Falls in Individuals with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
|
|
|
- Vivian Gibson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Falls in Individuals with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities LEARNING OBJECTIVES To understand the Scope and complications of falls Causes of falls and fall risk Preventive strategies that can reduce falls SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM AND COMPLICATIONS Falls are a significant issue for individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD); each year, up to one third of individuals fall. About two thirds of these individuals experience multiple falls. Although the majority of falls do not result in injury, the more falls an individual has, the greater the chance of injury. Approximately 15% of falls result in physical injury serious enough to warrant medical attention. About 10% of falls lead to minor injuries (e.g., head and soft tissue trauma, musculoskeletal sprains) and the remaining 3% 5% result in serious injuries (e.g., head trauma, hip and extremity fractures, spinal cord injury). Individuals with I/DD may not have the protective reflexes to prevent serious injuries when they fall. As many as 43% of all injuries reported in individuals with I/DD are a result of falls. Injury due to falls represents one of the leading causes of liability claims against group homes and other care providers. Falls often lead to a fear of falling, which can result in reduced mobility and independence, particularly if a person loses confidence in the ability to perform everyday activities. As many as 50% of individuals who have fallen avoid activities particularly activities that led to a previous fall because of fear of further falls or injury. Falls can also lead to episodes of depression, particularly if a person experiences any loss of independence and mobility as a result. When individuals with I/DD fall, family members are affected as well. They often become worried and concerned about the safety of their loved one. CIRCUMSTANCES OF FALLING In individuals with I/DD, the majority of falls occur when individuals are going about their usual activities of daily living. Most falls occur in activity rooms, dining rooms, hallways, bathrooms, and outdoors. The most frequent activities at the time of falling include walking up or down stairs and steps; getting on and off buses and vans; falling 1
2 from a chair or wheelchair; tripping over objects on the floor; and slipping on water or urine on the floor. Falls in individuals with I/DD can be reduced by understanding Why falls occur What factors are associated with fall risk Which strategies reduce fall risk What actions can be taken to prevent falls CAUSES OF FALLING Falls have many different causes, and individuals with I/DD may have several predisposing risk factors. The relative contribution of each risk factor differs according to the individual s underlying medical condition, functional level, and environmental circumstances. Falls in individuals with I/DD are typically caused by a combination of internal factors (e.g., acute and chronic disease states, adverse medication effects) and external factors (e.g., environmental hazards and obstacles interfering with mobility). The likelihood of falling increases with the number of risk factors a person has (see Understanding Fall Risk). Internal factors resulting from the client s physical or mental condition that contribute to the risk of falls include Poor vision and hearing Unsteady gait and balance Neurological disorders Seizures Cardiac or heart abnormalities Muscle weakness Arthritis Foot problems Low blood pressure Cognitive or mental impairment Thyroid abnormalities Medication side effects Dizziness Pain 2
3 Fatigue Urinary frequency or incontinence Behavior problems External factors associated with fall risk consist of environmental obstacles and design features that interfere with safe mobility. Some of these include Floor spills and clutter Slippery floor surfaces Wet outdoor walking surfaces Unstable or low chairs or beds Poor/dim lighting Lack of bathroom grab bars Low toilet seats Faulty stairs/steps Improper footwear Improper utilization or poor repair (worn tips, structural defects) of canes, walkers, and wheelchairs The risk of the environment contributing to falls is greatest for individuals who have mobility problems because hazardous environmental conditions can interfere with safe mobility. FALL PREVENTION Preventing falls in individuals with I/DD should focus on minimizing fall risk and the risk of injurious falls while maximizing individual independence. The ability to prevent falls generally follows a step-by-step process (see Fall Prevention Protocol). Step 1: Fall Potential Is the client at risk of falling? Recall that many factors are associated with falls. The best way to determine a client s fall potential and individual risk factors is to complete a fall risk assessment. Does the client have a history of falls? Ask all clients and their caregivers about the occurrence of falls during the preceding month. Detecting a recent history of falling is crucial because having one or more falls is a strong predictor of future falls. A fall risk assessment includes listing significant risk factors, reviewing the circumstances surrounding previous falls (if the client has fallen), and briefly assessing the client s mobility (see Fall Risk Intervention and Screening Tool). 3
4 It is important to recognize that fall risk prediction is imprecise. Some low-risk clients may fall, and some high-risk individuals may not. Effective risk assessment should enable staff to anticipate risks correctly more often than not, however. Step 2: Identification of Risk Following fall risk screening, it is important for all staff members to be aware of the client s fall risk status. Simple reminders such as colored wrist bracelets for at-risk individuals or the use of colored stickers or tags placed on a client s clothing can be used to communicate risk status. These identification methods remind staff that the client is at high risk for falls and should trigger interventions that reduce the risk of falls, such as supervision or assistance with ambulation. Step 3: A Plan for Managing Fall Risk Once a client s potential or risk of falling has been identified, it is important to plan interventions or strategies aimed at reducing the likelihood of falling. Fall prevention strategies that are put into place should be based on the specific risk factors identified from the client s fall risk assessment. Since risk or the occurrence of falls in clients with I/DD may have more than one cause, several interventions or strategies may be required. Strategies should address both internal and external risk factors. Medical Strategies Because falls and fall risk factors may be caused by underlying diseases, adverse medication effects, and resulting disabilities, all clients should be referred to their primary care provider for evaluation. Diagnosing and treating risk factors such as visual disorders, gait and balance impairment, muscle weakness, cognitive impairment, postural hypotension, and cardiovascular irregularities can greatly reduce fall risk. Also, discontinuing inappropriate or excessive medications and managing existing chronic diseases is important. Last, diagnosing and treating osteoporosis (i.e., weak bone strength caused by calcium deficits and prolonged periods of immobility or reduced weightbearing activity) can help to reduce the risk of injurious falls, such as hip fracture. Rehabilitative Approaches Clients with impaired mobility may benefit from one or more rehabilitative strategies. These consist of exercise programs, proper footwear, and ambulation devices to assist with mobility. Exercise programs can be grouped into two broad categories: general physical activity (walking, aerobic movements, other endurance exercises) and specific physical activity (training geared specifically toward increasing balance and strength). To be effective, exercise needs to be tailored to the client s physical capabilities and needs. 4
