age of 20 to 50 years are the most potential users of CRM 2.0 notably because of their basic Internet literacy which is the critical success factor for the empowerment through CRM % 79% 69% 81% 76% 84% 77% 78% 50% 73% 92% 62% 77% 72% 76% Empowerment of EMO Request appointment online View Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Update personal medical activities View health promotion online Record health activities online View payment online Online Health Educator Prescription online Referral online Paying service online Consultation online EMR only for trusted doctors Social Networks Discuss health service in social network Control of own EMR Discuss health status in social network Discuss with patients same condition Source (Both Tables): Authors Survey Results 145 Table 3 below shows the results of the survey in percentage. Interestingly, the survey reveals that the expectations of customers toward empowerment through CRM 2.0 are very promising. 5 Cronbach s alpha determines the internal consistency or average correlation of items in a survey instrument to gauge its reliability.
8 ASEAS 5(1) The Proposed CRM 2.0 Model Based on the literature review and the survey results, we propose a CRM 2.0 model to accommodate the features of patients empowerment. CRM functionalities are composed of Marketing, Sales, and Customer Service, which are operated to achieve the business strategy of a healthcare organisation. For example, a marketing strategy should accommodate social marketing to promote public health and commercial marketing to acquire more customers coming for services. Customer service will offer distinct value for each activity. CRM 2.0 accommodates various features and components of empowerment in healthcare systems, as its central role entails selfmanaged data and authorisation to encourage customers to provide full information in relation to their health. This is very important to healthcare organisations as it also enables customers to access more information especially on EMO. Organisations will benefit from the strategy of marketing, sales, and customer service, while customers will benefit from an empowerment which promises better customer satisfaction and health literacy. Figure 2 presents a proposed model of CRM 2.0 in healthcare organisations. It offers a starting point for identifying possible theoretical mechanisms that might account for ways in which CRM 2.0 provides one-stop service for building relationships between a healthcare organisation, patients, and community at large. The framework is developed from Enterprise Social Networks, Internal Social Networks, listening tool interfaces, and healthcare value configuration. The term social networks refers to any Web 2.0 technology accessed by patients or their families. We focus on two different types of interconnection: Enterprises Social Networks and Internal Social Networks. The Enterprises Social Networks refers to external and popular Web 2.0 applications such as Facebook, Twitter, Linkedln, MySpace, Friendster etc. which may serve as platforms for interaction between patients. The dashed line connecting Enterprises Social Networks and CRM systems means that none of these networks has control over the other directly. However, constructive conversation and information from Enterprises Social Networks should be captured for creating strategies, innovations, better services and, at the same time, respond accurately to emerging challenges. Furthermore, the model involves Internal Social Networks that are operated, managed, and maintained within the healthcare organi- 146
9 Anshari, Almunawar, Low, & Wint - Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0 sation s infrastructure. The pivotal target is a conversation between internal patients and their families with regard to similar health problems and illness. For example, patients with diabetes will be motivated to share their experience, process of learning, and knowledge with other patients. In general, the aim for having external and internal social networks is to engage patients and export ideas, foster innovations of new services, and ensure quick response/feedback for existing services and technologies from people inside and outside the organisation. Both provide a range of roles for the patient or his/her family; this is in line with the survey results presented in Table 3. Figure 2: Proposed Model of CRM 2.0 in Healthcare Social Networks SOCIAL CRM MARKETING & SALES CUSTOMER SERVICES Retrieve & Respond DATA SOCIAL / COMMERCIAL MARKETING TEAM WEB 2.0 ENTERPRISE Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, etc. Conversation PATIENT / FAMILY WEB 2.0 INTERNAL SOCIAL NETWORKS N1, N2, N3 Empowerment EMO LISTENING TOOLS LISTENING TOOLS Self Managed Data & Query Multi Channel Interactions, Call Center, , Feedback Form, etc. Patient Data (Contact Details, Insurance, etc.), Profiles, History (Medical Treatment, Genetic Medicine Consumption, Family History, Medical Images, X-Ray, etc.), Preferences, Transcations, Payment/ Billing Data, Activities, Health Promotion, Appointment, Friends in Networks, Logfile Activities, etc. DATA DATA Retrieve & Respond REGISTRATION PATIENT CARE DISCHARGE Online Health Educator MARKETING HEALTH EDUCATOR / HEALTH PROMOTER SERVICE Source: Authors Compilation 147
10 ASEAS 5(1) CRM 2.0 empowers patients (and their family) to control their own data. Once the patient registers for the service from the healthcare provider, it will enable him/her to enjoy the benefits of a personalised e-health system with CRM 2.0 as the frontline of the system. Authorisation will be provided for each patient. Hence, the authorisation and self-managed account/service grant the access to all applications and data offered by the system. Technical assistance is provided by the manual or by a health informatics officer (just like any other customer service in business/organisation), who is available online and assists patients and their family in utilising the system. Furthermore, since all information (medical record) can be accessed online anywhere and at any time, it can contribute to a collaborative treatment in telemedicine. This feature refers to the empowerment through EMO (see Figure 1 and Table 3). The model adopts a modular approach; it will assist a healthcare provider to initiate empowerment by stages, and measure the performance gradually. Some of the features available to the users include the update of personal data, access to medical records and history (medical treatment received, medicine consumption history, family illness history, genetic, medical imaging, x-ray and so forth), preference services, transaction, payment/billing data, activities, personal health promotion and education, , appointment, friend in networks, forums, chatting and so forth. Finally, a healthcare business scenario is a critical process that affects personal health as much as it affects healthcare organisations. It is important for healthcare organisations to ensure that CRM 2.0 is fully utilised by their customers. Patients need to collaborate with healthcare providers in order to gain sufficient know-how to use electronic and online services effectively. To support this function, we propose an Online Health Educator which enables patients to attain a better knowledge and control over their health data, and yet, contributes to the basic communication between patients and healthcare providers. Additionally, the Online Health Educator determines the success of the implementation as it ensures that there is a group of staff dedicated to guarantee that e-health services are managed in a professional way. 148
11 Anshari, Almunawar, Low, & Wint - Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0 Conclusion Patient expectations in healthcare are high, and this creates a serious challenge for healthcare providers. In this article, we suggest a model to address patients demand by combining the concept of value chain and value configuration in healthcare organisations, CRM, and Social Networks. The model incorporates customer empowerment through healthcare organisation to patient as well as patient to patient relationships. Recent Web technology offers a broader outlook on customers empowerment in many ways and levels depend on the needs and policies of the organisations. These range from digitalising medical records to the customers ability in accessing their EHR. We conducted a survey to verify our empowerment features established in the CRM 2.0 model. The result of the survey confirms that customers prefer the empowerment features deriving from the model. They prefer to have control over information on their health and over applications that may affect their health. Moreover, it also confirms that the availability of an online health educator proposed in the model is important in order to achieve the goals of e-health in educating and promoting better health to customers. CRM 2.0 shares the exceptional capabilities of social media and social networks that provide a new approach which transcends traditional CRM. The majority of respondents agreed that both social networks and social support online should be part of an e-health system. The future direction of the study is to design a prototype based on our model. The prototype will be used to validate our model and to confirm that the empowerment featured in an e-health system is essential and highly recommended. 149
