Trends in Environmental Information Processing
|
|
|
- Dorthy Bennett
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 To appear in: R. Raubold, K. Brunnstein (eds.): Proceedings of the IFIP Congress 94 - Volume 2. Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. (North Holland), 1994 Trends in Environmental Information Processing F.J. Radermacher a, W.-F. Riekert a, B. Page b, and L.M. Hilty b a Forschungsinstitut für anwendungsorientierte Wissensverarbeitung (FAW) an der Universität Ulm, Postfach 2060, Ulm, Germany; {radermac riekert}@faw.uni-ulm.de b Universität Hamburg, Vogt-Kölln-Str. 30, Hamburg, Germany; {page hilty}@informatik.uni-hamburg.de Abstract In recent years, systems for processing environmental information have been evolving from research and development systems to practical applications. Today, many of these systems already support environmental activities at the industrial, governmental, and worldwide levels. A broad range of applications in environmental protection is covered by these systems, including monitoring and control, conventional information management, computation and analysis, as well as planning and decision support. A new discipline, known as Environmental Informatics, is emerging which combines research fields such as data base systems, geographic information systems, modeling and simulation, computer graphics, user interfaces, neural networks, knowledge processing, and systems integration. Keyword Codes: H.0; I.0, J.2 Keywords: Information Systems, General; Computing Methodologies, General; Computer Applications, Physical Sciences and Engineering 1. INTRODUCTION The environment is one of the topics which are of crucial importance for the transition of industrial civilizations into the next century. To date, individual standards of living have been growing rapidly in the developed countries of the world while global population growth is exploding. Both trends are adding to ever increasing global consumption. We are now becoming aware of the limits of our natural resources, while producing global effects with our daily activities, thus leading to a situation which can hardly be controlled, and which may eventually lead to global instabilities. It is not surprising that the discussions about measures for preserving the environment often lack the necessary information. On the one hand, we suffer from the huge amount of available
2 data people sometimes speak of data graveyards on the other hand, the really relevant data may still be missing, either because they are not contained in the available data or because the researchers are not able to extract them. Therefore, the design of information processing systems for the appropriate utilization of environmental data is a big challenge for computer scientists and other interested parties. The existing solutions often suffer from a narrowed, unidisciplinary view of the problem scope. These solutions fail if additional requirements are introduced, such as interoperability with other environmental information systems and adaptability to future system environments or application scenarios. Another requirement, which has not yet been adequately covered, concerns the transformation of results into reports or other public communication formats which necessitates a strong integration with the domain of multimedia and desktop publishing. Moreover, a major obstacle on the way towards generalizable solutions is the nature of the environmental data which are sometimes very large, very complex, and which require non-standard data structures and processing methods in most cases. Finally, an even bigger problem may be the fact that many politicians, and also scientists, in this field do not yet fully understand the central importance of the proper incorporation of computer science know-how into this framework. For coping with all of these requirements and problems, a new discipline, known as Environmental Informatics, is emerging. In the following section, application domains and essential scientific aspects of this discipline are presented in more detail. 2. THE GLOBAL DIMENSION Global development and the environmental situation are becoming more and more critical and dangerous. Driving factors are the uncontrolled growth of the world population combined with the increase in consumption described above. Both trends (more people, more consumption) have been viewed throughout history as unanimously positive. However, this view is now changing. With more than half of the people living on Earth today below the age of reproduction, a time bomb is developing which will be difficult to manage. Even worse, the level of consumption in the developed world is viewed as a target by billions of people around the globe, influenced by modern worldwide communication, while, at the same time, we are already witnessing scarcity of water resources, extension of desert areas, loss of tropical rain forests, and, particularly, the accelerated growth of megacities with many negative effects on hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of people. It is quite clear that all these trends can only be broken with very decisive programs, limiting further population increase, or, preferably, reducing the world population over the coming generations. To achieve this, however, will mean radical changes in our general attitude. The political and the ethical leaders of the world do not yet seem to be willing or able to fully address these problems. However, the past several years have brought many changes in this direction. Particularly, the Rio Summit has finally led to the acceptance of a point of view that is best characterized by the term sustainable development. Here, sustainable development means a way of living and a form of using resources that does not discriminate against future generations. Sustainable development is an important concept. However, it is difficult to operationalize and to make concrete. We will probably be confronted with quite sophisticated counter-argu
3 ments, and it might happen as it has so often before that uncoordinated development will actually lead to a state of affairs that is acceptable to no one. It is not at all clear what can be done to help to fight such a negative development. Certainly, information will be a very critical resource in changing attitudes and making decisive political actions possible. Among the many information sources to be considered, remote sensing and the coupling of data streams from all over the world, a policy of sharing information, the formation of networks and broad-based discussions will probably be the best that can be achieved and arranged in this framework (GÜNT94). Certainly, the most advanced computer science techniques must be employed here, from networks to information processing, image analysis, federated database computing, artificial intelligence, and neural networks, among other topics. Environmental informatics is contributing here to a matter of utmost importance. More on this topic is presented in the following sections. 3. SUPPORTING THE PUBLIC SECTOR In recent years, environmental protection as an objective of public activities has reached quite a high standard in Europe, particularly in Germany. Communal tasks, for example, include land use planning, approving compliance with environmental standards, management of hazardous waste, and water and energy management for public facilities. Several states and regions of the European Union have already installed effective environmental information systems and powerful sensor networks. There is a broad laboratory infrastructure both in the public sector and in industry. Official systems such as the Environmental Information System Baden-Württemberg (MAYE93) support environmental tasks at various levels: Decision Support Systems are provided for the high-level environmental management, reporting and planning systems are available for middle management, while basic components support the acquisition and management of specific environmental data at the operational level. In addition, interdisciplinary information systems are being used in public environmental management; these systems are not restricted to environmental tasks such as the topographic or cadastral information systems of the surveying offices. 4. INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS The need for environmental management systems in industrial production is a recent challenge to information technology. An environmental management system is the overall framework for the actions that an enterprise takes to manage its effects on the environment (FAW94). European regulations such as the Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (COMM93) are intended to standardize this framework. Information systems designed to support such actions or the overall framework are called industrial environmental information systems or environmental management information systems (LITT93). In so far as such systems are used for production planning tasks, they may be designed in accordance with conventional production planning and control systems and incorporated into a CIM- or CIP-architecture (HAAS91). Their task is to continuously document the environ
