Networking. Network Performance Issues. Networking Overview. Networking Overview. To maintain high performance: Section Contents:
|
|
|
- Bertha Parker
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 143 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 145 Networking Network Performance Issues Section Contents: Overview The Socket API SKBuffs Network Devices Linux IP and TCP/UDP To maintain high performance: Perform as few copies as possible Perform copy+checksum Align headers on cache boundaries Keep interrupts enabled as much as possible Cache all recent routing decisions Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 144 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 146 Networking Overview Networking presents several problems to an O/S: Exposure to hostile, unvalidated activity Complex asynchronous operations Many protocols exist in many arrangements over many transports Performance is critical Networking Overview We can define networking as a stack of interacting, interchangeable components Separate functionality from transport Provide a uniform API layer Enable modular implementation Compare with the Streams model... (compromise between modularity and performance)
2 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 147 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 149 Networking components The struct socket Socket API VFS Socket layer Protocol drivers Queue Discipline (2.2+ only) Device drivers SKBuff services A socket deals only with the API s communication endpoint. It contains: Basic socket type information Strategy function entry points List of other sockets connected/awaiting connection The socket encodes no information about the state of an actual protocol Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 148 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 150 The Networking API Linux implements a BSD Socket API: Allocate a struct socket for each open socket Associate a struct inode with each socket The API is entirely portable between protocols Use socket/inode strategy functions to implement protocol-specific routines Moving data between layers All networking data is built up and passed around in struct sk_buff buffers. All packets are stored contiguously Data may be appended or prepended to the sk_buff if space allows Facilities are provided for easy queueing of sk_buffs Provide atomic (interrupt-safe) sk_buff operations
3 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 151 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 153 The SKBuff Getting data to a device driver Empty SKBuff Head Tail Tailroom Sending is relatively simple. The device management layer maintains one queue of sk_buffs for each priority at each device. dev_queue_xmit() queues a sk_buff to a device SKBuff in use Data Headroom Head Tail If necessary, build driver-specific headers when packet is queued (ARP) Drop packets if driver queue length is exceeded (device s LINK STATE XOFF state bit is set to throttle output) Send the packet only if the driver is idle Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 152 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 154 Network Device Drivers Provide a standard interface to networking device drivers. struct net device describes any single network device, containing: Interface name Resources allocated to the device Interface status Device driver strategy routines Getting data to a device driver: Scheduling Under 2.2+, device transmit queues have a struct Qdisc queue discipline to schedule packets. Presents a standard interface for inserting/removing packets on an output queue net/sched/sch *.c implements multiple queuing policies: FIFO, prioritised, traffic shaper... net/sched/cls *.c implements multiple classifier schemes: each packet can be selected on by route, firewall rull or by more complex policies.
4 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 155 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 157 Getting data to a device driver: dst_entry Getting data from a device driver We maintain a dst_entry structure to identify recent packet destinations, which: Corresponds to a higher protocol s routing decision (eg. IP s struct rtable) Maintains: hh_cache pointer (for ARP resolution) Per-path protocol state (MTU) Rate limiting counters (RSVP) The device driver receive path is first triggered in a top-half hard interrupt: Allocate a sk buff Receive the packet into the sk buff and queue it with netif_rx(), which: Adds the packet to the input queue for this CPU (global backlog on 2.2) Raises the soft IRQ to process the queue Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 156 Inside the Linux Kernel Networking 158 Getting data from a device driver Receiving data is harder: it is always received on an interrupt. 2.2 deals with synchronisation issues are dealt with by using the interrupt bottom-half 2.3 introduces the new softnet architecture: Separate transmit and receive soft irqs are maintained for each CPU All net data structures are now properly SMP-spinlocked to allow concurrent interrupts Extensive use of r/w locks The Network Soft IRQ net rx action (net bh on 2.2) must: Send any outstanding queued packets to their drivers/qdiscs Roll through the backlog: Try to bridge or fastroute the packet first Fetch the protocol ID (set by the device driver) Pass the packet to the appropriate protocol: hash protocol lists by protocol ID
5 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 159 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 161 Linux and TCP/IP Multiple protocols are supported well in the kernel. IP is just one, glued to the net stack with: All network devices maintain multiple protocol-specific pointers; for IP, use the per-device in_device (holds IP addresses etc.) struct The struct sock maintains much internal TCP-specific information for active, bound connections: Sequence numbers Window/congestion control Have one struct sock per connected struct socket IP Device Interface ip_rcv() handles all packets coming from the device driver layers, and performs: Accounting/Firewalling Assignment to alias device Reassembly of IP fragments Delivery of packet to a local protocol handler, or Forwarding of routable packets via ip_forward() Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 160 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 162 TCP/IP Components IP Routing Decisions Socket interface ip_rcv() needs to distinguish between packets destined for the local machine and those to be forwarded. TCP UDP ICMP Perform a full ip_route_input when we see the packet IP routing Firewall chains Route cache ARP We only make one pass over the routing tables The routing dst_entry is stored in the sk_buff Device drivers/qdisc Finally, pass the skb to the input method in the dst entry for forwarding or local delivery
6 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 163 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 165 IP Fragment Management Manage incoming fragments by maintaining a cache of incomplete datagrams: Maintain a struct ipq for each incomplete datagram Maintain a struct ipfrag for each fragment Hold all outstanding fragments on a ipq list, and all ipqs on the ipq_hash hash table IP Forwarding ip_forward() deals with packets not destined for a local socket: Use the sk_buff s existing routing information to work out the next hop Generate diagnostic ICMP for unroutable packets Call ip_send() to either fragment the packet, or directly dev_queue_xmit() on the destination interface Simply drop packets if we don t have enough memory Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 164 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 166 IP Fragment Processing Incoming IP fragments are passed to ip_defrag() either on local delivery or if a netfilter module wants to assemble fragments: Search the ipqueue for an incomplete datagram (ipq) which matches this packet, and create a new ipq if necessary Set a timer to expire the ipq in 30 seconds When all fragments have arrived, call ip_glue() to merge them, and return a new sk_buff IP Routing We maintain two separate routing databases: the permanent FIB (Forwarding Information Base) Set up by the user Indexed by route mask, type-of-service, and source address and interface; a transient route cache.