12 ASEAS 5(1) References AITI (2010). Brunei Darussalam Household ICT Survey Report Brunei Darussalam: Authority for Info- Communications Technology Industry of Brunei Darussalam. Anderson, R. M., Funnel, M. M., Butler, P. M., Arnold, M. S., Fitzgerald, J. T., & Feste, C. (1995). Patient empowerment: results of a randomised control trial. Diabetes Care, 18(7), Anshari M., & Almunawar, M. N. (2011). Evaluating CRM Implementation in Healthcare Organization. International Proceedings of Economics Development and Research, 9, Anshari, M., & Almunawar, M. N. (2012). Framework of Social Customer Relationship Management in E-Health Services. Retrieved 12 May 2012 from JEHM/2012/766268/ html Anshari, M., Almunawar, M. N., & Low, K. C. P. (2012). CRM 2.0 Within E-Health Systems: Towards Achieving Health Literacy and Customer Satisfaction. Journal of Development Informatics, 1(1), Almunawar, M. N., Wint, Z., Low, K. C. P., & Anshari, M. (2012). E-Health Initiative and Customer s Expectation: Case Brunei. CiiT International Journal of Automation and Autonomous System, February 2012, 1-8. Aujoulat, I., d Hoore, W., & Deccache, A. (2006). Patient empowerment in theory and practice: Polysemy or cacophony? Patient Education and Counselling, 66(1), Cipriani, F. (2008). Social CRM; Concept, Benefits and Approach to adopt. Retrieved 12 May 2012 from Davison, B. J., & Degner, L. F. (1997). Empowerment of men newly diagnosed with prostate cancer. Cancer Nursing, 20(3), Desbiens S. A., Wu, A. W., Yasui Y., Lynn J., Alzola, C., Wenger, N. S., Connors, A. F., Phillips, R. S., & Fulkerson W. (1998). Patient empowerment and feedback did not decrease pain in seriously ill hospitalised patients. Pain, 75(2-3), Dijkstra, R., Braspenning, J., & Grol, R. (2002). Empowering patients: how to implement a diabetes passport in hospital care. Patient Education and Counseling, 47(2), Golant, M., Altman, T., & Martin, C. (2003). Managing cancer side effects to improve quality of life: a cancer psychoeducation program. Cancer Nursing, 26(1), Kieffer, C. H. (1984). Citizen empowerment: a developmental perspective. In J. Rappaport, C. Swift, & R. Hess (Eds.), Studies in empowerment: steps towards understanding and action (pp. 9-36). New York: The Haworth Press. Low, P. K. C., (2002). Strategic Customer Management: Enhancing Customer Retention and Service Recovery. BusinesscrAFT Consultancy, Singapore. Maliski, S. L., Clerkin, B., & Letwin, M. S. (2004). Describing a nurse case manager intervention to empower low-income men with prostate cancer. Oncology Nursing Forum, 31(1), McCann, S., & Weinman, J. (1996). Empowering the patient in the consultation: a pilot study. Patient Education and Counselling, 27(3),
13 Anshari, Almunawar, Low, & Wint - Customer Empowerment in Healthcare Organisations Through CRM 2.0 McWilliam, C. L., Stewart, M., Brown, J. B., McNair, S., Desai, K., Patterson, M. L., Del Maestro, N., & Pittman, B. J. (1997). Creating empowering meaning: an interactive process of promoting health with chronically ill older Canadians. Health Promotion International, 12(2), NEHTA (2012). What is a PCEHR. Retrieved 12 May 2012 from Paterson, B. (2001). Myth of empowerment in chronic illness. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 34(5), Segal, L. (1998). The importance of patient empowerment in health system reform. Health Policy, 44(1), Skelton, A. M. (1997). Patient education for the millennium: beyond control and emancipation? Patient Education and Counselling, 31(2), van Dam, H. A., van der Horst, F., van den Borne, B., Ryckman, R., & Crebolder, H. (2003). Provider patient interaction in diabetes care: effects on patient self-care and outcomes. A systematic review. Patient Education and Counselling, 51(1),
Evaluating CRM Implementation in Healthcare Organization
 ISBN 978-1-84626-xxx-x Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Economics and Business Information (ICEBI 2011) Bangkok, Thailand, 7-9 May, 2011, pp. xxx-xxx Evaluating CRM Implementation in Healthcare
ISBN 978-1-84626-xxx-x Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Economics and Business Information (ICEBI 2011) Bangkok, Thailand, 7-9 May, 2011, pp. xxx-xxx Evaluating CRM Implementation in Healthcare
Building Healthcare Patient Relationship with CRM 2.0 Lesson Learnt from Prita Mulyasari s Case
 75 Building Healthcare Patient Relationship with CRM 2.0 Lesson Learnt from Prita Mulyasari s Case Muhammad Anshari 1 and Mohammad Nabil Almunawar 2 Faculty of Business, Economic & Policy Studies Universiti
75 Building Healthcare Patient Relationship with CRM 2.0 Lesson Learnt from Prita Mulyasari s Case Muhammad Anshari 1 and Mohammad Nabil Almunawar 2 Faculty of Business, Economic & Policy Studies Universiti
Framework of Social Customer Relationship Management in E-Health Services
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of e-health Management http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/jehm/jehm.html Vol. 2012 (2012), Article ID 766268, 15 pages DOI: 10.5171/2012.766268 Framework of Social Customer
IBIMA Publishing Journal of e-health Management http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/jehm/jehm.html Vol. 2012 (2012), Article ID 766268, 15 pages DOI: 10.5171/2012.766268 Framework of Social Customer
Few Touch Application Services extending a diabetes diary application. Tromsø, North Norway
 Scaling up ehealth facilitated personalised health services. WP 2: Personalised health services and patient-centred healthcare for an ageing population Case studies of Personalised Health Solutions and
Scaling up ehealth facilitated personalised health services. WP 2: Personalised health services and patient-centred healthcare for an ageing population Case studies of Personalised Health Solutions and
E-Health Initiative and Customer s Expectation: Case Brunei Mohammad Nabil Almunawar 1, Zaw Wint 2, Patrick Kim Cheng Low 3, Muhammad Anshari 4
 E-Health Initiative and Customer s Expectation: Case Brunei Mohammad Nabil Almunawar 1, Zaw Wint 2, Patrick Kim Cheng Low 3, Muhammad Anshari 4 Abstract This paper is to determine the dimension of e-health
E-Health Initiative and Customer s Expectation: Case Brunei Mohammad Nabil Almunawar 1, Zaw Wint 2, Patrick Kim Cheng Low 3, Muhammad Anshari 4 Abstract This paper is to determine the dimension of e-health
3/30/2011. HITECH and Meaningful Use: What it means for patients & families. HITECH and Meaningful Use
 HITECH and Meaningful Use: What it means for patients & families Gena Cook CEO, Navigating Cancer Five Major Goals of HITECH Improvements through a transformed delivery system 1 Improve the quality, safety
HITECH and Meaningful Use: What it means for patients & families Gena Cook CEO, Navigating Cancer Five Major Goals of HITECH Improvements through a transformed delivery system 1 Improve the quality, safety
e-health Initiative Lina Abou Mrad MBA, PMP Director, National E-Health Program Health Insight 4 -March 2014
 e-health Initiative Lina Abou Mrad MBA, PMP Director, National E-Health Program Health Insight 4 -March 2014 What is E-Health? The term e-health was barely in use before 1999 Terms such as medical informatics,
e-health Initiative Lina Abou Mrad MBA, PMP Director, National E-Health Program Health Insight 4 -March 2014 What is E-Health? The term e-health was barely in use before 1999 Terms such as medical informatics,
Position Statement on Physician Assistants
 Position Statement on Physician Assistants Team-based models of medical care that are characterised by responsiveness to local needs, mutual reliance and flexibility have always been a part of rural and
Position Statement on Physician Assistants Team-based models of medical care that are characterised by responsiveness to local needs, mutual reliance and flexibility have always been a part of rural and
Influence of Demographic Factors on Customers Perceptions towards CRM Practices among Banks
 Influence of Demographic Factors on Customers Perceptions towards CRM Practices among Banks Zuliana Zulkifli, *Izah Mohd Tahir Faculty of Business Management and Accountancy, University Sultan Zainal Abidin,
Influence of Demographic Factors on Customers Perceptions towards CRM Practices among Banks Zuliana Zulkifli, *Izah Mohd Tahir Faculty of Business Management and Accountancy, University Sultan Zainal Abidin,
Running Head: SOCIAL MEDIA RECRUITMENT: GETTING GENERATION Y S ATTENTION. Social Media Recruitment: Getting Generation Y s Attention.
