Lecture 7 Static Structural Analysis
|
|
|
- Blake Raymond Bennett
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 7 Static Structural Analysis 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
2 Chapter Overview In this chapter, performing linear static structural analyses in Mechanical will be covered: A. Basics of Linear Static Analysis B. Geometry C. Material Properties D. Contact E. Analysis Settings F. Loads G. Supports H. Load and Support Display I. Contact vs Supports J. Solving Models K. Workshop 7.1, Pump Assembly With Contact L. Results and Postprocessing M. Linear vs Non Linear N. Workshop 7.2, Using Beam Connections O. Appendix ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
3 A. Basics of Linear Static Analysis The schematic setup for a linear static structural analysis is shown here ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
4 ... Basics of Linear Static Analysis For a linear static structural analysis, the global displacement vector {x} is solved for in the matrix equation below: K x F Assumptions made for linear static structural analysis are: [K], which is the global stiffness matrix, is constant Linear elastic material behavior is assumed Small deflection theory is used {F}, which is the global load vector, is statically applied No time-varying forces are considered No damping effects It is important to remember these assumptions related to linear static analysis. Nonlinear static and dynamic analyses are covered in other training courses ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
5 B. Geometry In structural analyses, all types of bodies supported by Mechanical may be used. For surface bodies, thickness must be supplied in the Details view of the Geometry branch. The cross-section and orientation of line bodies are defined within DesignModeler and are imported into Mechanical automatically ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
6 ... Geometry Mechanical allows a part s stiffness behavior to be defined as rigid/flexible. A rigid body is not meshed with traditional finite elements. Rather it is represented using a single mass element and is thus very efficient in terms of solution times. Parts in an assembly that are included only to transfer loads can be designated as rigid to reduce solution times and model sizes ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
7 ... Point Mass A Point Mass can be added to a model s Geometry branch to simulate parts of the structure not explicitly modeled: Point mass is affected by Acceleration, Standard Earth Gravity, and Rotational Velocity. No other loads affect a point mass ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
8 C. Material Properties Young s Modulus and Poisson s Ratio are always required for linear static structural analyses: Density is required if any inertial loads are present. Thermal expansion coefficient is required if a temperature load is applied. Stress Limits are needed if a Stress Tool result is present. Fatigue Properties are needed if Fatigue Tool result is present. Requires Fatigue Module add-on license. As shown earlier material properties are assigned in the part details in Mechanical. The user can chose from the dropdown list materials available to this project ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
9 D. Contact Surface contact elements in Mechanical can be visualized as a skin covering the surfaces of the parts in an assembly. It is these elements that define the behavior when parts are in contact (e.g. friction, bonding, heat transfer, etc.). In Mechanical contact pairs are color coded as shown here. Note, contact is covered in more detail in connection lecture (L05_connections). Contact Side Target Side ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
10 Contact - Spot Weld Spot welds provide a means of connecting shell assemblies at discrete points: Spotweld definition is done in the CAD software. Currently, only DesignModeler and Unigraphics define supported spot weld definitions ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
11 E. Analysis Settings The Analysis Settings details provide general control over the solution process: Step Controls: Specify the number of steps in an analysis and an end time for each step. Solver Controls: Two solvers available (default program chosen): Direct solver (Sparse solver in MAPDL). Iterative solver (PCG solver in MAPDL). Weak springs: Mechanical tries to anticipate under-constrained models ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
12 ... Analysis Settings The Output Controls section of the analysis settings configures what items are to be written to the results file (defaults shown). Output controls are intended to allow users to write efficient results files containing only the desired information thereby limiting file sizes. The most general results quantities are written by default. Be sure to review the documentation before starting an analysis to make sure the desired results will be written. Note: the default configuration for output controls can be changed in Tools > Options > Analysis Settings and Solution ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
13 F. Loads Loads and supports respond in terms of the degrees of freedom (DOF) available for the elements used. With solid geometry the DOF are X, Y and Z translations (for shells and beams we add rotational DOF rotx, roty and rotz). Boundary conditions, regardless of actual names, are always defined in terms of these DOF. Boundary conditions can be scoped to geometry items or to nodes (depending on load type). Example: a Frictionless Support applied to the face of the block shown would indicate that the Z degree of freedom is no longer free (all other DOF are free). UZ UY UX Frictionless surface ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
14 ... Loads Most of loads and supports can be defined by components of by vector. Loads and supports having a direction component can be defined in global or local coordinate systems: In the Details view, change Define By to Components. Then, select the appropriate CS from the pull-down menu ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
15 ... Loads Acceleration (all bodies) Standard Earth Gravity (all bodies) Rotational Velocity (selected bodies) Units length/time 2 length/time 2 Radian/second or RPM Defined by Components Vector A Direction Local or global coordinate system Components Vector Resulting forces: Resulting forces: Notes ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
16 ... Loads Pressure Line Pressure Force Moment Scoping Units Force/area Force/length Mass*length/time² Force*length Definition Components Vector Normal to Vector Component direction Tangential (along line) Components Vector Components Vector Positive value into surface, negative value acts out of surface. If multiple entities are selected, the loads are evenly distributed ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
17 ... Loads Hydrostatic Pressure: Applies a linearly varying load to a surface (solid or shell) to simulate fluid force acting on the structure. Fluid may be Internal (contained fluid) or external (submerged body). Internal External ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
18 ... Loads Bearing Load (force): Forces are distributed in compression over the projected area: No axial components. Use only one bearing load per cylindrical surface. If the cylindrical surface is split, select both halves of cylinder when applying the load. Bearing loads can be defined via vector or component method. Bearing Load Force Load ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
19 ... Loads Remote Force Loading : The user supplies the origin of the force (geometry or coordinates). Mechanical automatically creates a remote point at the force location. Can be defined using vector or component method. Applies an equivalent force and moment on the surface. Example: 10 inch beam with a 1 lbf remote force scoped to the end of the beam. Remote force is located 20 inches from the fixed support. F=1 lbf 20 Details about remote points are covered in L06_Remote BC ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Moment Reaction
20 ... Loads Bolt Pretension: Applies a pretension load to a solid cylindrical section or beam using: Pretension load (force) OR Adjustment (length) For body loading a local coordinate system is required (preload in z direction). Face selection assumes axial direction of cylindrical surface. For multistep analyses additional options are available (covered later) ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
21 ... Loads Thermal Condition: x th y th z th T T ref Applies a uniform temperature in a structural analysis. A reference temperature must be provided (can apply to all bodies or individuals). Reference temperature in Environment (e.g. Static Structural), applies to all bodies ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Reference temperature can be applied to individual bodies