5 All shoes and slippers worn by clients should fit properly (i.e., not too tight or loose) and their soles should be slip resistant. Balance is generally better with shoes that have thin, nonslip soles rather than footwear such as sneakers or running shoes with thicker soles that actually interfere with balance. Shoes and slippers with rubber or crepe soles provide adequate slip resistance on slippery floor surfaces such as linoleum. If foot problems (e.g., hammertoes, bunions, calluses, nail disorders) prohibit wearing proper footwear, individuals should be referred for podiatric care. Clients who have gait and balance disorders should be using canes or walkers to maintain or improve balance and mobility. Canes and walkers also furnish clients with a visual presence of support that instills confidence during ambulation, which in turn helps reduce fears of instability. As with canes and walkers, wheelchairs should be tailored to meet the specific needs of the individual. All such devices should be evaluated routinely to ensure they are being used safely and are in good working order. It is important for staff to understand the proper use of canes, walkers, wheelchairs, and crutches (see Mobility Aids). Environmental Strategies Hazardous environmental conditions, such as low seats, poor illumination, slippery floors, and faulty stairways, can increase fall risk by interfering with safe mobility. Likewise, clients with diminished functional capacity due to chronic diseases may experience difficulty maneuvering around unsafe environments, which can place them at fall risk. An environment can be modified to maintain safe mobility or to compensate for individual functional problems by Identifying and eliminating specific hazardous environmental conditions that increase the risk of falls or that are associated with falls (see Environmental Safety) Simplifying or maximizing mobility tasks that are specific to one or more identified risk factors by modifying the environment and existing furnishings (see Environmental Precautions). Educational Strategies A general lack of awareness about falls and fall risks is a major fall risk factor. Consequently, educational activities geared toward staff, clients, and family members are important. Staff The attitudes, knowledge, and everyday practices of staff members are key to reducing falls. Ways to support staff members in their efforts include In-service education aimed at informing staff about the magnitude and importance of the problem of falls, fall risk factors, and preventive strategies (see Reducing the Risk of Falling) Education aimed at increasing awareness of high-risk clients and the preventive strategies recommended for the individuals in each staff member s care (see CAREing About Falls) 5
6 Awareness of simple environmental safety measures, such as keeping floors dry and uncluttered Follow-up education on specific problems identified from analyzing fall incidents, and especially about any changes in a client s plan of care Making staff aware of fall preventive guidelines, protocols, and polices (see Fall Prevention Guidelines; Fall Prevention Protocol; Fall Prevention Program Policy) to help reinforce what should be done and when it should be done Direct care staff can help promote client safety by Being aware of which clients are at fall risk Reporting any sudden change of condition (i.e., a change in client s physical, behavioral, cognitive, or functional status) to supervisors Anticipating the needs of clients who are at fall risk and meeting their needs, such as providing safe supervision and assistance with walking and transferring Providing extra supervision for clients who are at particular fall risk, such as those who are new to a program (i.e., many clients are at risk during the first few day in a new setting), have postural hypotension or low blood pressure, and have urinary incontinence or elimination problems (i.e., clients may benefit from scheduled toileting programs or placing clients with urgency near toilets) Knowing the proper use of canes, walkers, wheelchairs, and crutches Clients The main purpose of fall preventive education for clients, especially those who are cognitively competent or capable of understanding safety education, is to increase their awareness of individual risk factors and to encourage them to call for assistance if they need it. Orienting clients to the care environment, staff, and routines is especially important for all new clients. Family Members Educate family caregivers about falls, about their loved ones risk of falling, and about what they can do to prevent falls (see Facts About Preventing Falls). This information is especially important during those times when the client is not in the care facility and is being cared for by the family. It is also the responsiblity of family members to inform the care staff if their loved one is experiencing any physical or behavioral change that might increase the risk of falling. 6
7 Fall and Injury Prevention Devices Even after instituting all reasonable fall prevention measures, some clients will remain at risk for falls. Clients with cognitive and/or mobility impairment, especially those who fail to ask for staff assistance with their everyday activities, are at particular risk. For these individuals, available strategies aimed at reducing the risk of falls or injuries include the use of exit alarms and hip protectors. Exit Alarms Because of multiple chronic diseases and resulting mobility impairments, some clients with I/DD may be so frail that they are at risk of falling by merely getting out of their chairs or wheelchairs. As a result, it is often necessary for the staff to provide these clients with assistance. Exit alarms are designed to warn staff that clients who should not be attempting to leave their chairs or wheelchairs unassisted are doing so. A variety of exit alarms are available: Pressure-release alarms These alarms consist of pads, mats, or other devices that go on the chair or wheelchair seat. They sense changes in weight and pressure. If the client gets up, the alarm sounds. Pressure-sensitive alarms These alarms consist of pads or mats placed on the floor in front of a chair or wheelchair that sound when stepped on. Clip-on alarms These alarms consist of a small box that is attached to the chair or wheelchair and a clip that attaches to the client s clothing. When the client gets up, the tab detaches from the box, sounding the alarm. Leg cuff alarm This alarm consists of a small plastic-enclosed alarm unit and fabric band that wraps around the client s thigh. When the client gets up, the alarm shifts from the horizontal to the vertical position, which activates the alarm. Posture indicator alarm This alarm consists of a small adhesive transmitter patch that is applied to the client s upper leg and a receiver alarm box. When the client tries to get up without assistance, the alarm box sounds. (For more information on exit alarms, see the Guide to Exit Alarms CD-ROM from the Essential Falls Management Series.) Exit Alarm Criteria An exit alarm is most effective when used for specific situations: Client experiences fall(s) from chair or wheelchair. Client experiences fall(s) while ambulating shortly after leaving chair or wheelchair. Client has impaired mobility or demonstrates unsafe chair or wheelchair transfers. Client has cognitive/communication problems and forgets to ask for assistance or cannot remember to follow safety instructions. 7
8 Hip Protectors The likelihood of a fall-related hip fracture is greatest in clients who are experiencing a loss of bone strength (i.e., osteoporosis) and a reduction of soft tissue or fat covering the hip area. As a result, the hip s ability to withstand an impact with a hard ground surface and protect against a hip fracture is diminished. Hip protectors are devices designed to protect the hip bones during a fall. In essence, hip protectors act to reduce the risk of hip fracture by absorbing the force of the fall (i.e., performing as shock absorbers) and/or diverting this force away from the hip bone (i.e., the energy of the fall is then absorbed by soft tissues and muscles surrounding the hip bone). Hip protectors consist of two basic types: Absorptive pad protectors These consist of soft foam pads that are held in place at the hips with specially designed, removable briefs or underwear (i.e., the pads are either sewn into or inserted inside pockets located over each hip). These lightweight, stretchy garments come in a range of sizes to ensure proper fit. Absorptive pad hip protectors are also available in sweat pants and shorts, which might be more comfortable for some clients; in addition to hip pads, these models include pads to protect the tailbone and knees against