Language Development & Disorders in. Internationally Adopted Children. Today s Topics 9/11/2015. Age of Adoption for. Changing Demographics
|
|
|
- Raymond Mosley
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sharon Glennen, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Director, The Institute for Well-Being Professor, Audiology, Speech Pathology & Deaf Studies Towson University Development & Disorders in Internationally Children ISHA Fall Conference Indianapolis, IN September 19, 2015 Changing Demographics Today s Topics Children at ages 1-2 and 3-4 years Assessment Guidelines Typical Outcomes Children at 5+ years of age Dynamic Assessment Summary & Questions Age of Adoption for Internationally Children Yrs 8% 5+ Yrs 15% 1-2 Yrs 36% Under 1 Yr 41% 5+ Yrs 38% 3-4 Yrs 16% Under 1 Yr 8% 1-2 Yrs 38% U.S. State Department 1
2 Longitudinal Study of Development & Disorders in Internationally Children 14 Year Project 56 Children 392 Annual Evaluations Receptive Expressive Articulation Literacy Hearing Screen Goal: To Develop Local Norms Newly Assessment Results Communication & Symbolic Behavior Scales-DP CSBS Norm Social Interaction Speech Symbolic Total Score (Glennen, 2007) Putting it Together: New Arrivals Social Interaction What to Assess What to Expect When to Refer Eye Contact Normal eye contact Poor eye contact Frequency of Communication Communicative Intent Requests Attention Protests Comments Joint Attention Frequent communication attempts Variety of communicative intents Mild Delays Infrequent communication Lack of age appropriate intent No attention to pointing attempt 2
3 Putting it Together: New Arrivals Gestures What to Assess What to Expect When to Refer Use of Gestures Gestures + Variety of Gestures Age Appropriate Less than age appropriate use of gestures Vocalizations Gestures + Eyegaze Shifts Gesture Combinations Person to Object Eyegaze Shifts Age appropriate Lack of eyegaze while gesturing Putting it Together: New Arrivals Vocalizations & Speech What to Assess What to Expect When to Refer Frequency of Vocalizations Communicative Use of Vocalizations Complexity of Sounds Imitation of First Words History of Using Birth Words Fewer Vocalizations No vocalizations Infrequent use of vocalizations to communicate Mild Delay in Complexity Word Attempts by 15+ Months Word Attempts for Children 18+ Months Vocalizations not used communicatively More than mild delays in sound complexity No word imitations after 15+ months Putting it Together: New Arrivals Symbolic Play & Comprehension What to Assess What to Expect When to Refer Developmental Level of Play Variety of Objects Used in Play 2-3 step Play Sequences Early Word Comprehension Typical Developmental Play Age appropriate use of objects Age appropriate play sequences. Comprehension of some age appropriate words Mild Delays in Play Mild Delays Mild Delays Unable to comprehend any words or simple commands. 3
4 Table 2 Expressive Sentence Length (MLU Average for the 3 Longest Utterances) For Internationally Children by Age of Adoption (Glennen & Masters, 2002) Current Age 0 to 12 Months 13 to 18 Months 19 to 24 Months 25 to 30 Months Average Words Referral Criteria Average Words Referral Criteria Average Words Referral Criteria Average Words Referral Criteria 18 Months Months 2.6 > > Months 5.9 > > > > Months 9.5 > > > > Months 9.5 > > >3.9 Children Who Fall Below the Referral Criteria Should be Referred for Speech & Services MCDI Expressive Vocabulary Development 700 Number of Words Maximum = MCDI 50%ile MCDI 10%ile Intl Adoption 50%ile Internationally Children Chronological Age in Months Putting it Together: First Years Assessment Guidelines Children 0 12 Months of Age At Arrival Assess in English without accommodations Children Months of Age One Year Home Assess in English without accommodations MLU will be low average Child will not be at full potential 4
5 Standard Scores Standard Scores 9/11/2015 Children After Age 3 = Complex Issues Orphanage & Pre-adoption Environment Bilingualism and Development Limited English Exposure before starting School 110 Changes in Receptive Over Time Adoption Age mos mos yrs yrs yrs Mos 9 Mos 1.3 Yrs 2.3 Yrs 3.4 Yrs Time Home: Length of English Exposure Glennen, S. (2014). A Longitudinal study of language and speech in children who were internationally adopted at different ages. Speech & Hearing Services in Schools, 45, Changes in Expressive Over Time Adoption Age mos mos yrs yrs yrs Mos 9 Mos 1.3 Yrs 2.3 Yrs 3.4 Yrs Time Home: Length of English Exposure Glennen, S. (2014). A Longitudinal study of language and speech in children who were internationally adopted at different ages. Speech & Hearing Services in Schools, 45,
6 Standard Scores Standard Scores 9/11/ Changes in MLU SSE Over Time Adoption Age mos mos yrs yrs yrs MLU SSE = [( [Child s MLU-Predicted MLU]/Predicted MLU Standard Deviation) * 15] Mos 9 Mos 1.3 Yrs 2.3 Yrs 3.4 Yrs Time Home: Length of English Exposure Glennen, S. (2014). A Longitudinal study of language and speech in children who were internationally adopted at different ages. Speech & Hearing Services in Schools, 45, Changes in Articulation Over Time Adoption Age mos mos yrs yrs yrs Mos 9 Mos 1.3 Yrs 2.3 Yrs 3.4 Yrs Time Home: Length of English Exposure Glennen, S. (2014). A Longitudinal study of language and speech in children who were internationally adopted at different ages. Speech & Hearing Services in Schools, 45, Age of Adoption Glennen (2014) Length of Exposure to English Receptive Standardized Test Scores Expressive Standardized Test Scores MLU SSE Standardized Score Equivalent Articulation Standardized Test Scores Between Months of Age N = 17 Between Months of Age N = 8 Between Years of Age N = 13 Between Years of Age N = 12 Between Years of Age N = 6 M SD M SD M SD M SD (7.76) (6.49) (23.47) 2.5 mos Home 9 mos Home (14.27) (10.61) (8.63) 1.3 yrs Home (14.02) (16.53) (17.53) (12.34) 2.3 yrs Home (13.73).20 (10.40) (8.70) (8.25) 3.4 yrs Home (12.37).27 (10.82) (10.97) (10.87) 2.5 mos Home (21.23) (13.49) (18.27) 9 mos Home (15.13) (5.90) (11.69) 1.3 yrs Home (12.02) (9.78).26 (26.28) (7.15) 2.3 yrs Home (9.18) (10.71) (10.65) (7.87) 3.4 yrs Home (9.89) (9.32) (5.91) (12.65) 2.5 mos Home (14.17) (8.05) (7.74) 9 mos Home (14.96) (11.74) (23.44) (9.61) 1.3 yrs Home.75 (13.85) (16.77) (24.43) (11.75) 2.3 yrs Home (10.22) (12.55) (17.58) (13.38) 3.4 yrs Home (6.38) (15.20) (9.69) 2.5 mos Home (6.72) (3.09) (5.86) 9 mos Home (10.95) (10.47) (12.36) (12.49) 1.3 yrs Home (9.35) (11.29) (14.37) (14.53) 2.3 yrs Home (16.46) (13.73) (13.87) (12.42) 3.4 yrs Home.02 (14.82) (16.58) (9.69) 2.5 mos Home (15.87) (16.94) (9.10) 9 mos Home (9.96) (15.09) (16.65) (11.19) 1.3 yrs Home (2.31) (9.21) (15.83) (8.67) 2.3 yrs Home.13 (14.07) (16.36) (5.34) (3.16) 3.4 yrs Home (6.08) (7.48) (6.17) 6
