AEROBIC FITNESS 2ND EDITION
|
|
|
- Sherman Curtis
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AEROBIC FITNESS 2ND EDITION By John Mason
2 NOTE The information in this book is derived from a broad cross section of resources (research, reference materials and personal experience) from the authors and editorial assistants in the academic department of ACS Distance Education. It is, to the best of our knowledge, composed as an accurate representation of what is accepted and appropriate information about the subject, at the time of publication. The authors fully recognise that knowledge is continually changing, and awareness in all areas of study is constantly evolving. As such, we encourage the reader to recognise that nothing they read should ever be considered to be set in stone. They should always strive to broaden their perspective and deepen their understanding of a subject, and before acting upon any information or advice, should always seek to confirm the currency of that information, and the appropriateness to the situation in which they find themselves. As such, the publisher and author do not accept any liability for actions taken by the reader based upon their reading of this book ISBN PAGE 2
3 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION/PREFACE 5 Differences between aerobic and anaerobic exercise 5 CHAPTER 1 HUMAN BIOLOGY & AEROBIC FITNESS 7 Sources of atp 7 Energy definitions 8 Energy production pathways from different foods 8 What happens during exercise 9 Training response 9 More on fatigue 10 Recovery from exercise 11 Other factors affecting performance 11 Human anatomy 12 The muscular system 14 The respiratory system 16 The circulatory system 17 The physiology of the circulatory system 19 CHAPTER 2 EQUIPMENT & FACILITIES 21 Where to exercise 21 Outdoor areas 22 Clothing and footwear 23 Music 24 Characteristics of equipment 25 Examples of equipment used in aerobic activities 25 Other types of equipment specific to aerobics classes 32 Aerobic home equipment 33 Maintaining equipment 33 Outdoors/park equipment used for aerobic exercises 34 CHAPTER 3 EXERCISES 35 How often, how hard 35 Exercise movement components 36 Running/jogging/walking 39 Cycling 41 Swimming 42 Rowing 42 Stepping & climbing 43 Skipping 43 Ball sports 44 Surfing 45 Horse riding 45 Skating 45 Skiing 45
4 Jumping 45 Tai chi (tai qi) 46 Wilderness areas 46 Safety 46 Gym/class exercises 46 Stretching 49 Muscle conditioning 54 CHAPTER 4 SPECIAL PEOPLE & SITUATIONS 56 Pregnancy 56 Older adults 57 Children 58 People with disabilities &/or handicaps 58 Overweight people 59 Other health problems 60 CHAPTER 5 SAFETY 61 Aerobic classes 61 Safety related issues 61 Safety in other aerobic activities 61 First aid considerations 61 Identifying hazards 63 Pre-screening of clients 65 Legal liabilities for fitness instructors 67 CHAPTER 6 FITNESS TESTING/ASSESSMENT 69 What do we test? 69 What can we measure? 69 Designing fitness tests 77 CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING, MOTIVATION & LEADERSHIP 79 Fitness/aerobics class design 79 Programming an exercise session 80 Designing exercise programmes 80 A typical aerobics class 82 Writing an exercise programme 87 Classes for different types of people 88 Configurations or patterns for movement 90 Motivation 90 Dealing with complaints 90 CHAPTER 8 DIRECTORY/APPENDIX 91 Courses 91 Equipment 91
5 INTRODUCTION/PREFACE Aerobic fitness contributes more to your quality of life than perhaps any other aspect of fitness. If someone has reasonable aerobic fitness, they usually have a reasonably healthy heart, lungs and circulatory system. This means that they are able to breathe well, absorb plenty of oxygen into the blood, and efficiently transfer that oxygen throughout the body. It also means that waste products are able to be easily removed from the body by being absorbed into the blood and carried effectively to where they can be eliminated. A key ingredient for ensuring a long life is maintaining a healthy body and mind. By maintaining good aerobic fitness you will generally perform better in intellectual as well as physical pursuits; you will tend to resist illness better, live longer and find it easier to maintain a healthy mental condition. This book will assist you to improve your aerobic fitness levels, and improve your overall health. You will also learn about the body, its functions and how to assist others in obtaining their aerobic fitness goals. To remain aerobically fit, you need to regularly do something which will increase your heart rate above its normal level. This could be exercise, but it could also be work - in fact, it can be any physical activity that causes the heart to beat faster than normal. For this activity to be effective, the heart rate must be sustained at a raised level for at least 20 minutes in each session, and there must be at least three such sessions each week. If it is to be sustained at a raised level for 20 minutes, the session probably needs to go for at least 30 minutes, allowing time for the heart rate to gradually increase at the beginning, and then to gradually decrease at the end of the session. A Modern