injury. Energy-shunting protectors These consist of hard shields or shells contained in special pants (e.g., removable briefs or underwear). The shields or shells slip into pockets sewn over the hips. Similar to absorptive protectors, these garments come in a range of sizes to ensure proper fit. The risk of hip fracture when falling while wearing hip protectors compared with a fall with no hip protector in place is significantly reduced. The best use of hip protectors is in clients who are at greatest hip fracture risk (e.g., those who are highly medicated; those who experience seizure disorder, balance impairment, cognitive impairment, or multiple falls; those who have brittle or weak bones). In addition to preventing hip fractures, hip protectors have other benefits: Clients at risk for hip fracture (i.e., those individuals with gait and balance impairment, brittle bones, and frequent falls) feel much more confident in their everyday activities when wearing hip protectors, while staff members feel more comfortable in allowing at-risk clients to move about freely. (For more information about hip protectors, see the Guide to Hip Protectors CD- ROM from the Essential Falls Management Series.) Step 4: Post-Fall Assessment Despite the best efforts of staff and others, some clients will fall. The purpose of a post-fall assessment is to find out what caused the fall and to prevent future falls. The assessment follows a step-by-step approach (see Post-Fall Assessment). Important aspects of the post-fall assessment include the following: Evaluate for any fall-related injury and/or life-threatening medical problems that may have precipitated the fall. Immediately notify the client s doctor if any injury or serious medical problem is suspected. 8
9 For those clients who are medically stable, asking the individual about the circumstance of the fall or what happened can help determine the cause of the fall. Ask the client if he or she is feeling dizzy or weak. Did the individual trip or slip? Did the client s legs give out? Ask what the client was doing at the time (e.g., getting up from a chair or wheelchair, going to the bathroom). Also, asking other staff who may have witnessed the event may provide valuable details about the fall (i.e., people around a fall can usually see a fall just before it happens). Check for and modify any environmental factors or hazards that may have contributed to the fall (e.g., slippery/wet floors, unstable furnishings, room clutter). Reassess fall risk, including a review of the client s medications, functional status, ambulation device use, and cognitive status. Implement immediate interventions to prevent further falls (e.g., if a client fell while getting up from a chair, assistance with the activity and/or the use of an exit alarm might be appropriate for the short term). If falling occurs despite initial interventions, additional or different interventions may be needed; adjust the client s care plan as necessary. Notify the client s doctor for further evaluation of all falls that have occurred with or without injury. Step 5: Monitoring After a fall, close monitoring of the client may be called for. Clients with recurrent falls may require closer monitoring than isolated or occasional fallers. For those at-risk clients without falls, periodic follow-up of all interventions is useful to evaluate whether preventive strategies are working and acceptable to both the client and the staff. If interventions or care plans are successful, continue with current approaches; however, if a client continues to fall, reconsider current interventions and amend the care plan as necessary. CONCLUSION Preventing falls among individuals with I/DD is highly dependent on educating staff, clients, and family members about falls, identifying those most at risk of falling, and coordinating appropriate risk reduction strategies through an organized care process (see Components of a Successful Fall Prevention Program). 9
Preventing Patient Falls
 Preventing Patient Falls Patient Falls are the #1 cause of ALL sentinel events. All patients at Doctors Community Hospital are assessed for fall risk and, as appropriate, the Fall Risk Protocol is implemented.
Preventing Patient Falls Patient Falls are the #1 cause of ALL sentinel events. All patients at Doctors Community Hospital are assessed for fall risk and, as appropriate, the Fall Risk Protocol is implemented.
Catholic Mutual..."CARES"
 Catholic Mutual..."CARES" BACK INJURY LOSS CONTROL FOR HEALTH CARE FACILITIES Occupational back injuries are a major loss exposure in the health care industry. Serious back injuries can result when employees
Catholic Mutual..."CARES" BACK INJURY LOSS CONTROL FOR HEALTH CARE FACILITIES Occupational back injuries are a major loss exposure in the health care industry. Serious back injuries can result when employees
Accident Prevention: Slips, Trips & Falls
 Accident Prevention: Slips, Trips & Falls Judith Davies BSc (Hons) SROT Falls Service Development and Project Manager Central Norfolk NHS East of England Ambulance Service NHS Trust Slips, Trips & Falls
Accident Prevention: Slips, Trips & Falls Judith Davies BSc (Hons) SROT Falls Service Development and Project Manager Central Norfolk NHS East of England Ambulance Service NHS Trust Slips, Trips & Falls
Implementing a Fall Alarm Program to Reduce Fall Risk Rein Tideiksaar, PhD FallPrevent, LLC
 Implementing a Fall Alarm Program to Reduce Fall Risk Rein Tideiksaar, PhD FallPrevent, LLC This program was supported by a grant from Implementing a Fall Alarm Program to Reduce Fall Risk Rein Tideiksaar,
Implementing a Fall Alarm Program to Reduce Fall Risk Rein Tideiksaar, PhD FallPrevent, LLC This program was supported by a grant from Implementing a Fall Alarm Program to Reduce Fall Risk Rein Tideiksaar,
Preventing Falls & Injuries. Dr. Gregory Gatchell Assistant Professor UC Irvine Geriatrics
 Preventing Falls & Injuries Dr. Gregory Gatchell Assistant Professor UC Irvine Geriatrics Objectives Define fall and discuss common causes of falls. Discuss consequences of falls. Discuss home safety.
Preventing Falls & Injuries Dr. Gregory Gatchell Assistant Professor UC Irvine Geriatrics Objectives Define fall and discuss common causes of falls. Discuss consequences of falls. Discuss home safety.
Reducing Falls in a Care Environment Workbook
 Reducing Falls in a Care Environment Workbook 1 Welcome! Welcome to this workbook which goes with the scenarios from the Falls DVD or You Tube clips for East Midlands HIEC Falls Prevention project. We
Reducing Falls in a Care Environment Workbook 1 Welcome! Welcome to this workbook which goes with the scenarios from the Falls DVD or You Tube clips for East Midlands HIEC Falls Prevention project. We
Falls Prevention Strategy
 Falls Prevention Strategy Policy of the Fall Season October-November 2011 Revised for CCTC By: Krista Shea RN, BScN, CNCC(C) Did you know In Canada: Falls are the 6th leading cause of death among older
Falls Prevention Strategy Policy of the Fall Season October-November 2011 Revised for CCTC By: Krista Shea RN, BScN, CNCC(C) Did you know In Canada: Falls are the 6th leading cause of death among older
Falls Risk Assessment: A Literature Review. The purpose of this literature review is to determine falls risk among elderly individuals and
 Falls Risk Assessment: A Literature Review Purpose The purpose of this literature review is to determine falls risk among elderly individuals and identify the most common causes of falls. Also included
Falls Risk Assessment: A Literature Review Purpose The purpose of this literature review is to determine falls risk among elderly individuals and identify the most common causes of falls. Also included
Tool 5 Multifactorial falls risk assessment and management tool (includes an osteoporosis risk screen)
 Tool 5 Multifactorial falls risk assessment and management tool (includes an osteoporosis risk screen) Name of resident: DOB: Room no.: Name of assessor: Date of assessment: Record all risks and actions
Tool 5 Multifactorial falls risk assessment and management tool (includes an osteoporosis risk screen) Name of resident: DOB: Room no.: Name of assessor: Date of assessment: Record all risks and actions
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders
 Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders INTRODUCTION: Health and well being are the result of many factors: Physical activity is one of these factors.
Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders INTRODUCTION: Health and well being are the result of many factors: Physical activity is one of these factors.
The third report from the Patient Safety Observatory. Slips, trips and falls in hospital PSO/3 SUMMARY
 The third report from the Patient Safety Observatory Slips, trips and falls in hospital PSO/3 Patient falls have both human and financial costs. For individual patients, the consequences can range from
The third report from the Patient Safety Observatory Slips, trips and falls in hospital PSO/3 Patient falls have both human and financial costs. For individual patients, the consequences can range from
Falls Management: Assessment & Intervention Approval Signature: September, 2012
 Level: Policy ame: Falls Management: Assessment & Intervention Approval Signature: WRHA Policy #: Section: 1 of 7 Date: Original Signed by Sylvia Ptashnik, DORS September, 01 Safety & Comfort Supercedes:
Level: Policy ame: Falls Management: Assessment & Intervention Approval Signature: WRHA Policy #: Section: 1 of 7 Date: Original Signed by Sylvia Ptashnik, DORS September, 01 Safety & Comfort Supercedes:
II. RESIDENT FALL AND INJURY ASSESSMENT - DATA RETRIEVAL WORKSHEET
 II. RESIDENT FALL AND INJURY ASSESSMENT - DATA RETRIEVAL WORKSHEET Date: Unit: Nurse Completing Audit: Shift Completed: Falls can be a symptom of other disease processes and should be seriously considered
II. RESIDENT FALL AND INJURY ASSESSMENT - DATA RETRIEVAL WORKSHEET Date: Unit: Nurse Completing Audit: Shift Completed: Falls can be a symptom of other disease processes and should be seriously considered
Falls Awareness & Prevention Guide
 Falls Awareness & Prevention Guide Prepare your home or assist a loved one today by following these fall-proofing recommendations, courtesy of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons and The Orthopaedic
Falls Awareness & Prevention Guide Prepare your home or assist a loved one today by following these fall-proofing recommendations, courtesy of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons and The Orthopaedic
Module 4: The Biggest Fear Falls
 Module Introduction Module 4: The Biggest Fear Falls Module 4 addresses one of the biggest concerns within any assisted living facility falls. As we encourage older adults to move more, it is natural to
Module Introduction Module 4: The Biggest Fear Falls Module 4 addresses one of the biggest concerns within any assisted living facility falls. As we encourage older adults to move more, it is natural to
Falls and falls injury prevention activity audit for residential aged care facilities
 Falls and falls injury prevention activity audit for residential aged care facilities National Ageing Research Institute October 2009 www.nari.unimelb.edu.au This tool is based on a tool that was originally
Falls and falls injury prevention activity audit for residential aged care facilities National Ageing Research Institute October 2009 www.nari.unimelb.edu.au This tool is based on a tool that was originally
Policy for the Prevention of Slips, Trips and Falls for Inpatients within Western Health and Social Care Trust Facilities
 Policy for the Prevention of Slips, Trips and Falls for Inpatients within Western Health and Social Care Trust Facilities October 2010 Policy Title: Policy for the Prevention of Slips, Trips and Falls
Policy for the Prevention of Slips, Trips and Falls for Inpatients within Western Health and Social Care Trust Facilities October 2010 Policy Title: Policy for the Prevention of Slips, Trips and Falls
Slips, Trips, and Falls
 Slips, Trips, and Falls Slips, Trips, and Falls Cause Many Injuries Sometimes Serious Ones Thousands of disabling injuries- and even deaths- occur each year as a result of slips, trips, and falls: From
Slips, Trips, and Falls Slips, Trips, and Falls Cause Many Injuries Sometimes Serious Ones Thousands of disabling injuries- and even deaths- occur each year as a result of slips, trips, and falls: From
Healthy Steps. Your guide to falls prevention and home safety
 Healthy Steps Your guide to falls prevention and home safety Are you at risk for a fall? The best way to keep yourself safe and independent in your home is to know where the risks are. Risks include: Having
Healthy Steps Your guide to falls prevention and home safety Are you at risk for a fall? The best way to keep yourself safe and independent in your home is to know where the risks are. Risks include: Having
Slips, Trips and Falls
 Slips, Trips and Falls Introduction o Slips, trips and falls cause: The majority of general industry accidents 15 percent of all accidental deaths (~12,000/yr) More fatalities than all other causes but
Slips, Trips and Falls Introduction o Slips, trips and falls cause: The majority of general industry accidents 15 percent of all accidental deaths (~12,000/yr) More fatalities than all other causes but
Breaking the Fall Cycle: A Survey of State of the Art Technology and Protective Devices. Teaching Guide
 Breaking the Fall Cycle: A Survey of State of the Art Technology and Protective Devices Teaching Guide Rein Tideiksaar, PhD FallPrevent, LLC January 2009 This program was supported by a grant from 1 Biography
Breaking the Fall Cycle: A Survey of State of the Art Technology and Protective Devices Teaching Guide Rein Tideiksaar, PhD FallPrevent, LLC January 2009 This program was supported by a grant from 1 Biography
Slips, Trips and Falls Prevention
 Slips, Trips and Falls Prevention Session Objectives Recognize slips, trips, and falls as a serious safety problem Identify slip, trip, and fall hazards Avoid or eliminate slip, trip, and fall hazards
Slips, Trips and Falls Prevention Session Objectives Recognize slips, trips, and falls as a serious safety problem Identify slip, trip, and fall hazards Avoid or eliminate slip, trip, and fall hazards
Patient Falls in Hospitals and Nursing Homes: A Safety Challenge
 1 Patient Falls in Hospitals and Nursing Homes: A Safety Challenge Kathleen Martin, RN, MSN, MPA, LNHA, CPHQ, WCC Fall and injury prevention continues to be a considerable challenge in all health care
1 Patient Falls in Hospitals and Nursing Homes: A Safety Challenge Kathleen Martin, RN, MSN, MPA, LNHA, CPHQ, WCC Fall and injury prevention continues to be a considerable challenge in all health care
RoSPA CONFERENCE BELFAST. From little acorns. Goal. Jane Steven GOAL BACKGROUND EFFECTS OF FALLS & FRACTURES FALLS COLLABORATIVE DEVELOPMENTS
 RoSPA CONFERENCE BELFAST From little acorns Jane Steven Falls & Fracture Prevention Coordinator GOAL BACKGROUND EFFECTS OF FALLS & FRACTURES FALLS COLLABORATIVE DEVELOPMENTS Goal To reduce falls in the
RoSPA CONFERENCE BELFAST From little acorns Jane Steven Falls & Fracture Prevention Coordinator GOAL BACKGROUND EFFECTS OF FALLS & FRACTURES FALLS COLLABORATIVE DEVELOPMENTS Goal To reduce falls in the
Preventing slip and fall accidents in nursing homes and long term care facilities Risktopic 7-3.002
 Preventing slip and fall accidents in nursing homes and long term care facilities Risktopic 7-3.002 Introduction Slips and falls are a leading type of accident occurring in nursing homes and other long
