Pushing and Pulling In Health Care Environments A Review of the Risks and Ergonomic Solutions
|
|
|
- Edwina Simpson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pushing and Pulling In Health Care Environments A Review of the Risks and Ergonomic Solutions Perceived Impact of NHS Reform The Health and Social Care Act 2012 is changing the National Health Service (NHS) in an unprecedented way, (GB Parliament 2012). Increasing economic pressures are having an impact on staffing levels and healthcare professionals are facing additional stress as they endeavour to work more efficiently to deliver high quality care. Restructuring of job roles, stress and high workload are driving many nurses to consider leaving the profession. (RCN 2012) Musculo-Skeletal Disorders It is known that work related stress and musculo-skeletal disorders (MSDs) are significant causative factors for sickness absence in NHS staff with up to 40% attributed to MSDs (Topping 2011) There is also a link between stress and recovery outcomes for persons experiencing lower back pain (CSAG 1994 and Whysall 2008). Clearly the impact of psychosocial factors cannot be overlooked in the management of MSDs especially if work related anxiety, stress and depression are impeding recovery. There are six (6) worked related stress factors outlined by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE 2007), some of which could increase in severity due to increased work pressures, additional work demands and overall significant changes to the workload Demands Control Support Relationships Role Change Demands This is relevant as it includes stresses placed on the employee that may result from poor ergonomic design of the environment or the equipment being used. The job may be unnecessarily more difficult if it is not correctly and ergonomically matched to the employee; an example would include manually pushing patient trolleys frequently over long distances or up inclines. This failure to match the job to the person can result in stress and musculo-skeletal problems. Control Employees should be consulted and have some control regarding the tasks they carry out. They should be involved in risk assessments and the possible solutions including the trial and selection of equipment that is purchased to reduce musculo-skeletal risks. Change Organisational change within the NHS is inevitable and undue stress can be mitigated if employers consult with employees and advise them of change in a timely manner. Support should be provided for new roles and training given as necessary. This overview outlining some of the stress factors illustrate how significant changes to job roles; if combined with a lack of understanding and support from management; can be a recipe for occupationally-related ill health. This emphasises the need for sound management structures and systems of work, including risk assessment, to mitigate ergonomic hazards and stress related ill health. The evidence shows that MSDs are a cause for concern in the United Kingdom, particularly for those working in health care environments and having direct contact with patients. HSE Statistics - MSDs HSE statistics relating to MSD for the period 2011/12 indicate that there were 439,000 cases out of a total of 1,073,000 work related illnesses (HSE 2012a). Back disorders form part of this category and the industries with the highest prevalence rates averaged over 2009/10 and 2011/12 are construction and human health activities but notably those that are hospital related. Within these industries the main work factors giving rise to problems are:- Manual handling including lifting, pushing and pulling Awkward postures Workplace accidents Over a 5 year period 2006/ /11 pushing and pulling was the most common specified type of major manual handling injury. Lifting and lowering being the most common specified type that resulted in lost time injury >3 days (HSE 2012b). Legislation and Ergonomic Factors Employers have a responsibility to improve ergonomic standards and reduce the risks related to manual handling activities such as lifting, pushing and pulling. A European Directive 90/269/EEC was issued on 29 May 1990 (European Parliament 1990). The response in the United Kingdom was the implementation of The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (HSE 1992). These regulations offer guidance and some statutory obligations relating to lifting, pushing and pulling activities. Emphasis is often placed 1
2 on the guideline weights for lifting and lowering but equally important is the need to minimise the pushing and pulling forces. This is especially relevant with pushing and pulling incidents being cited as the most common cause of major handling injury within the HSE statistics and MSD category. There are a number of physical factors relating to pushing and pulling that can contribute to musculo-skeletal risk (Brace 2005) Friction Wheel design Load weight Posture handle height Figure 1 Scuff marks - Start of the Incline loss of traction Figure 2 Good posture can be attained during 90 degree turns Friction Friction can be defined as the resistance offered to the movement of one body past another body with which it is in contact. The hardness of the wheel material, floor surface, and wheel orientation are factors that can increase friction and influence the amount of force needed to push a trolley or bed. A harder wheel composition and floor surface will make pushing easier. This change in friction and forces required to initiate or sustain momentum is verified when riding a bicycle and noting what happens when the bicycle is pedalled on a dry paved surface, sand or ice? Wheel Design The diameter of the wheels is significantly important as the start-up forces are reduced as the diameter increases. This is demonstrated by Al-Eisawi et al. This research looked at factors affecting push and pull forces in which it was found that increasing the wheel diameter by a factor of 2 reduces the pushing and pulling force by half. The influence of wheel width was less significant with little change in start up forces when the wheel width was increased by 50%. The positioning of wheels has relevance and also which ones will swivel. When pushing it is better if the rear wheels will swivel, for pulling the front wheels should swivel. Trolleys having only 4 corner swivelling castors are harder to push as they may not be lined up in the same direction. Pushing in a straight line can be difficult due to lateral forces affecting the operator. (Al-Eisawi 1999) These issues can be improved by the addition of a fixed centre wheel or placing a fixed wheel at each edge of the trolley in the exact centre position. This combination has been shown to improve manoeuvrability by reducing the turning circle and also decreasing the forces required when changing direction. (Das 2002a) Figure 3 Inclined corridors no longer a problem -short wheelbase to drive unit Load Weight There is a correlation between trolley weight and the forces needed to gain and sustain momentum. The technology for beds and trolleys is constantly improving, one of these enhancements is the ability to carry heavier loads. A negative aspect of this can be an increase in the net trolley weight and total weight when transporting a patient. This increases the start up forces needed to gain momentum and relevant if being manually operated. The forces required to stop momentum may also be significant and often overlooked (Ferreira et al 2004) Start up and stop force guidelines are provided by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE 2004). These force guidelines are designed to act as a filter to help determine if a more in depth risk assessment is required. In the UK the start up and stop forces are 20kg for men and 15kg 2