22 G. Supports Fixed Support : Constraints all degrees of the selected entity: Solid bodies: constrains x, y, and z. Surface and line bodies: constrains x, y, z, rotx, roty and rotz. Displacement: Allows for imposed translational displacement in x, y, and z (in userdefined Coordinate System). Entering 0 means that the direction is constrained, leaving the direction blank means the direction is free. Elastic Support : Applies flexible frictionless support to a face. Foundation stiffness is the pressure required to produce unit normal deflection of the foundation ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
23 Supports Frictionless Support: Applies constraints (fixes) in the normal direction on surfaces. For solid bodies, this support can be used to apply a structural symmetry boundary condition. Examples... Fixed in radial direction Free translation in plane of support Fixed translation out of plane of support Free in tangential and axial directions ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
24 Supports Cylindrical Support: Provides individual controls (fixed/free) for axial, radial, or tangential constraints. Applied on cylindrical surfaces only. Radial Example... Tangential Axial ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
25 Supports Compression Only Support : Applies a constraint in the normal compressive direction only. Can be used on a cylindrical surface to model a pin, bolt, etc.. Requires an iterative (nonlinear) solution. Force Force Compression Only ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
26 Supports Simply Supported: Can be applied on edge or vertex of surface or line bodies Prevents all translations but all rotations are free Fixed Rotation: Can be applied on surface, edge, or vertex of surface or line bodies Constrains rotations but translations are free Translations free Translation fixed Rotations free Rotations fixed Simply Supported Edge Fixed Rotation Edge ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
27 H. Load and Support Display Two display options are available for boundary conditions: By default, boundary conditions are displayed using a color scheme relating to the class of the condition such as loads, supports, displacements, etc. (figure on left). Users can toggle on Random Colors to assign each boundary condition a unique color (figure on right) ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
28 I. Supports vs Contacts Contacts are used to define the interaction between two represented bodies on an assembly model. Supports are used to define the interaction between a body and the environment (ground for example) Supports will define interaction with the environment Contact will be defined at bodies interfaces ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
29 J. Solving the Model To solve the model click on the Solve button on the Standard Toolbar. Two processors used if present (default). To set the number of processors use, Tools > Solve Process Settings. Note : By default, Mechanical use two processors. In order to run faster your models, it is possible to define more CPUs to use for a solve. This feature is available using a specific license (HPC) ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
30 K. Workshop 7.1 Workshop 7.1 Structural Analysis With Contact Goal: A five part assembly representing an impeller type pump is analyzed with a 100N load on the belt ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
31 L. Results and Postprocessing Numerous structural results are available: Directional and total deformation. Components, principal, or invariants of stresses and strains. Contact output. Reaction forces. More.... In Mechanical, results may be requested before or after solving. If you solve a model then request results afterwards, click on the Solve button, and the results will be retrieved (the results file is re-read). You can also right click the Solution branch or a new result item and Evaluate All Results. A new solution is not required ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
32 ... Results and Postprocessing Contour and vector plots are usually shown on the deformed geometry. Use the Context Toolbar to change settings. Results can be scoped to various geometry and FE entities as well as named selections. (note these controls are covered in a later chapter) ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
33 ... Results and Postprocessing The deformation of the model can be plotted: Total deformation is a scalar quantity: U total U 2 x U 2 y U 2 z The x, y, and z components of deformation can be requested under Directional, in global or local coordinates. Vector plots of deformation are available (see below) ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
34 ... Results and Postprocessing Stresses and strains: Stresses and (elastic) strains have six components (x, y, z, xy, yz, xz) while thermal strains have three components (x, y, z) For stresses and strains, components can be requested under Normal (x, y, z) and Shear (xy, yz, xz). For thermal strains, (x, y, z) components are under Thermal. Principal stresses are always arranged such that s1 > s2 > s3 Intensity is defined as the largest of the absolute values s1 - s2, s2 - s3 or s3 - s ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
35 ... Results and Postprocessing Stress Tool: Calculates safety factors based on several material failure theories (4): Ductile Theories: Maximum Equivalent Stress Maximum Shear Stress Brittle Theories: Mohr-Coulomb Stress Maximum Tensile Stress Safety factor, safety margin and stress ratio can be plotted. User specified failure criteria can be entered ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
36 ... Results and Postprocessing In addition to the standard result items one can insert user defined results. These results can include mathematical expressions and can be combinations of multiple result items. Define in 2 ways: Select User Defined Result from the solution context menu OR - From the Solution Worksheet highlight result > RMB > Create User Defined Result ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
37 ... Results and Postprocessing Details allow an expression using various basic math operations as well as square root, absolute value, exponent, etc.. User defined results can be labeled with a user Identifier. Result legend contains identifier and expression ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
38 ... Results and Postprocessing Reaction forces at constraints or contacts can be obtained using a Reaction Probe. Probes can be inserted manually (like other results) or constraints/contacts can be drag and dropped onto the Solution branch as a shortcut. Drag and Drop ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
39 ... Results and Postprocessing After a static structural solve, you have to check results. A check consists of verify the static equilibrium: F applied = F reaction Reaction probes have to be used to calculate static equilibrium. Simple example : F applied : Acceleration : Fy=m*a => Fy=6.08 N F reaction : Drag and Drop ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
40 M. Linear vs Non Linear solve In a linear analysis, the matrix equation [K]{x}={F} is solved in one iteration. That means the model stiffness does not change during solve : [K] is constant. A non linear solve allow stiffness changes and uses an iterative process to solve the problem. In a static structural analysis, ANSYS runs a non linear solve automatically when the model contains : - Non linear material laws : Plasticity, Creep, Gasket, Viscoelasticity - Non linear contact : Frictionless, Rough, Frictional - Large deflection turned «ON» - Compression only support - Joints F - Bolt pretension - Compression only or tension only Spring K F K T LINEAR u u NON LINEAR ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
41 N. Workshop 7.2 Workshop 7.2 Using Beam Connections In the flange model shown we will use Mechanical s beam connection feature to simulate bolted fasteners in the model ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
42 O. APPENDIX Analysis Settings : Restart controls Nodal Load and Supports Results and Postprocessing ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
43 Analysis Settings : Restart controls The Restart Controls section of the analysis settings configures how ANSYS produces restart points throughout a solve. This is very handy for nonlinear analysis as a converged solution is not guaranteed, and the user has to occasionally adjust the solver setting from a particular intermediate stage of the solve. For linear static analysis, by default no restart points are created. This is covered in more detail in the Introduction to Structural Nonlinearity course ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
