How T cells see the world. Antigen Presentation. Mark S. Anderson UCSF
|
|
|
- Kelly Sparks
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 How T cells see the world Antigen Presentation Mark S. Anderson UCSF
2 Lecture outline Capture of antigens from sites of entry and display of antigens to T cells Function of MHC molecules as the peptide display molecules of adaptive immunity Recognition of protein antigens by different classes of T cells (helper vs cytotoxic)
3 What do T cells see? 3 Abbas & Lichtman. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed. W. B. Saunders 2003
4 The life history of T lymphocytes 4 Abbas, Lichtman and Pillai. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7 th edition, 2011 c Elsevier
5 The challenge for lymphocytes 5 Very few lymphocytes in the body are specific for any one microbe (or antigen) Specificity and diversity of antigen receptors: the immune system recognizes and distinguishes between antigens; therefore, few lymphocytes with the same receptors
6 6 The challenge for lymphocytes Very few lymphocytes in the body are specific for any one microbe (or antigen) Specificity and diversity of antigen receptors: the immune system recognizes and distinguishes between antigens Lymphocytes must be able to locate microbes that enter and reside anywhere in the body Usual routes of entry are through epithelia, but infections may take hold anywhere
7 7 The challenge for lymphocytes Very few lymphocytes in the body are specific for any one microbe (or antigen) Lymphocytes must be able to locate microbes that enter anywhere in the body Lymphocytes must respond to each microbe in ways that are able to eradicate that microbe; best exemplified by T cells Extracellular microbes: antibodies; destruction in phagocytes (need helper T cells) Intracellular microbes: killing of infected cells (need CTLs) How do T cells distinguish antigens in different cellular locations?
8 Capture of antigens 8 Sites of antigen entry Sites of initial antigen capture Sites of antigen collection and capture Abbas, Lichtman and Pillai. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th edition, 2011 c Elsevier
9 Capture and presentation of antigens by dendritic cells 9 Sites of microbe entry: skin, GI tract, airways (organs with continuous epithelia, populated with dendritic cells). Less often -- colonized tissues, blood Sites of lymphocyte activation: peripheral lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen), mucosal and cutaneous lymphoid tissues Abbas, Lichtman and Pillai. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7 th edition, 2011 c Elsevier Antigens and T cells come together in the same organs
10 Dendritic cell subsets 10 Conventional: CD11c+, role in presentation of most antigens Plasmacytoid: source of type I IFN Immature: in tissues; role in presentation of self antigen and maintenance of tolerance Mature: activated by TLR and other signals; role in T cell activation Many other subsets described
11 Maturation of Dendritic Cells Class II MHC molecules Number T ½ 10 6 ~10 hr 7 X 10 6 >100 hr
12 Why are dendritic cells the most efficient APCs for initiating immune responses? 12 Location: at sites of microbe entry (epithelia), tissues Receptors for capturing and reacting to microbes: Toll-like receptors, other receptors Migration to T cell zones of lymphoid organs Role of CCR7 Co-localize with naïve T cells Maturation during migration: Conversion from cells designed for antigen capture into cells for antigen presentation and T cell activation Practical application: dendritic cell-based vaccines for tumors Take home messages
13 What do T cells see? 13 Abbas & Lichtman. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed. W. B. Saunders 2003
14 What do T cells see? 14 All functions of T cells are mediated by interactions with other cells Helper T cells help B cells to make antibodies and help macrophages to destroy what they have eaten Cytotoxic (killer) T lymphocytes kill infected cells How does the immune system ensure that T cells see only antigens on other cells?
