6-2. Properties of Parallelograms. Focus on Reasoning INTR O D U C E. Standards for Mathematical Content 1. Investigate parallelograms.
|
|
|
- Amberlynn Daniel
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Focus on Reasoning Essential question: What can you conclude about the sides, angles, and diagonals of a parallelogram? TEH Standards for Mathematical ontent 1 G-O.3.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. G-SRT.2.5 Use congruence... criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Materials: geometry software Questioning Strategies s you use the software to drag points,,, and/or, does the quadrilateral remain a parallelogram? Why? Yes; the lines Vocabulary diagonal that form opposite sides remain parallel. What do you notice about consecutive angles in the parallelogram? Why does this make sense? onsecutive angles are supplementary. Prerequisites Theorems about parallel lines cut by a transversal Triangle congruence criteria This makes sense because opposite sides are parallel, so consecutive angles are same-side interior angles. y the Same-Side Interior ngles Postulate, these angles are supplementary. Math ackground In this lesson, students extend their earlier work with triangle congruence criteria and triangle properties to prove facts about parallelograms. This lesson gives students a chance to use inductive and deductive reasoning to investigate properties of the sides, angles, and diagonals of parallelograms. Students have encountered parallelograms in earlier grades. sk a volunteer to define parallelogram. Students may have only an informal idea of what a parallelogram is (e.g., a slanted rectangle ), so be sure they understand that the mathematical definition of a parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. You may want to show students how they can make a parallelogram by drawing lines on either side of a ruler, changing the position of the ruler, and drawing another pair of lines. sk students to explain why this method creates a parallelogram. 2 Prove that opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Questioning Strategies Why do you think the proof is based on drawing the diagonal? rawing the diagonal creates two triangles; then you can use triangle congruence criteria and PT. 245 Lesson 2 Teaching Strategy Some students may have difficulty with terms like opposite sides or consecutive angles. Remind students that opposite sides of a quadrilateral do not share a vertex (that is, they do not intersect). onsecutive sides of a quadrilateral do share a vertex (that is, they intersect). Opposite angles of a quadrilateral do not share a side. onsecutive angles of a quadrilateral do share a side. You may want to help students draw and label a quadrilateral for reference. INTR O U E hapter 6 Investigate parallelograms.
2 Name lass ate Properties of Parallelograms Focus on Reasoning Essential question: What can you conclude about the sides, angles, and diagonals of a parallelogram? Recall that a parallelogram is a quadrilateral that has two pairs of parallel sides. You use the symbol to name a parallelogram. For example, the figure shows. G-O.3.11, G-SRT Notes 1 Investigate parallelograms. Use the straightedge tool of your geometry software to draw a straight line. Then plot a point that is not on the line. Select the point and line, go to the onstruct menu, and construct a line through the point that is parallel to the line. This will give you a pair of parallel lines, as shown. Repeat Step to construct a second pair of parallel lines that intersect those from Step. The intersections of the parallel lines create a parallelogram. Plot points at these intersections. Label the points,,, and. Use the Measure menu to measure each angle of the parallelogram. E Use the Measure menu to measure the length of each side of the parallelogram. (You can do this by measuring the distance between consecutive vertices.) F rag the points and lines in your construction to change the shape of the parallelogram. s you do so, look for relationships in the measurements. = 2.60 cm = 1.74 cm = 2.60 cm = 1.74 cm m = m = m = m = REFLET 1a. Make a conjecture about the sides and angles of a parallelogram. Opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent. hapter Lesson 2 You may have discovered the following theorem about parallelograms. Theorem If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then opposite sides are congruent. 2 Prove that opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. omplete the proof. Given: is a parallelogram. Prove: _ and Statements Reasons 1. is a parallelogram. 1. Given 2. raw. 2. Through any two points there exists exactly one line. 3. ǁ ; ǁ 3. efinition of parallelogram 4. ; 4. lternate Interior ngles Theorem Reflexive Property of ongruence S ongruence riterion 7. ; 7. PT REFLET 2a. Explain how you can use the rotational symmetry of a parallelogram to give an argument that supports the above theorem. Under a 180 rotation about the center of the parallelogram, each side is mapped to its opposite side. Since rotations preserve distance, this shows that opposite sides are congruent. 2b. One side of a parallelogram is twice as long as another side. The perimeter of the parallelogram is 24 inches. Is it possible to find all the side lengths of the parallelogram? If so, find the lengths. If not, explain why not. Yes; consecutive sides have lengths x, 2x, x, and 2x, so x + 2x + x + 2x = 24, or 6x = 24. Therefore x = 4 and the side lengths are 4 in., 8 in., 4 in., and 8 in. hapter Lesson 2 hapter Lesson 2
3 TEH Investigate diagonals of 3 parallelograms. Materials: geometry software Questioning Strategies How many diagonals does a parallelogram have? Is this true for every quadrilateral? Two; yes If a quadrilateral is named PQRS, what are the diagonals? PR and QS re the diagonals of a parallelogram ever congruent? If so, when does this appear to happen? Yes; when the parallelogram is a rectangle Prove diagonals of a parallelogram 4 bisect each other. Questioning Strategies Why do you think this theorem was introduced after the theorems about the sides and angles of a parallelogram? The proof of this theorem depends upon the fact that opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Highlighting the Standards s students work on the proof in this lesson, ask them to think about how the format of the proof makes it easier to understand the underlying structure of the argument. This addresses elements of Standard 3 (onstruct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others). Students should recognize that a flow proof shows how one statement connects to the next. This may not be as apparent in a two-column format. You may want to have students rewrite the proof in a two-column format as a way of exploring this further. hapter Lesson 2
