Muscle/Nerve Cross Talk: Impact on Voluntary Muscle Action
|
|
|
- Donald Miles
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Muscle/Nerve Cross Talk: Impact on Voluntary Muscle Action OBJECTIVES I. Coordination of signaling for agonist and antagonistic muscle action II. Complexity of layered control over voluntary muscle movement Goals
2 concepts 1) Basic gross and micro anatomical structure of muscle movement 2) CNS signaling for monosynaptic & polysynaptic reflex muscle action 3) Coordinated CNS signaling of excitatory and inhibitory neurons 4) Cortical origin of voluntary muscle action 5) Influence of sensory input and learning on voluntary muscle action Goals
3 How is the Cerebral cortex involved in skeletal muscle movement? C5-T1 : Upper limb L4-S3 : Lower limb Skeletal Muscle related Neurology
4 How are motor units recruited to control fine movement? Skeletal Muscle related Neurology
5 How are Motor axons Arranged in the spinal cord? Extension Flexion Proximal Distal Skeletal Muscle related Neurology
6 How is muscle action Compartmentalized in the upper and lower limbs? Upper Limb Extension: Radial N. Flexion: Musculocutaneous N. Flexion: Femoral N. Extension: Tibial N. Lower Limb Skeletal Muscle related Anatomy
7 How does the primary mover differ from Synergistic muscles In Muscle action? Skeletal Muscle related Anatomy
8 How do agonist and antagonist muscles work coordinately? Skeletal Muscle related Anatomy
9 What skeletal muscle receptors Send signals about Proprioception to the CNS? Skeletal Muscle related histology
10 How do muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organ signals To the alpha motor neuron differ? Skeletal Muscle related histology
11 What is a reflex? [gastric distension>increased intestinal peristalsis] [appendicitis>muscle rigidity] /photo/22464/lightning+strike+over+desert Involuntary Muscle action
12 What action induces the monosynaptic knee jerk reflex? Knee Jerk Reflex Monosynaptic reflex loop through spinal cord Involuntary Skeletal Muscle action
13 What afferent signal is activated In the monosynaptic reflex arc? Involuntary Skeletal Muscle action
14 What neurons signal the muscle spindle intrafusal fibers to contract? Involuntary Skeletal Muscle action
15 What is the difference between a Monosynaptic and a polysynaptic reflex? Involuntary Skeletal Muscle action
16 How do signals from the golgi tendon organ Affect agonist and antagonist muscles? Involuntary Skeletal Muscle action
17 What is the role of The Cerebral cortex In voluntary muscle action? Cerebral Cortex Corticospinal Tract (Pyramidal Tract) ] Fiber Decussation Motor cortex control of voluntary muscle action
18 How are the cell bodies for motor axons in the cerebral cortex characterized? Motor cortex control of voluntary muscle action
19 How do muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs impact voluntary muscle movement? voluntary Skeletal Muscle action
20 What extra-pyramidal influences are exerted over voluntary muscle action? Complex neural influence over Voluntary muscle action
21 Where do Extra-pyramidal pathways And muscle proprioceptors interact? Neural regulation of muscle action
22 Why Do our runners reflexively pull the hot coffee cup From Their lips? Complex neural influence over muscle action
23 Complexity of Muscle/Nerve Cross Talk in Skeletal Muscle Action Summary of basic neurology, anatomy and histology Larger areas of motor cortex are dedicated to muscles that are used for fine movements. Fine movements are associated with small motor units while gross movements are associated with larger motor units. Location, Location, Location! of a lesion will determine what impact it has on muscle movement. Muscle spindles & Golgi tendon organs are receptors for proprioception and regulate muscle length and muscle tension respectively. Control of muscle movement
24 Complexity of Muscle/Nerve Cross Talk in Skeletal Muscle Action Summary of basic muscle movement Reflex movement can involve monosynaptic (without interneurons) or polysynaptic (with interneurons) synapses. Skeletal muscle movement is regulated by coordinated signaling of excitatory and inhibitory neurons. Upper motor neurons in the motor cortex signal lower motor neurons in the spinal cord via the corticospinal tract. Muscle movement is influenced by extra-pyramidal pathways, sensory input & learning. Control of muscle movement
25 Questions? Acknowledgments
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex
 Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28
 The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
SPINAL CORD CIRCUITS AND MOTOR CONTROL
 OVERVEW The proximate control of movement is provided by neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem. The primary motor neurons located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord gray matter (and the corresponding