3 for women, to sustain momentum a guideline of 10kg for men and 7kg for women is specified. It must be noted that these are recommendations only and not statutory requirements. The start up and stop force measurements are not the same as the compression and shear forces impacting on the lumbar vertebrae during pushing and pulling activities. Load weight and distance being pushed are important risk factors to consider Waters et al 2011 makes reference to the AORN Ergonomic Tool 7. The tool considers the risk factors and forces required to manoeuvre different items of equipment generally found in a perioperative environment. The tool offers guidance regarding the estimated forces, the number of staff that may be required and also the recommended maximum distance to travel (Waters 2011). It is interesting to note that loading a patient trolley with a 300lb load would limit the maximum pushing distance to 60 metres. Based on experience many wards in a large acute hospital are beyond this 60 metre range thus indicating that additional risk controls would be required. It is recommended that patient trolley loads be kept below 225kg in order to avoid excessive compression forces to the lumbar spine (Resnick & Chaffin 1995). In many circumstances this may not be possible especially as obesity becomes more prevalent creating an increased risk of hospital admissions for bariatric persons (Cookson & Rush 2011). Postural Concerns Assuming a pushing task cannot be avoided, there is a requirement to make the task safer and more efficient for the operator. There are a number of postural factors to consider; these can be affected by the trolley design e.g. a fixed height trolley would cause some carers to stoop or be unable to have their arms in a position to deliver optimum force. Stooping forward during a pushing activity has been shown to increase compression and shear forces in the lumbar spine. Trolley handle height, width and hand grip diameter are other areas to consider (Das 2002b and Jansen 2002). When pushing; it is generally accepted that the optimum hand height be approximately 1 metre or in the elbow to hip range. Feet position should be in a walking stance with one slightly in front of the other. Discussion - Ergonomic Solutions It is clear from the evidence cited that health care professionals are under pressure in a demanding working environment. Basic everyday manual handling tasks and especially pushing and pulling activities can be potentially hazardous unless the ergonomic problems are risk assessed and control measures introduced. Hospital staff having input into the purchase of beds or trolleys should have some insight into the potential problems linked to pushing and pulling tasks. Without this insight it is logical to assume that inappropriate purchases could be made. Stryker are keen to address these ergonomic challenges and actively consult with end users during the planning and design stage. This coupled with commissioned research projects provides a higher probability that the end product is fit for purpose. One of these recent research projects has clearly demonstrated that it is possible to reduce pushing risks by considering evidence based research principles and incorporating these into trolley design (Butt et al 2012). The Zoom motorised trolley incorporates many proven ergonomic features already featured in this article. Figure 4 External driving device two trolley wheels raised off the floor. How does the operator calculate how much weight is being applied to the machine? Figure 5 External device using a remote control option far superior to manually pushing but still a long wheelbase and distance to the drive wheel L4/L5 Compression Rate While Transpor ng on Carpet Fi h Wheel System Stryker Motorised Zoom L4/L5 Compression Rate (llb) Figure 6 Trolley Type Comparison - L4/L5 Compression Rate Reduction (Adapted from Butt et al 2012) 3
4 Fi h Wheel System Stryker Motorised Zoom Average RTE Figure 7 Trolley type comparison - Average Rate of Perceived Exertion (Adapted from Butt et al 2012) Learning: Points to Consider Calculate the overall distance for the chosen route What is the total weight including the trolley, patient and accessories Are there any inclines on the route Does the journey include any 90 degree turns Are there any spatial constraints i.e. manoeuvring in confined spaces What is the floor surface constructed from on the selected route Who will push the trolley Take a good look at the wheel design, composition, quantity and configuration. Ensure that the equipment you are about to purchase is designed and able to mitigate the risk Try before you buy Rate of Perceived Exer on(rpe) while Pushing on an incline The specific research compared two trolleys, one having the standard 5 th wheel design and the other having a large 5 th wheel and integral drive motor. 20 Registered Nurses aged between 24 and 61 years were selected, they did not disclose any history of MSDs. The tasks involved a series of manoeuvres using both trolleys; the first task involved pushing, cornering and stopping a trolley with a 300lb load. The second task involved pushing a trolley up an 8 degree incline; this was carried out using two flooring surfaces i.e. smooth laminate type and carpeted tiles. The results demonstrated that the Rate of Perceived Exertion was reduced by 42% when compared to the standard 5 th wheel trolley design. This figure was recorded moving from horizontal to the start of the incline. This move from flat to the incline is a point where some bed and trolley driving devices can lose traction due to the additional forces required. (Fig 1) A 35.4% reduction in the L4/L5 compression rate was also achieved when manoeuvring up the motorised Zoom trolley up the carpeted incline. (Fig 6 & Fig 7) In all the tests the compression forces were below the level of 3,400 to 6,400 Newton that is a generally accepted safety margins for potential tissue damage. (Marras 2008) The Stryker Zoom incorporates a number of ergonomic features in addition to the motorised unit. The trolley can be adjusted to attain the optimum height for pushing, the hand grips are soft touch and comfortable. The drive unit is central, shortening the wheelbase and making it easier to manoeuvre on inclines and 90 degree turns. (Fig 2 and Fig 3) The drive unit is also integral so the overall trolley length is not increased External trolley drivers are universally available and although an improvement compared to manual pushing they do have some inherent problems. (Fig 4 and Fig 5) When required the device must be secured to the bed or trolley, this can be castor cups that are designed to support the 2 wheels on a single axel. Other methods include jaws that grip the trolley at a specified point. These methods are sometimes marketed as universal adaptors or in some cases specific attachment bars have to be fabricated to match each different bed or trolley model that is being moved. In most cases the connection of a separate drive unit will increase the overall length, this can be hard to steer and may not fit in a lift. There can be some manual handling activity involved to connect the drive unit to the bed or trolley. Understanding the maximum safe working load can be confusing. Some devices raise one axel off the ground and staff may be unsure of the load being taken. Assuming a trolley weighs 150kg and the patient weighs 150kg how much load is taken if only one axel is lifted off the ground, this can be confusing for staff as they may wrongly assume they have overloaded the device. Conclusion Pushing and pulling hospital equipment such as bed and trolleys is a potential hazard. The level of risk is often overlooked or not fully understood with perhaps more importance being placed on the avoidance of lifting. There is however sufficient evidence based research to highlight the potential harm to the musculo-skeletal system. Fortunately there are a number of ergonomic solutions that will reduce or in some cases eliminate the risk. Providing training to personnel can help but this should not be regarded as the primary solution. Introducing ergonomic solutions matched to risk assessments is the way forward. Equipment purchases should be subject to discussion and collaboration with end users. Consider the ergonomic design features and supporting evidence supplied by the manufacturer. Staff should assess the whole pushing and pulling scenarios within their organisations. Before making any purchases consider a number of risk factors and question whether the item being purchased can reduce the risk. References Al-Eisawi K.W. Kerk C. Congleton J. Amendola A. Jenkins O. Gaines W. Factors Affecting Minimum Push and Pull Forces of Manual Carts Applied Ergonomics 30 (1999) P Brace, T (2005) The Dynamics of Pushing and Pulling in the Workplace Assessing and Treating the problem. AAOHN Journal May 2005 Vol53 No 5 P Butt S. Fredericks T. Cure L. Burns J. Harms K.(2012) Effects of Transport Stretcher Mobility Related Design Features On Healthcare Workers Department of Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering College of Engineering & Applied Sciences Western Michigan University Clinical Standards Advisory Group (1994) Back Pain Page 51 HMSO 1994 ISBN Cookson K. Rush A, (2011) The Guide to the Handling of People A systems Approach 6 th ed Chapter 12 Page 194 People handling for Bariatrics A systems Approach Edited by Jacqui Smith, Published by BackCare Teddington Middlesex 4