 Social Media Recruitment: Getting Generation Y s Attention Andrew Nixon Mihai Ciuca Adam Venditti Hailey Desormeaux Kayla Dynan University of Guelph SOCIAL MEDIA RECRUITMENT: GETTING GENERATION Y S ABSTRACT
Social Media Recruitment: Getting Generation Y s Attention Andrew Nixon Mihai Ciuca Adam Venditti Hailey Desormeaux Kayla Dynan University of Guelph SOCIAL MEDIA RECRUITMENT: GETTING GENERATION Y S ABSTRACT
CHAPTER 6. Discussion and Conclusion. patient health information, such as diagnosis, medicine orders, managing patient
 CHAPTER 6 Discussion and Conclusion 6.1 Introduction Health care information system is a computer application to represent patient information in a friendly user interface and allowing users to review
CHAPTER 6 Discussion and Conclusion 6.1 Introduction Health care information system is a computer application to represent patient information in a friendly user interface and allowing users to review
Improving Customer Service in Healthcare with CRM 2.0
 Improving Customer Service in Healthcare with CRM 2.0 Mohammad Nabil Almunawar #1 and Muhammad Anshari #2 Faculty of Business, Economic & Policy Studies Universiti Brunei Darussalam Brunei Darussalam 1
Improving Customer Service in Healthcare with CRM 2.0 Mohammad Nabil Almunawar #1 and Muhammad Anshari #2 Faculty of Business, Economic & Policy Studies Universiti Brunei Darussalam Brunei Darussalam 1
Health Consumers Queensland...your voice in health. Consumer and Community Engagement Framework
 Health Consumers Queensland...your voice in health Consumer and Community Engagement Framework February 2012 Definitions In this Framework, Health Consumers Queensland utilises the following definitions
Health Consumers Queensland...your voice in health Consumer and Community Engagement Framework February 2012 Definitions In this Framework, Health Consumers Queensland utilises the following definitions
Strengthening palliative care: Policy and strategic directions 2011 2015
 Strengthening palliative care: Policy and strategic directions 2011 2015 Second year report 2012 13 The Victorian Government s vision for how people dealing with a life-threatening illness, and their carers,
Strengthening palliative care: Policy and strategic directions 2011 2015 Second year report 2012 13 The Victorian Government s vision for how people dealing with a life-threatening illness, and their carers,
TNO. Self-Management. Healthy Lifestyle and Chronic Care. Self-Management Taking Health and Care in Own Hand
 for Personal Computer Assistants for a Healthy Lifestyle TNO Applies scientific knowledge to strengthening the innovative power of industry and government 4500 employees Governmental funding and contract
for Personal Computer Assistants for a Healthy Lifestyle TNO Applies scientific knowledge to strengthening the innovative power of industry and government 4500 employees Governmental funding and contract
EMPOWERING ELDERLY BY HEALTH EDUCATION
 EMPOWERING ELDERLY BY HEALTH EDUCATION ¹ ²Kirsi Johansson, PhD, RN, Coordinator; ¹Brita Pasila, MNSc, RN, PhD-student; ¹Sirkku Rankinen, MNSc, RN, PhD-student; ¹Sanna Salanterä, PhD, RN, Professor; ¹ ²
EMPOWERING ELDERLY BY HEALTH EDUCATION ¹ ²Kirsi Johansson, PhD, RN, Coordinator; ¹Brita Pasila, MNSc, RN, PhD-student; ¹Sirkku Rankinen, MNSc, RN, PhD-student; ¹Sanna Salanterä, PhD, RN, Professor; ¹ ²
RUNNING HEAD: Evaluation of nursing student s informatics competency
 RUNNING HEAD: Evaluation of nursing student s informatics competency Evaluation of Nursing Students Informatics Competency Using an Adapted Self-Assessment of Nursing Informatics Competency Scale (SANICS)
RUNNING HEAD: Evaluation of nursing student s informatics competency Evaluation of Nursing Students Informatics Competency Using an Adapted Self-Assessment of Nursing Informatics Competency Scale (SANICS)
Patient Empowerment Framework for Cardiac Patients
 Patient Empowerment Framework for Cardiac Patients Robert Mulrenin a, Manuela Plößnig a, Mihai Radulescu a, Gökçe Banu Laleci b, Catherine Chronaki c and Yildiray Kabak b a Salzburg Research Forschungsgesellschaft,
Patient Empowerment Framework for Cardiac Patients Robert Mulrenin a, Manuela Plößnig a, Mihai Radulescu a, Gökçe Banu Laleci b, Catherine Chronaki c and Yildiray Kabak b a Salzburg Research Forschungsgesellschaft,
Using a Multichannel Strategy to Deliver an Exceptional Customer Experience
 Using a Multichannel Strategy to Deliver an Exceptional Customer Experience 10 things to consider when building a multichannel strategy to improve the customer experience Jesús Hoyos CRM industry analyst,
Using a Multichannel Strategy to Deliver an Exceptional Customer Experience 10 things to consider when building a multichannel strategy to improve the customer experience Jesús Hoyos CRM industry analyst,
The review of the Personally Controlled Electronic Health Records System:
 APHA submission to The review of the Personally Controlled Electronic Health Records System: Proposals on how to improve the system Australian Private Hospitals Association ABN 82 008 623 809 November
APHA submission to The review of the Personally Controlled Electronic Health Records System: Proposals on how to improve the system Australian Private Hospitals Association ABN 82 008 623 809 November
DISCUSSION PAPER ON SEMANTIC AND TECHNICAL INTEROPERABILITY. Proposed by the ehealth Governance Initiative Date: October 22 nd, 2012
 DISCUSSION PAPER ON SEMANTIC AND TECHNICAL INTEROPERABILITY Proposed by the ehealth Governance Initiative Date: October 22 nd, 2012 Introduction Continuity of care is a key priority for modern healthcare
DISCUSSION PAPER ON SEMANTIC AND TECHNICAL INTEROPERABILITY Proposed by the ehealth Governance Initiative Date: October 22 nd, 2012 Introduction Continuity of care is a key priority for modern healthcare
Self Care in New Zealand
 Self Care in New Zealand A roadmap toward greater personal responsibility in managing health Prepared by the New Zealand Self Medication Industry Association. July 2009 What is Self Care? Self Care describes
Self Care in New Zealand A roadmap toward greater personal responsibility in managing health Prepared by the New Zealand Self Medication Industry Association. July 2009 What is Self Care? Self Care describes
