Service Oligopolies and Australia s Economy-Wide Performance*
|
|
|
- Sheila Sherman
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WORKING PAPERS IN ECONOMICS AND ECONOMETRICS Servce Olgopoles and Australa s Economy-Wde Performance* Rod Tyers College of Busness and Economcs Australan Natonal Unversty Lucy Rees** Ban and Company rst revson, May 2008 Key words: Regulaton, olgopoly, servces, prce caps, prvatsaton JEL codes: C68, D43, D58, L3, L43, L5, L80 Workng Papers n Economcs and Econometrcs No.490 College of Busness and Economcs Australan Natonal Unversty * undng for the research descrbed n ths paper s from Australan Research Councl Dscovery Grant No. DP Thanks are due to lavo Menezes for valuable nput at the formaton stage of ths project, Chrs Jones for useful dscussons, Marcn Pracz for assstance wth ths research durng 2006 and to Pngkun Hsu and Ian Ban for research assstance snce then. lavo Menezes also offered valuable comments on an earler draft as dd partcpants at a March 2008 semnar n the ANU s College of Busness and Economcs, ncludng Phllpa Dee, Ben Smth, Chrs Jones, Martn Rchardson, Wllam Coleman and Rchard Cornes. ** Lucy Rees contrbuted to the early development of ths research durng her studes at the ANU. The results presented and opnons offered n no way represent the postons of Ban and Company on regulaton polcy.
2 Servce Olgopoles and Australa s Economy-Wde Performance Abstract The retreat from publc ownershp of servce frms and ndustres has left behnd numerous prvate monopoles and olgopoles supervsed by regulatory agences. Servces ndustres n government and prvate ownershp generate two-thrds of Australa s value added, whle the newly prvatsed ones, utltes, telecommuncatons, fnance and transport, supply a ffth. Ths study offers an economy-wde approach that represents monopoly and olgopoly behavour explctly. It examnes the mplcatons of olgopoly rents for factor markets and the real exchange rate, the extent of sectoral nteractons and the potental economy wde gans from tghter prce cap regulaton, wth the results confrmng the mert of an economywde approach. External shocks, lke the present Chna boom, are also smulated. Such postve shocks are shown to expand the potental for olgopoly rents and therefore to rase the bar for regulatory agences. Moreover, less than tght prce caps are shown to exacerbate entry-ext hysteress n boom and bust cycles.. Introducton ollowng mcroeconomc reforms of the 980s and 990s, excludng government agences, corporatons subject to regulaton now provde almost half of Australan s employment and of ts GDP. The analyss of regulatory regmes must, therefore, account for economy-wde mplcatons, such as effects on the real exchange rate and factor markets as well as on other ndustres through the cost of ntermedate servces. Ths s best acheved by modellng the whole Australan economy n a way that allows explctly for the monopoly and olgopoly behavour requrng regulaton n the frst place. Such a model s offered n ths paper. It s desgned to help clarfy the mplcatons of changes n the regulaton of olgopoly prcng for the structure and performance of Australa s servce ndustres whle at the same tme examnng nter-sectoral effects and assocated changes n the performance of labour markets and the economy as a whole. The retreat from the government s drect provson of nfrastructure servces has left prvate frms and publcly-owned corporatsed enttes (government bodes subject to corporatons law) n ndustres that are lttered wth olgopoly structures and component monopoles. These frms and enttes are therefore supervsed by regulatory agences. They nclude: transport, electrcty, water supply, gas dstrbuton, telecommuncatons, fnance and nsurance, educaton and health. 2 Whle regulatory polces cover both product prcng and See ABS 2003: Tables 2.2 and 2.3, wth publc servce output and employment subtracted. 2 The health sector s not addressed ndependently n ths study, prmarly because ts actvty s dffcult to dstngush n the avalable economy-wde database we use but also because t s rfe wth nformaton asymmetres that make ts regulaton more complex than the sectors consdered. 2
3 qualty, we focus entrely on prce regulaton, ncludng prce survellance as well as prce caps, and hence the control of economc costs assocated wth dstortons due to mperfect competton. Some exstng studes suggest an ndrect lnk between the prvatsaton and regulatory reforms and productvty 3, whle other studes follow a long tradton n regulatory economcs of applyng ndustry-specfc (partal equlbrum) comparatve statcs. 4 In recent years economy-wde mplcatons have been examned usng models underpnned by perfectly compettve behavour, wth olgopoly rents mpled by the choce of parameters, closure or productvty shocks. 5 Industry-specfc fx-ups n such models stll requre the assumpton of perfect competton n all other ndustres to generate the economy-wde effects. Whle ths approach has been very useful durng the mcroeconomc reform transton, t tends to gnore the fact that most other economc actvty s also mperfectly compettve and subject to regulaton, and that regulatory changes to one ndustry are unlkely to occur wthout mplcatons for the regulaton of others or for the performance of the whole economy. 6 Central to ths paper s the mathematcal model of the Australan economy t ntroduces and the economy wde database that serves t. Ths model represents monopoly and olgopoly prcng behavour and the regulatory envronments facng major frms. Its behavoural structure s based on early work by Harrs (984), Horrdge (987), Gunasekera and Tyers (990) and Tyers (2005), whch emphassed homogeneous product olgopoles wth frms nteractng on producton n an almost small home economy. Subsequent extensons ncluded dfferentated product olgopoles nteractng on prces. The focus n these pror applcatons has been trade reform and manufacturng olgopoly, wheren consderable attenton has been gven to the pro-compettve effects of trade lberalsaton (Hertel 994; Ianchovchna et al. 2000; Tyers 2005). In ts new guse the model s structured to focus on the more commonly regulated servces ndustres. To ths end, a more complete representaton of the Australan tax system s ncorporated. Ths s needed for two reasons. rst, the response of frms to regulaton 3 See, for example, Productvty Commsson (999), Madden et al. (2002). 4 Classc partal equlbrum studes nclude those by Averch and Johnson (962), Courvlle (974) and Wellsz (963). 5 These nclude the global model by Dee (2003), whch s nnovatve n that t recognses the mportance of domestc locaton for overseas-based servce frms. requently appled s hghly detaled MONASH model of the Australan economy (Dxon and Rmmer 2002). Ours s not an attempt to compete wth ether of these approaches. Rather, we seek to construct a more drect means to evaluate regulatory polces by embeddng more realstc monopoly and olgopoly behavour n the economy-wde context. 6 Ths s notwthstandng the fact that regulaton can be appled dfferently across dfferent jursdctons n Australa and across dfferent ndustres. See, for example, NECG (2003). 3
4 depends on the rates of tax to whch they are subject, and second, taxes and transfers offer an alternatve approach to the achevement of regulatory objectves. urther, the model ncludes generc foregn ownershp, thereby allowng for proper representaton of net factor ncome flows and ther effects on the real exchange rate, the composton of the current account and GNP. Usng ths machnery, ths paper begns wth an assessment of the scale of costs the Australan economy would bear were ts olgopolstc servce ndustres to be allowed to cartelse. Ths hypothetcal experment s used to llustrate the extent of economy wde nteractons assocated wth olgopoly behavour. It then assesses the potental for further gans from tghter cappng of prces, once agan gvng emphass to economy wde nteractons. nally, t offers a stylsed representaton of the Australan economy s response to the recent Chna drven global commodty boom, whch drectly affects ts agrcultural and mnng sectors but whch has rased the relatve prces of Australan servces and so t has mportant mplcatons for olgopoly rents n servces and ther regulaton. Indeed, the results show that the mantenance of tght prce caps through the boom would measurably ncrease the beneft from t n the short run and avod excessve entry n the long run should the effects of the boom be transtory. The secton to follow brefly revews developments n the structure and regulaton of Australa s servces sector. Secton 3 revews the behavoural structure of the model used, the detaled descrpton of whch s consgned to appendces, and the economc structure emboded n ts database. The potental economc losses from olgopoly behavour are assessed n Secton 4 whle the gans to be derved from tghter prce cappng are consdered n Secton 5. The response of olgopolstc servces to external shocks s examned n Secton 6. Conclusons are offered n Secton Regulaton Research and Australa s Servces Australa s servce ndustres have experenced rapd growth over the last ffty years. Ther regulaton s seen as redress for market falures that nclude lack of nformaton, monopoly power, externaltes or socal objectves (ncome dstrbuton or servce qualty). 7 Many servce ndustres requre networks wth hubs that consttute substantal recurrent fxed 7 See ndlay (2000: 0). 4
5 profts. The reach of regulatory polces n Australa has rsen snce these Acts were wrtten, cost and the control of whch creates barrers to entry, conferrng monopoly power. 8 The economc ratonale for servce regulaton s therefore strong. Stgler (97) argued that the analyss of regulaton should concentrate on three mportant questons 9 : who wll receve the benefts and who wll bear the burden of regulaton, the form and nature of the regulatory nterventon and the effect of regulaton on resource allocaton. There are very substantal subsequent lteratures on the generc benefts from regulaton and, more partcularly, the specfc regulatons mposed on Australa s servces. 0 Devces range between prce controls, ownershp restrctons, lmts on foregn drect nvestment and capacty constrants. ederal responsblty for competton regulaton and montorng rests wth the Australan Competton and Consumer Commsson (ACCC), whch admnsters the Trade Practces Act 974 ( TPA ) and the Prces Survellance Act 983 ( PSA ). The TPA promotes competton and far tradng whle also provdng consumer protecton. The PSA crcumscrbes the ACCC s montorng of prces, costs and due to the extensve prvatsatons assocated wth the mcroeconomc reform era and the pace of technologcal change. The latter, partcularly n telecommuncatons, electrcty and gas, has made t possble to unbundle ndustry segments, leavng some as natural monopoles or olgopoles but wth others organsed around supervsed new markets that foster compettve behavour (such electrcty producton and the retalng of gas, electrcty and telephone servces). The ntroducton of prce caps as ncentve regulaton was amed at the monopoly and olgopoly elements, where compettve prcng could not be otherwse nduced. These consequences of prvatsaton dd, however, dstort behavour as nvestment sought to escape the prce caps. 2 In telecommuncatons, ar transport and the producton and dstrbuton of natural gas and electrcty these changes have been stark. 3 Inevtable dstortons notwthstandng, reforms have been shown to contrbute to mprovements n both economc and government performance, accordng to the OECD (997) to the tune of fve percent of GDP. 8 Ibd. In the Australan context a recent example of ant-compettve behavour attrbuted to monopoly power over a network s Telstra s prcng for ts broadband servce. See ACCC (2003). 9 See Stgler (97). 0 See Trade Practces Act 974 (Cth), revewed n Productvty Commsson (2003). See ACCC (2003). 2 We are grateful to lavo Menezes for ths pont. or related dscusson, see Menezes et al. (2006). 3 See Doove et al. (200: 43). 5
6 In the late 970s there was sgnfcant ant-regulatory sentment n developed countres. The practce of rate-of-return regulaton was found to be ncompatble wth ncreased competton. Lttlechld (983) changed ths negatve percepton of regulaton wth hs report on the Brtsh telecommuncatons ndustry n whch he suggested prce caps as a regulatory polcy tool. Ths sgnalled a movement towards a more ncentve-based and less heavy handed approach to regulaton. The result has been very wdespread applcaton of prce-caps n servces, whch are charactersed by: product-specfc prce celngs, basket celngs that offer frms greater flexblty, and perodc adjustments of celngs to ensure that consumers share n the gans from techncal change and market formaton. 4 Theoretcal studes have been hghly stylsed and sector-specfc but they demonstrate that prce-caps, even as second best measures, can protect consumers aganst monopoly power, promote competton, mprove productve effcency and nnovaton and reduce the admnstratve burden of regulaton. 5 Emprcal follow-up by Xaver (995) assesses prcecap schemes n the UK, the USA and Australa. Hs Australan focus s on the (then) Telecom basket prce cap between 989 and 992. He fnds that the scheme reduced the average prce of Telecom s domestc servces n real terms by 3 percent. Internatonal call prces fell n real terms by 25 percent n ths perod, however, suggestng that the scheme fell short of delverng a far share of technologcal gans to the Australan consumer. He takes a sceptcal vew of some prce-cap mechansms, preferrng the fosterng of compettve forces where ths s possble. Turnng to economy-wde approaches wth explct representaton of mperfect competton, Blanchard and Gavazz (2003) offer an elemental general equlbrum model to nvestgate the combned effects of product market and labour market regulaton. Ther closed economy model ncorporates monopolstc competton n the goods market and barganng n the sngle factor (labour) market. In seekng competton, a government mght try to rase the elastcty of substtuton. In the short-run they fnd that the ncreased competton s benefcal because t forces frms to lower ther mark-up, leadng n turn to reduced captal returns but a hgher real wage. In the long run, however, there s ext by frms and reduced product varety. The assumpton of monopolstc competton leaves no pure profts to erode and nvarant recurrent fxed costs must see the mark-up return to ts orgnal value, so there are no long run benefts. If, nstead, the government attacks barrers to entry (recurrent fxed costs), the effects are unambguously welfare mprovng n the short and long 4 See Vogelsang and Acton (989). 5 The key works n ths area are: Cabral and Rordan (989), Bradley and Prce (988), and Brennan (989). 6