44 Nodal Loads and Supports Certain loads and supports can be applied directly to the nodes. Nodal Loads: Must be applied to nodal named selections. Load directions depend on the orientation of the node. Note : for example it could be useful in case of restart when a load must be added after a full solve Each node has an associated local nodal coordinate system. By default these systems are aligned with the global Cartesian system but can be reoriented into a local system for loading purposes. It is with respect to these nodal coordinate systems that the X, Y, Z components of FE loads are defined ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
45 ... Nodal Loads and Supports To apply a nodal load, after choosing the type of load from the Direct FE menu the load details allow choice of named selection and magnitude ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
46 ... Nodal Loads and Supports To change a nodal load direction the node s orientation must be changed using a local coordinate system. Choose Nodal Orientation from the Direct FE menu: Pick the nodal named selection in the details from a drop down list. Pick the coordinate system to reference from a drop down list. Note: a Nodal Orientation branch will be placed in the tree s environment branch ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
47 ... Nodal Loads and Supports Notes on nodal boundary conditions: FE Rotation applies only when surface or line geometry is present (rotational DOF). Since Direct FE loads are often applied to multiple nodes there is a control for how the load is distributed. Divide Load by Nodes (default): Yes: divides the magnitude by the number of nodes and applies equal loads to each (F/Num to each node). No: applies the full load magnitude to each node (F applied to each node). Using the example at right choosing No results in a total load of (10 N * 12 Nodes = 120 N) ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
48 Results and Postprocessing Contact results are requested via a Contact Tool under the Solution branch. Contact regions can be selected in the graphics window or using a Worksheet ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015
Getting Started with ANSYS ANSYS Workbench Environment
 Getting Started with ANSYS ANSYS Workbench Environment Overview The purpose of this tutorial is to get you started with the ANSYS Workbench environment. We will use a simple, static analysis of a single
Getting Started with ANSYS ANSYS Workbench Environment Overview The purpose of this tutorial is to get you started with the ANSYS Workbench environment. We will use a simple, static analysis of a single
Piston Ring. Problem:
 Problem: A cast-iron piston ring has a mean diameter of 81 mm, a radial height of h 6 mm, and a thickness b 4 mm. The ring is assembled using an expansion tool which separates the split ends a distance
Problem: A cast-iron piston ring has a mean diameter of 81 mm, a radial height of h 6 mm, and a thickness b 4 mm. The ring is assembled using an expansion tool which separates the split ends a distance
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Best practices for efficient HPC performance with large models
 Best practices for efficient HPC performance with large models Dr. Hößl Bernhard, CADFEM (Austria) GmbH PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry Oriented HPC Simulations, September 21-27, University of Ljubljana,
Best practices for efficient HPC performance with large models Dr. Hößl Bernhard, CADFEM (Austria) GmbH PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry Oriented HPC Simulations, September 21-27, University of Ljubljana,
Tutorial for Assignment #2 Gantry Crane Analysis By ANSYS (Mechanical APDL) V.13.0
 Tutorial for Assignment #2 Gantry Crane Analysis By ANSYS (Mechanical APDL) V.13.0 1 Problem Description Design a gantry crane meeting the geometry presented in Figure 1 on page #325 of the course textbook
Tutorial for Assignment #2 Gantry Crane Analysis By ANSYS (Mechanical APDL) V.13.0 1 Problem Description Design a gantry crane meeting the geometry presented in Figure 1 on page #325 of the course textbook
3 Concepts of Stress Analysis
 3 Concepts of Stress Analysis 3.1 Introduction Here the concepts of stress analysis will be stated in a finite element context. That means that the primary unknown will be the (generalized) displacements.
3 Concepts of Stress Analysis 3.1 Introduction Here the concepts of stress analysis will be stated in a finite element context. That means that the primary unknown will be the (generalized) displacements.
Customer Training Material. ANSYS Mechanical Basics. Mechanical. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. WS2.
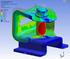 Workshop 2.1 ANSYS Mechanical Basics Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical WS2.1-1 Notes on Workshop 2.1 The first workshop is extensively documented. As this course progresses, students will become more familiar
Workshop 2.1 ANSYS Mechanical Basics Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical WS2.1-1 Notes on Workshop 2.1 The first workshop is extensively documented. As this course progresses, students will become more familiar
Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus. Second Semester 2013-2014
 Finite Element Method Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus Second Semester 2013-2014 Objectives Understand the basic theory of the FEM Know the behaviour and usage of each type of elements covered
Finite Element Method Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus Second Semester 2013-2014 Objectives Understand the basic theory of the FEM Know the behaviour and usage of each type of elements covered
COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING FOR AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATION USING ABAQUS
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 30 52, Article ID: IJARET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 30 52, Article ID: IJARET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=7&itype=2
CosmosWorks Centrifugal Loads
 CosmosWorks Centrifugal Loads (Draft 4, May 28, 2006) Introduction This example will look at essentially planar objects subjected to centrifugal loads. That is, loads due to angular velocity and/or angular
CosmosWorks Centrifugal Loads (Draft 4, May 28, 2006) Introduction This example will look at essentially planar objects subjected to centrifugal loads. That is, loads due to angular velocity and/or angular
ABAQUS Tutorial. 3D Modeling
 Spring 2011 01/21/11 ABAQUS Tutorial 3D Modeling This exercise intends to demonstrate the steps you would follow in creating and analyzing a simple solid model using ABAQUS CAE. Introduction A solid undergoes
Spring 2011 01/21/11 ABAQUS Tutorial 3D Modeling This exercise intends to demonstrate the steps you would follow in creating and analyzing a simple solid model using ABAQUS CAE. Introduction A solid undergoes
CHAPTER 3. INTRODUCTION TO MATRIX METHODS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
 1 CHAPTER 3. INTRODUCTION TO MATRIX METHODS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS Written by: Sophia Hassiotis, January, 2003 Last revision: February, 2015 Modern methods of structural analysis overcome some of the
1 CHAPTER 3. INTRODUCTION TO MATRIX METHODS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS Written by: Sophia Hassiotis, January, 2003 Last revision: February, 2015 Modern methods of structural analysis overcome some of the
Nonlinear Analysis Using Femap with NX Nastran
 Nonlinear Analysis Using Femap with NX Nastran Chip Fricke, Principal Applications Engineer, Agenda Nonlinear Analysis Using Femap with NX Nastran Who am I? Overview of Nonlinear Analysis Comparison of
Nonlinear Analysis Using Femap with NX Nastran Chip Fricke, Principal Applications Engineer, Agenda Nonlinear Analysis Using Femap with NX Nastran Who am I? Overview of Nonlinear Analysis Comparison of
The elements used in commercial codes can be classified in two basic categories:
 CHAPTER 3 Truss Element 3.1 Introduction The single most important concept in understanding FEA, is the basic understanding of various finite elements that we employ in an analysis. Elements are used for
CHAPTER 3 Truss Element 3.1 Introduction The single most important concept in understanding FEA, is the basic understanding of various finite elements that we employ in an analysis. Elements are used for
The Basics of FEA Procedure
 CHAPTER 2 The Basics of FEA Procedure 2.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the spring element, especially for the purpose of introducing various concepts involved in use of the FEA technique. A spring
CHAPTER 2 The Basics of FEA Procedure 2.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the spring element, especially for the purpose of introducing various concepts involved in use of the FEA technique. A spring
Learning Module 4 - Thermal Fluid Analysis Note: LM4 is still in progress. This version contains only 3 tutorials.