5 Das, B., Wimpee, J., & Das, B. (2002a). Ergonomics evaluation and redesign of a hospital meal cart. Applied Ergonomics, 33, Das, B., Wimpee, J., & Das, B. (2002b). Ergonomics evaluation and redesign of a hospital meal cart. Applied Ergonomics, 33, European Parliament (1990) Council Directive 90/269/EEC 29 th May 1990 On the minimum health and safety requirements for the manual handling of loads where there is a risk particularly of back injury to workers Accessed 29 th Nov 2012 Ferreira, J. Boocock M. Gray M (2004) Review of the risks associated with pushing and pulling heavy loads Research Report 228 HMSO ISBN Great Britain Parliament (2012) Health and Social Care Act London HMSO HSE (1992) The manual handling operations regulations 1992 (As amended) HMSO London HSE (2004) Manual Handling - Guidance on Regulations L23 HSE Books Accessed 29 th Nov 2012 HSE (2007) Managing the causes of work related stress A step by step approach using the management standards. HSE document HSG218 ISBN Accessed 29 th Nov 2012 HSE (2012a) Musculo-skeletal Disorders Accessed Nov 21 st 2012 HSE (2012b) Handling Injuries Accessed Nov 21 st 2012 Jansen, J.P., Hoozemans, M.J., van der Beek, A.J., & Frings-Dresen, M.H. (2002). Evaluation of ergonomic adjustments of catering carts to reduce external pushing forces. Applied Ergonomics, 33, Marras W. (2008) The Working Back, A systems Review John Wiley & Sons, IncHoboken, New Jersey, United States RCN (2012) Royal College of Nursing Evidence to the NHS Pay Review Body URL data/assets/pdf_file/0019/482230/prb_report.pdf accessed 20 th Nov 2012 Resnick, M.L., & Chaffin, D. (1995). An ergonomic evaluation of handle height and load in maximal and sub maximal cart pushing. Applied Ergonomics, 26, This relates to excessive compression forces above 225kg Topping J (2011) Getting back to work is the best medicine Nursing Times; Aug 30-Sep 5, 2011; 107, 34; P33 Waters T Lloyd J. Hernandez E. Nelson A (2011) AORN Ergonomic Tool 7: Pushing, Pulling and Moving Equipment on Wheels AORN Journal September 2011 Vol 94 No 3 p Whysall Z (2008) Stress and MSDs: Moving Towards Common Ground? Occupational Health February (02) link-between-stress-and-musculoskeletal-disorders.htm This document is intended solely for the use of healthcare professionals. A healthcare professional must always rely on his or her own professional clinical judgment when deciding whether to use a particular product when treating a particular patient. Stryker does not dispense medical advice and recommends that surgeons be trained in the use of any particular product before using it in surgery. The information presented is intended to demonstrate the breadth of Stryker product offerings. A surgeon must always refer to the package insert, product label and/or instructions for use before using any Stryker product. Products may not be available in all markets because product availability is subject to the regulatory and/or medical practices in individual markets. Please contact your Stryker representative if you have questions about the availability of Stryker products in your area. Stryker Corporation or its divisions or other corporate affiliated entities own, use or have applied for the following trademarks or service marks: Stryker, Zoom. All other trademarks are trademarks of their respective owners or holders. Stryker SA Cité-Centre Grand-Rue Montreux Switzerland t : f : The products listed above are CE marked according to the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC. *MTXMEDCS02EN* Mkt Lit- MTXMEDCS02EN Copyright 2013 Stryker 5
Safe Manual Handling Operation. Improving Everyone s Health & Safety
 Safe Manual Handling Operation Improving Everyone s Health & Safety What Is Manual Handling? Any transporting or supporting of a load by hand or bodily force This includes: Lifting, putting down, pushing,
Safe Manual Handling Operation Improving Everyone s Health & Safety What Is Manual Handling? Any transporting or supporting of a load by hand or bodily force This includes: Lifting, putting down, pushing,
MANUAL HANDLING IN OFFICES
 Manual Handling General risk assessments of work/teaching activities are required to be completed under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations. Where appropriate, manual handling should
Manual Handling General risk assessments of work/teaching activities are required to be completed under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations. Where appropriate, manual handling should
Standard Operating Procedure for Handling an Inanimate Load
 Standard Operating Procedure for Handling an Inanimate Load Moving and handling an inanimate load/s is a key part of the working day for most employees. Moving inanimate loads can take place in many different
Standard Operating Procedure for Handling an Inanimate Load Moving and handling an inanimate load/s is a key part of the working day for most employees. Moving inanimate loads can take place in many different
Manual Handling. Procedure
 ` Manual Handling Procedure *All Forth Valley College Health, Safety and Welfare Procedures are covered under the overarching Health, Safety and Welfare Policy. Status: Date of version: Review Date: Reviewed
` Manual Handling Procedure *All Forth Valley College Health, Safety and Welfare Procedures are covered under the overarching Health, Safety and Welfare Policy. Status: Date of version: Review Date: Reviewed
Risk Services Best Practices Bulletin Material Handling in Foodservice Presented by Office of the President Risk Services May 2012
 Material Handling in Foodservice Presented by Office of the President Risk Services May 2012 Throughout the UC system, dining staff are among the occupational groups most at risk for injury. The high frequency
Material Handling in Foodservice Presented by Office of the President Risk Services May 2012 Throughout the UC system, dining staff are among the occupational groups most at risk for injury. The high frequency
Prime TC. Transport Chair. Patient Transport Redefined.
 Prime TC Transport Chair Patient Transport Redefined. Stryker and the Michael Graves Design Group: A Patient-driven Partnership For over 70 years, Stryker has been a partner in patient transport for hospitals
Prime TC Transport Chair Patient Transport Redefined. Stryker and the Michael Graves Design Group: A Patient-driven Partnership For over 70 years, Stryker has been a partner in patient transport for hospitals
Manual Handling- The Whole Story!
 Manual Handling- The Whole Story! For Responsible Managers and Assessors Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager July 2005 Course Content 1 What is Manual Handling? 2 What s the Problem?
Manual Handling- The Whole Story! For Responsible Managers and Assessors Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager July 2005 Course Content 1 What is Manual Handling? 2 What s the Problem?
Lifting and Handling, a Risk Assessor s Guide
 Lifting and Handling, a Risk Assessor s Guide 1 Introduction Unfortunately manual handling accidents are all too common, and can lead to life-long problems with bad backs. While they do not have the same
Lifting and Handling, a Risk Assessor s Guide 1 Introduction Unfortunately manual handling accidents are all too common, and can lead to life-long problems with bad backs. While they do not have the same
These notes are designed to be used in conjunction with the Moving and Handling PowerPoint slides.
 CORE SKILLS FRAMEWORK MOVING AND HANDLING PRINCIPLES FOR STAFF: LESSON NOTES & TIPS FOR A SUGGESTED APPROACH These notes are designed to be used in conjunction with the Moving and Handling PowerPoint slides.
CORE SKILLS FRAMEWORK MOVING AND HANDLING PRINCIPLES FOR STAFF: LESSON NOTES & TIPS FOR A SUGGESTED APPROACH These notes are designed to be used in conjunction with the Moving and Handling PowerPoint slides.