7 runs. There s an ncrease n the number of frms, a hgher elastcty of demand, a lower mark-up and thus lower unemployment and a hgher real wage. Whle t s not made clear how a government mght alter the elastcty of substtuton or entry costs, ths research sgnals an mprovement over pror studes of regulaton through ts charactersaton of market structure n an economy-wde context and t s n ths sprt that the research presented n ths paper has been undertaken. The precse extent of mperfect competton n Australa s servce ndustres s dffcult to quantfy. We offer short qualtatve summares for the key sectors n whch prvatsaton and regulaton have brought most change. Telecommuncatons The ACCC s analyss ndcates that ths sector s slowly becomng more compettve, wth most mprovement at the retal level, as opposed to nfrastructure provson. In lne wth global changes n telecommuncatons technology, there have also been consderable mprovements n productvty, as ndcated by Madden et al. (2002). 6 Telstra contnues to be the domnant frm wth about two thrds of the sector s lsted market captalsaton and between a thrd and three quarters of the markets for the dfferent telecommuncatons products (Telstra 2003). Whle these facts suggest a hgh level of concentraton, n areas such as moble and long dstance telephony and data transfer, competton s ntense. Telstra s explotable market power s n fxed telephony and network access. 7 Electrcty New market mechansms as well as regulatory reform have been ntroduced n ths sector. It has nonetheless been found that generators, whose numbers reman small, have often been able to ncrease prces substantally above compettve levels for sustaned perods. Indeed, Short et al. (200) ndcate that the electrcty market s subject to sgnfcant departures from compettve outcomes. Hgh Lerner ndces (prce-margnal cost margns) suggest the collecton of substantal rents. Yet, gven ths ndustry s hgh fxed costs, a better measure mght have been the mark-up over average cost. Gas 6 The controversal lnk between the market power of frms and nvestments n R&D, along wth assocated productvty performance, s not the focus of ths paper. Our approach offers a capacty to nvestgate ths ssue, however, and so t wll be the subject of further research. 7 or ths pont we are grateful to lavo Menezes. 7
8 Whle offcal barrers to the free flow of natural gas across state borders have been removed, the market remans hghly concentrated on the supply sde and t carres many legacy agreements that lmt competton. The resultng lack of lqudty n Australan gas markets has mpeded the development of transparent spot markets. 8 There are three supplers n the eastern Australan gas markets that account for more than 95 percent of the supply gas. The two ncumbents BHP Bllton and ExxonMobl account for 38 percent and 4 percent respectvely. As to nfrastructure, the largest ppelne owner n Australa s Australan Ppelne Trust (APT) whch owns a thrd of the total transmsson ppelne system. 9 Australa s second largest ppelne owner s Epc Energy, wth about half the capacty of APT. In 997 the Australan Government ntroduced a Gas Code The Natonal Thrd Party Access Code for Natural Gas Ppelnes whch s admnstered by the ACCC and the Natonal Competton Councl (NCC). 20 The Code ensures that gas can be transmtted through the ppelne network on reasonable terms and condtons, though n practce these have attracted controversy. Ar Transport The Australan arlne domestc market has long had a duopoly structure, changes of players n the 990s notwthstandng. Because of volatlty assocated wth these changes, the market share of the only remanng ncumbent, Qantas, has been measured at and above 70 percent. 2 Nonetheless t remans n the nterest of both the major carrers to mantan an ndustry structure whch allows both to generate sustanable proftablty wthout encouragng further entry. Agan, the ACCC montors prces and frequent flyer schemes for antcompettve elements. As to avaton nfrastructure, pror to 2002, arports n Australa were subject to prce-cap regulaton. However, the Productvty Commsson concluded that whle the major metropoltan arports have substantal market power, t s not n ther nterests to abuse ths power n such a way that would confer large costs onto the economy. 22 Hence, the government has largely deregulated arports, replacng prce caps wth prce montorng. 23 Debate contnues, however, as new ar servce entrants seek access to arport servces. 8 See Short, C. et al. (2003). 9 See Australa Daly (2004). 20 See Moran (2002). 2 See reed (2004). 22 See Productvty Commsson (2002). 23 Rather than collude to rase carrer costs, owners of prvatsed arports have sought and found proftablty through the development of arport property by explotng relatvely relaxed federal regulatons governng the use of arport land. 8
9 Ths very bref revew makes t clear that the regulaton of olgopoly servce ndustres n Australa s made more complex by the trend toward the subdvson of each ndustry nto more and less compettve components. In ths paper, however, our purpose s to take a broad brush to the estmaton of economy wde effects of servce olgopoly behavour. We therefore work at the level of 0 sectors, necessarly averagng out sectoral detal. In nterpretng the research that follows t should be borne n mnd that the task of sectoral regulators s not only made dffcult by the non-transparency of the costs we model but also because product lnes and the degree of dfferentaton between frms are not stable through tme n the way we model them. 3. An Olgopoly Model of the Australan Economy The model s a development of that used to examne pro-compettveness effects of trade lberalsaton n manufacturng by Tyers (2004, 2005). 24 The verson descrbed here dffers n fve key respects. rst, behavoural equatons have been added to represent the effects of regulatory polcy, ncludng Ramsey prce-caps; second, a government sector has been ncluded to dstngush the government s expendtures from those of the collectve household. Prevously, net revenue from border taxes was transferred to the collectve household n lump-sum. Lke the model s sngle prvate household, the government now has Cobb-Douglas preferences over goods and a constant elastcty of substtuton (CES) subaggregaton of home goods wth mports. It s not, however, treated as an optmsng agent maxmsng a utlty functon lke the representatve household. 25 A balanced budget s assumed so that government spendng changes n lne wth tax revenue. Thrd, the border tax system n the earler verson of the model has been extended to nclude a more detaled representaton of Australa s tax system wth both drect (ncome) taxes leved separately on labour and captal ncome and ndrect taxes ncludng those on consumpton, mports and exports. 26 ourth, a new database s constructed that emphasses Australa s servce ndustres. Ths database ncorporates government consumpton and the complete tax system. 27 fth and fnally, stablty problems encountered n the tradable goods sectors due to a unform structure suted to the more closed servces sectors necesstated a 24 It s a dstant descendent of the models of Harrs (984) and Gunasekera and Tyers (990). 25 One approach, not adopted n ths paper, would be to ncorporate the government sector so that ts spendng and taxaton decsons are endogenous and determned by the maxmsaton of an assumed socal welfare functon. The dffculty wth such an approach s that t does not capture the poltcal economy of government polcy. Thanks are due to Chrs Jones for useful dscussons on ths topc. 26 Income taxes are approxmated by flat rates deduced as the quotent of revenue and the tax base n each case. 27 These frst four advances are due to Rees (2004). 9
10 restructurng of the model s treatment of foregn goods. These are now consdered homogeneous n each broad sector but dfferentated from correspondng home products, whch themselves are dfferentated by varety. 28 Model structure The scope of the model s defned n Table. It dvdes the Australan economy nto ten sectors, of whch seven offer servces, and four prmary factors. The ten sectors are chosen to reflect the domnance of servces n domestc demand and the mportance of regulaton to mperfectly compettve servces sectors. rms n all ten sectors are olgopolstc n ther product prcng behavour wth the degree of prce-settng colluson between frms represented by conjectural varatons parameters. The magntudes of these parameters are consdered to represent the flexblty allowed the frms prcng behavour by the survellance of regulatory agences. Each frm bears fxed captal and sklled labour costs, enablng the representaton of unrealsed economes of scale. Home products n each sector are dfferentated by varety 29 and output s Cobb-Douglas n varable factors and ntermedate nputs. Intermedate nput demands are CES subaggregates of home and mported products. Despte ther olgopoly power n product markets, frms have no olgopsony power n the markets for prmary factors or ntermedate nputs. The sophstcaton wth whch home product markets are represented notwthstandng, the modellng of a sngle economy necesstates crudeness n the representaton of foregn frms. Thus, mports are seen as homogeneous, dfferentated from home products as a group, so that mport varetal dversty never changes. 30 In the long run, physcal captal s homogeneous and fully moble between sectors and nternatonally, whle the domestc endowments of other factors are fxed. A short run closure s also constructed, wheren captal use n each ndustry s fxed and rates of return on captal can vary between sectors. In ths verson, the closure can be adjusted correspondngly, so that the real wage of unsklled labour s fxed and unsklled employment s endogenous. The quantty of domestcally-owned captal s fxed both n the short and long runs, so that 28 The earler verson requred very large elastctes of substtuton between varetes, leadng to unrealstc behavour n response to changes n border tarffs. Moreover, n a sngle economy model there s no satsfactory way to endogense the number of foregn product varetes. 29 Product dfferentaton s assumed to be of the Spence-Dxt-Stgltz type. Ths means that each ndvdual derves utlty from consumng a number of varetes of a gven product. 30 Snce all home varetes are exported there s no movement on the extensve margn of the type that s evdent n the models of non-homogeneous export sectors by Meltz(2003) and Balstrer et al. (2007). We see ths as acceptable n ths study because our focus s on largely non-traded servces. 0
11 changes n the total captal stock affect the foregn ownershp share and hence the level of ncome repatrated abroad. The economc profts or losses earned by frms are dependent on the closure, under whch ether the number of domestc frms (varetes) can be fxed whle profts are endogenous, or flexble whle economc profts are fxed. The economy modelled s almost small, mplyng that t has no power to nfluence border prces of ts mports but ts exports are dfferentated from competng products abroad and hence face fnte-elastc demand. 3 The effectve numerare s the mport product bundle, snce mport prces are exogenous n all experments. Its current account defct (of about a tenth of ts ntal GDP) s fxed n terms of foregn prces n all experments. 32 or presentatonal purposes, prces and values can be dvded through by the consumer prce or the GDP prce ndex so that the ntal consumpton or producton bundle becomes the numerare. The consumer prce ndex s constructed as a composte Cobb-Douglas-CES ndex of home product and after-tarff mport prces, derved from the sngle household s expendture functon and measured after consumpton taxes are appled. Ths formulaton of the CPI ads n the analyss of welfare mpacts. Because collectve utlty s also defned as a Cobb-Douglas combnaton of the volumes of consumpton by product aggregate, proportonal changes n overall economc welfare correspond wth those n real GNP. 33 rms n any sector supply dfferentated products and nteract on prce. Cobb- Douglas producton drves varable costs so that average varable costs are constant f factor and ntermedate product prces do not change. Consequently, whle ever factor and ntermedate product prces are constant, average total cost declnes wth output. The magntudes of recurrent fxed costs are calbrated from data on ndustry proftablty, gross 3 Ths follows the practce n natonal modellng snce the frst sgnfcant economy-wde model by Dxon et al. (982) and the frst publshed economy-wde olgopoly model by Harrs (984). 32 Ths mples that the acquston of Australan assets by foregners remans constant rrespectve of shocks mposed on the model and ther consequences. 33 When the utlty functon s Cobb-Douglas n consumpton volumes, the expendture functon s Cobb-Douglas C n prces. If the consumer prce level, P, s defned as a Cobb-Douglas ndex of prces, the equvalent varaton n ncome can be expressed n terms of the proportonal change n ths ndex. Thus, followng any shock, the ncome equvalent of the resultng changes to ncome and prces s: C C C ΔP Δ W = Y Y0 + EV ( P0, P, Y) = Y Y0 Y, P C whch can be expressed n proportonal change form as: C ΔP Y C Y0 C ΔW P ΔY ΔP =. C W Y0 Y0 P Ths s, approxmately, the proportonal change n real GNP.
