PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
|
|
|
- Betty Ross
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
2
3 Marijuana --Cannabis sativa THC content of 5% Female plant with flower clusters
4 Clusters of female flowers with long styles Trichomes on the leaves contain THC
5 Cannabis sativa leaf trichome Trichome consists of head and stalk cells THC is located in the head cell
6 HEMP Cannabis sativa without the THC Fibers are obtained from the stems Hemp seeds contain a nutrient-rich oil
7 Natural Bast Fibers are strong, cellulosic fibers obtained from the phloem or outer bark of jute, kenaf, flax and hemp plants Bast Fibers from Hemp Bark
8 Flowering Plants are known as Angiosperms Angiosperm means covered seed Angiosperm seed is enclosed in a fruit There are more than 250,000 species of angiosperms
9 31.2 The two main groups of angiosperms are the monocots and the dicots There are about 70,000 species of monocots and 180,000 species of dicots Monocots include: grasses, orchids, palms, lilies Dicots include: roses, oaks, tomatoes, sunflowers Monocots and dicots differ in Number of cotyledons (seed leaves) Pattern of leaf venation Arrangement of stem vascular tissue Number of flower parts Root structure Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
10 Seed leaves Leaf veins Stems Flowers Roots MONOCOTS One cotyledon Veins usually parallel Vascular bundles in complex arrangement Floral parts usually in multiples of three Fibrous root system DICOTS Two cotyledons Veins usually branched Vascular bundles arranged in ring Floral parts usually in multiples of four or five Taproot usually present
11 31.2 The two main groups of angiosperms are the monocots and the dicots Monocots One cotyledon Parallel leaf venation Scattered vascular bundles Flower parts in 3s or multiples of 3 Fibrous roots Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
12 31.2 The two main groups of angiosperms are the monocots and the dicots dicots most plants are dicots Two cotyledons Branched leaf venation Ring of vascular bundles Flower parts in 4s or 5s (or multiples) Taproot system Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
13 31.3 A typical plant body contains three basic organs: roots, stems, and leaves Plants absorb water and minerals from soil through roots Plants absorb the sun s energy and carbon dioxide from the air through shoots (stems and leaves) CO 2 Plant roots depend on shoots for carbohydrates produced via photosynthesis Plant shoots depend on roots for water and minerals Minerals H 2 O O 2 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
14 31.3 A typical plant body contains three basic organs: roots, stems, and leaves Plant roots Anchor plant Absorb water and nutrients Store food Plant shoots Stems, leaves, and reproductive structures Stems provide support Leaves carry out photosynthesis Root Hairs Absorb Water Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
15 Terminal bud Shoot system Leaf Stem Blade Petiole Axillary bud Flower Root hairs Node Internode Root hair Root system Taproot Epidermal cell
16 31.4 Many plants have modified roots, stems, and leaves Modifications of plant parts are adaptations for various functions Food or water storage Asexual reproduction Protection Climbing Photosynthesis Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
17 31.4 Many plants have modified roots, stems, and leaves Root modifications Food storage Large taproots store starches Examples include carrots, turnips, sugar beets, sweet potatoes Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
18 31.4 Many plants have modified roots, stems, and leaves Stem modifications Stolon asexual reproduction Rhizomes storage, asexual reproduction Tubers storage, asexual reproduction Cactus stem water storage and photosynthesis Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
19 Runners are Stem Adaptations for Asexual Propagation Strawberry plant Stolon or Runner
20 Rhizomes Adapted for Asexual Propagation
21 Potato Tuber Adapted for Food Storage and Asexual Propagation Taproot Rhizome Tuber
22 Potato Tubers are Stems not Roots because they have Lateral Buds that can produce new Shoots Eyes of potato growing into new shoot If potatos are exposed to light they turn green and make toxic alkaloids
23 Rhizomes Adapted for Food Storage Rhizome Ginger plant
24 Cactus Stem Modified for Water Storage
25 Many plants have modified roots, stems, and leaves Leaf modifications Protection Climbing Cactus spine Pea plant tendril Grape tendrils Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
26 Many plants have modified roots, stems, and leaves Leaf modifications Food Storage Onion bulb scales Celery petioles
27 REPRODUCTION OF FLOWERING PLANTS Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
28 31.9 The flower is the organ of sexual reproduction in angiosperms Flowers typically contain four types of highly modified leaves called floral organs Sepals enclose and protect flower bud Petals showy; attract pollinators Stamens male reproductive structures Carpels female reproductive structures Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
29 31.9 The flower is the organ of sexual reproduction in angiosperms A stamen has two parts Anther produces pollen, which house cells which develop into sperm Filament elevates anther A carpel has three parts Stigma site of pollination Style neck that leads to ovary Ovary houses ovules, which contain developing egg Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