Social Media Usage: 2005-2015
 NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD OCTOBER 8, 2015 Social Media Usage: 2005-2015 65% of adults now use social networking sites a nearly tenfold jump in the past decade BY Andrew Perrin FOR FURTHER
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD OCTOBER 8, 2015 Social Media Usage: 2005-2015 65% of adults now use social networking sites a nearly tenfold jump in the past decade BY Andrew Perrin FOR FURTHER
A Telehealth Platform for Patients with Cancer
 A Telehealth Platform for Patients with Cancer Dr. Antonia Arnaert, Associate Professor McGill School of Nursing, Associate Member DCECS-SMHC Antonia.arnaert@mcgill.ca / Tel: 514-398-5624 Mr. Zoumanan
A Telehealth Platform for Patients with Cancer Dr. Antonia Arnaert, Associate Professor McGill School of Nursing, Associate Member DCECS-SMHC Antonia.arnaert@mcgill.ca / Tel: 514-398-5624 Mr. Zoumanan
Claus Duedal Pedersen Chief Consultant Odense University Hospital Region of Southern Denmark
 Claus Duedal Pedersen Chief Consultant Odense University Hospital Region of Southern Denmark Table of Content It all takes time RENEWING HEALTH in a nutshell Evaluating telemedicine Results & Expectations
Claus Duedal Pedersen Chief Consultant Odense University Hospital Region of Southern Denmark Table of Content It all takes time RENEWING HEALTH in a nutshell Evaluating telemedicine Results & Expectations
ISSUES IN NURSE PRACTITIONER DEVELOPMENTS IN AUSTRALIA
 ISSUES IN NURSE PRACTITIONER DEVELOPMENTS IN AUSTRALIA Glenn Gardner Queensland University of Technology & Royal Brisbane and Women s Hospital Email: Ge.gardner@qut.edu.au Gardner, Glenn E. (2004) Issues
ISSUES IN NURSE PRACTITIONER DEVELOPMENTS IN AUSTRALIA Glenn Gardner Queensland University of Technology & Royal Brisbane and Women s Hospital Email: Ge.gardner@qut.edu.au Gardner, Glenn E. (2004) Issues
Sharing patient data through Integrated Personal Health Records. PhD in Digital Media, UT Austin Portugal Inês Rodolfo, Dr.
 Sharing patient data through Integrated Personal Health Records PhD in Digital Media, UT Austin Portugal Inês Rodolfo, Dr. Nuno Correia Research context with Human Behavior Medical records are now digital
Sharing patient data through Integrated Personal Health Records PhD in Digital Media, UT Austin Portugal Inês Rodolfo, Dr. Nuno Correia Research context with Human Behavior Medical records are now digital
Recent Researches in E-Activities
 A Framework for Electronic Health Record (EHR) Implementation Impact on System Service Quality and Individual Performance among Healthcare Practitioners NOR SHAHRIZA ABDUL KARIM International Business
A Framework for Electronic Health Record (EHR) Implementation Impact on System Service Quality and Individual Performance among Healthcare Practitioners NOR SHAHRIZA ABDUL KARIM International Business
Case Studies. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents 1 Integration with an Oncology EMR and an External Billing System 3 2 Automated Patient Portal 4 3 Client Scheduling 5 4 Client Server based EMR 6 Version 0.0 Page 2 of 8 1 INTEGRATION
Table of Contents 1 Integration with an Oncology EMR and an External Billing System 3 2 Automated Patient Portal 4 3 Client Scheduling 5 4 Client Server based EMR 6 Version 0.0 Page 2 of 8 1 INTEGRATION
How are your business programs adapting admissions content to meet today s mobile demands?
 How are your business programs adapting admissions content to meet today s mobile demands? Surveying the Mobile Habits of MBA Applicants Introduction: Mobile Is Even More Important Than You Think Although
How are your business programs adapting admissions content to meet today s mobile demands? Surveying the Mobile Habits of MBA Applicants Introduction: Mobile Is Even More Important Than You Think Although
Clintegrity 360 QualityAnalytics
 WHITE PAPER Clintegrity 360 QualityAnalytics Bridging Clinical Documentation and Quality of Care HEALTHCARE EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The US Healthcare system is undergoing a gradual, but steady transformation.
WHITE PAPER Clintegrity 360 QualityAnalytics Bridging Clinical Documentation and Quality of Care HEALTHCARE EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The US Healthcare system is undergoing a gradual, but steady transformation.
THE ROLE OF HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN PATIENT-CENTERED CARE COLLABORATION. 2012 Louisiana HIPAA & EHR Conference Presenter: Chris Williams
 THE ROLE OF HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN PATIENT-CENTERED CARE COLLABORATION 2012 Louisiana HIPAA & EHR Conference Presenter: Chris Williams Agenda Overview Impact of HIT on Patient-Centered Care (PCC)
THE ROLE OF HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN PATIENT-CENTERED CARE COLLABORATION 2012 Louisiana HIPAA & EHR Conference Presenter: Chris Williams Agenda Overview Impact of HIT on Patient-Centered Care (PCC)
An Empirical Study on the Use of Web 2.0 by Greek Adult Instructors in Educational Procedures
 An Empirical Study on the Use of Web 2.0 by Greek Adult Instructors in Educational Procedures John Vrettaros, Alexis Tagoulis, Niki Giannopoulou, and Athanasios Drigas NCSR DEMOKRITOS, Institute of Informatics
An Empirical Study on the Use of Web 2.0 by Greek Adult Instructors in Educational Procedures John Vrettaros, Alexis Tagoulis, Niki Giannopoulou, and Athanasios Drigas NCSR DEMOKRITOS, Institute of Informatics
Archetype-Based Knowledge Management for Semantic Interoperability of Electronic Health Records
 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-044-5-1007
Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-044-5-1007
Office ID Location: City State Date / / PRIMARY CARE SURVEY
 A. Organizational Characteristics PRIMARY CARE SURVEY We want to learn more about the general features of your office. A1. What health-related services does your office provide (check all that apply)?
A. Organizational Characteristics PRIMARY CARE SURVEY We want to learn more about the general features of your office. A1. What health-related services does your office provide (check all that apply)?
