Call Processing, SMS and VMS
|
|
|
- Emerald Foster
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Call Processing, SMS and VMS In this we discuss the call processing aspect and look into specifics case of a mobile originated (MO) call and a mobile terminated (MT) call. We also look into short message (SMS) and voice mail service (VMS) as implemented IMPCS pilot project. RF channel overview: - RF channel play important role in call processing case. These are basically three types of RF control channel. 1. Broadcast control channel : The broadcast channels are points to multipoint channel, which are defined only for down-link direction (BTS to mobile station). They are divided into: BCCH (Broad cast control channel:- BCCH acts as a beacon. It informs the mobile about system configuration parameters (e.g. LAI, CELLIDENTY, NEIGHBOURING all identify). Using this information MS choose the best cell to attach to. BCCH is always transmitted on full power and it is never frequency hopped. FCCHC frequency correction channel. MS must tune to FCCH to listen to BCCH. FCCH transmits a constant frequency shift of the radio carrier that is used by the MS for frequency correction. SCH (synchronization channel).. SCH is used to synchronize the MS in time.sch carries TDMA frame number and BSIC (Base Station Identity Code) 2. Common control channels : Common control channels are specified as point to multi-point, which operate only in one direction either in up-link or downlink direction. PCH (Paging Channel): - PCH is used in down-link direction for sending paging message to MS whenever there is incoming call. RACH (Random Access Channel ) :-RACH is used by the MS to request allocation of a specific dedicated control channel (SDCCH) either in response to a paging message or for call origination /registration from the MS. this is an uplink channel and operate in point to point mode. AGCH (Access Grant Channel ):- AGCH is a logical control channel which is used to allocated a specific dedicated control channel (SDCCH) to MS when MS request for a channel over RACH. AGCH is used in downlink direction. - 1-
2 3.Dedicated Control Channel : dedicated control channel are full duplex, point to point channel. They are used for signalling between the BTS and certain MS. They are divided into: - (I). SACCH (Slow Associated Control Channel): the SACCH is a duplex channel, which is always allocated to TCH or SDCCH. The SACCH is used for - Radio link supervision measurements. - Power control. - Timing advance information. In 26 frame traffic multi-frame 13th frame (frame no.12) is used for SACCH.SACCH is used only for non-urgent procedures. (II). FACCH (Fast Associated Control Channel). FACCH is requested in case the requirement of signaling is urgent and signaling requirement can not be met by SACCH. This is the case when hand-over is required during conversation phase. During the call FACCH data is transmitted over allocated TCH instead of traffic data. This is marked by a flag known as stealing flag. (III). SDCCH (Stand Alone Dedicated Control Channel)- The SDCCH is a duplex, point to point channel which is used for signaling in higher layer. It carries all the signaling between BTS & MS when no TCH is allocated to MS. The SDCCH is used for service request, location updates, subscriber authentication, ciphering. equipment validation and assignment of a TCH. Mobile originated (MO) call: - There are four distinct phase of a mobile originated call- -Setup phase. -Ringing phase. -Conversation phase. -Release phase. Out of these phases the setup phase is the most important phase and includes authentication of the subscriber, Ciphering of data over radio interface, validation of mobile equipment, validation of subscriber data at VLR for requests service and assignment of a voice channel on A-interface by MSC. Whenever MS wants to initiate on outgoing call or want to send an SMS it requested for a channel to BSS over RACH. On receiving request from MS, BSS assigns a stand-alone dedicated control channel (SDCCH) to MS over access grant channel (AGCH). Once a SDCCH has been allocated to MS all the call set up information flow takes place over SDCCH. - 2-
3 A connection management (CM) entity initiates a CM Service Request message to the network. Network tries to establish an MM connections between the MS and the network and upon successful establishment of MM connection a CM Service Accept message is received by MS from the network. MS now sends a Call Set up Request to the network which contains the dialed digits (DD) of the called party. As the call setup message is received at the MSC/VLR certain check are performed at MSC/VLR like- whether the requested service is provisioned for the subscriber or not, whether the dialed digits are sufficient or not, any operator determined barring (ODB) does not allow call to proceed further etc. As these checks are performed at MSC/VLR a Call Proceeding Message is sent from the network towards the MS. After all the checks are successfully passed MSC sends Assignment command to the BSS which contains a free voice channel on A-interface On getting this message BSS allocates a free TCH to the MS and informs the MS to attach to it. MS on attaching to this TCH informs the BSS about it. On receiving a response from the BSS, MSC switches the