Preventing slip and fall accidents in nursing homes and long term care facilities Risktopic 7-3.002 Introduction Slips and falls are a leading type of accident occurring in nursing homes and other long
Mobility After Stroke
 Mobility After Stroke Issues facing stroke survivors and their families Regaining Mobility Moving around safely and easily is not something you may think about, until you have had a stroke. Each year more
Mobility After Stroke Issues facing stroke survivors and their families Regaining Mobility Moving around safely and easily is not something you may think about, until you have had a stroke. Each year more
UL Listed monitoring center CSAA Certified Care Specialists No long-term contract Cancel at any time Simple 10 minute setup 24/7 customer assistance
 Medical Alert System MEDICAL ALERT SYSTEMS PROVIDE SECURITY, PEACE OF MIND, AND INDEPENDENCE... AT HOME. Live in the comfort of your home. Living at home surrounded by things that are familiar makes you
Medical Alert System MEDICAL ALERT SYSTEMS PROVIDE SECURITY, PEACE OF MIND, AND INDEPENDENCE... AT HOME. Live in the comfort of your home. Living at home surrounded by things that are familiar makes you
Slips Trips & Falls. What To Avoid
 Slips Trips & Falls What To Avoid Did You Know? According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics: Fatal falls, slips, or trips took the lives of 666 workers in 2011, or about 14 percent of all fatal work injuries
Slips Trips & Falls What To Avoid Did You Know? According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics: Fatal falls, slips, or trips took the lives of 666 workers in 2011, or about 14 percent of all fatal work injuries
Slip, Trip & Fall Prevention Handbook
 Slip, Trip & Fall Prevention Handbook This prevention handbook provides you with a basic understanding of what causes a slip, trip or fall and gives you some ideas on what you can do to stop these incidents
Slip, Trip & Fall Prevention Handbook This prevention handbook provides you with a basic understanding of what causes a slip, trip or fall and gives you some ideas on what you can do to stop these incidents
Slips, Trips and Falls. Awareness Month. February 2005. Slips, Trips and Falls
 THE SCHOOL DISTRICT OF PITTSBURGH Slips, Trips and Falls Awareness Month Joint Labor / Management Safety Committee Please open the attachment for additional information that will answer safety questions
THE SCHOOL DISTRICT OF PITTSBURGH Slips, Trips and Falls Awareness Month Joint Labor / Management Safety Committee Please open the attachment for additional information that will answer safety questions
Let s work together to prevent falls
 Let s work together to prevent falls Let s work together to prevent falls Every year in New Zealand one in three people over the age of 65 will fall 1. For those aged over 80, the rate of falls is one
Let s work together to prevent falls Let s work together to prevent falls Every year in New Zealand one in three people over the age of 65 will fall 1. For those aged over 80, the rate of falls is one
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Balance and Vestibular Center Programs to treat dizziness and reduce your risk of falling
 Balance and Vestibular Center Programs to treat dizziness and reduce your risk of falling Helping you overcome dizziness and vertigo Most people will experience dizziness at some point in their lives.
Balance and Vestibular Center Programs to treat dizziness and reduce your risk of falling Helping you overcome dizziness and vertigo Most people will experience dizziness at some point in their lives.
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: FALL PREVENTION NURSE TRACK
 IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: FALL PREVENTION NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency to support reducing avoidable hospitalizations
IN-HOME QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BEST PRACTICE: FALL PREVENTION NURSE TRACK Best Practice Intervention Packages were designed for use by any In-Home Provider Agency to support reducing avoidable hospitalizations
Falls Prevention and Management
 Falls Prevention and Management Best Practices Initiative Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Presentation Prepared By: Hazelynn Kinney Regional Best Practice Coordinator - Central East Region Based
Falls Prevention and Management Best Practices Initiative Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Presentation Prepared By: Hazelynn Kinney Regional Best Practice Coordinator - Central East Region Based
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
 Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds
 Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds Training conducted by: Michael Fishman and Sandrine Fisher 1 Objectives To become familiar with the application of the rating
Evaluating muscle injuries and residuals of shell fragment and gunshot wounds Training conducted by: Michael Fishman and Sandrine Fisher 1 Objectives To become familiar with the application of the rating
If you fall or witness a fall, do you know what to do?
 If you fall or witness a fall, do you know what to do? We all fall from time to time. With age, both the number of falls and the likelihood of injury increase. So, it s important to know what to do if
If you fall or witness a fall, do you know what to do? We all fall from time to time. With age, both the number of falls and the likelihood of injury increase. So, it s important to know what to do if
<< INSERT COMPANY NAME
 > SLIIP-TRIIP-FALL & STRAIIN IINJURY TRAIINIING > Fall Prevention Slips, trips, and falls constitute the majority of general industry accidents. They cause 15% of
> SLIIP-TRIIP-FALL & STRAIIN IINJURY TRAIINIING > Fall Prevention Slips, trips, and falls constitute the majority of general industry accidents. They cause 15% of
TITLE: FALL PREVENTION PROTOCOL POLICY # F 01.5 MANUAL: CLINICAL PROCEDURE MANUAL Page 1 of 11
 TITLE: FALL PREVENTION PROTOCOL POLICY # F 01.5 MANUAL: CLINICAL PROCEDURE MANUAL Page 1 of 11 Effective Date: 10/00 Reviewed/Revised: 5/02; 6/02, 11/05, 11/06, 2/07, 12/09, 11/10, 4/11, 7/12, 8/13, 8/14
TITLE: FALL PREVENTION PROTOCOL POLICY # F 01.5 MANUAL: CLINICAL PROCEDURE MANUAL Page 1 of 11 Effective Date: 10/00 Reviewed/Revised: 5/02; 6/02, 11/05, 11/06, 2/07, 12/09, 11/10, 4/11, 7/12, 8/13, 8/14
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Slip, trip and fall assessment guide. The framework to evaluate and assess the potential risk
 Slip, trip and fall assessment guide The framework to evaluate and assess the potential risk Slips, trips and falls How safe are your floors? How about your stairs? Have people fallen recently? You are
Slip, trip and fall assessment guide The framework to evaluate and assess the potential risk Slips, trips and falls How safe are your floors? How about your stairs? Have people fallen recently? You are
PRINTED: 07/09/2013 FORM APPROVED CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES OMB NO. 0938-0391 (X2) MULTIPLE CONSTRUCTION A.
 CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICA SERVICES OMB NO. 0938-0391 (X1) PROVER/SUPPLIER/CLIA ENTIFICATION NUMBER: (X3) SURVEY NAME OF PROVER OR SUPPLIER (X4) FINAL OBSERVATIONS LICENSURE VIOLATIONS: 300.610)a) 300.1210)a)
CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICA SERVICES OMB NO. 0938-0391 (X1) PROVER/SUPPLIER/CLIA ENTIFICATION NUMBER: (X3) SURVEY NAME OF PROVER OR SUPPLIER (X4) FINAL OBSERVATIONS LICENSURE VIOLATIONS: 300.610)a) 300.1210)a)
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital
 By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
The Morse Fall Scale Training Module Partners HealthCare System Fall Prevention Task Force
 The Morse Fall Scale Training Module Partners HealthCare System Fall Prevention Task Force Based on J. Morse (1997). Preventing Patient Falls. CA: Sage Publishing Co. 1 2 Objectives 1. What is fall risk
The Morse Fall Scale Training Module Partners HealthCare System Fall Prevention Task Force Based on J. Morse (1997). Preventing Patient Falls. CA: Sage Publishing Co. 1 2 Objectives 1. What is fall risk
Discussion Leaders Guide Session Slips, Trips and Falls
 Discussion Leaders Guide Session Slips, Trips and Falls 1. Preparation You will need a DVD player and a television. Review the Tell, Ask and Review portions of the Discussion Leaders Guide. You will be
Discussion Leaders Guide Session Slips, Trips and Falls 1. Preparation You will need a DVD player and a television. Review the Tell, Ask and Review portions of the Discussion Leaders Guide. You will be
From Hospital to Home: Fall Prevention in an Acute Care Setting
 From Hospital to Home: Fall Prevention in an Acute Care Setting Patricia A. MacCulloch MS, APRN, BC Adult Nurse Practitioner UMass Memorial Dept. of Orthopedics Mission UMass Memorial is committed to improving
From Hospital to Home: Fall Prevention in an Acute Care Setting Patricia A. MacCulloch MS, APRN, BC Adult Nurse Practitioner UMass Memorial Dept. of Orthopedics Mission UMass Memorial is committed to improving
Fall into Fall. Fall prevention in-service for Dementia clients. Lisa Reidinger LNHA,CSW,CTRS, CDP National Council of Certified Dementia Practioners
 Fall into Fall Fall prevention in-service for Dementia clients Lisa Reidinger LNHA,CSW,CTRS, CDP National Council of Certified Dementia Practioners Falls and the elderly Falls are responsible for 1 in
Fall into Fall Fall prevention in-service for Dementia clients Lisa Reidinger LNHA,CSW,CTRS, CDP National Council of Certified Dementia Practioners Falls and the elderly Falls are responsible for 1 in
Why Back Safety is Important
 Back Safety Why Back Safety is Important Back injuries are considered by OSHA (the Occupational Safety and Health Administration) as the nation's #1 workplace safety problem. Back Injuries are often: Very
Back Safety Why Back Safety is Important Back injuries are considered by OSHA (the Occupational Safety and Health Administration) as the nation's #1 workplace safety problem. Back Injuries are often: Very
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form
 IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
Illinois Department of Public Health STATEMENT OF DEFICIENCIES AND PLAN OF CORRECTION C 04/26/2015. Statement of Licensure Violations:
 (X1) PROVER/SUPPLIER/LIA ENTIFIATION NUMBER: (X3) SURVEY D NAME OF PROVER OR SUPPLIER (X4) REGULATORY OR LS ENTIFYING INFORMATION) Final Observations Statement of Licensure Violations: 300.610a) 300.1210b)
(X1) PROVER/SUPPLIER/LIA ENTIFIATION NUMBER: (X3) SURVEY D NAME OF PROVER OR SUPPLIER (X4) REGULATORY OR LS ENTIFYING INFORMATION) Final Observations Statement of Licensure Violations: 300.610a) 300.1210b)
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Preventing Slips, Trips and Falls. Presented by: Mark Hargett
 Preventing Slips, Trips and Falls Presented by: Mark Hargett Objectives At the end of this workshop, you will be able to: Describe the true costs of slips, trips, and falls Identify elements of effective
Preventing Slips, Trips and Falls Presented by: Mark Hargett Objectives At the end of this workshop, you will be able to: Describe the true costs of slips, trips, and falls Identify elements of effective
Preventing Falls, Slips and Trips
 Preventing Falls, Slips and Trips Falls/Slips/Trips (FSTs) You take hundreds of steps every day, but how many of those steps do you take seriously? Please take a few minutes to understand how Falls/Slips/Trips
Preventing Falls, Slips and Trips Falls/Slips/Trips (FSTs) You take hundreds of steps every day, but how many of those steps do you take seriously? Please take a few minutes to understand how Falls/Slips/Trips
Back Pain Musculoskeletal Disorder Updated October 2010
 Back Pain Musculoskeletal Disorder Updated October 2010 According to the Health and Safety Executive back pain is the most common health problem for British workers. Approximately 80% of people experience
Back Pain Musculoskeletal Disorder Updated October 2010 According to the Health and Safety Executive back pain is the most common health problem for British workers. Approximately 80% of people experience
Strength Training HEALTHY BONES, HEALTHY HEART
 Strength Training HEALTHY BONES, HEALTHY HEART No matter what your age, strength training can improve your bone health and your balance. As we age, our bones lose both tissue and strength. This condition
Strength Training HEALTHY BONES, HEALTHY HEART No matter what your age, strength training can improve your bone health and your balance. As we age, our bones lose both tissue and strength. This condition
Minimising the Risk of Falls & Fall-related Injuries. Education Supplement
 Minimising the Risk of Falls & Fall-related Injuries Guidelines for Acute, Sub-acute and Residential Care Education Supplement Published by the Metropolitan Health and Aged Care Services Division Victorian
Minimising the Risk of Falls & Fall-related Injuries Guidelines for Acute, Sub-acute and Residential Care Education Supplement Published by the Metropolitan Health and Aged Care Services Division Victorian
Introduction: Anatomy of the spine and lower back:
 Castleknock GAA club member and Chartered Physiotherapist, James Sherry MISCP, has prepared an informative article on the common causes of back pain and how best it can be treated. To book a physiotherapy
Castleknock GAA club member and Chartered Physiotherapist, James Sherry MISCP, has prepared an informative article on the common causes of back pain and how best it can be treated. To book a physiotherapy
How To Write Long Term Care Insurance
 By Lori Boyce, AVP Risk Management and R&D Underwriting long term care insurance: a primer Every day Canadians die, are diagnosed with cancer, have heart attacks and become disabled and our insurance solutions
By Lori Boyce, AVP Risk Management and R&D Underwriting long term care insurance: a primer Every day Canadians die, are diagnosed with cancer, have heart attacks and become disabled and our insurance solutions
These consequences include:
 1 Slide 3 Introduction (Time for this section-10 minutes) These consequences include: Physical Discomfort and pain - caused by skeletal or soft tissue damage Serious injury Hypothermia, pressure-related
1 Slide 3 Introduction (Time for this section-10 minutes) These consequences include: Physical Discomfort and pain - caused by skeletal or soft tissue damage Serious injury Hypothermia, pressure-related
Slips, Trips, & Falls. Supervisors Notes
 Slips, Trips, & Falls Supervisors Notes Walking is one of those things we are so accustomed to we take it for granted we will get from one place to another without incident. Unfortunately this isn t always
Slips, Trips, & Falls Supervisors Notes Walking is one of those things we are so accustomed to we take it for granted we will get from one place to another without incident. Unfortunately this isn t always
How to Prevent Slips, Trips, Falls. For the Employees of Cascade County
 How to Prevent Slips, Trips, Falls For the Employees of Cascade County Walking is Risky Business Think about the things that you do frequently. Often these tasks are done without thought or planning.