15 What do T cells see? 15 All functions of T cells are mediated by interactions with other cells Helper T cells help B cells to make antibodies and help macrophages to destroy what they have eaten Cytotoxic (killer) T lymphocytes kill infected cells To ensure cellular communications, T cells see antigens NOT in the circulation but only when displayed by molecules on the surface of other cells These molecules are HLA (generic name: MHC) and the cells displaying the antigen are APCs Take home messages
16 A model of T cell recognition of peptide displayed by an MHC molecule 16 Abbas, Lichtman and Pillai. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7 th edition, 2011 c Elsevier Human MHC = HLA Because MHC molecules are on cells and can display only peptides, T lymphocytes can recognize only cell-associated protein antigens
17 What is the MHC? 17 A genetic locus discovered on the basis of transplantation (major histocompatibility complex) Different individuals express products of different MHC alleles and reject grafts from one another Human MHC: HLA (human leukocyte antigens) MHC molecules are the peptide display molecules of the immune system
18 What is the MHC? 18 A genetic locus discovered on the basis of transplantation (major histocompatibility complex) Different individuals express products of different MHC alleles and reject grafts from one another Human MHC: HLA (human leukocyte antigens) MHC molecules are the peptide display molecules of the immune system Different alleles of MHC molecules bind and display distinct but overlapping sets of peptides Determines which protein antigens are recognized in different individuals MHC genes are highly polymorphic (>7500 alleles [variants] in the population); the MHC molecules in the population can display many different peptides
19 What is the MHC? 19 A genetic locus discovered on the basis of transplantation (major histocompatibility complex) Different individuals express products of different MHC alleles and reject grafts from one another Human MHC: HLA (human leukocyte antigens) MHC molecules are the peptide display molecules of the immune system Different alleles of MHC molecules bind and display distinct but overlapping sets of peptides Determines which protein antigens are recognized in different individuals MHC genes are highly polymorphic; the MHC molecules in the population can display many different peptides MHC molecules determine how antigens in different cellular compartments are recognized by different classes of T cells (CD4+ and CD8+)
20 20 MHC-restricted antigen recognition by T cells Any T cell can recognize an antigen on an APC only if that antigen is displayed by MHC molecules Antigen receptors of T cells have dual specificities: 1. for peptide antigen (responsible for specificity of immune response) and 2. for MHC molecules (responsible for MHC restriction) During maturation in the thymus, T cells whose antigen receptors see MHC are selected to survive and mature; therefore, mature T cells are MHCrestricted
21 T cell Recognition of Virus is Genetically Controlled Abbas & Lichtman. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed. W. B. Saunders 2003
22 Self MHC Restriction of T cells The genes that differ between strains A and B and control T cell recognition were found to map to a locus called the MHC Abbas & Lichtman. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed. W. B. Saunders 2003
23 The genes of the MHC locus 23 Genes in the MHC locus encode most of the proteins that form the machinery of antigen processing and presentation
24 Some important properties of MHC molecules MHC molecules are the immune system s mechanism for displaying peptide antigens to T lymphocytes: Highly polymorphic genes: large number of alleles in the population Co-dominantly expressed: each cell has six class I molecules (3 from each parent) and class II molecules (3 from each parent + some hybrid molecules) Class I MHC molecules are expressed on all nucleated cells Class II MHC molecules are expressed on few cells types (specialized APCs, e.g. dendritic cells; B lymphocytes, macrophages) Stable expression of MHC molecules on cell surfaces requires the peptide cargo MHC molecules present foreign and self peptides Expression of Class II MHC molecules, in particular, is up-regulated by activation of the innate immune response (IFNs, etc.)
25 25 peptide binds CD4 binds CD8 All MHC molecules have a similar basic structure: the cleft at the N-terminal region binds peptide antigens and is recognized by T cell receptors and the membrane-proximal domain binds CD4 or CD8.
26 26 The typical footprint of T cell receptor (TcR) when bound to MHC-peptide TcR-β CDR1 TcR-β CDR2 NH 2 TcR-α CDR1 TcR- α CDR3 TcR-α CDR2 TcR-β CDR3 COOH Leddon and Sant, Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2010
27 27 Antigen processing Conversion of native antigen (large globular protein) into peptides capable of binding to MHC molecules Occurs in cellular compartments where MHC molecules are synthesized and assembled Determines how antigen in different cellular compartments generates peptides that are displayed by class I or class II MHC molecules
28 Presentation of Extracellular and Cytosolic Antigens Abbas & Lichtman. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed. W. B. Saunders 2003