30 Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Anther Filament Stamen Petal Ovule Sepal
31 31.9 The flower is the organ of sexual reproduction in angiosperms Angiosperm life cycle overview Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anthers of the stamen to the stigmatic surface of the carpel Fertilization is the union of egg and sperm and occurs in the ovule; the fertilized egg develops into an embryo encased in a seed The ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seed and aids in dispersal The seed germinates under suitable conditions to produce a seedling, which grows into a mature plant Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
32 Pollen Grains Pollen grains germinate and produce a pollen tube and sperm Pollen grains are transferred by wind or animals
33 Some Typical Plant Pollinators Bees Birds Bats
34 Seeds Are Also Dispersed By Animals Or Wind
35 Ovary, containing ovule Embryo Fruit (mature ovary), containing seed Seed Mature plant with flowers, where fertilization occurs Seedling Germinating seed
36 Embryonic leaves Embryonic root Seed coat Embryonic shoot Cotyledons Common bean (dicot) Fruit tissue Corn (monocot) Cotyledon Embryonic leaf Sheath Seed coat Endosperm Embryonic Shoot Embryonic root
37 31.12 The ovary develops into a fruit Hormonal changes induced by fertilization trigger the ovary to develop into a fruit Fruits protect the seed and aid in dispersal Mature fruits may be fleshy or dry Fleshy fruits oranges, tomatoes, grapes Dry fruits beans, nuts, grains Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
38 1
39 2
40 3
41 Upper part of carpel Ovule Ovary wall Seed Pod (opened) Sepal
42 Morphology of Fleshy Fruit
43 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. PLANT ANATOMY
44 31.5 Three tissue systems make up the plant body Dermal tissue Outer protective covering Vascular tissue Support and long-distance transport Ground tissue Bulk of the plant body Food production, storage, support Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
45 31.5 Three tissue systems make up the plant body Dermal tissue Layer of tightly packed cells called the epidermis First line of defense against damage and infection Waxy layer called cuticle reduces water loss Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
46 31.5 Three tissue systems make up the plant body Vascular tissue Composed of xylem and phloem Arranged in bundles Ground tissue Lies between dermal and vascular tissue Dicot stem ground tissue is divided into pith and cortex Leaf ground tissue is called mesophyll Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
47 31.6 Plant cells and tissues are diverse in structure and function Water conducting cells tracheids and vessel elements Both have thick secondary cell walls Both are dead at maturity Chains of tracheids and vessel elements form tubes that make up the vascular tissue called xylem Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
48 Pits Vessel element Tracheids Openings in end wall Pits
49 31.6 Plant cells and tissues are diverse in structure and function Food-conducting cells sieve tube members No secondary cell wall Alive at maturity but lack most organelles Companion cells Contain organelles Control operations of sieve tube members Chains of sieve tube members, separated by porous sieve plates, form the vascular tissue called phloem Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
50 Sieve plate Primary cell wall Companion cell Cytoplasm
51 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. PLANT GROWTH
52 31.7 Primary growth lengthens roots and shoots Plant growth is indeterminate Growth occurs throughout a plant s life Plants are categorized based on how long they live Annuals complete their life cycle in one year Biennials complete their life cycle in two years Perennials live for many years Animal growth is determinate Growth stops after a certain size is reached Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
53 31.7 Primary growth lengthens roots and shoots Plant growth occurs in specialized tissues called meristems Meristems are regions of active cell division Apical meristems are found at the tips of roots and shoots Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
54 Terminal bud Axillary buds Root tips Arrows = direction of growth
55 Apical meristem Leaves Microscopic view of a longitudinal shoot tip section Axillary bud meristems
56 APICAL DOMINANCE The apical bud suppresses the growth of the lateral buds Remove the apical bud and the lateral buds grow
57 Testing Your Knowledge Which of the following statements in false? A. Plant roots need oxygen to absorb water and minerals from the soil B. The tubers of a white potato are roots C. The bulb scales of an onion are leaves D. The rhizomes of a grass plant are stems Click again for answer: B
58 Testing Your Knowledge What type of vascular tissue cell in a plant conducts water A. Companion cell B. Sieve tube cell C. Vessel cell D. Bast Fiber cell E. Meristematic cell Click again for answer: C
59 Testing Your Knowledge The female organ of a flower is A. Sepal B. Petal C. Stamen D. Carpel Click again for answer D
60 Testing Your Knowledge Which of the following is a characteristic of a monocot A. Fibrous root system B. Flower parts in 4 or 5 s C. Long Taproots D. Vascular bundles in a ring pattern Click again for answer A