Epidemic The lack of aerobic fitness is in many ways a problem fostered by modern living. If you are not physically active at work or in your leisure, then it is likely that you could have a serious problem with your aerobic fitness. Combined with this, if you find physical activity difficult (e.g. climbing stairs, going for long walks, etc), and if you are overweight or frequently stressed, then you need to consider paying more attention to your aerobic fitness. What Can You Do The obvious way to improve aerobic fitness is to start exercising regularly by either attending classes or a gym, or perhaps jogging or walking regularly. Playing sport is another option but remember, you need three sessions a week, so playing sport once a week is not sufficient - even if it is for a couple of hours. Many people simply find these options very difficult to commit to. If you feel that way, there are lots of other choices which can be equally beneficial - remember, anything that raises the heart rate can be effective. Consider working in the garden, taking up a part-time job that involves physical activity, playing with your children more often, or if you don t have children of your own, perhaps becoming a scout or guide leader and getting active with a group of teenagers. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC EXERCISE Exercises fall into two different categories: 1) Anaerobic Exercises Anaerobic exercises concentrate on movements that require no, or minimal oxygen. They are quick, explosive actions that often last no more than 1.5 to 2 minutes. Anaerobic exercises concentrate on improving the strength, speed and power of muscular movements. During the first 2 minutes of exercise, the body cannot get enough oxygen to supply the heart and muscles (which need to work faster than normal). This is referred to as oxygen debt. Once the heart and lungs increase activity though, they are providing oxygen faster than normal to the body, allowing aerobic activity to supply sufficient energy for movement. Anaerobic exercise utilises the ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and creatine phosphate already stored in the muscles to meet energy requirements for the first 15 seconds of exercise. Then the body utilises glucose in the blood and glycogen in the muscles, which still requires no oxygen. This energy system can continue for up to around 2 minutes before demanding oxygen. Energy demand then switches to the aerobic system, where the body can use and deliver oxygen to the muscles. The body therefore cannot work at a fast, powerful manner for longer than 2 minutes because of its need for oxygen. This first phase of exercise produces a quick rise in heart rate. 2) Aerobic Exercise This phase focuses on making heart and respiration rates work more efficiently and, in doing so, they improve cardiorespiratory fitness. The heart rate will increase to a certain level and if it remains there then the aerobic energy system is predominant. Muscles are generally moved repeatedly and for a longer period of time when aerobically exercising and this occurs with the use of oxygen. The body wants more oxygen which it must breathe in allowing it to travel to the muscles (through the blood). Aerobic exercise normally burns carbohydrates already stored in the blood (glucose), muscle and liver (glycogen) to meet the energy needs and then resorts to burning fat to supply energy. This system usually kicks in after approximately 1 minute and can continue for up to an hour or longer. PAGE 5
6 EXAMPLES OF GENERAL AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC EXERCISES Anaerobic exercises are high energy, usually flat out and rely on stored fuel. A 100-metre sprint, shot put and high jump are all good examples, however aerobic exercise is continuous like cycling, swimming and walking. Even sitting and reading a book is aerobic because the body is breathing at a constant rate which can be maintained. The more intense an aerobic activity is, then the greater the level of fitness that can be achieved. It can be said that aerobics classes, such as those commonly run at a gymnasium, are not just aerobic - because of the varied intensity of exercise they have. Participants may find themselves doing anaerobic-type exercises at some stages during the class. This provides variety to purely aerobic exercise and enables other aspects of fitness to be improved as well, such as muscular strength and endurance. Walking a dog is a common form of aerobic exercise PAGE 6