4 Essential question: What can you conclude about the diagonals of a parallelogram? segment that connects any two nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon is a diagonal. parallelogram has two diagonals. In the figure, and are diagonals of. Notes 3 Investigate diagonals of parallelograms. Use geometry software to construct a parallelogram. (See Lesson 4-2 for detailed instructions.) Label the vertices of the parallelogram,,, and. Use the segment tool to construct the diagonals, and. Plot a point at the intersection of the diagonals. Label this point E. Use the Measure menu to measure the length of E, E, E, and E. (You can do this by measuring the distance between the relevant endpoints.) E rag the points and lines in your construction to change the shape of the parallelogram. s you do so, look for relationships in the measurements. E E = 1.52 cm E = 2.60 cm E = 1.52 cm E = 2.60 cm REFLET 3a. Make a conjecture about the diagonals of a parallelogram. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. 3b. student claims that the perimeter of E is always equal to the perimeter of E. Without doing any further measurements in your construction, explain whether or not you agree with the student s statement. gree; E = E, E = E, and = since opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. So, E + E + = E + E +. hapter Lesson 2 You may have discovered the following theorem about parallelograms. Theorem If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then the diagonals bisect each other. 4 Prove diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. omplete the proof. Given: is a parallelogram. Prove: E E and E E. E E lternate Interior ngles Theorem REFLET efinition of parallelogram is a parallelogram. Given E E lternate Interior ngles Theorem 4a. Explain how you can prove the theorem using a different congruence criterion. E E S ongruence riterion E E and E E. PT E Opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. E E because they are vertical angles. Using this fact plus the fact that E E and, it is possible to prove the theorem using the S ongruence riterion. hapter Lesson 2 hapter Lesson 2
5 Teaching Strategy The lesson concludes with the theorem that states that opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent. The proof of this theorem is left as an exercise (Exercise 1). e sure students recognize that the proof of this theorem is similar to the proof that opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Noticing such similarities is an important problem-solving skill. Highlighting the Standards Exercise 4 is a multi-part exercise that includes opportunities for mathematical modeling, reasoning, and communication. It is a good opportunity to address Standard 4 (Model with mathematics). raw students attention to the way they interpret their mathematical results in the context of the real-world situation. Specifically, ask students to explain what their mathematical findings tell them about the appearance and layout of the park. LOSE Essential Question What can you conclude about the sides, angles, and diagonals of a parallelogram? Opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. Summarize Have students make a graphic organizer to summarize what they know about the sides, angles, and diagonals of a parallelogram. sample is shown below. PRTIE Exercise 1: Students practice what they learned in part 2 of the lesson. Exercise 2: Students use reasoning to extend what they know about parallelograms. Exercise 3: Students use reasoning and/or algebra to find unknown angle measures. Exercise 4: Students apply their learning to solve a multi-step real-world problem. Parallelogram Opposite sides are congruent. The diagonals bisect each other. If E is the point where diagonals and intersect, then E E and E E. Opposite angles are congruent. hapter Lesson 2
6 The angles of a parallelogram also have an important property. It is stated in the following theorem, which you will prove as an exercise. Notes Theorem If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then opposite angles are congruent. PRTIE 1. Prove the above theorem about opposite angles of a parallelogram. Given: is a parallelogram. Prove: and (Hint: You only need to prove that. similar argument can be used to prove that. lso, you may or may not need to use all the rows of the table in your proof.) Statements Reasons 1. is a parallelogram. 1. Given 2. raw Through any two points there. 2. exists exactly one line. 3. ; ; efinition of parallelogram 2. Explain why consecutive angles of a parallelogram are supplementary. lternate Interior ngles Theorem Reflexive Property of ongruence S ongruence riterion PT onsecutive angles of a parallelogram are same-side interior angles for a pair of parallel lines (the opposite sides of the parallelogram), so the angles are supplementary by the Same-Side Interior ngles Postulate. 3. In the figure, JKLM is a parallelogram. Find the measure of each of the numbered angles. J K N m 1 = 19 ; m 2 = 43 ; m 3 = 118 ; m 4 = 118 ; m 5 = M L hapter Lesson 2 4. city planner is designing a park in the shape of a parallelogram. s shown in the figure, there will be two straight paths through which visitors may enter the park. The paths are bisectors of consecutive angles of the parallelogram, and the paths intersect at point P. P a. Work directly on the parallelograms below and use a compass and straightedge to construct the bisectors of and. Then use a protractor to measure P in each case. P Make a conjecture about P. P is a right angle. b. Write a paragraph proof to show that your conjecture is always true. (Hint: Suppose m P = x, m P = y, and m P = z. What do you know about x + y + z? What do you know about 2x + 2y?) y the Triangle Sum Theorem, x + y + z = 180. lso, m = (2x) and m = (2y). y the Same-Side Interior ngles Postulate m + m = 180. So 2x + 2y = 180 and x + y = 90. Substituting this in the first equation gives 90 + z = 180 and z = 90. c. When the city planner takes into account the dimensions of the park, she finds that point P lies on x y x y, as shown. Explain why it must be the case that = 2. (Hint: Use congruent base angles to show z that P and P are isosceles.) P P P since P is an angle bisector. lso, P P by the lternate Interior ngles Theorem. Therefore, P P. This means P is isosceles, with P. Similarly, P. lso, as opposite sides of a parallelogram. So, = P + P = + = + P = 2. hapter Lesson 2 hapter Lesson 2
7 ITIONL PRTIE N PROLEM SOLVING ssign these pages to help your students practice and apply important lesson concepts. For additional exercises, see the Student Edition. nswers dditional Practice cm cm cm (0, -3) 15. Possible answer: Statements Problem Solving 1. m = 135 ; m = 45 Reasons 1. EFG is a parallelogram. 1. Given 2. m EG = m EH + 2. ngle dd. Post. m GH, m FG = m FGH + m GH 3. m EG + m FG = cons. s supp. 4. m EH + m GH + m FGH + m GH = m GH + m GH + m HG = m GH + m GH + m HG = m EH + m GH + m FGH + m GH 7. m HG = m EH + m FGH 4. Subst. (Steps 2, 3) 5. Triangle Sum Thm. 6. Trans. Prop. of = 7. Subtr. Prop. of = in ft H 7. hapter Lesson 2
8 Name lass ate dditional Practice 6-2 Notes hapter Lesson 2 Problem Solving hapter Lesson 2 hapter Lesson 2
1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Which type of construction is best represented by the steps given above?