7 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 167 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 169 The Route Cache The struct rtable encodes and caches a single routing decision: ip_route_output returns a struct rtable (processes like ICMP may want to know a route before they have a sk buff to send) ip_route_input sets the sk_buff route directly. For performance, use a hash table to cache routes If route not cached, pass it to ip_route_*_slow NetFilter The 2.3 kernel s NetFilter code replaces the old firewalling/nat code: Separate rule sets (iptables) for incoming; forwarded; locally received; locally injected; and output packets, plus user-defined iptables A generic NF HOOK call can be called anywhere in any network stack, specifying which iptable to run New tables or rule types may be registered dynamically Rules may return a verdict of accept or drop, and may also modify or steal the sk buff Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 168 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 170 The Route Database FIB organisation is optimised for performance: Group routes into zones according to the netmask length For each zone, maintain a separate 256-entry hash table of routing nodes Allow fib_node routing nodes to share as much data (interface, protocol, metrics etc.) as possible via shared fib_info Allow update via netlink character device NetFilter uses The NetFilter framework implements many pieces of the old 2.2 IP stack: Firewalling is accomplished by calling the filter iptable The NAT iptable can be used to modify packets: source-address NAT is used to implement masquerading dest-address NAT is used to implement transparent proxying
8 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 171 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 173 IP Aliases Kernel transparently supports IP aliases: Autodetect interface names of the form dev:num Link each alias to its root interface Routing logic reroutes packets destined to an alias to the root interface ARP support is automatic for all defined interfaces Neighbourhood maps The ARP database is just one special case of a neighbourhood table (also used for IPv6 neighbourhood discovery): struct neigh_table provides hashed lookup and management of struct neighbours Each neighbour references a hh_cache hardware header for the link level The ARP database creates provides neighbourhood methods for ARP solicitation Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 172 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 174 The Address Resolution Protocol ARP is the protocol which resolves IP addresses into ethernet HW addresses. The old style code special-cased ARP: struct arp_table maintains a single ARP entry Maintain a hash table of ARP entries Each entry references a list of sk_buffs held up for this ARP request ARP is called by the device s rebuild_header() Use netlink interface to the arpd user-mode cache The UDP Protocol UDP has no connections: all we need to do is route packets to open sockets. Rely on the socket API layer to create sockets for us Use udp v4 lookup() to identify the destination socket for incoming packets Maintain a per-protocol hash table of sockets Maintain a single-entry last-used-socket cache Transmitted packets go straight to the IP layer
9 Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 175 The TCP Protocol TCP has major differences from UDP, including: Connections maintained: sockets have a backlog list of pending connections Many non-data types of packet to be dealt with: maintain connection state machine Data transport is reliable Maintain flow rates and round-trip times for flow control Inside the Linux Kernel Linux TCP/IP 176 TCP Reliable Data Stream In order to present reliable communications to the API: Keep sk_buffs on the struct sock write queue until acknowledged Retry transmits automatically on timeouts Queue incoming packets until they can be presented in order
Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets
 Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Sockets IP lets us send data between machines TCP & UDP are transport layer protocols Contain port number to identify
Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Sockets IP lets us send data between machines TCP & UDP are transport layer protocols Contain port number to identify
Network packet capture in Linux kernelspace
 Network packet capture in Linux kernelspace An overview of the network stack in the Linux kernel Beraldo Leal beraldo@ime.usp.br http://www.ime.usp.br/~beraldo/ Institute of Mathematics and Statistics
Network packet capture in Linux kernelspace An overview of the network stack in the Linux kernel Beraldo Leal beraldo@ime.usp.br http://www.ime.usp.br/~beraldo/ Institute of Mathematics and Statistics
Chapter 9. IP Secure
 Chapter 9 IP Secure 1 Network architecture is usually explained as a stack of different layers. Figure 1 explains the OSI (Open System Interconnect) model stack and IP (Internet Protocol) model stack.
Chapter 9 IP Secure 1 Network architecture is usually explained as a stack of different layers. Figure 1 explains the OSI (Open System Interconnect) model stack and IP (Internet Protocol) model stack.
Firewalls. Chien-Chung Shen cshen@cis.udel.edu
 Firewalls Chien-Chung Shen cshen@cis.udel.edu The Need for Firewalls Internet connectivity is essential however it creates a threat vs. host-based security services (e.g., intrusion detection), not cost-effective
Firewalls Chien-Chung Shen cshen@cis.udel.edu The Need for Firewalls Internet connectivity is essential however it creates a threat vs. host-based security services (e.g., intrusion detection), not cost-effective
Ethernet. Ethernet. Network Devices
 Ethernet Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design Ethernet Ethernet is a term used to refer to a diverse set of frame based networking
Ethernet Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design Ethernet Ethernet is a term used to refer to a diverse set of frame based networking
Intro to Linux Kernel Firewall
 Intro to Linux Kernel Firewall Linux Kernel Firewall Kernel provides Xtables (implemeted as different Netfilter modules) which store chains and rules x_tables is the name of the kernel module carrying
Intro to Linux Kernel Firewall Linux Kernel Firewall Kernel provides Xtables (implemeted as different Netfilter modules) which store chains and rules x_tables is the name of the kernel module carrying
RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
 SFWR 4C03: Computer Networks and Computer Security January 19-22 2004 Lecturer: Kartik Krishnan Lectures 7-9 RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol When a system with a local disk is bootstrapped it
SFWR 4C03: Computer Networks and Computer Security January 19-22 2004 Lecturer: Kartik Krishnan Lectures 7-9 RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol When a system with a local disk is bootstrapped it
Chapter 11 I/O Management and Disk Scheduling
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 11 I/O Management and Disk Scheduling Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, NZ 2008, Prentice Hall I/O Devices Roadmap Organization
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 11 I/O Management and Disk Scheduling Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, NZ 2008, Prentice Hall I/O Devices Roadmap Organization