7 CHAPTER 1 HUMAN BIOLOGY & AEROBIC FITNESS To completely understand how aerobic exercise is performed and fitness is achieved, we need to know what happens from the moment we start to exert ourselves. When a movement in the human body occurs, energy must be released to cause that movement. This energy release occurs via a chemical reaction where adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is converted to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) plus free phosphorus, and large amounts of energy. The energy produced is primarily motion (i.e. the movement of muscles), and heat (which is lost). The body s use of energy is not particularly efficient since a lot of energy is usually lost during any movement. The small amount of available ATP in muscles is only sufficient to support a single explosive muscle contraction - such as throwing a ball, or a golf swing. If a sport, or some other performance, demands repeated muscle contractions then the ATP required must be constantly replenished from other fuel sources in the muscle. ADP can be reconstituted by adding energy to it - this converts it back to ATP. ATP is stored in every cell of the body, and is able to be transported throughout the body. SOURCES OF ATP ATP can be supplied to the body by three different ways: 1) ATP-PC System Here, the compound phosphocreatine is broken down to produce ATP. When phosphocreatine breaks down it produces phosphorus, creatine and energy. The energy produced is then able to be used by ADP to create ATP. Phosphocreatine is then able to be reconstituted with the addition of energy (which comes from foodstuffs and not from stored ATP/ADP reactions). These sources of energy are quickly rebuilt after effort, to the extent that 50% of the energy source is available around 30 seconds later, and 80% of this energy is restored within 2 minutes. 2) Lactic Acid System When a maximal effort is continued beyond the extent of the phosphate energy system, energy is provided from glycogen stored in the muscles. This system involves glucose (or glycogen) going through various chemical processes to produce ATP plus lactic acid. One glucose molecule is broken down into carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen, and in turn, produces two ATP molecules. The amount of ATP produced this way is small. This is a more complex procedure using only carbohydrates as its food fuel, and not requiring oxygen for the process. This energy is used, for example, in 400 metre track races and 100 metre swimming events. Continuous activities which lead to exhaustion in seconds result in maximal values for lactic acid accumulation. A problem with this process is that increased lactic acid levels can affect blood ph. Blood ph should be around 7.3, and never drop below 6.8. Nevertheless, the lactic acid system is self-limiting and so should not normally develop such problems. Generally, the result will be a feeling of fatigue which will cause an athlete (or someone doing heavy bursts of work) to slow down. Once lactic acid is produced, it requires 45 to 60 minutes to be removed, and for the athlete to recover. 3) Oxygen System This process involves the formation of carbon dioxide, water and ATP - from fats, proteins and/or carbohydrates, in the presence of oxygen. This process can produce large amounts of ATP. One molecule of sugar can result in the production of 36 molecules of ATP. This is more complex than the ATP-PC system. The only limiting factor for this system is usually the supply of oxygen. The body will normally try to use this system, and only use other systems to produce ATP if oxygen is in short supply. The short supply of oxygen can occur when: Activity first starts. Activity is placing higher demands on oxygen than what can be supplied by breathing. The Oxygen System is an AEROBIC system. The ATP-PC and Lactic Acid Systems are ANAEROBIC systems. The body uses anaerobic systems for energy supply only when aerobic systems cannot meet the demand. Example If a person is running a marathon, breathing may not be supplying ample oxygen to produce ATP through this system. Hence, the lactic acid system may be used, resulting in a build-up of lactic acid - OR, the ATP-PC system may be used, resulting in a depletion of phosphocreatine in the muscles. After completing exercise, there may be a lactic acid build-up, and if so, the body needs to remove this excess. This lactic acid removal requires energy which is supplied aerobically - hence extra oxygen may be required. This extra oxygen requirement (after exercise) is called the oxygen debt. Krebs Cycle This is one particular series of reactions occurring in the oxygen system. Two main chemical reactions occur in this cycle: 1. Production of carbon dioxide. 2. Oxidation (i.e. removal of electrons). PAGE 7
Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance
 Learning aim B Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance Assessment criteria 2B.P5 2B.M5 2B.D2 Describe the function of the three energy systems in the production and release
Learning aim B Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance Assessment criteria 2B.P5 2B.M5 2B.D2 Describe the function of the three energy systems in the production and release
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes.
 This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
Understanding energy systems
 Understanding energy systems Key terms & definitions: Anaerobic: A process that does not require oxygen. Aerobic: A process that requires oxygen. ATP Yield: The total amount of ATP produced by an energy
Understanding energy systems Key terms & definitions: Anaerobic: A process that does not require oxygen. Aerobic: A process that requires oxygen. ATP Yield: The total amount of ATP produced by an energy
What is Physical Fitness?