[Project name] Standard Operating Procedures. Body Mechanics
![[Project name] Standard Operating Procedures. Body Mechanics [Project name] Standard Operating Procedures. Body Mechanics](/thumbs/27/11986346.jpg) [Project name] Standard Operating Procedures Body Mechanics PURPOSE. The purpose of this SOP is to provide information to minimize staff injuries with the focus on back injuries resulting from improper
[Project name] Standard Operating Procedures Body Mechanics PURPOSE. The purpose of this SOP is to provide information to minimize staff injuries with the focus on back injuries resulting from improper
Guidance for Manual Handling of Gas Cylinder
 Guidance for Manual Handling of Gas Cylinder The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (updated 1998) came into force in January 1993. The purpose of the regulations is to reduce the risk of injury
Guidance for Manual Handling of Gas Cylinder The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (updated 1998) came into force in January 1993. The purpose of the regulations is to reduce the risk of injury
Back Pain Musculoskeletal Disorder Updated October 2010
 Back Pain Musculoskeletal Disorder Updated October 2010 According to the Health and Safety Executive back pain is the most common health problem for British workers. Approximately 80% of people experience
Back Pain Musculoskeletal Disorder Updated October 2010 According to the Health and Safety Executive back pain is the most common health problem for British workers. Approximately 80% of people experience
Flooring Selection for Acute Care Facilities: Safety Implications
 Flooring Selection for Acute Care Facilities: Safety Implications Slipping and falling, pushing heavy objects and standing all day are the three main culprits of flooring-associated injuries in hospitals.
Flooring Selection for Acute Care Facilities: Safety Implications Slipping and falling, pushing heavy objects and standing all day are the three main culprits of flooring-associated injuries in hospitals.
Ergonomics in the Workplace
 Ergonomics in the Workplace Ergonomics in the Workplace 1 Introduction The purpose of this short guide is to provide information to the reader on the subject of Ergonomics. It also provides guidance on
Ergonomics in the Workplace Ergonomics in the Workplace 1 Introduction The purpose of this short guide is to provide information to the reader on the subject of Ergonomics. It also provides guidance on
CCG CO11 Moving and Handling Policy
 Corporate CCG CO11 Moving and Handling Policy Version Number Date Issued Review Date V2 06/11/2015 01/10/2017 Prepared By: Consultation Process: Formally Approved: 05/11/2015 Governance Manager, North
Corporate CCG CO11 Moving and Handling Policy Version Number Date Issued Review Date V2 06/11/2015 01/10/2017 Prepared By: Consultation Process: Formally Approved: 05/11/2015 Governance Manager, North
Health and Safety Initial Induction Training. Manual Handling
 Health and Safety Initial Induction Training Manual Handling This training has been designed to provide information to help you understand the problems associated with the manual handling of loads and
Health and Safety Initial Induction Training Manual Handling This training has been designed to provide information to help you understand the problems associated with the manual handling of loads and
DEMOLITION Photocopy this profile and distribute it as widely as possible!
 Musculoskeletal hazards and controls DEMOLITION Photocopy this profile and distribute it as widely as possible! Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), such as chronic back pain or shoulder problems, often take
Musculoskeletal hazards and controls DEMOLITION Photocopy this profile and distribute it as widely as possible! Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), such as chronic back pain or shoulder problems, often take
Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work
 Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work The Optimal Office Work Station Use an adjustable chair with good lumbar support. Keep your feet flat on a supportive surface (floor or foot rest). Your knees should
Preventing Overuse Injuries at Work The Optimal Office Work Station Use an adjustable chair with good lumbar support. Keep your feet flat on a supportive surface (floor or foot rest). Your knees should
Manual handling at work
 Manual handling at work A brief guide Introduction This leaflet describes what you, as an employer, may need to do to protect your employees from the risk of injury through manual handling tasks in the
Manual handling at work A brief guide Introduction This leaflet describes what you, as an employer, may need to do to protect your employees from the risk of injury through manual handling tasks in the
Manual handling. Introduction. The legal position
 Manual handling Introduction Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), including manual handling injuries, are the most common type of occupational ill health in the UK. Back pain and other MSDs account
Manual handling Introduction Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), including manual handling injuries, are the most common type of occupational ill health in the UK. Back pain and other MSDs account
Moving and Handling Techniques
 Moving and Handling Techniques Introduction Manual handling involves any activity that requires the use of force exerted by a person to lift, lower, push, pull, carry or otherwise move or hold an object.
Moving and Handling Techniques Introduction Manual handling involves any activity that requires the use of force exerted by a person to lift, lower, push, pull, carry or otherwise move or hold an object.
How To Treat Musculoskeletal Injury In Sonographers
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS IN SONOGRAPHERS: ARE WE DOING ENOUGH? Many terms are used to refer to work related injuries among sonographers. Musculosketetal injury (MSI) Repetitive motion injury (RMI) Repetitive
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS IN SONOGRAPHERS: ARE WE DOING ENOUGH? Many terms are used to refer to work related injuries among sonographers. Musculosketetal injury (MSI) Repetitive motion injury (RMI) Repetitive
Safe Lifting/Back Safety Training. Presented by Rita Gagnon Occupational Health Outreach Coordinator Benefis Health Systems 406-731-8328
 Safe Lifting/Back Safety Training Presented by Rita Gagnon Occupational Health Outreach Coordinator Benefis Health Systems 406-731-8328 Risk Factors Involved with Manual Handling Tasks: Bending at Trunk
Safe Lifting/Back Safety Training Presented by Rita Gagnon Occupational Health Outreach Coordinator Benefis Health Systems 406-731-8328 Risk Factors Involved with Manual Handling Tasks: Bending at Trunk
Stryker S3 Safe. Simple. Secure.