4 mental load caused by the production process (emission monitoring) and to optimize the material and energy flow through the production system. Other approaches emerge from the field of ecobalances. This term refers to studies or methods that are used to investigate and evaluate the total mass and energy throughput of a given system. In most cases, the system under investigation is a product life cycle. Such an investigation is then called life cycle analysis or life cycle assessment (LCA). The goal is to assess the environmental impacts of a product from cradle to grave, i.e., from the extraction of raw materials up to waste disposal. There is a growing number of software tools for LCA (MIET93). A general tool for modeling systems of mass and energy flow (at the company, production process, and product life cycle levels) based on Petri Nets was proposed by Schmidt et al. (SCHM94). Other industrial applications of environmental information processing are found in logistics, where the ecological challenge has led to the concept of eco-logistics. In this new field, methods of modeling and simulation are used to assess the resource efficiency and the specific emission rates of alternative logistical strategies (HILT94a). 5. ENVIRONMENTAL INFORMATION PROCESSING SYSTEMS There is a broad spectrum of environmental information processing systems which can be differentiated based on the nature of the information to be processed. This includes monitoring and control systems, conventional information systems, computation and analysis systems, planning and decision support systems, and integrated environmental information systems (PAGE92). Monitoring and control systems interact very closely with environmental objects and processes. Monitoring systems serve in the automation of measurements (including remote sensing) in water, air, soil, noise, and radiation control. These also includes preliminary analysis: time series data need to be aggregated, environmental objects need to be classified (e.g., in satellite images), and chemical substances need to be identified based on the measured data. Computerized process control is either directly employed in environmental technology such as in air or exhaust gas cleaning, sewage, sludge, or refuse processing, or used in production process automation with secondary effects on environmental protection (e.g., energy conservation, emission reduction). Monitoring and control systems often require the processing of vague information, e.g., using the evidence theory of Dempster and Shafer, fuzzy logic, or artificial neural networks. Conventional information systems are systems for input, storage, structuring, integration, retrieval, and presentation of various kinds of environmental information such as raw measurement data, descriptions of environmental objects (such as geographic objects or chemical substances), as well as formal, semi-formal and unformal documents such as environmental regulations or literature references. Spatial and temporal aspects often play an important role in the management of these kinds of information. Various kinds of software tools, including geographic information systems, hypermedia systems, thesauri, etc., are necessary for coping with all of these data. Computational evaluation and analysis systems support the processing of environmental data using complex mathematical-statistical analysis methods and modeling techniques. This includes simulating and forecasting various environmental scenarios. Possible applications of - 4 -
5 these systems are the identification of possible causes of various kinds of environmental loads or the derivation of possible effects of different planning scenarios (e.g., causal models in forest damage research or forecast of emission loads over time and region). Planning and decision support systems directly support decision makers by offering criteria for the evaluation of alternatives or for justifying decisions, e.g., for comparing eco-balances or approving eco-audits, for conducting environmental impact analyses, and for handling hazardous substances. Integrated environmental information systems, as the last category mentioned, cannot be uniquely associated with a single system class, since they consist of multiple components serving various purposes. It can be expected that integrated environmental information systems will be increasingly designed as distributed systems. The integration of various concepts for information processing, which is required for building these kinds of systems, presents a special challenge to the discipline of applied computer science, with similar importance to other application fields. 6. FROM DATA TO INFORMATION Environmental data differ from traditional data in many respects. Often the data are related to a certain location and time interval. Measurement data that are acquired for discrete locations and points in time belong to a special category; these data need to be interpolated if continuous profiles are required (e.g., air pollution data or elevation models). A special case is image data (e.g., satellite sensor data), which typically consist of very large raster data sets. NASA experts often handle terabytes of satellite data; this is more than two orders of magnitude greater than the amount of data managed today in large international financial transaction systems. This requires new storage models for environmental databases, e.g., the use of automatic tape archives and CD ROM jukeboxes as tertiary storage medium. The most demanding problem concerns the derivation of the requested information from the existing data. Usually, the transition from data to information requires an appropriate application of algorithms on data, possibly in an iterative way, and supported by an appropriate model or theory of the application domain. Models may have to be calibrated, algorithms may have to be parameterized, and, depending on the results, these processes may have to be repeated. These tasks are very demanding and require massive knowledge processing and the availability of an appropriate model base. In addition, the translation of information into reports, documentations, balances, etc. needs to be supported by appropriate report generators and publishing tools. In the ideal case, an environmental database contains all the necessary data which are needed to conduct these translation processes and to derive the information requested by the user. Apart from the raw environmental data, this requires the availability of additional information, known as metainformation (RADE91). In a broad sense, this includes information about location, time, precision, and revision dates of the data under consideration, as well as descriptions of the data structures and data formats used. Metainformation is missing today in most existing environmental information processing systems. Often the only data source consists of a magnetic tape containing the raw data (e.g., image data or measurement data) to be analyzed. All of the additional information which is necessary for the correct interpretation of the raw data is implicitly coded in the application - 5 -
6 programs or must be contributed by the user. Such a tape may become completely useless after a change of the personnel or of the data processing software. Therefore, environmental metainformation systems, also known - with a reduced scope - as environmental data directories (SCHÜ93), are currently being developed to overcome the prevailing lack of metainformation. They constitute one of the central scientific challenges to be adressed in this field, as does coping with heterogeneous hard- and software, as well as network environments. 7. SPATIOTEMPORAL ASPECTS Environmental data often describe environmental objects with a spatial and temporal extent. These objects, also known as geographic objects, possess a geometry consisting of point-form (0D), linear (1D), flat (2D), or solid (3D) features. Often geographic objects also have a lifetime which is given by their dates of construction and destruction. During the lifetime of an environmental object, its attributes may change. That is, the values of the attributes are only valid during a certain time interval, and a given attribute (e.g., the population of a city or the land use of a parcel) may possess many possible values during the lifetime of the object. A special case is the change of the geometry of a geographic object such as the growth of a city or the shrinking of a lake or a forest. The adequate representation of spatio-temporal environmental objects is a special challenge to applied computer scientists. Abstract data types are required for representing concepts such as the partonomy, the topology, and the spatio-temporal extension of geographic objects as well as the thematic information associated with these objects, such as alpha-numeric attributes and relationships to other geographic objects. An important task is also the (carto-)graphic presentation of these objects. In most cases, non-standard data types are required for representing these kinds of information and, therefore, a trend towards systems which allow the definition of such data types, such as extended relational or object-oriented databases (CACM91), can be recognized in current developments (GÜNT93). The special nature of environmental data also requires a query language with special characteristics. Apart from typical SQL-like questions, the forthcoming object-oriented database management systems (CATT93) also allow navigational queries and queries that include userdefined predicates. In particular the latter allows the usage of spatio-temporal predicates in queries. The optimization of spatio-temporal query-processing is a scientifically demanding problem which concerns both storage models and indexing techniques for multi-dimensional data. The integration of these techniques with existing databases is a hard problem which will still require major research activities in the future. 8. OVERCOMING THE HETEROGENEITY The harmonization of environmental information at national, European and worldwide levels is of central importance for gaining a reliable description of the environmental situation and, at the same time, is a basic requirement for any reporting system in this context. These requirements, however, are confronted with the existing heterogeneity of hardware and software environments, of database systems, of method bases, of network technology, and of various computer languages. Approaches for overcoming the heterogeneity, one of the major - 6 -