 What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
Training our energy systems
 Training our energy systems By: Kelly Mackenzie, MSC, BPE, AFLCA trainer Regardless of what mode of exercise we are using, we can train all three of our energy systems. There are physiological adaptations
Training our energy systems By: Kelly Mackenzie, MSC, BPE, AFLCA trainer Regardless of what mode of exercise we are using, we can train all three of our energy systems. There are physiological adaptations
Work and Energy in Muscles
 Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Rowing Physiology. Intermediate. Editors: Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) Author: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR)
 2 Intermediate Rowing Physiology Author: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR) Editors: Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) 34 1.0 INTRODUCTION The FISA CDP booklet titled BASIC ROWING PHYSIOLOGY provided information
2 Intermediate Rowing Physiology Author: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR) Editors: Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) 34 1.0 INTRODUCTION The FISA CDP booklet titled BASIC ROWING PHYSIOLOGY provided information
Heart Monitor Training for the Compleat Idiot By John L. Parker, Jr.
 Estimating Your Max Heart Rate There are a number of ways to estimate your maximum heart rate. The best way is to get on a treadmill and slowly increase the speed or the incline until your heart rate is
Estimating Your Max Heart Rate There are a number of ways to estimate your maximum heart rate. The best way is to get on a treadmill and slowly increase the speed or the incline until your heart rate is
Interval Training. Interval Training
 Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE. Content Title: Methods of training. Practical Application/Explanation. Fartlek training. Continuous training
 Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
5TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
Energy System Demands of Fastpitch Softball
 Energy System Demands of Fastpitch Softball Salma Mehter Smith College 1/31/2011 Introduction A wise person once said, Practice doesn't make perfect; perfect practice makes perfect. This is clear when
Energy System Demands of Fastpitch Softball Salma Mehter Smith College 1/31/2011 Introduction A wise person once said, Practice doesn't make perfect; perfect practice makes perfect. This is clear when
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
 reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
A1 Reasons for taking part in activity. A2 Health, fitness, exercise and performance
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
- Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells.
![- Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells. - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells.](/thumbs/40/21014327.jpg) Cellular respiration - how cells make energy - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - ATP - this is provided by the lungs - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood
Cellular respiration - how cells make energy - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - ATP - this is provided by the lungs - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas
 Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
Unit 5 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Unit 5 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Advanced Concepts What is the abbreviated name of this molecule? What is its purpose? What are the three parts of this molecule? Label each part with the
Unit 5 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Advanced Concepts What is the abbreviated name of this molecule? What is its purpose? What are the three parts of this molecule? Label each part with the
Biology I. Chapter 8/9
 Biology I Chapter 8/9 NOTEBOOK #1 Interest Grabber Suppose you earned extra money by having a part-time job. At first, you might be tempted to spend all of the money, but then you decide to open a bank
Biology I Chapter 8/9 NOTEBOOK #1 Interest Grabber Suppose you earned extra money by having a part-time job. At first, you might be tempted to spend all of the money, but then you decide to open a bank
TRAINING. chapter. how does. affect performance? Energy
 chapter 5 how does TRAINING affect performance? When individuals begin to train they are trying to improve the way their bodies function. They may wish to improve a particular way their bodies deliver
chapter 5 how does TRAINING affect performance? When individuals begin to train they are trying to improve the way their bodies function. They may wish to improve a particular way their bodies deliver
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT
 THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
Is ATP worth the investment?
 Is ATP worth the investment? ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) can be thought of as the currency of the cell. Most cellular metabolic processes cost a certain amount of ATP in order to happen. Furthermore,
Is ATP worth the investment? ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) can be thought of as the currency of the cell. Most cellular metabolic processes cost a certain amount of ATP in order to happen. Furthermore,
Gym Instructor. 01227 831 840 www.amactraining.co.uk. Course Guide. Course Package. Pre requisites
 Gym Instructor Course Guide Thank for you your interest in the Gym Instructor course with Amac. Within this course guide, you will find information on the different parts of the course and working as a
Gym Instructor Course Guide Thank for you your interest in the Gym Instructor course with Amac. Within this course guide, you will find information on the different parts of the course and working as a
Biology for Science Majors
 Biology for Science Majors Lab 10 AP BIOLOGY Concepts covered Respirometers Metabolism Glycolysis Respiration Anaerobic vs. aerobic respiration Fermentation Lab 5: Cellular Respiration ATP is the energy
Biology for Science Majors Lab 10 AP BIOLOGY Concepts covered Respirometers Metabolism Glycolysis Respiration Anaerobic vs. aerobic respiration Fermentation Lab 5: Cellular Respiration ATP is the energy
Calories. 23 calories from fat + 48 calories from carbohydrates + 32 calories from protein = 103 Calories in 1 cup of 1% milk
 Calories What's the magical formula to achieve your weight goals? Calorie needs are based on individual needs. In order for your weight to stay the same, the energy (or Calories) you consume must equal
Calories What's the magical formula to achieve your weight goals? Calorie needs are based on individual needs. In order for your weight to stay the same, the energy (or Calories) you consume must equal
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline
 AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR BARIATRIC SURGERY PATIENTS
 PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR BARIATRIC SURGERY PATIENTS The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment of Obesity (March 2005) BENEFITS OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY In order
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR BARIATRIC SURGERY PATIENTS The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment of Obesity (March 2005) BENEFITS OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY In order
Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes. What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it?
 Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it? Where does Energy come from? Ultimately, from the sun. It is transferred between organisms in the earth s lithosphere,
Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it? Where does Energy come from? Ultimately, from the sun. It is transferred between organisms in the earth s lithosphere,
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down
 Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX B4
 DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX B4 FAQ S 1. How does DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX B4 ingredients differ from over the counter typical energy drinks? DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX B4 is designed for a completely different reason.
DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX B4 FAQ S 1. How does DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX B4 ingredients differ from over the counter typical energy drinks? DYNAMAXX DYNAMAXX B4 is designed for a completely different reason.
Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration
 1 of 5 11/9/2011 8:11 PM Name: Hour: Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration Energy in General 1. Differentiate an autotroph from a hetertroph as it relates to obtaining energy and the processes
1 of 5 11/9/2011 8:11 PM Name: Hour: Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration Energy in General 1. Differentiate an autotroph from a hetertroph as it relates to obtaining energy and the processes
01227 831 840 www.amactraining.co.uk
 Children s Fitness Instructor Course Guide Thank for you your interest in the Children s Fitness Instructor course w ith Amac. Within this course guide, you will find in for mation on the different par
Children s Fitness Instructor Course Guide Thank for you your interest in the Children s Fitness Instructor course w ith Amac. Within this course guide, you will find in for mation on the different par
Standard Grade. Swimming. Name. Teacher. Class. P.E. Department Crieff High School. Miss Steele Jan 10 1
 Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism)
 Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011. Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011 Physical Education 48901 (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011 Physical Education 48901 (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
GCSE P.E. REVISION BOOKLET
 GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
Chapter 9: Strength Training Program Design. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 9: Strength Training Program Design ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction There are six (6) types of resistance training: 1. Isometric force development 2. Concentric force development
Chapter 9: Strength Training Program Design ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction There are six (6) types of resistance training: 1. Isometric force development 2. Concentric force development
Biology 20 Cellular Respiration Review NG Know the process of Cellular Respiration (use this picture if it helps):
 Biology 20 Cellular Respiration Review NG Know the process of Cellular Respiration (use this picture if it helps): 1) How many ATP molecules are produced for each glucose molecule used in fermentation?
Biology 20 Cellular Respiration Review NG Know the process of Cellular Respiration (use this picture if it helps): 1) How many ATP molecules are produced for each glucose molecule used in fermentation?
Photo Cell Resp Practice. A. ATP B. oxygen C. DNA D. water. The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants.
 Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
THE LIVING CELL. Cells also have variety of shapes. Plant cells are often rectangular or polygonal, while egg cells are usually spherical.
 THE LIVING CELL A Tour of the cell The cell is the smallest and the basic unit of structure of all organisms. There are two main types or categories of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic
THE LIVING CELL A Tour of the cell The cell is the smallest and the basic unit of structure of all organisms. There are two main types or categories of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic
1. Enzymes. Biochemical Reactions. Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism. 1. Enzymes. 2. ATP Production. 3. Autotrophic Processes
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
2. Which type of macromolecule contains high-energy bonds and is used for long-term energy storage?
 Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Text, Diagrams, Assessments, and Link to Standards Focus Questions 1) What is cellular respiration? 2) How is cellular respiration connected to breathing? 3) If
Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Text, Diagrams, Assessments, and Link to Standards Focus Questions 1) What is cellular respiration? 2) How is cellular respiration connected to breathing? 3) If
Topic 3: Nutrition, Photosynthesis, and Respiration
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
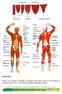 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Twenty Three 1
 23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
Cellular Energy. 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following?
 Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
In structured sports programs, participation and enjoyment should be emphasized rather than competition and winning.
 Preschool Children The California Department of Health Services Physical Activity for Children, Youth, and Adults All preschool children should participate every in a form of physical activity appropriate
Preschool Children The California Department of Health Services Physical Activity for Children, Youth, and Adults All preschool children should participate every in a form of physical activity appropriate
BACKPACKING TRIP DIFFICULTY SNAPSHOT
 BACKPACKING TRIP DIFFICULTY SNAPSHOT Of course these ratings are only an indicator of hike difficulty - every hike has its variables beyond elevation gain and distance including weather, experience/fitness,
BACKPACKING TRIP DIFFICULTY SNAPSHOT Of course these ratings are only an indicator of hike difficulty - every hike has its variables beyond elevation gain and distance including weather, experience/fitness,
The correct answer is d C. Answer c is incorrect. Reliance on the energy produced by others is a characteristic of heterotrophs.
 1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis
 Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
Training for a 10k Event By Ben Wisbey
 Training for a 10k Event By Ben Wisbey Introduction Many runners set their sights on running the marathon as they feel they have no speed, and are therefore not suited to shorter races, such as 5 and 10km
Training for a 10k Event By Ben Wisbey Introduction Many runners set their sights on running the marathon as they feel they have no speed, and are therefore not suited to shorter races, such as 5 and 10km
Physical Activity and Weight Control
 Physical Activity and Weight Control WIN Weight-control Information Network U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Physical Activity and Weight Control Physical activity
Physical Activity and Weight Control WIN Weight-control Information Network U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Physical Activity and Weight Control Physical activity
Cellular Respiration An Overview
 Why? Cellular Respiration An Overview What are the phases of cellular respiration? All cells need energy all the time, and their primary source of energy is ATP. The methods cells use to make ATP vary
Why? Cellular Respiration An Overview What are the phases of cellular respiration? All cells need energy all the time, and their primary source of energy is ATP. The methods cells use to make ATP vary
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form
 IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
ABOUT US. Why train using the ACTIV8 Program? - Restoration of movement. Performance Enhancement & Injury Prevention
 ABOUT US Mission Statement - ACTIV8 Strength and Conditioning Program is committed to providing training experience for each participant. Our focus is on building a strong and functionally fit human being
ABOUT US Mission Statement - ACTIV8 Strength and Conditioning Program is committed to providing training experience for each participant. Our focus is on building a strong and functionally fit human being
Fit for Flight. Developing a Personal Fitness Program
 Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
What are the similarities between this equation for burning glucose and the equation for cellular respiration of glucose when oxygen is available?
 Cellular Respiration in Yeast Adapted from Alcoholic Fermentation in Yeast Investigation in the School District of Philadelphia Biology Core Curriculum 2009 by Dr. Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron,
Cellular Respiration in Yeast Adapted from Alcoholic Fermentation in Yeast Investigation in the School District of Philadelphia Biology Core Curriculum 2009 by Dr. Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron,
The Impact of Alcohol
 A Newsletter From Your EAP and WorkLife Service The Impact of Alcohol Why is it that two people can drink the same amount of alcohol and one will seem fine while the other will appear buzzed? Many factors
A Newsletter From Your EAP and WorkLife Service The Impact of Alcohol Why is it that two people can drink the same amount of alcohol and one will seem fine while the other will appear buzzed? Many factors
Respiration Worksheet. Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food. Types of Respiration. Aerobic Respiration
 Respiration Worksheet Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food The food involved in respiration is usually Internal respiration is controlled by which allow energy to be released in The
Respiration Worksheet Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food The food involved in respiration is usually Internal respiration is controlled by which allow energy to be released in The
The Physiology of Fitness
 Unit 2: The Physiology of Fitness Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 5 Guided learning hours: 30 Aim and purpose R/502/5486 BTEC National This unit provides an opportunity for learners to explore the
Unit 2: The Physiology of Fitness Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 5 Guided learning hours: 30 Aim and purpose R/502/5486 BTEC National This unit provides an opportunity for learners to explore the
energy and training module ITU Competitive Coach
 37 energy and training module ITU Competitive Coach Produced by the International Triathlon Union, 2007 38 39 energy & training Have you ever wondered why some athletes shoot off the start line while others
37 energy and training module ITU Competitive Coach Produced by the International Triathlon Union, 2007 38 39 energy & training Have you ever wondered why some athletes shoot off the start line while others
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines
 USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1
 Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Fitness Training Program