 Medical Stryker S3 Safe. Simple. Secure. Stryker S3 Med/Surg Bed Stryker S3 The standard of care preferred by more hospitals than any other. Retractable Frame Exclusive retractable frame allows proximal
Medical Stryker S3 Safe. Simple. Secure. Stryker S3 Med/Surg Bed Stryker S3 The standard of care preferred by more hospitals than any other. Retractable Frame Exclusive retractable frame allows proximal
CCG CO11 Moving and Handling Policy
 Corporate CCG CO11 Moving and Handling Policy Version Number Date Issued Review Date V1: 28/02/2013 04/03/2013 31/08/2014 Prepared By: Consultation Process: Formally Approved: Information Governance Advisor
Corporate CCG CO11 Moving and Handling Policy Version Number Date Issued Review Date V1: 28/02/2013 04/03/2013 31/08/2014 Prepared By: Consultation Process: Formally Approved: Information Governance Advisor
HealthandSafetyOntario.ca. Hazards. Introduction. Legislation
 Manual Materials handling Introduction Manual materials handling operations are carried out in most workplaces. Each handling task poses unique demands on the worker. However, workplaces can help workers
Manual Materials handling Introduction Manual materials handling operations are carried out in most workplaces. Each handling task poses unique demands on the worker. However, workplaces can help workers
Guidance notes for completing a detailed manual handling risk assessment
 Guidance notes for completing a detailed manual handling risk assessment This guidance should be used in conjunction with the detailed manual handling assessment form in appendix 1. When filling out the
Guidance notes for completing a detailed manual handling risk assessment This guidance should be used in conjunction with the detailed manual handling assessment form in appendix 1. When filling out the
ERGONOMICS IN CONSTRUCTION
 1.0 1.0 Facilitator / Leader Tasks Before the Tool Box Talk (TBT): 1. Read through this TBT guide. 2. Walk the job site to find ergonomics examples based on the TBT. If possible, take photos of safe and
1.0 1.0 Facilitator / Leader Tasks Before the Tool Box Talk (TBT): 1. Read through this TBT guide. 2. Walk the job site to find ergonomics examples based on the TBT. If possible, take photos of safe and
HOSPITALITY RISK FACTORS & BEST PRACTICES - LAUNDRY
 Responsibilities of commercial laundry staff can include washing, drying, steaming, ironing, and chemically treating fabrics for use in hospitals, hotels, and other settings. Laundry can be heavy, treated
Responsibilities of commercial laundry staff can include washing, drying, steaming, ironing, and chemically treating fabrics for use in hospitals, hotels, and other settings. Laundry can be heavy, treated
Workplace Job Accommodations Solutions for Effective Return to Work
 Workplace Job Accommodations Solutions for Effective Return to Work Workplace Job Accommodations Solutions for Effective Return to Work Published by 102 275 Broadway Winnipeg, MB R3C 4M6 www.mflohc.mb.ca
Workplace Job Accommodations Solutions for Effective Return to Work Workplace Job Accommodations Solutions for Effective Return to Work Published by 102 275 Broadway Winnipeg, MB R3C 4M6 www.mflohc.mb.ca
POLICY FOR SAFER MANUAL HANDLING OPERATIONS
 POLICY FOR SAFER MANUAL HANDLING OPERATIONS DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 6 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 19 December 2012 Name of originator/author: Back Care Advisor Name of responsible
POLICY FOR SAFER MANUAL HANDLING OPERATIONS DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 6 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 19 December 2012 Name of originator/author: Back Care Advisor Name of responsible
The Advantages of Ergonomics
 The Advantages of Ergonomics Workers come in all different sizes. Ergonomics can help make the work more comfortable for the individual worker. What is ergonomics? Ergonomics is designing a job to fit
The Advantages of Ergonomics Workers come in all different sizes. Ergonomics can help make the work more comfortable for the individual worker. What is ergonomics? Ergonomics is designing a job to fit
ERGONOMICS. Improve your ergonomic intelligence by avoiding these issues: Awkward postures Repetitive tasks Forceful exertions Lifting heavy objects
 ERGONOMICS The goal of ergonomics is to reduce your exposure to work hazards. A hazard is defined as a physical factor within your work environment that can harm your body. Ergonomic hazards include working
ERGONOMICS The goal of ergonomics is to reduce your exposure to work hazards. A hazard is defined as a physical factor within your work environment that can harm your body. Ergonomic hazards include working
Evaluation of Z-Slider for Lateral Patient Transfers, Repositioning, and Staff Musculoskeletal Injuries (Abstract) Laurie J. Bacastow RN, MSN, CNRN
 Evaluation of Z-Slider 1 Evaluation of Z-Slider for Lateral Patient Transfers, Repositioning, and Staff Musculoskeletal Injuries (Abstract) Laurie J. Bacastow RN, MSN, CNRN Stanford Hospital and Clinics
Evaluation of Z-Slider 1 Evaluation of Z-Slider for Lateral Patient Transfers, Repositioning, and Staff Musculoskeletal Injuries (Abstract) Laurie J. Bacastow RN, MSN, CNRN Stanford Hospital and Clinics
Electric profiling beds
 Electric profiling beds in health care The wrong bed will waste scarce human resources and put them at risk Rabbi Julia Neuberger, former CE,The King s Fund. 1 A bed is the one piece of equipment nearly
Electric profiling beds in health care The wrong bed will waste scarce human resources and put them at risk Rabbi Julia Neuberger, former CE,The King s Fund. 1 A bed is the one piece of equipment nearly
REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONING
 Musculoskeletal hazards and controls REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONING Photocopy this profile and distribute it as widely as possible! Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), such as chronic back pain or shoulder
Musculoskeletal hazards and controls REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONING Photocopy this profile and distribute it as widely as possible! Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), such as chronic back pain or shoulder
MODEL GENERIC RISK ASSESSMENTS - MANUAL HANDLING OF LOADS
 APPENDIX E MODEL GENERIC RISK ASSESSMENTS - MANUAL HANDLING OF LOADS Model Generic Risk Assessments To assist managers with complying with their duties under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations
APPENDIX E MODEL GENERIC RISK ASSESSMENTS - MANUAL HANDLING OF LOADS Model Generic Risk Assessments To assist managers with complying with their duties under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations
Patient handling techniques to prevent MSDs in health care
 28 Introduction Patient handling techniques Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are a serious problem among hospital personnel, and in particular the nursing staff. Of primary concern are back
28 Introduction Patient handling techniques Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are a serious problem among hospital personnel, and in particular the nursing staff. Of primary concern are back
LIFTING AND BACK SAFETY TRAINING LESSON PLAN
 LIFTING AND BACK SAFETY TRAINING LESSON PLAN Topic: Back Safety and Proper Lifting Techniques This presentation is designed to assist trainers conducting Lifting and Back Safety training for workers. Back
LIFTING AND BACK SAFETY TRAINING LESSON PLAN Topic: Back Safety and Proper Lifting Techniques This presentation is designed to assist trainers conducting Lifting and Back Safety training for workers. Back
Guide to manual tasks high impact function (HIF) audit 2010 March 2010
 Guide to manual tasks high impact function (HIF) audit 2010 March 2010 1 Adelaide Terrace, East Perth WA 6004 Postal address: Mineral House, 100 Plain Street, East Perth WA 6004 Telephone: (08) 9358 8002
Guide to manual tasks high impact function (HIF) audit 2010 March 2010 1 Adelaide Terrace, East Perth WA 6004 Postal address: Mineral House, 100 Plain Street, East Perth WA 6004 Telephone: (08) 9358 8002
WHAT IS ERGONOMICS? What exactly does ergonomics mean? And what features should a product have to be called ergonomic?
 WHAT IS ERGONOMICS? Often, when we decide to buy a chair, a sofa or even a car, we come across the term ergonomic seating. It means that the particular product has been designed with the body s need for
WHAT IS ERGONOMICS? Often, when we decide to buy a chair, a sofa or even a car, we come across the term ergonomic seating. It means that the particular product has been designed with the body s need for
Musculoskeletal disorders in construction
 1 Musculoskeletal disorders Construction is a high-risk sector, but it is not just a worker's safety at risk, but also his health. While there are well over a thousand workers killed each year in accidents
1 Musculoskeletal disorders Construction is a high-risk sector, but it is not just a worker's safety at risk, but also his health. While there are well over a thousand workers killed each year in accidents
A guide for employees
 A guide for employees This booklet has been developed as a guide to assist in the prevention of muscular discomfort and strain that can sometimes be associated with computer use. The information provided
A guide for employees This booklet has been developed as a guide to assist in the prevention of muscular discomfort and strain that can sometimes be associated with computer use. The information provided
Safe Lifting and Carrying
 PART 1 Basic Lifts Proper lifting and handling will help protect against injury and make your job easier. It takes training and practice to do it right. The following are basic steps in safe lifting and
PART 1 Basic Lifts Proper lifting and handling will help protect against injury and make your job easier. It takes training and practice to do it right. The following are basic steps in safe lifting and
Aching arms (or RSI) in small businesses. Is ill health due to upper limb disorders a problem in your workplace?