7 L2 Second Proficiency Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills (BICS) Acquired Rapidly Masks True Proficiency Cognitive Academic Proficiency (CALP) Acquired Slowly Learning Implications when the Child has no Proficient L1 Internationally Children with or Speech Delays (-1SD Below Mean) Ages 3 & 4 Years 2 Yrs Post Adoption Age 3 n = 11 Age 4 n = 6 3 Yrs Post Adoption Age 3 n = 10 Age 4 n = 6 Receptive 18% 16% 0% 0% Expressive 18% 33% 20% 0% MLU SSE 27% 16% 20% 0% Articulation 18% 0% 10% 0% One Delay Area 45% 50% 30% 0% Two or More Delay Areas 27% 0% 10% 0% Conclusion Ages 3-4 years <2 Years Exposure Assess in English but use local norms >3 Years Exposure Assess in English and use standard norms Strength = Receptive language, Articulation Weakness = Expressive Syntax & Morphology Incidence of Delays 7
8 Reason 1: The Lens IA Children SES Matched Children 3-yr olds (Cohen et al., 2010) 8-yr olds (Desmarais et al., 2012) PLS Receptive PLS Expressive CASL Paragraph Comprehension 7-yr olds (Delcenserie et al., 2011) CELF CFD CELF-R Sentence Recall EOWPVT Written Age 7 8 (Scott, Roberts, & Krakow, 2008) Written Test Scores Test of Word Reading WDRB Passage Comp WDRB Word Attack WRAT3 Reading WRAT3 Spelling Reason 2: Weaknesses Ages 6 & 8 (Glennen, 2015) Area Vocabulary (Age 6) Syntax & Morphology (Age 6) Memory for (Age 6) Auditory & Working Memory (Age 8) CELF-IV, CTOPP, Subtests Standard Score (Mean = 10) Percentage Of Children 1SD < Mean Expressive Vocabulary % Word Classes Receptive % Sentence Structure (Rec) % Formulated Sentences (Exp) % Word Structure (Exp) % Concepts & Following % Directions Recalling Sentences % Number Repetition % Familiar Sequences % CTOPP Nonword Repetition % Rapid Naming CTOPP Rapid Naming % 8
9 Pre-Adoption History BICS - Develops Rapidly CALP Progresses over Time Articulation L1-L2 Errors Grammar/Syntax L1-L2 Errors Non-linguistic Assessment Verbal Memory Rate of Learning Dynamic Assessment: Multiple Data Sources Context at Home and School Pre-Adoption History Birth/Orphanage Medical Developmental & Speech Living environments, parent/caregiver to child ratios Estimates on quality of care and language stimulation Relevant developmental or medical history What were the parents told about the child s language and speech development? Did others in the birth country have a difficult time understanding the child? Did the child appear to understand and follow instructions? Did the child enjoy socially interacting with known adults and peers? Did those interactions appear normal? Academics Did the child attend school in the birth country? Was the school in the community or isolated in the orphanage? Are there any records of how the child was progressing in school? Was the child learning to read and if so, were there any concerns? Goal: Was there a language or speech disorder in the Birth L1? Post-Adoption History Exposure How Long has the Child Been Exposed to English? Is the child still exposed to the birth language? Is English the only language spoken in the home? Medical Significant medical concerns discovered post-adoption BICS Development How quickly did the child start using English words? How quickly did English become the primary language? Does the child comprehend simple instructions, basic conversations about routine events, conversations about shared past events? Does the child s English appear fluent, or are there differences in pronunciation, grammar, or vocabulary? Academics Is the child attending school? Are they placed in the age-appropriate grade? If not, why? Are they receiving ESL or special services? Are they doing well academically when compared to class peers? Goal: Is there a language or speech disorder in the new adopted L1? 9
10 Glennen, S., & Bright, B., (2005). Five years later: in school age internationally adopted children. Seminars in Speech and, 26, Glennen, S. (2014). A Longitudinal Study of and Speech in Children who were Internationally at Different Ages: Outcomes and Assessment Guidelines., Speech and Hearing Services in Schools, 45, References Delcenserie, A., Genesee, F., & Gauthier, K. (2011). abilities of internationally adopted children from China during the early school years: Evidence for early age effects? Applied Psycholinguistics, 34, Desmarais, C., Roeber, B., Smith, M., & Pollak, S. (2012). Sentence comprehension in postinstitutionalized school-age children. Journal of Speech,, and Hearing Research, 55, Glennen, S. (2009). Speech and language guidelines for children adopted from abroad at older ages. Topics in Disorders, 29(1) Glennen, S. (2015). Internationally adopted children in the early school years: Relative strengths and weaknesses in language abilities., Speech and Hearing Services in Schools, 46. Glennen, S., & Masters, G. (2002). Typical and atypical language development in infants and toddlers adopted from Eastern Europe. American Journal of Speech- Pathology, 11, Scott, K., Roberts, & Krakow, R. (2008). Oral and written language development of children adopted from China. American Journal of Speech Pathology, 17, Scott, K., Roberts. J., & Glennen, S. (2011). How well do children who are internationally adopted acquire language? A meta-analysis. Journal of Speech,, and Hearing Research, 54, Sheridan, M., Fox, N., Zeanah, C., McLaughlin, K., & Nelson, C. (2012). Variation in neural development as a result of exposure to institutionalization early in childhood. PNAS: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109,
ALBUQUERQUE PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 ALBUQUERQUE PUBLIC SCHOOLS Speech and Language Initial Evaluation Name: Larry Language School: ABC Elementary Date of Birth: 8-15-1999 Student #: 123456 Age: 8-8 Grade:6 Gender: male Referral Date: 4-18-2008
ALBUQUERQUE PUBLIC SCHOOLS Speech and Language Initial Evaluation Name: Larry Language School: ABC Elementary Date of Birth: 8-15-1999 Student #: 123456 Age: 8-8 Grade:6 Gender: male Referral Date: 4-18-2008
INCREASE YOUR PRODUCTIVITY WITH CELF 4 SOFTWARE! SAMPLE REPORTS. To order, call 1-800-211-8378, or visit our Web site at www.pearsonassess.