speech path toward the calling MS. Thus at the end of Assignment the speech path is through from MS to MSC. It is important to note that at this stage mobile has not connected user connection as yet. MS at this stage does not listen anything. After assignment MSC sends a network set-up message to the PSTN requesting that a call be set up. Included in the message are the MS dialed digits (DD) and details specifying which trunk should be used for the call. The PSTN may involve several switching exchanges before finally reaching the final local exchange responsible for applying the ringing tone to the destination phone. The local exchange will generate the ringing tone over the trunk, or series of trunk (if several intermediate switching exchange are involved), to the MSC. At this point in time MS will hear ringing tone. The PSTN notifies the MSC with a networkalerting message when this event occurs. MSC informs the MS that the destination number is being alerted. It is important to note that this is primarily a status message to the MS. The MS hears the ringing tone from the destination local exchange through the established voice path. When the destination party goes off hook, PSTN informs the MSC of this event. At this point, MS is connected to the destination party and billing is started. MSC informs the MS that connection has been established and MS acknowledges the receipts of the connect message. Under normal condition, the termination of a call is MS initiated or network initiated. In this scenario, we have assumed that MS initiates the release of the call by pressing end button and MS send a disconnect message to the MSC. The PSTN party is notified of the termination of the call by a release message from the MSC. The end- to- end connection is terminated. When MSC is left with no side task (e.g. charging indication etc.) to complete a release message is sent to the MS. MS acknowledges with a release complete message. All the resources between MSC and the MS are released completely. - 3-
4 Mobile Terminated (MT) call- The different phases of a mobile terminated call are - Routing analysis - Paging. - Call setup. - Call release. The phases of mobile terminated (MT) call are similar to a mobile originated (MO) call except routing analysis and paging phase. Call to a mobile subscriber in a PLMN first comes to gateway MSC (GMSC). GMSC is the MSC, which is the capable of querying HLR for subscriber routing information. GMSC need not to be part of home PLMN, though it is normal practice to have GMSC as part of PLMN in commercially deployed networks. GMSC opens a MAP (Mobile Application Part) dialogue towards HLR and Send / Routing / Info-Request (SRI request) specific service message is sent to HLR. SRI request contains MSISDN of the subscriber. HLR based on location information of this subscriber in its database, opens a MAP dialogue towards VLR and sends Provide / Roaming / Number-request (PRN request)to the VLR. VLR responds to PRN request with PRN response message, which carries an MSRN (mobile subscriber roaming number), which can be used for routing toward visiting MSC in the network. HLR returns MSRN to GMSC (MSC that queried HLR) in SRI response message. On getting MSRN the GMSC routes the call towards VMSC The purpose of this entire exercise is to locate where the terminating mobile subscriber is. The MSRN received at GMSC is in international format (Country Code + Area Code + subscriber number). Normally, based on the routing info at GMSC, the call may be routed out of the GMSC towards VMSC of the terminating subscriber, in which case appropriate signaling protocol (MF or ISUP) depending on the nature of connecting of GMSC with subsequent exchange along the route will apply. If at VMSC the terminating mobile subscriber is found to be free (idle), paging is initiated for terminating mobile subscriber. MSC uses the LAI provided by the VLR to determine which BSS s should page the MS. MSC transmit a message to each of these BSS requesting that a page be performed. Included in the message is the TMSI of the MS. Each of the BSS s broadcasts the TMSI of the mobile in a page message on paging channel (PCH). When MS detects its TMSI broadcast on the paging channel, it responds with a channel request message over Random Access Channel (RACH). Once BSS receives a channel request message, it allocates a stand alone Dedicated Control Channel(SDCCH) and forwards this channel assignment information to the MS over Access Grant Channel (AGCH). It is over this SDCCH that the MS communicates with the BSS and MSC until a traffic channel assigned to the MS. MS transmits paging response message to the BSS over the SDCCH. Included in this message is MS TMSI and LAI. BSS forwards this paging response - 4-
