Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Low Molecular Weight Heparin
|
|
|
- Kristopher Hudson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Low Molecular Weight Heparin Information for patients and families UHN Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how low molecular weight heparin is used to treat them what you need to know about taking this medicine what problems to look out for where you can find more information What is venous thrombosis? Venous thrombosis is a blood clot inside a deep vein. The blood clot can form in deep veins anywhere in your body, such as your leg, arm or abdomen. Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: University Health Network. All rights reserved. This information is to be used for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult your health care provider for advice about a specific medical condition. A single copy of these materials may be reprinted for non-commercial personal use only. Author: Sarah Boross-Harmer, RN Revised: 07/2014 Form: D-5592
2 Can venous thrombosis be serious? Yes, in some cases. A pulmonary embolism is when a blood clot breaks off and travels through your veins to the blood vessels in your lungs. A pulmonary embolism is dangerous and could be life threatening. The risk of a clot breaking off and becoming a pulmonary embolism is highest before starting treatment and in the first few days of starting treatment. After a week, the risk becomes very low. What is the difference between blood clots in veins and blood clots in arteries? Veins carry blood from the different parts of your body back to your heart. Blood clots in veins may cause pulmonary embolism or other problems depending on where the blood clot is. Arteries carry blood from your heart to all the different parts of your body. Blood clots in arteries may cause a stroke, a mini-stroke (also called a TIA or transient ischemic attack), or a heart attack. They may also block blood flow to your leg, arm or central artery, which can cause gangrene (some of your tissue to die) or other problems. 2
3 The treatments for blood clots in veins and blood clots in arteries are different. The risks, symptoms and how they can be prevented are also very different. What if I have blood clots in veins close to the surface of my skin? Clotting in small veins close to the surface of your skin is called superficial thrombophlebitis. These blood clots may be very painful and cause your skin to become red and irritated. But, they are not dangerous. The risk of the clot breaking off and travelling to your lung (pulmonary embolism) is very small. Superficial thrombophlebitis is not always treated. This will depend on the size and where it is on your body. If it is treated, we may ask you to use a cold compress on the area and take ant-inflammatory medicine (for example, Advil, Aspirin or Motrin ) for about 2 to 6 weeks. How common is venous thrombosis? Venous thrombosis happens in about 1 of every 1,000 people, but the risk increases as you get older. What could cause venous thrombosis? There are many things that can increase the risk of venous thrombosis. These include: aging being overweight going through major surgery cancer or cancer therapy having an intravenous catheter (for example, a PICC line, port-a-cath, or Hickman line) an autoimmune disease or inflammatory disorder like Lupus, ulcerative colitis or Crohn s disease 3
4 a major injury or broken bone not being able to move as much while in a cast or wheelchair pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy a family history of venous thrombosis or clotting problems Sometimes the reason why a patient has venous thrombosis isn t clear. Will I need to have a test to see why I developed venous thrombosis? This will depend on many things like your family history, whether you are male or female, or your age. Your health care provider will talk to you if they decide you need to be tested. How is venous thrombosis treated? Several medicines are used to treat venous thrombosis. These types of medicines are called anticoagulants. Anticoagulants don t dissolve the blood clot. They: slow down blood clotting in your body prevent your blood clot from becoming larger prevent you from developing new blood clots reduce problems such as swelling and pain in the area of your clot (for example your arm or leg) or problems breathing Once you start taking the medicines, your body will naturally break down or reabsorb the blood clot. In most patients the blood clot breaks down after many weeks to many months. In some people the blood clot never completely goes away, but it changes to scar tissue. This scar tissue is not dangerous, and it can t break off. It becomes a part of your vein wall. Your body will develop new veins to go around this scar tissue. Not all medicines are suitable for every patient. We will talk to you about the medicines that are best for you. 4
5 The type of medicine we will use to treat your venous thrombosis is called Low Molecular Weight Heparin. You can only get this medicine by injection (a needle). There are many different brand names for this medicine that we may use. When we talk to you about this medicine, we usually just call it Heparin injections. What do I need to know about Heparin injections? Heparin injections treat venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. You inject this medicine in the fat on your abdomen or the top of your thigh once a day. It starts to work right away to slow down blood clotting and prevent new thrombosis. The amount (also called dose) of Heparin you inject depends on how much you weigh. The dose will be the same each day. If you lose or gain weight, call the thrombosis clinic as soon as possible. 5