12 value of output and value added. 34 rms charge a mark-up over average varable cost so that t s at least possble for them to cover ther average fxed cost n a zero-pure-proft monopolstc competton equlbrum. They choose ths mark-up strategcally, however, so that ther capacty to push ther prce beyond ther average varable costs wthout beng undercut by exstng compettors then determnes the level of any pure profts and the potental for entry by new frms. As ntuton would suggest, under free entry pure profts are eroded and the mark-up just covers average total costs. Each frm n ndustry s regarded as producng a unque varety of ts product and t faces a downward-slopng demand curve wth elastcty ε (< 0). The optmal mark-up s then: () where p m = =, v + ε p s the frm s product prce, ν s ts average varable cost and ε s the elastcty of demand t faces. rms choose ther optmal prce by takng account of the prce-settng behavour of other frms. A conjectural varatons parameter n ndustry s then defned as the nfluence of any ndvdual frm k, on the prce of frm j: (2) μ p j =. pk These parameters are consdered to ndcate the power of prce survellance by such nsttutons as the ACCC. The Nash equlbrum case s a non-collusve dfferentated Bertrand olgopoly n whch each frm chooses ts prce, takng the prces of all other frms as gven. In ths case the conjectural varatons parameter (2) s zero. When frms behave as a perfect cartel, t has the value unty. Ths parameter enters the analyss through the varetal demand elastcty, whch s formulated n Appendx 2. To study the effects of prce-caps a regulated Ramsey mark-up, R m s formulated as: (3) m afc + ν =. R ν rms are permtted to choose compromse mark-ups by alterng the parameter ϕ n the followng: ( ) ( ) C R (4) m = ϕ m + 2 ϕ m. 34 In the startng equlbrum t s assumed that each ndustry has pure profts equal to one percent of gross earnngs. Consstent secondary data are not readly avalable to determne the share of pure profts n captal returns n all ndustres. 2
13 C C R Thus, when ϕ =, m = m, and when ϕ = 2, m = m. Crtcal to the mplcatons of mperfect competton n the model s that the product of each ndustry has exposure to four dfferent markets. It can be consumed by prvate households or by government, used as an ntermedate nput n another ndustry or t can be exported. The elastcty of demand faced by frms n ndustry, ε, s therefore dependent on the elastctes of demand n each of these four markets, as well as the shares of the home product n each. More precsely, the four sources of demand for home produced products are fnal demand (), ntermedate demand (I), export demand (X) and government demand (G). or sector, the elastcty sought s a composte of the elastctes of all four sources of demand. (5) ε I I X X G G = s ε + s ε + s ε + s ε, where j s denotes the volume share of the home product n market for each source of demand j. These share parameters are fully endogenous n the model. Because the dfferent sources of demand are dfferently elastc, wth export demand most elastc and ntermedate demand least, any shock that reapportons demand between them necessarly changes the compettve behavour of the frms. 35 Almost all concevable shocks do ths to some degree. Thus, the strategc behavour of frms, and hence the economc cost of servce olgopoles, s affected by conjectural varatons parameters as they represent collusve capacty on the one hand and regulatory prce survellance on the other, and by the composton of demand as t nfluences the elastctes of demand faced by each frm. Of course, the capacty frms have to reduce ther prces also depends on ther productvty performance, whch we do not examne n ths paper, and on ther numbers, hence the sectoral fxed cost burden. The database and ts representaton of broad economc structure The model database s constructed from the GTAP Verson 5 global database for 997 (Dmaranan and McDougall 2002). 36 It combnes detaled blateral trade, transport and protecton data characterzng economc lnkages among regons, together wth ndvdual country natonal accounts, government accounts, balance of payments data and nput-output 35 Export demand s found to be more elastc because of the larger number of substtutable product varetes avalable abroad whle ntermedate demand s relatvely nelastc because of frms reluctance to alter arrangements for ntermedate nput supply whch may depend on locaton or just n tme relatonshps. These ssues are addressed by Harrs and Cox (983). 36 Documentaton on the GTAP 5 Data Package may be vewed at: < 3
14 tables whch enable the quantfcaton of nter-sectoral flows wthn regons. rom the database key elements of our representaton of the Australan economy emerge. rom Table 2, t s evdent that the prvatsed servces, electrcty, water, gas, telecommuncatons, fnance and transport, supply about a ffth of the economy s GDP, yet ther partcpaton n nternatonal trade s tny compared wth agrculture, manufacturng and mnng. Moreover, the prvatsed servces are shown n Table 3 to be more ntensve n skll and physcal captal than are the tradable sectors so that ther comparatve performance has partcular mplcatons for the sklled wage premum and total captal use. The flows represented n the database do not reveal detals of ndustral structure. In partcular, addtonal nformaton s requred on frm numbers, pure profts, fxed costs and mnmum effcent scale for each sector. Whle some detals are avalable on these varables for some ndustres, there s no readly avalable source that s consstent and comparable across sectors. Wth the support of the few ndustry studes already mentoned and the Mornngstar nancal Analyss Database, 37 these varables are calbrated n the followng manner. rst, pure profts are requred as a share of total captal ncome (operatng surplus) n each ndustry. Ths s needed to fnalse the flow database but also to calbrate ndustry compettve structure. or ths we have resorted to data on the proftablty of lsted frms from the Mornngstar Database. 38 Addtonal detal as to our approach s offered n Appendx 3. Second, rough estmates of strategcally nteractng frm numbers n each ndustry and ther correspondng conjectural varatons parameters are requred. It s not suffcent smply to record the number of establshments n each ndustry, however. Unless ndustres are subdvded fnely, consderable dversty of frm sze and product s emboded n each. Indeed, wthn a partcular ndustry classfcaton, many frms supply ntermedate nputs to other frms n the same classfcaton. Prces of the products that emerge from a partcular ndustry are very lkely determned by a small proporton of the frms wthn t. Agan, we resort to the Mornngstar database for measures of ndustry concentraton. rom ths we assgn the crude ndex of frm numbers ndcated n Table 4 and we also post the correspondng conjectural varatons parameters shown n the same table. Agan, addtonal detal as to our approach s provded n Appendx The database s formally the Aspect nancal Analyss Database. It s suppled by Aspect-Huntley, and the copyrght s held by Huntleys' Investment Informaton Pty Ltd (HII) (a wholly owned subsdary of Mornngstar, Inc). 38 After tax profts rates are compared wth the prme borrowng rate n the perod to obtan measures of pure profts. rm statstcs were drawn from and the data on ndustral borrowng rates was from 4
15 Thrd, to complete the formulaton of ndustry demand elastctes, elastctes of substtuton between home product varetes and between generc home and foregn products are requred for each sector. These are drawn from the estmaton lterature. 39 Intal ndustry demand elastctes are then calculated for each source of demand (fnal, ntermedate, government and export), va the equatons n the appendces, and the results are also lsted n Table 4. Intal shares of the demand facng each ndustry are then drawn from the database to enable the calculaton of weghted average demand elastctes for each ndustry. Mark-up ratos are then deduced from these, fxng average varable cost n each sector, va equaton (). The ntal equlbrum ndustry shares, average elastctes and mark-up ratos for each sector are gven n Table 5. Note that the elastctes appear large n magntude at frst glance. Ths s because they do not represent the slopes of ndustry demand curves for generc goods. Rather, they are the elastctes faced by supplers of ndvdual varetes and are made larger by nter-varetal substtuton. Ths completes the demand sde calbraton. It enables us to turn to the calbraton of the supply sde, where we begn by usng the mark-up ratos to deduce the ntal level of average varable cost n each sector. Next, we turn to pure profts. The proporton these make up of total turnover s deducted from the mark-up to arrve at fxed cost shares of total turnover. 40 Total recurrent fxed cost n each sector then follows. The results of ths calbraton are summarsed n the frst three columns of Table 6. It s now possble to obtan a sense of the scale of producton. 4 Under our assumpton of Cobb-Douglas technology n varable factor use, combned wth recurrent fxed costs, f ndustres could expand ndefntely wthout changng unt factor rewards (the partal equlbrum assumpton that s relaxed here), average fxed cost would approach average varable cost asymptotcally from above. ollowng Harrs and Cox (983) we choose an arbtrary mnmum effcent scale (MES) product volume at the pont where average fxed cost would declne to a twenteth of average varable cost. The mpled scale parameters are dsplayed n the fnal column of Table 6. They confrm expectatons that fxed costs are most promnent n electrcty, gas, water, telecommuncatons and transport servces, due to fxed physcal nfrastructure and 39 Summares of ths lterature are offered by Dmaranan and McDougall (2002) and at purdue.edu/databases/.. 40 xed costs take the form of both physcal and human captal costs usng the rule of thumb (based on estmates by Harrs and Cox, 983) that physcal captal has a fxed cost share of 5/6. 4 The actual calbraton process s more complex than ths because the elastctes of ntermedate demand depend on ntermedate cost shares, whch depend on the varable cost share. It s therefore necessary to calbrate teratvely for consstency of elastctes and shares. 5
16 network mantenance costs. The results also suggest, plausbly, that the sectors closest to ther mnmum effcent scale are agrculture, mnng, fnance and other servces. 4. Sectoral Interactons wth Olgopoly To explore the nterdependence of the prvatsed servce sectors and the potental mpacts of ther non-compettve behavour on the economy as a whole we begn by consderng the effects of complete explotaton of market power n all sectors. In partcular, on the presumpton that olgopoly frms fal to collude and form cartels (or consoldate nto monopoles) manly because of government prce survellance and (the threat of) ant-trust actons, 42 we magne what the Australan economy would have looked lke had these government actvtes never occurred. A long run closure s selected n whch physcal captal s nternatonally and ntersectorally moble and labour markets clear at flexble wages. The entre economy s frst allowed to cartelse, by rasng all conjectural varatons parameters to unty. 43 Then, ndvdual sectors are cartelsed one by one n a bd to dentfy non-lneartes that mght mply the necessty of economy-wde analyss. The results of ths exercse are summarsed n Table Clearly the economy would have been substantally smaller f all sectors had been cartelsed. Real GDP would have been smaller by a thrd and real wages smaller by more than half. In general, cartel rents mply hgher home product prces and hence an apprecated real exchange rate and reduced trade wth the rest of the world. The agrcultural and mnng sectors are exceptons n that, there, cartelsaton reduces home producton wth less mpact on product prces due to foregn competton. Moble factors are shed, however, reducng ther rewards and ths tends to reduce servces costs and hence to deprecate the real exchange rate. Manufacturng s specal because, as Table 8 shows, t uses and supples manly ntermedate nputs. Snce elastctes of substtuton between ntermedate nputs are low, home cartelsaton sees servce ndustry costs rse due to lmted substtuton to competng mports. If the cartelsaton had only occurred n the recently prvatsed servces, electrcty, 42 Ths gnores the roles of contestablty and the free rder problem n the mantenance of cartels. 43 The number of frms s held constant n ths closure but t s, n any case, mmateral so far as prcng s concerned when ndustres are cartelsed. Consoldaton to a monopoly would reduce fxed costs and thereby ncrease monopoly profts, however, a development not explored here. 44 It stretches credblty to magne that sectors wth large numbers of small frms, such as agrculture, could overcome free rder and communcaton costs n ths way. Takng agrculture as an example, however, the Australan sector s rfe wth organsed boards desgned to extract rents for farmers (Seper, 982). Even the other servces sector s full of state and local government regulatons drected at reducng competton, such as zonng rules for such specalst retal outlets as pharmaces and news agents. All ths sad, our purpose here s not to suggest that full cartelsaton s possble or lkely but merely to use ths carcature of olgopolstc behavour to explore economy-wde effects. 6
17 water, gas, telecommuncatons, fnance, transport and other servces, GDP would have been smaller by just over a tenth and real wages by almost a thrd. The central block n the table ndcates how cartelsaton by each ndvdual sector affects overall economc performance. It s clear that sectors lke manufacturng and other servces, whch have large ntal shares of GDP, also have the largest mpacts on the economy followng cartelsaton. 45 Cartelsaton creates rents that accrue to captal owners. Yet t reduces output and therefore varable factor and nput demand. Unt factor rewards to moble factors therefore fall n all cases. 46 The only cartelsaton that reduces the average gross rate of return on captal s that of the manufacturng sector. Ths s, agan, because manufactured nputs are extensvely used n other sectors, as ndcated n Table 8, the performance of whch are retarded by hgh manufactured product prces. The bottom rows of Table 7 allow an assessment of the model s lnearty n proportonal changes followng cartelsaton shocks. Where collectve cartelsaton yelds results dfferent from the sum of the proportonal changes due to sectoral cartelsaton, the case for economy-wde analyss s made clearer. Whle ths non-lnearty s evdent when the cartelsng sectors nclude the tradable ones and the government-ntensve other servces, t s not strong when only the prvatsed servce sectors are ncluded. Opposng sectoral nteractons mght be expected to cancel when cartelsaton occurs n all sectors and so t follows that the gross effects are smaller n ths case than when sectoral cartelsatons are summed. When the traded sectors are ncluded, however, the elastc supply of competng products from abroad appears to further damp the collectve, relatve to the sectoral, mpacts of cartelsaton. Even though non-lnearty s not always strong, the case for economy-wde analyss s further supported by the substantal mpacts on GDP and real wages of the ndvdual sectoral cartelsatons shown n the table. The extent to whch sectors nteract s further clarfed from Table 9, whch shows the effects of cartelsaton by the column sectors on gross rates of return n row sectors. The frst row reproduces the sxth column of Table 7. The frst column gves the effects on all sectors of cartelsaton throughout the economy. rom ths t s evdent that nteracton between sectors causes gross returns n some to fall n spte of cartelsaton. Manufacturng s one of these, for the reasons ndcated above. Electrcty, water, fnance and transport all yeld net 45 The water sector also has a comparatvely large mpact. Ths s because the frms nvolved are few and manly state-owned and because they do not presently explot ther market power. The water prce would ncrease by 600 per cent f they dd! 46 The possblty that rents mght be shared wth sectoral workforces s real n Australa, though t s not modelled here. See Dowrck (993) and Mumford and Dowrck (994). 7