5 message to the MSC. Now Authentication and Ciphering phases are performed to check the authenticity of MS and encrypt data over radio interface. On the network side after paging is initiated, while waiting for paging response, a defensive timer called, Early ACM timer is run at MSC to avoid network timeouts. On successfully getting paging response, a setup message is constructed to be sent towards terminating MS. In case paging fails due to authentication failure or when the subscriber is out of radio-coverage, the call is cleared. In case CLIP is not subscribed by the terminating mobile subscriber, calling number is not included in set-up message. In case CLIP is subscribed and PI value in calling number parameter indicates presentation allowed the number is included in the set-up message. In case CLIP is subscribed but PI received in calling number parameter indicates presentation restricted then number is included only if CLIRO is also subscribed to. MS on receiving the set-up message performs compatibility Checking before responding to the set-up message it is possible that MS might be incompatible for certain types of call set-ups. Assuming that MS passes compatibility checking, it acknowledges the call setup with set-up confirm message. After getting set-up confirm message from the MS, MSC performs assignment phase (similar to one discussed in MO call) and a voice path is established from MSC to the MS. MS begins altering the user after it receives the traffic channel assignment. MS send alerting message to the MSC.MSC upon receiving the alerting indication from the MS, begins generating an audible ringing tone to the calling party and sends a network alerting via GMSC to the PSTN. Prior to this the calling party heard silence. At this point in the call, MS is alerting the called party by generating on audible tone. One of the three events can occur-calling party hangs-up, mobile subscriber answers the phone, or the MSC times out waiting for the mobile subscriber to the answer the call. Since radio traffic channel is a valuable resource, GSM does not allow a MS to ring forever. In the present scenario we have assumed that the mobile subscriber answers the phone. The MS in response to this action stops alerting and sends a connect message to the MSC. MSC removes the audible tone to the PSTN and connects the PSTN trunk to BSS trunk (terrestrial channel) and sends a connect message via GMSC to the PSTN. The caller and the called party now have a complete talk path. This event typically marks the beginning of the call for billing purposes. MSC sends a connect acknowledge message to the MS. The release triggered by the land user is done in similar way as the release triggered by mobile user. MSC receives a release message from the network to terminate end-to-end connection. PSTN stops billing the calling landline subscriber. MSC sends a disconnect message towards the MS and MS responds by a Release message. MSC release the connection to the PSTN and - 5-
6 acknowledges by sending a Release Complete message to PSTN. Now the voice trunk between MSC and BSS is cleared, traffic channel (TCH) is released and the resources are completely released. The mobile-to-mobile call scenario is a combination of phases encountered in mobile originated (MO) and mobile terminated (MT) call. Short Message Service (SMS) SMS is a simple bearer service and acts as a bi-directional alphanumeric paging service, which allows value added service provision as well as management services provision such as advice of charge. A short message can carry at most 160 characters (it can be less depending upon the type of characters and their coding scheme). The SMS could be either in broadcast mode (via CBCH channel) or in a point-to-point mode (via either SDCCH channel if mobile is in idle state, or SACCH if the mobile is in dedicated mode). SMS allows to provide many values added service to individual/ corporate clients. Individuals may be interested in messaging (transmitting messages in compact way) or leisure services (weather forecast, road traffic, restaurant booking, movies, TV programs etc.). Business users may be interested in corporate information (company performance, stock value), e- commerce etc. SMS involves specific entities in the GSM network: first is the SMS Service Centre (SMS-SC simply SMSC) which can be connected to several networks and many MSC s (SMS- GMSC s or SMS-IWMSC s) within the same PLMN and which is addressed by a mobile using a E.164 number of the numbering plan of the PLMN. SMSC is capable of following functionality s: - Transmission of short message towards a mobile, retaining the responsibility of the message until reception of acknowledgement or expiration of the validity period. - Reception of the short messages from MS and transmission of acknowledgement to the PLMN. - Transferring messages received from Internet to mobile. The second entity involved by the SMS is the SME (short message entity), which is responsible for producing or receiving a short message. The SME can be connected to the SMSC via a data network such as X.25 or IP. - 6-