7 obstacles to open software solutions, can have a tremendous impact on the productivity in environmental management, and can also lead to a greater stability in system design and system usage. The task of overcoming heterogeneity is a challenge which is mainly addressed to applied computer science and which must be tackled primarily by applied computer science. Doubtless the development and promotion of standards is of particular importance in this respect. Experience shows, however, that we will still have to cope with competing standards in the future. In addition, technological advances will always produce new heterogeneity problems and will require strategies for migrating the software towards new solutions. The proper handling of questions of this kind is very important for obtaining powerful solutions in the environmental domain. A pragmatic usage of the currently evolving architectures such as client/server architectures, object request brokers, hypermedia technology for identifying and accessing services and data, and remote procedure components are important in this field (RIEK94). 9. ENVIRONMENTAL INFORMATICS The solution of the versatile, strongly interrelated, and highly interdisciplinary tasks in the environmental field requires the intensive use of modern information processing methods and techniques. This has led to a new scientific discipline, known as Environmental Informatics. This discipline has been maturing since the eighties. In Germany this is nicely documented by the yearly conference series on Environmental Informatics. These conferences, which have been organized by the working group Informatics in Environmental Protection in the German Society for Informatics (GI) since 1987, have yielded a growing number of participants, projects, and publications (e.g., JAES93, PAGE94, HILT94b). Today, environmental informatics is an integral part of applied computer science. It provides methodological support for computer utilization in environmental protection by combining advanced research fields such as database systems, geographic information systems, modeling and simulation, computer graphics, user interfaces, neural networks, knowledge processing, and systems integration. REFERENCES CACM91 Special Section: Next Generation Database Systems. Communications of the ACM. 34(10):30-120, October CATT93 Cattel, R.G.G.: The Object Database Standard: ODMG-93. Morgan Kaufmann, COMM93 Commission of the European Communities: Council Regulation (EEC) No. 1836/93 of 29 June 1993 allowing participation by companies in the industrial sector in a Community eco-management and audit scheme. Official Journal of the European Communities, L168/1-18, 10 July FAW94 FAW Ulm (ed.): Umweltmanagement Herausforderung für den Mittelstand. Reihe Wissensverarbeitung und Gesellschaft, Band 7, Universitätsverlag Ulm, GÜNT93 Günther, O.; Riekert, W.-F.: The Design of GODOT: An Object-Oriented Geographic Information System. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin 16(3), September,
8 GÜNT94 Günther, O.; Radermacher, F.J.; Riekert, W.-F.: Umweltmonitoring: Modelle, Methoden und Systeme. In PAGE94, pp HAAS92 Haasis, H.D., Rentz, O.: Umwelt-PPS Ein weiterer Baustein der CIM- Architektur? In: Görke, W.; Rininsland, H.; Syrbe, M. (eds.): Information als Produktionsfaktor. Proceedings 22. GI-Jahrestagung Karlsruhe, 28. Sept. 2. Okt. 1992, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, HILT94a Hilty, L.M.; Page, B.; Martinssen, D.: Designing a Simulation Tool for the Environmental Assessment of Logistical Systems and Strategies. In: Guariso, G.; Page, B. (eds.): Computer Support for Environmental Impact Assessment. IFIP Transactions B-16. North-Holland, Amsterdam HILT94b Hilty, L.M.; Jaeschke, A.; Page, B.; Schwabl, A. (eds.): Umweltinformatik 94 Environmental Informatics 94, Proceedings. Hamburg. Metropolis Verlag, Marburg JAES93 Jaeschke, A.; Kämpke, T.; Page, B.; Radermacher, F.J.: Informatik für den Umweltschutz. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, LITT93 Little, B.; Pedersen Weidema, B: Environmental Management Systems. In: Pedersen Weidema, B. (Ed.): Environmental Assessment of Products. UETP-EEE The Finnish Association of Graduate Engineers, Helsinki MAYE93 Mayer-Föll, R.: Das Umweltinformationssystem Baden-Württemberg; Zielsetzung und Stand der Realisierung. In: JAES93, pp MIET93 Miettinen, P.: Software Tools in Life Cycle Assessment. In: Pedersen Weidema, B. (Ed.): Environmental Assessment of Products. UETP-EEE The Finnish Association of Graduate Engineers, Helsinki PAGE92 PAGE94 RADE91 RIEK94 SCHM94 SCHÜ93 Page, B.: Environmental Protection as a Challenge to Applied Informatics A Workshop Introduction. In: Aiken, R. (ed): Education and Society. Information Processing 92, Volume II. Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. (North Holland), pp , Page, B.; Hilty, L.M. (eds.): Umweltinformatik. Informatikmethoden für Umweltschutz und Umweltforschung. Handbuch der Informatik, Band R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München Wien, Radermacher, F.J.: The Importance of Metaknowledge for Environmental Information Systems. In: Günther, O.; Schek, H.-J. (eds.): Large Spatial Databases. Proceedings. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 525, pp Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, Riekert, W.-F.; Henning, I.; Schmidt, F.: Integration von heterogenen Komponenten des Umweltinformationssystems (UIS) Baden-Württemberg. In: 2. Workshop Integration von Umweltdaten, KfK 5314, Kernforschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Schmidt, M.; Giegrich, J.; Hilty, L. M.: Experiences with ecobalances and the development of an interactive software tool. In: HILT94b. Schütz, T.; Lessing, H.: Metainformationen von Umwelt-Datenobjekten Zum Datenmodell des Umwelt-Datenkataloges Niedersachsen. In: JAES93, pp
Cooperative Management of Data and Services for Environmental Applications
 In: F. Huber-Wäschle, H. Schauer, P. Widmayer (Hrsg.): GISI 95 Herausforderungen eines globalen Informationsverbundes für die Informatik. pp. 618 625. Springer-Verlag. Berlin Heidelberg New York, 1995.
In: F. Huber-Wäschle, H. Schauer, P. Widmayer (Hrsg.): GISI 95 Herausforderungen eines globalen Informationsverbundes für die Informatik. pp. 618 625. Springer-Verlag. Berlin Heidelberg New York, 1995.
How To Create A Networked Information System
 In: R. Denzer, D.A. Swayne, G. Schimak (eds.): Environmental Software Systems. Volume 2, Chapman & Hall, London, 1997. Management of Distributed and Heterogeneous Information Resources for Environmental
In: R. Denzer, D.A. Swayne, G. Schimak (eds.): Environmental Software Systems. Volume 2, Chapman & Hall, London, 1997. Management of Distributed and Heterogeneous Information Resources for Environmental
Metadata Support for Customization in Environmental Information Management Systems
 Metadata Support for Customization in Environmental Information Management Systems David Hicks and Klaus Tochtermann 1 Abstract Modern information management technology is an effective means by which to
Metadata Support for Customization in Environmental Information Management Systems David Hicks and Klaus Tochtermann 1 Abstract Modern information management technology is an effective means by which to
The Design of a Multi-catalog System for Distributed Environmental Information Resources
 1 The Design of a Multi-catalog System for Distributed Environmental Information Resources Wolf-Fritz Riekert 1, Gerlinde Wiest 2, Oliver Günther 3, Jan Röttgers 3, Jo van Nouhuys 4, Birgit Mohaupt-Jahr
1 The Design of a Multi-catalog System for Distributed Environmental Information Resources Wolf-Fritz Riekert 1, Gerlinde Wiest 2, Oliver Günther 3, Jan Röttgers 3, Jo van Nouhuys 4, Birgit Mohaupt-Jahr
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WHAT IS A GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM? A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer-based tool for mapping and analyzing spatial data. GIS technology integrates
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WHAT IS A GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM? A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer-based tool for mapping and analyzing spatial data. GIS technology integrates
Review of Environmental Informatics Education in Germany and selected European Universities 2
 EnviroInfo 2009 (Berlin) Environmental Informatics and Industrial Environmental Protection: Concepts, Methods and Tools Review of Environmental Informatics Education in Germany and selected European Universities
EnviroInfo 2009 (Berlin) Environmental Informatics and Industrial Environmental Protection: Concepts, Methods and Tools Review of Environmental Informatics Education in Germany and selected European Universities
DATA MINING TECHNOLOGY. Keywords: data mining, data warehouse, knowledge discovery, OLAP, OLAM.