 1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Step 1: Place the compass on one endpoint of the line segment. Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width
1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Step 1: Place the compass on one endpoint of the line segment. Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width
Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: lass: _ ate: _ I: SSS Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Given the lengths marked on the figure and that bisects E, use SSS to explain
Name: lass: _ ate: _ I: SSS Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Given the lengths marked on the figure and that bisects E, use SSS to explain
Final Review Geometry A Fall Semester
 Final Review Geometry Fall Semester Multiple Response Identify one or more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question. 1. Which graph shows a triangle and its reflection image over
Final Review Geometry Fall Semester Multiple Response Identify one or more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question. 1. Which graph shows a triangle and its reflection image over
Geometry Course Summary Department: Math. Semester 1
 Geometry Course Summary Department: Math Semester 1 Learning Objective #1 Geometry Basics Targets to Meet Learning Objective #1 Use inductive reasoning to make conclusions about mathematical patterns Give
Geometry Course Summary Department: Math Semester 1 Learning Objective #1 Geometry Basics Targets to Meet Learning Objective #1 Use inductive reasoning to make conclusions about mathematical patterns Give
GEOMETRIC FIGURES, AREAS, AND VOLUMES
 HPTER GEOMETRI FIGURES, RES, N VOLUMES carpenter is building a deck on the back of a house. s he works, he follows a plan that he made in the form of a drawing or blueprint. His blueprint is a model of
HPTER GEOMETRI FIGURES, RES, N VOLUMES carpenter is building a deck on the back of a house. s he works, he follows a plan that he made in the form of a drawing or blueprint. His blueprint is a model of
GEOMETRY. Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12
 GEOMETRY Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12 OBJECTIVE Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic
GEOMETRY Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12 OBJECTIVE Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic
Geometry Enduring Understandings Students will understand 1. that all circles are similar.
 High School - Circles Essential Questions: 1. Why are geometry and geometric figures relevant and important? 2. How can geometric ideas be communicated using a variety of representations? ******(i.e maps,
High School - Circles Essential Questions: 1. Why are geometry and geometric figures relevant and important? 2. How can geometric ideas be communicated using a variety of representations? ******(i.e maps,
Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Triangles in Parallelograms I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In this task, students will
 Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Triangles in Parallelograms I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In this task, students will discover and prove the relationship between the triangles
Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Triangles in Parallelograms I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In this task, students will discover and prove the relationship between the triangles
Curriculum Map by Block Geometry Mapping for Math Block Testing 2007-2008. August 20 to August 24 Review concepts from previous grades.
 Curriculum Map by Geometry Mapping for Math Testing 2007-2008 Pre- s 1 August 20 to August 24 Review concepts from previous grades. August 27 to September 28 (Assessment to be completed by September 28)
Curriculum Map by Geometry Mapping for Math Testing 2007-2008 Pre- s 1 August 20 to August 24 Review concepts from previous grades. August 27 to September 28 (Assessment to be completed by September 28)
A summary of definitions, postulates, algebra rules, and theorems that are often used in geometry proofs:
 summary of definitions, postulates, algebra rules, and theorems that are often used in geometry proofs: efinitions: efinition of mid-point and segment bisector M If a line intersects another line segment
summary of definitions, postulates, algebra rules, and theorems that are often used in geometry proofs: efinitions: efinition of mid-point and segment bisector M If a line intersects another line segment
Selected practice exam solutions (part 5, item 2) (MAT 360)
 Selected practice exam solutions (part 5, item ) (MAT 360) Harder 8,91,9,94(smaller should be replaced by greater )95,103,109,140,160,(178,179,180,181 this is really one problem),188,193,194,195 8. On
Selected practice exam solutions (part 5, item ) (MAT 360) Harder 8,91,9,94(smaller should be replaced by greater )95,103,109,140,160,(178,179,180,181 this is really one problem),188,193,194,195 8. On
Geometry. Higher Mathematics Courses 69. Geometry
 The fundamental purpose of the course is to formalize and extend students geometric experiences from the middle grades. This course includes standards from the conceptual categories of and Statistics and
The fundamental purpose of the course is to formalize and extend students geometric experiences from the middle grades. This course includes standards from the conceptual categories of and Statistics and
Mathematics Geometry Unit 1 (SAMPLE)
 Review the Geometry sample year-long scope and sequence associated with this unit plan. Mathematics Possible time frame: Unit 1: Introduction to Geometric Concepts, Construction, and Proof 14 days This
Review the Geometry sample year-long scope and sequence associated with this unit plan. Mathematics Possible time frame: Unit 1: Introduction to Geometric Concepts, Construction, and Proof 14 days This
New York State Student Learning Objective: Regents Geometry
 New York State Student Learning Objective: Regents Geometry All SLOs MUST include the following basic components: Population These are the students assigned to the course section(s) in this SLO all students
New York State Student Learning Objective: Regents Geometry All SLOs MUST include the following basic components: Population These are the students assigned to the course section(s) in this SLO all students
39 Symmetry of Plane Figures
 39 Symmetry of Plane Figures In this section, we are interested in the symmetric properties of plane figures. By a symmetry of a plane figure we mean a motion of the plane that moves the figure so that
39 Symmetry of Plane Figures In this section, we are interested in the symmetric properties of plane figures. By a symmetry of a plane figure we mean a motion of the plane that moves the figure so that
Chapter 3.1 Angles. Geometry. Objectives: Define what an angle is. Define the parts of an angle.
 Chapter 3.1 Angles Define what an angle is. Define the parts of an angle. Recall our definition for a ray. A ray is a line segment with a definite starting point and extends into infinity in only one direction.
Chapter 3.1 Angles Define what an angle is. Define the parts of an angle. Recall our definition for a ray. A ray is a line segment with a definite starting point and extends into infinity in only one direction.
Algebra III. Lesson 33. Quadrilaterals Properties of Parallelograms Types of Parallelograms Conditions for Parallelograms - Trapezoids
 Algebra III Lesson 33 Quadrilaterals Properties of Parallelograms Types of Parallelograms Conditions for Parallelograms - Trapezoids Quadrilaterals What is a quadrilateral? Quad means? 4 Lateral means?
Algebra III Lesson 33 Quadrilaterals Properties of Parallelograms Types of Parallelograms Conditions for Parallelograms - Trapezoids Quadrilaterals What is a quadrilateral? Quad means? 4 Lateral means?