WHITE PAPER. QualityAnalytics. Bridging Clinical Documentation and Quality of Care
 WHITE PAPER QualityAnalytics Bridging Clinical Documentation and Quality of Care 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The US Healthcare system is undergoing a gradual, but steady transformation. At the center of this transformation
WHITE PAPER QualityAnalytics Bridging Clinical Documentation and Quality of Care 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The US Healthcare system is undergoing a gradual, but steady transformation. At the center of this transformation
Policy Statement 16/2006. Acute and Multidisciplinary Working
 RCN Policy Unit Policy Statement 16/2006 Acute and Multidisciplinary Working The Royal College of Nursing of the United Kingdom and the Royal College of Physicians (London) September 2006 Royal College
RCN Policy Unit Policy Statement 16/2006 Acute and Multidisciplinary Working The Royal College of Nursing of the United Kingdom and the Royal College of Physicians (London) September 2006 Royal College
QUM and Continuity of Care A Prescribed Medicines Services and Programs
 Community Pharmacy Roadmap Program Development Template Program/Service: Quadrant: 1. Program/Service Description QUM and Continuity of Care A Prescribed Medicines Services and Programs a) Background The
Community Pharmacy Roadmap Program Development Template Program/Service: Quadrant: 1. Program/Service Description QUM and Continuity of Care A Prescribed Medicines Services and Programs a) Background The
A Framework to Enhance Rural Healthcare Services Utilizing Cloud Computing and Videoconferencing
 Open Access Journal of Information Systems (OAJIS) Available at http://is.its.ac.id/pubs/oajis/index.php The Third Information Systems International Conference A Framework to Enhance Rural Healthcare Services
Open Access Journal of Information Systems (OAJIS) Available at http://is.its.ac.id/pubs/oajis/index.php The Third Information Systems International Conference A Framework to Enhance Rural Healthcare Services
Health Information & Resources Service (HIRS) Action Plan 2015-2018. Health Promotion Team. Department of Public Health
 DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION Health Information & Resources Service (HIRS) Action Plan 2015-2018 Health Promotion Team Department of Public Health Version No: Prepared by 2.0 (draft for consultation) Clare Black
DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION Health Information & Resources Service (HIRS) Action Plan 2015-2018 Health Promotion Team Department of Public Health Version No: Prepared by 2.0 (draft for consultation) Clare Black
Health Policy, Administration and Expenditure
 Submission to the Parliament of Australia Senate Community Affairs Committee Enquiry into Health Policy, Administration and Expenditure September 2014 Introduction The Australian Women s Health Network
Submission to the Parliament of Australia Senate Community Affairs Committee Enquiry into Health Policy, Administration and Expenditure September 2014 Introduction The Australian Women s Health Network
A Study among Chinese Tourists in their 20s and 30s for Determining their Choice of Medical Tourism Destinations
 , pp.13-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2015.8.9.02 A Study among Chinese Tourists in their 20s and 30s for Determining their Choice of Medical Tourism Destinations Mi Joon Lee 1, In Soon Min 2
, pp.13-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2015.8.9.02 A Study among Chinese Tourists in their 20s and 30s for Determining their Choice of Medical Tourism Destinations Mi Joon Lee 1, In Soon Min 2
SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING TRENDS IN TURKEY
 SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING TRENDS IN TURKEY June 2012 About the Authors AYŞEGÜL TOKER is a professor of Information Systems at the Department of Management, and the Dean of the Faculty of Economics and Administrative
SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING TRENDS IN TURKEY June 2012 About the Authors AYŞEGÜL TOKER is a professor of Information Systems at the Department of Management, and the Dean of the Faculty of Economics and Administrative
Adoption of Information Technology in Healthcare: Benefits & Constraints
 Adoption of Information Technology in Healthcare: Benefits & Constraints A WiredFox Technologies White Paper 2 Adoption of Information Technology in Healthcare: Benefits & Constraints By Jeff Yelton 3
Adoption of Information Technology in Healthcare: Benefits & Constraints A WiredFox Technologies White Paper 2 Adoption of Information Technology in Healthcare: Benefits & Constraints By Jeff Yelton 3
Agenda. Danish EHR History. Danish EHR History. Status and perspective of personal health informatics in Denmark
 Status and perspective of personal health informatics in Mads Ronald Dahl PhD, Assistant Professor Institute of Public Health Section for Health Informatics University of Aarhus MD@HI.AU.DK WWW.HI.AU.DK
Status and perspective of personal health informatics in Mads Ronald Dahl PhD, Assistant Professor Institute of Public Health Section for Health Informatics University of Aarhus MD@HI.AU.DK WWW.HI.AU.DK
Overcoming barriers to ehealth
 POSITION PAPER 21 April 2011 Rev. 15 September 2011 Overcoming barriers to ehealth Page 1 of 5 What is ehealth? Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has changed the way people carry out a broad
POSITION PAPER 21 April 2011 Rev. 15 September 2011 Overcoming barriers to ehealth Page 1 of 5 What is ehealth? Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has changed the way people carry out a broad
Concept Series Paper on Disease Management
 Concept Series Paper on Disease Management Disease management is the concept of reducing health care costs and improving quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions by preventing or minimizing
Concept Series Paper on Disease Management Disease management is the concept of reducing health care costs and improving quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions by preventing or minimizing
Workshop 2.14. IT, 905 TERRACE 2 Wednesday June, 26 th 10.30-12.00. Patients reading their medical records online - implications for the doctor
 Workshop 2.14. IT, 905 TERRACE 2 Wednesday June, 26 th 10.30-12.00 Patients reading their medical records online - implications for the doctor Ture Ålander PhD, MD, Anna Hamne MD 2013-06-23 Patients reading
Workshop 2.14. IT, 905 TERRACE 2 Wednesday June, 26 th 10.30-12.00 Patients reading their medical records online - implications for the doctor Ture Ålander PhD, MD, Anna Hamne MD 2013-06-23 Patients reading
28 ehealth: Redefining Health Care
 28 ehealth: Redefining Health Care in the Light of Technology Mike W. Chiasson Lancaster University, Lancaster, U.K. Donal Flynn University of Manchester, Manchester, U.K. Bonnie Kaplan Yale University,
28 ehealth: Redefining Health Care in the Light of Technology Mike W. Chiasson Lancaster University, Lancaster, U.K. Donal Flynn University of Manchester, Manchester, U.K. Bonnie Kaplan Yale University,
THE THEORY OF PLANNED BEHAVIOR AND ITS ROLE IN TECHNOLOGY ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS IMPLEMENTATION
 THE THEORY OF PLANNED BEHAVIOR AND ITS ROLE IN TECHNOLOGY ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS IMPLEMENTATION Elaine Seeman, Department of Management Information Systems College of Business, East Carolina
THE THEORY OF PLANNED BEHAVIOR AND ITS ROLE IN TECHNOLOGY ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS IMPLEMENTATION Elaine Seeman, Department of Management Information Systems College of Business, East Carolina
Customer Experience Management
 Customer Experience Management Best Practices for Voice of the Customer (VoC) Programmes Jörg Höhner Senior Vice President Global Head of Automotive SPA Future Thinking The Evolution of Customer Satisfaction
Customer Experience Management Best Practices for Voice of the Customer (VoC) Programmes Jörg Höhner Senior Vice President Global Head of Automotive SPA Future Thinking The Evolution of Customer Satisfaction
Pre registration nurses: an investigation of knowledge, experience and comprehension of e health
 Pre registration nurses: an investigation of knowledge, experience and comprehension of e health AUTHORS Sisira Edirippulige PhD, MSc, Lecturer Centre for Online Health, University of Queensland, Australia.
Pre registration nurses: an investigation of knowledge, experience and comprehension of e health AUTHORS Sisira Edirippulige PhD, MSc, Lecturer Centre for Online Health, University of Queensland, Australia.