6 My Heparin information Date: Brand name: Time of day to inject: Dose: My weight today is: Call the clinic at if: I weigh more than: I weigh less than: You will need a blood test 1 week after starting heparin injections. This blood test is called a complete blood count. We do this test to make sure you are not reacting to the Heparin injections. My blood test will be on (date): Take the Heparin injection at the same time every day. This is important because once the heparin has been injected, it only lasts for 24 hours. You can choose to take the injection in the morning or at night, but take it at the same time each day. You can take Heparin with or without food. If you drink alcohol don t drink more than these amounts daily: 1 to 2 bottles of beer or 1 to 2 glasses of wine or 1 to 2 ounces liquor Keep your Heparin medicine at room temperature, not in the refrigerator. 6
7 What about pregnancy and breastfeeding? Heparin injections are safe to take if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. They won t harm your baby. If you are planning on becoming pregnant, please talk to your health care provider. If you become pregnant while taking Heparin injections, call the Thrombosis Clinic. What do I do if I forget an injection? If you forget an injection, take it as soon as you remember, even if you are several hours late taking it. If you miss an injection completely, take your regular dose the next day. Never take more than your regular dose of Heparin on the same day. This is dangerous and can increase your risk of bleeding. Forgetting to take your Heparin injection may increase your risk of having another thrombosis. If you forget to take your Heparin for more than 2 days, call the Thrombosis Clinic. Are there any side effects? It's normal to have some bruising at the injection site (area where you inject the Heparin). This bruising may last up to several weeks. You may be able to lessen the amount of bruising by injecting the Heparin slowly (over 30 seconds). It may sting when you inject the Heparin, and it may continue to sting for about 10 minutes after the injection. The Heparin injections will not cause any new bleeding, but the injections may make any bleeding you have last for a longer time. For example: Your menstrual cycle (period) may be heavier and last longer. A cut on your finger may bleed longer than usual. You may bruise more easily than usual. A nose bleed may last longer than usual and take longer to stop. 7
8 Most bleeding will stop if you apply steady pressure on the area for at least 5 minutes. If you get a nose bleed, pinch the bridge of your nose for at least 20 minutes. Don't put anything up your nose. You may develop some small, pea-sized lumps at your injection site. These may take several months to go away. Who needs to know I am taking this medicine? Tell your family doctor, dentist, nurse, acupuncturist, or any health care provider that you are taking Heparin. This is very important if you are having a procedure that may cause you to bleed. Remind them each time you visit. Carry a wallet card so you will always have the name of the medicine with you. Tell your pharmacist you are taking Heparin every time you buy any new medicines (even vitamins and cold remedies). This will allow them to check for problems that can happen when some medicines are taken together (drug interactions). Talk to your health care provider before stopping Heparin. It may be dangerous to stop. You don t need to stop it before minor dental work. If you are planning to have surgery or major dental work, make sure the person doing the surgery knows you are taking Heparin. You may need to stop taking it for 24 hours before your procedure. If you have an accident, get medical help right away. You will need to be checked for signs of bleeding. 8
9 Can other medicines or vitamins affect how Heparin works? Yes. If you are prescribed any new medicines, talk to your health care provider and pharmacist about any possible drug interactions. You should tell your health care provider if you start any new medicines, including vitamins, homeopathic treatments and medicines you can buy without a prescription. When you are taking Heparin injections, don't take: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines like Ibuprofen, Advil, Motrin, or Aleve medicines with ASA acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin, Anacin ) some homeopathic or herbal supplements. Please call your pharmacist or health care provider to check. any medicine which may increase your risk of bleeding (unless your doctor has prescribed it and knows that you are taking Heparin). You may take: Acetaminophen (Tylenol ) for pain allergy medicines such as Benadryl, Claritin or Reactine most cough and cold medicines as long as they don t have Ibuprofen, (Advil, Motrin ) or ASA (Aspirin, Anacin ) How much activity can I do? How much activity you can do will depend on: where your blood clot is how you feel how much activity you are used to other health problems you may have 9
