GUIDELINES FOR MEASURING VITAL SIGNS AND WEIGHT LESSON PLAN
|
|
|
- Benjamin Preston
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VITAL SIGNS: GUIDELINES FOR MEASURING VITAL SIGNS AND WEIGHT LESSON PLAN Lesson Overview Time: One Hour This lesson discusses the principles and techniques of measuring vital signs and weight. Although it may be review for most workers, many state regulatory agencies require that this material be taught annually. Learning Goals At the end of this session, the learner will: 1. Demonstrate correct methods of measuring vital signs and weight. 2. Know how to document and report vital signs. 3. Recognize normal ranges for vital signs. Teaching Plan Preparation: Gather the following equipment: blood pressure cuff, stethoscope, thermometer, scale, and forms for documentation. Use the same equipment that is used in your facility for measuring vital signs and weight. Provide a copy of your documentation procedures, or an example of the correct way to document vital signs in your facility, to every learner. Self-Study: If your workers are using this lesson plan for self-study, have them work with at least one other employee (two others is better) so they can check each other s performance of the required skills according to the skills checklist. The learners will need to read all the material, including this teaching plan, take and check the pretest, and perform the skills on the checklists before they receive the certificate. They should also review the correct way to document vital signs in your facility. Introduction: 1. Give all learners a copy of the learning guide, and ask them to complete the pretest by following the instructions in each section. 2. Go over the pretest with the learners, being sure they understand the correct answers, using the answer key. Allow for questions and explanations. What s Normal? Point out to your learners that older adults tend to have slightly lower temperatures that younger people, as well as slightly higher blood pressure, pulse, and respirations. Although older people may be in a lower or higher part of the normal range, this may still be normal for the individual and the age. Some people may have conditions that mean their normal vital signs are different from the ranges given. When a resident can be expected to operate outside the normal range most of the time, the physician should be contacted to establish a normal and acceptable range for the resident. Otherwise, all vital signs outside normal ranges should be reported to the physician. Testing Vital Signs Measurements 1. Give the learners time to review the vital sign measurement techniques on pages 3 and 4 of the learning guide. Allow for questions. 2. Give each learner a copy of the approved documentation used in your facility for recording vital signs. Review the correct procedure in your facility for documenting vital signs and weight. 3. Explain that each learner will demonstrate his or her ability to correctly measure vital signs and weight as the test for this session. 4. Arrange learners into groups of three. Ask one learner in each group to be the resident, while the other two learners measure his or her vital signs and weight. Each learner should document the vital signs they obtain. The vital signs obtained by two different people on the same resident should be very close to the same measurement. Variations should be checked by the teacher to see if there is a problem with the technique used by one of the learners. 5. Have the resident change places with other learners so that everyone has an opportunity to demonstrate their ability to measure vital signs correctly. Use the check-off boxes on pages 3 and 4 of the learning guide to document that each learner has demonstrated the abilities on the checklists, and keep these in your training files. 6. Give the learners their certificates.
2 VITAL SIGNS: GUIDELINES FOR MEASURING VITAL SIGNS AND WEIGHT LEARNING GUIDE PRETEST How Much Do You Know? 1. We measure four vital signs to get a picture of someone s basic health status. What are they? (Circle four) Skin color Strength Temperature Height Blood pressure Pulse Age Respirations Weight 2. Match the vital sign with equipment you might use to measure it: Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood pressure Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Thermometer Watch or clock 3. Write the full name of the vital sign beside the abbreviation: TPR is BP means 4. Three ways to measure temperature are: O stands for A stands for R stands for 5. Match the type of pulse with its location on the body: Brachial Chest Carotid Radial Apical Wrist Inner arm Neck What s Normal? Temperature: Fill in the Chart Our bodies make heat to keep our internal systems working. It is usually a symptom of disease when the body s temperature is above or below its normal range. The normal range varies depending on how the temperature measurement is obtained. Fill in normal ranges on the chart. If measured orally (older adults run at the lower end of the range) If measured rectally or in the ears (tympanic) If measured under the arm (axillary): degrees Fahrenheit degrees Fahrenheit degrees Fahrenheit Pulse: Fill in the Blanks Measuring the pulse tells us how often the heart beats. The normal adult range is from to beats per minute. While it is usually measured at the wrist by placing the fingertips on the radial artery, you may also count it at the chest (apical pulse) with a stethoscope. Respiration: Fill in the Blanks Counting the respirations tells us how many breaths the resident takes. The normal adult range is from to per minute. Blood Pressure: Fill in the Blanks Blood pressure measurement tells us two things about the circulation of blood through the arteries. 1. Systolic pressure tells how much force is being put on the arteries when the heart is contracting and pushing the blood outward through the arteries. This is the top number in a written blood pressure, and is normally between to in adults. A higher range of 140 to 160 systolic pressure is normal for older adults. 2. Diastolic pressure measures how much force is on the arteries when the heart is relaxing and not pushing the blood outward. This is the bottom number in a blood pressure, and a normal adult reading is between to.