18 rses n rates of return n spte of hgher nput costs due to correspondng changes n other sectors. The second column shows that the effects of market power n the prvatsed servces s large at the natonal level and as t affects returns n the tradable sectors. Scannng the other columns, the non-dagonal elements ndcate the extent of sectoral nteracton. Ths s largest for manufacturng, for reasons dscussed above, but t s also sgnfcant for servces lke electrcty, telecommuncatons, fnance and transport. 5. Sectoral Interactons under Prce Cap Regulaton Here the ntal equlbrum, wth the pure profts generated n all sectors as ndcated n Table 6, s subjected to tght prce cap regulaton, whereby product prces are forced to equal average costs. No such regulaton s represented n the calbrated ntal equlbrum, even though t was probably nfluental n 997. Instead, the conjectural varatons parameters are set to ndcate consderable constrants to colluson n the olgopoles of the tme, due to regulatory polces. In our experment, tght prce caps are frst mposed, va equaton (4), smultaneously on all sectors. Because sx of the 0 sectors do not earn pure profts ths mples that mark-ups are regulated to decrease n only four and to ncrease n the remanng sx an unrealstc prospect ncluded only for completeness. The next experment mposes tght prce caps only on the four ndustres earnng pure profts (agrculture and food, mnng and energy, telecommuncatons and fnance). Then tght prce caps are mposed on the proftable prvatsed servces only. Ths s followed by prce caps on each of the proftable sectors ndvdually. The effects on overall economc performance are gven n Table 0. The very frst row of the table shows the effects of average cost prcng n all ndustres and, snce sx ntally earn less than market rates of return, the results are net ncreases n mark-ups and prces, and declnes n real wages. The more realstc mposton of tght prce caps on the four proftable sectors, however, shows that consderable addtonal economc actvty mght be obtaned n ths way. GDP and real wages are consderably boosted, at the expense of gross returns on assets. Interestngly, although the two proftable servce ndustres are not sgnfcantly larger contrbutors to GDP than ether agrculture and food on the one hand or mnng and metals on the other, ther prce caps are the more sgnfcant because ther ntal proftablty s hgher (Table 6). The results for ndvdual ndustres bear ths out. Indeed, t s the fnancal sector where reduced pure profts and hence lower product prces would have the most natonal 8
19 mpact. As n the cartelsaton experments of the prevous secton there s agan a contrast between the real exchange rate effects of prce caps n the tradable and the servces sectors. In the tradable sectors reduced home product prces cause ncreased demand and expanded output and hence ncreased wages and resource rents. The servces sectors face hgher wage costs and hence rase ther prces. But they also redrect ther demand to meetng the ntermedate requrements of the expanded tradable sectors and so the elastctes they face fall and ther mark-ups rse. Ths further contrbutes to hgher servce prces and hence to net ncreases n the real exchange rate. The prce caps on prevously proftable servces, on the other hand, merely reduce non-traded prces and the results are straght-forward Balassa- Samuelson real deprecatons. As n the case of cartelsaton, the non-lnearty of economy-wde responses to sectoral prce caps s tested n the last two rows of the table. By contrast wth the case of cartelsaton, prce caps on the four proftable sectors exhbt neglgble non-lnearty n proportonal changes. These do not nclude shocks to the large and dosyncratc manufacturng and other servces sectors, and the magntudes of the shocks are smaller than those due to cartelsaton. So t would seem that the non-lneartes are assocated wth the scale of shocks to prces and the partcular behavour of manufacturng and other servces. Ths offers weak support for economy-wde analyss. The drect nter-sectoral effects summarsed n Table offer further weak support n the sense that prce caps n the servces sectors have measurable economywde effects and that, especally n the case of fnance, nteractons are strong wth the tradable goods sectors. 6. Olgopoly and External Shocks: the Chna Boom Shocks to Australa s external terms of trade, to nflows on ts captal account and n ts trade polcy regme all have obvous effects on ts relatvely small agrcultural and ndustral sectors. They also change the real exchange rate and hence they ndrectly affect the state of ts largely non-traded servces sector. We show n ths secton that these ndrect effects have mplcatons for compettve behavour n both the tradable and servces sectors of the economy. They occur through the reapportonment of demand for olgopolstcally suppled goods and servces toward more elastc exports or less elastc ntermedate demand, va equaton (5). Both the terms of trade and the current account balance have been affected by the recent Chna boom. The extraordnary nature of the assocated commodty prce shocks s 9
20 clear from gure. Money prces of wheat and ron ore, both major Australan exports, have rsen n the last year or so by several hundreds of per cent. And the shocks go beyond those two commodtes. Australa s overall terms of trade rose n ths perod by 50 per cent, as shown n gure 2. At the same tme, foregn acquston of Australan assets has also rsen, almost doublng the current account defct (captal account surplus) between the turn of the century and To examne the effects of these shocks on prvatsed servce performance, we subject the model to 50 per cent ncreases n the foregn prces of agrcultural products and mnng and energy products, combned wth an expanson of the current account defct by 50 per cent. Ths tme we use both a short run closure, n whch physcal captal s fxed and specfc to each sector and producton (unsklled) employment s flexble at a fxed real wage, and a long run closure n whch captal s nternatonally and ntersectorally moble and employment s fxed. The number of frms n each sector s held constant n the short run, allowng pure profts to vary. Two versons of the short run experment are carred out. In the frst, no prce caps are mposed and frms are permtted to choose ther mark-ups. 48 In the second, two new ntal equlbra are frst calculated, by mposng prce caps ether n all proftable sectors or n the proftable prvatsed servces only. These prce caps are then retaned whle the economy s subjected to the Chna boom shocks n each case. or the long run analyss the boom shock s frst mposed wth fxed numbers of frms. Then a new ntal equlbrum s calculated n whch entry and ext are allowed and pure profts reduced to zero. To ths ntal equlbrum the Chna boom shocks are appled n such a way as to retan zero pure profts but to allow entry of new frms. Taken collectvely, n both the short and long runs, these shocks are very postve for Australa. Ther prncpal short run effects are ndcated n the frst column of Table 2. Real GNP, whch serves as a preparedness to pay measure gven the formulaton we use (as dscussed n Secton 3), rses sgnfcantly, captal returns ncrease and ether real wages or employment levels rse. There are Dutch dsease elements, however (Corden and Neary 982). The natural resource based sectors expand at the expense of manufacturng, whch suffers from hgher prced factors and nputs and a real apprecaton mpars ts competton 47 It must be noted that these extraordnary shocks stem not only from the surge n the growth of Chna and other economes n transton. The US-ntated fnancal crss that began n 2007 saw a retreat to commodtes, further boostng prces and captal flght from the US. 48 Of course, ther strategc nteracton s assumed to be constraned by survellance, whch prevents the enlargement of ther conjectural varatons parameters. 20
Answer: A). There is a flatter IS curve in the high MPC economy. Original LM LM after increase in M. IS curve for low MPC economy
 4.02 Quz Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons (30/00 ponts) Please, crcle the correct answer for each of the followng 0 multple-choce questons. For each queston, only one of the answers s correct.
4.02 Quz Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons (30/00 ponts) Please, crcle the correct answer for each of the followng 0 multple-choce questons. For each queston, only one of the answers s correct.
17 Capital tax competition
 17 Captal tax competton 17.1 Introducton Governments would lke to tax a varety of transactons that ncreasngly appear to be moble across jursdctonal boundares. Ths creates one obvous problem: tax base flght.
17 Captal tax competton 17.1 Introducton Governments would lke to tax a varety of transactons that ncreasngly appear to be moble across jursdctonal boundares. Ths creates one obvous problem: tax base flght.
Addendum to: Importing Skill-Biased Technology
 Addendum to: Importng Skll-Based Technology Arel Bursten UCLA and NBER Javer Cravno UCLA August 202 Jonathan Vogel Columba and NBER Abstract Ths Addendum derves the results dscussed n secton 3.3 of our
Addendum to: Importng Skll-Based Technology Arel Bursten UCLA and NBER Javer Cravno UCLA August 202 Jonathan Vogel Columba and NBER Abstract Ths Addendum derves the results dscussed n secton 3.3 of our
Trade Adjustment and Productivity in Large Crises. Online Appendix May 2013. Appendix A: Derivation of Equations for Productivity
 Trade Adjustment Productvty n Large Crses Gta Gopnath Department of Economcs Harvard Unversty NBER Brent Neman Booth School of Busness Unversty of Chcago NBER Onlne Appendx May 2013 Appendx A: Dervaton
Trade Adjustment Productvty n Large Crses Gta Gopnath Department of Economcs Harvard Unversty NBER Brent Neman Booth School of Busness Unversty of Chcago NBER Onlne Appendx May 2013 Appendx A: Dervaton
Analysis of Premium Liabilities for Australian Lines of Business
 Summary of Analyss of Premum Labltes for Australan Lnes of Busness Emly Tao Honours Research Paper, The Unversty of Melbourne Emly Tao Acknowledgements I am grateful to the Australan Prudental Regulaton
Summary of Analyss of Premum Labltes for Australan Lnes of Busness Emly Tao Honours Research Paper, The Unversty of Melbourne Emly Tao Acknowledgements I am grateful to the Australan Prudental Regulaton
An Alternative Way to Measure Private Equity Performance
 An Alternatve Way to Measure Prvate Equty Performance Peter Todd Parlux Investment Technology LLC Summary Internal Rate of Return (IRR) s probably the most common way to measure the performance of prvate
An Alternatve Way to Measure Prvate Equty Performance Peter Todd Parlux Investment Technology LLC Summary Internal Rate of Return (IRR) s probably the most common way to measure the performance of prvate
Institute of Informatics, Faculty of Business and Management, Brno University of Technology,Czech Republic
 Lagrange Multplers as Quanttatve Indcators n Economcs Ivan Mezník Insttute of Informatcs, Faculty of Busness and Management, Brno Unversty of TechnologCzech Republc Abstract The quanttatve role of Lagrange
Lagrange Multplers as Quanttatve Indcators n Economcs Ivan Mezník Insttute of Informatcs, Faculty of Busness and Management, Brno Unversty of TechnologCzech Republc Abstract The quanttatve role of Lagrange
Structural Estimation of Variety Gains from Trade Integration in a Heterogeneous Firms Framework
 Journal of Economcs and Econometrcs Vol. 55, No.2, 202 pp. 78-93 SSN 2032-9652 E-SSN 2032-9660 Structural Estmaton of Varety Gans from Trade ntegraton n a Heterogeneous Frms Framework VCTOR RVAS ABSTRACT
Journal of Economcs and Econometrcs Vol. 55, No.2, 202 pp. 78-93 SSN 2032-9652 E-SSN 2032-9660 Structural Estmaton of Varety Gans from Trade ntegraton n a Heterogeneous Frms Framework VCTOR RVAS ABSTRACT
Intra-year Cash Flow Patterns: A Simple Solution for an Unnecessary Appraisal Error
 Intra-year Cash Flow Patterns: A Smple Soluton for an Unnecessary Apprasal Error By C. Donald Wggns (Professor of Accountng and Fnance, the Unversty of North Florda), B. Perry Woodsde (Assocate Professor
Intra-year Cash Flow Patterns: A Smple Soluton for an Unnecessary Apprasal Error By C. Donald Wggns (Professor of Accountng and Fnance, the Unversty of North Florda), B. Perry Woodsde (Assocate Professor
Game theory in Oligopoly
 Game theory n Olgopoly Prof. Marx Boopath, Nkolaj Sujen. Abstract The game theory technques are used to fnd the equlbrum of a market. Game theory refers to the ways n whch strategc nteractons among economc
Game theory n Olgopoly Prof. Marx Boopath, Nkolaj Sujen. Abstract The game theory technques are used to fnd the equlbrum of a market. Game theory refers to the ways n whch strategc nteractons among economc
Chapter 7: Answers to Questions and Problems
 19. Based on the nformaton contaned n Table 7-3 of the text, the food and apparel ndustres are most compettve and therefore probably represent the best match for the expertse of these managers. Chapter
19. Based on the nformaton contaned n Table 7-3 of the text, the food and apparel ndustres are most compettve and therefore probably represent the best match for the expertse of these managers. Chapter
Problem Set 3. a) We are asked how people will react, if the interest rate i on bonds is negative.