 DATA MINING TECHNOLOGY Georgiana Marin 1 Abstract In terms of data processing, classical statistical models are restrictive; it requires hypotheses, the knowledge and experience of specialists, equations,
DATA MINING TECHNOLOGY Georgiana Marin 1 Abstract In terms of data processing, classical statistical models are restrictive; it requires hypotheses, the knowledge and experience of specialists, equations,
Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems
 LIBER QUARTERLY, ISSN 1435-5205 LIBER 1999. All rights reserved K.G. Saur, Munich. Printed in Germany Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems by PIOTR CICHOCINSKI ABSTRACT This paper presents
LIBER QUARTERLY, ISSN 1435-5205 LIBER 1999. All rights reserved K.G. Saur, Munich. Printed in Germany Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems by PIOTR CICHOCINSKI ABSTRACT This paper presents
SPATIAL DATA CLASSIFICATION AND DATA MINING
 , pp.-40-44. Available online at http://www. bioinfo. in/contents. php?id=42 SPATIAL DATA CLASSIFICATION AND DATA MINING RATHI J.B. * AND PATIL A.D. Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Jawaharlal
, pp.-40-44. Available online at http://www. bioinfo. in/contents. php?id=42 SPATIAL DATA CLASSIFICATION AND DATA MINING RATHI J.B. * AND PATIL A.D. Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Jawaharlal
Information Management course
 Università degli Studi di Milano Master Degree in Computer Science Information Management course Teacher: Alberto Ceselli Lecture 01 : 06/10/2015 Practical informations: Teacher: Alberto Ceselli (alberto.ceselli@unimi.it)
Università degli Studi di Milano Master Degree in Computer Science Information Management course Teacher: Alberto Ceselli Lecture 01 : 06/10/2015 Practical informations: Teacher: Alberto Ceselli (alberto.ceselli@unimi.it)
Master of Science Service Oriented Architecture for Enterprise. Courses description
 Master of Science Service Oriented Architecture for Enterprise Courses description SCADA and PLC networks The course aims to consolidate and transfer of extensive knowledge regarding the architecture,
Master of Science Service Oriented Architecture for Enterprise Courses description SCADA and PLC networks The course aims to consolidate and transfer of extensive knowledge regarding the architecture,
PRACTICAL DATA MINING IN A LARGE UTILITY COMPANY
 QÜESTIIÓ, vol. 25, 3, p. 509-520, 2001 PRACTICAL DATA MINING IN A LARGE UTILITY COMPANY GEORGES HÉBRAIL We present in this paper the main applications of data mining techniques at Electricité de France,
QÜESTIIÓ, vol. 25, 3, p. 509-520, 2001 PRACTICAL DATA MINING IN A LARGE UTILITY COMPANY GEORGES HÉBRAIL We present in this paper the main applications of data mining techniques at Electricité de France,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Available online at www.sciencedirect.com. Advanced in Control Engineering and Information Science
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Procedia Engineering Engineering 00 (2011) 15 (2011) 000 000 1822 1826 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Procedia Engineering Engineering 00 (2011) 15 (2011) 000 000 1822 1826 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia
Information Visualization WS 2013/14 11 Visual Analytics
 1 11.1 Definitions and Motivation Lot of research and papers in this emerging field: Visual Analytics: Scope and Challenges of Keim et al. Illuminating the path of Thomas and Cook 2 11.1 Definitions and
1 11.1 Definitions and Motivation Lot of research and papers in this emerging field: Visual Analytics: Scope and Challenges of Keim et al. Illuminating the path of Thomas and Cook 2 11.1 Definitions and
Modelling Economic and Ecological Aspects of Inventory Management Strategies within a Component-based Material-flow Simulator
 Modelling Economic and Ecological Aspects of Inventory Management Strategies within a Component-based Material-flow Simulator V. Wohlgemuth 1, B. Page 1, W. Kreutzer 2, O.Gromyko 1, L.Heydt 1 1 Motivation
Modelling Economic and Ecological Aspects of Inventory Management Strategies within a Component-based Material-flow Simulator V. Wohlgemuth 1, B. Page 1, W. Kreutzer 2, O.Gromyko 1, L.Heydt 1 1 Motivation
Designing an Object Relational Data Warehousing System: Project ORDAWA * (Extended Abstract)
 Designing an Object Relational Data Warehousing System: Project ORDAWA * (Extended Abstract) Johann Eder 1, Heinz Frank 1, Tadeusz Morzy 2, Robert Wrembel 2, Maciej Zakrzewicz 2 1 Institut für Informatik
Designing an Object Relational Data Warehousing System: Project ORDAWA * (Extended Abstract) Johann Eder 1, Heinz Frank 1, Tadeusz Morzy 2, Robert Wrembel 2, Maciej Zakrzewicz 2 1 Institut für Informatik
Gerard Mc Nulty Systems Optimisation Ltd gmcnulty@iol.ie/0876697867 BA.,B.A.I.,C.Eng.,F.I.E.I
 Gerard Mc Nulty Systems Optimisation Ltd gmcnulty@iol.ie/0876697867 BA.,B.A.I.,C.Eng.,F.I.E.I Data is Important because it: Helps in Corporate Aims Basis of Business Decisions Engineering Decisions Energy
Gerard Mc Nulty Systems Optimisation Ltd gmcnulty@iol.ie/0876697867 BA.,B.A.I.,C.Eng.,F.I.E.I Data is Important because it: Helps in Corporate Aims Basis of Business Decisions Engineering Decisions Energy
Technology Implications of an Instrumented Planet presented at IFIP WG 10.4 Workshop on Challenges and Directions in Dependability
 Technology Implications of an Instrumented Planet presented at IFIP WG 10.4 Workshop on Challenges and Directions in Dependability Nick Bowen Colin Harrison IBM June 2008 1 Background Global Technology
Technology Implications of an Instrumented Planet presented at IFIP WG 10.4 Workshop on Challenges and Directions in Dependability Nick Bowen Colin Harrison IBM June 2008 1 Background Global Technology
Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 03 Issue 07 July, 2014 Page No. 7058-7064 Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques 1 Dr.A.Shaik
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 03 Issue 07 July, 2014 Page No. 7058-7064 Healthcare Measurement Analysis Using Data mining Techniques 1 Dr.A.Shaik
ICT-ENSURE A 7 th Framework Program Support Action for Building the European Research Area in the Field of ICT for Environmental Sustainability
 EnviroInfo 2008 (Lüneburg) Environmental Informatics and Industrial Ecology ICT-ENSURE A 7 th Framework Program Support Action for Building the European Research Area in the Field of ICT for Environmental
EnviroInfo 2008 (Lüneburg) Environmental Informatics and Industrial Ecology ICT-ENSURE A 7 th Framework Program Support Action for Building the European Research Area in the Field of ICT for Environmental
First Steps towards a Frequent Pattern Mining with Nephrology Data in the Medical Domain. - Extended Abstract -
 First Steps towards a Frequent Pattern Mining with Nephrology Data in the Medical Domain - Extended Abstract - Matthias Niemann 1, Danilo Schmidt 2, Gabriela Lindemann von Trzebiatowski 3, Carl Hinrichs
First Steps towards a Frequent Pattern Mining with Nephrology Data in the Medical Domain - Extended Abstract - Matthias Niemann 1, Danilo Schmidt 2, Gabriela Lindemann von Trzebiatowski 3, Carl Hinrichs
Tokyo University of Information Sciences Graduate School of Informatics
 Tokyo University of Information Sciences Graduate School of Informatics (1) Field of Business and Information Class (Class Code) & Descriptions Advance Study of Marketing Theory (G1-1) Expansion of the
Tokyo University of Information Sciences Graduate School of Informatics (1) Field of Business and Information Class (Class Code) & Descriptions Advance Study of Marketing Theory (G1-1) Expansion of the
Information Services for Smart Grids
 Smart Grid and Renewable Energy, 2009, 8 12 Published Online September 2009 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/sgre/). ABSTRACT Interconnected and integrated electrical power systems, by their very dynamic
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy, 2009, 8 12 Published Online September 2009 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/sgre/). ABSTRACT Interconnected and integrated electrical power systems, by their very dynamic
FACULTY OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AUTUMN 2016 BACHELOR COURSES
 FACULTY OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Please note! This is a preliminary list of courses for the study year 2016/2017. Changes may occur! AUTUMN 2016 BACHELOR COURSES DIP217 Applied Software
FACULTY OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Please note! This is a preliminary list of courses for the study year 2016/2017. Changes may occur! AUTUMN 2016 BACHELOR COURSES DIP217 Applied Software
Introduction to Data Mining
 Bioinformatics Ying Liu, Ph.D. Laboratory for Bioinformatics University of Texas at Dallas Spring 2008 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Motivation: Why data mining? What is data mining? Data Mining: On what
Bioinformatics Ying Liu, Ph.D. Laboratory for Bioinformatics University of Texas at Dallas Spring 2008 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Motivation: Why data mining? What is data mining? Data Mining: On what
Technology Trends In Geoinformation
 Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: drkadir@jupem.gov.my www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: drkadir@jupem.gov.my www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
Data Mining System, Functionalities and Applications: A Radical Review
 Data Mining System, Functionalities and Applications: A Radical Review Dr. Poonam Chaudhary System Programmer, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra Abstract: Data Mining is the process of locating potentially
Data Mining System, Functionalities and Applications: A Radical Review Dr. Poonam Chaudhary System Programmer, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra Abstract: Data Mining is the process of locating potentially
ADVANCED GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Vol. II - Using Ontologies for Geographic Information Intergration Frederico Torres Fonseca
 USING ONTOLOGIES FOR GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION INTEGRATION Frederico Torres Fonseca The Pennsylvania State University, USA Keywords: ontologies, GIS, geographic information integration, interoperability Contents
USING ONTOLOGIES FOR GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION INTEGRATION Frederico Torres Fonseca The Pennsylvania State University, USA Keywords: ontologies, GIS, geographic information integration, interoperability Contents