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types
 Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function. I. Background
 Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions. Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9. Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
 1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Plant Parts. Background Information
 Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones
 Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY
 Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Plant Structure and Function Notes
 For plants, when they made the transition from water to land, they had to make adaptations for obtaining water and prevent loss by desiccation (drying out) -water also needed for fertilization of eggs
For plants, when they made the transition from water to land, they had to make adaptations for obtaining water and prevent loss by desiccation (drying out) -water also needed for fertilization of eggs
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS
 PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All. Evolution of Plants
 And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
Germination is the process in which a
 The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
Chapter 3. Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction. Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Look at the back of this paper
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Look at the back of this paper
Laboratory. Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs
 Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
Laboratory. Plant Structure
 Laboratory 4 Plant Structure 2 Laboratory 4: Plant Structure OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Differentiate between dicots and monocots within the following categories: a. root
Laboratory 4 Plant Structure 2 Laboratory 4: Plant Structure OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Differentiate between dicots and monocots within the following categories: a. root
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to
 Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Anatomy and Physiology of Leaves
 I. Leaf Structure and Anatomy Anatomy and Physiology of Leaves A. Structural Features of the Leaf Question: How do plants respire? Plants must take in CO 2 from the atmosphere in order to photosynthesize.
I. Leaf Structure and Anatomy Anatomy and Physiology of Leaves A. Structural Features of the Leaf Question: How do plants respire? Plants must take in CO 2 from the atmosphere in order to photosynthesize.
Parts of a Flower and Pollination
 Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Lab: Plant tissue systems and cell types
 Lab: Plant tissue systems and cell types In this lab we will become familiar with the main types of plant cells and tissues. You ll look at cells in the ground tissue, dermal tissue and vascular tissue.
Lab: Plant tissue systems and cell types In this lab we will become familiar with the main types of plant cells and tissues. You ll look at cells in the ground tissue, dermal tissue and vascular tissue.
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds
 Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Photosynthesis. Chemical Energy (e.g. glucose) - They are the ultimate source of chemical energy for all living organisms: directly or indirectly.
 Photosynthesis Light Energy transduction Chemical Energy (e.g. glucose) - Only photosynthetic organisms can do this (e.g. plants) - They are the ultimate source of chemical energy for all living organisms:
Photosynthesis Light Energy transduction Chemical Energy (e.g. glucose) - Only photosynthetic organisms can do this (e.g. plants) - They are the ultimate source of chemical energy for all living organisms:
What's in a Flower. Ages: 8 to 12. Contributor: Susan Jaquette, Cornell Plantations volunteer
 Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
2. Fill in the blank. The of a cell is like a leader, directing and telling the different parts of the cell what to do.
 1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
nucleus cytoplasm membrane wall A cell is the smallest unit that makes up living and nonliving things.
 1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
Plant Parts and Their Function
 Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!
 Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
Biology 3B Laboratory Land Plant Structure
 Biology 3B Laboratory Land Plant Structure Objectives Learn and recognize the basic tissues and structures of land plants Understand how these morphological features relate to plant structure and function
Biology 3B Laboratory Land Plant Structure Objectives Learn and recognize the basic tissues and structures of land plants Understand how these morphological features relate to plant structure and function
II. Vegetative Propagation. Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting
 II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout
 PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Stages. Differences in the Developmental Mechanisms of Plants and Animals. Development
 Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions Sepals Anther Stamens (male) Filament Stigma Pistil Style (female) Ovary Petals sepals petals stamens pistil
 Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN VASCULAR AND NON- VASCULAR PLANTS?
 WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN VASCULAR AND NON- VASCULAR PLANTS? Let s take a closer look. What makes them different on the outside and inside? Learning Intentions To understand how vascular plant cells
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN VASCULAR AND NON- VASCULAR PLANTS? Let s take a closer look. What makes them different on the outside and inside? Learning Intentions To understand how vascular plant cells
Transport in Plants. Lab Exercise 25. Introduction. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Transport in Plants Objectives - Become familiar and be able to recognize the different types of cells found in the plant s vascular tissue. - Be able to describe root pressure and transpiration
Lab Exercise Transport in Plants Objectives - Become familiar and be able to recognize the different types of cells found in the plant s vascular tissue. - Be able to describe root pressure and transpiration
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education. April, 2006
 Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Unit 3 Lesson 5: People Need Plants
 Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
1. The leaf is the main photosynthetic factory (Fig. 36.1, p. 702)
 TRANSPORT IN PLANTS A. Introduction 1. The leaf is the main photosynthetic factory (Fig. 36.1, p. 702) a. This requires a transport system to move water and minerals from the roots to the leaf. This is
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS A. Introduction 1. The leaf is the main photosynthetic factory (Fig. 36.1, p. 702) a. This requires a transport system to move water and minerals from the roots to the leaf. This is
Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land,
 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
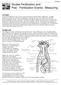 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY
 PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
Introduction to Plant Propagation. Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM
 Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
THIRD GRADE PLANT LIFE
 THIRD GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing and contrasting invertebrates and vertebrates. LAB: Learning about different
THIRD GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing and contrasting invertebrates and vertebrates. LAB: Learning about different
Chapter 36: Resource Acquisition & Transport in Vascular Plants
 Chapter 36: Resource Acquisition & Transport in Vascular Plants 1. Overview of Transport in Plants 2. Transport of Water & Minerals 3. Transport of Sugars 1. Overview of Transport in Plants H 2 O CO 2
Chapter 36: Resource Acquisition & Transport in Vascular Plants 1. Overview of Transport in Plants 2. Transport of Water & Minerals 3. Transport of Sugars 1. Overview of Transport in Plants H 2 O CO 2
Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort
 The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
Transport in Plants Notes AP Biology Mrs. Laux 3 levels of transport occur in plants: 1. Uptake of water and solutes by individual cells
 3 levels of transport occur in plants: 1. Uptake of water and solutes by individual cells -for photosynthesis and respiration -ex: absorption of H 2 O /minerals by root hairs 2. Short distance cell-to-cell
3 levels of transport occur in plants: 1. Uptake of water and solutes by individual cells -for photosynthesis and respiration -ex: absorption of H 2 O /minerals by root hairs 2. Short distance cell-to-cell
PLANT DIVERSITY. EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae
 PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
Leaf Structure and Transpiration
 10 LESSON Leaf Structure and Transpiration INTRODUCTION Have you wondered what happens to all that water that disappears from the reservoir of your growing system? Although some might have evaporated from
10 LESSON Leaf Structure and Transpiration INTRODUCTION Have you wondered what happens to all that water that disappears from the reservoir of your growing system? Although some might have evaporated from
Bio Factsheet January 2001 Number 82
 January 2001 Number 82 Transport in Flowering Plants This Factsheet covers the relevant AS syllabus content of the major examination boards. By studying this Factsheet candidates will gain a knowledge
January 2001 Number 82 Transport in Flowering Plants This Factsheet covers the relevant AS syllabus content of the major examination boards. By studying this Factsheet candidates will gain a knowledge
BIOL 1030 TOPIC 5 LECTURE NOTES TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29)
 TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
3MNN Behavioral Outcomes Eat fruits and veggies, etc. SNAP-Education Nutrition Messages Eat fruits and veggies as healthy snacks, MyPyramid servings
 DRAFT 1 Lesson Plan Title: Phenomenal Plant Parts Grade Level: 3 Content Area: Science Setting: School garden, or classroom Instructional Time: 60 to 90 minutes Grade Level Expectations: Life Science L.OL.E3:
DRAFT 1 Lesson Plan Title: Phenomenal Plant Parts Grade Level: 3 Content Area: Science Setting: School garden, or classroom Instructional Time: 60 to 90 minutes Grade Level Expectations: Life Science L.OL.E3:
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones
 Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination
 Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers
 Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator
 Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Functional Biology of Plants
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2252012/ Functional Biology of Plants Description: Functional Biology of Plants provides students and researchers with a clearly
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2252012/ Functional Biology of Plants Description: Functional Biology of Plants provides students and researchers with a clearly
Plant Structure and Function
 NQF Level: 2 US No: 116057 Learner Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Structure and Function My name:. Company:. Commodity:.................... Date:............... The availability of this product is due
NQF Level: 2 US No: 116057 Learner Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Structure and Function My name:. Company:. Commodity:.................... Date:............... The availability of this product is due
Figure 1: Seagrass structural detail. Differences in leaf shapes, leaf sheaths etc. are characteristics for taxonomic distinction.