3 Learner s Name and Title: Date of Evaluation: Evaluator: Measuring Pulse and Respirations Place the resident s hand in a resting position on a surface, palm up. Feel along the inside of the wrist with your fingertips, locating the pulse below the resident s thumb and just below the bend of the wrist. Do not use your thumb, as it has a strong pulse of its own. Look at your watch and find a starting point. Count the beats you feel for thirty seconds, and then multiply that number by two. If the pulse is irregular, count for a full minute and don t multiply. When you have finished counting the pulse, stay in the same position and watch the resident s chest. It is best if the resident is not aware that you are counting his breathing, because he may alter his breathing rate if he is conscious of being watched. Look at your watch and find a starting point. Count each time the resident s chest rises and falls as one single respiration. Count respirations for thirty seconds and multiply by two. If breathing is irregular, count for a full minute and don t multiply. Document both the pulse and the respirations; writing down the number of heartbeats and the number of breaths you counted per minute. Notify your supervisor of irregularities or measurements outside the normal range. Measuring Body Temperature: Oral Temperature Wait at least fifteen minutes after the resident has eaten, smoked, or had a drink. If using a glass thermometer, hold the end and shake the thermometer by snapping your wrist downward several times, shaking the mercury to the bottom of the glass. If you are using an electronic thermometer, check to be sure it is working. Use equipment designed for oral use, not rectal. Place a disposable cover on the thermometer, or follow your facility s policy for disinfecting thermometers before reusing them. Never wash a glass thermometer in hot water. Be sure the thermometer is not broken, chipped, or cracked. Ask the resident to wet his lips, and then insert the tip of the thermometer under the resident s tongue and slightly to the side. You may have to push a button on an electronic thermometer to activate it. Ask the resident to close his lips over the thermometer. A glass thermometer should stay in place for at least three minutes. An electronic thermometer should stay in place until it beeps. When finished, remove the thermometer from the resident s mouth and dispose of the cover. Hold a glass thermometer horizontally at eye level, turning it until you can see a solid line of mercury. The point at which the line stops is the temperature reading. Electronic thermometers will tell you the temperature with a digital reading. Document the reading. Disinfect and store the thermometer according to policy. Axillary Temperature Under the Arm Hold the thermometer in the center of the resident s armpit for at least nine minutes, or until it beeps. Rectal Temperature Assist the resident to lie on her side with her upper leg pulled up toward her chest as much as possible. Lubricate the covered rectal thermometer or rectal electronic probe and gently insert it no further than one inch into the resident s rectum. Keep the resident covered during this procedure to protect privacy. Hold in place for at least 3 minutes, while supporting the resident to prevent any movement that could cause injury. Be careful to avoid trauma to the rectum. Use gloves and Standard Precautions.
4 Learner s Name and Title: Date of Evaluation: Evaluator: Measuring Blood Pressure The resident should be relaxed and comfortable, either sitting or lying down. Be sure there is no tight clothing restricting circulation on the arm. The arm should be bare. Loose sleeves can be pushed up. Rest the resident s arm on a surface such as a table or chair arm, with the palm up and the arm out straight. The resident should not hold his arm up, as using muscles could raise the pressure. Use a blood pressure cuff that is the right size for the resident. The cuff should fit easily around the arm and overlap, but not be so large that it overlaps itself too far. A cuff that is the wrong size will give an incorrect reading. Wrap the fully deflated cuff snugly (not too tight) around the resident s arm about an inch above the bend in the elbow. The cuff contains a sensor, usually marked with an arrow, which should be placed over the brachial artery. The brachial artery runs along the inside of the arm, on the side next to the body. Place the gauge where you can easily see it. Put your stethoscope earpieces in your ears. Close the valve on the sphygmomanometer bulb. This usually means turning the valve clockwise. Find the brachial pulse by placing your fingers just above the bend in the elbow along the side of the arm closest to the body. Keeping your fingers on the brachial artery, inflate the cuff until you can no longer feel the pulse, and then continue inflating for an additional 30 mm on the gauge. Usually you will inflate the cuff until the gauge reads between 170 and 200. Place the flat disk part of your stethoscope (the diaphragm) on the brachial artery just below the cuff and just above the bend in the elbow. Open the valve on the bulb slowly and steadily, turning it counter-clockwise. The cuff will begin to deflate. Listen closely to the sounds coming through the stethoscope. At the first pulse sound you hear, note the gauge reading. This is the systolic pressure reading. Note the gauge reading again when the pulse sound disappears. This is the diastolic pressure. Deflate the cuff and remove it. Record the blood pressure according to your facility s policy. Weight Measurement Weight is not a vital sign, but changes in weight can be important symptoms of illness. Weigh the resident at about the same time of day each time, using the same scale. Periodically check the scale s accuracy by weighing yourself and comparing this weight with your weight on other scales. Place the scale on a stable, solid surface, preferably a hard floor without carpeting. Have the resident remove shoes and unneeded clothing. Put a paper towel on the scale. Be sure the scale is set at zero before having the resident step on it. Make sure the resident is able to stand safely, and be prepared to provide support. Wait until the scale stops moving before reading the measurement. Document the weight measurement.