 INCREASE YOUR PRODUCTIVITY WITH CELF 4 SOFTWARE! Report Assistant SAMPLE REPORTS To order, call 1-800-211-8378, or visit our Web site at www.pearsonassess.com In Canada, call 1-800-387-7278 In United Kingdom,
INCREASE YOUR PRODUCTIVITY WITH CELF 4 SOFTWARE! Report Assistant SAMPLE REPORTS To order, call 1-800-211-8378, or visit our Web site at www.pearsonassess.com In Canada, call 1-800-387-7278 In United Kingdom,
Any Town Public Schools Specific School Address, City State ZIP
 Any Town Public Schools Specific School Address, City State ZIP XXXXXXXX Supertindent XXXXXXXX Principal Speech and Language Evaluation Name: School: Evaluator: D.O.B. Age: D.O.E. Reason for Referral:
Any Town Public Schools Specific School Address, City State ZIP XXXXXXXX Supertindent XXXXXXXX Principal Speech and Language Evaluation Name: School: Evaluator: D.O.B. Age: D.O.E. Reason for Referral:
Technical Report. Overview. Revisions in this Edition. Four-Level Assessment Process
 Technical Report Overview The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals Fourth Edition (CELF 4) is an individually administered test for determining if a student (ages 5 through 21 years) has a language
Technical Report Overview The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals Fourth Edition (CELF 4) is an individually administered test for determining if a student (ages 5 through 21 years) has a language
Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date)
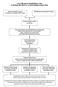 Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date) Home information session (Carried out by a member of the CI team) Rehabilitationist allocated to family Cochlear
Care Pathway for Rehabilitation Team (Following allocation of Cochlear Implant surgery date) Home information session (Carried out by a member of the CI team) Rehabilitationist allocated to family Cochlear
The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals, fourth edition (CELF-4;
 The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals, Fourth Edition (CELF-4) A Review Teresa Paslawski University of Saskatchewan Canadian Journal of School Psychology Volume 20 Number 1/2 December 2005 129-134
The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals, Fourth Edition (CELF-4) A Review Teresa Paslawski University of Saskatchewan Canadian Journal of School Psychology Volume 20 Number 1/2 December 2005 129-134
Career Paths for the CDS Major
 College of Education COMMUNICATION DISORDERS AND SCIENCES (CDS) Advising Handout Career Paths for the CDS Major Speech Language Pathology Speech language pathologists work with individuals with communication
College of Education COMMUNICATION DISORDERS AND SCIENCES (CDS) Advising Handout Career Paths for the CDS Major Speech Language Pathology Speech language pathologists work with individuals with communication
General Education What is the SLP s role? Materials/Resources Needed:
 Speech-Language SLP s Role in Tiers of RtI Originally developed by Georgia Organization of School Based SLPs http://www.omnie.org/guidelines/files/role-of-the-slp-in-response-to-intervention.pdf http://www.asha.org/slp/schools/prof-consult/newrolesslp.htm
Speech-Language SLP s Role in Tiers of RtI Originally developed by Georgia Organization of School Based SLPs http://www.omnie.org/guidelines/files/role-of-the-slp-in-response-to-intervention.pdf http://www.asha.org/slp/schools/prof-consult/newrolesslp.htm
SPEECH OR LANGUAGE IMPAIRMENT EARLY CHILDHOOD SPECIAL EDUCATION
 I. DEFINITION Speech or language impairment means a communication disorder, such as stuttering, impaired articulation, a language impairment (comprehension and/or expression), or a voice impairment, that
I. DEFINITION Speech or language impairment means a communication disorder, such as stuttering, impaired articulation, a language impairment (comprehension and/or expression), or a voice impairment, that
TEXAS RISING STAR WEBINAR SERIES: CURRICULUM AND EARLY LEARNING GUIDELINES RECORDED OCTOBER 29, 2015 NOTES
 TEXAS RISING STAR WEBINAR SERIES: CURRICULUM AND EARLY LEARNING GUIDELINES RECORDED OCTOBER 29, 2015 NOTES The topics that will be addressed during these webinars include: 1. The General Overview: Curriculum
TEXAS RISING STAR WEBINAR SERIES: CURRICULUM AND EARLY LEARNING GUIDELINES RECORDED OCTOBER 29, 2015 NOTES The topics that will be addressed during these webinars include: 1. The General Overview: Curriculum
3030. Eligibility Criteria.
 3030. Eligibility Criteria. 5 CA ADC 3030BARCLAYS OFFICIAL CALIFORNIA CODE OF REGULATIONS Barclays Official California Code of Regulations Currentness Title 5. Education Division 1. California Department
3030. Eligibility Criteria. 5 CA ADC 3030BARCLAYS OFFICIAL CALIFORNIA CODE OF REGULATIONS Barclays Official California Code of Regulations Currentness Title 5. Education Division 1. California Department
Speech-Language Pathology Interventional Services for Autism Spectrum Disorders
 Last Review Date: September 11, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.45bv2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: September 11, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.45bv2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Grace Fleming, School of Graduate Studies
 MEMORANDUM To: From: Graduate Curriculum Committee Grace Fleming, School of Graduate Studies Date: 2/11/2008 Subject: Minutes for January 30, 2008 The Graduate Curriculum Committee met in Victor 219, Wednesday,
MEMORANDUM To: From: Graduate Curriculum Committee Grace Fleming, School of Graduate Studies Date: 2/11/2008 Subject: Minutes for January 30, 2008 The Graduate Curriculum Committee met in Victor 219, Wednesday,
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND BEST PRACTICES MANUAL Speech-Language Pathology in the Schools
 I. Definition and Overview Central Consolidated School District No. 22 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND BEST PRACTICES MANUAL Speech-Language Pathology in the Schools Speech and/or language impairments are those
I. Definition and Overview Central Consolidated School District No. 22 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE AND BEST PRACTICES MANUAL Speech-Language Pathology in the Schools Speech and/or language impairments are those
How To Teach A Deaf Person
 Appendix F. New Hampshire Certification Requirements for Educational Interpreters/Transliterators and for Special Education Teachers in the Area of Deaf and Hearing Disabilities Educational Interpreter/Transliterator
Appendix F. New Hampshire Certification Requirements for Educational Interpreters/Transliterators and for Special Education Teachers in the Area of Deaf and Hearing Disabilities Educational Interpreter/Transliterator
Lesli H. Cleveland, PhD, CCC- SLP Associate Professor and Chair
 , PhD, CCC- SLP Associate Professor and Chair Office Department of Communication Disorders Eastern Washington University 310 N Riverpoint Blvd Health Sciences Building Spokane WA 99202 lcleveland@ewu.edu
, PhD, CCC- SLP Associate Professor and Chair Office Department of Communication Disorders Eastern Washington University 310 N Riverpoint Blvd Health Sciences Building Spokane WA 99202 lcleveland@ewu.edu
Test Administrator Requirements
 CELF 4 CTOPP Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals, Fourth Edition Comprehensive Phonological Processing The CELF 4, like its predecessors, is an individually administered clinical tool for the
CELF 4 CTOPP Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals, Fourth Edition Comprehensive Phonological Processing The CELF 4, like its predecessors, is an individually administered clinical tool for the
Age Birth to Four Months Four to Eight Months
 Healthy Beginnings: Supporting Development and Learning Birth through Three Years of In order for individually developed comprehensive curricula for infants and toddlers to be considered for acceptance
Healthy Beginnings: Supporting Development and Learning Birth through Three Years of In order for individually developed comprehensive curricula for infants and toddlers to be considered for acceptance
SPEECH AND LANGUAGE EVALUATION CLIENT : RESP. PARTY : ADDRESS : INFORMANT : REFERRAL SOURCE : BIRTH DATE : EVALUATION DATE : PHONE : REPORT DATE :