 Learning Module 4 - Thermal Fluid Analysis Note: LM4 is still in progress. This version contains only 3 tutorials. Attachment C1. SolidWorks-Specific FEM Tutorial 1... 2 Attachment C2. SolidWorks-Specific
Learning Module 4 - Thermal Fluid Analysis Note: LM4 is still in progress. This version contains only 3 tutorials. Attachment C1. SolidWorks-Specific FEM Tutorial 1... 2 Attachment C2. SolidWorks-Specific
Solved with COMSOL Multiphysics 4.3
 Vibrating String Introduction In the following example you compute the natural frequencies of a pre-tensioned string using the 2D Truss interface. This is an example of stress stiffening ; in fact the
Vibrating String Introduction In the following example you compute the natural frequencies of a pre-tensioned string using the 2D Truss interface. This is an example of stress stiffening ; in fact the
Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Using Beam Library (SI Units)
 APPENDIX A Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Using Beam Library (SI Units) Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a cantilever beam. Use the geometry model to define an MSC.Nastran
APPENDIX A Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Using Beam Library (SI Units) Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a cantilever beam. Use the geometry model to define an MSC.Nastran
List of Problems Solved Introduction p. 1 Concept p. 1 Nodes p. 3 Elements p. 4 Direct Approach p. 5 Linear Spring p. 5 Heat Flow p.
 Preface p. v List of Problems Solved p. xiii Introduction p. 1 Concept p. 1 Nodes p. 3 Elements p. 4 Direct Approach p. 5 Linear Spring p. 5 Heat Flow p. 6 Assembly of the Global System of Equations p.
Preface p. v List of Problems Solved p. xiii Introduction p. 1 Concept p. 1 Nodes p. 3 Elements p. 4 Direct Approach p. 5 Linear Spring p. 5 Heat Flow p. 6 Assembly of the Global System of Equations p.
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Lecture 1 Introduction to the CFD Methodology
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Lecture 1 Introduction to the CFD Methodology Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Lecture 1 Introduction to the CFD Methodology Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
ANSYS TUTORIAL ANSYS 8.1 Analysis of a Spring System. John R. Baker; phone: 270-534-3114; email: jbaker@engr.uky.edu
 Copyright 2001-2005, John R. Baker ANSYS TUTORIAL ANSYS 8.1 Analysis of a Spring System John R. Baker; phone: 270-534-3114; email: jbaker@engr.uky.edu This exercise is intended only as an educational tool
Copyright 2001-2005, John R. Baker ANSYS TUTORIAL ANSYS 8.1 Analysis of a Spring System John R. Baker; phone: 270-534-3114; email: jbaker@engr.uky.edu This exercise is intended only as an educational tool
AN INTRODUCTORY ANSYS TUTORIAL: SOLVING A STATIC TRUSS PROBLEM
 AN INTRODUCTORY ANSYS TUTORIAL: SOLVING A STATIC TRUSS PROBLEM Rajesh Bhaskaran Cornell University E-mail: rb88@cornell.edu This is a quick-and-dirty introductory tutorial to the ANSYS software package
AN INTRODUCTORY ANSYS TUTORIAL: SOLVING A STATIC TRUSS PROBLEM Rajesh Bhaskaran Cornell University E-mail: rb88@cornell.edu This is a quick-and-dirty introductory tutorial to the ANSYS software package
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra
 Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis
 Chapter 7 Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis In this section the structural analysis of the test tower cross arm is done in Prokon and compared to a full finite element analysis using Ansys. This is done
Chapter 7 Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis In this section the structural analysis of the test tower cross arm is done in Prokon and compared to a full finite element analysis using Ansys. This is done
Shell Elements in ABAQUS/Explicit
 ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics Appendix 2 Shell Elements in ABAQUS/Explicit ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.2 Overview ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.4 Triangular
ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics Appendix 2 Shell Elements in ABAQUS/Explicit ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.2 Overview ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.4 Triangular
CAE -Finite Element Method
 16.810 Engineering Design and Rapid Prototyping Lecture 3b CAE -Finite Element Method Instructor(s) Prof. Olivier de Weck January 16, 2007 Numerical Methods Finite Element Method Boundary Element Method
16.810 Engineering Design and Rapid Prototyping Lecture 3b CAE -Finite Element Method Instructor(s) Prof. Olivier de Weck January 16, 2007 Numerical Methods Finite Element Method Boundary Element Method
Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 -
 Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Definitions A plate is a three dimensional solid body with one of the plate dimensions much smaller than the
Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Definitions A plate is a three dimensional solid body with one of the plate dimensions much smaller than the
Customer Training Material. Lecture 2. Introduction to. Methodology ANSYS FLUENT. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Lecture 2 Introduction to CFD Methodology Introduction to ANSYS FLUENT L2-1 What is CFD? Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat and mass transfer, chemical reactions,
Lecture 2 Introduction to CFD Methodology Introduction to ANSYS FLUENT L2-1 What is CFD? Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat and mass transfer, chemical reactions,
ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING APDL CONTROL
 ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING AP... Page 1 of 19 ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING APDL CONTROL Yasumasa Shoji, Satoshi Nagata, Toyo Engineering Corporation,
ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING AP... Page 1 of 19 ANALYSIS OF GASKETED FLANGES WITH ORDINARY ELEMENTS USING APDL CONTROL Yasumasa Shoji, Satoshi Nagata, Toyo Engineering Corporation,
Customer Training Material. Lecture 4. Meshing in Mechanical. Mechanical. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Lecture 4 Meshing in Mechanical Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical L4-1 Chapter Overview In this chapter controlling meshing operations is described. Topics: A. Global Meshing Controls B. Local Meshing Controls
Lecture 4 Meshing in Mechanical Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical L4-1 Chapter Overview In this chapter controlling meshing operations is described. Topics: A. Global Meshing Controls B. Local Meshing Controls
ME 24-688 Week 11 Introduction to Dynamic Simulation
 The purpose of this introduction to dynamic simulation project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Inventor Professional. This environment allows you to perform rigid body dynamic
The purpose of this introduction to dynamic simulation project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Inventor Professional. This environment allows you to perform rigid body dynamic
Begin creating the geometry by defining two Circles for the spherical endcap, and Subtract Areas to create the vessel wall.