CHAPTER-24 Mining Spatial Databases
 CHAPTER-24 Mining Spatial Databases 24.1 Introduction 24.2 Spatial Data Cube Construction and Spatial OLAP 24.3 Spatial Association Analysis 24.4 Spatial Clustering Methods 24.5 Spatial Classification
CHAPTER-24 Mining Spatial Databases 24.1 Introduction 24.2 Spatial Data Cube Construction and Spatial OLAP 24.3 Spatial Association Analysis 24.4 Spatial Clustering Methods 24.5 Spatial Classification
The Big Data methodology in computer vision systems
 The Big Data methodology in computer vision systems Popov S.B. Samara State Aerospace University, Image Processing Systems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences Abstract. I consider the advantages of
The Big Data methodology in computer vision systems Popov S.B. Samara State Aerospace University, Image Processing Systems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences Abstract. I consider the advantages of
NAPCS Product List for NAICS 54162: Environmental Consulting Services
 NAPCS List for NAICS : Environmental Consulting Services National 1 Environmental consulting Providing objective information, advice, and guidance to clients concerning the preservation of air, water,
NAPCS List for NAICS : Environmental Consulting Services National 1 Environmental consulting Providing objective information, advice, and guidance to clients concerning the preservation of air, water,
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS
 INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative Analysis of the Main Providers
 60 Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative Analysis of the Main Providers Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative
60 Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative Analysis of the Main Providers Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative
Split Lane Traffic Reporting at Junctions
 Split Lane Traffic Reporting at Junctions White paper 1 Executive summary Split Lane Traffic Reporting at Junctions (SLT) from HERE is a major innovation in real time traffic reporting. The advanced algorithm
Split Lane Traffic Reporting at Junctions White paper 1 Executive summary Split Lane Traffic Reporting at Junctions (SLT) from HERE is a major innovation in real time traffic reporting. The advanced algorithm
Christoph Schlenzig 1
 EnviroInfo 2002 (Wien) Environmental Communication in the Information Society - Proceedings of the 16th Conference The MESAP Software for the German Emission Inventory An integrated information system
EnviroInfo 2002 (Wien) Environmental Communication in the Information Society - Proceedings of the 16th Conference The MESAP Software for the German Emission Inventory An integrated information system
Spatial Data Mining Methods and Problems
 Spatial Data Mining Methods and Problems Abstract Use summarizing method,characteristics of each spatial data mining and spatial data mining method applied in GIS,Pointed out that the space limitations
Spatial Data Mining Methods and Problems Abstract Use summarizing method,characteristics of each spatial data mining and spatial data mining method applied in GIS,Pointed out that the space limitations
COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING
 CHAPTER COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING 1 An overview of CIM is presented in this chapter. A brief account of the evolution of CIM is included. The major functions carried out in a manufacturing plant
CHAPTER COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING 1 An overview of CIM is presented in this chapter. A brief account of the evolution of CIM is included. The major functions carried out in a manufacturing plant
ISTANBUL DECLARATION ON CADASTRE IN THE WORLD CADASTRE SUMMIT 2015
 ISTANBUL DECLARATION ON CADASTRE IN THE WORLD CADASTRE SUMMIT 2015 Let us Cadastre the World... 1. INTRODUCTION Land had represented wealth and power from the first settlement to the end of 1700s. As a
ISTANBUL DECLARATION ON CADASTRE IN THE WORLD CADASTRE SUMMIT 2015 Let us Cadastre the World... 1. INTRODUCTION Land had represented wealth and power from the first settlement to the end of 1700s. As a
USING COMPLEX EVENT PROCESSING TO MANAGE PATTERNS IN DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS
 USING COMPLEX EVENT PROCESSING TO MANAGE PATTERNS IN DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS Foued BAROUNI Eaton Canada FouedBarouni@eaton.com Bernard MOULIN Laval University Canada Bernard.Moulin@ift.ulaval.ca ABSTRACT
USING COMPLEX EVENT PROCESSING TO MANAGE PATTERNS IN DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS Foued BAROUNI Eaton Canada FouedBarouni@eaton.com Bernard MOULIN Laval University Canada Bernard.Moulin@ift.ulaval.ca ABSTRACT
Towards Analytical Data Management for Numerical Simulations
 Towards Analytical Data Management for Numerical Simulations Ramon G. Costa, Fábio Porto, Bruno Schulze {ramongc, fporto, schulze}@lncc.br National Laboratory for Scientific Computing - RJ, Brazil Abstract.
Towards Analytical Data Management for Numerical Simulations Ramon G. Costa, Fábio Porto, Bruno Schulze {ramongc, fporto, schulze}@lncc.br National Laboratory for Scientific Computing - RJ, Brazil Abstract.
GIS Initiative: Developing an atmospheric data model for GIS. Olga Wilhelmi (ESIG), Jennifer Boehnert (RAP/ESIG) and Terri Betancourt (RAP)
 GIS Initiative: Developing an atmospheric data model for GIS Olga Wilhelmi (ESIG), Jennifer Boehnert (RAP/ESIG) and Terri Betancourt (RAP) Unidata seminar August 30, 2004 Presentation Outline Overview
GIS Initiative: Developing an atmospheric data model for GIS Olga Wilhelmi (ESIG), Jennifer Boehnert (RAP/ESIG) and Terri Betancourt (RAP) Unidata seminar August 30, 2004 Presentation Outline Overview
HUGO BOSS ENVIRONMENTAL COMMITMENT. Our claim. Our approach
 HUGO BOSS ENVIRONMENTAL COMMITMENT HUGO BOSS assumes responsibility for future generations. This entails that we also pursue our high standards for quality and performance in environmental protection.
HUGO BOSS ENVIRONMENTAL COMMITMENT HUGO BOSS assumes responsibility for future generations. This entails that we also pursue our high standards for quality and performance in environmental protection.
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Why Data Mining? Explosive Growth of Data Data collection and data availability Automated data collection tools, Internet, smartphones, Major sources of abundant data Business:
Introduction to Data Mining 1 Why Data Mining? Explosive Growth of Data Data collection and data availability Automated data collection tools, Internet, smartphones, Major sources of abundant data Business:
Process Automation Markets 2010
 PRESS RELEASE Important Findings of the New Market, Strategy, and Technology Report Process Automation Markets 2010 Development of the automation world market for the process industries until 2010 World
PRESS RELEASE Important Findings of the New Market, Strategy, and Technology Report Process Automation Markets 2010 Development of the automation world market for the process industries until 2010 World
Data Quality Mining: Employing Classifiers for Assuring consistent Datasets
 Data Quality Mining: Employing Classifiers for Assuring consistent Datasets Fabian Grüning Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Germany, fabian.gruening@informatik.uni-oldenburg.de Abstract: Independent
Data Quality Mining: Employing Classifiers for Assuring consistent Datasets Fabian Grüning Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Germany, fabian.gruening@informatik.uni-oldenburg.de Abstract: Independent
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization
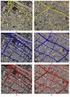 Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
ARTICLE Cloud Computing in automation technology
 Author: Klaus Hübschle, Josha Dittgen, Thomas Gaus Created on: June 2015 Version: 1.0 Fig. 1: Promising future anticipated for cloud computing in automation technology. All key facts that you should know
Author: Klaus Hübschle, Josha Dittgen, Thomas Gaus Created on: June 2015 Version: 1.0 Fig. 1: Promising future anticipated for cloud computing in automation technology. All key facts that you should know
The Scientific Data Mining Process
 Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
Collecting and Analyzing Big Data for O&G Exploration and Production Applications October 15, 2013 G&G Technology Seminar
 Eldad Weiss Founder and Chairman Collecting and Analyzing Big Data for O&G Exploration and Production Applications October 15, 2013 G&G Technology Seminar About Paradigm 700+ 26 700+ 29 7 15,000+ 15+ 200M+
Eldad Weiss Founder and Chairman Collecting and Analyzing Big Data for O&G Exploration and Production Applications October 15, 2013 G&G Technology Seminar About Paradigm 700+ 26 700+ 29 7 15,000+ 15+ 200M+
Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables
 Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables Praveen Kumar 1, Peter Bajcsy 2, David Tcheng 2, David Clutter 2, Vikas Mehra 1, Wei-Wen Feng 2, Pratyush
Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables Praveen Kumar 1, Peter Bajcsy 2, David Tcheng 2, David Clutter 2, Vikas Mehra 1, Wei-Wen Feng 2, Pratyush
Integration of Sustainable Approaches in the Building Design Process
 Integration of Sustainable Approaches in the Building Design Process U. Forgber, N. Kohler, V. Koch, University of Karlsruhe Englerstrasse 7 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany F. Schmidt, R. Haller, University of
Integration of Sustainable Approaches in the Building Design Process U. Forgber, N. Kohler, V. Koch, University of Karlsruhe Englerstrasse 7 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany F. Schmidt, R. Haller, University of
A Hypertext-based Information Retrieval Network for Environmental Protection Regulations
 W. Geiger, A. Jaeschke, D. Rentz, E. Simon, T. Spengler, L. Zilliox, T. Zundel (Hrsg.): Umweltinformatik 97 11. Internationales Symposium. Straßburg, 10.-12. Sept. 1997. Tagungsband, Metropolis-Verlag,
W. Geiger, A. Jaeschke, D. Rentz, E. Simon, T. Spengler, L. Zilliox, T. Zundel (Hrsg.): Umweltinformatik 97 11. Internationales Symposium. Straßburg, 10.-12. Sept. 1997. Tagungsband, Metropolis-Verlag,
Introduction. Introduction. Spatial Data Mining: Definition WHAT S THE DIFFERENCE?