10 Listen to your body, and only do what is comfortable for you. Some people have few symptoms and are able to be active right away. But, some people have symptoms like leg pain and/or difficulty breathing. It may take many weeks before they can increase the amount of activity they do. For the first 3 days after you start Heparin injections: Rest. You can walk around your home and do light activities such as climbing up 1 to 2 flights of stairs. Don t do tiring activities such as running, biking, weight training, shoveling snow or gardening. After 3 days: You may increase your activity slowly. If the area of your clot is painful and swollen, wait until the pain and swelling decreases before increasing your activity. Once your pain decreases, you can increase your activity slowly each day until you are back to your regular activities. You can usually go back to your regular activities after about 1 month of having your venous thrombosis. But, recovery may take longer for some patients. As long as you are taking any anticoagulant medicines: Don t do contact sports (such as hockey, soccer or football) and other activities where there is a high risk you could get hurt. Will I be able to travel by airplane? Yes. Once you start Heparin injections and your blood clot is stable (usually after 1 week), you can fly, unless you continue to be short of breath or have chest pain. You should drink plenty of fluids and get up during flights to stretch your legs. Carry your Heparin medicine in its original package with you on the airplane (carry-on luggage). 10
11 When will I feel better? Venous thrombosis Most people with venous thrombosis feel better in 3 to 4 weeks. It takes about this long for your body to start breaking it down and for the swelling in the area of the thrombosis to reduce. If you don t feel better after 3 weeks or you feel worse, call your health care provider. They may recommend special support socks called compression socks. These socks will help reduce any swelling you may have after having thrombosis. You will need to have a prescription and be measured for these socks to make sure they fit properly. You wear these socks during the day and remove them at night. Pulmonary embolism If you had a pulmonary embolism, you may: feel short of breath feel dizzy have heart palpitations (your heart isn t beating normally) have pain in your lungs feel very tired This is normal for people with a pulmonary embolism. You may feel better in 3 to 4 weeks, but it may take many months before you feel better. If you continue to feel short of breath after 3 weeks, let your health care provider know. In a few people, the clot does not completely break down. You may need further tests to see if there is any damage to your lung or strain on your heart. If you feel much more short of breath than usual or you feel a crushing chest pain, go to your closest emergency department right away. 11
12 How long will I need to take Heparin injections? How long you will need to take it will depend on: the reason you developed the thrombosis where your thrombosis is anything that may increase your risk of having another thrombosis your risk of developing bleeding You may need to take this medicine for many weeks, months, or years. You may even need to take it for the rest of your life. Your health care provider will talk with you about this during your treatment. Take Heparin injections until your health care provider tells you that you can stop or decides that you can start taking anticoagulant medicine in pill form. What problems should I look out for? Go to the nearest emergency department if: you have a hard time catching your breath you have severe chest pain the pain you have from the thrombosis or pulmonary embolus gets much worse (you can expect your pain to stay about the same for 2 to 3 weeks) you have a very bad headache (worse than you have ever had before) you start vomiting blood or passing blood in your urine or bowel movements your bowel movements look black (like black tar) you hit your head hard or have a major accident Contact your health care provider if you have any other questions or concerns. 12
13 Where can I find more information about venous thrombosis? You can find more information about venous thrombosis at these websites: Thrombosis Canada Clot Connect National Blood Clot Alliance Clot Care 13
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium)
 MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking COUMADIN (warfarin sodium) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking COUMADIN (warfarin sodium) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Treatment with Apixaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis This handout explains the medicine apixaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name Eliquis) is an anticoagulant
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis This handout explains the medicine apixaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name Eliquis) is an anticoagulant
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine
 What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
Guide to Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban and Apixaban
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban and Apixaban Medicines to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban and Apixaban Medicines to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language
Warfarin. (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely
 Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients. Information For Patients
 Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients Information For Patients 1 This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots during and after your stay in hospital. If
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Medication Information. (a pix a ban)
 Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Guide to Warfarin Therapy
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Guide to Warfarin Therapy
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
FRAGMIN Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery.