Lesson 18: Looking More Carefully at Parallel Lines
 Student Outcomes Students learn to construct a line parallel to a given line through a point not on that line using a rotation by 180. They learn how to prove the alternate interior angles theorem using
Student Outcomes Students learn to construct a line parallel to a given line through a point not on that line using a rotation by 180. They learn how to prove the alternate interior angles theorem using
POTENTIAL REASONS: Definition of Congruence:
 Sec 6 CC Geometry Triangle Pros Name: POTENTIAL REASONS: Definition Congruence: Having the exact same size and shape and there by having the exact same measures. Definition Midpoint: The point that divides
Sec 6 CC Geometry Triangle Pros Name: POTENTIAL REASONS: Definition Congruence: Having the exact same size and shape and there by having the exact same measures. Definition Midpoint: The point that divides
Duplicating Segments and Angles
 CONDENSED LESSON 3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles In this lesson, you Learn what it means to create a geometric construction Duplicate a segment by using a straightedge and a compass and by using patty
CONDENSED LESSON 3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles In this lesson, you Learn what it means to create a geometric construction Duplicate a segment by using a straightedge and a compass and by using patty
Conjectures. Chapter 2. Chapter 3
 Conjectures Chapter 2 C-1 Linear Pair Conjecture If two angles form a linear pair, then the measures of the angles add up to 180. (Lesson 2.5) C-2 Vertical Angles Conjecture If two angles are vertical
Conjectures Chapter 2 C-1 Linear Pair Conjecture If two angles form a linear pair, then the measures of the angles add up to 180. (Lesson 2.5) C-2 Vertical Angles Conjecture If two angles are vertical
Geometry 8-1 Angles of Polygons
 . Sum of Measures of Interior ngles Geometry 8-1 ngles of Polygons 1. Interior angles - The sum of the measures of the angles of each polygon can be found by adding the measures of the angles of a triangle.
. Sum of Measures of Interior ngles Geometry 8-1 ngles of Polygons 1. Interior angles - The sum of the measures of the angles of each polygon can be found by adding the measures of the angles of a triangle.
Lesson 3.1 Duplicating Segments and Angles
 Lesson 3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles In Exercises 1 3, use the segments and angles below. Q R S 1. Using only a compass and straightedge, duplicate each segment and angle. There is an arc in each
Lesson 3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles In Exercises 1 3, use the segments and angles below. Q R S 1. Using only a compass and straightedge, duplicate each segment and angle. There is an arc in each
Discovering Math: Exploring Geometry Teacher s Guide
 Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Mathematics Lesson Duration: Three class periods Program Description Discovering Math: Exploring Geometry From methods of geometric construction and threedimensional
Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Mathematics Lesson Duration: Three class periods Program Description Discovering Math: Exploring Geometry From methods of geometric construction and threedimensional
GEOMETRY CONCEPT MAP. Suggested Sequence:
 CONCEPT MAP GEOMETRY August 2011 Suggested Sequence: 1. Tools of Geometry 2. Reasoning and Proof 3. Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 4. Congruent Triangles 5. Relationships Within Triangles 6. Polygons
CONCEPT MAP GEOMETRY August 2011 Suggested Sequence: 1. Tools of Geometry 2. Reasoning and Proof 3. Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 4. Congruent Triangles 5. Relationships Within Triangles 6. Polygons
Angles that are between parallel lines, but on opposite sides of a transversal.
 GLOSSARY Appendix A Appendix A: Glossary Acute Angle An angle that measures less than 90. Acute Triangle Alternate Angles A triangle that has three acute angles. Angles that are between parallel lines,
GLOSSARY Appendix A Appendix A: Glossary Acute Angle An angle that measures less than 90. Acute Triangle Alternate Angles A triangle that has three acute angles. Angles that are between parallel lines,
Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary TERM DEFINITION GEOMETRIC FIGURE. Cannot be defined by using other figures.
 Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary 1.1 Undefined terms Cannot be defined by using other figures. Point A specific location. It has no dimension and is represented by a dot. Line Plane A connected straight path.
Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary 1.1 Undefined terms Cannot be defined by using other figures. Point A specific location. It has no dimension and is represented by a dot. Line Plane A connected straight path.
2.1. Inductive Reasoning EXAMPLE A
 CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Inductive Reasoning In this lesson you will Learn how inductive reasoning is used in science and mathematics Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures about sequences of numbers
CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Inductive Reasoning In this lesson you will Learn how inductive reasoning is used in science and mathematics Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures about sequences of numbers
Grade 8 Mathematics Geometry: Lesson 2
 Grade 8 Mathematics Geometry: Lesson 2 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
Grade 8 Mathematics Geometry: Lesson 2 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
Geometry 1. Unit 3: Perpendicular and Parallel Lines
 Geometry 1 Unit 3: Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Geometry 1 Unit 3 3.1 Lines and Angles Lines and Angles Parallel Lines Parallel lines are lines that are coplanar and do not intersect. Some examples
Geometry 1 Unit 3: Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Geometry 1 Unit 3 3.1 Lines and Angles Lines and Angles Parallel Lines Parallel lines are lines that are coplanar and do not intersect. Some examples
Unit 2 - Triangles. Equilateral Triangles
 Equilateral Triangles Unit 2 - Triangles Equilateral Triangles Overview: Objective: In this activity participants discover properties of equilateral triangles using properties of symmetry. TExES Mathematics
Equilateral Triangles Unit 2 - Triangles Equilateral Triangles Overview: Objective: In this activity participants discover properties of equilateral triangles using properties of symmetry. TExES Mathematics
How does one make and support a reasonable conclusion regarding a problem? How does what I measure influence how I measure?
 Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Mathematics Grade/Course Grade 7 Unit 3 Two and Three Dimensional Geometry Duration 23 instructional days (+4 days reteaching/enrichment)
Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Mathematics Grade/Course Grade 7 Unit 3 Two and Three Dimensional Geometry Duration 23 instructional days (+4 days reteaching/enrichment)
Week 1 Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Geometry. Week 2 Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Geometry. Week 3 Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Geometry Chapter 1 Test
 Thinkwell s Homeschool Geometry Course Lesson Plan: 34 weeks Welcome to Thinkwell s Homeschool Geometry! We re thrilled that you ve decided to make us part of your homeschool curriculum. This lesson plan
Thinkwell s Homeschool Geometry Course Lesson Plan: 34 weeks Welcome to Thinkwell s Homeschool Geometry! We re thrilled that you ve decided to make us part of your homeschool curriculum. This lesson plan
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Thursday, January 26, 2012 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXMINTION GEOMETRY Thursday, January 26, 2012 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXMINTION GEOMETRY Thursday, January 26, 2012 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name
Lesson 1: Introducing Circles
 IRLES N VOLUME Lesson 1: Introducing ircles ommon ore Georgia Performance Standards M9 12.G..1 M9 12.G..2 Essential Questions 1. Why are all circles similar? 2. What are the relationships among inscribed
IRLES N VOLUME Lesson 1: Introducing ircles ommon ore Georgia Performance Standards M9 12.G..1 M9 12.G..2 Essential Questions 1. Why are all circles similar? 2. What are the relationships among inscribed
Geometry Module 4 Unit 2 Practice Exam
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry Module 4 Unit 2 Practice Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which diagram shows the most useful positioning
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry Module 4 Unit 2 Practice Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which diagram shows the most useful positioning
Estimating Angle Measures
 1 Estimating Angle Measures Compare and estimate angle measures. You will need a protractor. 1. Estimate the size of each angle. a) c) You can estimate the size of an angle by comparing it to an angle
1 Estimating Angle Measures Compare and estimate angle measures. You will need a protractor. 1. Estimate the size of each angle. a) c) You can estimate the size of an angle by comparing it to an angle
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Tuesday, August 13, 2013 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Tuesday, August 13, 2013 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any communications
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Tuesday, August 13, 2013 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any communications
3.1. Angle Pairs. What s Your Angle? Angle Pairs. ACTIVITY 3.1 Investigative. Activity Focus Measuring angles Angle pairs
 SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share, Use Manipulatives Two rays with a common endpoint form an angle. The common endpoint is called the vertex. You can use a protractor to draw and measure
SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share, Use Manipulatives Two rays with a common endpoint form an angle. The common endpoint is called the vertex. You can use a protractor to draw and measure
GEOMETRY COMMON CORE STANDARDS
 1st Nine Weeks Experiment with transformations in the plane G-CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
1st Nine Weeks Experiment with transformations in the plane G-CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Classifying Quadrilaterals
 1 lassifying Quadrilaterals Identify and sort quadrilaterals. 1. Which of these are parallelograms?,, quadrilateral is a closed shape with 4 straight sides. trapezoid has exactly 1 pair of parallel sides.
1 lassifying Quadrilaterals Identify and sort quadrilaterals. 1. Which of these are parallelograms?,, quadrilateral is a closed shape with 4 straight sides. trapezoid has exactly 1 pair of parallel sides.
Definitions, Postulates and Theorems
 Definitions, s and s Name: Definitions Complementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 o Supplementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 o A statement that can be proven
Definitions, s and s Name: Definitions Complementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 o Supplementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 o A statement that can be proven
Lesson 2: Circles, Chords, Diameters, and Their Relationships
 Circles, Chords, Diameters, and Their Relationships Student Outcomes Identify the relationships between the diameters of a circle and other chords of the circle. Lesson Notes Students are asked to construct
Circles, Chords, Diameters, and Their Relationships Student Outcomes Identify the relationships between the diameters of a circle and other chords of the circle. Lesson Notes Students are asked to construct
Quadrilaterals GETTING READY FOR INSTRUCTION
 Quadrilaterals / Mathematics Unit: 11 Lesson: 01 Duration: 7 days Lesson Synopsis: In this lesson students explore properties of quadrilaterals in a variety of ways including concrete modeling, patty paper
Quadrilaterals / Mathematics Unit: 11 Lesson: 01 Duration: 7 days Lesson Synopsis: In this lesson students explore properties of quadrilaterals in a variety of ways including concrete modeling, patty paper
CCGPS UNIT 3 Semester 1 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Page 1 of 32. Circles and Volumes Name:
 GPS UNIT 3 Semester 1 NLYTI GEOMETRY Page 1 of 3 ircles and Volumes Name: ate: Understand and apply theorems about circles M9-1.G..1 Prove that all circles are similar. M9-1.G.. Identify and describe relationships
GPS UNIT 3 Semester 1 NLYTI GEOMETRY Page 1 of 3 ircles and Volumes Name: ate: Understand and apply theorems about circles M9-1.G..1 Prove that all circles are similar. M9-1.G.. Identify and describe relationships
The Triangle and its Properties
 THE TRINGLE ND ITS PROPERTIES 113 The Triangle and its Properties Chapter 6 6.1 INTRODUCTION triangle, you have seen, is a simple closed curve made of three line segments. It has three vertices, three
THE TRINGLE ND ITS PROPERTIES 113 The Triangle and its Properties Chapter 6 6.1 INTRODUCTION triangle, you have seen, is a simple closed curve made of three line segments. It has three vertices, three
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Thursday, August 13, 2015 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 13, 2015 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any communications
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 13, 2015 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any communications
with functions, expressions and equations which follow in units 3 and 4.
 Grade 8 Overview View unit yearlong overview here The unit design was created in line with the areas of focus for grade 8 Mathematics as identified by the Common Core State Standards and the PARCC Model
Grade 8 Overview View unit yearlong overview here The unit design was created in line with the areas of focus for grade 8 Mathematics as identified by the Common Core State Standards and the PARCC Model
Intermediate Math Circles October 10, 2012 Geometry I: Angles
 Intermediate Math Circles October 10, 2012 Geometry I: Angles Over the next four weeks, we will look at several geometry topics. Some of the topics may be familiar to you while others, for most of you,
Intermediate Math Circles October 10, 2012 Geometry I: Angles Over the next four weeks, we will look at several geometry topics. Some of the topics may be familiar to you while others, for most of you,
Geometry of 2D Shapes
 Name: Geometry of 2D Shapes Answer these questions in your class workbook: 1. Give the definitions of each of the following shapes and draw an example of each one: a) equilateral triangle b) isosceles
Name: Geometry of 2D Shapes Answer these questions in your class workbook: 1. Give the definitions of each of the following shapes and draw an example of each one: a) equilateral triangle b) isosceles
Parallel and Perpendicular. We show a small box in one of the angles to show that the lines are perpendicular.