Presentation of Diagnosing performance overheads in the Xen virtual machine environment
 Presentation of Diagnosing performance overheads in the Xen virtual machine environment September 26, 2005 Framework Using to fix the Network Anomaly Xen Network Performance Test Using Outline 1 Introduction
Presentation of Diagnosing performance overheads in the Xen virtual machine environment September 26, 2005 Framework Using to fix the Network Anomaly Xen Network Performance Test Using Outline 1 Introduction
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. 1. IP address for this host computer 2. Subnet mask 3. Default gateway address
 Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
Technical Support Information Belkin internal use only
 The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR
 Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
Subnetting,Supernetting, VLSM & CIDR WHAT - IP Address Unique 32 or 128 bit Binary, used to identify a system on a Network or Internet. Network Portion Host Portion CLASSFULL ADDRESSING IP address space
Network Programming TDC 561
 Network Programming TDC 561 Lecture # 1 Dr. Ehab S. Al-Shaer School of Computer Science & Telecommunication DePaul University Chicago, IL 1 Network Programming Goals of this Course: Studying, evaluating
Network Programming TDC 561 Lecture # 1 Dr. Ehab S. Al-Shaer School of Computer Science & Telecommunication DePaul University Chicago, IL 1 Network Programming Goals of this Course: Studying, evaluating
Transport and Network Layer
 Transport and Network Layer 1 Introduction Responsible for moving messages from end-to-end in a network Closely tied together TCP/IP: most commonly used protocol o Used in Internet o Compatible with a
Transport and Network Layer 1 Introduction Responsible for moving messages from end-to-end in a network Closely tied together TCP/IP: most commonly used protocol o Used in Internet o Compatible with a
Understanding TCP/IP. Introduction. What is an Architectural Model? APPENDIX
 APPENDIX A Introduction Understanding TCP/IP To fully understand the architecture of Cisco Centri Firewall, you need to understand the TCP/IP architecture on which the Internet is based. This appendix
APPENDIX A Introduction Understanding TCP/IP To fully understand the architecture of Cisco Centri Firewall, you need to understand the TCP/IP architecture on which the Internet is based. This appendix
Linux firewall. Need of firewall Single connection between network Allows restricted traffic between networks Denies un authorized users
 Linux firewall Need of firewall Single connection between network Allows restricted traffic between networks Denies un authorized users Linux firewall Linux is a open source operating system and any firewall
Linux firewall Need of firewall Single connection between network Allows restricted traffic between networks Denies un authorized users Linux firewall Linux is a open source operating system and any firewall
Linux Kernel Networking. Raoul Rivas
 Linux Kernel Networking Raoul Rivas Kernel vs Application Programming No memory protection Memory Protection We share memory with devices, scheduler Sometimes no preemption Can hog the CPU Segmentation
Linux Kernel Networking Raoul Rivas Kernel vs Application Programming No memory protection Memory Protection We share memory with devices, scheduler Sometimes no preemption Can hog the CPU Segmentation
Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3
 Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3 ARP - RFC 826, STD 37 DHCP - RFC 2131 ICMP - RFC 0792, STD 05 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Bootstrapping an end host Learning its own configuration parameters
Internet Control Protocols Reading: Chapter 3 ARP - RFC 826, STD 37 DHCP - RFC 2131 ICMP - RFC 0792, STD 05 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Bootstrapping an end host Learning its own configuration parameters
Lecture Computer Networks
 Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Thomas Nau, kiz Lecture Computer Networks
Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Thomas Nau, kiz Lecture Computer Networks
Objectives of Lecture. Network Architecture. Protocols. Contents
 Objectives of Lecture Network Architecture Show how network architecture can be understood using a layered approach. Introduce the OSI seven layer reference model. Introduce the concepts of internetworking
Objectives of Lecture Network Architecture Show how network architecture can be understood using a layered approach. Introduce the OSI seven layer reference model. Introduce the concepts of internetworking
21.4 Network Address Translation (NAT) 21.4.1 NAT concept
 21.4 Network Address Translation (NAT) This section explains Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT is also known as IP masquerading. It provides a mapping between internal IP addresses and officially
21.4 Network Address Translation (NAT) This section explains Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT is also known as IP masquerading. It provides a mapping between internal IP addresses and officially
Netfilter s connection tracking system
 PABLO NEIRA AYUSO Netfilter s connection tracking system Pablo Neira Ayuso has an M.S. in computer science and has worked for several companies in the IT security industry, with a focus on open source
PABLO NEIRA AYUSO Netfilter s connection tracking system Pablo Neira Ayuso has an M.S. in computer science and has worked for several companies in the IT security industry, with a focus on open source
AN833. The Microchip TCP/IP Stack INTRODUCTION STACK ARCHITECTURE REFERENCE MODEL
 M AN833 The Microchip TCP/IP Stack Author: INTRODUCTION Nilesh Rajbharti Microchip Technology Inc. There is nothing new about implementing TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) on Microchip
M AN833 The Microchip TCP/IP Stack Author: INTRODUCTION Nilesh Rajbharti Microchip Technology Inc. There is nothing new about implementing TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) on Microchip
NAT & IP Masquerade. Internet NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION INTRODUCTION. NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5. Internal PC 192.168.0.25
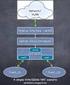 NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
Linux Network Security
 Linux Network Security Course ID SEC220 Course Description This extremely popular class focuses on network security, and makes an excellent companion class to the GL550: Host Security course. Protocols
Linux Network Security Course ID SEC220 Course Description This extremely popular class focuses on network security, and makes an excellent companion class to the GL550: Host Security course. Protocols
Transport Layer Protocols
 Transport Layer Protocols Version. Transport layer performs two main tasks for the application layer by using the network layer. It provides end to end communication between two applications, and implements
Transport Layer Protocols Version. Transport layer performs two main tasks for the application layer by using the network layer. It provides end to end communication between two applications, and implements
Improving DNS performance using Stateless TCP in FreeBSD 9