 ME 477 Pressure Vessel Example 1 ANSYS Example: Axisymmetric Analysis of a Pressure Vessel The pressure vessel shown below is made of cast iron (E = 14.5 Msi, ν = 0.21) and contains an internal pressure
ME 477 Pressure Vessel Example 1 ANSYS Example: Axisymmetric Analysis of a Pressure Vessel The pressure vessel shown below is made of cast iron (E = 14.5 Msi, ν = 0.21) and contains an internal pressure
Nonlinear analysis and form-finding in GSA Training Course
 Nonlinear analysis and form-finding in GSA Training Course Non-linear analysis and form-finding in GSA 1 of 47 Oasys Ltd Non-linear analysis and form-finding in GSA 2 of 47 Using the GSA GsRelax Solver
Nonlinear analysis and form-finding in GSA Training Course Non-linear analysis and form-finding in GSA 1 of 47 Oasys Ltd Non-linear analysis and form-finding in GSA 2 of 47 Using the GSA GsRelax Solver
Steady Flow: Laminar and Turbulent in an S-Bend
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Steady Flow: Laminar and Turbulent in an S-Bend This tutorial demonstrates the flow of an incompressible gas through an s-bend of constant diameter (2 cm), for both laminar and
STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Steady Flow: Laminar and Turbulent in an S-Bend This tutorial demonstrates the flow of an incompressible gas through an s-bend of constant diameter (2 cm), for both laminar and
Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques
 Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Sr. Analysis Engineer Ahmad.Abbas@AdvancedCAE.com www.advancedcae.com Sunday, July 11, 2010 Advanced CAE All contents Copyright
Lap Fillet Weld Calculations and FEA Techniques By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Sr. Analysis Engineer Ahmad.Abbas@AdvancedCAE.com www.advancedcae.com Sunday, July 11, 2010 Advanced CAE All contents Copyright
Learning Module 6 Linear Dynamic Analysis
 Learning Module 6 Linear Dynamic Analysis What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner
Learning Module 6 Linear Dynamic Analysis What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner
Benchmark Tests on ANSYS Parallel Processing Technology
 Benchmark Tests on ANSYS Parallel Processing Technology Kentaro Suzuki ANSYS JAPAN LTD. Abstract It is extremely important for manufacturing industries to reduce their design process period in order to
Benchmark Tests on ANSYS Parallel Processing Technology Kentaro Suzuki ANSYS JAPAN LTD. Abstract It is extremely important for manufacturing industries to reduce their design process period in order to
ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Analysis of an Aluminum Bracket
 H. Kim FEA Tutorial 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Analysis of an Aluminum Bracket Hyonny Kim last updated: August 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: 1. Sketch 2D geometry & define part. 2. Define material
H. Kim FEA Tutorial 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Analysis of an Aluminum Bracket Hyonny Kim last updated: August 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: 1. Sketch 2D geometry & define part. 2. Define material
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TWO METHODOLOGIES FOR NON LINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNIFE EDGE GATE VALVE SLEEVE
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 6, Issue 12, Dec 2015, pp. 81-90, Article ID: IJMET_06_12_009 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=6&itype=12
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 6, Issue 12, Dec 2015, pp. 81-90, Article ID: IJMET_06_12_009 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=6&itype=12
Finite Elements for 2 D Problems
 Finite Elements for 2 D Problems General Formula for the Stiffness Matrix Displacements (u, v) in a plane element are interpolated from nodal displacements (ui, vi) using shape functions Ni as follows,
Finite Elements for 2 D Problems General Formula for the Stiffness Matrix Displacements (u, v) in a plane element are interpolated from nodal displacements (ui, vi) using shape functions Ni as follows,
Mesh Discretization Error and Criteria for Accuracy of Finite Element Solutions
 Mesh Discretization Error and Criteria for Accuracy of Finite Element Solutions Chandresh Shah Cummins, Inc. Abstract Any finite element analysis performed by an engineer is subject to several types of
Mesh Discretization Error and Criteria for Accuracy of Finite Element Solutions Chandresh Shah Cummins, Inc. Abstract Any finite element analysis performed by an engineer is subject to several types of
Advanced bolt assessment through process automation
 Titelmasterformat Bolt Assessment inside durch ANSYS Klicken bearbeiten Advanced bolt assessment through process automation Contents Short presentation of VDI 2230 Workflow with Bolt Assessment inside
Titelmasterformat Bolt Assessment inside durch ANSYS Klicken bearbeiten Advanced bolt assessment through process automation Contents Short presentation of VDI 2230 Workflow with Bolt Assessment inside
(Seattle is home of Boeing Jets)
 Dr. Faeq M. Shaikh Seattle, Washington, USA (Seattle is home of Boeing Jets) 1 Pre Requisites for Today s Seminar Basic understanding of Finite Element Analysis Working Knowledge of Laminate Plate Theory
Dr. Faeq M. Shaikh Seattle, Washington, USA (Seattle is home of Boeing Jets) 1 Pre Requisites for Today s Seminar Basic understanding of Finite Element Analysis Working Knowledge of Laminate Plate Theory
CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
 41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid.
 Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
CAD-BASED DESIGN PROCESS FOR FATIGUE ANALYSIS, RELIABILITY- ANALYSIS, AND DESIGN OPTIMIZATION
 CAD-BASED DESIGN PROCESS FOR FATIGUE ANALYSIS, RELIABILITY- ANALYSIS, AND DESIGN OPTIMIZATION K.K. Choi, V. Ogarevic, J. Tang, and Y.H. Park Center for Computer-Aided Design College of Engineering The
CAD-BASED DESIGN PROCESS FOR FATIGUE ANALYSIS, RELIABILITY- ANALYSIS, AND DESIGN OPTIMIZATION K.K. Choi, V. Ogarevic, J. Tang, and Y.H. Park Center for Computer-Aided Design College of Engineering The
Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 4.0 Basic Design
 Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
Laminar Flow in a Baffled Stirred Mixer
 Laminar Flow in a Baffled Stirred Mixer Introduction This exercise exemplifies the use of the rotating machinery feature in the CFD Module. The Rotating Machinery interface allows you to model moving rotating
Laminar Flow in a Baffled Stirred Mixer Introduction This exercise exemplifies the use of the rotating machinery feature in the CFD Module. The Rotating Machinery interface allows you to model moving rotating
Cylinder Head Gasket Contact Pressure Simulation for a Hermetic Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Cylinder Head Gasket Contact Pressure Simulation for a Hermetic Compressor Pavan P.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Cylinder Head Gasket Contact Pressure Simulation for a Hermetic Compressor Pavan P.