 Marine Angiosperms There are a wide variety of marine angiosperms some, such an the mangals, saltmarsh grasses and seagrasses that will either partly or entirely submerged (or submerged dependent on the
Marine Angiosperms There are a wide variety of marine angiosperms some, such an the mangals, saltmarsh grasses and seagrasses that will either partly or entirely submerged (or submerged dependent on the
The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed?
 The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed? Grade Level: K-4 Catalog Number: 15-8973 Time to pollinate the flowers Time to harvest the seeds True leaves grow Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Day
The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed? Grade Level: K-4 Catalog Number: 15-8973 Time to pollinate the flowers Time to harvest the seeds True leaves grow Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Day
What Do Plants Need to Grow?
 Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
Get It Right. Answers. Chapter 1: The Science of Life. A biologist studies all living things.
 Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents?
 2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
Water movement in the xylem Water moves from roots to leaves through the xylem. But how? Hypotheses: 1. Capillary action - water will move upward in
 Transport in Plants Two Transport Processes Occur in Plants 1. Carbohydrates carried from leaves (or storage organs) to where they are needed (from sources to sinks) 2. Water transported from roots to
Transport in Plants Two Transport Processes Occur in Plants 1. Carbohydrates carried from leaves (or storage organs) to where they are needed (from sources to sinks) 2. Water transported from roots to
Growth of Pasture Plants
 Growth of Pasture Plants 3 GREG J. BISHOP-HURLEY In a grazing situation it is important to understand both how plants function and their form and structure. Every plant growth response is caused by a series
Growth of Pasture Plants 3 GREG J. BISHOP-HURLEY In a grazing situation it is important to understand both how plants function and their form and structure. Every plant growth response is caused by a series
Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification
 1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Introducing the parts of a flower
 Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Transpiration. C should equal D.BUT SOMETIMES. 1. Loss in mass is greater than volume of water added.
 Transpiration Transpiration is the loss of water by evaporation from the leaves through the stomata. The source of water for the plants is soil water. It is taken up by root hair cells by osmosis. Once
Transpiration Transpiration is the loss of water by evaporation from the leaves through the stomata. The source of water for the plants is soil water. It is taken up by root hair cells by osmosis. Once
Life Science. A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park. Middle School Biology
 Life Science A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park Middle School Biology Life Science Biology Curriculum I. Introduction... 1 II. Curriculum unit overview and activities A.
Life Science A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park Middle School Biology Life Science Biology Curriculum I. Introduction... 1 II. Curriculum unit overview and activities A.
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FUNDAMENTALS AND SYSTEMATICS Vol. I Cell and Tissue Structure in Animals and Plants - M.K. Richardson, L.