 (Leave room for letterhead) SPEECH AND LANGUAGE EVALUATION CLIENT : RESP. PARTY : ADDRESS : INFORMANT : REFERRAL SOURCE : BIRTH DATE : EVALUATION DATE : PHONE : REPORT DATE : All pages following the letterhead
(Leave room for letterhead) SPEECH AND LANGUAGE EVALUATION CLIENT : RESP. PARTY : ADDRESS : INFORMANT : REFERRAL SOURCE : BIRTH DATE : EVALUATION DATE : PHONE : REPORT DATE : All pages following the letterhead
DR. PAT MOSSMAN Tutoring
 DR. PAT MOSSMAN Tutoring INDIVIDUAL INSTRuction Reading Writing Math Language Development Tsawwassen and ladner pat.moss10.com - 236.993.5943 tutormossman@gmail.com Testing in each academic subject is
DR. PAT MOSSMAN Tutoring INDIVIDUAL INSTRuction Reading Writing Math Language Development Tsawwassen and ladner pat.moss10.com - 236.993.5943 tutormossman@gmail.com Testing in each academic subject is
Running head: ENGLISH LANGUAGE IN ADOPTEES. Running fast but running behind:
 English Language in Adoptees 1 Running head: ENGLISH LANGUAGE IN ADOPTEES Running fast but running behind: Language abilities in internationally-adopted children arriving between ages 2 and 9 Joy Geren
English Language in Adoptees 1 Running head: ENGLISH LANGUAGE IN ADOPTEES Running fast but running behind: Language abilities in internationally-adopted children arriving between ages 2 and 9 Joy Geren
IDENTIFICATION, EVALUATION AND INTERVENTION FOR ELL STUDENTS WITH COMMUNICATION DISORDERS
 IDENTIFICATION, EVALUATION AND INTERVENTION FOR ELL STUDENTS WITH COMMUNICATION DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Public school systems in the United States have experienced a significant increase in the number of
IDENTIFICATION, EVALUATION AND INTERVENTION FOR ELL STUDENTS WITH COMMUNICATION DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Public school systems in the United States have experienced a significant increase in the number of
English Learners and the Special Education Process The English Learner (EL) An EL is a student whose native and/or dominant language is a language
 English Learners and the Special Education Process The English Learner (EL) An EL is a student whose native and/or dominant language is a language other than English. Native language is: In all direct
English Learners and the Special Education Process The English Learner (EL) An EL is a student whose native and/or dominant language is a language other than English. Native language is: In all direct
Early Childhood Study of Language and Literacy Development of Spanish-Speaking Children
 Early Childhood Study of Language and Literacy Development of Spanish-Speaking Children Subproject 1 of Acquiring Literacy in English: Crosslinguistic, Intralinguistic, and Developmental Factors Project
Early Childhood Study of Language and Literacy Development of Spanish-Speaking Children Subproject 1 of Acquiring Literacy in English: Crosslinguistic, Intralinguistic, and Developmental Factors Project
Register of Students with Severe Disabilities
 Department of Education Learners first, connected and inspired Register of Students with Severe Disabilities Department of Education Register of Students with Severe Disabilities 1. Eligibility Criteria
Department of Education Learners first, connected and inspired Register of Students with Severe Disabilities Department of Education Register of Students with Severe Disabilities 1. Eligibility Criteria
TESOL Standards for P-12 ESOL Teacher Education 2010. 1 = Unacceptable 2 = Acceptable 3 = Target
 TESOL Standards for P-12 ESOL Teacher Education 2010 1 = Unacceptable 2 = Acceptable 3 = Target Standard 1. Language: Candidates know, understand, and use the major theories and research related to the
TESOL Standards for P-12 ESOL Teacher Education 2010 1 = Unacceptable 2 = Acceptable 3 = Target Standard 1. Language: Candidates know, understand, and use the major theories and research related to the
ELPS TELPAS. Proficiency Level Descriptors
 ELPS TELPAS Proficiency Level Descriptors Permission to copy the ELPS TELPAS Proficiency Level Descriptors is hereby extended to Texas school officials and their agents for their exclusive use in determining
ELPS TELPAS Proficiency Level Descriptors Permission to copy the ELPS TELPAS Proficiency Level Descriptors is hereby extended to Texas school officials and their agents for their exclusive use in determining
SPEECH OR LANGUAGE IMPAIRMENT
 I. DEFINITION "Speech or Language Impairment" means a communication disorder, such as stuttering, impaired articulation, a language impairment, or a voice impairment, that adversely affects a child's educational
I. DEFINITION "Speech or Language Impairment" means a communication disorder, such as stuttering, impaired articulation, a language impairment, or a voice impairment, that adversely affects a child's educational
Early Childhood Foundations to the Indiana Academic Standards
 Alignment of the Early Childhood Foundations to the Indiana Academic Standards for Young Children from Birth to Age 5 with the Preschool Child Observation Record (COR), 2 nd edition The Preschool Child
Alignment of the Early Childhood Foundations to the Indiana Academic Standards for Young Children from Birth to Age 5 with the Preschool Child Observation Record (COR), 2 nd edition The Preschool Child
THE FRAMEWORK FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION GRADES PRE K- 8 & 7-12 PROGRAM GUIDELINES PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION
 THE FRAMEWORK FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION GRADES PRE K- 8 & 7-12 PROGRAM GUIDELINES PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Why Quality Teacher Preparation Programs Are Important...3 Philosophy
THE FRAMEWORK FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION GRADES PRE K- 8 & 7-12 PROGRAM GUIDELINES PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Why Quality Teacher Preparation Programs Are Important...3 Philosophy
Identifying dyslexia and other learning problems using LASS
 Identifying dyslexia and other learning problems using LASS 1 Outline of presentation What is LASS? What is dyslexia? Indicators of dyslexia Components and features of LASS Uses of LASS for screening and
Identifying dyslexia and other learning problems using LASS 1 Outline of presentation What is LASS? What is dyslexia? Indicators of dyslexia Components and features of LASS Uses of LASS for screening and
Patterns of Strengths and Weaknesses in L.D. Identification
 Patterns of Strengths and Weaknesses in L.D. Identification October 3, 2013 Jody Conrad, M.S., N.C.S.P School Psychologist, SOESD Definitions of SLD Federal and State A disorder in one or more basic psychological
Patterns of Strengths and Weaknesses in L.D. Identification October 3, 2013 Jody Conrad, M.S., N.C.S.P School Psychologist, SOESD Definitions of SLD Federal and State A disorder in one or more basic psychological
Categories of Exceptionality and Definitions
 7. CATEGORIES and DEFINITIONS of EXCEPTIONALITIES Purpose of the standard To provide the ministry with details of the categories and definitions of exceptionalities available to the public, including parents
7. CATEGORIES and DEFINITIONS of EXCEPTIONALITIES Purpose of the standard To provide the ministry with details of the categories and definitions of exceptionalities available to the public, including parents
Functional Auditory Performance Indicators (FAPI)
 Functional Performance Indicators (FAPI) An Integrated Approach to Skill FAPI Overview The Functional (FAPI) assesses the functional auditory skills of children with hearing loss. It can be used by parents,
Functional Performance Indicators (FAPI) An Integrated Approach to Skill FAPI Overview The Functional (FAPI) assesses the functional auditory skills of children with hearing loss. It can be used by parents,
Culture and Language. What We Say Influences What We Think, What We Feel and What We Believe
 Culture and Language What We Say Influences What We Think, What We Feel and What We Believe Unique Human Ability Ability to create and use language is the most distinctive feature of humans Humans learn
Culture and Language What We Say Influences What We Think, What We Feel and What We Believe Unique Human Ability Ability to create and use language is the most distinctive feature of humans Humans learn
CURRICULUM VITAE Allan B. Smith, Ph.D., CCC-SLP. Education Ph.D. 2002, University of Connecticut (Communication Science).