A Study of Durability Analysis Methodology for Engine Valve Considering Head Thermal Deformation and Dynamic Behavior
 A Study of Durability Analysis Methodology for Engine Valve Considering Head Thermal Deformation and Dynamic Behavior Kum-Chul, Oh 1, Sang-Woo Cha 1 and Ji-Ho Kim 1 1 R&D Center, Hyundai Motor Company
A Study of Durability Analysis Methodology for Engine Valve Considering Head Thermal Deformation and Dynamic Behavior Kum-Chul, Oh 1, Sang-Woo Cha 1 and Ji-Ho Kim 1 1 R&D Center, Hyundai Motor Company
ME6130 An introduction to CFD 1-1
 ME6130 An introduction to CFD 1-1 What is CFD? Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat and mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena by solving numerically
ME6130 An introduction to CFD 1-1 What is CFD? Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat and mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena by solving numerically
4.3 Results... 27 4.3.1 Drained Conditions... 27 4.3.2 Undrained Conditions... 28 4.4 References... 30 4.5 Data Files... 30 5 Undrained Analysis of
 Table of Contents 1 One Dimensional Compression of a Finite Layer... 3 1.1 Problem Description... 3 1.1.1 Uniform Mesh... 3 1.1.2 Graded Mesh... 5 1.2 Analytical Solution... 6 1.3 Results... 6 1.3.1 Uniform
Table of Contents 1 One Dimensional Compression of a Finite Layer... 3 1.1 Problem Description... 3 1.1.1 Uniform Mesh... 3 1.1.2 Graded Mesh... 5 1.2 Analytical Solution... 6 1.3 Results... 6 1.3.1 Uniform
PREDICTION OF MACHINE TOOL SPINDLE S DYNAMICS BASED ON A THERMO-MECHANICAL MODEL
 PREDICTION OF MACHINE TOOL SPINDLE S DYNAMICS BASED ON A THERMO-MECHANICAL MODEL P. Kolar, T. Holkup Research Center for Manufacturing Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Czech
PREDICTION OF MACHINE TOOL SPINDLE S DYNAMICS BASED ON A THERMO-MECHANICAL MODEL P. Kolar, T. Holkup Research Center for Manufacturing Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Czech
Design Analysis and Review of Stresses at a Point
 Design Analysis and Review of Stresses at a Point Need for Design Analysis: To verify the design for safety of the structure and the users. To understand the results obtained in FEA, it is necessary to
Design Analysis and Review of Stresses at a Point Need for Design Analysis: To verify the design for safety of the structure and the users. To understand the results obtained in FEA, it is necessary to
Understanding Connectors
 TECHNICAL PAPER Understanding Connectors SolidWorks software helps you move through the design cycle smarter. With fast and accurate virtual connectors, your team will be able to focus on the behavior
TECHNICAL PAPER Understanding Connectors SolidWorks software helps you move through the design cycle smarter. With fast and accurate virtual connectors, your team will be able to focus on the behavior
CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Releases 12 & 13
 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Releases 12 & 13 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com Visit our website to learn more about
CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Releases 12 & 13 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com Visit our website to learn more about
CAE -Finite Element Method
 16.810 Engineering Design and Rapid Prototyping CAE -Finite Element Method Instructor(s) Prof. Olivier de Weck January 11, 2005 Plan for Today Hand Calculations Aero Æ Structures FEM Lecture (ca. 45 min)
16.810 Engineering Design and Rapid Prototyping CAE -Finite Element Method Instructor(s) Prof. Olivier de Weck January 11, 2005 Plan for Today Hand Calculations Aero Æ Structures FEM Lecture (ca. 45 min)
Computer Aided Design (CAD), ME 530.414, JHU Professor Dan Stoianovici, dss@jhu.edu
 Computer Aided Design (CAD), ME 530.414, JHU Professor Dan Stoianovici, dss@jhu.edu COURSE DESCRIPTION: The course outlines modern solid modeling design, analysis, simulation, and manufacturing of mechanical
Computer Aided Design (CAD), ME 530.414, JHU Professor Dan Stoianovici, dss@jhu.edu COURSE DESCRIPTION: The course outlines modern solid modeling design, analysis, simulation, and manufacturing of mechanical
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS Workbench
 Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS Workbench 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS Workbench 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate
CATIA V5 Tutorials. Mechanism Design & Animation. Release 18. Nader G. Zamani. University of Windsor. Jonathan M. Weaver. University of Detroit Mercy
 CATIA V5 Tutorials Mechanism Design & Animation Release 18 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Jonathan M. Weaver University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
CATIA V5 Tutorials Mechanism Design & Animation Release 18 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Jonathan M. Weaver University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Workshop. Tennis Racket Simulation using Abaqus
 Introduction Workshop Tennis Racket Simulation using Abaqus In this workshop you will become familiar with the process of creating a model interactively by using Abaqus/CAE. You will create the tennis
Introduction Workshop Tennis Racket Simulation using Abaqus In this workshop you will become familiar with the process of creating a model interactively by using Abaqus/CAE. You will create the tennis
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME 2 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS
 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
Feature Commercial codes In-house codes
 A simple finite element solver for thermo-mechanical problems Keywords: Scilab, Open source software, thermo-elasticity Introduction In this paper we would like to show how it is possible to develop a
A simple finite element solver for thermo-mechanical problems Keywords: Scilab, Open source software, thermo-elasticity Introduction In this paper we would like to show how it is possible to develop a
An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis
 CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
Tutorial for laboratory project #2 Using ANSYS Workbench. For Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
 Tutorial for laboratory project #2 Using ANSYS Workbench For Double Pipe Heat Exchanger 1. Preparing ANSYS Workbench Go to Start Menu/All Programs/Simulation/ANSYS 12.1/Workbench. In the toolbox menu in