7 A short message is characterized by its parameters the most significant are the validity period, the service center time stamp which indicates the SM arrival time at the SC, etc. In IMPCS (pilot project), the SMS architecture has been implemented by C-DoT. The hardware architecture of SMSC is similar to HLR and is located on same physical platform. It services as an inter-working and relaying function of the message transfer between two MS. The service provided are- (i) Mobile Originated short message- Enables MS to send an SMS ( up-to 140 bytes) to another MS via SMSC. (ii)mobile terminated short message- Enables delivery of an SMS to a particular MS. (iii)operator initiated SMS- This facility enables fixed network subscriber to send an SMS to a mobile subscriber through an operator at SMSC. (iv)sms Newsletter Service- A group of mobile subscriber can subscribe to SMSC for receiving periodic news regarding sports, weather, traffic etc. The subscription is done through on operator at SMSC. The operator feeds the news segments, which are transferred, to the subscriber periodically. Voice Mail System (VMS) VMS offers function of call answering device in the system. It provides personal voice mailbox to the subscribers. VMS redirects/forwards voice calls of a temporarily in accessible subscriber (busy or no reply) to a personal mailbox of the subscriber connected to the MSC. Whenever a call is redirected to VMS, it first greets the caller with a personalised greeting message and prompts the caller to leave the message in the mailbox. Later on the called party (mobile subscriber) can access the VMS from PLMN/PSTN phone by means of access code. VMS interfaces with MSC on E1 lines using R2 MF/CCS#7 signaling protocol. In IMPCS network the VMS consists of Pentium PC equipped with Dialogic card loaded with Windows NT 4.0. Dialogic card provides telephony network interface, voice recording, compression and play. The disk capacity requirement of the PC is totally application dependent. For 10,000 subscribers, if each subscriber stores 10 minutes of voice data then disk storage for subscriber voice information is around 20 GB. References: 1. The GSM system for mobile communication-michel Mouly & Marie- Bernadette Pautet. 2. GSM system Engineering-Asha Mehrotra (Artech House Publisher). 3. ETSI standard ETS July 1994 on ISDN, ISDN-GSM, PLMN signalling interface. - 7-
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing
 GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
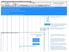 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The Network Layer Layer 3
 CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning
 GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
-The equipment was limited to operate only within the boundaries of each country. -The market for each mo bile equipment was limited.
 1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
ETSI TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12)
 TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Basic call handling (3GPP TS 03.18 version 7.5.0 1998) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Basic call handling (3GPP TS 03.18 version 7.5.0 1998) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure
 GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Databases. Virginia Location Area HLR Vienna Cell Virginia BSC. Virginia MSC VLR
 Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
1 Introduction. 2 Assumptions. Implementing roaming for OpenBTS
 Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
CHANGE REQUEST. 03.35 CR xx
 3GPP TSG SA WG3 #16 Document S3-000676 Sophia Antipolis (France), 28 th 30 th November, 2000 e.g. for 3GPP use the format TP-99xxx or for SMG, use the format P-99-xxx CHANGE REQUEST Please see embedded
3GPP TSG SA WG3 #16 Document S3-000676 Sophia Antipolis (France), 28 th 30 th November, 2000 e.g. for 3GPP use the format TP-99xxx or for SMG, use the format P-99-xxx CHANGE REQUEST Please see embedded
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0
 GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Wireless Short Message Service (SMS)
 Wireless Short Message Service (SMS) Definition Short message service (SMS) is a globally accepted wireless service that enables the transmission of alphanumeric messages between mobile subscribers and
Wireless Short Message Service (SMS) Definition Short message service (SMS) is a globally accepted wireless service that enables the transmission of alphanumeric messages between mobile subscribers and
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
RELEASE NOTE. Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08. Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90
 ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
Using TEMS Pocket. Johan Montelius
 Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
1. Introduction: The Evolution of Mobile Telephone Systems
 IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
MITEL SX3300 AX Controller w/ NSU or Internal T1 Card
 Avaya Modular Messaging Configuration Note 88035 Version C (7/09) MITEL SX3300 AX Controller w/ NSU or Internal T1 Card T1/QSIG MITEL 3300 AX w/outboard NSU or internal T1 card Avaya MM The PBX and MM
Avaya Modular Messaging Configuration Note 88035 Version C (7/09) MITEL SX3300 AX Controller w/ NSU or Internal T1 Card T1/QSIG MITEL 3300 AX w/outboard NSU or internal T1 card Avaya MM The PBX and MM
Mobile Networking. SS7 Network Architecture. Purpose. Mobile Network Signaling
 Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks
 Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Feature Reference. Features: Call Forwarding Call Waiting Conference Calling Outbound Caller ID Block Last Call Return VoiceMail
 Feature Reference This document will provide you with information on and how to use the following features of your phone service with Standard Broadband. Features: Call Forwarding Call Waiting Conference
Feature Reference This document will provide you with information on and how to use the following features of your phone service with Standard Broadband. Features: Call Forwarding Call Waiting Conference