 Queston roblem Set 3 a) We are asked how people wll react, f the nterest rate on bonds s negatve. When
Queston roblem Set 3 a) We are asked how people wll react, f the nterest rate on bonds s negatve. When
Can Auto Liability Insurance Purchases Signal Risk Attitude?
 Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 2011, Vol. 10, No. 2, 159-164 Can Auto Lablty Insurance Purchases Sgnal Rsk Atttude? Chu-Shu L Department of Internatonal Busness, Asa Unversty, Tawan Sheng-Chang
Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 2011, Vol. 10, No. 2, 159-164 Can Auto Lablty Insurance Purchases Sgnal Rsk Atttude? Chu-Shu L Department of Internatonal Busness, Asa Unversty, Tawan Sheng-Chang
benefit is 2, paid if the policyholder dies within the year, and probability of death within the year is ).
 REVIEW OF RISK MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS AND INSURANCE Loss and nsurance: When someone s subject to the rsk of ncurrng a fnancal loss, the loss s generally modeled usng a random varable or
REVIEW OF RISK MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS AND INSURANCE Loss and nsurance: When someone s subject to the rsk of ncurrng a fnancal loss, the loss s generally modeled usng a random varable or
FIGHTING INFORMALITY IN SEGMENTED LABOR MARKETS A general equilibrium analysis applied to Uruguay *
 Vol. 48, No. 1 (May, 2011), 1-37 FIGHTING INFORMALITY IN SEGMENTED LABOR MARKETS A general equlbrum analyss appled to Uruguay * Carmen Estrades ** María Inés Terra ** As n other Latn Amercan countres,
Vol. 48, No. 1 (May, 2011), 1-37 FIGHTING INFORMALITY IN SEGMENTED LABOR MARKETS A general equlbrum analyss appled to Uruguay * Carmen Estrades ** María Inés Terra ** As n other Latn Amercan countres,
1.1 The University may award Higher Doctorate degrees as specified from time-to-time in UPR AS11 1.
 HIGHER DOCTORATE DEGREES SUMMARY OF PRINCIPAL CHANGES General changes None Secton 3.2 Refer to text (Amendments to verson 03.0, UPR AS02 are shown n talcs.) 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 The Unversty may award Hgher
HIGHER DOCTORATE DEGREES SUMMARY OF PRINCIPAL CHANGES General changes None Secton 3.2 Refer to text (Amendments to verson 03.0, UPR AS02 are shown n talcs.) 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 The Unversty may award Hgher
Medium and long term. Equilibrium models approach
 Medum and long term electrcty prces forecastng Equlbrum models approach J. Vllar, A. Campos, C. íaz, Insttuto de Investgacón Tecnológca, Escuela Técnca Superor de Ingenería-ICAI Unversdad ontfca Comllas
Medum and long term electrcty prces forecastng Equlbrum models approach J. Vllar, A. Campos, C. íaz, Insttuto de Investgacón Tecnológca, Escuela Técnca Superor de Ingenería-ICAI Unversdad ontfca Comllas
Module 2 LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Lesson 3 Lossless Compresson: Huffman Codng Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:. Defne and measure source entropy..
Module LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Lesson 3 Lossless Compresson: Huffman Codng Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:. Defne and measure source entropy..
Trading system competition and market-maker competition
 Tradng system competton and market-maker competton Mark Wahrenburg. Introducton The recent success of some alternatve tradng systems (ATSs) has had a strong mpact on the tradtonal stock exchange ndustry
Tradng system competton and market-maker competton Mark Wahrenburg. Introducton The recent success of some alternatve tradng systems (ATSs) has had a strong mpact on the tradtonal stock exchange ndustry
The Current Employment Statistics (CES) survey,
 Busness Brths and Deaths Impact of busness brths and deaths n the payroll survey The CES probablty-based sample redesgn accounts for most busness brth employment through the mputaton of busness deaths,
Busness Brths and Deaths Impact of busness brths and deaths n the payroll survey The CES probablty-based sample redesgn accounts for most busness brth employment through the mputaton of busness deaths,
Kiel Institute for World Economics Duesternbrooker Weg 120 24105 Kiel (Germany) Kiel Working Paper No. 1120
 Kel Insttute for World Economcs Duesternbrooker Weg 45 Kel (Germany) Kel Workng Paper No. Path Dependences n enture Captal Markets by Andrea Schertler July The responsblty for the contents of the workng
Kel Insttute for World Economcs Duesternbrooker Weg 45 Kel (Germany) Kel Workng Paper No. Path Dependences n enture Captal Markets by Andrea Schertler July The responsblty for the contents of the workng
Staff Paper. Farm Savings Accounts: Examining Income Variability, Eligibility, and Benefits. Brent Gloy, Eddy LaDue, and Charles Cuykendall
 SP 2005-02 August 2005 Staff Paper Department of Appled Economcs and Management Cornell Unversty, Ithaca, New York 14853-7801 USA Farm Savngs Accounts: Examnng Income Varablty, Elgblty, and Benefts Brent
SP 2005-02 August 2005 Staff Paper Department of Appled Economcs and Management Cornell Unversty, Ithaca, New York 14853-7801 USA Farm Savngs Accounts: Examnng Income Varablty, Elgblty, and Benefts Brent
Regulation, Market Structure and Service Trade Liberalization
 2006s-18 Regulaton, Market Structure and Servce Trade Lberalzaton Dense Eby Konan, Ar Van Assche Sére Scentfque Scentfc Seres Montréal Septembre 2006 2006 Dense Eby Konan, Ar Van Assche. Tous drots réservés.
2006s-18 Regulaton, Market Structure and Servce Trade Lberalzaton Dense Eby Konan, Ar Van Assche Sére Scentfque Scentfc Seres Montréal Septembre 2006 2006 Dense Eby Konan, Ar Van Assche. Tous drots réservés.
HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA*
 HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA* Luísa Farnha** 1. INTRODUCTION The rapd growth n Portuguese households ndebtedness n the past few years ncreased the concerns that debt
HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA* Luísa Farnha** 1. INTRODUCTION The rapd growth n Portuguese households ndebtedness n the past few years ncreased the concerns that debt
Robert Wilson for their comments on the a predecessor version of this paper.
 Procurng Unversal Telephone ervce Paul Mlgrom 1 tanford Unversty, August, 1997 Reprnted from 1997 Industry Economcs Conference Proceedngs, AGP Canberra Introducton One of the hallmarks of modern socety
Procurng Unversal Telephone ervce Paul Mlgrom 1 tanford Unversty, August, 1997 Reprnted from 1997 Industry Economcs Conference Proceedngs, AGP Canberra Introducton One of the hallmarks of modern socety
PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIGIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION
 PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION Danny Cohen-Zada Department of Economcs, Ben-uron Unversty, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel Wllam Sander Department of Economcs, DePaul
PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION Danny Cohen-Zada Department of Economcs, Ben-uron Unversty, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel Wllam Sander Department of Economcs, DePaul
World Economic Vulnerability Monitor (WEVUM) Trade shock analysis
 World Economc Vulnerablty Montor (WEVUM) Trade shock analyss Measurng the mpact of the global shocks on trade balances va prce and demand effects Alex Izureta and Rob Vos UN DESA 1. Non-techncal descrpton
World Economc Vulnerablty Montor (WEVUM) Trade shock analyss Measurng the mpact of the global shocks on trade balances va prce and demand effects Alex Izureta and Rob Vos UN DESA 1. Non-techncal descrpton
On the Optimal Control of a Cascade of Hydro-Electric Power Stations
 On the Optmal Control of a Cascade of Hydro-Electrc Power Statons M.C.M. Guedes a, A.F. Rbero a, G.V. Smrnov b and S. Vlela c a Department of Mathematcs, School of Scences, Unversty of Porto, Portugal;
On the Optmal Control of a Cascade of Hydro-Electrc Power Statons M.C.M. Guedes a, A.F. Rbero a, G.V. Smrnov b and S. Vlela c a Department of Mathematcs, School of Scences, Unversty of Porto, Portugal;
STAMP DUTY ON SHARES AND ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES
 STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond Mke Hawkns Alexander Klemm THE INSTITUTE FOR FISCAL STUIES WP04/11 STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond (IFS and Unversty
STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond Mke Hawkns Alexander Klemm THE INSTITUTE FOR FISCAL STUIES WP04/11 STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond (IFS and Unversty
The Development of Web Log Mining Based on Improve-K-Means Clustering Analysis
 The Development of Web Log Mnng Based on Improve-K-Means Clusterng Analyss TngZhong Wang * College of Informaton Technology, Luoyang Normal Unversty, Luoyang, 471022, Chna wangtngzhong2@sna.cn Abstract.
The Development of Web Log Mnng Based on Improve-K-Means Clusterng Analyss TngZhong Wang * College of Informaton Technology, Luoyang Normal Unversty, Luoyang, 471022, Chna wangtngzhong2@sna.cn Abstract.
Oligopoly Theory Made Simple
 Olgopoly Theory Made Smple Huw Dxon Chapter 6, Surfng Economcs, pp 5-60. Olgopoly made smple Chapter 6. Olgopoly Theory Made Smple 6. Introducton. Olgopoly theory les at the heart of ndustral organsaton
Olgopoly Theory Made Smple Huw Dxon Chapter 6, Surfng Economcs, pp 5-60. Olgopoly made smple Chapter 6. Olgopoly Theory Made Smple 6. Introducton. Olgopoly theory les at the heart of ndustral organsaton
Overview of monitoring and evaluation
 540 Toolkt to Combat Traffckng n Persons Tool 10.1 Overvew of montorng and evaluaton Overvew Ths tool brefly descrbes both montorng and evaluaton, and the dstncton between the two. What s montorng? Montorng
540 Toolkt to Combat Traffckng n Persons Tool 10.1 Overvew of montorng and evaluaton Overvew Ths tool brefly descrbes both montorng and evaluaton, and the dstncton between the two. What s montorng? Montorng
APPLICATION OF PROBE DATA COLLECTED VIA INFRARED BEACONS TO TRAFFIC MANEGEMENT
 APPLICATION OF PROBE DATA COLLECTED VIA INFRARED BEACONS TO TRAFFIC MANEGEMENT Toshhko Oda (1), Kochro Iwaoka (2) (1), (2) Infrastructure Systems Busness Unt, Panasonc System Networks Co., Ltd. Saedo-cho
APPLICATION OF PROBE DATA COLLECTED VIA INFRARED BEACONS TO TRAFFIC MANEGEMENT Toshhko Oda (1), Kochro Iwaoka (2) (1), (2) Infrastructure Systems Busness Unt, Panasonc System Networks Co., Ltd. Saedo-cho
DO LOSS FIRMS MANAGE EARNINGS AROUND SEASONED EQUITY OFFERINGS?