 CURRICULUM VITAE Allan B. Smith, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Education Ph.D. 2002, University of Connecticut (Communication Science). M.S. 1996, Massachusetts General Hospital Institute of Health Professions (Speech-Language
CURRICULUM VITAE Allan B. Smith, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Education Ph.D. 2002, University of Connecticut (Communication Science). M.S. 1996, Massachusetts General Hospital Institute of Health Professions (Speech-Language
Reading: Text level guide
 Reading: Text level guide Text level guide for seen text and accompanying background information. As teachers we provide the range of experiences and the instruction necessary to help children become good
Reading: Text level guide Text level guide for seen text and accompanying background information. As teachers we provide the range of experiences and the instruction necessary to help children become good
One Stop Shop For Educators
 Modern Languages Level II Course Description One Stop Shop For Educators The Level II language course focuses on the continued development of communicative competence in the target language and understanding
Modern Languages Level II Course Description One Stop Shop For Educators The Level II language course focuses on the continued development of communicative competence in the target language and understanding
CELF-4 Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals FOURTH EDITION
 Student: Matthew F. Franklin Test Date: 5/13/2003 Date of Birth: 4/13/1990 Age at Testing: 13 years 1 month Gender: Male Report Date: 5/16/2003 Grade: 6th Examiner: Maria Randolph Parent(s): Tom Franklin
Student: Matthew F. Franklin Test Date: 5/13/2003 Date of Birth: 4/13/1990 Age at Testing: 13 years 1 month Gender: Male Report Date: 5/16/2003 Grade: 6th Examiner: Maria Randolph Parent(s): Tom Franklin
Central Auditory System
 Auditory Processing Disorder Sarah (King) Zlomke, Au.D., CCC-A September 16, 2011 Kansas Speech-Language-Hearing Association Conference Auditory processing is not only what we hear, it is how we process
Auditory Processing Disorder Sarah (King) Zlomke, Au.D., CCC-A September 16, 2011 Kansas Speech-Language-Hearing Association Conference Auditory processing is not only what we hear, it is how we process
CHARACTERISTICS FOR STUDENTS WITH: LIMITED ENGLISH PROFICIENCY (LEP)
 CHARACTERISTICS FOR STUDENTS WITH: LIMITED ENGLISH PROFICIENCY (LEP) Research has shown that students acquire a second language in the same way that they acquire the first language. It is an exploratory
CHARACTERISTICS FOR STUDENTS WITH: LIMITED ENGLISH PROFICIENCY (LEP) Research has shown that students acquire a second language in the same way that they acquire the first language. It is an exploratory
SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITY
 I. DEFINITION "Specific learning disability" means a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding or in using language, spoken or written, that may manifest itself
I. DEFINITION "Specific learning disability" means a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding or in using language, spoken or written, that may manifest itself
San Jose State University College of Education Department of Special Education. EDSE 102: Speech, Language, Typical and Atypical Development
 San Jose State University College of Education Department of Special Education EDSE 102: Speech, Language, Typical and Atypical Development Spring 2015 Instructor: Alicia Henderson, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Class
San Jose State University College of Education Department of Special Education EDSE 102: Speech, Language, Typical and Atypical Development Spring 2015 Instructor: Alicia Henderson, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Class
The National Reading Panel: Five Components of Reading Instruction Frequently Asked Questions
 The National Reading Panel: Five Components of Reading Instruction Frequently Asked Questions Phonemic Awareness What is a phoneme? A phoneme is the smallest unit of sound in a word. For example, the word
The National Reading Panel: Five Components of Reading Instruction Frequently Asked Questions Phonemic Awareness What is a phoneme? A phoneme is the smallest unit of sound in a word. For example, the word
62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02
 62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact Information Test Development
62 Hearing Impaired MI-SG-FLD062-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact Information Test Development
How To Teach English To Other People
 TESOL / NCATE Program Standards STANDARDS FOR THE ACCREDIATION OF INITIAL PROGRAMS IN P 12 ESL TEACHER EDUCATION Prepared and Developed by the TESOL Task Force on ESL Standards for P 12 Teacher Education
TESOL / NCATE Program Standards STANDARDS FOR THE ACCREDIATION OF INITIAL PROGRAMS IN P 12 ESL TEACHER EDUCATION Prepared and Developed by the TESOL Task Force on ESL Standards for P 12 Teacher Education
Parent Education Activities
 PART III: PARENT EDUCATION Parent education sessions need to be planned and should follow a similar sequence each time. The suggested sequence is listed here and is explained later in this article. Also,
PART III: PARENT EDUCATION Parent education sessions need to be planned and should follow a similar sequence each time. The suggested sequence is listed here and is explained later in this article. Also,
Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230]
![Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230] Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230]](/thumbs/40/21177704.jpg) Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230] STANDARD 1 - Content Knowledge The competent speech-language pathologist understands the philosophical, historical, and legal foundations of speech-language
Standards for the Speech-Language Pathologist [28.230] STANDARD 1 - Content Knowledge The competent speech-language pathologist understands the philosophical, historical, and legal foundations of speech-language
The University of North Carolina at Pembroke 2015-2016 Academic Catalog
 338 The University of North Carolina at Pembroke 2015-2016 Academic Catalog COURSES BIRTH TO KINDERGARTEN (ECE) ECE 2020. Foundations of Early Childhood (3 credits) This course is designed to introduce
338 The University of North Carolina at Pembroke 2015-2016 Academic Catalog COURSES BIRTH TO KINDERGARTEN (ECE) ECE 2020. Foundations of Early Childhood (3 credits) This course is designed to introduce
FLORIDA EARLY LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENTAL STANDARDS: Birth to Five
 FLORIDA EARLY LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENTAL STANDARDS: Birth to Five The Florida Early Learning and Developmental Standards were created by using multiple resources, of which, one was the Alaska Guidelines.
FLORIDA EARLY LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENTAL STANDARDS: Birth to Five The Florida Early Learning and Developmental Standards were created by using multiple resources, of which, one was the Alaska Guidelines.