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Voice Processing Features
 Voice Processing Features CONTENTS PAGE 1. Introduction........................................................ 4-3 A. Voice Processing Applications....................................... 4-3 B. Time Slot
Voice Processing Features CONTENTS PAGE 1. Introduction........................................................ 4-3 A. Voice Processing Applications....................................... 4-3 B. Time Slot
GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030307Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030307Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
How To Test Gsm Cell Phone Network On A Cell Phone
 G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Introduction Ericsson Handheld Telephone 1341-B
 Ericsson Handheld Telephone 1341-B 2 Contents General 5 The Mobile Telephone Network 6 Base Station and Cell 7 Radio Channels 7 Radio Coverage 8 Transmission Control and Communication 9 Quality Control
Ericsson Handheld Telephone 1341-B 2 Contents General 5 The Mobile Telephone Network 6 Base Station and Cell 7 Radio Channels 7 Radio Coverage 8 Transmission Control and Communication 9 Quality Control
Error and Confirmation Codes
 Error and Confirmation s The following two tables list the error and confirmation codes that can be returned within SMS replies or notifications. Table 14: Error s 8 008 10 00A 21 015 27 01B 28 01C 29
Error and Confirmation s The following two tables list the error and confirmation codes that can be returned within SMS replies or notifications. Table 14: Error s 8 008 10 00A 21 015 27 01B 28 01C 29
DraftEN 302 405 V7.0.1 (1999-05)
 DraftEN 302 405 V7.0.1 (1999-05) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); GSM Cordless Telephony System (CTS), Phase 1; CTS Architecture Description;
DraftEN 302 405 V7.0.1 (1999-05) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); GSM Cordless Telephony System (CTS), Phase 1; CTS Architecture Description;
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
 General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN. Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification
 TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
3GPP TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12)
 TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP Operations
 Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
Configuring Interoperability between Avaya IP Office and Avaya Communication Manager
 Configuring Interoperability between Avaya IP Office and Avaya Communication Issue 01.01 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 3 1.1 Supported Features... 3 1.2 Network Diagram... 6 1.3 Supported Phones... 6 1.4
Configuring Interoperability between Avaya IP Office and Avaya Communication Issue 01.01 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 3 1.1 Supported Features... 3 1.2 Network Diagram... 6 1.3 Supported Phones... 6 1.4
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Operation Manual Voice Overview (Voice Volume) Table of Contents
 Operation Manual Voice Over (Voice Volume) Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Voice Over... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to VoIP... 1-1 1.1.1 VoIP System... 1-1 1.1.2 Basic VoIP Call Flow... 1-2 1.1.3
Operation Manual Voice Over (Voice Volume) Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Voice Over... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to VoIP... 1-1 1.1.1 VoIP System... 1-1 1.1.2 Basic VoIP Call Flow... 1-2 1.1.3
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系
 Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
GeoSIM Global SIM Card User Guide IMPORTANT PLEASE READ BEFORE INSERTING YOUR SIM CARD
 GeoSIM Global SIM Card User Guide IMPORTANT PLEASE READ BEFORE INSERTING YOUR SIM CARD Thank you for purchasing GeoSIM, a global GSM service for mobile phones. GeoSIM will reduce your mobile roaming charges
GeoSIM Global SIM Card User Guide IMPORTANT PLEASE READ BEFORE INSERTING YOUR SIM CARD Thank you for purchasing GeoSIM, a global GSM service for mobile phones. GeoSIM will reduce your mobile roaming charges
GSM and IN Architecture
 GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP Raimo.Kantola@netlab.hut.fi Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP Raimo.Kantola@netlab.hut.fi Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
Avaya one-x Mobile User Guide for iphone
 Avaya one-x Mobile User Guide for iphone Release 5.2 January 2010 0.3 2009 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved. Notice While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the information in this document was
Avaya one-x Mobile User Guide for iphone Release 5.2 January 2010 0.3 2009 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved. Notice While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the information in this document was
NTT DOCOMO Technical Journal. Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications
 M2M 3GPP Standardization Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications The number
M2M 3GPP Standardization Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications The number