 Improving DNS performance using Stateless TCP in FreeBSD 9 David Hayes, Mattia Rossi, Grenville Armitage Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures, Technical Report 101022A Swinburne University of Technology
Improving DNS performance using Stateless TCP in FreeBSD 9 David Hayes, Mattia Rossi, Grenville Armitage Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures, Technical Report 101022A Swinburne University of Technology
TCP/IP Fundamentals. OSI Seven Layer Model & Seminar Outline
 OSI Seven Layer Model & Seminar Outline TCP/IP Fundamentals This seminar will present TCP/IP communications starting from Layer 2 up to Layer 4 (TCP/IP applications cover Layers 5-7) IP Addresses Data
OSI Seven Layer Model & Seminar Outline TCP/IP Fundamentals This seminar will present TCP/IP communications starting from Layer 2 up to Layer 4 (TCP/IP applications cover Layers 5-7) IP Addresses Data
Introduction to Network Operating Systems
 As mentioned earlier, different layers of the protocol stack use different kinds of addresses. We can now see that the Transport Layer (TCP) uses port addresses to route data to the correct process, the
As mentioned earlier, different layers of the protocol stack use different kinds of addresses. We can now see that the Transport Layer (TCP) uses port addresses to route data to the correct process, the
IP Layer Implementatoin of Linux Kernel Stack
 IP Layer Implementatoin of Linux Kernel Stack Fida Ullah Khattak Department of Communication and Networking School of Electrical Engineering Aalto University fidaullahkhattak@aaltofi ABSTRACT The foundations
IP Layer Implementatoin of Linux Kernel Stack Fida Ullah Khattak Department of Communication and Networking School of Electrical Engineering Aalto University fidaullahkhattak@aaltofi ABSTRACT The foundations
ΕΠΛ 674: Εργαστήριο 5 Firewalls
 ΕΠΛ 674: Εργαστήριο 5 Firewalls Παύλος Αντωνίου Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2011 Department of Computer Science Firewalls A firewall is hardware, software, or a combination of both that is used to prevent unauthorized
ΕΠΛ 674: Εργαστήριο 5 Firewalls Παύλος Αντωνίου Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2011 Department of Computer Science Firewalls A firewall is hardware, software, or a combination of both that is used to prevent unauthorized
Stateful Firewalls. Hank and Foo
 Stateful Firewalls Hank and Foo 1 Types of firewalls Packet filter (stateless) Proxy firewalls Stateful inspection Deep packet inspection 2 Packet filter (Access Control Lists) Treats each packet in isolation
Stateful Firewalls Hank and Foo 1 Types of firewalls Packet filter (stateless) Proxy firewalls Stateful inspection Deep packet inspection 2 Packet filter (Access Control Lists) Treats each packet in isolation
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 02 NAT and DHCP Tópicos Avançados de Redes
 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 1 1 Dynamic Assignment of IP addresses Dynamic assignment of IP addresses is desirable for several reasons: IP addresses are assigned on-demand Avoid manual IP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 1 1 Dynamic Assignment of IP addresses Dynamic assignment of IP addresses is desirable for several reasons: IP addresses are assigned on-demand Avoid manual IP
Mobile IP Network Layer Lesson 02 TCP/IP Suite and IP Protocol
 Mobile IP Network Layer Lesson 02 TCP/IP Suite and IP Protocol 1 TCP/IP protocol suite A suite of protocols for networking for the Internet Transmission control protocol (TCP) or User Datagram protocol
Mobile IP Network Layer Lesson 02 TCP/IP Suite and IP Protocol 1 TCP/IP protocol suite A suite of protocols for networking for the Internet Transmission control protocol (TCP) or User Datagram protocol
Internet Protocols Fall 2005. Lectures 7-8 Andreas Terzis
 Internet Protocols Fall 2005 Lectures 7-8 Andreas Terzis Outline Internet Protocol Service Model Fragmentation Addressing Original addressing scheme Subnetting CIDR Forwarding ICMP ARP Address Shortage
Internet Protocols Fall 2005 Lectures 7-8 Andreas Terzis Outline Internet Protocol Service Model Fragmentation Addressing Original addressing scheme Subnetting CIDR Forwarding ICMP ARP Address Shortage
Internet Architecture and Philosophy
 Internet Architecture and Philosophy Conceptually, TCP/IP provides three sets of services to the user: Application Services Reliable Transport Service Connectionless Packet Delivery Service The underlying
Internet Architecture and Philosophy Conceptually, TCP/IP provides three sets of services to the user: Application Services Reliable Transport Service Connectionless Packet Delivery Service The underlying
How do I get to www.randomsite.com?
 Networking Primer* *caveat: this is just a brief and incomplete introduction to networking to help students without a networking background learn Network Security. How do I get to www.randomsite.com? Local
Networking Primer* *caveat: this is just a brief and incomplete introduction to networking to help students without a networking background learn Network Security. How do I get to www.randomsite.com? Local
04 Internet Protocol (IP)
 SE 4C03 Winter 2007 04 Internet Protocol (IP) William M. Farmer Department of Computing and Software McMaster University 29 January 2007 Internet Protocol (IP) IP provides a connectionless packet delivery
SE 4C03 Winter 2007 04 Internet Protocol (IP) William M. Farmer Department of Computing and Software McMaster University 29 January 2007 Internet Protocol (IP) IP provides a connectionless packet delivery
Network Protocol Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring IP Addressing... 1 1.1 IP Introduction... 1 1.1.1 IP... 1 1.1.2 IP Routing Protocol... 1 1.2 Configuring IP Address Task List... 2 1.3 Configuring
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring IP Addressing... 1 1.1 IP Introduction... 1 1.1.1 IP... 1 1.1.2 IP Routing Protocol... 1 1.2 Configuring IP Address Task List... 2 1.3 Configuring
IP Network Layer. Datagram ID FLAG Fragment Offset. IP Datagrams. IP Addresses. IP Addresses. CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP
 CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
HONE: Correlating Host activities to Network communications to produce insight
 HONE: Correlating Host activities to Network communications to produce insight GLENN A. FINK, PH.D. Senior Scientist, Secure Cyber Systems SEAN STORY, PMP Project Manager, Software Engineering & Architectures
HONE: Correlating Host activities to Network communications to produce insight GLENN A. FINK, PH.D. Senior Scientist, Secure Cyber Systems SEAN STORY, PMP Project Manager, Software Engineering & Architectures
8.2 The Internet Protocol
 TCP/IP Protocol Suite HTTP SMTP DNS RTP Distributed applications Reliable stream service TCP UDP User datagram service Best-effort connectionless packet transfer Network Interface 1 IP Network Interface
TCP/IP Protocol Suite HTTP SMTP DNS RTP Distributed applications Reliable stream service TCP UDP User datagram service Best-effort connectionless packet transfer Network Interface 1 IP Network Interface
ACHILLES CERTIFICATION. SIS Module SLS 1508
 ACHILLES CERTIFICATION PUBLIC REPORT Final DeltaV Report SIS Module SLS 1508 Disclaimer Wurldtech Security Inc. retains the right to change information in this report without notice. Wurldtech Security