 Sample Endurance Factor Introduction Fitness Training Congratulations on completing your Metabolic Profile! Until recently, this type of assessment was available only to human performance labs and training
Sample Endurance Factor Introduction Fitness Training Congratulations on completing your Metabolic Profile! Until recently, this type of assessment was available only to human performance labs and training
12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey
 12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey Introduction The half marathon is often the intermediate goal for those runners looking at doing their first marathon. It is also the longest distance
12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey Introduction The half marathon is often the intermediate goal for those runners looking at doing their first marathon. It is also the longest distance
One Stop Shop For Educators. Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Physical Education
 PE3.1: Demonstrates competency in motor skills and movement patterns needed to perform a variety of physical activities. Description: Students demonstrate mature form in all locomotor and non-locomotor
PE3.1: Demonstrates competency in motor skills and movement patterns needed to perform a variety of physical activities. Description: Students demonstrate mature form in all locomotor and non-locomotor
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Bioenergetics Module A Anchor 3
 Bioenergetics Module A Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - ATP can easily release and store energy by breaking and re-forming the bonds between its phosphate groups. This characteristic of ATP makes it exceptionally
Bioenergetics Module A Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - ATP can easily release and store energy by breaking and re-forming the bonds between its phosphate groups. This characteristic of ATP makes it exceptionally
1. Explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration.
 : Harvesting Chemical Energy Name Period Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second to look at the big picture. Photosynthesis and cellular
: Harvesting Chemical Energy Name Period Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second to look at the big picture. Photosynthesis and cellular
4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program
 Natural Health Solutions 14698 Galaxie Ave. Apple Valley, MN 55124 (952) 891-22225 4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program Welcome and Congratulations! This is an important decision towards improving
Natural Health Solutions 14698 Galaxie Ave. Apple Valley, MN 55124 (952) 891-22225 4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program Welcome and Congratulations! This is an important decision towards improving
9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS
 Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
Cellular Respiration Worksheet 1. 1. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain.
 Cellular Respiration Worksheet 1 1. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain. 2. Where in the cell does the glycolysis part of cellular
Cellular Respiration Worksheet 1 1. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain. 2. Where in the cell does the glycolysis part of cellular
Todays Outline. Metabolism. Why do cells need energy? How do cells acquire energy? Metabolism. Concepts & Processes. The cells capacity to:
 and Work Metabolic Pathways Enzymes Features Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Membrane Transport Diffusion Osmosis Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Todays Outline -Releasing Pathways
and Work Metabolic Pathways Enzymes Features Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Membrane Transport Diffusion Osmosis Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Todays Outline -Releasing Pathways
What affects an enzyme s activity? General environmental factors, such as temperature and ph. Chemicals that specifically influence the enzyme.
 CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
pathway that involves taking in heat from the environment at each step. C.
 Study Island Cell Energy Keystone Review 1. Cells obtain energy by either capturing light energy through photosynthesis or by breaking down carbohydrates through cellular respiration. In both photosynthesis
Study Island Cell Energy Keystone Review 1. Cells obtain energy by either capturing light energy through photosynthesis or by breaking down carbohydrates through cellular respiration. In both photosynthesis
rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul
 rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul Contents Acknowledgements Introduction ix xi Mandatory units 1 Anatomy for
rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul Contents Acknowledgements Introduction ix xi Mandatory units 1 Anatomy for
Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness. To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical
 Chapter 1 Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Chapter objectives: To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical fitness. To describe different
Chapter 1 Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Chapter objectives: To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical fitness. To describe different
Strength Training For Runners
 Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Written examination. Friday 8 November 2002
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2002 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter PHYSICAL EDUCATION Written examination Friday 8 November 2002 Reading time: 3.00 pm
Victorian Certificate of Education 2002 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter PHYSICAL EDUCATION Written examination Friday 8 November 2002 Reading time: 3.00 pm