 Introduction Spatial Data Mining: Progress and Challenges Survey Paper Krzysztof Koperski, Junas Adhikary, and Jiawei Han (1996) Review by Brad Danielson CMPUT 695 01/11/2007 Authors objectives: Describe
Introduction Spatial Data Mining: Progress and Challenges Survey Paper Krzysztof Koperski, Junas Adhikary, and Jiawei Han (1996) Review by Brad Danielson CMPUT 695 01/11/2007 Authors objectives: Describe
01219211 Software Development Training Camp 1 (0-3) Prerequisite : 01204214 Program development skill enhancement camp, at least 48 person-hours.
 (International Program) 01219141 Object-Oriented Modeling and Programming 3 (3-0) Object concepts, object-oriented design and analysis, object-oriented analysis relating to developing conceptual models
(International Program) 01219141 Object-Oriented Modeling and Programming 3 (3-0) Object concepts, object-oriented design and analysis, object-oriented analysis relating to developing conceptual models
DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7
 DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7 Contents GIS and maps The visualization process Visualization and strategies
DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7 Contents GIS and maps The visualization process Visualization and strategies
Material models as recorders of academic communities: A new project on university collections in Germany
 Material models as recorders of academic communities: A new project on university collections in Germany CORNELIA WEBER Abstract Transdisciplinary research on university collections is most rewarding.
Material models as recorders of academic communities: A new project on university collections in Germany CORNELIA WEBER Abstract Transdisciplinary research on university collections is most rewarding.
LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE MEMORANDUM
 LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE MEMORANDUM DATE: May 5, 2000 TO: Academic Senate Equivalency Committee FROM: John Hugunin Department Head for CBIS SUBJECT: Equivalency statement for Computer Science Instructor
LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE MEMORANDUM DATE: May 5, 2000 TO: Academic Senate Equivalency Committee FROM: John Hugunin Department Head for CBIS SUBJECT: Equivalency statement for Computer Science Instructor
ONTOLOGY-BASED APPROACH TO DEVELOPMENT OF ADJUSTABLE KNOWLEDGE INTERNET PORTAL FOR SUPPORT OF RESEARCH ACTIVITIY
 ONTOLOGY-BASED APPROACH TO DEVELOPMENT OF ADJUSTABLE KNOWLEDGE INTERNET PORTAL FOR SUPPORT OF RESEARCH ACTIVITIY Yu. A. Zagorulko, O. I. Borovikova, S. V. Bulgakov, E. A. Sidorova 1 A.P.Ershov s Institute
ONTOLOGY-BASED APPROACH TO DEVELOPMENT OF ADJUSTABLE KNOWLEDGE INTERNET PORTAL FOR SUPPORT OF RESEARCH ACTIVITIY Yu. A. Zagorulko, O. I. Borovikova, S. V. Bulgakov, E. A. Sidorova 1 A.P.Ershov s Institute
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK A SURVEY ON BIG DATA ISSUES AMRINDER KAUR Assistant Professor, Department of Computer
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK A SURVEY ON BIG DATA ISSUES AMRINDER KAUR Assistant Professor, Department of Computer
NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND THEIR IMPACT ON AGRICULTURE, ENVIRONMENT AND THE FOOD INDUSTRY
 NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND THEIR IMPACT ON AGRICULTURE, ENVIRONMENT AND THE FOOD INDUSTRY Gerhard Schiefer, schiefer@uni-bonn.de University of Bonn, Germany Abstract: The agri-food sector is facing global challenges
NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND THEIR IMPACT ON AGRICULTURE, ENVIRONMENT AND THE FOOD INDUSTRY Gerhard Schiefer, schiefer@uni-bonn.de University of Bonn, Germany Abstract: The agri-food sector is facing global challenges
Principles and Practices of Data Integration
 Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
ATLAS2000 Atlases of the Future in Internet
 ATLAS2000 Atlases of the Future in Internet M. Friedrich Institute for Physical Geography, University of Freiburg i.br., Germany (mafri@ipg.uni-freiburg.de) M. Melle Institute for Computer Science, University
ATLAS2000 Atlases of the Future in Internet M. Friedrich Institute for Physical Geography, University of Freiburg i.br., Germany (mafri@ipg.uni-freiburg.de) M. Melle Institute for Computer Science, University
STATISTICA Solutions for Financial Risk Management Management and Validated Compliance Solutions for the Banking Industry (Basel II)
 STATISTICA Solutions for Financial Risk Management Management and Validated Compliance Solutions for the Banking Industry (Basel II) With the New Basel Capital Accord of 2001 (BASEL II) the banking industry
STATISTICA Solutions for Financial Risk Management Management and Validated Compliance Solutions for the Banking Industry (Basel II) With the New Basel Capital Accord of 2001 (BASEL II) the banking industry
An Intelligent Approach for Integrity of Heterogeneous and Distributed Databases Systems based on Mobile Agents
 An Intelligent Approach for Integrity of Heterogeneous and Distributed Databases Systems based on Mobile Agents M. Anber and O. Badawy Department of Computer Engineering, Arab Academy for Science and Technology
An Intelligent Approach for Integrity of Heterogeneous and Distributed Databases Systems based on Mobile Agents M. Anber and O. Badawy Department of Computer Engineering, Arab Academy for Science and Technology
GAO EARTH OBSERVING SYSTEM. Concentration on Near-term EOSDIS Development May Jeopardize Long-term Success i
 GAO United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics, Committee on Science, House of Representatives For Release on Delivery Expected at 9 a.m. TtJurSdaY,
GAO United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics, Committee on Science, House of Representatives For Release on Delivery Expected at 9 a.m. TtJurSdaY,
Master s Program in Information Systems
 The University of Jordan King Abdullah II School for Information Technology Department of Information Systems Master s Program in Information Systems 2006/2007 Study Plan Master Degree in Information Systems
The University of Jordan King Abdullah II School for Information Technology Department of Information Systems Master s Program in Information Systems 2006/2007 Study Plan Master Degree in Information Systems
ACQUIRING, ORGANISING AND PRESENTING INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE ON THE WEB. Pavol Návrat
 Computing and Informatics, Vol. 28, 2009, 393 398 ACQUIRING, ORGANISING AND PRESENTING INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE ON THE WEB Pavol Návrat Institute of Informatics and Software Engineering Faculty of Informatics
Computing and Informatics, Vol. 28, 2009, 393 398 ACQUIRING, ORGANISING AND PRESENTING INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE ON THE WEB Pavol Návrat Institute of Informatics and Software Engineering Faculty of Informatics
Digital Preservation. OAIS Reference Model
 Digital Preservation OAIS Reference Model Stephan Strodl, Andreas Rauber Institut für Softwaretechnik und Interaktive Systeme TU Wien http://www.ifs.tuwien.ac.at/dp Aim OAIS model Understanding the functionality
Digital Preservation OAIS Reference Model Stephan Strodl, Andreas Rauber Institut für Softwaretechnik und Interaktive Systeme TU Wien http://www.ifs.tuwien.ac.at/dp Aim OAIS model Understanding the functionality
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction
 Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
PART 1. Representations of atmospheric phenomena