Tutorial for laboratory project #2 Using ANSYS Workbench For Double Pipe Heat Exchanger 1. Preparing ANSYS Workbench Go to Start Menu/All Programs/Simulation/ANSYS 12.1/Workbench. In the toolbox menu in
Opto-Mechanical I/F for ANSYS
 Abstract Opto-Mechanical I/F for ANSYS Victor Genberg, Keith Doyle, Gregory Michels Sigmadyne, Inc., 803 West Ave, Rochester, NY 14611 genberg@sigmadyne.com Thermal and structural output from ANSYS is
Abstract Opto-Mechanical I/F for ANSYS Victor Genberg, Keith Doyle, Gregory Michels Sigmadyne, Inc., 803 West Ave, Rochester, NY 14611 genberg@sigmadyne.com Thermal and structural output from ANSYS is
Tutorial for Assignment #3 Heat Transfer Analysis By ANSYS (Mechanical APDL) V.13.0
 Tutorial for Assignment #3 Heat Transfer Analysis By ANSYS (Mechanical APDL) V.13.0 1 Problem Description This exercise consists of an analysis of an electronics component cooling design using fins: All
Tutorial for Assignment #3 Heat Transfer Analysis By ANSYS (Mechanical APDL) V.13.0 1 Problem Description This exercise consists of an analysis of an electronics component cooling design using fins: All
Tutorial: 3D Pipe Junction Using Hexa Meshing
 Tutorial: 3D Pipe Junction Using Hexa Meshing Introduction In this tutorial, you will generate a mesh for a three-dimensional pipe junction. After checking the quality of the first mesh, you will create
Tutorial: 3D Pipe Junction Using Hexa Meshing Introduction In this tutorial, you will generate a mesh for a three-dimensional pipe junction. After checking the quality of the first mesh, you will create
STRESS AND DEFORMATION ANALYSIS OF LINEAR ELASTIC BARS IN TENSION
 Chapter 11 STRESS AND DEFORMATION ANALYSIS OF LINEAR ELASTIC BARS IN TENSION Figure 11.1: In Chapter10, the equilibrium, kinematic and constitutive equations for a general three-dimensional solid deformable
Chapter 11 STRESS AND DEFORMATION ANALYSIS OF LINEAR ELASTIC BARS IN TENSION Figure 11.1: In Chapter10, the equilibrium, kinematic and constitutive equations for a general three-dimensional solid deformable
Lecture 6 - Boundary Conditions. Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Lecture 6 - Boundary Conditions Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Instructor: André Bakker http://www.bakker.org André Bakker (2002-2006) Fluent Inc. (2002) 1 Outline Overview. Inlet and outlet boundaries.
Lecture 6 - Boundary Conditions Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Instructor: André Bakker http://www.bakker.org André Bakker (2002-2006) Fluent Inc. (2002) 1 Outline Overview. Inlet and outlet boundaries.
Introduction to ANSYS
 Lecture 3 Introduction to ANSYS Meshing 14. 5 Release Introduction to ANSYS Meshing 2012 ANSYS, Inc. March 27, 2014 1 Release 14.5 Introduction to ANSYS Meshing What you will learn from this presentation
Lecture 3 Introduction to ANSYS Meshing 14. 5 Release Introduction to ANSYS Meshing 2012 ANSYS, Inc. March 27, 2014 1 Release 14.5 Introduction to ANSYS Meshing What you will learn from this presentation
MASTER DEGREE PROJECT
 MASTER DEGREE PROJECT Finite Element Analysis of a Washing Machine Cylinder Thesis in Applied Mechanics one year Master Degree Program Performed : Spring term, 2010 Level Author Supervisor s Examiner :
MASTER DEGREE PROJECT Finite Element Analysis of a Washing Machine Cylinder Thesis in Applied Mechanics one year Master Degree Program Performed : Spring term, 2010 Level Author Supervisor s Examiner :
This tutorial provides a recipe for simulating L
 Pipe Flow Tutorial for STAR-CCM+ ME 448/548 February 5, 2014 Gerald Recktenwald gerry@me.pdx.edu 1 Overview This tutorial provides a recipe for simulating laminar flow in a pipe with STAR- L CCM+. The
Pipe Flow Tutorial for STAR-CCM+ ME 448/548 February 5, 2014 Gerald Recktenwald gerry@me.pdx.edu 1 Overview This tutorial provides a recipe for simulating laminar flow in a pipe with STAR- L CCM+. The
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope
 Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Finite Element Formulation for Beams - Handout 2 -
 Finite Element Formulation for Beams - Handout 2 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Review of Euler-Bernoulli Beam Physical beam model midline Beam domain in three-dimensions Midline, also called
Finite Element Formulation for Beams - Handout 2 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Review of Euler-Bernoulli Beam Physical beam model midline Beam domain in three-dimensions Midline, also called
Embankment Consolidation
 Embankment Consolidation 36-1 Embankment Consolidation In this tutorial, RS2 is used for a coupled analysis of a road embankment subject to loading from typical daily traffic. Model Start the RS2 9.0 Model
Embankment Consolidation 36-1 Embankment Consolidation In this tutorial, RS2 is used for a coupled analysis of a road embankment subject to loading from typical daily traffic. Model Start the RS2 9.0 Model
INJECTION MOLDING COOLING TIME REDUCTION AND THERMAL STRESS ANALYSIS
 INJECTION MOLDING COOLING TIME REDUCTION AND THERMAL STRESS ANALYSIS Tom Kimerling University of Massachusetts, Amherst MIE 605 Finite Element Analysis Spring 2002 ABSTRACT A FEA transient thermal structural
INJECTION MOLDING COOLING TIME REDUCTION AND THERMAL STRESS ANALYSIS Tom Kimerling University of Massachusetts, Amherst MIE 605 Finite Element Analysis Spring 2002 ABSTRACT A FEA transient thermal structural
Creo Simulate 1.0 April 2011
 Creo Simulate 1.0 April 2011 Creo Simulate a Creo family app Installed / Un-installed separately Creo Simulate in two modes: Embedded mode module of Creo Parametric Standalone mode In Standalone mode:
Creo Simulate 1.0 April 2011 Creo Simulate a Creo family app Installed / Un-installed separately Creo Simulate in two modes: Embedded mode module of Creo Parametric Standalone mode In Standalone mode:
ANALYTICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF SPRING BACK EFFECTS IN A TYPICAL COLD ROLLED SHEET
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2016, pp. 119-130, Article ID: IJMET_07_01_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=1
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2016, pp. 119-130, Article ID: IJMET_07_01_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=1
8.2 Elastic Strain Energy
 Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
Objectives. Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity and ductility of given materials.
 Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments
 Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments Positive Internal Forces Acting Recall from mechanics of materials that the internal forces P (generic axial), V (shear) and M (moment) represent resultants
Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments Positive Internal Forces Acting Recall from mechanics of materials that the internal forces P (generic axial), V (shear) and M (moment) represent resultants
FUNDAMENTAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS
 FUNDAMENTAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS With Mathematica and MATLAB Computations M. ASGHAR BHATTI WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. CONTENTS OF THE BOOK WEB SITE PREFACE xi xiii 1 FINITE ELEMENT
FUNDAMENTAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS With Mathematica and MATLAB Computations M. ASGHAR BHATTI WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. CONTENTS OF THE BOOK WEB SITE PREFACE xi xiii 1 FINITE ELEMENT
The simulation of machine tools can be divided into two stages. In the first stage the mechanical behavior of a machine tool is simulated with FEM
 1 The simulation of machine tools can be divided into two stages. In the first stage the mechanical behavior of a machine tool is simulated with FEM tools. The approach to this simulation is different
1 The simulation of machine tools can be divided into two stages. In the first stage the mechanical behavior of a machine tool is simulated with FEM tools. The approach to this simulation is different
Finite Element Method
 16.810 (16.682) Engineering Design and Rapid Prototyping Finite Element Method Instructor(s) Prof. Olivier de Weck deweck@mit.edu Dr. Il Yong Kim kiy@mit.edu January 12, 2004 Plan for Today FEM Lecture
16.810 (16.682) Engineering Design and Rapid Prototyping Finite Element Method Instructor(s) Prof. Olivier de Weck deweck@mit.edu Dr. Il Yong Kim kiy@mit.edu January 12, 2004 Plan for Today FEM Lecture
Instructors Manual Finite Element Method Laboratory Sessions
 Instructors Manual Finite Element Method Laboratory Sessions Dr. Waluyo Adi Siswanto 6 July 2010 Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM) This document is written in LYX 1.6.7 a frontend of LATEX Contents
Instructors Manual Finite Element Method Laboratory Sessions Dr. Waluyo Adi Siswanto 6 July 2010 Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM) This document is written in LYX 1.6.7 a frontend of LATEX Contents
Reliable FE-Modeling with ANSYS
 Reliable FE-Modeling with ANSYS Thomas Nelson, Erke Wang CADFEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract ANSYS is one of the leading commercial finite element programs in the world and can be applied to a large
Reliable FE-Modeling with ANSYS Thomas Nelson, Erke Wang CADFEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract ANSYS is one of the leading commercial finite element programs in the world and can be applied to a large
Structural Integrity Analysis
 Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
PARAMETRIC MODELING. David Rosen. December 1997. By carefully laying-out datums and geometry, then constraining them with dimensions and constraints,
 1 of 5 11/18/2004 6:24 PM PARAMETRIC MODELING David Rosen December 1997 The term parametric modeling denotes the use of parameters to control the dimensions and shape of CAD models. Think of a rubber CAD
1 of 5 11/18/2004 6:24 PM PARAMETRIC MODELING David Rosen December 1997 The term parametric modeling denotes the use of parameters to control the dimensions and shape of CAD models. Think of a rubber CAD
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF BRIDGE WITH TWO ENDS FIXED ON VERTICAL WALL USING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 34-44, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_003 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 34-44, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_003 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
Differential Relations for Fluid Flow. Acceleration field of a fluid. The differential equation of mass conservation
 Differential Relations for Fluid Flow In this approach, we apply our four basic conservation laws to an infinitesimally small control volume. The differential approach provides point by point details of
Differential Relations for Fluid Flow In this approach, we apply our four basic conservation laws to an infinitesimally small control volume. The differential approach provides point by point details of
Technology of EHIS (stamping) applied to the automotive parts production
 Laboratory of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Technology of EHIS (stamping) applied to the automotive parts production Churilova Maria, Saint-Petersburg State Polytechnical University Department of Applied
Laboratory of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Technology of EHIS (stamping) applied to the automotive parts production Churilova Maria, Saint-Petersburg State Polytechnical University Department of Applied
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31)
 Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS SKILLS
 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS SKILLS ***This document is held up to a basic level to represent a sample for our both theoretical background & software capabilities/skills. (Click on each link to see the detailed
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS SKILLS ***This document is held up to a basic level to represent a sample for our both theoretical background & software capabilities/skills. (Click on each link to see the detailed
Graduate Courses in Mechanical Engineering
 Graduate Courses in Mechanical Engineering MEEG 501 ADVANCED MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS An advanced, unified approach to the solution of mechanical engineering problems, with emphasis on the formulation
Graduate Courses in Mechanical Engineering MEEG 501 ADVANCED MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS An advanced, unified approach to the solution of mechanical engineering problems, with emphasis on the formulation
CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Texas 77058 REVISION A JULY 6, 1998 REPLACES BASELINE SPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION..............................................
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Texas 77058 REVISION A JULY 6, 1998 REPLACES BASELINE SPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION..............................................
Course in. Nonlinear FEM
 Course in Introduction Outline Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometric nonlinearity Lecture 3 Material nonlinearity Lecture 4 Material nonlinearity continued Lecture 5 Geometric nonlinearity revisited
Course in Introduction Outline Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometric nonlinearity Lecture 3 Material nonlinearity Lecture 4 Material nonlinearity continued Lecture 5 Geometric nonlinearity revisited
METHODS FOR ACHIEVEMENT UNIFORM STRESSES DISTRIBUTION UNDER THE FOUNDATION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 45-66, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 45-66, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
ANSYS Example: Transient Thermal Analysis of a Pipe Support Bracket
 ME 477 Transient Thermal Example 1 ANSYS Example: Transient Thermal Analysis of a Pipe Support Bracket The section of pipe shown below is a representative section of a longer pipe carrying a hot fluid
ME 477 Transient Thermal Example 1 ANSYS Example: Transient Thermal Analysis of a Pipe Support Bracket The section of pipe shown below is a representative section of a longer pipe carrying a hot fluid
FEA Analysis of a Caliper Abutment Bracket ME 404
 FEA Analysis of a Caliper Abutment Bracket ME 404 Jesse Doty March 17, 2008 Abstract As braking forces are applied at the wheel of an automobile, those forces must be transmitted to the suspension of the
FEA Analysis of a Caliper Abutment Bracket ME 404 Jesse Doty March 17, 2008 Abstract As braking forces are applied at the wheel of an automobile, those forces must be transmitted to the suspension of the