5 VITAL SIGNS: PRETEST ANSWER KEY How Much Do You Know? 1. We measure four vital signs to get a picture of someone s basic health status. What are they? (Circle four) Skin color Strength Temperature Height Blood pressure Pulse Age Respirations Weight 2. Match the vital sign with equipment you might use to measure it: Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood pressure Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Thermometer Watch or clock 3. Write the full name of the vital sign beside the abbreviation: TPR is temperature, pulse, respirations BP means blood pressure 4. Three ways to measure temperature are: O stands for orally (by mouth) A stands for axillary (under the arm) R stands for rectally (in the rectum) 5. Match the type of pulse with its location on the body: Brachial Chest Carotid Radial Apical Wrist Inner Arm Neck What s Normal? Temperature Our bodies make heat to keep our internal systems working. It is usually a symptom of disease when the body s temperature is above or below its normal range. The normal range varies depending on how the temperature measurement is obtained. This chart shows normal ranges. If measured orally (older adults run at the lower end of the range) If measured rectally or in the ears (tympanic) If measured under the arm (axillary): 96.5 to 99.6 degrees Fahrenheit 98.6 to 99.6 degrees Fahrenheit 96.6 to 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit Pulse Measuring the pulse tells us how often the heart beats. The normal adult range is from 60 to 100 beats per minute. While it is usually measured at the wrist by placing the fingertips on the radial artery, sometimes you may need to count it at the chest (apical pulse) using a stethoscope. Respiration Counting the respirations tells us how many breaths the resident takes. The normal adult range is from 14 to 25 respirations per minute. Blood Pressure Blood pressure measurement tells us two things about the circulation of blood through the arteries. 1. Systolic pressure tells us how much force is being put on the arteries when the heart is contracting and pushing the blood outward through the arteries. This is the top number in a written blood pressure, and is normally between 100 to 140 in adults. A higher range of 140 to 160 systolic pressure is normal for older adults. 2. Diastolic pressure measures how much force is being put on the arteries when the heart is relaxing and not pushing the blood outward. This is the bottom number in a written blood pressure, and a normal adult reading is between 60 to 90.
6 Certificate of Completion Is hereby granted to: To certify satisfactory completion of the one-hour course: Measuring Vital Signs and Weight Participant demonstrated proficiency in measuring vital signs and weight. Date Granted: Facility: Signature of Presenter
MEASURING VITAL SIGNS TRAINING CHECKLIST
 Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
Health Technician skills checklist Health Services Department Lincoln Public Schools TEMPERATURE
 Rev. 2/07 Health Technician skills checklist TEMPERATURE 1. Explain to student what you are going to do. 2. Wait for Welch-Allyn thermometer to beep, then apply probe cover. Make sure probe cover is secure.
Rev. 2/07 Health Technician skills checklist TEMPERATURE 1. Explain to student what you are going to do. 2. Wait for Welch-Allyn thermometer to beep, then apply probe cover. Make sure probe cover is secure.
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group)
 Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors
 How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
Manual Blood Pressure Measurement
 Manual Blood Pressure Measurement 1 Peter Mahoney, CETL Clinical Skills Facilitator Measuring Blood Pressure manually can be difficult if not practised regularly. However it is important to be able to
Manual Blood Pressure Measurement 1 Peter Mahoney, CETL Clinical Skills Facilitator Measuring Blood Pressure manually can be difficult if not practised regularly. However it is important to be able to
Vital and Diagnostic Signs
 GENERAL The four vital signs and the five diagnostic signs evaluated during patient assessment provide valuable information to the care provider, and when recorded properly, to the receiving facility/personnel.
GENERAL The four vital signs and the five diagnostic signs evaluated during patient assessment provide valuable information to the care provider, and when recorded properly, to the receiving facility/personnel.
Blood Pressure Assessment Program Screening Guidelines
 Blood Pressure Assessment Program Screening Guidelines Assessment Pre-Assessment Prior to/during assessment, explain to client the following: What is meant by high blood pressure; What are the effects
Blood Pressure Assessment Program Screening Guidelines Assessment Pre-Assessment Prior to/during assessment, explain to client the following: What is meant by high blood pressure; What are the effects
Standing with legs slightly apart, inhale and expand chest and shoulders; exhale and draw in chest and shoulders.