ACHILLES CERTIFICATION PUBLIC REPORT Final DeltaV Report SIS Module SLS 1508 Disclaimer Wurldtech Security Inc. retains the right to change information in this report without notice. Wurldtech Security
Network Layer: Network Layer and IP Protocol
 1 Network Layer: Network Layer and IP Protocol Required reading: Garcia 7.3.3, 8.1, 8.2.1 CSE 3213, Winter 2010 Instructor: N. Vlajic 2 1. Introduction 2. Router Architecture 3. Network Layer Protocols
1 Network Layer: Network Layer and IP Protocol Required reading: Garcia 7.3.3, 8.1, 8.2.1 CSE 3213, Winter 2010 Instructor: N. Vlajic 2 1. Introduction 2. Router Architecture 3. Network Layer Protocols
SEP Packet Capturing Using the Linux Netfilter Framework Ivan Pronchev pronchev@in.tum.de
 SEP Packet Capturing Using the Linux Netfilter Framework Ivan Pronchev pronchev@in.tum.de Today's Agenda Goals of the Project Motivation Revision Design Enhancements tcpdump vs kernel sniffer Interesting
SEP Packet Capturing Using the Linux Netfilter Framework Ivan Pronchev pronchev@in.tum.de Today's Agenda Goals of the Project Motivation Revision Design Enhancements tcpdump vs kernel sniffer Interesting
Internet Infrastructure Measurement: Challenges and Tools
 Internet Infrastructure Measurement: Challenges and Tools Internet Infrastructure Measurement: Challenges and Tools Outline Motivation Challenges Tools Conclusion Why Measure? Why Measure? Internet, with
Internet Infrastructure Measurement: Challenges and Tools Internet Infrastructure Measurement: Challenges and Tools Outline Motivation Challenges Tools Conclusion Why Measure? Why Measure? Internet, with
Availability Digest. www.availabilitydigest.com. Redundant Load Balancing for High Availability July 2013
 the Availability Digest Redundant Load Balancing for High Availability July 2013 A large data center can comprise hundreds or thousands of servers. These servers must not only be interconnected, but they
the Availability Digest Redundant Load Balancing for High Availability July 2013 A large data center can comprise hundreds or thousands of servers. These servers must not only be interconnected, but they
Customized Data Exchange Gateway (DEG) for Automated File Exchange across Networks
 Customized Data Exchange Gateway (DEG) for Automated File Exchange across Networks *Abhishek Vora B. Lakshmi C.V. Srinivas National Remote Sensing Center (NRSC), Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO),
Customized Data Exchange Gateway (DEG) for Automated File Exchange across Networks *Abhishek Vora B. Lakshmi C.V. Srinivas National Remote Sensing Center (NRSC), Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO),
The Lagopus SDN Software Switch. 3.1 SDN and OpenFlow. 3. Cloud Computing Technology
 3. The Lagopus SDN Software Switch Here we explain the capabilities of the new Lagopus software switch in detail, starting with the basics of SDN and OpenFlow. 3.1 SDN and OpenFlow Those engaged in network-related
3. The Lagopus SDN Software Switch Here we explain the capabilities of the new Lagopus software switch in detail, starting with the basics of SDN and OpenFlow. 3.1 SDN and OpenFlow Those engaged in network-related
Stateful Connection Tracking & Stateful NAT
 Stateful Connection Tracking & Stateful NAT Justin Pettit VMware Thomas Graf Noiro Networks, Cisco Agenda Connection Tracking NAT Integration of other stateful services We had a performance problem With
Stateful Connection Tracking & Stateful NAT Justin Pettit VMware Thomas Graf Noiro Networks, Cisco Agenda Connection Tracking NAT Integration of other stateful services We had a performance problem With
Removing The Linux Routing Cache
 Removing The Red Hat Inc. Columbia University, New York, 2012 Removing The 1 Linux Maintainership 2 3 4 5 Removing The My Background Started working on the kernel 18+ years ago. First project: helping
Removing The Red Hat Inc. Columbia University, New York, 2012 Removing The 1 Linux Maintainership 2 3 4 5 Removing The My Background Started working on the kernel 18+ years ago. First project: helping
VXLAN: Scaling Data Center Capacity. White Paper
 VXLAN: Scaling Data Center Capacity White Paper Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) Overview This document provides an overview of how VXLAN works. It also provides criteria to help determine when and where
VXLAN: Scaling Data Center Capacity White Paper Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) Overview This document provides an overview of how VXLAN works. It also provides criteria to help determine when and where
LECTURE 4 NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE
 SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION MTAT.08.021 LECTURE 4 NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE Prepared By: Amnir Hadachi and Artjom Lind University of Tartu, Institute of Computer Science amnir.hadachi@ut.ee / artjom.lind@ut.ee
SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION MTAT.08.021 LECTURE 4 NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE Prepared By: Amnir Hadachi and Artjom Lind University of Tartu, Institute of Computer Science amnir.hadachi@ut.ee / artjom.lind@ut.ee
www.mindteck.com 6LoWPAN Technical Overview
 www.mindteck.com 6LoWPAN Technical Overview 6LoWPAN : Slide Index Introduction Acronyms Stack Architecture Stack Layers Applications IETF documents References Confidential Mindteck 2009 2 6LoWPAN - Introduction
www.mindteck.com 6LoWPAN Technical Overview 6LoWPAN : Slide Index Introduction Acronyms Stack Architecture Stack Layers Applications IETF documents References Confidential Mindteck 2009 2 6LoWPAN - Introduction
Network Administration and Monitoring
 Network Administration and Monitoring Alessandro Barenghi Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingengeria Politecnico di Milano barenghi - at - elet.polimi.it April 17, 2013 Recap What did we
Network Administration and Monitoring Alessandro Barenghi Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingengeria Politecnico di Milano barenghi - at - elet.polimi.it April 17, 2013 Recap What did we
Hands On Activities: TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management
 Hands On Activities: TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management 1. TCP/IP Network Management Tasks TCP/IP network management tasks include Examine your physical and IP network address Traffic monitoring
Hands On Activities: TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management 1. TCP/IP Network Management Tasks TCP/IP network management tasks include Examine your physical and IP network address Traffic monitoring
Network-Oriented Software Development. Course: CSc4360/CSc6360 Instructor: Dr. Beyah Sessions: M-W, 3:00 4:40pm Lecture 2
 Network-Oriented Software Development Course: CSc4360/CSc6360 Instructor: Dr. Beyah Sessions: M-W, 3:00 4:40pm Lecture 2 Topics Layering TCP/IP Layering Internet addresses and port numbers Encapsulation
Network-Oriented Software Development Course: CSc4360/CSc6360 Instructor: Dr. Beyah Sessions: M-W, 3:00 4:40pm Lecture 2 Topics Layering TCP/IP Layering Internet addresses and port numbers Encapsulation
Software Datapath Acceleration for Stateless Packet Processing