The Road to Rehabilitation
 The Road to Rehabilitation Part 5 Crossing the Communication Bridge: Speech, Language & Brain Injury Written by Jean L. Blosser, EdD, CCC/SCLP Roberta DePompei, PhD, CCC/SCLP Content reveiwed by Gregory
The Road to Rehabilitation Part 5 Crossing the Communication Bridge: Speech, Language & Brain Injury Written by Jean L. Blosser, EdD, CCC/SCLP Roberta DePompei, PhD, CCC/SCLP Content reveiwed by Gregory
Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss
 With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
With early detection, Early Intervention can begin! Guide for families of infants and children with hearing loss Birth to 3 2008 Cover photograph Geneva Marie Durgin was born January 20, 2007. She lives
Reading Competencies
 Reading Competencies The Third Grade Reading Guarantee legislation within Senate Bill 21 requires reading competencies to be adopted by the State Board no later than January 31, 2014. Reading competencies
Reading Competencies The Third Grade Reading Guarantee legislation within Senate Bill 21 requires reading competencies to be adopted by the State Board no later than January 31, 2014. Reading competencies
3-1 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 C A S E S T U D Y 3 : T o d d l e r Adapted from Thomson Delmar Learning s Case Study Series: Pediatrics, by Bonita E. Broyles, RN, BSN, MA, PhD. Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning, Clifton Park, NY.
C A S E S T U D Y 3 : T o d d l e r Adapted from Thomson Delmar Learning s Case Study Series: Pediatrics, by Bonita E. Broyles, RN, BSN, MA, PhD. Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning, Clifton Park, NY.
Thomas L. Layton, Ph.D.
 Developmental Scale for Children with Down Syndrome Thomas L. Layton, Ph.D. Extraordinary Learning Foundation T and T Communication Services, Inc. 100 Meredith Drive, Suite 100 Durham, NC 27713 Developmental
Developmental Scale for Children with Down Syndrome Thomas L. Layton, Ph.D. Extraordinary Learning Foundation T and T Communication Services, Inc. 100 Meredith Drive, Suite 100 Durham, NC 27713 Developmental
COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY IN TEACHING READING
 Лю Пэн COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY IN TEACHING READING Effective Elementary Reading Program Effective approach must contain the following five components: 1. Phonemic awareness instruction to help children learn
Лю Пэн COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY IN TEACHING READING Effective Elementary Reading Program Effective approach must contain the following five components: 1. Phonemic awareness instruction to help children learn
SPECIAL EDUCATION ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA AND IEP PLANNING GUIDELINES
 SPECIAL EDUCATION ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA AND IEP PLANNING GUIDELINES CHAPTER 6 INDEX 6.1 PURPOSE AND SCOPE...6 1 6.2 PRIOR TO REFERRAL FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION.. 6 1 6.3 REFFERRAL...6 2 6.4 ASSESMENT.....6
SPECIAL EDUCATION ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA AND IEP PLANNING GUIDELINES CHAPTER 6 INDEX 6.1 PURPOSE AND SCOPE...6 1 6.2 PRIOR TO REFERRAL FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION.. 6 1 6.3 REFFERRAL...6 2 6.4 ASSESMENT.....6
Foundations of the Montessori Method (3 credits)
 MO 634 Foundations of the Montessori Method This course offers an overview of human development through adulthood, with an in-depth focus on childhood development from birth to age six. Specific topics
MO 634 Foundations of the Montessori Method This course offers an overview of human development through adulthood, with an in-depth focus on childhood development from birth to age six. Specific topics
Tips for Working With ELL Students
 Session One: Increasing Comprehensibility One goal for every teacher working with ELL students is to increase comprehensibility. In other words, to increase understanding or make course content more intelligible.
Session One: Increasing Comprehensibility One goal for every teacher working with ELL students is to increase comprehensibility. In other words, to increase understanding or make course content more intelligible.
Ohio Early Learning and Development Standards Domain: Language and Literacy Development
 Ohio Early Learning and Development Standards Domain: Language and Literacy Development Strand: Listening and Speaking Topic: Receptive Language and Comprehension Infants Young Toddlers (Birth - 8 months)
Ohio Early Learning and Development Standards Domain: Language and Literacy Development Strand: Listening and Speaking Topic: Receptive Language and Comprehension Infants Young Toddlers (Birth - 8 months)
PRESCHOOL PLACEMENT CATEGORIES
 PRESCHOOL PLACEMENT CATEGORIES CASEMIS 20 EARLY CHILDHOOD SPECIAL EDUCATION SETTING Early Childhood Special Education Setting: This is a placement setting where children receive all of their special education
PRESCHOOL PLACEMENT CATEGORIES CASEMIS 20 EARLY CHILDHOOD SPECIAL EDUCATION SETTING Early Childhood Special Education Setting: This is a placement setting where children receive all of their special education
AUGMENTATIVE COMMUNICATION EVALUATION
 AUGMENTATIVE COMMUNICATION EVALUATION Date: Name: Age: Date of Birth: Address: Telephone: Referral Source: Diagnosis: Participants: Social History and Current Services: lives with his in a private home
AUGMENTATIVE COMMUNICATION EVALUATION Date: Name: Age: Date of Birth: Address: Telephone: Referral Source: Diagnosis: Participants: Social History and Current Services: lives with his in a private home
TELPAS. Texas English Language Proficiency Assessment System. grades K 12 Revised July 2011. texas Education agency student assessment division
 Educator guide to telpas TELPAS Texas English Language Proficiency Assessment System grades K 12 Revised July 2011 texas Education agency student assessment division Copyright 2011, Texas Education Agency.
Educator guide to telpas TELPAS Texas English Language Proficiency Assessment System grades K 12 Revised July 2011 texas Education agency student assessment division Copyright 2011, Texas Education Agency.