 CONDENSED L E S S O N. Parallel and Perpendicular In this lesson you will learn the meaning of parallel and perpendicular discover how the slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines are related use slopes
CONDENSED L E S S O N. Parallel and Perpendicular In this lesson you will learn the meaning of parallel and perpendicular discover how the slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines are related use slopes
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking Deeply About Simple Things
 The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking Deeply About Simple Things PCMI SSTP Tuesday, July 15 th, 2008 By Troy Jones Willowcreek Middle School Important Terms (the word line may be replaced by the word
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking Deeply About Simple Things PCMI SSTP Tuesday, July 15 th, 2008 By Troy Jones Willowcreek Middle School Important Terms (the word line may be replaced by the word
Situation: Proving Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane
 Situation: Proving Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 1 Prepared at the University of Georgia EMAT 6500 Date Last Revised: 07/31/013 Michael Ferra Prompt A teacher in a high school Coordinate Algebra
Situation: Proving Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 1 Prepared at the University of Georgia EMAT 6500 Date Last Revised: 07/31/013 Michael Ferra Prompt A teacher in a high school Coordinate Algebra
A Correlation of Pearson Texas Geometry Digital, 2015
 A Correlation of Pearson Texas Geometry Digital, 2015 To the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Geometry, High School, and the Texas English Language Proficiency Standards (ELPS) Correlations
A Correlation of Pearson Texas Geometry Digital, 2015 To the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Geometry, High School, and the Texas English Language Proficiency Standards (ELPS) Correlations
Tangent Properties. Line m is a tangent to circle O. Point T is the point of tangency.
 CONDENSED LESSON 6.1 Tangent Properties In this lesson you will Review terms associated with circles Discover how a tangent to a circle and the radius to the point of tangency are related Make a conjecture
CONDENSED LESSON 6.1 Tangent Properties In this lesson you will Review terms associated with circles Discover how a tangent to a circle and the radius to the point of tangency are related Make a conjecture
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. biconditional statement. conclusion. conditional statement. conjecture.
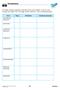 CHAPTER Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. biconditional statement conclusion
CHAPTER Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. biconditional statement conclusion
Right Triangles 4 A = 144 A = 16 12 5 A = 64
 Right Triangles If I looked at enough right triangles and experimented a little, I might eventually begin to notice a relationship developing if I were to construct squares formed by the legs of a right
Right Triangles If I looked at enough right triangles and experimented a little, I might eventually begin to notice a relationship developing if I were to construct squares formed by the legs of a right
CAMI Education linked to CAPS: Mathematics
 - 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers _CAPS curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 12 Ordering and comparing whole numbers Revise prime numbers to
- 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers _CAPS curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 12 Ordering and comparing whole numbers Revise prime numbers to
END OF COURSE GEOMETRY CORE 1
 SESSION: 24 PE: 1 5/5/04 13:29 OIN IS-glenn PT: @sunultra1/raid/s_tpc/rp_va_sprg04/o_04-ribsg11/iv_g11geom-1 VIRINI STNRS O ERNIN SSESSMENTS Spring 2004 Released Test EN O OURSE EOMETRY ORE 1 Property
SESSION: 24 PE: 1 5/5/04 13:29 OIN IS-glenn PT: @sunultra1/raid/s_tpc/rp_va_sprg04/o_04-ribsg11/iv_g11geom-1 VIRINI STNRS O ERNIN SSESSMENTS Spring 2004 Released Test EN O OURSE EOMETRY ORE 1 Property
Circle Theorems. This circle shown is described an OT. As always, when we introduce a new topic we have to define the things we wish to talk about.
 Circle s circle is a set of points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, called the center. The center is often used to name the circle. T This circle shown is described an OT. s always,
Circle s circle is a set of points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, called the center. The center is often used to name the circle. T This circle shown is described an OT. s always,
CONGRUENCE BASED ON TRIANGLES
 HTR 174 5 HTR TL O ONTNTS 5-1 Line Segments ssociated with Triangles 5-2 Using ongruent Triangles to rove Line Segments ongruent and ngles ongruent 5-3 Isosceles and quilateral Triangles 5-4 Using Two
HTR 174 5 HTR TL O ONTNTS 5-1 Line Segments ssociated with Triangles 5-2 Using ongruent Triangles to rove Line Segments ongruent and ngles ongruent 5-3 Isosceles and quilateral Triangles 5-4 Using Two
Name Period 11/2 11/13
 Name Period 11/2 11/13 Vocabulary erms: ongruent orresponding Parts ongruency statement Included angle Included side GOMY UNI 6 ONGUN INGL HL Non-included side Hypotenuse Leg 11/5 and 11/12 eview 11/6,,
Name Period 11/2 11/13 Vocabulary erms: ongruent orresponding Parts ongruency statement Included angle Included side GOMY UNI 6 ONGUN INGL HL Non-included side Hypotenuse Leg 11/5 and 11/12 eview 11/6,,
Triangle Similarity: AA, SSS, SAS Quiz
 Name: lass: ate: I: Triangle Similarity:, SSS, SS Quiz Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Explain why the triangles are similar and write a
Name: lass: ate: I: Triangle Similarity:, SSS, SS Quiz Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Explain why the triangles are similar and write a
The Use of Dynamic Geometry Software in the Teaching and Learning of Geometry through Transformations
 The Use of Dynamic Geometry Software in the Teaching and Learning of Geometry through Transformations Dynamic geometry technology should be used to maximize student learning in geometry. Such technology
The Use of Dynamic Geometry Software in the Teaching and Learning of Geometry through Transformations Dynamic geometry technology should be used to maximize student learning in geometry. Such technology
Conjectures for Geometry for Math 70 By I. L. Tse
 Conjectures for Geometry for Math 70 By I. L. Tse Chapter Conjectures 1. Linear Pair Conjecture: If two angles form a linear pair, then the measure of the angles add up to 180. Vertical Angle Conjecture:
Conjectures for Geometry for Math 70 By I. L. Tse Chapter Conjectures 1. Linear Pair Conjecture: If two angles form a linear pair, then the measure of the angles add up to 180. Vertical Angle Conjecture:
Geometry Chapter 1. 1.1 Point (pt) 1.1 Coplanar (1.1) 1.1 Space (1.1) 1.2 Line Segment (seg) 1.2 Measure of a Segment
 Geometry Chapter 1 Section Term 1.1 Point (pt) Definition A location. It is drawn as a dot, and named with a capital letter. It has no shape or size. undefined term 1.1 Line A line is made up of points
Geometry Chapter 1 Section Term 1.1 Point (pt) Definition A location. It is drawn as a dot, and named with a capital letter. It has no shape or size. undefined term 1.1 Line A line is made up of points
Geometry and Measurement