29 Pathways of antigen processing 29 Protein antigen in cytosol (cytoplasm) --> class I MHC -- CTLs Protein antigen in vesicles --> class II MHC --> helper T cells
30 The class II MHC pathway of processing of internalized vesicular protein antigens Endocytosed proteins are cleaved into peptides in vesicles; class II MHC molecules are available to bind the peptides in the same vesicles
31 Class II MHC pathway of presentation of vesicular peptide antigens Helper T cells need to help macrophages and B cells that have encountered (and ingested) microbes Proteins ingested into endosomes/lysosomes (vesicles) are processed and their peptides are presented in association with class II MHC molecules Most vesicular peptides are derived from extracellular proteins that are ingested into vesicles Class II MHC is expressed only on specialized cells (e.g. B cells, macrophages) that are capable of ingesting microbes and antigens into vesicles
32 Class II MHC pathway of presentation of vesicular peptide antigens Proteins ingested into endosomes/lysosomes are processed and their peptides are presented in association with class II molecules Most vesicular peptides are derived from extracellular proteins that are ingested Class II MHC is expressed only on specialized cells (e.g. B cells, macrophages) that are capable of ingesting microbes and antigens into vesicles CD4 binds to class II MHC; therefore, CD4+ T cells recognize class II-displayed peptides CD4+ T cells are helper cells that activate B lymphocytes and macrophages Antibodies (products of activated B cells) and activated macrophages combat extracellular microbes
33 The class I MHC pathway of processing of endogenous cytosolic protein antigens Cytoplasmic peptides are actively transported into the ER; class I MHC molecules are available to bind peptides in the ER
34 The Immunoproteasome: Interferon g induces new subunit proteases to alter peptides presented Spaapen and Neefjes, Nat. Immunol. 2012
35 Class I MHC pathway of presentation of cytosolic peptide antigens Cytotoxic T lymphocytes need to kill cells containing cytoplasmic microbes, and tumor cells (which contain tumor antigens in the cytoplasm) Cytosolic proteins are processed into peptides that are presented in association with class I molecules Most cytosolic peptides are derived from endogenously synthesized (e.g. viral, tumor) proteins All nucleated cells (which are capable of being infected by viruses or transformed) express class I
36 Class I MHC pathway of presentation of cytosolic peptide antigens Cytosolic proteins are processed into peptides that are presented in association with class I molecules Most cytosolic peptides are derived from endogenously synthesized (e.g. viral, tumor) proteins; all nucleated cells (which are capable of being infected by viruses or transformed) express class I CD8 binds to class I MHC; therefore, CD8+ T cells recognize class I-displayed peptides CD8+ T cells are cytotoxic cells that kill any nucleated cells that harbor infections (thus eliminating reservoirs of infection) or are transformed
37 How class I- and class II-associated antigen presentation influences the nature of the T cell response
38 Immunodominance of Peptide Epitopes Abbas & Lichtman. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed. W. B. Saunders 2003 Determinant Selection - MHC alleles select best binding peptides and thereby select which determinants will be immunogenic in an individual.
39 The Problem for CD8 T cells Viruses and tumors may be present in any nucleated cells; therefore, the immune system has to be able to generate CTL responses (class I-restricted) to any nucleated cell Only some APCs, particularly DCs, are able to initiate the responses of naïve T cells How are antigens from virus-infected or neoplastic non-apc cell types transferred to APCs?
40 Cross presentation of microbial antigens from infected cells to CD8+ T cells Antigens of viruses or tumors that are produced in cells other than APCs have to elicit CTL responses, which usually requires DCs; antigen-producing cell is phagocytosed by DCs, and phagocytosed antigen enters the class I pathway (exception to the rule!)
41 Potential Mechanisms for Cross Presentation Multiple mechanisms may allow vesicular proteins to get to cytosol or to Class I MHC molecules.
42 Functions of APCs Capture antigens and take them to the correct anatomic site Antigens are concentrated in peripheral lymphoid organs, through which naïve lymphocytes circulate Display antigens in a form that can be recognized by specific lymphocytes For T cells: MHC-associated peptides (cytosolic peptides to class I, vesicular peptides to class II) For B cells: native antigens Provide second signals for T cell activation
43 APCs and self antigens Normally, APCs are constantly presenting self antigens MHC molecules do not distinguish self from foreign If MHC molecules are bathed in self peptides, how can they ever be free to present microbial peptides? Very few peptides (complexed with MHC) are enough to activate specific T cells Microbes induce second signals on APCs If self peptides are always being displayed, why do we not react against our own antigens?