The Patient Centered Medical Home (PCMH): Looking at Examples. and Research on Staffing Models. Nancy Chang. GE-NMF PCLP Scholar 2013
 Running head: PATIENT CENTERED MEDICAL HOME 1 The Patient Centered Medical Home (PCMH): Looking at Examples and Research on Staffing Models Nancy Chang GE-NMF PCLP Scholar 2013 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICAL
Running head: PATIENT CENTERED MEDICAL HOME 1 The Patient Centered Medical Home (PCMH): Looking at Examples and Research on Staffing Models Nancy Chang GE-NMF PCLP Scholar 2013 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICAL
Session Name: e-health (collaborative)
 Session Name: e-health (collaborative) In accordance with the policy of The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists, the Australian Institute of Radiography and the Australasian College
Session Name: e-health (collaborative) In accordance with the policy of The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists, the Australian Institute of Radiography and the Australasian College
CONTENTS. About the report 3. Methodology & survey demographics. Key findings. SECTION 1: Most-used online resources and devices
 Published July 2014 Published July 2014 Contents CONTENTS About the report 3 Methodology & survey demographics 4 Key findings 5 SECTION 1: Most-used online resources and devices Online versus offline resources
Published July 2014 Published July 2014 Contents CONTENTS About the report 3 Methodology & survey demographics 4 Key findings 5 SECTION 1: Most-used online resources and devices Online versus offline resources
Health Promotion, Prevention, Medical care, Rehabilitation under the CBR Matrix heading of "Health
 Health Promotion, Prevention, Medical care, Rehabilitation under the CBR Matrix heading of "Health Dr Deepthi N Shanbhag Assistant Professor Department of Community Health St. John s Medical College Bangalore
Health Promotion, Prevention, Medical care, Rehabilitation under the CBR Matrix heading of "Health Dr Deepthi N Shanbhag Assistant Professor Department of Community Health St. John s Medical College Bangalore
Hospital physicians' tasks and the use and nonuse of EHR-system functions
 Hospital physicians' tasks and the use and nonuse of EHR-system functions Associate professor Arild Faxvaag Norwegian centre for electronic health records research (NSEP) Faculty of medicine, NTNU 1 learning
Hospital physicians' tasks and the use and nonuse of EHR-system functions Associate professor Arild Faxvaag Norwegian centre for electronic health records research (NSEP) Faculty of medicine, NTNU 1 learning
Elevate Customer Experience and Engagement in the New Digital World
 Elevate Customer Experience and Engagement in the New Digital World John Chan CRM Solutions Lead, Microsoft Business Solutions Microsoft Asia Customer buying behavior has fundamentally changed therefore,
Elevate Customer Experience and Engagement in the New Digital World John Chan CRM Solutions Lead, Microsoft Business Solutions Microsoft Asia Customer buying behavior has fundamentally changed therefore,
Role of Social Media on Public Relation, Brand Involvement and. Brand Commitment
 Role of Social Media on Public Relation, Brand Involvement and Brand Commitment Noor-e-Hira Naveed Foundation University Islamabad Abstract The study is focused on finding out the role of social media
Role of Social Media on Public Relation, Brand Involvement and Brand Commitment Noor-e-Hira Naveed Foundation University Islamabad Abstract The study is focused on finding out the role of social media
ehealth, HIS, etc ehealth All information about health HMIS mhealth HIS Statistical IS Credited: Karl Brown, Rockefeller Foundation
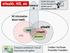 ehealth, HIS, etc Statistical IS Health Informatics: Formal discipline that studies use of information in health All information about health HIS HMIS ehealth mhealth Tele-medicine Enterprise architecture:
ehealth, HIS, etc Statistical IS Health Informatics: Formal discipline that studies use of information in health All information about health HIS HMIS ehealth mhealth Tele-medicine Enterprise architecture:
A Home-Based Care Model for Outpatient Cardiac Rehabilitation Based on Mobile Technologies
 A Home-Based Care Model for Outpatient Cardiac Rehabilitation Based on Mobile Technologies Jukka Salminen Nokia Antti Särelä CSIRO Esa Koskinen Nokia Ilkka Korhonen VTT Ole Kirkeby Nokia Darren Walters
A Home-Based Care Model for Outpatient Cardiac Rehabilitation Based on Mobile Technologies Jukka Salminen Nokia Antti Särelä CSIRO Esa Koskinen Nokia Ilkka Korhonen VTT Ole Kirkeby Nokia Darren Walters
To Improve Outcomes & Clinical Efficiency
 To Improve Outcomes & Clinical Efficiency 1 New England Home Care Conference & Trade Show June 6, 2013 Carolyn J Humphrey, RN, MS, FAAN President, CJ Humphrey Associates Louisville, Kentucky 502 767 9817
To Improve Outcomes & Clinical Efficiency 1 New England Home Care Conference & Trade Show June 6, 2013 Carolyn J Humphrey, RN, MS, FAAN President, CJ Humphrey Associates Louisville, Kentucky 502 767 9817
Jobvite Hire Review - The Next Generation of Recruitment
 Jobvite Hire: Health & Sciences The revolutionary recruiting solution that keeps your hiring processes in good health. While Health & Science businesses are facing significant growth opportunities, both
Jobvite Hire: Health & Sciences The revolutionary recruiting solution that keeps your hiring processes in good health. While Health & Science businesses are facing significant growth opportunities, both
Quality in and Equality of Access to Healthcare Services
 Quality in and Equality of Access to Healthcare Services Executive Summary European Commission Directorate-General for Employment, Social Affairs and Equal Opportunities Manuscript completed in March 2008
Quality in and Equality of Access to Healthcare Services Executive Summary European Commission Directorate-General for Employment, Social Affairs and Equal Opportunities Manuscript completed in March 2008
Social Journalism Study 2013 United Kingdom. Report by Cision & Canterbury Christ Church University (UK)
 Social Journalism Study 2013 United Kingdom Report by Cision & Canterbury Christ Church University (UK) 1. Executive Summary Social media is now an everyday professional tool with 96% of UK journalists
Social Journalism Study 2013 United Kingdom Report by Cision & Canterbury Christ Church University (UK) 1. Executive Summary Social media is now an everyday professional tool with 96% of UK journalists
Developing clinician competencies in self-management support for people with chronic conditions: The Flinders model
 Developing clinician competencies in self-management support for people with chronic conditions: The Flinders model Introduction Self-management support is one of the 6 elements of the Chronic Care Model
Developing clinician competencies in self-management support for people with chronic conditions: The Flinders model Introduction Self-management support is one of the 6 elements of the Chronic Care Model
Best Practices in Patient Navigation and Cancer Survivorship Survey Results
 Best Practices in Patient Navigation and Cancer Survivorship Survey Results December 2013 Best Practices in Navigation and Cancer Survivorship Survey Results The George Washington University Cancer Institute
Best Practices in Patient Navigation and Cancer Survivorship Survey Results December 2013 Best Practices in Navigation and Cancer Survivorship Survey Results The George Washington University Cancer Institute
PREDICTING ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS: WHAT FACTORS MATTER MOST?