 FRAGMIN Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#72 Fragmin (dalteparin sodium injection); an anticoagulant (blood thinner) is used to help prevent blood clots after surgery. While on Fragmin,
FRAGMIN Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#72 Fragmin (dalteparin sodium injection); an anticoagulant (blood thinner) is used to help prevent blood clots after surgery. While on Fragmin,
Medication Information. (a pix a ban)
 Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
 Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Blood Clots
 Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Blood Clots U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 540 Gaither Road Rockville, MD 20850 AHRQ Pub. No. 09 0067 C May
Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Blood Clots U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 540 Gaither Road Rockville, MD 20850 AHRQ Pub. No. 09 0067 C May
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
Medication Information. (Ri va rox xa - ban)
 Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
Medication Information. (Ri va rox xa - ban)
 Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication are: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication are: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
what is warfarin? Treatment with Warfarin (Coumadin ) What is warfarin?
 What is warfarin? Warfarin sodium (Coumadin ) is a medication that works as an anti-coagulant. Anti means against and coagulant refers to blood clotting. An anticoagulant helps to prevent clots from forming
What is warfarin? Warfarin sodium (Coumadin ) is a medication that works as an anti-coagulant. Anti means against and coagulant refers to blood clotting. An anticoagulant helps to prevent clots from forming
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin) or Heparin
 Contents www.bcwomens.ca What is Dalteparin (Fragmin)...1 Where do I get this medication from?...1 How often do I give myself this medication?...1 Side effects...1 Steps to Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin)..1
Contents www.bcwomens.ca What is Dalteparin (Fragmin)...1 Where do I get this medication from?...1 How often do I give myself this medication?...1 Side effects...1 Steps to Giving Yourself Dalteparin (Fragmin)..1
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin )
 FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
Through Thick and Thin
 Through Thick and Thin Learning to Live with Warfarin South Denver Cardiology Associates PC What is Anticoagulation? Anti = against Coagulation = blood clotting An anticoagulant is a medication that reduces
Through Thick and Thin Learning to Live with Warfarin South Denver Cardiology Associates PC What is Anticoagulation? Anti = against Coagulation = blood clotting An anticoagulant is a medication that reduces
Emergency Care for Patients of The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
ADVICE ON TRAVEL-RELATED DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS
 ADVICE ON TRAVEL-RELATED DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS Introduction 1. A possible link between deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and long haul air travel was first suggested by reports in medical journals in the 1950s.
ADVICE ON TRAVEL-RELATED DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS Introduction 1. A possible link between deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and long haul air travel was first suggested by reports in medical journals in the 1950s.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
Medication Guide Plavix (PLAV-iks) (clopidogrel bisulfate) tablets
 Medication Guide Plavix (PLAV-iks) (clopidogrel bisulfate) tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Plavix and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication
Medication Guide Plavix (PLAV-iks) (clopidogrel bisulfate) tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Plavix and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP. Primary Care Provider:
 Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
Preparing for your Ultrasound-Guided Core Biopsy
 Preparing for your Ultrasound-Guided Core Biopsy UHN For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre Read this resource to learn: How to prepare What to expect during the biopsy What you need to do after When
Preparing for your Ultrasound-Guided Core Biopsy UHN For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre Read this resource to learn: How to prepare What to expect during the biopsy What you need to do after When
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
AC: Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is AC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Doxorubicin (Adriamycin
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is AC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Doxorubicin (Adriamycin
Hysterectomy Vaginal hysterectomy Abdominal hysterectomy
 Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgery to remove a woman s uterus. The uterus is one of the organs of the female reproductive system and is about the size of a closed hand. You can no longer have children
Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgery to remove a woman s uterus. The uterus is one of the organs of the female reproductive system and is about the size of a closed hand. You can no longer have children
A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
 Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count What is a low platelet count? A platelet count measures the number of platelets you have in your blood.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count What is a low platelet count? A platelet count measures the number of platelets you have in your blood.
Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC)
 Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian
Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Your Guide to Coumadin / Warfarin Therapy
 Your Guide to Coumadin / Warfarin Therapy 5 Things You MUST Know About Coumadin (Generic Name Warfarin) 1. You must have your blood checked regularly to prevent clots and bleeding. 2. Many medicines interact
Your Guide to Coumadin / Warfarin Therapy 5 Things You MUST Know About Coumadin (Generic Name Warfarin) 1. You must have your blood checked regularly to prevent clots and bleeding. 2. Many medicines interact
For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP
 1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE)
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) This leaflet aims to answer your questions about rivaroxaban that may be prescribed for you when you are diagnosed
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) This leaflet aims to answer your questions about rivaroxaban that may be prescribed for you when you are diagnosed
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism
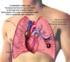 What You Need to Know After Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease,
What You Need to Know After Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease,
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Patient Guide. Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab)
 Patient Guide Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety
Patient Guide Important information for patients starting therapy with LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery
 After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment
After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment
Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps
 Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best for me?
Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best for me?
How To Take Xarelto
 A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil What is CMF? This is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil What is CMF? This is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules. What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST?
 MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
11 Serious and life-threatening side effects can occur while taking EVISTA. These include 12 blood clots and dying from stroke:
 1 1 BNL 3123 AMP 2 Medication Guide 3 EVISTA (E-VISS-tah) 4 (raloxifene hydrochloride) 5 Tablets for Oral Use 6 Read the Medication Guide that comes with EVISTA before you start taking it and each time
1 1 BNL 3123 AMP 2 Medication Guide 3 EVISTA (E-VISS-tah) 4 (raloxifene hydrochloride) 5 Tablets for Oral Use 6 Read the Medication Guide that comes with EVISTA before you start taking it and each time
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate
 MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving mitoxantrone and each time you receive mitoxantrone. There may be new information.
MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving mitoxantrone and each time you receive mitoxantrone. There may be new information.
AXIRON (AXE-e-RON) CIII
 Medication Guide 1 AXIRON (AXE-e-RON) CIII (testosterone) topical solution Read this Medication Guide before you start using AXIRON and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information
Medication Guide 1 AXIRON (AXE-e-RON) CIII (testosterone) topical solution Read this Medication Guide before you start using AXIRON and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information
Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
Foot or Ankle Surgery
 Foot or Ankle Surgery Instructions for patients going home UHN You had a general anesthetic. Do not drive a car or drink alcohol for 24 hours. What can I eat and drink after my operation? You can go back
Foot or Ankle Surgery Instructions for patients going home UHN You had a general anesthetic. Do not drive a car or drink alcohol for 24 hours. What can I eat and drink after my operation? You can go back
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants
 York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact:
York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact:
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services
 Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
TC: Docetaxel and Cyclophosphamide
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is TC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Docetaxel (Taxotere
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is TC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Docetaxel (Taxotere
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Sudden dizziness, trouble walking, loss of balance or coordination
 rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
Warfarin Counseling. Clinic Patient Education
 Warfarin Counseling Clinic Patient Education The UCSD Anticoagulation Clinic The UCSD Anticoagulation clinic is run by pharmacists The 2 clinic locations Hillcrest: 330 Lewis Street (@ 4 th Ave) La Jolla:
Warfarin Counseling Clinic Patient Education The UCSD Anticoagulation Clinic The UCSD Anticoagulation clinic is run by pharmacists The 2 clinic locations Hillcrest: 330 Lewis Street (@ 4 th Ave) La Jolla:
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
It is important that you tell your family and the people closest to you of this increased sensitivity to opioids and the risk of overdose.
 MEDICATION GUIDE VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving VIVITROL injections and each time you receive an injection.
MEDICATION GUIDE VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving VIVITROL injections and each time you receive an injection.
Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
 Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Learn About: 1. What is atrial fibrillation? 2. How will I feel? 3. Who gets AFib? 4. Risk of stroke 5. AFib treatment 6. How to live well with AFib 1. What is
Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Learn About: 1. What is atrial fibrillation? 2. How will I feel? 3. Who gets AFib? 4. Risk of stroke 5. AFib treatment 6. How to live well with AFib 1. What is
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Ask your healthcare provider about LONG-ACTING AVEED (testosterone undecanoate) AVEED TESTOSTERONE INJECTION 5 SHOTS A YEAR. Not an actual patient.
 Ask your healthcare provider about LONG-ACTING AVEED (testosterone undecanoate) AVEED TESTOSTERONE INJECTION 5 SHOTS A YEAR AFTER THE FIRST MONTH OF THERAPY Not an actual patient. CONSUMERS What is the
Ask your healthcare provider about LONG-ACTING AVEED (testosterone undecanoate) AVEED TESTOSTERONE INJECTION 5 SHOTS A YEAR AFTER THE FIRST MONTH OF THERAPY Not an actual patient. CONSUMERS What is the
Form ### Transgender Hormone Therapy - Estrogen Informed Consent SAMPLE
 What are the different medications that can help to feminize me? Estrogen - Different types of the hormone estrogen can help you appear more feminine. Estrogen is the female sex hormone. Androgen blocker
What are the different medications that can help to feminize me? Estrogen - Different types of the hormone estrogen can help you appear more feminine. Estrogen is the female sex hormone. Androgen blocker
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Hormone Therapy with Tamoxifen
 What is hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer? Many breast cancers need estrogen and/or progesterone (female hormones), to grow and spread. When breast cancer is found, the cancer is tested for two proteins,
What is hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer? Many breast cancers need estrogen and/or progesterone (female hormones), to grow and spread. When breast cancer is found, the cancer is tested for two proteins,
Getting Older ]Wiser: safer drinking. as you age. Massachusetts Department of Public Health Office of Healthy Aging
![Getting Older ]Wiser: safer drinking. as you age. Massachusetts Department of Public Health Office of Healthy Aging Getting Older ]Wiser: safer drinking. as you age. Massachusetts Department of Public Health Office of Healthy Aging](/thumbs/25/6007827.jpg) Massachusetts Department of Public Health Office of Healthy Aging Getting Older ]Wiser: safer drinking as you age Do you drink alcohol even just one drink now and then? Are you over 50? Do you ever take
Massachusetts Department of Public Health Office of Healthy Aging Getting Older ]Wiser: safer drinking as you age Do you drink alcohol even just one drink now and then? Are you over 50? Do you ever take
(Atrial Fibrillation) What You and Your Family Should Know
 Afib (Atrial Fibrillation) What You and Your Family Should Know BRING THIS BOOKLET TO YOUR NEXT DOCTOR S VISIT. Getting Started This guide will: 1. Provide you with information to help you and your family
Afib (Atrial Fibrillation) What You and Your Family Should Know BRING THIS BOOKLET TO YOUR NEXT DOCTOR S VISIT. Getting Started This guide will: 1. Provide you with information to help you and your family
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery
 medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This Medicine Update is for people who have been prescribed
medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This Medicine Update is for people who have been prescribed
Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia.
 Hemophilia Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia. Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Hemophilia Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia. Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT. low blood counts.
 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT low blood counts. 1 INTRODUCTION Overview It is important for you to be aware that cancer, and some treatments for cancer, may affect your blood counts. Radiation therapy and
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT low blood counts. 1 INTRODUCTION Overview It is important for you to be aware that cancer, and some treatments for cancer, may affect your blood counts. Radiation therapy and
For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine
 For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant NP = Navelbine (vinorelbine), cisplatin ABOUT THIS
For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant NP = Navelbine (vinorelbine), cisplatin ABOUT THIS
Paclitaxel and Carboplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation
 Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
You. guide to tuberculosis treatment and services
 Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA
 MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA (stel ar a) (ustekinumab) Injection What is the most important information I should know about STELARA? STELARA is a medicine that affects your immune system. STELARA can increase
MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA (stel ar a) (ustekinumab) Injection What is the most important information I should know about STELARA? STELARA is a medicine that affects your immune system. STELARA can increase