44 How do T lymphocytes meet their challenges? Very few lymphocytes in the body are specific for any one microbe (or antigen) Lymphocytes must be able to locate and respond to microbes that enter anywhere in the body Antigens are transported to and concentrated in the lymphoid organs through which naïve T cells constantly circulate, increasing likelihood of encounter Lymphoid organs, which are specialized to initiate immune responses, drain all tissue sites
45 How do T lymphocytes meet their challenges? Very few lymphocytes in the body are specific for any one microbe (or antigen) Lymphocytes must be able to locate and respond to microbes that enter anywhere in the body Lymphocytes must respond to each microbe in ways that are best able to eradicate that microbe Antigens of endogenous and extracellular microbes are displayed to different subsets of T cells by class I and class II MHC molecules Even the same microbe may be recognized by CD4+ or CD8+ T cells depending on its cellular location
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6)
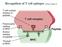 Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX)
 MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX) MHC complex is group of genes on a single chromosome that codes the MHC antigens. Major as well as minor histocompatibility antigens (also called transplantation
MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX) MHC complex is group of genes on a single chromosome that codes the MHC antigens. Major as well as minor histocompatibility antigens (also called transplantation
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Dendritic Cells: A Basic Review *last updated May 2003
 *last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
*last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
Immunity. Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity
 Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells. Effector T cells. After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells
 After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
Final Review. Aptamers. Making Aptamers: SELEX 6/3/2011. sirna and mirna. Central Dogma. RNAi: A translation regulation mechanism.
 Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity
 Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Core Topic 2. The immune system and how vaccines work
 Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data.
 Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Viral Replication. Viral Replication: Basic Concepts
 Viral Replication Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Viral Replication: Basic Concepts Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites Viruses carry their genome (RNA or DNA) and sometimes functional proteins required
Viral Replication Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Viral Replication: Basic Concepts Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites Viruses carry their genome (RNA or DNA) and sometimes functional proteins required
LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
The Immune System. How your immune system works. Organs of the Immune System
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION The Immune System How your immune system works The immune system is a network of special cells, tissues, and organs that defend the body against attacks from foreign invaders,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION The Immune System How your immune system works The immune system is a network of special cells, tissues, and organs that defend the body against attacks from foreign invaders,
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
Antigen Processing and Presentation; Direct and Cross
 Antigen Processing and Presentation; Direct and Cross Dr. E. Allison Green Cambridge Institute for Medical Research Addenbrooke s Hospital eag28@cam.ac.uk BSI Summer School, Bristol 2009 Why do we need
Antigen Processing and Presentation; Direct and Cross Dr. E. Allison Green Cambridge Institute for Medical Research Addenbrooke s Hospital eag28@cam.ac.uk BSI Summer School, Bristol 2009 Why do we need
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation. B cell maturation
 B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
The Adaptive Immune System
 Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1
 Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells
 Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of General Medicine, CUMC September 16, 2009 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared purpose:
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of General Medicine, CUMC September 16, 2009 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared purpose:
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center
 Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute
 Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Module 2: Antibodies and Antigens
 Module 2: Antibodies and Antigens Lecture 7: Antibodies and Antigens (part I) Antibodies may be defined as the proteins that recognize and neutralize any microbial toxin or foreign substance such as bacteria
Module 2: Antibodies and Antigens Lecture 7: Antibodies and Antigens (part I) Antibodies may be defined as the proteins that recognize and neutralize any microbial toxin or foreign substance such as bacteria
Why use passive immunity?
 Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
Antibody Function & Structure
 Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
Mechanical barriers are a crucial first line of defence. It would be impossible to provide an exhaustive list. Two examples are:
 Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
1 The Immune System. j 5. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Host Defence Against Infection
 j 5 1 The Immune System 1.1 Introduction All living things animals, plants and even bacteria can act as hosts for infectious organisms and thus have evolved mechanisms to defend themselves against infection.
j 5 1 The Immune System 1.1 Introduction All living things animals, plants and even bacteria can act as hosts for infectious organisms and thus have evolved mechanisms to defend themselves against infection.
BioMmune Technologies Inc. Corporate Presentation 2015
 BioMmune Technologies Inc Corporate Presentation 2015 * Harnessing the body s own immune system to fight cancer & other autoimmune diseases BioMmune Technologies Inc. (IMU) ABOUT A public biopharmaceutical
BioMmune Technologies Inc Corporate Presentation 2015 * Harnessing the body s own immune system to fight cancer & other autoimmune diseases BioMmune Technologies Inc. (IMU) ABOUT A public biopharmaceutical
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education. Su et al.
 Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Human Leukocyte Antigens - HLA
 Human Leukocyte Antigens - HLA Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA) are cell surface proteins involved in immune function. HLA molecules present antigenic peptides to generate immune defense reactions. HLA-class
Human Leukocyte Antigens - HLA Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA) are cell surface proteins involved in immune function. HLA molecules present antigenic peptides to generate immune defense reactions. HLA-class
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Disclosures Outline Starting with the Immune System The Innate Immune System The Adaptive Immune System
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins that compete with animal A) Antibodies. B) Red blood cells. C) Transferrin. D) White blood cells. E) Receptors.
 Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES
 ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer
 Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
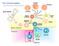 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS.
 TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity CHAPTER 4 04/05/15. Different Immunoglobulins
 Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
If you have a cold or the flu, you can spread the sickness to someone else. How does the sickness spread? Write your ideas on the lines below.
 The Immune System Textbook pages 100 109 Before You Read Section 3.1 Summary If you have a cold or the flu, you can spread the sickness to someone else. How does the sickness spread? Write your ideas on
The Immune System Textbook pages 100 109 Before You Read Section 3.1 Summary If you have a cold or the flu, you can spread the sickness to someone else. How does the sickness spread? Write your ideas on
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
The Four Pillars of Cancer Therapy
 Improving the Overall Understanding of Immunotherapy in Multiple Myeloma Webinar 2, August 19, 2015 Myeloma Vaccines: A New Use of a Time-Tested Treatment The Four Pillars of Cancer Therapy Surgery Radiation
Improving the Overall Understanding of Immunotherapy in Multiple Myeloma Webinar 2, August 19, 2015 Myeloma Vaccines: A New Use of a Time-Tested Treatment The Four Pillars of Cancer Therapy Surgery Radiation
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014)
 Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells
 Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
TABLE OF CONTENT. Page ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. iii ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT. vii LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES. xvi ABBREVIATIONS.
 x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6
 CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
Lecture 8. Protein Trafficking/Targeting. Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm.
 Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY A TOLEROGENIC VACCINATION A USING sirna MODIFIED DENDRITIC CELLS.
 TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY A TOLEROGENIC VACCINATION A USING sirna MODIFIED DENDRITIC CELLS. B.Sai Mrudula*, N.K. Durga Devi, B.Radha Madhavi,M.Madhu Babu,V.L.Annapurna ABSTRACT: KVSR Siddhartha
TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY A TOLEROGENIC VACCINATION A USING sirna MODIFIED DENDRITIC CELLS. B.Sai Mrudula*, N.K. Durga Devi, B.Radha Madhavi,M.Madhu Babu,V.L.Annapurna ABSTRACT: KVSR Siddhartha
PEPVAC: a web server for multi-epitope vaccine development based on the prediction of supertypic MHC ligands
 W138 W142 doi:10.1093/nar/gki357 PEPVAC: a web server for multi-epitope vaccine development based on the prediction of supertypic MHC ligands Pedro A. Reche 1,2, * and Ellis L. Reinherz 1,2 1 Laboratory
W138 W142 doi:10.1093/nar/gki357 PEPVAC: a web server for multi-epitope vaccine development based on the prediction of supertypic MHC ligands Pedro A. Reche 1,2, * and Ellis L. Reinherz 1,2 1 Laboratory
Ph.D. in Molecular Medicine
 Ph.D. in Molecular Medicine and Translational Research College of Medicine 1. Introduction: The College of Medicine, while consolidating on its undergraduate innovative educational programs, decided to
Ph.D. in Molecular Medicine and Translational Research College of Medicine 1. Introduction: The College of Medicine, while consolidating on its undergraduate innovative educational programs, decided to
Candy Antigens and Antibodies
 LAB ACTIVITY: Candy Antigens and Antibodies TEACHER S EDITION Curricular Links: Biology 20, Science 30 Class Time: 1 period Suggested Answers: Question 1: What is the main function of red blood cells?
LAB ACTIVITY: Candy Antigens and Antibodies TEACHER S EDITION Curricular Links: Biology 20, Science 30 Class Time: 1 period Suggested Answers: Question 1: What is the main function of red blood cells?