 June 22, 2010 Software Datapath Acceleration for Stateless Packet Processing FTF-NET-F0817 Ravi Malhotra Software Architect Reg. U.S. Pat. & Tm. Off. BeeKit, BeeStack, CoreNet, the Energy Efficient Solutions
June 22, 2010 Software Datapath Acceleration for Stateless Packet Processing FTF-NET-F0817 Ravi Malhotra Software Architect Reg. U.S. Pat. & Tm. Off. BeeKit, BeeStack, CoreNet, the Energy Efficient Solutions
Computer Networks/DV2 Lab
 Computer Networks/DV2 Lab Room: BB 219 Additional Information: http://www.fb9dv.uni-duisburg.de/ti/en/education/teaching/ss08/netlab Equipment for each group: - 1 Server computer (OS: Windows 2000 Advanced
Computer Networks/DV2 Lab Room: BB 219 Additional Information: http://www.fb9dv.uni-duisburg.de/ti/en/education/teaching/ss08/netlab Equipment for each group: - 1 Server computer (OS: Windows 2000 Advanced
A Transport Protocol for Multimedia Wireless Sensor Networks
 A Transport Protocol for Multimedia Wireless Sensor Networks Duarte Meneses, António Grilo, Paulo Rogério Pereira 1 NGI'2011: A Transport Protocol for Multimedia Wireless Sensor Networks Introduction Wireless
A Transport Protocol for Multimedia Wireless Sensor Networks Duarte Meneses, António Grilo, Paulo Rogério Pereira 1 NGI'2011: A Transport Protocol for Multimedia Wireless Sensor Networks Introduction Wireless
ΕΠΛ 475: Εργαστήριο 9 Firewalls Τοίχοι πυρασφάλειας. University of Cyprus Department of Computer Science
 ΕΠΛ 475: Εργαστήριο 9 Firewalls Τοίχοι πυρασφάλειας Department of Computer Science Firewalls A firewall is hardware, software, or a combination of both that is used to prevent unauthorized Internet users
ΕΠΛ 475: Εργαστήριο 9 Firewalls Τοίχοι πυρασφάλειας Department of Computer Science Firewalls A firewall is hardware, software, or a combination of both that is used to prevent unauthorized Internet users
IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF SMTP RELAY SERVERS AN IN-KERNEL APPROACH MAYURESH KASTURE. (Under the Direction of Kang Li) ABSTRACT
 IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF SMTP RELAY SERVERS AN IN-KERNEL APPROACH by MAYURESH KASTURE (Under the Direction of Kang Li) ABSTRACT With continuous increase in average size and number of e-mails on the Internet,
IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF SMTP RELAY SERVERS AN IN-KERNEL APPROACH by MAYURESH KASTURE (Under the Direction of Kang Li) ABSTRACT With continuous increase in average size and number of e-mails on the Internet,
Exam 1 Review Questions
 CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Exam 1 Review Questions Jon Turner 10/2013 1. A user in St. Louis, connected to the internet via a 20 Mb/s (b=bits) connection retrieves a 250 KB (B=bytes) web
CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Exam 1 Review Questions Jon Turner 10/2013 1. A user in St. Louis, connected to the internet via a 20 Mb/s (b=bits) connection retrieves a 250 KB (B=bytes) web
Lecture 15. IP address space managed by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
 Lecture 15 IP Address Each host and router on the Internet has an IP address, which consist of a combination of network number and host number. The combination is unique; no two machines have the same
Lecture 15 IP Address Each host and router on the Internet has an IP address, which consist of a combination of network number and host number. The combination is unique; no two machines have the same
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks. Chapter 5: Ethernet
 CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza 2012. Network Chapter# 19 INTERNETWORK OPERATION
 Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza 2012 Network Chapter# 19 INTERNETWORK OPERATION Review Questions ٢ Network Chapter# 19 INTERNETWORK OPERATION 19.1 List
Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza 2012 Network Chapter# 19 INTERNETWORK OPERATION Review Questions ٢ Network Chapter# 19 INTERNETWORK OPERATION 19.1 List
Firewall Tutorial. KAIST Dept. of EECS NC Lab.
 Firewall Tutorial KAIST Dept. of EECS NC Lab. Contents What is Firewalls? Why Firewalls? Types of Firewalls Limitations of firewalls and gateways Firewalls in Linux What is Firewalls? firewall isolates
Firewall Tutorial KAIST Dept. of EECS NC Lab. Contents What is Firewalls? Why Firewalls? Types of Firewalls Limitations of firewalls and gateways Firewalls in Linux What is Firewalls? firewall isolates
Optimizing TCP Forwarding
 Optimizing TCP Forwarding Vsevolod V. Panteleenko and Vincent W. Freeh TR-2-3 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 {vvp, vin}@cse.nd.edu Abstract
Optimizing TCP Forwarding Vsevolod V. Panteleenko and Vincent W. Freeh TR-2-3 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 {vvp, vin}@cse.nd.edu Abstract
Quality of Service in the Internet. QoS Parameters. Keeping the QoS. Traffic Shaping: Leaky Bucket Algorithm
 Quality of Service in the Internet Problem today: IP is packet switched, therefore no guarantees on a transmission is given (throughput, transmission delay, ): the Internet transmits data Best Effort But:
Quality of Service in the Internet Problem today: IP is packet switched, therefore no guarantees on a transmission is given (throughput, transmission delay, ): the Internet transmits data Best Effort But:
Understanding Slow Start
 Chapter 1 Load Balancing 57 Understanding Slow Start When you configure a NetScaler to use a metric-based LB method such as Least Connections, Least Response Time, Least Bandwidth, Least Packets, or Custom
Chapter 1 Load Balancing 57 Understanding Slow Start When you configure a NetScaler to use a metric-based LB method such as Least Connections, Least Response Time, Least Bandwidth, Least Packets, or Custom
Internet Ideal: Simple Network Model
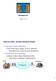 Middleboxes Reading: Ch. 8.4 Internet Ideal: Simple Network Model Globally unique identifiers Each node has a unique, fixed IP address reachable from everyone and everywhere Simple packet forwarding Network
Middleboxes Reading: Ch. 8.4 Internet Ideal: Simple Network Model Globally unique identifiers Each node has a unique, fixed IP address reachable from everyone and everywhere Simple packet forwarding Network
Firewall Implementation
 CS425: Computer Networks Firewall Implementation Ankit Kumar Y8088 Akshay Mittal Y8056 Ashish Gupta Y8410 Sayandeep Ghosh Y8465 October 31, 2010 under the guidance of Prof. Dheeraj Sanghi Department of
CS425: Computer Networks Firewall Implementation Ankit Kumar Y8088 Akshay Mittal Y8056 Ashish Gupta Y8410 Sayandeep Ghosh Y8465 October 31, 2010 under the guidance of Prof. Dheeraj Sanghi Department of
Virtualization: TCP/IP Performance Management in a Virtualized Environment Orlando Share Session 9308
 Virtualization: TCP/IP Performance Management in a Virtualized Environment Orlando Share Session 9308 Laura Knapp WW Business Consultant Laurak@aesclever.com Applied Expert Systems, Inc. 2011 1 Background
Virtualization: TCP/IP Performance Management in a Virtualized Environment Orlando Share Session 9308 Laura Knapp WW Business Consultant Laurak@aesclever.com Applied Expert Systems, Inc. 2011 1 Background
Introduction To Computer Networking
 Introduction To Computer Networking Alex S. 1 Introduction 1.1 Serial Lines Serial lines are generally the most basic and most common communication medium you can have between computers and/or equipment.