 Aching arms (or RSI) in small businesses Is ill health due to upper limb disorders a problem in your workplace? This booklet is designed to help employers and managers in small businesses to understand
Aching arms (or RSI) in small businesses Is ill health due to upper limb disorders a problem in your workplace? This booklet is designed to help employers and managers in small businesses to understand
Contents. Working safely with manual handling
 learning Enable Skills Bulletin September 2008 To keep you informed in community services. FREE Circulating accommodation and residential services educational Services and community services in general.
learning Enable Skills Bulletin September 2008 To keep you informed in community services. FREE Circulating accommodation and residential services educational Services and community services in general.
Ergonomics for Schoolchildren and Young Workers
 Ergonomics for Schoolchildren and Young Workers Schoolchildren and Backpacks Schoolchildren everywhere are being asked to carry more and more weight around on their backs. There are many reasons why children
Ergonomics for Schoolchildren and Young Workers Schoolchildren and Backpacks Schoolchildren everywhere are being asked to carry more and more weight around on their backs. There are many reasons why children
Ergonomics and Repetitive Strain Injury
 Ergonomics and Repetitive Strain Injury Desk Research conducted by StrategyOne for Microsoft April 2008 Ergonomics and Repetitive Strain Injury What is RSI? Repetitive Strain Injury, commonly known as
Ergonomics and Repetitive Strain Injury Desk Research conducted by StrategyOne for Microsoft April 2008 Ergonomics and Repetitive Strain Injury What is RSI? Repetitive Strain Injury, commonly known as
Professor Alan Hedge, Cornell University, August 2013
 Lifting and Back Stress DEA3250/6510 Professor Alan Hedge Low Back Pain Low back pain occurs in 80% of adults at some point in their lives Low back pain is second only to upper respiratory infections as
Lifting and Back Stress DEA3250/6510 Professor Alan Hedge Low Back Pain Low back pain occurs in 80% of adults at some point in their lives Low back pain is second only to upper respiratory infections as
Safe moving and handling in our schools
 Safe moving and handling in our schools Dorset County Council Improving the quality of life for people in Dorset, now and for the future May 2009 Introduction The guidance in this booklet has been designed
Safe moving and handling in our schools Dorset County Council Improving the quality of life for people in Dorset, now and for the future May 2009 Introduction The guidance in this booklet has been designed
MANUAL HANDLING POLICY
 Northumberland Street Alnwick Northumberland NE 66 1 LT Tel: 01665 510 241 MANUAL HANDLING POLICY Designated Health and Safety Officer for the above address: Sally Lane (Deputy Manager) It is the responsibility
Northumberland Street Alnwick Northumberland NE 66 1 LT Tel: 01665 510 241 MANUAL HANDLING POLICY Designated Health and Safety Officer for the above address: Sally Lane (Deputy Manager) It is the responsibility
MSD Hazards & Solutions FORCE
 FORCE Lower Force Good Posture Less Repetition Reduced MSD Risk Lifting/Lowering Hazards Lifting from the floor Overhead Lifting Lifting out of a Bin Lifting while reaching Lifting heavy loads Lifting/Lowering
FORCE Lower Force Good Posture Less Repetition Reduced MSD Risk Lifting/Lowering Hazards Lifting from the floor Overhead Lifting Lifting out of a Bin Lifting while reaching Lifting heavy loads Lifting/Lowering
The bariatric journey in Australia: Hospital Case study
 The bariatric journey in Australia: Hospital Case study MARCH 2009 The Bariatric Journey in Australia: Hospital Case Study The Bariatric Journey in Australia: Hospital Case Study Acknowledgement This review
The bariatric journey in Australia: Hospital Case study MARCH 2009 The Bariatric Journey in Australia: Hospital Case Study The Bariatric Journey in Australia: Hospital Case Study Acknowledgement This review
Working together. The role of the TAC. Your role
 Returning to work Current from 1 July 2014 A Working together Your role The most important person in your return to work is you. A large part of recovering from your accident and getting on with your life
Returning to work Current from 1 July 2014 A Working together Your role The most important person in your return to work is you. A large part of recovering from your accident and getting on with your life
Ergonomics In The Laundry / Linen Industry
 Ergonomics In The Laundry / Linen Industry Ergonomics is a key topic of discussion throughout industry today. With multiple changes announced, anticipated, and then withdrawn the Occupational Safety and
Ergonomics In The Laundry / Linen Industry Ergonomics is a key topic of discussion throughout industry today. With multiple changes announced, anticipated, and then withdrawn the Occupational Safety and
BODY STRESSING RISK MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST
 BODY STRESSING RISK MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST BODY STRESSING RISK MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST This checklist is designed to assist managers, workplace health staff and rehabilitation providers with identifying and
BODY STRESSING RISK MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST BODY STRESSING RISK MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST This checklist is designed to assist managers, workplace health staff and rehabilitation providers with identifying and
Procedure for Managing Injury Risks Associated with Manual Tasks
 Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 Procedure for Managing Injury Risks Associated with Manual Tasks Burgess-Limerick, R. (2008). Procedure for Managing Injury
Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 Procedure for Managing Injury Risks Associated with Manual Tasks Burgess-Limerick, R. (2008). Procedure for Managing Injury
Material 1. Dolly, hand cart, wheel cart, large box, back belt
 29CFR 1926.20(b)-Accident Reduction, 29CFR 1926.21- Safety Training & Education Back and Lifting Safety Preparation 1. Read Applicable Background information and related Company Policy Chapter. 2. Make
29CFR 1926.20(b)-Accident Reduction, 29CFR 1926.21- Safety Training & Education Back and Lifting Safety Preparation 1. Read Applicable Background information and related Company Policy Chapter. 2. Make
Fundamental of a Successful Team Environmental Services and Patient Transport Best Practices
 Fundamental of a Successful Team Environmental Services and Patient Transport Best Practices September 29, 2010 Tangee B. Kizer, BSM Executive Director Environmental and Guest Services Carolinas HealthCare
Fundamental of a Successful Team Environmental Services and Patient Transport Best Practices September 29, 2010 Tangee B. Kizer, BSM Executive Director Environmental and Guest Services Carolinas HealthCare
Advise and Do s and Don ts for low back pain
 Advise and Do s and Don ts for low back pain ADVISE : Wear lumbar belt. Do hot fomentation (with hot moist towel/hot water bottle) thrice a day. Keeps a towel roll under your lower back while doing exercise,
Advise and Do s and Don ts for low back pain ADVISE : Wear lumbar belt. Do hot fomentation (with hot moist towel/hot water bottle) thrice a day. Keeps a towel roll under your lower back while doing exercise,
a patient s guide Physiotherapy advice and exercises from four weeks after neck dissection surgery
 Physiotherapy advice and exercises from four weeks after neck dissection surgery Patient Information Series PI 47 East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust 2 This leaflet has been produced by professionals,
Physiotherapy advice and exercises from four weeks after neck dissection surgery Patient Information Series PI 47 East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust 2 This leaflet has been produced by professionals,
Handling the news HANDLING THE NEWS. Who is this leaflet for? What s the problem with newspaper and magazine bundles?