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Sport & Recreation. Simple steps to plan your cardio workouts
 Sport & Recreation Simple steps to plan your cardio workouts What is it and why would you do it? Getting your heart rate up to certain levels and making your lungs work harder for 20-60 minutes, 3 to 5
Sport & Recreation Simple steps to plan your cardio workouts What is it and why would you do it? Getting your heart rate up to certain levels and making your lungs work harder for 20-60 minutes, 3 to 5
Exercise Metabolism II
 Exercise Metabolism II Oxygen debt & deficit Lactate threshold --------------------------------------------------------------- VO2max, VO2max and Lactate threshold CHO and fat metabolism during exercise
Exercise Metabolism II Oxygen debt & deficit Lactate threshold --------------------------------------------------------------- VO2max, VO2max and Lactate threshold CHO and fat metabolism during exercise
FAT 411: Why you can t live without it
 FAT 411: Why you can t live without it In the many nutrition talks I have done in the past, I have received numerous questions surrounding the somewhat misunderstood macronutrient of fat. Question range
FAT 411: Why you can t live without it In the many nutrition talks I have done in the past, I have received numerous questions surrounding the somewhat misunderstood macronutrient of fat. Question range
Diabetes and Exercise:
 Diabetes and Exercise: The Great Blood Sugar Balancing Act By Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Last month, I saw two very different clients with two very similar problems. One was a 62 year-old man named Anthony
Diabetes and Exercise: The Great Blood Sugar Balancing Act By Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Last month, I saw two very different clients with two very similar problems. One was a 62 year-old man named Anthony
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Two Forms of Energy
 Module 2D - Energy and Metabolism Objective # 19 All living organisms require energy for survival. In this module we will examine some general principles about chemical reactions and energy usage within
Module 2D - Energy and Metabolism Objective # 19 All living organisms require energy for survival. In this module we will examine some general principles about chemical reactions and energy usage within
Strength and Conditioning Program
 Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
Rehabilitation. Modalities and Rehabilitation. Basics of Injury Rehabilitation. Injury Rehabilitation. Vocabulary. Vocabulary
 Modalities and Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Chapter 12: Basics of Injury Rehabilitation Vocabulary Balance: ability to maintain our center of gravity over a base of support Kinesthesia: the ability to
Modalities and Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Chapter 12: Basics of Injury Rehabilitation Vocabulary Balance: ability to maintain our center of gravity over a base of support Kinesthesia: the ability to
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4890)
 Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2012 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2012 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES. Bio 171 Week 6
 RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Bio 171 Week 6 Procedure Label test tubes well, including group name 1) Add solutions listed to small test tubes 2) For
RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Bio 171 Week 6 Procedure Label test tubes well, including group name 1) Add solutions listed to small test tubes 2) For
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Electrons carried in NADH Mitochondrion Glucose Glycolysis Pyruvic acid Krebs Cycle Electrons carried in NADH and FADH 2 Electron Transport Chain Cytoplasm Mitochondrion
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Electrons carried in NADH Mitochondrion Glucose Glycolysis Pyruvic acid Krebs Cycle Electrons carried in NADH and FADH 2 Electron Transport Chain Cytoplasm Mitochondrion
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration. Chapter 8
 Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration Chapter 8 Overview of Glucose Breakdown The overall equation for the complete breakdown of glucose is: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + ATP The
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration Chapter 8 Overview of Glucose Breakdown The overall equation for the complete breakdown of glucose is: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + ATP The
NUTRITION MACRONUTRIENT RATIO
 It s that time of year again when we say goodbye to summertime shorts, slops and vests and say hello to long pants, coats and thermal underwear. While most people despise the chilly winter, for those of
It s that time of year again when we say goodbye to summertime shorts, slops and vests and say hello to long pants, coats and thermal underwear. While most people despise the chilly winter, for those of
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes?
 Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
CLASS DESCRIPTIONS BY FITNESS LEVEL
 LOW IMPACT/ BEGINNER FITNESS: Beginner s Yoga: Come explore the basics of yoga. This class is perfect for beginner students, seniors or someone interested in exploring the foundations of the practice in
LOW IMPACT/ BEGINNER FITNESS: Beginner s Yoga: Come explore the basics of yoga. This class is perfect for beginner students, seniors or someone interested in exploring the foundations of the practice in
Nutrition for Endurance: Cycling
 Nutrition for Endurance: Cycling Superior cycling ability comes from good training. However, without good food choices and the correct timing of meals, your training and performance will suffer. You need
Nutrition for Endurance: Cycling Superior cycling ability comes from good training. However, without good food choices and the correct timing of meals, your training and performance will suffer. You need