Introduction To Computer Networking Alex S. 1 Introduction 1.1 Serial Lines Serial lines are generally the most basic and most common communication medium you can have between computers and/or equipment.
Efficient Addressing. Outline. Addressing Subnetting Supernetting CS 640 1
 Efficient Addressing Outline Addressing Subnetting Supernetting CS 640 1 IPV4 Global Addresses Properties IPv4 uses 32 bit address space globally unique hierarchical: network + host 7 24 Dot Notation 10.3.2.4
Efficient Addressing Outline Addressing Subnetting Supernetting CS 640 1 IPV4 Global Addresses Properties IPv4 uses 32 bit address space globally unique hierarchical: network + host 7 24 Dot Notation 10.3.2.4
Allocating Network Bandwidth to Match Business Priorities
 Allocating Network Bandwidth to Match Business Priorities Speaker Peter Sichel Chief Engineer Sustainable Softworks psichel@sustworks.com MacWorld San Francisco 2006 Session M225 12-Jan-2006 10:30 AM -
Allocating Network Bandwidth to Match Business Priorities Speaker Peter Sichel Chief Engineer Sustainable Softworks psichel@sustworks.com MacWorld San Francisco 2006 Session M225 12-Jan-2006 10:30 AM -
Linux Kernel Architecture
 Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah payberah@yahoo.com Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah payberah@yahoo.com Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
Network layer: Overview. Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding
 Network layer: Overview Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding 1 Network layer functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every host, router application
Network layer: Overview Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding 1 Network layer functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every host, router application
Active-Active Firewall Cluster Support in OpenBSD
 Active-Active Firewall Cluster Support in OpenBSD David Gwynne School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, University of Queensland Submitted for the degree of Bachelor of Information
Active-Active Firewall Cluster Support in OpenBSD David Gwynne School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, University of Queensland Submitted for the degree of Bachelor of Information
OSBRiDGE 5XLi. Configuration Manual. Firmware 3.10R
 OSBRiDGE 5XLi Configuration Manual Firmware 3.10R 1. Initial setup and configuration. OSBRiDGE 5XLi devices are configurable via WWW interface. Each device uses following default settings: IP Address:
OSBRiDGE 5XLi Configuration Manual Firmware 3.10R 1. Initial setup and configuration. OSBRiDGE 5XLi devices are configurable via WWW interface. Each device uses following default settings: IP Address:
What is CSG150 about? Fundamentals of Computer Networking. Course Outline. Lecture 1 Outline. Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.
 What is CSG150 about? Fundamentals of Computer Networking Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.edu CSG150 Understand the basic principles of networking: Description of existing networks, and networking mechanisms
What is CSG150 about? Fundamentals of Computer Networking Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.edu CSG150 Understand the basic principles of networking: Description of existing networks, and networking mechanisms
Middleboxes. Firewalls. Internet Ideal: Simple Network Model. Internet Reality. Middleboxes. Firewalls. Globally unique idenpfiers
 Ideal: Simple Network Model Middleboxes Jennifer Rexford COS 461: Computer Networks Lectures: MW 10-10:50am in Architecture N101 hgp://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr12/cos461/ Globally unique
Ideal: Simple Network Model Middleboxes Jennifer Rexford COS 461: Computer Networks Lectures: MW 10-10:50am in Architecture N101 hgp://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr12/cos461/ Globally unique
Internetworking Microsoft TCP/IP on Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
 Internetworking Microsoft TCP/IP on Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Course length: 5 Days Course No. 688 - Five days - Instructor-led Introduction This course provides students with the knowledge and skills required
Internetworking Microsoft TCP/IP on Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Course length: 5 Days Course No. 688 - Five days - Instructor-led Introduction This course provides students with the knowledge and skills required
10CS64: COMPUTER NETWORKS - II
 QUESTION BANK 10CS64: COMPUTER NETWORKS - II Part A Unit 1 & 2: Packet-Switching Networks 1 and Packet-Switching Networks 2 1. Mention different types of network services? Explain the same. 2. Difference
QUESTION BANK 10CS64: COMPUTER NETWORKS - II Part A Unit 1 & 2: Packet-Switching Networks 1 and Packet-Switching Networks 2 1. Mention different types of network services? Explain the same. 2. Difference
Networking Test 4 Study Guide
 Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
TECHNICAL NOTE. Technical Note P/N 300-999-649 REV 03. EMC NetWorker Simplifying firewall port requirements with NSR tunnel Release 8.