OVERVEW The proximate control of movement is provided by neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem. The primary motor neurons located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord gray matter (and the corresponding
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Human Physiology Study Questions-2
 Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Lab #7: Nerve Pathways and Somatosensory Physiology
 Lab #7: Nerve Pathways and Somatosensory Physiology Background The nervous system plays a central role in homeostasis. The central nervous system functions as the primary controller and integrator for
Lab #7: Nerve Pathways and Somatosensory Physiology Background The nervous system plays a central role in homeostasis. The central nervous system functions as the primary controller and integrator for
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
The Science Behind MAT
 The Science Behind MAT Muscle Activation Techniques (MAT) is a system designed to evaluate and treat muscular imbalances, I will expand on the process of evaluation in response and the use of isometrics
The Science Behind MAT Muscle Activation Techniques (MAT) is a system designed to evaluate and treat muscular imbalances, I will expand on the process of evaluation in response and the use of isometrics
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System I. An Overview of Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System, p. 496 Figure 15-1 Specialized cells called sensory
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System I. An Overview of Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System, p. 496 Figure 15-1 Specialized cells called sensory
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Physiology of the central nervous system
 Physiology of the central nervous system Motor division of the CNS Reflex General function of the nervous system (NS) Nervous system -communication network of neurons that allows the organism to interact
Physiology of the central nervous system Motor division of the CNS Reflex General function of the nervous system (NS) Nervous system -communication network of neurons that allows the organism to interact
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
The Motor System: Lecture 1 Spinal motor system
 The Motor System: Lecture 1 Spinal motor system Reza Shadmehr Traylor 410, School of Medicine, shadmehr@jhu.edu NOTE: All slides and lecture notes for the motor lectures of Dr. Shadmehr are available at:
The Motor System: Lecture 1 Spinal motor system Reza Shadmehr Traylor 410, School of Medicine, shadmehr@jhu.edu NOTE: All slides and lecture notes for the motor lectures of Dr. Shadmehr are available at:
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab. Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Reflex Response (Patellar Tendon) Using BIOPAC Reflex Hammer Transducer SS36L
 Updated 7.31.06 BSL PRO Lesson H28: Reflex Response (Patellar Tendon) Using BIOPAC Reflex Hammer Transducer SS36L This PRO lesson describes basic reflex exercises and details hardware and software setup
Updated 7.31.06 BSL PRO Lesson H28: Reflex Response (Patellar Tendon) Using BIOPAC Reflex Hammer Transducer SS36L This PRO lesson describes basic reflex exercises and details hardware and software setup
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944
 http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
Brain & Mind. Bicester Community College Science Department
 B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 3: Brain s Building Blocks. Module 3. Brain s Building Blocks
 Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses
 The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses 1 Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy November 2009, 38, pp.
The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses 1 Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy November 2009, 38, pp.
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential
 Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
 CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Basal Ganglia. Motor systems
 409 systems Basal Ganglia You have just read about the different motorrelated cortical areas. Premotor areas are involved in planning, while MI is involved in execution. What you don t know is that the
409 systems Basal Ganglia You have just read about the different motorrelated cortical areas. Premotor areas are involved in planning, while MI is involved in execution. What you don t know is that the
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON. created by Dr. Joanne Hsu
 NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function. Skeletal muscles act on bones to produce movement of the limb and to move (lift and carry) objects.
 ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
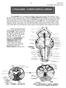 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Supplementary documents for Computational Neurobiology of Reaching and Pointing, by R. Shadmehr and S. P. Wise
 A SIMPLE MUSCLE MODEL Muscle produces two kinds of force, active and passive, which sum to compose a muscle s total force. A muscle s contractile elements provide its active force through the actin and
A SIMPLE MUSCLE MODEL Muscle produces two kinds of force, active and passive, which sum to compose a muscle s total force. A muscle s contractile elements provide its active force through the actin and
Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
 Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia 1 Contents Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia... 1 Introduction... 3 A brief review of cerebellar anatomy... 4 Basic Circuit... 4 Parallel and climbing fiber input has a very different
Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia 1 Contents Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia... 1 Introduction... 3 A brief review of cerebellar anatomy... 4 Basic Circuit... 4 Parallel and climbing fiber input has a very different
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone
 Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone In this article we wish to document some of the electrical stimulation techniques we use for the upper limb, primarily
Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone In this article we wish to document some of the electrical stimulation techniques we use for the upper limb, primarily
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Motoneuron recruitment
 Motoneuron recruitment Daniel Bullock February,2002 Technical Report CAS/CNS-02-001 Permission to copy without fcc a!! or part of this material is granted provided that: 1. The copies arc not made or distributed
Motoneuron recruitment Daniel Bullock February,2002 Technical Report CAS/CNS-02-001 Permission to copy without fcc a!! or part of this material is granted provided that: 1. The copies arc not made or distributed
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
Best Teaching Practices Conference. Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY. Class: X. TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System
 Best Teaching Practices Conference Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY Class: X TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System OBJECTIVES: Use Information Technology to enable the students to: Explain the general
Best Teaching Practices Conference Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY Class: X TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System OBJECTIVES: Use Information Technology to enable the students to: Explain the general
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HN-2: Stretch Receptors and Reflexes
 Experiment HN-2: Stretch Receptors and Reflexes Exercise 1: Achilles Tendon Reflex Aim: To determine conduction time from tendon tap to response of the gastrocnemius muscle in the Achilles tendon reflex
Experiment HN-2: Stretch Receptors and Reflexes Exercise 1: Achilles Tendon Reflex Aim: To determine conduction time from tendon tap to response of the gastrocnemius muscle in the Achilles tendon reflex
Journal of Neuroscience Methods
 Journal of Neuroscience Methods 171 (2008) 1 12 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Neuroscience Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jneumeth Invited review The H-reflex
Journal of Neuroscience Methods 171 (2008) 1 12 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Neuroscience Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jneumeth Invited review The H-reflex
Video. Virtual Webinar Corporate. 1.800.55.4CEUS HomeCEUConnection.com
 Video Text Live Virtual Webinar Corporate 1.800.55.4CEUS HomeCEUConnection.com Modalities for Massage and Body Work Module 1 This Package Contains: Table of Contents 1 Steps to Complete This Course 2 Course
Video Text Live Virtual Webinar Corporate 1.800.55.4CEUS HomeCEUConnection.com Modalities for Massage and Body Work Module 1 This Package Contains: Table of Contents 1 Steps to Complete This Course 2 Course
Exercise 5 Nervous Tissue
 Exercise 5 Nervous Tissue Objectives After completing the laboratory exercise for nervous tissue you should be able to: Introduction Identify a "typical" multipolar neuron in the light microscope. Identify
Exercise 5 Nervous Tissue Objectives After completing the laboratory exercise for nervous tissue you should be able to: Introduction Identify a "typical" multipolar neuron in the light microscope. Identify
Muscle Fatigue and the Mechanisms of Task Failure
 ARTICLE Muscle Fatigue and the Mechanisms of Task Failure Sandra K. Hunter 1, Jacques Duchateau, 2 and Roger M. Enoka 3 1 Exercise Science Program, Department of Physical Therapy, Marquette University,
ARTICLE Muscle Fatigue and the Mechanisms of Task Failure Sandra K. Hunter 1, Jacques Duchateau, 2 and Roger M. Enoka 3 1 Exercise Science Program, Department of Physical Therapy, Marquette University,
THE SCIENCE BEHIND BALANCE TRAINING
 THE SCIENCE BEHIND BALANCE TRAINING Balance represents an ability to stabilize and maintain a desired body position. Balance can also be thought of as correct, or efficient, positioning of a body part
THE SCIENCE BEHIND BALANCE TRAINING Balance represents an ability to stabilize and maintain a desired body position. Balance can also be thought of as correct, or efficient, positioning of a body part
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue
 12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
Barbara St. Marie, PhD Candidate Nurse Practitioner Supervisor Pain and Palliative Care Fairview Ridges Hospital Minneapolis, MN
 Barbara St. Marie, PhD Candidate Nurse Practitioner Supervisor Pain and Palliative Care Fairview Ridges Hospital Minneapolis, MN Pain Physiology Objectives: Explain how pain is transmitted through the
Barbara St. Marie, PhD Candidate Nurse Practitioner Supervisor Pain and Palliative Care Fairview Ridges Hospital Minneapolis, MN Pain Physiology Objectives: Explain how pain is transmitted through the
THE SENSE OF TOUCH. Roope Raisamo and Jukka Raisamo
 THE SENSE OF TOUCH Roope Raisamo and Jukka Raisamo Tampere Unit for Computer-Human Interaction School of Information Sciences University of Tampere, Finland Outline for the talk Introduction to the sense
THE SENSE OF TOUCH Roope Raisamo and Jukka Raisamo Tampere Unit for Computer-Human Interaction School of Information Sciences University of Tampere, Finland Outline for the talk Introduction to the sense
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing
 3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
3nd Biennial Contemporary Clinical Neurophysiological Symposium October 12, 2013 Fundamentals of NCS and NMJ Testing Peter D. Donofrio, M.D. Professor of Neurology Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc).
 Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Proprioception: The Sensations of Joint Motion and Position
 1 Proprioception: The Sensations of Joint Motion and Position Scott M. Lephart, Ph.D., ATC Director, Sports Medicine/Athletic Training Assistant Professor, Education Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic
1 Proprioception: The Sensations of Joint Motion and Position Scott M. Lephart, Ph.D., ATC Director, Sports Medicine/Athletic Training Assistant Professor, Education Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic
Adrian Owens Research
 *Classic View: Not entirely correct Nervous System Central Nervous System is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System is broken down into a component called the somatic division.
*Classic View: Not entirely correct Nervous System Central Nervous System is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System is broken down into a component called the somatic division.
MCQ : Central Nervous System. General Functional Organization of the Nervous System
 Section 1 MCQ : Central Nervous System General Functional Organization of the Nervous System 1 ) The central nervous system includes all the following components, except :- a- spinal cord b- medulla oblongata
Section 1 MCQ : Central Nervous System General Functional Organization of the Nervous System 1 ) The central nervous system includes all the following components, except :- a- spinal cord b- medulla oblongata
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Plyometric Training. Plyometric Training. chapter
 chapter 16 Plyometric Training Plyometric Training David H. Potach, PT; MS; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D Donald A. Chu, PhD; PT; ATC; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D; FNSCA Chapter Objectives Explain the physiology of plyometric
chapter 16 Plyometric Training Plyometric Training David H. Potach, PT; MS; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D Donald A. Chu, PhD; PT; ATC; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D; FNSCA Chapter Objectives Explain the physiology of plyometric
Name. Most of the bones of the limbs (arms & legs) act as levers. These levers are powered by muscles.
 Bones as Levers 1 Name Bones as Levers You may not think of your limbs as being machines, but they are. The action of a muscle pulling on a bone often works like a type of simple machine called a lever.
Bones as Levers 1 Name Bones as Levers You may not think of your limbs as being machines, but they are. The action of a muscle pulling on a bone often works like a type of simple machine called a lever.
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
Chapter 6. Components of Elasticity. Musculotendinous Unit. Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit. Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture
 The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
Spinal-Like Regulator Facilitates Control of a Two-Degree-of-Freedom Wrist
 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 14, 2010 30(28):9431 9444 9431 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Spinal-Like Regulator Facilitates Control of a Two-Degree-of-Freedom Wrist Giby Raphael, George A. Tsianos,
The Journal of Neuroscience, July 14, 2010 30(28):9431 9444 9431 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Spinal-Like Regulator Facilitates Control of a Two-Degree-of-Freedom Wrist Giby Raphael, George A. Tsianos,
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician
 EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Ascending Sensory Pathways
 CHAPTER 10 Ascending Sensory Pathways CLINICAL CASE SENSORY RECEPTORS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM TACTILE SENSATION AND PROPRIOCEPTION SENSORY PATHWAYS TO THE CEREBELLUM CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS MODULATION OF
CHAPTER 10 Ascending Sensory Pathways CLINICAL CASE SENSORY RECEPTORS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM TACTILE SENSATION AND PROPRIOCEPTION SENSORY PATHWAYS TO THE CEREBELLUM CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS MODULATION OF
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