 DO LOSS FIRMS MANAGE EARNINGS AROUND SEASONED EQUITY OFFERINGS? Fernando Comran, Unversty of San Francsco, School of Management, 2130 Fulton Street, CA 94117, Unted States, fcomran@usfca.edu Tatana Fedyk,
DO LOSS FIRMS MANAGE EARNINGS AROUND SEASONED EQUITY OFFERINGS? Fernando Comran, Unversty of San Francsco, School of Management, 2130 Fulton Street, CA 94117, Unted States, fcomran@usfca.edu Tatana Fedyk,
Calculation of Sampling Weights
 Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Number of Levels Cumulative Annual operating Income per year construction costs costs ($) ($) ($) 1 600,000 35,000 100,000 2 2,200,000 60,000 350,000
 Problem Set 5 Solutons 1 MIT s consderng buldng a new car park near Kendall Square. o unversty funds are avalable (overhead rates are under pressure and the new faclty would have to pay for tself from
Problem Set 5 Solutons 1 MIT s consderng buldng a new car park near Kendall Square. o unversty funds are avalable (overhead rates are under pressure and the new faclty would have to pay for tself from
An Empirical Study of Search Engine Advertising Effectiveness
 An Emprcal Study of Search Engne Advertsng Effectveness Sanjog Msra, Smon School of Busness Unversty of Rochester Edeal Pnker, Smon School of Busness Unversty of Rochester Alan Rmm-Kaufman, Rmm-Kaufman
An Emprcal Study of Search Engne Advertsng Effectveness Sanjog Msra, Smon School of Busness Unversty of Rochester Edeal Pnker, Smon School of Busness Unversty of Rochester Alan Rmm-Kaufman, Rmm-Kaufman
DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT
 CelersSystems DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT PREPARED BY James E Aksel, PMP, PMI-SP, MVP For Addtonal Informaton about Earned Value Management Systems and reportng, please contact: CelersSystems,
CelersSystems DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT PREPARED BY James E Aksel, PMP, PMI-SP, MVP For Addtonal Informaton about Earned Value Management Systems and reportng, please contact: CelersSystems,
Multiple-Period Attribution: Residuals and Compounding
 Multple-Perod Attrbuton: Resduals and Compoundng Our revewer gave these authors full marks for dealng wth an ssue that performance measurers and vendors often regard as propretary nformaton. In 1994, Dens
Multple-Perod Attrbuton: Resduals and Compoundng Our revewer gave these authors full marks for dealng wth an ssue that performance measurers and vendors often regard as propretary nformaton. In 1994, Dens
Course outline. Financial Time Series Analysis. Overview. Data analysis. Predictive signal. Trading strategy
 Fnancal Tme Seres Analyss Patrck McSharry patrck@mcsharry.net www.mcsharry.net Trnty Term 2014 Mathematcal Insttute Unversty of Oxford Course outlne 1. Data analyss, probablty, correlatons, vsualsaton
Fnancal Tme Seres Analyss Patrck McSharry patrck@mcsharry.net www.mcsharry.net Trnty Term 2014 Mathematcal Insttute Unversty of Oxford Course outlne 1. Data analyss, probablty, correlatons, vsualsaton
LIFETIME INCOME OPTIONS
 LIFETIME INCOME OPTIONS May 2011 by: Marca S. Wagner, Esq. The Wagner Law Group A Professonal Corporaton 99 Summer Street, 13 th Floor Boston, MA 02110 Tel: (617) 357-5200 Fax: (617) 357-5250 www.ersa-lawyers.com
LIFETIME INCOME OPTIONS May 2011 by: Marca S. Wagner, Esq. The Wagner Law Group A Professonal Corporaton 99 Summer Street, 13 th Floor Boston, MA 02110 Tel: (617) 357-5200 Fax: (617) 357-5250 www.ersa-lawyers.com
The Effects of Tax Rate Changes on Tax Bases and the Marginal Cost of Public Funds for Canadian Provincial Governments
 The Effects of Tax Rate Changes on Tax Bases and the Margnal Cost of Publc Funds for Canadan Provncal Governments Bev Dahlby a and Ergete Ferede b a Department of Economcs, Unversty of Alberta, Edmonton,
The Effects of Tax Rate Changes on Tax Bases and the Margnal Cost of Publc Funds for Canadan Provncal Governments Bev Dahlby a and Ergete Ferede b a Department of Economcs, Unversty of Alberta, Edmonton,
Asia-Pacific Research and Training Network on Trade. Working Paper Series, No. 81, July 2010. Truong P. Truong
 Asa-Pacfc Research and Tranng Network on Trade Workng Paper Seres, No. 8, July 00 Revew of Analytcal Tools for Assessng Trade and Clmate Change Lnkages By Truong P. Truong Truong P. Truong s Honorary Professor
Asa-Pacfc Research and Tranng Network on Trade Workng Paper Seres, No. 8, July 00 Revew of Analytcal Tools for Assessng Trade and Clmate Change Lnkages By Truong P. Truong Truong P. Truong s Honorary Professor
WORKING PAPERS. The Impact of Technological Change and Lifestyles on the Energy Demand of Households
 ÖSTERREICHISCHES INSTITUT FÜR WIRTSCHAFTSFORSCHUNG WORKING PAPERS The Impact of Technologcal Change and Lfestyles on the Energy Demand of Households A Combnaton of Aggregate and Indvdual Household Analyss
ÖSTERREICHISCHES INSTITUT FÜR WIRTSCHAFTSFORSCHUNG WORKING PAPERS The Impact of Technologcal Change and Lfestyles on the Energy Demand of Households A Combnaton of Aggregate and Indvdual Household Analyss
Financial Mathemetics
 Fnancal Mathemetcs 15 Mathematcs Grade 12 Teacher Gude Fnancal Maths Seres Overvew In ths seres we am to show how Mathematcs can be used to support personal fnancal decsons. In ths seres we jon Tebogo,
Fnancal Mathemetcs 15 Mathematcs Grade 12 Teacher Gude Fnancal Maths Seres Overvew In ths seres we am to show how Mathematcs can be used to support personal fnancal decsons. In ths seres we jon Tebogo,
Depreciation of Business R&D Capital
 Deprecaton of Busness R&D Captal U.S. Bureau of Economc Analyss Abstract R&D deprecaton rates are crtcal to calculatng the rates of return to R&D nvestments and captal servce costs, whch are mportant for
Deprecaton of Busness R&D Captal U.S. Bureau of Economc Analyss Abstract R&D deprecaton rates are crtcal to calculatng the rates of return to R&D nvestments and captal servce costs, whch are mportant for
To manage leave, meeting institutional requirements and treating individual staff members fairly and consistently.
 Corporate Polces & Procedures Human Resources - Document CPP216 Leave Management Frst Produced: Current Verson: Past Revsons: Revew Cycle: Apples From: 09/09/09 26/10/12 09/09/09 3 years Immedately Authorsaton:
Corporate Polces & Procedures Human Resources - Document CPP216 Leave Management Frst Produced: Current Verson: Past Revsons: Revew Cycle: Apples From: 09/09/09 26/10/12 09/09/09 3 years Immedately Authorsaton:
Analysis of Demand for Broadcastingng servces
 Analyss of Subscrpton Demand for Pay-TV Manabu Shshkura * Norhro Kasuga ** Ako Tor *** Abstract In ths paper, we wll conduct an analyss from an emprcal perspectve concernng broadcastng demand behavor and
Analyss of Subscrpton Demand for Pay-TV Manabu Shshkura * Norhro Kasuga ** Ako Tor *** Abstract In ths paper, we wll conduct an analyss from an emprcal perspectve concernng broadcastng demand behavor and
Buy-side Analysts, Sell-side Analysts and Private Information Production Activities
 Buy-sde Analysts, Sell-sde Analysts and Prvate Informaton Producton Actvtes Glad Lvne London Busness School Regent s Park London NW1 4SA Unted Kngdom Telephone: +44 (0)0 76 5050 Fax: +44 (0)0 774 7875
Buy-sde Analysts, Sell-sde Analysts and Prvate Informaton Producton Actvtes Glad Lvne London Busness School Regent s Park London NW1 4SA Unted Kngdom Telephone: +44 (0)0 76 5050 Fax: +44 (0)0 774 7875
How Sets of Coherent Probabilities May Serve as Models for Degrees of Incoherence
 1 st Internatonal Symposum on Imprecse Probabltes and Ther Applcatons, Ghent, Belgum, 29 June 2 July 1999 How Sets of Coherent Probabltes May Serve as Models for Degrees of Incoherence Mar J. Schervsh
1 st Internatonal Symposum on Imprecse Probabltes and Ther Applcatons, Ghent, Belgum, 29 June 2 July 1999 How Sets of Coherent Probabltes May Serve as Models for Degrees of Incoherence Mar J. Schervsh
How To Trade Water Quality
 Movng Beyond Open Markets for Water Qualty Tradng: The Gans from Structured Blateral Trades Tanl Zhao Yukako Sado Rchard N. Bosvert Gregory L. Poe Cornell Unversty EAERE Preconference on Water Economcs
Movng Beyond Open Markets for Water Qualty Tradng: The Gans from Structured Blateral Trades Tanl Zhao Yukako Sado Rchard N. Bosvert Gregory L. Poe Cornell Unversty EAERE Preconference on Water Economcs
SIMULATING THE EFFECTS OF THE EUROPEAN SINGLE MARKET: A CGE ANALYSIS FOR SPAIN
 SIMULATING THE EFFECTS OF THE EUROPEAN SINGLE MARKET: A CGE ANALYSIS FOR SPAIN Oscar Bajo Antono Gómez D.T.2005/03 SIMULATING THE EFFECTS OF THE EUROPEAN SINGLE MARKET: A CGE ANALYSIS FOR SPAIN * Oscar
SIMULATING THE EFFECTS OF THE EUROPEAN SINGLE MARKET: A CGE ANALYSIS FOR SPAIN Oscar Bajo Antono Gómez D.T.2005/03 SIMULATING THE EFFECTS OF THE EUROPEAN SINGLE MARKET: A CGE ANALYSIS FOR SPAIN * Oscar
WORKING PAPER. C.D. Howe Institute. The Effects of Tax Rate Changes on Tax Bases and the Marginal Cost of Public Funds for Provincial Governments
 MARCH 211 C.D. Howe Insttute WORKING PAPER FISCAL AND TAX COMPETITIVENESS The Effects of Tax Rate Changes on Tax Bases and the Margnal Cost of Publc Funds for Provncal Governments Bev Dahlby Ergete Ferede
MARCH 211 C.D. Howe Insttute WORKING PAPER FISCAL AND TAX COMPETITIVENESS The Effects of Tax Rate Changes on Tax Bases and the Margnal Cost of Publc Funds for Provncal Governments Bev Dahlby Ergete Ferede
Kiel Institute for World Economics Duesternbrooker Weg 120 24105 Kiel (Germany) Kiel Working Paper No. 1119
 Kel Insttute for World Economcs Duesternbrooker Weg 120 24105 Kel (Germany) Kel Workng Paper No. 1119 Under What Condtons Do Venture Captal Markets Emerge? by Andrea Schertler July 2002 The responsblty
Kel Insttute for World Economcs Duesternbrooker Weg 120 24105 Kel (Germany) Kel Workng Paper No. 1119 Under What Condtons Do Venture Captal Markets Emerge? by Andrea Schertler July 2002 The responsblty
Searching and Switching: Empirical estimates of consumer behaviour in regulated markets
 Searchng and Swtchng: Emprcal estmates of consumer behavour n regulated markets Catherne Waddams Prce Centre for Competton Polcy, Unversty of East Angla Catherne Webster Centre for Competton Polcy, Unversty
Searchng and Swtchng: Emprcal estmates of consumer behavour n regulated markets Catherne Waddams Prce Centre for Competton Polcy, Unversty of East Angla Catherne Webster Centre for Competton Polcy, Unversty
Using Series to Analyze Financial Situations: Present Value
 2.8 Usng Seres to Analyze Fnancal Stuatons: Present Value In the prevous secton, you learned how to calculate the amount, or future value, of an ordnary smple annuty. The amount s the sum of the accumulated
2.8 Usng Seres to Analyze Fnancal Stuatons: Present Value In the prevous secton, you learned how to calculate the amount, or future value, of an ordnary smple annuty. The amount s the sum of the accumulated
Information Technology and the U.S. Productivity Revival: What Do the Industry Data Say?