 PREDICTING ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS: WHAT FACTORS MATTER MOST? Shanan G. Gibson & Elaine D. Seeman College of Business, East Carolina University gibsons@ecu.edu; seemane@ecu.edu ABSTRACT
PREDICTING ACCEPTANCE OF ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS: WHAT FACTORS MATTER MOST? Shanan G. Gibson & Elaine D. Seeman College of Business, East Carolina University gibsons@ecu.edu; seemane@ecu.edu ABSTRACT
CAHPS Clinician & Group Survey: Overview of the Questionnaires (Four-Point Scale)
 CAHPS Clinician & Group Survey: Overview of the Questionnaires (Four-Point Scale) Available Questionnaires... 1 Core Items...1 Supplemental Items...2 Development of the Survey... 2 Appendix Exhibit 1:
CAHPS Clinician & Group Survey: Overview of the Questionnaires (Four-Point Scale) Available Questionnaires... 1 Core Items...1 Supplemental Items...2 Development of the Survey... 2 Appendix Exhibit 1:
Removal of paper-based health records from Norwegian hospitals: Effects on clinical workflow
 Removal of paper-based health records from Norwegian hospitals: Effects on clinical workflow Jan Tore LIUM a,1 and Arild FAXVAAG b a Norwegian university of science and technology, Trondheim, Norway b
Removal of paper-based health records from Norwegian hospitals: Effects on clinical workflow Jan Tore LIUM a,1 and Arild FAXVAAG b a Norwegian university of science and technology, Trondheim, Norway b
Update on the Integrated Hospital-Community EMR
 Update on the Integrated Hospital-Community EMR Country: Israel Partner Institute: The Myers-JDC-Brookdale Institute, Jerusalem Survey no: (12) 2008 Author(s): Nirel, Nurit and Revital Gross Health Policy
Update on the Integrated Hospital-Community EMR Country: Israel Partner Institute: The Myers-JDC-Brookdale Institute, Jerusalem Survey no: (12) 2008 Author(s): Nirel, Nurit and Revital Gross Health Policy
Question & Answer Guide
 Joint Commission Primary Care Medical Home (PCMH) Certification for Accredited Ambulatory Health Care Organizations Question & Answer Guide A. SCORING/DECISION-RELATED Question: We are already Joint Commission
Joint Commission Primary Care Medical Home (PCMH) Certification for Accredited Ambulatory Health Care Organizations Question & Answer Guide A. SCORING/DECISION-RELATED Question: We are already Joint Commission
Nursing Knowledge for Your Benefit
 Nursing Knowledge for Your Benefit Policy of the Icelandic Nurses Association on Nursing and Health Care 2011-2020 About this Policy The present Policy of the Icelandic Nurses Association (INA) was developed
Nursing Knowledge for Your Benefit Policy of the Icelandic Nurses Association on Nursing and Health Care 2011-2020 About this Policy The present Policy of the Icelandic Nurses Association (INA) was developed
Research Agenda for General Practice / Family Medicine and Primary Health Care in Europe Summary EGPRN
 Research Agenda for General Practice / Family Medicine and Primary Health Care in Europe Summary EGPRN EUROPEAN GENERAL PRACTICE RESEARCH NETWO RK EGPRN is a network organisation within WONCA Region Europe
Research Agenda for General Practice / Family Medicine and Primary Health Care in Europe Summary EGPRN EUROPEAN GENERAL PRACTICE RESEARCH NETWO RK EGPRN is a network organisation within WONCA Region Europe
An Investigation of the Factors Influencing the Adoption of E-Health Services:
 An Investigation of the Factors Influencing the Adoption of E-Health Services: The Case for Selected Hospitals in Lagos State, Nigeria 1 Senanu Okuboyejo & 2 Valerie Ochiotu Department of Computer and
An Investigation of the Factors Influencing the Adoption of E-Health Services: The Case for Selected Hospitals in Lagos State, Nigeria 1 Senanu Okuboyejo & 2 Valerie Ochiotu Department of Computer and
Quality Standard Customer Service Complaints Handling
 Quality Standard Customer Service Complaints Handling Version 1 Date:- 2 nd December 2010 Page 1 Contents INTRODUCTION 4 OVERVIEW OF THE COMPLAINTS STANDARD 5 FRAMEWORK 6 MANDATORY SECTIONS 7 SECTION 1
Quality Standard Customer Service Complaints Handling Version 1 Date:- 2 nd December 2010 Page 1 Contents INTRODUCTION 4 OVERVIEW OF THE COMPLAINTS STANDARD 5 FRAMEWORK 6 MANDATORY SECTIONS 7 SECTION 1
Hospital Authority. Update on the Development of the Community Health Call Centre
 For information on 26.6.2014 HAB-P206 Hospital Authority Update on the Development of the Community Health Call Centre Purpose This paper aims to update Members on the development of the Community Health
For information on 26.6.2014 HAB-P206 Hospital Authority Update on the Development of the Community Health Call Centre Purpose This paper aims to update Members on the development of the Community Health
Master of Nursing Science Stage 2
 Master of Nursing Science Stage 2 Overview The Master of Nursing Science is an academic program designed to provide opportunities for nurses to develop advanced skills in clinical inquiry, practice and
Master of Nursing Science Stage 2 Overview The Master of Nursing Science is an academic program designed to provide opportunities for nurses to develop advanced skills in clinical inquiry, practice and
Nurse Practitioner Frequently Asked Questions
 HEALTH SERVICES Nurse Practitioner Frequently Asked Questions The Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) have been designed to increase awareness and understanding of the Nurse Practitioner role within the
HEALTH SERVICES Nurse Practitioner Frequently Asked Questions The Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) have been designed to increase awareness and understanding of the Nurse Practitioner role within the
Health Program in the Library of Alexandria
 Submitted on: 4 August 2015 Health Program in the Library of Alexandria Suzanne Samir Head of Educational Services Section, Library of Alexandria, Alexandria, Egypt. suzanne.samir@bibalex.org Copyright
Submitted on: 4 August 2015 Health Program in the Library of Alexandria Suzanne Samir Head of Educational Services Section, Library of Alexandria, Alexandria, Egypt. suzanne.samir@bibalex.org Copyright
A Population Health Management Approach in the Home and Community-based Settings
 A Population Health Management Approach in the Home and Community-based Settings Mark Emery Linda Schertzer Kyle Vice Charles Lagor Philips Home Monitoring Philips Healthcare 2 Executive Summary Philips
A Population Health Management Approach in the Home and Community-based Settings Mark Emery Linda Schertzer Kyle Vice Charles Lagor Philips Home Monitoring Philips Healthcare 2 Executive Summary Philips
The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly
 The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly Context of Nursing Today Surviving the economic downturn Recent growth in healthcare jobs Public perceptions of nursing Growth of technology Drivers of the Nursing Profession
The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly Context of Nursing Today Surviving the economic downturn Recent growth in healthcare jobs Public perceptions of nursing Growth of technology Drivers of the Nursing Profession
An International Comparison of the Career of Social Work by Students in Social Work
 Acta Medicina et Sociologica Vol 5., 2014 5 An International Comparison of the Career of Social Work by Students in Social Work Gergely Fábián*, Thomas R. Lawson**, Mihály Fónai***, János Kiss*, Eric R.
Acta Medicina et Sociologica Vol 5., 2014 5 An International Comparison of the Career of Social Work by Students in Social Work Gergely Fábián*, Thomas R. Lawson**, Mihály Fónai***, János Kiss*, Eric R.