 Advice for employers on manual handling of bundles Who is this leaflet for? HANDLING THE NEWS Advice for employers on manual handling of bundles This is a web friendly version of leaflet IACL105 (now withdrawn
Advice for employers on manual handling of bundles Who is this leaflet for? HANDLING THE NEWS Advice for employers on manual handling of bundles This is a web friendly version of leaflet IACL105 (now withdrawn
MANAGING MANUAL HANDLING A Guide for Managers and Heads of Departments
 MANAGING MANUAL HANDLING A Guide for Managers and Heads of Departments HEALTH & SAFETY UNIT SPRING 2006 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...2 REGULATION...2 WHAT IS MANUAL HANDLING?...2 RESPONSIBILITIES...2 STRATEGY...2
MANAGING MANUAL HANDLING A Guide for Managers and Heads of Departments HEALTH & SAFETY UNIT SPRING 2006 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...2 REGULATION...2 WHAT IS MANUAL HANDLING?...2 RESPONSIBILITIES...2 STRATEGY...2
Transferring Safety: Prevent Back Injuries
 Transferring Safety: Prevent Back Injuries OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class you will be able to: 1. Describe the back and what it does. 2. List things that you can do everyday in your home and at work
Transferring Safety: Prevent Back Injuries OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class you will be able to: 1. Describe the back and what it does. 2. List things that you can do everyday in your home and at work
Code of Practice for the Manual Handling of Gas Cylinder and exchange of regulators
 Code of Practice for the Manual Handling of Gas Cylinder and exchange of regulators General information The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (updated 1998) came into force in January 1993. The
Code of Practice for the Manual Handling of Gas Cylinder and exchange of regulators General information The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (updated 1998) came into force in January 1993. The
CARDIAC REHABILITATION Follow-up Options & Dismissal Instructions Open Heart Surgery
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION Follow-up Options & Dismissal Instructions Open Heart Surgery For patients of Jeffrey Kramer, MD As you re discharged from the hospital, you may have questions about your continuing
CARDIAC REHABILITATION Follow-up Options & Dismissal Instructions Open Heart Surgery For patients of Jeffrey Kramer, MD As you re discharged from the hospital, you may have questions about your continuing
Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..?
 Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..? Staying healthy at work is easier than you might think: Try building the following desk based exercises into your
Do you sit at a desk all day? Does your 9 to 5 leave no time for structured exercise..? Staying healthy at work is easier than you might think: Try building the following desk based exercises into your
Moving & Handling Level 1
 FACTSHEET Moving & Handling Level 1 Legal responsibili es Safer handling technique TILE Musculoskeletal disorders Looking a er your back A quick way to update mandatory training Please note: there are
FACTSHEET Moving & Handling Level 1 Legal responsibili es Safer handling technique TILE Musculoskeletal disorders Looking a er your back A quick way to update mandatory training Please note: there are
Why Back Safety is Important
 Back Safety Why Back Safety is Important Back injuries are considered by OSHA (the Occupational Safety and Health Administration) as the nation's #1 workplace safety problem. Back Injuries are often: Very
Back Safety Why Back Safety is Important Back injuries are considered by OSHA (the Occupational Safety and Health Administration) as the nation's #1 workplace safety problem. Back Injuries are often: Very
LEVEL I SKATING TECHNICAL. September 2007 Page 1
 SKATING September 2007 Page 1 SKATING SKILLS The game of Ice Hockey is a fast-paced, complex, team sport, which demands quick thinking, fast reactions and special athletic skills. Skating is the most important
SKATING September 2007 Page 1 SKATING SKILLS The game of Ice Hockey is a fast-paced, complex, team sport, which demands quick thinking, fast reactions and special athletic skills. Skating is the most important
WSN ERGONOMIC SAFETY TALK #3
 What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
What is a safety talk? This safety talk is one of a series of brief meetings held on regular basis with workers and their supervisors to discuss problems and concerns about health and safety. All safety
1. The science and art of fitting the job and the workplace to workers' needs.
 Ergonomics 1. The science and art of fitting the job and the workplace to workers' needs. 2. Use your brain, not your back. Fix the job, not the worker. Work smarter, not harder. 3. General ergonomic hazards
Ergonomics 1. The science and art of fitting the job and the workplace to workers' needs. 2. Use your brain, not your back. Fix the job, not the worker. Work smarter, not harder. 3. General ergonomic hazards
Manual handling assessment charts (the MAC tool)
 Manual handling assessment charts (the MC tool) Introduction Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), including manual handling injuries, are the most common type of occupational ill health in the
Manual handling assessment charts (the MC tool) Introduction Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), including manual handling injuries, are the most common type of occupational ill health in the
Functional Job Requirements For the Position of Special Education Teacher Department of Education, Training and the Arts Queensland
 Department of Education, Training and the Arts Queensland This document was developed for the following purposes: assisting in the development of rehabilitation programs for injured or ill employees, and
Department of Education, Training and the Arts Queensland This document was developed for the following purposes: assisting in the development of rehabilitation programs for injured or ill employees, and
Plyometric Training for Track and Field Indiana High School Clinic 2008 Larry Judge, Ph.D. Ball State University
 Plyometric Training for Track and Field Indiana High School Clinic 2008 Larry Judge, Ph.D. Ball State University What is Plyometric Training? Exercises like hopping, skipping, jumping, bounding, depth
Plyometric Training for Track and Field Indiana High School Clinic 2008 Larry Judge, Ph.D. Ball State University What is Plyometric Training? Exercises like hopping, skipping, jumping, bounding, depth
Wellness & Lifestyles Australia
 Wellness & Lifestyles Australia MANUAL HANDLING IN AGED CARE AND THE HEALTH CARE INDUSTRY E-BOOK prepared by Wellness & Lifestyles Australia 2007,2008,2009 Table of Contents Page No. IMPORTANT NOTICE...
Wellness & Lifestyles Australia MANUAL HANDLING IN AGED CARE AND THE HEALTH CARE INDUSTRY E-BOOK prepared by Wellness & Lifestyles Australia 2007,2008,2009 Table of Contents Page No. IMPORTANT NOTICE...