 The student will be able to: Geometry and Measurement 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the principles of geometry and measurement and operations using measurements Use the US system of measurement for
The student will be able to: Geometry and Measurement 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the principles of geometry and measurement and operations using measurements Use the US system of measurement for
Geometry Progress Ladder
 Geometry Progress Ladder Maths Makes Sense Foundation End-of-year objectives page 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 2 End-of-block objectives page 3 Maths Makes Sense 3 4 End-of-block objectives page 4 Maths Makes
Geometry Progress Ladder Maths Makes Sense Foundation End-of-year objectives page 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 2 End-of-block objectives page 3 Maths Makes Sense 3 4 End-of-block objectives page 4 Maths Makes
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Student Name:
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, June 17, 2010 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, June 17, 2010 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
Tessellating with Regular Polygons
 Tessellating with Regular Polygons You ve probably seen a floor tiled with square tiles. Squares make good tiles because they can cover a surface without any gaps or overlapping. This kind of tiling is
Tessellating with Regular Polygons You ve probably seen a floor tiled with square tiles. Squares make good tiles because they can cover a surface without any gaps or overlapping. This kind of tiling is
NAME DATE PERIOD. Study Guide and Intervention
 opyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of he McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc. 5-1 M IO tudy Guide and Intervention isectors, Medians, and ltitudes erpendicular isectors and ngle isectors perpendicular bisector
opyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of he McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc. 5-1 M IO tudy Guide and Intervention isectors, Medians, and ltitudes erpendicular isectors and ngle isectors perpendicular bisector
Algebra Geometry Glossary. 90 angle
 lgebra Geometry Glossary 1) acute angle an angle less than 90 acute angle 90 angle 2) acute triangle a triangle where all angles are less than 90 3) adjacent angles angles that share a common leg Example:
lgebra Geometry Glossary 1) acute angle an angle less than 90 acute angle 90 angle 2) acute triangle a triangle where all angles are less than 90 3) adjacent angles angles that share a common leg Example:
11.3 Curves, Polygons and Symmetry
 11.3 Curves, Polygons and Symmetry Polygons Simple Definition A shape is simple if it doesn t cross itself, except maybe at the endpoints. Closed Definition A shape is closed if the endpoints meet. Polygon
11.3 Curves, Polygons and Symmetry Polygons Simple Definition A shape is simple if it doesn t cross itself, except maybe at the endpoints. Closed Definition A shape is closed if the endpoints meet. Polygon
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Thursday, August 16, 2012 8:30 to 11:30 a.m.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 16, 2012 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 16, 2012 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Thursday, August 13, 2009 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 13, 2009 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 13, 2009 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
Conjunction is true when both parts of the statement are true. (p is true, q is true. p^q is true)
 Mathematical Sentence - a sentence that states a fact or complete idea Open sentence contains a variable Closed sentence can be judged either true or false Truth value true/false Negation not (~) * Statement
Mathematical Sentence - a sentence that states a fact or complete idea Open sentence contains a variable Closed sentence can be judged either true or false Truth value true/false Negation not (~) * Statement
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Session 5 Dissections and Proof
 Key Terms for This Session Session 5 Dissections and Proof Previously Introduced midline parallelogram quadrilateral rectangle side-angle-side (SAS) congruence square trapezoid vertex New in This Session
Key Terms for This Session Session 5 Dissections and Proof Previously Introduced midline parallelogram quadrilateral rectangle side-angle-side (SAS) congruence square trapezoid vertex New in This Session
E XPLORING QUADRILATERALS
 E XPLORING QUADRILATERALS E 1 Geometry State Goal 9: Use geometric methods to analyze, categorize and draw conclusions about points, lines, planes and space. Statement of Purpose: The activities in this
E XPLORING QUADRILATERALS E 1 Geometry State Goal 9: Use geometric methods to analyze, categorize and draw conclusions about points, lines, planes and space. Statement of Purpose: The activities in this
Show all work for credit. Attach paper as needed to keep work neat & organized.
 Geometry Semester 1 Review Part 2 Name Show all work for credit. Attach paper as needed to keep work neat & organized. Determine the reflectional (# of lines and draw them in) and rotational symmetry (order
Geometry Semester 1 Review Part 2 Name Show all work for credit. Attach paper as needed to keep work neat & organized. Determine the reflectional (# of lines and draw them in) and rotational symmetry (order
/27 Intro to Geometry Review
 /27 Intro to Geometry Review 1. An acute has a measure of. 2. A right has a measure of. 3. An obtuse has a measure of. 13. Two supplementary angles are in ratio 11:7. Find the measure of each. 14. In the
/27 Intro to Geometry Review 1. An acute has a measure of. 2. A right has a measure of. 3. An obtuse has a measure of. 13. Two supplementary angles are in ratio 11:7. Find the measure of each. 14. In the
The Half-Circle Protractor
 The Half-ircle Protractor Objectives To guide students as they classify angles as acute, right, obtuse, straight, and reflex; and to provide practice using a half-circle protractor to measure and draw
The Half-ircle Protractor Objectives To guide students as they classify angles as acute, right, obtuse, straight, and reflex; and to provide practice using a half-circle protractor to measure and draw
Chapters 6 and 7 Notes: Circles, Locus and Concurrence
 Chapters 6 and 7 Notes: Circles, Locus and Concurrence IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of
Chapters 6 and 7 Notes: Circles, Locus and Concurrence IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Wednesday, January 28, 2015 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Wednesday, January 28, 2015 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Wednesday, January 28, 2015 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any
Mathematics Georgia Performance Standards
 Mathematics Georgia Performance Standards K-12 Mathematics Introduction The Georgia Mathematics Curriculum focuses on actively engaging the students in the development of mathematical understanding by
Mathematics Georgia Performance Standards K-12 Mathematics Introduction The Georgia Mathematics Curriculum focuses on actively engaging the students in the development of mathematical understanding by
Geometry Unit 10 Notes Circles. Syllabus Objective: 10.1 - The student will differentiate among the terms relating to a circle.