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM
 Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems
 Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
SPYTEC 3000 The system for GSM communication monitoring
 SPYTEC 3000 The system for GSM communication monitoring The SPYTEC 3000 system is intended for passive (if system encryption is absent of if A5.2 encryption is used) or semi-active (if A5.1 encryption
SPYTEC 3000 The system for GSM communication monitoring The SPYTEC 3000 system is intended for passive (if system encryption is absent of if A5.2 encryption is used) or semi-active (if A5.1 encryption
Citynet Telephone Features
 Citynet Telephone Features Feature Activate De-Activate NOTES Activation/De-Activation Calling Number Calling Name Caller ID Block *67 Caller ID unblock *82 Call reject *77 *87 Call Waiting *70 Calling
Citynet Telephone Features Feature Activate De-Activate NOTES Activation/De-Activation Calling Number Calling Name Caller ID Block *67 Caller ID unblock *82 Call reject *77 *87 Call Waiting *70 Calling
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04. Simon Sörman
 Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
1. Public Switched Telephone Networks vs. Internet Protocol Networks
 Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Tutorial Definition Internet telephony switches enable voice calls between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol
Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Tutorial Definition Internet telephony switches enable voice calls between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
SVMi-4 & SVM-400. Voice Mail System. System Administration Manual
 SVMi-4 & SVM-400 Voice Mail System System Administration Manual Contents About this Book 3 How to use this online manual 4 How to print this online manual 5 Feature Descriptions 6 SYSTEM FEATURES 6 AUTO
SVMi-4 & SVM-400 Voice Mail System System Administration Manual Contents About this Book 3 How to use this online manual 4 How to print this online manual 5 Feature Descriptions 6 SYSTEM FEATURES 6 AUTO
Optimization. Log File Analysis GSM
 Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
Unified Messaging and Fax
 April 25, 2007 Telecom White Paper Presented By: Toshiba Telecommunications Systems Division www.telecom.toshiba.com Unified Messaging and Fax Toshiba s Stratagy Enterprise Server Overview: Unified Messaging
April 25, 2007 Telecom White Paper Presented By: Toshiba Telecommunications Systems Division www.telecom.toshiba.com Unified Messaging and Fax Toshiba s Stratagy Enterprise Server Overview: Unified Messaging
ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT
 ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DTR/SMG-101020Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile communications (GSM)
ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DTR/SMG-101020Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile communications (GSM)
SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service
 SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service Takuya Shinozaki, Etsuko Matsubara, Masahiro Kadono and Mayumi Takahashi DoCoMo s SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service have been launched. It
SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service Takuya Shinozaki, Etsuko Matsubara, Masahiro Kadono and Mayumi Takahashi DoCoMo s SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service have been launched. It
[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]
![[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]](/thumbs/26/8506801.jpg) JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3-
 Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
ETSI TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06)
 TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
Mission Critical Voice Communications Requirements for Public Safety National Public Safety Telecommunications Council Broadband Working Group
 Mission Critical Voice Communications Requirements for Public Safety National Public Safety Telecommunications Council Broadband Working Group Executive Summary The term mission critical voice has been
Mission Critical Voice Communications Requirements for Public Safety National Public Safety Telecommunications Council Broadband Working Group Executive Summary The term mission critical voice has been
Cisco Unity Connection Voicemail User Guide
 Cisco Unity Connection Voicemail User Guide University of Alberta IST Voice & Data Networks Telephones Effective July 25, 2011 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 CISCO UNITY VOICEMAIL USER TRAINING
Cisco Unity Connection Voicemail User Guide University of Alberta IST Voice & Data Networks Telephones Effective July 25, 2011 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 CISCO UNITY VOICEMAIL USER TRAINING
Configuring Shared Line Appearances over Analog Trunks
 61200796L1-29.1G March 2013 Configuration Guide Configuring Shared Line Appearances over Analog Trunks This configuration guide explains how to configure shared line appearances (SLAs) on AOS voice products
61200796L1-29.1G March 2013 Configuration Guide Configuring Shared Line Appearances over Analog Trunks This configuration guide explains how to configure shared line appearances (SLAs) on AOS voice products