 PART 1 Representations of atmospheric phenomena Atmospheric data meet all of the criteria for big data : they are large (high volume), generated or captured frequently (high velocity), and represent a
PART 1 Representations of atmospheric phenomena Atmospheric data meet all of the criteria for big data : they are large (high volume), generated or captured frequently (high velocity), and represent a
A STUDY OF DATA MINING ACTIVITIES FOR MARKET RESEARCH
 205 A STUDY OF DATA MINING ACTIVITIES FOR MARKET RESEARCH ABSTRACT MR. HEMANT KUMAR*; DR. SARMISTHA SARMA** *Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology (IT), Institute of Innovation in Technology
205 A STUDY OF DATA MINING ACTIVITIES FOR MARKET RESEARCH ABSTRACT MR. HEMANT KUMAR*; DR. SARMISTHA SARMA** *Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology (IT), Institute of Innovation in Technology
Revealing the Where of Business
 Revealing the Where of Business Intelligence using Location Analytics Brought to you compliments of: Increasingly, data is viewed as the lifeblood of organizations. Across industries, information is sliced,
Revealing the Where of Business Intelligence using Location Analytics Brought to you compliments of: Increasingly, data is viewed as the lifeblood of organizations. Across industries, information is sliced,
ASSIGNMENT OF ITM 613 DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM
 ASSIGNMENT OF ITM 613 DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM Lecture: Prof. Kudang B. Seminar, MSc, PhD By: DEDI PRIYANTO G051124031 BOGOR AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY MASTER OF SCIENCE IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FOR NATURAL
ASSIGNMENT OF ITM 613 DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM Lecture: Prof. Kudang B. Seminar, MSc, PhD By: DEDI PRIYANTO G051124031 BOGOR AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY MASTER OF SCIENCE IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FOR NATURAL
Service-Oriented Visualization of Virtual 3D City Models
 Service-Oriented Visualization of Virtual 3D City Models Authors: Jan Klimke, Jürgen Döllner Computer Graphics Systems Division Hasso-Plattner-Institut, University of Potsdam, Germany http://www.hpi3d.de
Service-Oriented Visualization of Virtual 3D City Models Authors: Jan Klimke, Jürgen Döllner Computer Graphics Systems Division Hasso-Plattner-Institut, University of Potsdam, Germany http://www.hpi3d.de
Relational Databases in the Cloud
 Contact Information: February 2011 zimory scale White Paper Relational Databases in the Cloud Target audience CIO/CTOs/Architects with medium to large IT installations looking to reduce IT costs by creating
Contact Information: February 2011 zimory scale White Paper Relational Databases in the Cloud Target audience CIO/CTOs/Architects with medium to large IT installations looking to reduce IT costs by creating
Data mining and official statistics
 Quinta Conferenza Nazionale di Statistica Data mining and official statistics Gilbert Saporta président de la Société française de statistique 5@ S Roma 15, 16, 17 novembre 2000 Palazzo dei Congressi Piazzale
Quinta Conferenza Nazionale di Statistica Data mining and official statistics Gilbert Saporta président de la Société française de statistique 5@ S Roma 15, 16, 17 novembre 2000 Palazzo dei Congressi Piazzale
7th Framework Programme Theme 6 Environment (including climate change)
 7th Framework Programme Theme 6 Environment (including climate change) «Environnement» et «Énergie» Programme D. Deybe DG RTD Environment Directorate 1 Cooperation Collaborative Research Ten themes 1.
7th Framework Programme Theme 6 Environment (including climate change) «Environnement» et «Énergie» Programme D. Deybe DG RTD Environment Directorate 1 Cooperation Collaborative Research Ten themes 1.
Big Data Strategies Creating Customer Value In Utilities
 Big Data Strategies Creating Customer Value In Utilities National Conference ICT For Energy And Utilities Sofia, October 2013 Valery Peykov Country CIO Bulgaria Veolia Environnement 17.10.2013 г. One Core
Big Data Strategies Creating Customer Value In Utilities National Conference ICT For Energy And Utilities Sofia, October 2013 Valery Peykov Country CIO Bulgaria Veolia Environnement 17.10.2013 г. One Core
Big Data Just Noise or Does it Matter?
 Big Data Just Noise or Does it Matter? Opportunities for Continuous Auditing Presented by: Solon Angel Product Manager Servers The CaseWare Group. Founded in 1988. An industry leader in providing technology
Big Data Just Noise or Does it Matter? Opportunities for Continuous Auditing Presented by: Solon Angel Product Manager Servers The CaseWare Group. Founded in 1988. An industry leader in providing technology
Cleaner Production as a Graduate Level Energy and Environmental Engineering and Management Course at AIT
 Cleaner Production as a Graduate Level Energy and Environmental Engineering and Management Course at AIT C. Visvanathan and S. Kumar School of Environment. Resources and Development, Asian Institute of
Cleaner Production as a Graduate Level Energy and Environmental Engineering and Management Course at AIT C. Visvanathan and S. Kumar School of Environment. Resources and Development, Asian Institute of
Web-based Information Systems: Data Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting for Measurements and Simulations
 Web-based Information Systems: Data Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting for Measurements and Simulations Frank Molkenthin, TU Berlin (frank@bauinf.tu-cottbus.de) Summary This paper describes the concept,
Web-based Information Systems: Data Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting for Measurements and Simulations Frank Molkenthin, TU Berlin (frank@bauinf.tu-cottbus.de) Summary This paper describes the concept,
HYBRID MODELLING AND ANALYSIS OF UNCERTAIN DATA
 HYBRID MODELLING AND ANALYSIS OF UNCERTAIN DATA Michael GLEMSER, Ulrike KLEIN Institute for Photogrammetry (ifp), Stuttgart University, Germany Geschwister-Scholl-Strasse 24D, D-7074 Stuttgart Michael.Glemser@ifp.uni-stuttgart.de
HYBRID MODELLING AND ANALYSIS OF UNCERTAIN DATA Michael GLEMSER, Ulrike KLEIN Institute for Photogrammetry (ifp), Stuttgart University, Germany Geschwister-Scholl-Strasse 24D, D-7074 Stuttgart Michael.Glemser@ifp.uni-stuttgart.de
Knowledge-Based Visualization to Support Spatial Data Mining
 Knowledge-Based Visualization to Support Spatial Data Mining Gennady Andrienko and Natalia Andrienko GMD - German National Research Center for Information Technology Schloss Birlinghoven, Sankt-Augustin,
Knowledge-Based Visualization to Support Spatial Data Mining Gennady Andrienko and Natalia Andrienko GMD - German National Research Center for Information Technology Schloss Birlinghoven, Sankt-Augustin,
Brazil, the land of the future, needs for a resource-conserving waste management:
 Brazil, the land of the future, needs for a resource-conserving waste management: Even in the 21st. century? a reliable environmental legislation and a complete implementation government funds to promote
Brazil, the land of the future, needs for a resource-conserving waste management: Even in the 21st. century? a reliable environmental legislation and a complete implementation government funds to promote
A Contribution to Expert Decision-based Virtual Product Development
 A Contribution to Expert Decision-based Virtual Product Development László Horváth, Imre J. Rudas Institute of Intelligent Engineering Systems, John von Neumann Faculty of Informatics, Óbuda University,