FIGHTING AIDS AT THE GATE
 FIGHTING AIDS AT THE GATE T h e r a m p a n t s p r e a d o f H I V i n f e c t i o n a c r o s s t h e g l o b e i s n o l o n g e r t h e m e d i a c r i s i s o f t h e m o m e n t. B u t A I D S h
FIGHTING AIDS AT THE GATE T h e r a m p a n t s p r e a d o f H I V i n f e c t i o n a c r o s s t h e g l o b e i s n o l o n g e r t h e m e d i a c r i s i s o f t h e m o m e n t. B u t A I D S h
Immunology. B lymphocytes & Antibodies. 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de
 Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Focus on Preventing Disease. keeping an eye on a healthy bottom line. Cattle Industry
 Focus on Preventing Disease keeping an eye on a healthy bottom line Cattle Industry Multimin + VACCINES : University OF FLORIDA study data Study 1 Effect of injectable trace minerals on the humoral immune
Focus on Preventing Disease keeping an eye on a healthy bottom line Cattle Industry Multimin + VACCINES : University OF FLORIDA study data Study 1 Effect of injectable trace minerals on the humoral immune
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Summary and Conclusions This study has attempted to document the following effects of targeting protein antigens to the macrophage scavenger receptors by maleylation. 1. Modification
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Summary and Conclusions This study has attempted to document the following effects of targeting protein antigens to the macrophage scavenger receptors by maleylation. 1. Modification
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237)
 Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
PEPVAC: A web server for multi-epitope vaccine development based on the prediction of supertypic
 PEPVAC: A web server for multi-epitope vaccine development based on the prediction of supertypic MHC ligands Pedro A. Reche and Ellis L. Reinherz Laboratory of Immunobiology and Department of Medical Oncology,
PEPVAC: A web server for multi-epitope vaccine development based on the prediction of supertypic MHC ligands Pedro A. Reche and Ellis L. Reinherz Laboratory of Immunobiology and Department of Medical Oncology,
The Human Immune System
 The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
SYSTEM Teacher Pages THE IMMUNE. Your students will learn:
 Grade Level 3-5 Sergeant Cell s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Activity Summary Comparing immune cells with a police team, the webquest activity guides students to research the immune system online.
Grade Level 3-5 Sergeant Cell s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Activity Summary Comparing immune cells with a police team, the webquest activity guides students to research the immune system online.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System
 The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
THE INFLUENCE OF TISSUE (IN)COMPATIBILITY IN UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION
 THE INFLUENCE OF TISSUE (IN)COMPATIBILITY IN UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION Matjaž Jeras Blood Transfusion Centre of Slovenia Tissue Typing Center Šlajmerjeva 6, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia matjaz.jeras@ztm.si
THE INFLUENCE OF TISSUE (IN)COMPATIBILITY IN UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION Matjaž Jeras Blood Transfusion Centre of Slovenia Tissue Typing Center Šlajmerjeva 6, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia matjaz.jeras@ztm.si
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions
 Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
Antigenic variation in Plasmodium falciparum : Erythrocyte invasion and immune escape mechanisms
 Antigenic variation in Plasmodium falciparum : Erythrocyte invasion and immune escape mechanisms Introduction Why does immunity to malaria take so long to develop? The parasite s survival depends on its
Antigenic variation in Plasmodium falciparum : Erythrocyte invasion and immune escape mechanisms Introduction Why does immunity to malaria take so long to develop? The parasite s survival depends on its
New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies
 Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual
 Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Ph.D. Program Molecular Microbiology and Immunology (MMI) Saint Louis University School of Medicine
 Ph.D. Program Molecular Microbiology and Immunology (MMI) Saint Louis University School of Medicine I. Overview The Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology and Immunology (MMI) offers a graduate
Ph.D. Program Molecular Microbiology and Immunology (MMI) Saint Louis University School of Medicine I. Overview The Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology and Immunology (MMI) offers a graduate
MISSION DEBRIEFING: Teacher Guide
 Activity on the IMMUNE SYSTEM: The Body Fights Back In this activity, the students will use a hands-on approach to learn about the immune system and how it fights off pathogens that invade the body. They
Activity on the IMMUNE SYSTEM: The Body Fights Back In this activity, the students will use a hands-on approach to learn about the immune system and how it fights off pathogens that invade the body. They
Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. Genetic Contributions to Autoimmunity. Targets of Autoimmunity
 Autoimmunity Factors predisposing an individual to autoimmune disease Mechanisms of initiation of autoimmunity Pathogenesis of particular autoimmune disease Animal models of autoimmune disease Treatment
Autoimmunity Factors predisposing an individual to autoimmune disease Mechanisms of initiation of autoimmunity Pathogenesis of particular autoimmune disease Animal models of autoimmune disease Treatment
Helices From Readily in Biological Structures
 The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