 ILLUSTRATED EXERCISE #4 PAGE 1 2012 Bringing the Body to the Stage and Screen and Beyond by Annette Lust 1 Standing with legs slightly apart, inhale and expand chest and shoulders; exhale and draw in chest
ILLUSTRATED EXERCISE #4 PAGE 1 2012 Bringing the Body to the Stage and Screen and Beyond by Annette Lust 1 Standing with legs slightly apart, inhale and expand chest and shoulders; exhale and draw in chest
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate
 Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
P R E S S U R E P O I N T S S E R I E S : Measuring your blood pressure at home
 P R E S S U R E P O I N T S S E R I E S : NO.5 Measuring your blood pressure at home B L O O D P R E S S U R E A S S O C I AT I O N Pressure Points series Pressure Points is a series of booklets produced
P R E S S U R E P O I N T S S E R I E S : NO.5 Measuring your blood pressure at home B L O O D P R E S S U R E A S S O C I AT I O N Pressure Points series Pressure Points is a series of booklets produced
Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with
 Instruction Manual Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with Model HEM-609 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction...................................... 3 Important Safety Notes.............................
Instruction Manual Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with Model HEM-609 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction...................................... 3 Important Safety Notes.............................
Take a few minutes for yourself and incorporate some Office Yoga into your daily routine.
 OFFICE YOGA Working in an office or at a computer for prolonged periods of time can put strain on the neck, shoulder and back muscles which in turn can lead to tension and stiffness. This tension can cause
OFFICE YOGA Working in an office or at a computer for prolonged periods of time can put strain on the neck, shoulder and back muscles which in turn can lead to tension and stiffness. This tension can cause
Strengthening Exercises - Below Knee Amputation
 Strengthening Exercises - Below Knee Amputation These exercises will help you strengthen your muscles to best use your prosthetic leg. Do these exercises as directed by your therapist or doctor. Do the
Strengthening Exercises - Below Knee Amputation These exercises will help you strengthen your muscles to best use your prosthetic leg. Do these exercises as directed by your therapist or doctor. Do the
Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* has told you that you may have high blood pressure, also called hypertension.
Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* has told you that you may have high blood pressure, also called hypertension.
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion Exercises
 Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Whole Hand Activities
 Activities Walk & Flip 5 Baton Twirl Rotate the pencil in, around and between all your fingers like it was a baton. 10 Walk your fingers up the pencil (your index will look like an inchworm climbing the
Activities Walk & Flip 5 Baton Twirl Rotate the pencil in, around and between all your fingers like it was a baton. 10 Walk your fingers up the pencil (your index will look like an inchworm climbing the
UNIT 1 Admitting patients
 UNIT 1 Admitting patients Welcoming a patient on admission Checking a patient s identity (ID) bracelet Describing parts of the body Using equipment to take patient Observations Giving instructions to a
UNIT 1 Admitting patients Welcoming a patient on admission Checking a patient s identity (ID) bracelet Describing parts of the body Using equipment to take patient Observations Giving instructions to a
SELF-MASSAGE HANDOUTS
 SELF-MASSAGE HANDOUTS Self-Massage for the Head and Face Self-Massage for the Low Back and Buttocks Self-Massage for Runners Self-Massage for the Neck Self-Massage for the Feet Self-Massage for the Arms
SELF-MASSAGE HANDOUTS Self-Massage for the Head and Face Self-Massage for the Low Back and Buttocks Self-Massage for Runners Self-Massage for the Neck Self-Massage for the Feet Self-Massage for the Arms
How To Stretch Your Body
 Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
MEDICAL ASSISTING CLINICAL
 MEDICAL ASSISTING CLINICAL Purpose: Description of Event: Dress Code: To provide the Health Science student with an opportunity to develop and demonstrate knowledge and skills in clinical medical assisting.
MEDICAL ASSISTING CLINICAL Purpose: Description of Event: Dress Code: To provide the Health Science student with an opportunity to develop and demonstrate knowledge and skills in clinical medical assisting.