How To Get A Cloud Service For A Small Business In Canada
 2015 SMB Cloud InsightsTM CANADA Categories and Definitions SMB Defined We define SMBs also known as small and medium enterprises (SMEs) as companies with one to 250 employees. There are around 1.1 million
2015 SMB Cloud InsightsTM CANADA Categories and Definitions SMB Defined We define SMBs also known as small and medium enterprises (SMEs) as companies with one to 250 employees. There are around 1.1 million
New York ehealth Collaborative. Health Information Exchange and Interoperability April 2012
 New York ehealth Collaborative Health Information Exchange and Interoperability April 2012 1 Introductions Information exchange patient, information, care team How is Health information exchanged Value
New York ehealth Collaborative Health Information Exchange and Interoperability April 2012 1 Introductions Information exchange patient, information, care team How is Health information exchanged Value
WHITE PAPER. Social media analytics in the insurance industry
 WHITE PAPER Social media analytics in the insurance industry Introduction Insurance is a high involvement product, as it is an expense. Consumers obtain information about insurance from advertisements,
WHITE PAPER Social media analytics in the insurance industry Introduction Insurance is a high involvement product, as it is an expense. Consumers obtain information about insurance from advertisements,
Status of Customer Relationship Management in India
 Status of Customer Relationship Management in India by Dr. G. Shainesh & Ramneesh Mohan Management Development Institute Gurgaon, India Introduction Relationship marketing is emerging as the core marketing
Status of Customer Relationship Management in India by Dr. G. Shainesh & Ramneesh Mohan Management Development Institute Gurgaon, India Introduction Relationship marketing is emerging as the core marketing
A Provider s Perspective on Electronic Health Record Systems Adoption in Small Practices
 A Provider s Perspective on Electronic Health Record Systems Adoption in Small Practices Research-in-Progress Chi Zhang Southern Polytechnic State University chizhang@spsu.edu ABSTRACT This research-in-progress
A Provider s Perspective on Electronic Health Record Systems Adoption in Small Practices Research-in-Progress Chi Zhang Southern Polytechnic State University chizhang@spsu.edu ABSTRACT This research-in-progress
Tele-care and tele-alarms for the elderly: preliminary experiences in Mexico
 Rev Saúde Pública 2013;47(4):1-6 Original Articles DOI: 10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047004574 Liliana Giraldo-Rodríguez I Sara Torres-Castro I David Martínez-Ramírez II Luis Miguel Gutiérrez-Robledo I Tele-care
Rev Saúde Pública 2013;47(4):1-6 Original Articles DOI: 10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047004574 Liliana Giraldo-Rodríguez I Sara Torres-Castro I David Martínez-Ramírez II Luis Miguel Gutiérrez-Robledo I Tele-care
Wider Implementation of Telemedicine in Estonia
 Wider Implementation of Telemedicine in Estonia A summary of the study s results Full version (in Estonian) accessible at: http://www.praxis.ee/index.php?id=1140 Contact: priit.kruus@praxis.ee Authors:
Wider Implementation of Telemedicine in Estonia A summary of the study s results Full version (in Estonian) accessible at: http://www.praxis.ee/index.php?id=1140 Contact: priit.kruus@praxis.ee Authors:
RGPs of Ontario Education Day 2014. Maryanne Brown, RN MSc Creating Gerontological Excellence Clinical Leadership Services in Gerontology
 RGPs of Ontario Education Day 2014 Maryanne Brown, RN MSc Creating Gerontological Excellence Clinical Leadership Services in Gerontology Acknowledgement To the seniors, caregivers and core PATH team 2
RGPs of Ontario Education Day 2014 Maryanne Brown, RN MSc Creating Gerontological Excellence Clinical Leadership Services in Gerontology Acknowledgement To the seniors, caregivers and core PATH team 2
HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS
 HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS "HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS" HOPE EXCHANGE PROGRAMME 2009 HOPE, the European Hospital and Healthcare Federation, is a non-profit
HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS "HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS" HOPE EXCHANGE PROGRAMME 2009 HOPE, the European Hospital and Healthcare Federation, is a non-profit
10 Steps to a Multichannel Strategy and an Exceptional Customer Experience
 10 Steps to a Multichannel Strategy and an Exceptional Customer Experience Jesús Hoyos CRM industry analyst and advisor Brad Herrington Principal Solutions Architect Interactive Intelligence, Inc. Contents
10 Steps to a Multichannel Strategy and an Exceptional Customer Experience Jesús Hoyos CRM industry analyst and advisor Brad Herrington Principal Solutions Architect Interactive Intelligence, Inc. Contents
Interactive Intelligence
 Interactive Intelligence Customer Service Experience Study (Wave II) by Joe Staples Chief Marketing Officer Interactive Intelligence, Inc. and Thomas Bailey Content Editor Interactive Intelligence, Inc.
Interactive Intelligence Customer Service Experience Study (Wave II) by Joe Staples Chief Marketing Officer Interactive Intelligence, Inc. and Thomas Bailey Content Editor Interactive Intelligence, Inc.
Improving Health Outcomes and Reducing Costs with Video Conferencing Technology
 Case Study Intel Intel Health & Life Sciences Improving Health Outcomes and Reducing Costs with Video Conferencing Technology The fundamental concept is to provide the patient with care where they are
Case Study Intel Intel Health & Life Sciences Improving Health Outcomes and Reducing Costs with Video Conferencing Technology The fundamental concept is to provide the patient with care where they are
Big Chat 4. Strategy into action. NHS Southport and Formby CCG
 Big Chat 4 Strategy into action NHS Southport and Formby CCG Royal Clifton Hotel, Southport, 19 November 2014 Contents What is the Big Chat? 3 About Big Chat 4 4 How the event worked 4 Presentations 5
Big Chat 4 Strategy into action NHS Southport and Formby CCG Royal Clifton Hotel, Southport, 19 November 2014 Contents What is the Big Chat? 3 About Big Chat 4 4 How the event worked 4 Presentations 5
australian nursing federation
 australian nursing federation Submission to Department of Health and Ageing in response to the Personally Controlled Electronic Health Record (PCEHR) System Legislation Issues Paper August 2011 Lee Thomas
australian nursing federation Submission to Department of Health and Ageing in response to the Personally Controlled Electronic Health Record (PCEHR) System Legislation Issues Paper August 2011 Lee Thomas
MANAGEMENT OF DATA, INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE IN MEDICINE AND HEALTH SERVICES in SR
 MANAGEMENT OF DATA, INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE IN MEDICINE AND HEALTH SERVICES in SR Viera Rusnáková, Slovak Medical University, Bratislava, Slovak Republic Ljuba Bachárová, International Laser Centre,
MANAGEMENT OF DATA, INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE IN MEDICINE AND HEALTH SERVICES in SR Viera Rusnáková, Slovak Medical University, Bratislava, Slovak Republic Ljuba Bachárová, International Laser Centre,
NATIONAL INFORMATION BOARD WORK STREAM 1.1 ROADMAP
 NATIONAL INFORMATION BOARD Personalised Health and Care 2020 WORK STREAM 1.1 ROADMAP Enable me to make the right health and care choices Providing patients and the public with digital access to health
NATIONAL INFORMATION BOARD Personalised Health and Care 2020 WORK STREAM 1.1 ROADMAP Enable me to make the right health and care choices Providing patients and the public with digital access to health
The research was carried out by: Carol Borrill, Michael West, Jeremy Dawson Aston Business School, Aston University.
 The research was carried out by: Carol Borrill, Michael West, Jeremy Dawson Aston Business School, Aston University. David Shapiro, Anne Rees, Ann Richards University of Leeds. Simon Garrod, Jean Carletta
The research was carried out by: Carol Borrill, Michael West, Jeremy Dawson Aston Business School, Aston University. David Shapiro, Anne Rees, Ann Richards University of Leeds. Simon Garrod, Jean Carletta