 Informaton Technology and the U.S. Productvty Revval: What Do the Industry Data Say? Kevn J. Stroh Federal Reserve Bank of New York January 24, 2001 Abstract Ths paper examnes the lnk between nformaton
Informaton Technology and the U.S. Productvty Revval: What Do the Industry Data Say? Kevn J. Stroh Federal Reserve Bank of New York January 24, 2001 Abstract Ths paper examnes the lnk between nformaton
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK. Sample Stability Protocol
 CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
Follow links for Class Use and other Permissions. For more information send email to: permissions@pupress.princeton.edu
 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: Jord Galí: Monetary Polcy, Inflaton, and the Busness Cycle s publshed by Prnceton Unversty Press and copyrghted, 28, by Prnceton Unversty Press. All rghts reserved. No part of ths book
COPYRIGHT NOTICE: Jord Galí: Monetary Polcy, Inflaton, and the Busness Cycle s publshed by Prnceton Unversty Press and copyrghted, 28, by Prnceton Unversty Press. All rghts reserved. No part of ths book
iavenue iavenue i i i iavenue iavenue iavenue
 Saratoga Systems' enterprse-wde Avenue CRM system s a comprehensve web-enabled software soluton. Ths next generaton system enables you to effectvely manage and enhance your customer relatonshps n both
Saratoga Systems' enterprse-wde Avenue CRM system s a comprehensve web-enabled software soluton. Ths next generaton system enables you to effectvely manage and enhance your customer relatonshps n both
Section 5.4 Annuities, Present Value, and Amortization
 Secton 5.4 Annutes, Present Value, and Amortzaton Present Value In Secton 5.2, we saw that the present value of A dollars at nterest rate per perod for n perods s the amount that must be deposted today
Secton 5.4 Annutes, Present Value, and Amortzaton Present Value In Secton 5.2, we saw that the present value of A dollars at nterest rate per perod for n perods s the amount that must be deposted today
Bank Credit Conditions and their Influence on Productivity Growth: Company-level Evidence
 Bank Credt Condtons and ther Influence on Productvty Growth: Company-level Evdence Rebecca Rley*, Chara Rosazza Bondbene* and Garry Young** *Natonal Insttute of Economc and Socal Research & Centre For
Bank Credt Condtons and ther Influence on Productvty Growth: Company-level Evdence Rebecca Rley*, Chara Rosazza Bondbene* and Garry Young** *Natonal Insttute of Economc and Socal Research & Centre For
MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS IN THE SPANISH BANKING INDUSTRY: SOME EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE
 MERGERS AN ACQUISITIONS IN THE SPANISH BANKING INUSTRY: SOME EMPIRICA EVIENCE Ignaco Fuentes and Teresa Sastre Banco de España Banco de España Servco de Estudos ocumento de Trabajo n.º 9924 MERGERS AN
MERGERS AN ACQUISITIONS IN THE SPANISH BANKING INUSTRY: SOME EMPIRICA EVIENCE Ignaco Fuentes and Teresa Sastre Banco de España Banco de España Servco de Estudos ocumento de Trabajo n.º 9924 MERGERS AN
Modelling the Cocaine and Heroin Markets in the Era of Globalization and Drug Reduction Policies Claudia Costa Storti and Paul De Grauwe
 Modellng the Cocane and Heron Markets n the Era of Globalzaton and Drug Reducton Polces Clauda Costa Stort and Paul De Grauwe Modellng the Cocane and Heron Markets n the Era of Globalzaton and Drug Reducton
Modellng the Cocane and Heron Markets n the Era of Globalzaton and Drug Reducton Polces Clauda Costa Stort and Paul De Grauwe Modellng the Cocane and Heron Markets n the Era of Globalzaton and Drug Reducton
An Interest-Oriented Network Evolution Mechanism for Online Communities
 An Interest-Orented Network Evoluton Mechansm for Onlne Communtes Cahong Sun and Xaopng Yang School of Informaton, Renmn Unversty of Chna, Bejng 100872, P.R. Chna {chsun,yang}@ruc.edu.cn Abstract. Onlne
An Interest-Orented Network Evoluton Mechansm for Onlne Communtes Cahong Sun and Xaopng Yang School of Informaton, Renmn Unversty of Chna, Bejng 100872, P.R. Chna {chsun,yang}@ruc.edu.cn Abstract. Onlne
THE DISTRIBUTION OF LOAN PORTFOLIO VALUE * Oldrich Alfons Vasicek
 HE DISRIBUION OF LOAN PORFOLIO VALUE * Oldrch Alfons Vascek he amount of captal necessary to support a portfolo of debt securtes depends on the probablty dstrbuton of the portfolo loss. Consder a portfolo
HE DISRIBUION OF LOAN PORFOLIO VALUE * Oldrch Alfons Vascek he amount of captal necessary to support a portfolo of debt securtes depends on the probablty dstrbuton of the portfolo loss. Consder a portfolo
The literature on many-server approximations provides significant simplifications toward the optimal capacity
 Publshed onlne ahead of prnt November 13, 2009 Copyrght: INFORMS holds copyrght to ths Artcles n Advance verson, whch s made avalable to nsttutonal subscrbers. The fle may not be posted on any other webste,
Publshed onlne ahead of prnt November 13, 2009 Copyrght: INFORMS holds copyrght to ths Artcles n Advance verson, whch s made avalable to nsttutonal subscrbers. The fle may not be posted on any other webste,
Study on Model of Risks Assessment of Standard Operation in Rural Power Network
 Study on Model of Rsks Assessment of Standard Operaton n Rural Power Network Qngj L 1, Tao Yang 2 1 Qngj L, College of Informaton and Electrcal Engneerng, Shenyang Agrculture Unversty, Shenyang 110866,
Study on Model of Rsks Assessment of Standard Operaton n Rural Power Network Qngj L 1, Tao Yang 2 1 Qngj L, College of Informaton and Electrcal Engneerng, Shenyang Agrculture Unversty, Shenyang 110866,
SPECIALIZED DAY TRADING - A NEW VIEW ON AN OLD GAME
 August 7 - August 12, 2006 n Baden-Baden, Germany SPECIALIZED DAY TRADING - A NEW VIEW ON AN OLD GAME Vladmr Šmovć 1, and Vladmr Šmovć 2, PhD 1 Faculty of Electrcal Engneerng and Computng, Unska 3, 10000
August 7 - August 12, 2006 n Baden-Baden, Germany SPECIALIZED DAY TRADING - A NEW VIEW ON AN OLD GAME Vladmr Šmovć 1, and Vladmr Šmovć 2, PhD 1 Faculty of Electrcal Engneerng and Computng, Unska 3, 10000
The impact of hard discount control mechanism on the discount volatility of UK closed-end funds
 Investment Management and Fnancal Innovatons, Volume 10, Issue 3, 2013 Ahmed F. Salhn (Egypt) The mpact of hard dscount control mechansm on the dscount volatlty of UK closed-end funds Abstract The mpact
Investment Management and Fnancal Innovatons, Volume 10, Issue 3, 2013 Ahmed F. Salhn (Egypt) The mpact of hard dscount control mechansm on the dscount volatlty of UK closed-end funds Abstract The mpact
IMPACT ANALYSIS OF A CELLULAR PHONE
 4 th ASA & μeta Internatonal Conference IMPACT AALYSIS OF A CELLULAR PHOE We Lu, 2 Hongy L Bejng FEAonlne Engneerng Co.,Ltd. Bejng, Chna ABSTRACT Drop test smulaton plays an mportant role n nvestgatng
4 th ASA & μeta Internatonal Conference IMPACT AALYSIS OF A CELLULAR PHOE We Lu, 2 Hongy L Bejng FEAonlne Engneerng Co.,Ltd. Bejng, Chna ABSTRACT Drop test smulaton plays an mportant role n nvestgatng
High Correlation between Net Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Willingness to Pay (Empirical Evidence from European Mobile Markets)
 Hgh Correlaton between et Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Wllngness to Pay (Emprcal Evdence from European Moble Marets Ths paper shows that the correlaton between the et Promoter Score
Hgh Correlaton between et Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Wllngness to Pay (Emprcal Evdence from European Moble Marets Ths paper shows that the correlaton between the et Promoter Score
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES CARBON MOTIVATED REGIONAL TRADE ARRANGEMENTS: ANALYTICS AND SIMULATIONS. Yan Dong John Whalley
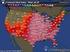 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES CARBON MOTIVATED REGIONAL TRADE ARRANGEMENTS: ANALYTICS AND SIMULATIONS Yan Dong John Whalley Workng Paper 14880 http://www.nber.org/papers/w14880 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES CARBON MOTIVATED REGIONAL TRADE ARRANGEMENTS: ANALYTICS AND SIMULATIONS Yan Dong John Whalley Workng Paper 14880 http://www.nber.org/papers/w14880 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC
Elements of Advanced International Trade 1
 Elements of Advanced Internatonal Trade 1 Treb Allen 2 and Costas Arkolaks 3 January 2015 [New verson: prelmnary] 1 Ths set of notes and the homeworks accomodatng them s a collecton of materal desgned
Elements of Advanced Internatonal Trade 1 Treb Allen 2 and Costas Arkolaks 3 January 2015 [New verson: prelmnary] 1 Ths set of notes and the homeworks accomodatng them s a collecton of materal desgned
Chapter 11 Practice Problems Answers
 Chapter 11 Practce Problems Answers 1. Would you be more wllng to lend to a frend f she put all of her lfe savngs nto her busness than you would f she had not done so? Why? Ths problem s ntended to make
Chapter 11 Practce Problems Answers 1. Would you be more wllng to lend to a frend f she put all of her lfe savngs nto her busness than you would f she had not done so? Why? Ths problem s ntended to make
The Journal of Applied Business Research January/February 2010 Volume 26, Number 1
 Product Dversfcaton In Compettve R&D-Intensve Frms: An Emprcal Study Of The Computer Software Industry C. Catherne Chang, Elon Unversty, USA ABSTRACT Ths paper studes the effect of dversfcaton nto dfferent
Product Dversfcaton In Compettve R&D-Intensve Frms: An Emprcal Study Of The Computer Software Industry C. Catherne Chang, Elon Unversty, USA ABSTRACT Ths paper studes the effect of dversfcaton nto dfferent
Risk Model of Long-Term Production Scheduling in Open Pit Gold Mining
 Rsk Model of Long-Term Producton Schedulng n Open Pt Gold Mnng R Halatchev 1 and P Lever 2 ABSTRACT Open pt gold mnng s an mportant sector of the Australan mnng ndustry. It uses large amounts of nvestments,
Rsk Model of Long-Term Producton Schedulng n Open Pt Gold Mnng R Halatchev 1 and P Lever 2 ABSTRACT Open pt gold mnng s an mportant sector of the Australan mnng ndustry. It uses large amounts of nvestments,
Power-of-Two Policies for Single- Warehouse Multi-Retailer Inventory Systems with Order Frequency Discounts
 Power-of-wo Polces for Sngle- Warehouse Mult-Retaler Inventory Systems wth Order Frequency Dscounts José A. Ventura Pennsylvana State Unversty (USA) Yale. Herer echnon Israel Insttute of echnology (Israel)
Power-of-wo Polces for Sngle- Warehouse Mult-Retaler Inventory Systems wth Order Frequency Dscounts José A. Ventura Pennsylvana State Unversty (USA) Yale. Herer echnon Israel Insttute of echnology (Israel)