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
PTA 210 PTA Technique. Vital Signs
 PTA 210 PTA Technique Vital Signs Review Last Lecture Why learn aseptic technique? 3 modes of infection transmission 3 levels of cleanliness Standard precautions (hand hygiene, PPE, respiratory hygiene,
PTA 210 PTA Technique Vital Signs Review Last Lecture Why learn aseptic technique? 3 modes of infection transmission 3 levels of cleanliness Standard precautions (hand hygiene, PPE, respiratory hygiene,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
Nurse Aide Training Skills
 Nursing Fundamentals 7243 AHSII 7212 (2012 2013 is the last year) Nurse Aide Training Skills Use for 2012 2013 NURSE AIDE TRAINING SUMMARY (NATS) NURSING FUNDAMENTALS 7243 & AHSII 7212 (last year 2012-2013)
Nursing Fundamentals 7243 AHSII 7212 (2012 2013 is the last year) Nurse Aide Training Skills Use for 2012 2013 NURSE AIDE TRAINING SUMMARY (NATS) NURSING FUNDAMENTALS 7243 & AHSII 7212 (last year 2012-2013)
General Guidelines. Neck Stretch: Side. Neck Stretch: Forward. Shoulder Rolls. Side Stretch
 Stretching Exercises General Guidelines Perform stretching exercises at least 2 3 days per week and preferably more Hold each stretch for 15 20 seconds Relax and breathe normally Stretching is most effective
Stretching Exercises General Guidelines Perform stretching exercises at least 2 3 days per week and preferably more Hold each stretch for 15 20 seconds Relax and breathe normally Stretching is most effective
Preventing Falls. Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing
 Preventing Falls Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing Exercise should be comfortable and fun. To get the most out of your home exercise book, join a class for older people to check your exercises
Preventing Falls Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing Exercise should be comfortable and fun. To get the most out of your home exercise book, join a class for older people to check your exercises
How To Use A Thermometer
 Home Healthcare Range Information Module Surgipack Thermometers Caring, Protecting, Supporting Normal Body Temperature What s a normal temperature? Normal body temperatures can vary and are influenced
Home Healthcare Range Information Module Surgipack Thermometers Caring, Protecting, Supporting Normal Body Temperature What s a normal temperature? Normal body temperatures can vary and are influenced
The Super 7 For Tennis Elbow
 Exercises for Tennis elbow Tennis elbow recovery time varies with each person and may take several weeks. Recovery may be faster and more successful when a combination of local injections (e.g. steroids
Exercises for Tennis elbow Tennis elbow recovery time varies with each person and may take several weeks. Recovery may be faster and more successful when a combination of local injections (e.g. steroids
Qigong. Ba Duan Jin. The Eight Pieces of Brocade
 Qigong Ba Duan Jin The Eight Pieces of Brocade by Col and g Hamilton Yiheyuan Martial Arts Contents Page Introduction 2 Preparation 2 1. Hold up the Sky 3 2. The Archer 4 3. Join Heaven and Earth 5 4a.
Qigong Ba Duan Jin The Eight Pieces of Brocade by Col and g Hamilton Yiheyuan Martial Arts Contents Page Introduction 2 Preparation 2 1. Hold up the Sky 3 2. The Archer 4 3. Join Heaven and Earth 5 4a.
stretches and exercises
 stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation
 Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and
 A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca
 www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
This document fully describes the 30 Day Flexibility Challenge and allows you to keep a record of your improvements in flexibility.
 Welcome to the StretchTowel 30 Day Flexibility Challenge! You can Be More Flexible in 30 days by following our stretching program for 10 minutes a day. The best part is that you can stretch using the StretchTowel
Welcome to the StretchTowel 30 Day Flexibility Challenge! You can Be More Flexible in 30 days by following our stretching program for 10 minutes a day. The best part is that you can stretch using the StretchTowel
AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING QUICK START GUIDE
 C A R D I O P E R F E C T AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING QUICK START GUIDE UNDERSTANDING ERROR CODES ERROR CODE DESCRIPTION 1 Unknown error 2 This can indicate one of the following problems: After
C A R D I O P E R F E C T AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING QUICK START GUIDE UNDERSTANDING ERROR CODES ERROR CODE DESCRIPTION 1 Unknown error 2 This can indicate one of the following problems: After
digital fever alert ear thermometer suitable from birth instruction manual
 digital fever alert ear thermometer suitable from birth instruction manual digital fever alert ear thermometer instruction manual Please read these instructions carefully before using the thermometer and
digital fever alert ear thermometer suitable from birth instruction manual digital fever alert ear thermometer instruction manual Please read these instructions carefully before using the thermometer and
OEM MAXNIBP Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Why does the monitor sometimes inflate the BP cuff, then shortly thereafter reinflate the cuff? How will I know if the monitor is experiencing motion artifact during a measurement?
Frequently Asked Questions Why does the monitor sometimes inflate the BP cuff, then shortly thereafter reinflate the cuff? How will I know if the monitor is experiencing motion artifact during a measurement?
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques
 Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Taking patients blood pressure during dental examinations is critical to their overall
Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Taking patients blood pressure during dental examinations is critical to their overall
Routine For: OT - General Guidelines/Energy Conservation (Caregiver)
 GENERAL GUIDELINES - 9 Tips for Exercise: Body Mechanics for Helper - To protect back, stay as upright as possible and keep head in line with trunk. - Always position yourself as close as possible to the
GENERAL GUIDELINES - 9 Tips for Exercise: Body Mechanics for Helper - To protect back, stay as upright as possible and keep head in line with trunk. - Always position yourself as close as possible to the
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
Body cavities. Body Planes
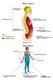 Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Exercises for older people
 Exercise for older people Exercises for older people Sitting Getting started If you ve not done much physical activity for a while, you may want to get the all-clear from a GP before starting. For the
Exercise for older people Exercises for older people Sitting Getting started If you ve not done much physical activity for a while, you may want to get the all-clear from a GP before starting. For the
2. (U4C2L3:F2) If your friend received a deep cut on her wrist, what would you do?
 Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Evaluation copy. Blood Pressure. Project PROJECT DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
 Blood Pressure Project 9 Blood pressure is a measure of the fluid pressure within the circulatory system. This pressure is required to ensure the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to, and the removal of
Blood Pressure Project 9 Blood pressure is a measure of the fluid pressure within the circulatory system. This pressure is required to ensure the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to, and the removal of
Monitoring Blood Pressure
 Introduction Why monitor your blood pressure? Low blood pressure symptoms Hot to choose a monitor How to record your blood pressure General tips Twenty-four hour monitoring Helpful contacts Monitoring
Introduction Why monitor your blood pressure? Low blood pressure symptoms Hot to choose a monitor How to record your blood pressure General tips Twenty-four hour monitoring Helpful contacts Monitoring
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Prepared by: Westat, Inc. 1650 Research Boulevard Rockville, MD 20850. September 1989
 NATIONAL HEALTH AND NUTRITION EXAMINATION SURVEY III CYCLE 2 PULSE AND BLOOD PRESSURE PROCEDURES FOR HOUSEHOLD INTERVIEWERS Prepared by: Westat, Inc. 1650 Research Boulevard Rockville, MD 20850 September
NATIONAL HEALTH AND NUTRITION EXAMINATION SURVEY III CYCLE 2 PULSE AND BLOOD PRESSURE PROCEDURES FOR HOUSEHOLD INTERVIEWERS Prepared by: Westat, Inc. 1650 Research Boulevard Rockville, MD 20850 September
Achieving Independence
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
BLS PRETEST BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS (CREATED BY LAST MINUTE CPR & FIRST AID)
 BLS PRETEST BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS (CREATED BY LAST MINUTE CPR & FIRST AID) 1. THIS BLS FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS COURSE IS GIVEN TO: a. Nurses, Doctors, Paramedics, & Healthcare Workers.
BLS PRETEST BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS (CREATED BY LAST MINUTE CPR & FIRST AID) 1. THIS BLS FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS COURSE IS GIVEN TO: a. Nurses, Doctors, Paramedics, & Healthcare Workers.
Aquatic Exercises: Upper Body Strengthening
 Aquatic Exercises: Upper Body Strengthening These exercises will strengthen your muscles in your arms, shoulders, chest and neck. Exercising in water allows you to have less stress on your joints. When
Aquatic Exercises: Upper Body Strengthening These exercises will strengthen your muscles in your arms, shoulders, chest and neck. Exercising in water allows you to have less stress on your joints. When
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body
 How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises
 Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..?
 Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..? Staying healthy at work is easier than you might think: Try building the following desk based exercises into your
Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..? Staying healthy at work is easier than you might think: Try building the following desk based exercises into your
Vtial sign #1: PULSE. Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation. Factors that influence pulse rate: Importance of Vital Signs
 Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
INSTRUCTION MANUAL HEM-6052
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor Model HEM-6052 Contents Before using the unit Introduction... 3 Important Safety Information... 4 1. Overview... 6 2. Preparation... 8 2.1 Installing/Replacing
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor Model HEM-6052 Contents Before using the unit Introduction... 3 Important Safety Information... 4 1. Overview... 6 2. Preparation... 8 2.1 Installing/Replacing
Reduce Stress with This 15-Minute Restorative Yoga Sequence
 Reduce Stress with This 15-Minute Restorative Yoga Sequence Try this short, stress-busting restorative yoga sequence to ease tension around the holidays, at work, and more Stress it s something everyone
Reduce Stress with This 15-Minute Restorative Yoga Sequence Try this short, stress-busting restorative yoga sequence to ease tension around the holidays, at work, and more Stress it s something everyone
Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear.
 Page 1 Safety Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear. Prepare a space and have your exercise band and a glass of water (for afterwards) ready
Page 1 Safety Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear. Prepare a space and have your exercise band and a glass of water (for afterwards) ready
Important Things to Know
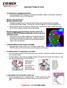 EXERGEN TemporalScanner Important Things to Know TA temperature is real time temperature Just like pulmonary artery temperature, TA temperature identifies changes in your patient s temperature sooner than
EXERGEN TemporalScanner Important Things to Know TA temperature is real time temperature Just like pulmonary artery temperature, TA temperature identifies changes in your patient s temperature sooner than
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness. and pain
 TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
Strength Training HEALTHY BONES, HEALTHY HEART
 Strength Training HEALTHY BONES, HEALTHY HEART No matter what your age, strength training can improve your bone health and your balance. As we age, our bones lose both tissue and strength. This condition
Strength Training HEALTHY BONES, HEALTHY HEART No matter what your age, strength training can improve your bone health and your balance. As we age, our bones lose both tissue and strength. This condition
IMPORTANT INFORMATION - PLEASE READ. Table of Contents. Introduction. General Information
 IMPORTANT INFORMATION - PLEASE READ Introduction Congratulations! Welcome to the world of the ELLIPTICAL CROSS TRAINER. The ELLIPTICAL CROSS TRAINER is one of the finest and most comprehensive pieces of
IMPORTANT INFORMATION - PLEASE READ Introduction Congratulations! Welcome to the world of the ELLIPTICAL CROSS TRAINER. The ELLIPTICAL CROSS TRAINER is one of the finest and most comprehensive pieces of
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress.
 Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Chair Exercises For Older Adults
 Chair Exercises For Older Adults Many of these exercises were adapted from these sources: National Institute on Aging, Exercise: A Guide from the National Institute on Aging, 2001, http://www.nia.nih.gov/healthinformation/publications/exerciseguide/.
Chair Exercises For Older Adults Many of these exercises were adapted from these sources: National Institute on Aging, Exercise: A Guide from the National Institute on Aging, 2001, http://www.nia.nih.gov/healthinformation/publications/exerciseguide/.
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema
 Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery UHN A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read
INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE
 Hughes Undergraduate Biological Science Education Initiative HHMI INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE Learn how to measure heart rate and blood pressure. Learn the normal values for heart rate
Hughes Undergraduate Biological Science Education Initiative HHMI INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE Learn how to measure heart rate and blood pressure. Learn the normal values for heart rate
Above Knee Amputee Exercise Program
 Above Knee Amputee Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent any complications. After an above the
Above Knee Amputee Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent any complications. After an above the
Exercises after breast or upper body lymph node surgery
 Exercises after breast or upper body lymph node surgery Surgery may limit the strength and movement of your arm. These exercises are helpful if you have had: breast surgery with or without lymph node removal
Exercises after breast or upper body lymph node surgery Surgery may limit the strength and movement of your arm. These exercises are helpful if you have had: breast surgery with or without lymph node removal
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
Brachial Plexus Palsy
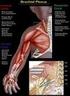 Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work
 Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work The Optimal Office Work Station Use an adjustable chair with good lumbar support. Keep your feet flat on a supportive surface (floor or foot rest). Your knees should
Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work The Optimal Office Work Station Use an adjustable chair with good lumbar support. Keep your feet flat on a supportive surface (floor or foot rest). Your knees should
GRASP. Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program. Exercise manual. Level. This research project is funded by UBC and the Heart and Stroke Foundation
 GRASP Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program Exercise manual Level 1 This research project is funded by UBC and the Heart and Stroke Foundation 1 Welcome to the Grasp study! Thank you for volunteering
GRASP Graded Repetitive Arm Supplementary Program Exercise manual Level 1 This research project is funded by UBC and the Heart and Stroke Foundation 1 Welcome to the Grasp study! Thank you for volunteering
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Anna M. Lamb DO FACOFP OMED 2010 San Francisco
 Anna M. Lamb DO FACOFP OMED 2010 San Francisco When we started; Solo practitioner One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist 3000 Patients Where we are now: One physician, one PA One RN, One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist
Anna M. Lamb DO FACOFP OMED 2010 San Francisco When we started; Solo practitioner One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist 3000 Patients Where we are now: One physician, one PA One RN, One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist
ABOUT THE FUNCTIONAL FITNESS TEST: ABOUT THE AUTHORS:
 The Interactive Health Partner Wellness Program addresses fall prevention with assessments and outcomes tracking in an easy to use, comprehensive online system. Website: www.interactivehealthpartner.com
The Interactive Health Partner Wellness Program addresses fall prevention with assessments and outcomes tracking in an easy to use, comprehensive online system. Website: www.interactivehealthpartner.com
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Ultra Premium Blood Pressure Monitor featuring ComFit TM Cuff. Model HEM-775
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Ultra Premium Blood Pressure Monitor featuring ComFit TM Cuff Model HEM-775 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL TABLE OF CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction..................................................4
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Ultra Premium Blood Pressure Monitor featuring ComFit TM Cuff Model HEM-775 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL TABLE OF CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction..................................................4
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. 7 series Blood Pressure Monitor with ComFit TM Cuff. Model BP760 ESPAÑOL ENGLISH
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7 series Blood Pressure Monitor with ComFit TM Cuff Model BP760 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL TABLE OF CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction................................................4
INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7 series Blood Pressure Monitor with ComFit TM Cuff Model BP760 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL TABLE OF CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction................................................4
Keeping your lungs healthy
 Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
Activity: Build Your Own Lung
 Activity: Build Your Own Lung Supplies per group: 2 liter pop bottle Scissors 2 straws 2 balloons 3 rubber bands clay piece of clear wrap paper binder clip Directions: 1. Carefully, cut the bottom off
Activity: Build Your Own Lung Supplies per group: 2 liter pop bottle Scissors 2 straws 2 balloons 3 rubber bands clay piece of clear wrap paper binder clip Directions: 1. Carefully, cut the bottom off
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: Instructions/Exercises
 Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: Instructions/Exercises The following activities have been approved by your physician to help you increase the motion and strength of your shoulder and improve your posture
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: Instructions/Exercises The following activities have been approved by your physician to help you increase the motion and strength of your shoulder and improve your posture
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM
 ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
Workstation and Work Area Ergonomics
 Workstation and Work Area Ergonomics If you answer "yes" to one of the following questions, you need to read further. Do you spend hours working on a computer, either at work or home? Does your computer
Workstation and Work Area Ergonomics If you answer "yes" to one of the following questions, you need to read further. Do you spend hours working on a computer, either at work or home? Does your computer
How does your heart pump blood in one direction?