A Contribution to Expert Decision-based Virtual Product Development László Horváth, Imre J. Rudas Institute of Intelligent Engineering Systems, John von Neumann Faculty of Informatics, Óbuda University,
Implementing an Imagery Management System at Mexican Navy
 Implementing an Imagery Management System at Mexican Navy The Mexican Navy safeguards 11,000 kilometers of Mexican coastlines, inland water bodies suitable for navigation, and the territorial sea and maritime
Implementing an Imagery Management System at Mexican Navy The Mexican Navy safeguards 11,000 kilometers of Mexican coastlines, inland water bodies suitable for navigation, and the territorial sea and maritime
Exploratory Data Analysis for Ecological Modelling and Decision Support
 Exploratory Data Analysis for Ecological Modelling and Decision Support Gennady Andrienko & Natalia Andrienko Fraunhofer Institute AIS Sankt Augustin Germany http://www.ais.fraunhofer.de/and 5th ECEM conference,
Exploratory Data Analysis for Ecological Modelling and Decision Support Gennady Andrienko & Natalia Andrienko Fraunhofer Institute AIS Sankt Augustin Germany http://www.ais.fraunhofer.de/and 5th ECEM conference,
Center of Maritime Technologies e.v. A Maritime Network for Research and Innovation
 Center of Maritime Technologies e.v. A Maritime Network for Research and Innovation The association Center of Maritime Technologies e.v. (CMT) - Centre of the national network of maritime innovation CMT
Center of Maritime Technologies e.v. A Maritime Network for Research and Innovation The association Center of Maritime Technologies e.v. (CMT) - Centre of the national network of maritime innovation CMT
Some Thoughts on Climate Change and Software Engineering Research
 Some Thoughts on Climate Change and Software Engineering Research Lin Liu 1, He Zhang 1, Sheikh Iqbal Ahamed 2 1 School of Software, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China 2 Department of Mathematics, Statistics
Some Thoughts on Climate Change and Software Engineering Research Lin Liu 1, He Zhang 1, Sheikh Iqbal Ahamed 2 1 School of Software, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China 2 Department of Mathematics, Statistics
Strategien für einen einheitlichen Zugang zu Umweltinformation
 Strategien für einen einheitlichen Zugang zu Umweltinformation Ergebnisse aus dem Projekt ICT-ENSURE Werner Pillmann IGU Internationale Gesellschaft für Umweltschutz, Wien Workshop AK Umweltinformationssysteme
Strategien für einen einheitlichen Zugang zu Umweltinformation Ergebnisse aus dem Projekt ICT-ENSURE Werner Pillmann IGU Internationale Gesellschaft für Umweltschutz, Wien Workshop AK Umweltinformationssysteme
Maximization versus environmental compliance
 Maximization versus environmental compliance Increase use of alternative fuels with no risk for quality and environment Reprint from World Cement March 2005 Dr. Eduardo Gallestey, ABB, Switzerland, discusses
Maximization versus environmental compliance Increase use of alternative fuels with no risk for quality and environment Reprint from World Cement March 2005 Dr. Eduardo Gallestey, ABB, Switzerland, discusses
Impact of Big Data in Oil & Gas Industry. Pranaya Sangvai Reliance Industries Limited 04 Feb 15, DEJ, Mumbai, India.
 Impact of Big Data in Oil & Gas Industry Pranaya Sangvai Reliance Industries Limited 04 Feb 15, DEJ, Mumbai, India. New Age Information 2.92 billions Internet Users in 2014 Twitter processes 7 terabytes
Impact of Big Data in Oil & Gas Industry Pranaya Sangvai Reliance Industries Limited 04 Feb 15, DEJ, Mumbai, India. New Age Information 2.92 billions Internet Users in 2014 Twitter processes 7 terabytes
Miracle Integrating Knowledge Management and Business Intelligence
 ALLGEMEINE FORST UND JAGDZEITUNG (ISSN: 0002-5852) Available online www.sauerlander-verlag.com/ Miracle Integrating Knowledge Management and Business Intelligence Nursel van der Haas Technical University
ALLGEMEINE FORST UND JAGDZEITUNG (ISSN: 0002-5852) Available online www.sauerlander-verlag.com/ Miracle Integrating Knowledge Management and Business Intelligence Nursel van der Haas Technical University
AN EFFICIENT SELECTIVE DATA MINING ALGORITHM FOR BIG DATA ANALYTICS THROUGH HADOOP
 AN EFFICIENT SELECTIVE DATA MINING ALGORITHM FOR BIG DATA ANALYTICS THROUGH HADOOP Asst.Prof Mr. M.I Peter Shiyam,M.E * Department of Computer Science and Engineering, DMI Engineering college, Aralvaimozhi.
AN EFFICIENT SELECTIVE DATA MINING ALGORITHM FOR BIG DATA ANALYTICS THROUGH HADOOP Asst.Prof Mr. M.I Peter Shiyam,M.E * Department of Computer Science and Engineering, DMI Engineering college, Aralvaimozhi.
National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP)
 Draft National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP) 1. Introduction 1.1 Data are recognized at all levels as a valuable resource that should be made publicly available and maintained over time
Draft National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP) 1. Introduction 1.1 Data are recognized at all levels as a valuable resource that should be made publicly available and maintained over time
AdTheorent s. The Intelligent Solution for Real-time Predictive Technology in Mobile Advertising. The Intelligent Impression TM
 AdTheorent s Real-Time Learning Machine (RTLM) The Intelligent Solution for Real-time Predictive Technology in Mobile Advertising Worldwide mobile advertising revenue is forecast to reach $11.4 billion
AdTheorent s Real-Time Learning Machine (RTLM) The Intelligent Solution for Real-time Predictive Technology in Mobile Advertising Worldwide mobile advertising revenue is forecast to reach $11.4 billion
Towards a Field-Data-Driven Productivity Analysis and Planning System for Industrial Service
 Towards a Field-Data-Driven Productivity Analysis and Planning System for Industrial Service Simone Turrin, Ralf Gitzel ABB AG, Forschungszentrum Service quality in a maintenance context can be measured
Towards a Field-Data-Driven Productivity Analysis and Planning System for Industrial Service Simone Turrin, Ralf Gitzel ABB AG, Forschungszentrum Service quality in a maintenance context can be measured
Big Workflow: More than Just Intelligent Workload Management for Big Data
 Big Workflow: More than Just Intelligent Workload Management for Big Data Michael Feldman White Paper February 2014 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Big data applications represent a fast-growing category of high-value
Big Workflow: More than Just Intelligent Workload Management for Big Data Michael Feldman White Paper February 2014 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Big data applications represent a fast-growing category of high-value
Data Cleansing for Remote Battery System Monitoring
 Data Cleansing for Remote Battery System Monitoring Gregory W. Ratcliff Randall Wald Taghi M. Khoshgoftaar Director, Life Cycle Management Senior Research Associate Director, Data Mining and Emerson Network
Data Cleansing for Remote Battery System Monitoring Gregory W. Ratcliff Randall Wald Taghi M. Khoshgoftaar Director, Life Cycle Management Senior Research Associate Director, Data Mining and Emerson Network
Programming Risk Assessment Models for Online Security Evaluation Systems
 Programming Risk Assessment Models for Online Security Evaluation Systems Ajith Abraham 1, Crina Grosan 12, Vaclav Snasel 13 1 Machine Intelligence Research Labs, MIR Labs, http://www.mirlabs.org 2 Babes-Bolyai
Programming Risk Assessment Models for Online Security Evaluation Systems Ajith Abraham 1, Crina Grosan 12, Vaclav Snasel 13 1 Machine Intelligence Research Labs, MIR Labs, http://www.mirlabs.org 2 Babes-Bolyai