A Simple Guide to Health Risk Assessment Office Environment Series OE 5/2003
 A Simple Guide to Health Risk Assessment Office Environment Series OE 5/2003 Occupational Safety and Health Branch Labour Department Occupational Safety and Health Council Contents Introduction 1 Office
A Simple Guide to Health Risk Assessment Office Environment Series OE 5/2003 Occupational Safety and Health Branch Labour Department Occupational Safety and Health Council Contents Introduction 1 Office
Move and position individuals in accordance with their plan of care
 Move and position individuals in accordance with their plan of care Page 1 of 21 Level 2 Diploma in Health and Social Care Unit HSC 2028 Tutor Name: Akua Quao Thursday 12 th September 2013 Release Date:
Move and position individuals in accordance with their plan of care Page 1 of 21 Level 2 Diploma in Health and Social Care Unit HSC 2028 Tutor Name: Akua Quao Thursday 12 th September 2013 Release Date:
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland
 Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
ALENTI. with people in mind
 ALENTI The comfortable lift hygiene chair with people in mind 2 Alenti Safety and comfort Alenti is an integral part of a safe, comfortable bathing cycle. This lift hygiene chair from ArjoHuntleigh gives
ALENTI The comfortable lift hygiene chair with people in mind 2 Alenti Safety and comfort Alenti is an integral part of a safe, comfortable bathing cycle. This lift hygiene chair from ArjoHuntleigh gives
TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY-COMMERCE COMPUTER ERGONOMICS. Making Things a Little Easier
 COMPUTER ERGONOMICS Making Things a Little Easier COURSE OBJECTIVES Understand the definition of ergonomics Understand Primary Causes of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs). Understand ways to prevent CTDs
COMPUTER ERGONOMICS Making Things a Little Easier COURSE OBJECTIVES Understand the definition of ergonomics Understand Primary Causes of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs). Understand ways to prevent CTDs
HealthStream Regulatory Script
 HealthStream Regulatory Script Back Safety Version: May 2007 Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Back Injury Lesson 3: Spinal Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 4: Safe Operation of the Spine Lesson 5: Preventive
HealthStream Regulatory Script Back Safety Version: May 2007 Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Back Injury Lesson 3: Spinal Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 4: Safe Operation of the Spine Lesson 5: Preventive
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
ARE YOU HIRING YOUR NEXT INJURY?
 ARE YOU HIRING YOUR NEXT INJURY? White Paper Musculoskeletal injuries account for 25 60% of workers compensation claims across Canada. The following white paper will provide details on the benefits of
ARE YOU HIRING YOUR NEXT INJURY? White Paper Musculoskeletal injuries account for 25 60% of workers compensation claims across Canada. The following white paper will provide details on the benefits of
Tyre Awareness Training
 Tyre Awareness Training Tyre Law Tread depth Tyres on cars, light vans (not exceeding 3,500kg gross weight) and light trailers must have a tread depth of at least 1.6mm across the central three-quarters
Tyre Awareness Training Tyre Law Tread depth Tyres on cars, light vans (not exceeding 3,500kg gross weight) and light trailers must have a tread depth of at least 1.6mm across the central three-quarters
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Biomechanics of cycling - Improving performance and reducing injury through biomechanics
 Biomechanics of cycling - Improving performance and reducing injury through biomechanics Biomechanics is the science concerned with the forces that act on the human body and the effects these forces produce.
Biomechanics of cycling - Improving performance and reducing injury through biomechanics Biomechanics is the science concerned with the forces that act on the human body and the effects these forces produce.
Making the best use of lifting and handling aids
 Making the best use of lifting and handling aids Frequent and heavy lifting and handling can cause back injuries. But using lifting and handling aids can remove or reduce that risk and keep workers healthy
Making the best use of lifting and handling aids Frequent and heavy lifting and handling can cause back injuries. But using lifting and handling aids can remove or reduce that risk and keep workers healthy
ERGONOMICS. University at Albany Office of Environmental Health and Safety 2010
 ERGONOMICS University at Albany Office of Environmental Health and Safety 2010 WHAT IS ERGONOMICS? From the Greek: ergon work and nomoi natural laws Defined by Webster as: Biotechnology WHAT IS ERGONOMICS?
ERGONOMICS University at Albany Office of Environmental Health and Safety 2010 WHAT IS ERGONOMICS? From the Greek: ergon work and nomoi natural laws Defined by Webster as: Biotechnology WHAT IS ERGONOMICS?
Equipment loan arrangements and loan form
 Safety and Health Services Equipment loan arrangements and loan form Document control information Published document name: Work-equip-loan-gn Date issued: February 2016 Version: 4.1 Previous review dates:
Safety and Health Services Equipment loan arrangements and loan form Document control information Published document name: Work-equip-loan-gn Date issued: February 2016 Version: 4.1 Previous review dates:
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM
 ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
ROTATOR CUFF HOME EXERCISE PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information on this and other
Functional Job Requirements For the Position of Business Service Manager Department of Education, Training and the Arts Queensland
 Department of Education, Training and the Arts Queensland This document was developed for the following purposes: assisting in the development of rehabilitation programs for injured or ill employees, and
Department of Education, Training and the Arts Queensland This document was developed for the following purposes: assisting in the development of rehabilitation programs for injured or ill employees, and
Policy & Procedure. Safe Patient Handling (No Lift Policy)
 Effective date signifies approval of this MHS policy by the Performance Improvement Leadership Oversight Team (PILOT) (see minutes). Policy. Policy & Procedure Safe Patient Handling ( Lift Policy) Effective
Effective date signifies approval of this MHS policy by the Performance Improvement Leadership Oversight Team (PILOT) (see minutes). Policy. Policy & Procedure Safe Patient Handling ( Lift Policy) Effective
Occupational health and safety of physical therapists
 Occupational health and safety of physical therapists The World Confederation for Physical Therapy (WCPT) advocates for the right of physical therapists to a safe and healthy practice environment * that
Occupational health and safety of physical therapists The World Confederation for Physical Therapy (WCPT) advocates for the right of physical therapists to a safe and healthy practice environment * that
WELSH LOCAL GOVERNMENT ASSOCIATION MANUAL HANDLING PASSPORT SCHEME MANUAL HANDLING OF PEOPLE
 WELSH LOCAL GOVERNMENT ASSOCIATION MANUAL HANDLING PASSPORT SCHEME MANUAL HANDLING OF PEOPLE Version 3.2 Manual Handling of People October 2011 INDEX Page Title 4 Index of Hyperlinks 6 Introduction to
WELSH LOCAL GOVERNMENT ASSOCIATION MANUAL HANDLING PASSPORT SCHEME MANUAL HANDLING OF PEOPLE Version 3.2 Manual Handling of People October 2011 INDEX Page Title 4 Index of Hyperlinks 6 Introduction to
WHS Policies and Procedures Package
 WHS Policies and Procedures Package The following is an extract to highlight the style and layout of this publication, as well as a snapshot of the content. Some samples may not be included in their entirety
WHS Policies and Procedures Package The following is an extract to highlight the style and layout of this publication, as well as a snapshot of the content. Some samples may not be included in their entirety
We ve got your back. Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery
 We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
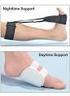 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
The Back Saver. Ergonomic Lifting Guide For Roll Handling
 The Back Saver Ergonomic Lifting Guide For Roll Handling Since 1990, Alum-a-lift has conceived, designed, developed and manufactured ergonomic lifting devices; Devices to lift, lower, move, position and
The Back Saver Ergonomic Lifting Guide For Roll Handling Since 1990, Alum-a-lift has conceived, designed, developed and manufactured ergonomic lifting devices; Devices to lift, lower, move, position and