 Have a Heart How does your heart pump blood in one direction? Description How does your heart move blood in one direction, around in a loop? In this activity, you will make a model of one of the heart
Have a Heart How does your heart pump blood in one direction? Description How does your heart move blood in one direction, around in a loop? In this activity, you will make a model of one of the heart
ASSISTIVE MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION PERSONNEL EXAM (AMAP)
 ASSISTIVE MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION PERSONNEL EXAM (AMAP) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When administering eye medications,
ASSISTIVE MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION PERSONNEL EXAM (AMAP) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When administering eye medications,
WSN ERGONOMIC SAFETY TALK #3
 What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
Stretching in the Office
 Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
ADVICE FOR PATIENTS WITH NECK PAIN
 ADVICE FOR PATIENTS WITH NECK PAIN Patient Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department (Information sheet code SHOT/SHOA) A SMOKING FREE ENVIRONMENT WAHT-TH-007-1 - Version 1.2 Dear Patient This advice
ADVICE FOR PATIENTS WITH NECK PAIN Patient Information Leaflet Physiotherapy Department (Information sheet code SHOT/SHOA) A SMOKING FREE ENVIRONMENT WAHT-TH-007-1 - Version 1.2 Dear Patient This advice
Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Pendulum Exercise: Wal Walk: Back Scratcher:
 Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Begin these exercises when your pain has decreased about 25% from the time when your injury was most painful. Pendulum Exercise: Lean over with your uninjured
Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Injuries Begin these exercises when your pain has decreased about 25% from the time when your injury was most painful. Pendulum Exercise: Lean over with your uninjured
Easy Yogic Breathing for a Restful Sleep
 YOGA POSES Enliven your days with the benefits of yoga. Discover physical and breathing poses to complement your mood, calm your mind and achieve balance in your body. Easy Yogic Breathing for a Restful
YOGA POSES Enliven your days with the benefits of yoga. Discover physical and breathing poses to complement your mood, calm your mind and achieve balance in your body. Easy Yogic Breathing for a Restful
ISOMETRIC EXERCISE HELPS REVERSE JOINT STIFFNESS, BUILDS MUSCLE, AND BOOSTS OVERALL FITNESS.
 ISOMETRIC EXERCISE HELPS REVERSE JOINT STIFFNESS, BUILDS MUSCLE, AND BOOSTS OVERALL FITNESS. By Askari A. Kazmi KazmisBioscienceLabs exercise helps reverse joint stiffness, builds muscle, and boosts overall
ISOMETRIC EXERCISE HELPS REVERSE JOINT STIFFNESS, BUILDS MUSCLE, AND BOOSTS OVERALL FITNESS. By Askari A. Kazmi KazmisBioscienceLabs exercise helps reverse joint stiffness, builds muscle, and boosts overall
elearning at Ramsay Online Orientation Program Guide Version 2.0 Please email any elearning questions to rtisupport@ramsayhealth.com.
 elearning at Ramsay Online Orientation Program Guide Version 2.0 Please email any elearning questions to rtisupport@ramsayhealth.com.au Table of contents Introduction to elearning... 3 Ergonomics... 3
elearning at Ramsay Online Orientation Program Guide Version 2.0 Please email any elearning questions to rtisupport@ramsayhealth.com.au Table of contents Introduction to elearning... 3 Ergonomics... 3
The Energy Medicine Daily Routine
 The Energy Medicine Daily Routine Improve your well-being in less than 10 minutes a day! Through years of practice we have designed a Daily Energy Routine that combines the most potent techniques we know
The Energy Medicine Daily Routine Improve your well-being in less than 10 minutes a day! Through years of practice we have designed a Daily Energy Routine that combines the most potent techniques we know
Reading Assignment: Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant, pages 467-473, Appendix L, O and P
 Patient Monitoring Reading Assignment: Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant, pages 467-473, Appendix L, O and P Patient monitoring during surgery is an extremely important task that is commonly the responsibility
Patient Monitoring Reading Assignment: Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant, pages 467-473, Appendix L, O and P Patient monitoring during surgery is an extremely important task that is commonly the responsibility