 TECHNICAL NOTE EMC NetWorker Simplifying firewall port requirements with NSR tunnel Release 8.0 and later Technical Note P/N 300-999-649 REV 03 February 6, 2014 This technical note describes how to configure
TECHNICAL NOTE EMC NetWorker Simplifying firewall port requirements with NSR tunnel Release 8.0 and later Technical Note P/N 300-999-649 REV 03 February 6, 2014 This technical note describes how to configure
NetFlow/IPFIX Various Thoughts
 NetFlow/IPFIX Various Thoughts Paul Aitken & Benoit Claise 3 rd NMRG Workshop on NetFlow/IPFIX Usage in Network Management, July 2010 1 B #1 Application Visibility Business Case NetFlow (L3/L4) DPI Application
NetFlow/IPFIX Various Thoughts Paul Aitken & Benoit Claise 3 rd NMRG Workshop on NetFlow/IPFIX Usage in Network Management, July 2010 1 B #1 Application Visibility Business Case NetFlow (L3/L4) DPI Application
Project 4: IP over DNS Due: 11:59 PM, Dec 14, 2015
 CS168 Computer Networks Jannotti Project 4: IP over DNS Due: 11:59 PM, Dec 14, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Components 1 2.1 Creating the tunnel..................................... 2 2.2 Using the
CS168 Computer Networks Jannotti Project 4: IP over DNS Due: 11:59 PM, Dec 14, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Components 1 2.1 Creating the tunnel..................................... 2 2.2 Using the
Network Defense Tools
 Network Defense Tools Prepared by Vanjara Ravikant Thakkarbhai Engineering College, Godhra-Tuwa +91-94291-77234 www.cebirds.in, www.facebook.com/cebirds ravikantvanjara@gmail.com What is Firewall? A firewall
Network Defense Tools Prepared by Vanjara Ravikant Thakkarbhai Engineering College, Godhra-Tuwa +91-94291-77234 www.cebirds.in, www.facebook.com/cebirds ravikantvanjara@gmail.com What is Firewall? A firewall
OpenBSD. network stack internals
 OpenBSD network stack internals by The OpenBSD network stack is under constant development mainly to implement features that are more and more used in todays core networks. Various changes were made over
OpenBSD network stack internals by The OpenBSD network stack is under constant development mainly to implement features that are more and more used in todays core networks. Various changes were made over
19531 - Telematics. 14th Tutorial - Proxies, Firewalls, P2P
 19531 - Telematics 14th Tutorial - Proxies, Firewalls, P2P Bastian Blywis Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Institute of Computer Science 10. February, 2011 Institute of Computer Science Telematics
19531 - Telematics 14th Tutorial - Proxies, Firewalls, P2P Bastian Blywis Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Institute of Computer Science 10. February, 2011 Institute of Computer Science Telematics
Review: Lecture 1 - Internet History
 Review: Lecture 1 - Internet History late 60's ARPANET, NCP 1977 first internet 1980's The Internet collection of networks communicating using the TCP/IP protocols 1 Review: Lecture 1 - Administration
Review: Lecture 1 - Internet History late 60's ARPANET, NCP 1977 first internet 1980's The Internet collection of networks communicating using the TCP/IP protocols 1 Review: Lecture 1 - Administration
Network Layer IPv4. Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS. School of Computing, UNF
 Network Layer IPv4 Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF IPv4 Internet Protocol (IP) is the glue that holds the Internet together.
Network Layer IPv4 Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF IPv4 Internet Protocol (IP) is the glue that holds the Internet together.
OpenFlow with Intel 82599. Voravit Tanyingyong, Markus Hidell, Peter Sjödin
 OpenFlow with Intel 82599 Voravit Tanyingyong, Markus Hidell, Peter Sjödin Outline Background Goal Design Experiment and Evaluation Conclusion OpenFlow SW HW Open up commercial network hardware for experiment
OpenFlow with Intel 82599 Voravit Tanyingyong, Markus Hidell, Peter Sjödin Outline Background Goal Design Experiment and Evaluation Conclusion OpenFlow SW HW Open up commercial network hardware for experiment
Firewalls. configuring a sophisticated GNU/Linux firewall involves understanding
 Firewalls slide 1 configuring a sophisticated GNU/Linux firewall involves understanding iptables iptables is a package which interfaces to the Linux kernel and configures various rules for allowing packets
Firewalls slide 1 configuring a sophisticated GNU/Linux firewall involves understanding iptables iptables is a package which interfaces to the Linux kernel and configures various rules for allowing packets
Firewalls. Firewalls. Idea: separate local network from the Internet 2/24/15. Intranet DMZ. Trusted hosts and networks. Firewall.
 Firewalls 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks 2 1 Castle and
Firewalls 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks 2 1 Castle and
MBP_MSTR: Modbus Plus Master 12
 Unity Pro MBP_MSTR 33002527 07/2011 MBP_MSTR: Modbus Plus Master 12 Introduction This chapter describes the MBP_MSTR block. What s in this Chapter? This chapter contains the following topics: Topic Page
Unity Pro MBP_MSTR 33002527 07/2011 MBP_MSTR: Modbus Plus Master 12 Introduction This chapter describes the MBP_MSTR block. What s in this Chapter? This chapter contains the following topics: Topic Page
OpenFlow Based Load Balancing
 OpenFlow Based Load Balancing Hardeep Uppal and Dane Brandon University of Washington CSE561: Networking Project Report Abstract: In today s high-traffic internet, it is often desirable to have multiple
OpenFlow Based Load Balancing Hardeep Uppal and Dane Brandon University of Washington CSE561: Networking Project Report Abstract: In today s high-traffic internet, it is often desirable to have multiple
Bridgewalling - Using Netfilter in Bridge Mode
 Bridgewalling - Using Netfilter in Bridge Mode Ralf Spenneberg, ralf@spenneberg.net Revision : 1.5 Abstract Firewalling using packet filters is usually performed by a router. The packet filtering software
Bridgewalling - Using Netfilter in Bridge Mode Ralf Spenneberg, ralf@spenneberg.net Revision : 1.5 Abstract Firewalling using packet filters is usually performed by a router. The packet filtering software
ICS 351: Today's plan. IP addresses Network Address Translation Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Small Office / Home Office configuration
 ICS 351: Today's plan IP addresses Network Address Translation Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Small Office / Home Office configuration IP address exhaustion IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long so there
ICS 351: Today's plan IP addresses Network Address Translation Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Small Office / Home Office configuration IP address exhaustion IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long so there