 CELL AND TISSUE STRUCTURE IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS M.K. Richardson Institute of Evolutionary and Ecological Sciences, Leiden University, Kaiserstraat 63, Postbus 9516, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands L. Goosen-de
CELL AND TISSUE STRUCTURE IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS M.K. Richardson Institute of Evolutionary and Ecological Sciences, Leiden University, Kaiserstraat 63, Postbus 9516, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands L. Goosen-de
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification
 Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
The Parts of a Flower
 The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
Transport of Water and Solutes in Plants
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44708 1 Transport of Water and Solutes in Plants OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end
OpenStax-CNX module: m44708 1 Transport of Water and Solutes in Plants OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end
most modern cladograms have Amborella and water lilies as a sister group (or groups) to the rest of the angiosperms
 Topic 7: Angiosperms, Flowers and Pollination Syndromes Phylum Anthophyta (Chs. 30, 38) Ι. Phylum Anthophyta flowering plants (antho flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion vessel or enclosure; sperma
Topic 7: Angiosperms, Flowers and Pollination Syndromes Phylum Anthophyta (Chs. 30, 38) Ι. Phylum Anthophyta flowering plants (antho flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion vessel or enclosure; sperma
Photosynthesis and (Aerobic) Respiration. Photosynthesis
 Photosynthesis and (Aerobic) Respiration These two processes have many things in common. 1. occur in organelles that seem to be descended from bacteria (endosymbiont theory): chloroplasts and mitochondria
Photosynthesis and (Aerobic) Respiration These two processes have many things in common. 1. occur in organelles that seem to be descended from bacteria (endosymbiont theory): chloroplasts and mitochondria
How To Understand Plant Biology
 SECOND GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics of
SECOND GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics of
I. PLANT CELL, CELL WALL Bot 404--Fall 2004
 I. PLANT CELL, CELL WALL Bot 404--Fall 2004 A. Review of General Anatomy 1. Major organs are stem, leaf, root. Flower is usually interpreted as a modified shoot, so sepals, petals, stamens and carpels
I. PLANT CELL, CELL WALL Bot 404--Fall 2004 A. Review of General Anatomy 1. Major organs are stem, leaf, root. Flower is usually interpreted as a modified shoot, so sepals, petals, stamens and carpels
Plant and Soil Science I
 Plant and Soil Science I Levels: Grades 9-12 Units of Credit: 1.00 CIP Code: 02.0411 Core Code: 30-02-00-00-080 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: # 140 COURSE DESCRIPTION Students will develop knowledge and
Plant and Soil Science I Levels: Grades 9-12 Units of Credit: 1.00 CIP Code: 02.0411 Core Code: 30-02-00-00-080 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: # 140 COURSE DESCRIPTION Students will develop knowledge and
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) A - liver; 1 B -brain; 1 C - heart; 1 D - lung; 1 E - kidney; 1. (b) (i) E/kidney; 1. (ii) C/heart; 1.
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 A - liver; 1 B -brain; 1 C - heart; 1 D - lung; 1 E - kidney; 1 (b) (i) E/kidney; 1 C/heart; 1 (iii) B/brain; 1 (iv) D/lungs; 1 QUESTIONSHEET 2 (i) artery; 1 eye; 1 (iii) stomach; 1 (iv)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 A - liver; 1 B -brain; 1 C - heart; 1 D - lung; 1 E - kidney; 1 (b) (i) E/kidney; 1 C/heart; 1 (iii) B/brain; 1 (iv) D/lungs; 1 QUESTIONSHEET 2 (i) artery; 1 eye; 1 (iii) stomach; 1 (iv)
version if desired, and Teacher Preparation Notes are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/.
 Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Mighty Oaks From Little Acorns
 Science Process: Observe and Measure / Life Science / Math: Measurement (Length), data Analysis (graphing) / reading: Sequencing / Listening / Writing / Visual Arts expression Background Buds are on the
Science Process: Observe and Measure / Life Science / Math: Measurement (Length), data Analysis (graphing) / reading: Sequencing / Listening / Writing / Visual Arts expression Background Buds are on the
NQF Level: 2 US No: 116119
 NQF Level: 2 US No: 116119 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Propagation Assessor:.......................................... Workplace / Company:................................. Commodity:...................
NQF Level: 2 US No: 116119 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Propagation Assessor:.......................................... Workplace / Company:................................. Commodity:...................
Plants Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Name: Plants Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them
Name: Plants Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them
How Trees Grow in the Urban Environment 1
 CIR1093 1 Mary L. Duryea and Marlene M. Malavasi2 Background What happens to a birdhouse if you hang it on a tree and come back in two years? Will it be at the same height or out of your reach because
CIR1093 1 Mary L. Duryea and Marlene M. Malavasi2 Background What happens to a birdhouse if you hang it on a tree and come back in two years? Will it be at the same height or out of your reach because