Create stories, songs, plays, and rhymes in play activities. Act out familiar stories, songs, rhymes, plays in play activities
 PRESCHOOL Language Arts Literacy Expectation 1 Children listen and respond to environmental sounds, directions, and conversations. NJCCC K-12 Standard 3.4 Listening Strand A: Active Listening Strand B:
PRESCHOOL Language Arts Literacy Expectation 1 Children listen and respond to environmental sounds, directions, and conversations. NJCCC K-12 Standard 3.4 Listening Strand A: Active Listening Strand B:
PRE AND POST TEST TO SEE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN YEARS OF ANIMATED LITERACY AND KNOWLEDGE OF LETTERS STEPHANIE, BUCK. Submitted to
 Animated Literacy 1 RUNNING HEAD: Years of Animated Literacy Letters PRE AND POST TEST TO SEE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN YEARS OF ANIMATED LITERACY AND KNOWLEDGE OF LETTERS By STEPHANIE, BUCK Submitted to
Animated Literacy 1 RUNNING HEAD: Years of Animated Literacy Letters PRE AND POST TEST TO SEE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN YEARS OF ANIMATED LITERACY AND KNOWLEDGE OF LETTERS By STEPHANIE, BUCK Submitted to
SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITIES (SLD)
 Together, We Can Make A Difference Office 770-577-7771 Toll Free1-800-322-7065 www.peppinc.org SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITIES (SLD) Definition (1) Specific learning disability is defined as a disorder
Together, We Can Make A Difference Office 770-577-7771 Toll Free1-800-322-7065 www.peppinc.org SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITIES (SLD) Definition (1) Specific learning disability is defined as a disorder
Professional Learning Guide
 Professional Learning Guide Professional Learning Guide Published by the Student Wellbeing and Health Support Division Office for Government School Education Department of Education and Early Childhood
Professional Learning Guide Professional Learning Guide Published by the Student Wellbeing and Health Support Division Office for Government School Education Department of Education and Early Childhood
Interpretive Report of WISC-IV and WIAT-II Testing - (United Kingdom)
 EXAMINEE: Abigail Sample REPORT DATE: 17/11/2005 AGE: 8 years 4 months DATE OF BIRTH: 27/06/1997 ETHNICITY: EXAMINEE ID: 1353 EXAMINER: Ann Other GENDER: Female Tests Administered: WISC-IV
EXAMINEE: Abigail Sample REPORT DATE: 17/11/2005 AGE: 8 years 4 months DATE OF BIRTH: 27/06/1997 ETHNICITY: EXAMINEE ID: 1353 EXAMINER: Ann Other GENDER: Female Tests Administered: WISC-IV
Which WJ-III Subtests Should I Administer?
 Which WJ-III Subtests Should I Administer? P R E S E N T E D B Y : J U D D F R E D S T R O M A R E A S P E C I A L E D U C A T I O N C O O P A S E C. N E T Woodcock-Johnson III tests of Achievement Eligibility
Which WJ-III Subtests Should I Administer? P R E S E N T E D B Y : J U D D F R E D S T R O M A R E A S P E C I A L E D U C A T I O N C O O P A S E C. N E T Woodcock-Johnson III tests of Achievement Eligibility
Common Educational Tests used for Assessments for Special Education
 Cognition/Intelligence Ability to reason, to think abstractly, and to solve problems. Wechsler tests: WISC-III, WAIS-R, WPPSI-R Stanford-Binet: Fourth Edition Differential Ability Scales (DAS) Verbal Intelligence
Cognition/Intelligence Ability to reason, to think abstractly, and to solve problems. Wechsler tests: WISC-III, WAIS-R, WPPSI-R Stanford-Binet: Fourth Edition Differential Ability Scales (DAS) Verbal Intelligence
Evaluation Report Structure for Funding of Speech Generating Devices
 Evaluation Report Structure for Funding of Speech Generating Devices Request for Speech Generating Device (SGD) Funding: Section 1: Demographic Information Patient: full name, complete address & telephone
Evaluation Report Structure for Funding of Speech Generating Devices Request for Speech Generating Device (SGD) Funding: Section 1: Demographic Information Patient: full name, complete address & telephone
Asset 1.6 What are speech, language and communication needs?
 1 of 5 The National Strategies Asset 1.6 What are speech, language and needs? a) Summary of key points Taken from the Primary and Secondary Inclusion Development Programme (IDP): Dyslexia and speech, language
1 of 5 The National Strategies Asset 1.6 What are speech, language and needs? a) Summary of key points Taken from the Primary and Secondary Inclusion Development Programme (IDP): Dyslexia and speech, language
There are basically three options available for overcoming barriers to learning:
 COGNITIVE SKILLS DEVELOPMENT Teacher Introduction Determining Your Students Weaknesses (Excerpts from article by Dr. Ken Gibson, Founder and CEO of LearningRx) Do you have students who struggle to understand
COGNITIVE SKILLS DEVELOPMENT Teacher Introduction Determining Your Students Weaknesses (Excerpts from article by Dr. Ken Gibson, Founder and CEO of LearningRx) Do you have students who struggle to understand
Assessing Young English Learners Across Purposes and Domains: Promises and Pitfalls
 Assessing Young English Learners Across Purposes and Domains: Promises and Pitfalls By Linda M. Espinosa, Ph.D. Language Minority Children Roundtable April 2008 5/5/2008 1 Bilingual Children are Different
Assessing Young English Learners Across Purposes and Domains: Promises and Pitfalls By Linda M. Espinosa, Ph.D. Language Minority Children Roundtable April 2008 5/5/2008 1 Bilingual Children are Different
OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools. Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs
 OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs UNIT SUMMARY Who is this unit for? This unit is for those who provide support
OCR Levels 2 and 3 in Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools Unit 39 Support pupils with communication and interaction needs UNIT SUMMARY Who is this unit for? This unit is for those who provide support
ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES SPEECH PATHOLOGY
 ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES SPEECH PATHOLOGY These guidelines are consistent with the Texas Speech- Language-Hearing Association s (TSHA) eligibility templates. It is recommended that you contact the TSHA Vice
ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES SPEECH PATHOLOGY These guidelines are consistent with the Texas Speech- Language-Hearing Association s (TSHA) eligibility templates. It is recommended that you contact the TSHA Vice
Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss. A Guide to Services for Students with a
 Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss A Guide to Services for Students with a Learning Disability (Revised 4.28.14) Do I Have A Learning
Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss A Guide to Services for Students with a Learning Disability (Revised 4.28.14) Do I Have A Learning
Technical Report #2 Testing Children Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing
 Technical Report #2 Testing Children Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing September 4, 2015 Lori A. Day, PhD 1, Elizabeth B. Adams Costa, PhD 2, and Susan Engi Raiford, PhD 3 1 Gallaudet University 2 The River
Technical Report #2 Testing Children Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing September 4, 2015 Lori A. Day, PhD 1, Elizabeth B. Adams Costa, PhD 2, and Susan Engi Raiford, PhD 3 1 Gallaudet University 2 The River
APEC Online Consumer Checklist for English Language Programs
 APEC Online Consumer Checklist for English Language Programs The APEC Online Consumer Checklist For English Language Programs will serve the training needs of government officials, businesspeople, students,
APEC Online Consumer Checklist for English Language Programs The APEC Online Consumer Checklist For English Language Programs will serve the training needs of government officials, businesspeople, students,
Planning Commentary Respond to the prompts below (no more than 9 single-spaced pages, including prompts).