 Geometry Unit 0 Notes ircles Syllabus Objective: 0. - The student will differentiate among the terms relating to a circle. ircle the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point,
Geometry Unit 0 Notes ircles Syllabus Objective: 0. - The student will differentiate among the terms relating to a circle. ircle the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point,
Preparation Prepare a set of standard triangle shapes for each student. The shapes are found in the Guess My Rule Cards handout.
 Classifying Triangles Student Probe How are triangles A, B, and C alike? How are triangles A, B, and C different? A B C Answer: They are alike because they each have 3 sides and 3 angles. They are different
Classifying Triangles Student Probe How are triangles A, B, and C alike? How are triangles A, B, and C different? A B C Answer: They are alike because they each have 3 sides and 3 angles. They are different
CK-12 Geometry: Parts of Circles and Tangent Lines
 CK-12 Geometry: Parts of Circles and Tangent Lines Learning Objectives Define circle, center, radius, diameter, chord, tangent, and secant of a circle. Explore the properties of tangent lines and circles.
CK-12 Geometry: Parts of Circles and Tangent Lines Learning Objectives Define circle, center, radius, diameter, chord, tangent, and secant of a circle. Explore the properties of tangent lines and circles.
Centers of Triangles Learning Task. Unit 3
 Centers of Triangles Learning Task Unit 3 Course Mathematics I: Algebra, Geometry, Statistics Overview This task provides a guided discovery and investigation of the points of concurrency in triangles.
Centers of Triangles Learning Task Unit 3 Course Mathematics I: Algebra, Geometry, Statistics Overview This task provides a guided discovery and investigation of the points of concurrency in triangles.
Geometry Made Easy Handbook Common Core Standards Edition
 Geometry Made Easy Handbook ommon ore Standards Edition y: Mary nn asey. S. Mathematics, M. S. Education 2015 Topical Review ook ompany, Inc. ll rights reserved. P. O. ox 328 Onsted, MI. 49265-0328 This
Geometry Made Easy Handbook ommon ore Standards Edition y: Mary nn asey. S. Mathematics, M. S. Education 2015 Topical Review ook ompany, Inc. ll rights reserved. P. O. ox 328 Onsted, MI. 49265-0328 This
Geometry Review Flash Cards
 point is like a star in the night sky. However, unlike stars, geometric points have no size. Think of them as being so small that they take up zero amount of space. point may be represented by a dot on
point is like a star in the night sky. However, unlike stars, geometric points have no size. Think of them as being so small that they take up zero amount of space. point may be represented by a dot on
Angle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles?
 ngle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles? MOUL 11 LSSON 11.1 Parallel Lines ut by a Transversal OMMON OR SSNTIL QUSTION How can you use angle relationships in parallel lines and triangles to
ngle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles? MOUL 11 LSSON 11.1 Parallel Lines ut by a Transversal OMMON OR SSNTIL QUSTION How can you use angle relationships in parallel lines and triangles to
1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes
 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Objective: Name and sketch geometric figures. Key Vocabulary Undefined terms - These words do not have formal definitions, but there is agreement aboutwhat they mean.
1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Objective: Name and sketch geometric figures. Key Vocabulary Undefined terms - These words do not have formal definitions, but there is agreement aboutwhat they mean.
Advanced Euclidean Geometry
 dvanced Euclidean Geometry What is the center of a triangle? ut what if the triangle is not equilateral?? Circumcenter Equally far from the vertices? P P Points are on the perpendicular bisector of a line
dvanced Euclidean Geometry What is the center of a triangle? ut what if the triangle is not equilateral?? Circumcenter Equally far from the vertices? P P Points are on the perpendicular bisector of a line
WORK SCHEDULE: MATHEMATICS 2007
 , K WORK SCHEDULE: MATHEMATICS 00 GRADE MODULE TERM... LO NUMBERS, OPERATIONS AND RELATIONSHIPS able to recognise, represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check
, K WORK SCHEDULE: MATHEMATICS 00 GRADE MODULE TERM... LO NUMBERS, OPERATIONS AND RELATIONSHIPS able to recognise, represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check
EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY: (±50 marks)
 ULIN GMTRY: (±50 marks) Grade theorems:. The line drawn from the centre of a circle perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord. 2. The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the centre of the
ULIN GMTRY: (±50 marks) Grade theorems:. The line drawn from the centre of a circle perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord. 2. The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the centre of the
Circles in Triangles. This problem gives you the chance to: use algebra to explore a geometric situation
 Circles in Triangles This problem gives you the chance to: use algebra to explore a geometric situation A This diagram shows a circle that just touches the sides of a right triangle whose sides are 3 units,
Circles in Triangles This problem gives you the chance to: use algebra to explore a geometric situation A This diagram shows a circle that just touches the sides of a right triangle whose sides are 3 units,
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 8th Grade Unit 6
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 8th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 Measurement Math 806 Measurement Introduction 3 1. Angle Measures and Circles 5 Classify and Measure Angles 5 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines, Part 1 12 Perpendicular
MATH STUDENT BOOK 8th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 Measurement Math 806 Measurement Introduction 3 1. Angle Measures and Circles 5 Classify and Measure Angles 5 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines, Part 1 12 Perpendicular
56 questions (multiple choice, check all that apply, and fill in the blank) The exam is worth 224 points.
 6.1.1 Review: Semester Review Study Sheet Geometry Core Sem 2 (S2495808) Semester Exam Preparation Look back at the unit quizzes and diagnostics. Use the unit quizzes and diagnostics to determine which
6.1.1 Review: Semester Review Study Sheet Geometry Core Sem 2 (S2495808) Semester Exam Preparation Look back at the unit quizzes and diagnostics. Use the unit quizzes and diagnostics to determine which
Chapter 6 Notes: Circles
 Chapter 6 Notes: Circles IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle. Any line segment
Chapter 6 Notes: Circles IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle. Any line segment