THE DETERMINANTS OF THE TUNISIAN BANKING INDUSTRY PROFITABILITY: PANEL EVIDENCE
 THE DETERMINANTS OF THE TUNISIAN BANKING INDUSTRY PROFITABILITY: PANEL EVIDENCE Samy Ben Naceur ERF Research Fellow Department of Fnance Unversté Lbre de Tuns Avenue Khéreddne Pacha, 002 Tuns Emal : sbennaceur@eudoramal.com
THE DETERMINANTS OF THE TUNISIAN BANKING INDUSTRY PROFITABILITY: PANEL EVIDENCE Samy Ben Naceur ERF Research Fellow Department of Fnance Unversté Lbre de Tuns Avenue Khéreddne Pacha, 002 Tuns Emal : sbennaceur@eudoramal.com
An Evaluation of the Extended Logistic, Simple Logistic, and Gompertz Models for Forecasting Short Lifecycle Products and Services
 An Evaluaton of the Extended Logstc, Smple Logstc, and Gompertz Models for Forecastng Short Lfecycle Products and Servces Charles V. Trappey a,1, Hsn-yng Wu b a Professor (Management Scence), Natonal Chao
An Evaluaton of the Extended Logstc, Smple Logstc, and Gompertz Models for Forecastng Short Lfecycle Products and Servces Charles V. Trappey a,1, Hsn-yng Wu b a Professor (Management Scence), Natonal Chao
Foreign Direct Investment in a World of Multiple Taxes
 Foregn Drect Investment n a World of Multple Taxes by Mhr A. Desa Harvard Unversty and NBER James R. Hnes Jr. Unversty of Mchgan and NBER July 2001 We thank Yumng Zou for excellent research assstance,
Foregn Drect Investment n a World of Multple Taxes by Mhr A. Desa Harvard Unversty and NBER James R. Hnes Jr. Unversty of Mchgan and NBER July 2001 We thank Yumng Zou for excellent research assstance,
Traffic-light a stress test for life insurance provisions
 MEMORANDUM Date 006-09-7 Authors Bengt von Bahr, Göran Ronge Traffc-lght a stress test for lfe nsurance provsons Fnansnspetonen P.O. Box 6750 SE-113 85 Stocholm [Sveavägen 167] Tel +46 8 787 80 00 Fax
MEMORANDUM Date 006-09-7 Authors Bengt von Bahr, Göran Ronge Traffc-lght a stress test for lfe nsurance provsons Fnansnspetonen P.O. Box 6750 SE-113 85 Stocholm [Sveavägen 167] Tel +46 8 787 80 00 Fax
When Talk is Free : The Effect of Tariff Structure on Usage under Two- and Three-Part Tariffs
 0 When Talk s Free : The Effect of Tarff Structure on Usage under Two- and Three-Part Tarffs Eva Ascarza Ana Lambrecht Naufel Vlcassm July 2012 (Forthcomng at Journal of Marketng Research) Eva Ascarza
0 When Talk s Free : The Effect of Tarff Structure on Usage under Two- and Three-Part Tarffs Eva Ascarza Ana Lambrecht Naufel Vlcassm July 2012 (Forthcomng at Journal of Marketng Research) Eva Ascarza
Technical Memorandum Number 815. Bigger Slice or Larger Pie? Optimal Marketing Strategies for New Firms. John Angelis Moren Lévesque
 Techncal Memorandum Number 815 Bgger Slce or Larger Pe? Optmal Marketng Strateges for New Frms by John Angels Moren Lévesque June 26 Department of Operatons Weatherhead School of Management Case Western
Techncal Memorandum Number 815 Bgger Slce or Larger Pe? Optmal Marketng Strateges for New Frms by John Angels Moren Lévesque June 26 Department of Operatons Weatherhead School of Management Case Western
RESEARCH DISCUSSION PAPER
 Reserve Bank of Australa RESEARCH DISCUSSION PAPER Competton Between Payment Systems George Gardner and Andrew Stone RDP 2009-02 COMPETITION BETWEEN PAYMENT SYSTEMS George Gardner and Andrew Stone Research
Reserve Bank of Australa RESEARCH DISCUSSION PAPER Competton Between Payment Systems George Gardner and Andrew Stone RDP 2009-02 COMPETITION BETWEEN PAYMENT SYSTEMS George Gardner and Andrew Stone Research
Quantity-setting Oligopolies in Complementary Input Markets - the Case of Iron Ore and Coking Coal
 Quantty-settng Olgopoles n Complementary Input Markets - the Case of Iron Ore and Cokng Coal AUTHORS Harald Heckng Tmo Panke EWI Workng Paper No. 14/06 February 2014 Insttute of Energy Economcs at the
Quantty-settng Olgopoles n Complementary Input Markets - the Case of Iron Ore and Cokng Coal AUTHORS Harald Heckng Tmo Panke EWI Workng Paper No. 14/06 February 2014 Insttute of Energy Economcs at the
Designing and Implementing a Performance Management System in a Textile Company for Competitive Advantage
 Desgnng and Implementng a Performance Management System n a Textle Company for Compettve Advantage Muhttn Oral Fehm Peker December 2009 CIRRELT-2009-54 Bureaux de Montréal : Bureaux de uébec : Unversté
Desgnng and Implementng a Performance Management System n a Textle Company for Compettve Advantage Muhttn Oral Fehm Peker December 2009 CIRRELT-2009-54 Bureaux de Montréal : Bureaux de uébec : Unversté
Recurrence. 1 Definitions and main statements
 Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
Construction Rules for Morningstar Canada Target Dividend Index SM
 Constructon Rules for Mornngstar Canada Target Dvdend Index SM Mornngstar Methodology Paper October 2014 Verson 1.2 2014 Mornngstar, Inc. All rghts reserved. The nformaton n ths document s the property
Constructon Rules for Mornngstar Canada Target Dvdend Index SM Mornngstar Methodology Paper October 2014 Verson 1.2 2014 Mornngstar, Inc. All rghts reserved. The nformaton n ths document s the property
Nordea G10 Alpha Carry Index
 Nordea G10 Alpha Carry Index Index Rules v1.1 Verson as of 10/10/2013 1 (6) Page 1 Index Descrpton The G10 Alpha Carry Index, the Index, follows the development of a rule based strategy whch nvests and
Nordea G10 Alpha Carry Index Index Rules v1.1 Verson as of 10/10/2013 1 (6) Page 1 Index Descrpton The G10 Alpha Carry Index, the Index, follows the development of a rule based strategy whch nvests and
Leveraged Firms, Patent Licensing, and Limited Liability
 Leveraged Frms, Patent Lcensng, and Lmted Lablty Kuang-Cheng Andy Wang Socal Scence Dvson Center for General Educaton Chang Gung Unversty and Y-Je Wang Department of Economcs Natonal Dong Hwa Unversty
Leveraged Frms, Patent Lcensng, and Lmted Lablty Kuang-Cheng Andy Wang Socal Scence Dvson Center for General Educaton Chang Gung Unversty and Y-Je Wang Department of Economcs Natonal Dong Hwa Unversty
Chapter 15: Debt and Taxes
 Chapter 15: Debt and Taxes-1 Chapter 15: Debt and Taxes I. Basc Ideas 1. Corporate Taxes => nterest expense s tax deductble => as debt ncreases, corporate taxes fall => ncentve to fund the frm wth debt
Chapter 15: Debt and Taxes-1 Chapter 15: Debt and Taxes I. Basc Ideas 1. Corporate Taxes => nterest expense s tax deductble => as debt ncreases, corporate taxes fall => ncentve to fund the frm wth debt
Dynamics of Toursm Demand Models in Japan
 hort-run and ong-run structural nternatonal toursm demand modelng based on Dynamc AID model -An emprcal research n Japan- Atsush KOIKE a, Dasuke YOHINO b a Graduate chool of Engneerng, Kobe Unversty, Kobe,
hort-run and ong-run structural nternatonal toursm demand modelng based on Dynamc AID model -An emprcal research n Japan- Atsush KOIKE a, Dasuke YOHINO b a Graduate chool of Engneerng, Kobe Unversty, Kobe,
Reporting Forms ARF 113.0A, ARF 113.0B, ARF 113.0C and ARF 113.0D FIRB Corporate (including SME Corporate), Sovereign and Bank Instruction Guide
 Reportng Forms ARF 113.0A, ARF 113.0B, ARF 113.0C and ARF 113.0D FIRB Corporate (ncludng SME Corporate), Soveregn and Bank Instructon Gude Ths nstructon gude s desgned to assst n the completon of the FIRB
Reportng Forms ARF 113.0A, ARF 113.0B, ARF 113.0C and ARF 113.0D FIRB Corporate (ncludng SME Corporate), Soveregn and Bank Instructon Gude Ths nstructon gude s desgned to assst n the completon of the FIRB
Numerical General Equilibrium Analysis of China s. Impacts from Possible Mega Trade Deals
 Numercal General Equlbrum Analyss of Chna s Impacts from Possble Mega Trade Deals Chundng L a, b, c a Insttute of World Economcs and Poltcs, Chnese Academy of Socal Scences; b Department of Economcs, Western
Numercal General Equlbrum Analyss of Chna s Impacts from Possble Mega Trade Deals Chundng L a, b, c a Insttute of World Economcs and Poltcs, Chnese Academy of Socal Scences; b Department of Economcs, Western
The program for the Bachelor degrees shall extend over three years of full-time study or the parttime equivalent.
 Bachel of Commerce Bachel of Commerce (Accountng) Bachel of Commerce (Cpate Fnance) Bachel of Commerce (Internatonal Busness) Bachel of Commerce (Management) Bachel of Commerce (Marketng) These Program
Bachel of Commerce Bachel of Commerce (Accountng) Bachel of Commerce (Cpate Fnance) Bachel of Commerce (Internatonal Busness) Bachel of Commerce (Management) Bachel of Commerce (Marketng) These Program
Quarterly Non-financial Accounts by Institutional Sector (QSA) in Belgium Sources and Methods
 Quarterly Non-fnancal Accounts by Insttutonal Sector (QSA) n Belgum and Second edton May 2010 2. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. General descrpton... 4 1.1. Organsatonal aspects... 4 1.2.... 5 1.3.... 7 1.3.1. General
Quarterly Non-fnancal Accounts by Insttutonal Sector (QSA) n Belgum and Second edton May 2010 2. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. General descrpton... 4 1.1. Organsatonal aspects... 4 1.2.... 5 1.3.... 7 1.3.1. General
Evaluating the Effects of FUNDEF on Wages and Test Scores in Brazil *
 Evaluatng the Effects of FUNDEF on Wages and Test Scores n Brazl * Naérco Menezes-Flho Elane Pazello Unversty of São Paulo Abstract In ths paper we nvestgate the effects of the 1998 reform n the fundng
Evaluatng the Effects of FUNDEF on Wages and Test Scores n Brazl * Naérco Menezes-Flho Elane Pazello Unversty of São Paulo Abstract In ths paper we nvestgate the effects of the 1998 reform n the fundng
Winners and Losers in a Free Trade Area between The United States and MERCOSUR
 Wnners and Losers n a Free Trade rea between The Unted States and MERCOSUR Marcel Vallant lvaro Ons Resumen Este documento consdera una eventual zona de lbre comerco entre los EU y el MERCOSUR con el propósto
Wnners and Losers n a Free Trade rea between The Unted States and MERCOSUR Marcel Vallant lvaro Ons Resumen Este documento consdera una eventual zona de lbre comerco entre los EU y el MERCOSUR con el propósto
Industry export competitiveness and optimal quantitative strategies for international emissions trading
 Envronmental Economcs, Volume 5, Issue 4, 04 Tsung-Chen Lee (Tawan) Industry export compettveness and optmal quanttatve strateges for nternatonal emssons tradng Abstract Ths paper analyzes how quanttatve
Envronmental Economcs, Volume 5, Issue 4, 04 Tsung-Chen Lee (Tawan) Industry export compettveness and optmal quanttatve strateges for nternatonal emssons tradng Abstract Ths paper analyzes how quanttatve