 Planning Commentary Respond to the prompts below (no more than 9 single-spaced pages, including prompts). 1. Central Focus a. Describe the central focus and purpose for the content you will teach in this
Planning Commentary Respond to the prompts below (no more than 9 single-spaced pages, including prompts). 1. Central Focus a. Describe the central focus and purpose for the content you will teach in this
Tool for Analysis of Language and Communication (TALC)
 Tool for Analysis of Language and Communication (TALC) Language Sampling Tool for Multimodal Communicators Student: Date: Partner Name / Relationship Activity: Learning Context: SG= Small Group, LG= Large
Tool for Analysis of Language and Communication (TALC) Language Sampling Tool for Multimodal Communicators Student: Date: Partner Name / Relationship Activity: Learning Context: SG= Small Group, LG= Large
synthetic phonics teaching? Rhona Johnston and Joyce Watson Department of Psychology University of Hull r.s.johnston@hull.ac.uk
 What are the benefits of synthetic phonics teaching? Rhona Johnston and Joyce Watson Department of Psychology University of Hull r.s.johnston@hull.ac.uk Our studies of analytic and synthetic phonics From
What are the benefits of synthetic phonics teaching? Rhona Johnston and Joyce Watson Department of Psychology University of Hull r.s.johnston@hull.ac.uk Our studies of analytic and synthetic phonics From
Online Literacy Solution
 Online Literacy Solution Failure Free Reading is a research-proven, language development and reading comprehension program founded in 1988. It has been implemented in 1000 s of schools across the United
Online Literacy Solution Failure Free Reading is a research-proven, language development and reading comprehension program founded in 1988. It has been implemented in 1000 s of schools across the United
SAME DIVERSE DIFFERENT. Understanding Children Who Are Dual Language Learners (DLLs)
 Understanding Who Are Dual Language Learners (DLLs) One third of the children enrolled in Early Head Start and Head Start are Dual Language Learners (DLLs). They are a diverse group who have different
Understanding Who Are Dual Language Learners (DLLs) One third of the children enrolled in Early Head Start and Head Start are Dual Language Learners (DLLs). They are a diverse group who have different
Given the increasing diversity of
 Culturally Competent Assessment and Consultation PHOTO BY DAVID HATHCOX Because the outcome of a consultation or an assessment can have significant implications for students, principals should ensure that
Culturally Competent Assessment and Consultation PHOTO BY DAVID HATHCOX Because the outcome of a consultation or an assessment can have significant implications for students, principals should ensure that
NFL Quarterback Bernie Kosar told
 RESEARCH PAPER VOLUME 1 Why It Is Important to Teach Phonemic Awareness and Alphabet Recognition by Dr. Cathy Collins Block Professor of Education Texas Christian University NFL Quarterback Bernie Kosar
RESEARCH PAPER VOLUME 1 Why It Is Important to Teach Phonemic Awareness and Alphabet Recognition by Dr. Cathy Collins Block Professor of Education Texas Christian University NFL Quarterback Bernie Kosar
Test Review: Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals Fifth Edition (CELF-5)
 Test Review: Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals Fifth Edition (CELF-5) Version: 5 th Edition Copyright date: 2013 Grade or Age Range: 5-21 Author: Elizabeth Wiig, Eleanor Semel and Wayne Secord
Test Review: Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals Fifth Edition (CELF-5) Version: 5 th Edition Copyright date: 2013 Grade or Age Range: 5-21 Author: Elizabeth Wiig, Eleanor Semel and Wayne Secord
Alphabetic Knowledge / Exploring with Letters
 Alphabetic Knowledge / Exploring with Letters Reading Goal 67: demonstrate awareness of the alphabetic principle Reads books with repetitive sounds and/or pronounces words deliberately and slowly when
Alphabetic Knowledge / Exploring with Letters Reading Goal 67: demonstrate awareness of the alphabetic principle Reads books with repetitive sounds and/or pronounces words deliberately and slowly when
Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]
![Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]](/thumbs/24/3436110.jpg) I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
Modern foreign languages
 Modern foreign languages Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment targets (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007
Modern foreign languages Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment targets (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007
Down Syndrome And Language Development
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Spring 2012 Down Syndrome And Language Development Colleen D. Oliver Southern Illinois University Carbondale, oliverc@siu.edu
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Spring 2012 Down Syndrome And Language Development Colleen D. Oliver Southern Illinois University Carbondale, oliverc@siu.edu
ACRONYMS & TERMS RELATED TO ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEARNERS
 ACRONYMS & TERMS RELATED TO ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEARNERS Academic Language ACCESS for ELLs Accommodations Additive Bilingualism Language used in the learning of academic subject matter in formal schooling
ACRONYMS & TERMS RELATED TO ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEARNERS Academic Language ACCESS for ELLs Accommodations Additive Bilingualism Language used in the learning of academic subject matter in formal schooling
Predicting the development of communication skills by children with motor disorders
 Predicting the development of communication skills by children with motor disorders Dr Lindsay Pennington, Dr Mark Pearce, Professor Allan Colver, Professor Helen McConachie, Newcastle University Dr Mary
Predicting the development of communication skills by children with motor disorders Dr Lindsay Pennington, Dr Mark Pearce, Professor Allan Colver, Professor Helen McConachie, Newcastle University Dr Mary
Supporting Families in Transition between Early Intervention and School Age Programs
 Supporting Families in Transition between Early Intervention and School Age Programs by Cheryl Johnson, Special Education Unit, Colorado Department of Education The transitions between early intervention
Supporting Families in Transition between Early Intervention and School Age Programs by Cheryl Johnson, Special Education Unit, Colorado Department of Education The transitions between early intervention
Alignment of the Hawaii Preschool Content Standards With HighScope s Preschool Child Observation Record (COR), 2nd edition
 Alignment of the Hawaii Preschool Content Standards With HighScope s Preschool Child Observation Record (COR), 2nd edition The following chart shows how items from the Hawaii Preschool Content Standards
Alignment of the Hawaii Preschool Content Standards With HighScope s Preschool Child Observation Record (COR), 2nd edition The following chart shows how items from the Hawaii Preschool Content Standards
assessment report ... Academic & Social English for ELL Students: Assessing Both with the Stanford English Language Proficiency Test
 . assessment report Academic & Social English for ELL Students: Assessing Both with the Stanford English Language Proficiency Test.......... Diane F. Johnson September 2003 (Revision 1, November 2003)
. assessment report Academic & Social English for ELL Students: Assessing Both with the Stanford English Language Proficiency Test.......... Diane F. Johnson September 2003 (Revision 1, November 2003)
AUGMENTATIVE/ALTERNATIVE COMMUNICATION (AAC) EVALUATION CHECKLIST
 OKLAHOMA ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY CENTER UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER DIVISION OF REHABILITATION SCIENCES COLLEGE OF ALLIED HEALTH 1600 N. Phillips Oklahoma City, OK 73104 405/271-3625; TDD
OKLAHOMA ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY CENTER UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER DIVISION OF REHABILITATION SCIENCES COLLEGE OF ALLIED HEALTH 1600 N. Phillips Oklahoma City, OK 73104 405/271-3625; TDD
Alignment of the National Standards for Learning Languages with the Common Core State Standards
 Alignment of the National with the Common Core State Standards Performance Expectations The Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts (ELA) and Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science,
Alignment of the National with the Common Core State Standards Performance Expectations The Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts (ELA) and Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science,
MAP for Language & International Communication Spanish Language Learning Outcomes by Level
 Novice Abroad I This course is designed for students with little or no prior knowledge of the language. By the end of the course, the successful student will develop a basic foundation in the five skills:
Novice Abroad I This course is designed for students with little or no prior knowledge of the language. By the end of the course, the successful student will develop a basic foundation in the five skills:
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
 CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE This chapter consists of two parts. The first part starts with the definition of learning styles, the importance of understanding the students learning styles, models
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE This chapter consists of two parts. The first part starts with the definition of learning styles, the importance of understanding the students learning styles, models