How to Prevent Slips, Trips, Falls For the Employees of Cascade County Walking is Risky Business Think about the things that you do frequently. Often these tasks are done without thought or planning.
Working feet and footwear. Health and safety at work guidance
 Working feet and footwear Health and safety at work guidance Many workers face problems with their feet or legs because of the wrong footwear or because they are forced to stand for too long. Feet bear
Working feet and footwear Health and safety at work guidance Many workers face problems with their feet or legs because of the wrong footwear or because they are forced to stand for too long. Feet bear
Chapter 12. Client Safety. safe, effective care environment
 chapter 12 Unit 1 Section Chapter 12 safe, effective care environment safety and Infection Control Client Safety Overview Providing for safety and preventing injury are major nursing responsibilities.
chapter 12 Unit 1 Section Chapter 12 safe, effective care environment safety and Infection Control Client Safety Overview Providing for safety and preventing injury are major nursing responsibilities.
How To Treat Heel Pain
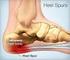 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
A compressive dressing that you apply around your ankle, and
 Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
NORTHEAST HOSPITAL CORPORATION
 NORTHEAST HOSPITAL CORPORATION Title: Fall Prevention Program Date Effective: 9/02 Date Revised: 3/05, 7/08, 12/08, 2/11/10, 2/14/11, 5/14/13 Date Reviewed: 4/05 Joint Commission Chapter: Provision of
NORTHEAST HOSPITAL CORPORATION Title: Fall Prevention Program Date Effective: 9/02 Date Revised: 3/05, 7/08, 12/08, 2/11/10, 2/14/11, 5/14/13 Date Reviewed: 4/05 Joint Commission Chapter: Provision of
Check for Safety. A Home Fall Prevention Checklist for Older Adults
 P Safety This checklist was produced with support from the MetLife Foundation. Centers Disease Control and Prevention National Center Injury Prevention and Control A Home Fall Prevention list Older Adults
P Safety This checklist was produced with support from the MetLife Foundation. Centers Disease Control and Prevention National Center Injury Prevention and Control A Home Fall Prevention list Older Adults
HealthStream Regulatory Script
 HealthStream Regulatory Script Back Safety Version: May 2007 Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Back Injury Lesson 3: Spinal Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 4: Safe Operation of the Spine Lesson 5: Preventive
HealthStream Regulatory Script Back Safety Version: May 2007 Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Back Injury Lesson 3: Spinal Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 4: Safe Operation of the Spine Lesson 5: Preventive
WSN ERGONOMIC SAFETY TALK #3
 What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
Preventing Slips, Trips and Falls (Basic Awareness Level 1) Staff information leaflet. RDaSH. Corporate Services
 Preventing Slips, Trips and Falls (Basic Awareness Level 1) Staff information leaflet RDaSH Corporate Services Staff Safety in the Workplace: Did you know? Slips and trips are the biggest cause of serious
Preventing Slips, Trips and Falls (Basic Awareness Level 1) Staff information leaflet RDaSH Corporate Services Staff Safety in the Workplace: Did you know? Slips and trips are the biggest cause of serious
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Total Hip Replacement
 NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
Healthy Balance Is in Your Control. Perspectives on Fall Prevention
 Healthy Balance Is in Your Control Perspectives on Fall Prevention National data indicate that falls are the largest single cause of restrictedactivity days among older adults; are a leading precipitating
Healthy Balance Is in Your Control Perspectives on Fall Prevention National data indicate that falls are the largest single cause of restrictedactivity days among older adults; are a leading precipitating
WalkAide. Long term cost effectiveness of FES. J of Rehab Med 2013; 45(2):154 60 Humphreys et al
 WalkAide Long term cost effectiveness of FES J of Rehab Med 2013; 45(2):154 60 Humphreys et al 126 people (62 stroke, 39 MS, 7 SCI, 3 CP, 15 other) Mean time of FES use 3.6 years 33 using FES after 11.1
WalkAide Long term cost effectiveness of FES J of Rehab Med 2013; 45(2):154 60 Humphreys et al 126 people (62 stroke, 39 MS, 7 SCI, 3 CP, 15 other) Mean time of FES use 3.6 years 33 using FES after 11.1
WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING All Euramax Subsidiaries BACK SAFETY / PROPER LIFTING. Safety Meeting Contents. Meeting Notice. Leaders Guide.
 Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read through the and
Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read through the and
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Patient Labeling Information System Description
 Patient Labeling Information System Description The Trident Ceramic Acetabular System is an artificial hip replacement device that features a new, state-of-the-art ceramic-on-ceramic bearing couple. The
Patient Labeling Information System Description The Trident Ceramic Acetabular System is an artificial hip replacement device that features a new, state-of-the-art ceramic-on-ceramic bearing couple. The
How To Prevent A Slip, Trip And Fall
 Slip, Trip, and Fall Prevention Guide Presentation: Risk Management Office 2015 Objectives The objectives of the Slip, Trip and Fall Prevention Guide are to provide direction on: a) Identifying working
Slip, Trip, and Fall Prevention Guide Presentation: Risk Management Office 2015 Objectives The objectives of the Slip, Trip and Fall Prevention Guide are to provide direction on: a) Identifying working
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych
 Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Most people living with epilepsy do not experience serious problems with their thinking. However, there are aspects of thinking that can be affected
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Most people living with epilepsy do not experience serious problems with their thinking. However, there are aspects of thinking that can be affected
Preventing Falls In and Around Homes
 Preventing Falls In and Around Homes Authors: Robert Bobby Grisso, Extension Engineer, Biological Systems Engineering, Virginia Tech; John Perumpral, Professor Emeritus, Biological Systems Engineering,
Preventing Falls In and Around Homes Authors: Robert Bobby Grisso, Extension Engineer, Biological Systems Engineering, Virginia Tech; John Perumpral, Professor Emeritus, Biological Systems Engineering,
Working together to prevent pressure ulcers (prevention and pressure-relieving devices)
 Working together to prevent pressure ulcers (prevention and pressure-relieving devices) Understanding NICE guidance information for people at risk of pressure ulcers, their carers, and the public Draft
Working together to prevent pressure ulcers (prevention and pressure-relieving devices) Understanding NICE guidance information for people at risk of pressure ulcers, their carers, and the public Draft
Falls Prevention. Your Guide to. Geriatric Medicine. 2 Simei Street 3 Singapore 529889 Tel: 6788 8833 Fax: 6788 0933 www.cgh.com.sg Reg No 198904226R
 Geriatric Medicine 2 Simei Street 3 Singapore 529889 Tel: 6788 8833 Fax: 6788 0933 www.cgh.com.sg Reg No 198904226R For appointments and enquiries, please call the CGH Appointment Centre at Tel: (65) 6850
Geriatric Medicine 2 Simei Street 3 Singapore 529889 Tel: 6788 8833 Fax: 6788 0933 www.cgh.com.sg Reg No 198904226R For appointments and enquiries, please call the CGH Appointment Centre at Tel: (65) 6850
Subject: Preventing Falls
 Patient Information Kingston Hospital Subject: Preventing Falls What You Need To Know About Preventing Falls Taking Positive Steps Information for Patients Falls Steering Group Content Introduction.. 1
Patient Information Kingston Hospital Subject: Preventing Falls What You Need To Know About Preventing Falls Taking Positive Steps Information for Patients Falls Steering Group Content Introduction.. 1
OUTPATIENT PHYSICAL AND OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY PROTOCOL GUIDELINES
 OUTPATIENT PHYSICAL AND OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY PROTOCOL GUIDELINES General Therapy Guidelines 1. Therapy evaluations must be provided by licensed physical and/or occupational therapists. Therapy evaluations
OUTPATIENT PHYSICAL AND OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY PROTOCOL GUIDELINES General Therapy Guidelines 1. Therapy evaluations must be provided by licensed physical and/or occupational therapists. Therapy evaluations
Physiotherapy Database Exercises for people with Spinal Cord Injury
 Physiotherapy Database Exercises for people with Spinal Cord Injury Compiled by the physiotherapists associated with the following Sydney (Australian) spinal units : Last Generated on Mon Mar 29 16:57:20
Physiotherapy Database Exercises for people with Spinal Cord Injury Compiled by the physiotherapists associated with the following Sydney (Australian) spinal units : Last Generated on Mon Mar 29 16:57:20
April No Falls bingo game
 April No Falls bingo game Bingo playing cards with falls prevention themes, can be used as a recreational activity and at the same time help educate participants on how to prevent falls. These cards can
April No Falls bingo game Bingo playing cards with falls prevention themes, can be used as a recreational activity and at the same time help educate participants on how to prevent falls. These cards can
Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents
 Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents I. Introduction...2 II. Scope...2 III. IV. Definitions...2 Responsibilities...4 V. Practices...5 VI. Slip-Fall Facility Checklist...7 VII. VIII. Training...8
Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents I. Introduction...2 II. Scope...2 III. IV. Definitions...2 Responsibilities...4 V. Practices...5 VI. Slip-Fall Facility Checklist...7 VII. VIII. Training...8
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI)
 Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Occupational & Physical Therapy Guidelines for Service Provision within the Schools
 1 Occupational & Physical Therapy Guidelines for Service Provision within the Schools 2012 2 Introduction* Purpose The purpose of this document is to provide guidance regarding school-based Occupational
1 Occupational & Physical Therapy Guidelines for Service Provision within the Schools 2012 2 Introduction* Purpose The purpose of this document is to provide guidance regarding school-based Occupational
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
Understanding the Aging Process: General Information, Risk Factors and Approaches to Care
 Understanding the Aging Process: General Information, Risk Factors and Approaches to Care 1 Understanding the Aging Process In 2004, the life expectancy for the United States population reached a record
Understanding the Aging Process: General Information, Risk Factors and Approaches to Care 1 Understanding the Aging Process In 2004, the life expectancy for the United States population reached a record
Therapy Functional Reassessment: It s a good thing. Objectives. Oasis-not just a requirement 3/19/2012. Vicki D. Gines PT DPT CEEAA
 Therapy Functional Reassessment: It s a good thing Missouri Alliance For Home Care Annual Conference 2012 Vicki D. Gines PT DPT CEEAA Objectives State how Oasis ties to Therapy evaluations State key components
Therapy Functional Reassessment: It s a good thing Missouri Alliance For Home Care Annual Conference 2012 Vicki D. Gines PT DPT CEEAA Objectives State how Oasis ties to Therapy evaluations State key components
How To Prevent A Fall
 Slips, Trips, Falls ISABEL KRUEGER, CRSP Slips Trips and Falls HOW THEY HAPPEN AND WHAT WE CAN DO ABOUT IT. 1 Definition Slip too little friction or traction between a person s feet and the walking surface.
Slips, Trips, Falls ISABEL KRUEGER, CRSP Slips Trips and Falls HOW THEY HAPPEN AND WHAT WE CAN DO ABOUT IT. 1 Definition Slip too little friction or traction between a person s feet and the walking surface.
Patient handling techniques to prevent MSDs in health care
 28 Introduction Patient handling techniques Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are a serious problem among hospital personnel, and in particular the nursing staff. Of primary concern are back
28 Introduction Patient handling techniques Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are a serious problem among hospital personnel, and in particular the nursing staff. Of primary concern are back
Escalator incidents occur frequently at airports (some airports experience several per month).
 ESIS, Inc. Global Risk Control Services Airport Risk Management Series Escalator Safety Prepared by: Ginga Griffin, CPCU. ALCM Introduction As airports and terminals expanded, the number of escalators
ESIS, Inc. Global Risk Control Services Airport Risk Management Series Escalator Safety Prepared by: Ginga Griffin, CPCU. ALCM Introduction As airports and terminals expanded, the number of escalators
Move and position individuals in accordance with their plan of care
 Move and position individuals in accordance with their plan of care Page 1 of 21 Level 2 Diploma in Health and Social Care Unit HSC 2028 Tutor Name: Akua Quao Thursday 12 th September 2013 Release Date:
Move and position individuals in accordance with their plan of care Page 1 of 21 Level 2 Diploma in Health and Social Care Unit HSC 2028 Tutor Name: Akua Quao Thursday 12 th September 2013 Release Date:
The menopausal transition usually has three parts:
 The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
The menopausal transition usually has three parts: Perimenopause begins several years before a woman s last menstrual period, when the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen. In the last 1-2 years of
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
