Neonatal abdominal real-time sonography
|
|
|
- Gwenda Dickerson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neonatal abdominal real-time sonography Thomas E. Sumner, M.D. Charles Phelps, II, M.D. J ames E. Crowe, M.D. James F. Martin, M.D. Because it makes rapid, reliable imagingpossible at the cribside, real-time ultrasonography is rapidly gaining in popularity for the diagnostic evaluation ofpediatric patients. Real-time ultrasonography is rapidly gaining popularity over conven- Introduction tional static B-scanning in pediatrics. In a B-scanner, the transducer is attached to an articulated arm that confines its motion to a single plane. Real-time imaging employs single or multiple specialized transducers capable of rapidly scanning in various planes. As a result, a set of B-scans is so quickly performed that the dynamics of the echo sources can be traced. It is especially valuable in the evaluation of moving structures, such as the heart. Instead of static B-scan images, real-time sonography provides dynamic images similar to fluoroscopy. Real-time sonographic imaging can be used to survey all portions of the abdomen rapidly and thoroughly, to follow a vessel to its origin and visualize its movement, to localize an organ, and to identify a mass quickly. Its versatility and speed are particularly applicable to neonatal abdominal examination. An additional major advantage of some real-time scanning devices is that they are portable. This permits cribside examination, making it unnecessary to remove an infant from his isolette. Recent advances in the resolution and documentation of real-time images tend to offset the disadvantage of their small size. In general, real-time systems provide a fast and effective imaging modality for screening neonates with suspected abdominal masses. Furthermore, real-time sonography is often diagnostic and may obviate the need for other more complex, more costly or invasive studies. From the Department of Radiology, Wake Forest University, Bowman Gray School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N. C. Address reprint requests to Dr. Thomas Sumner, 300 South Hawthorne Road, Winston-Salem, N. C Volume 1, Number S November 1981 RadioGraphics 29
2 Sumner, et al. Diffuse Hepatic Hemangiomata Case 1 Case 1 is an 18-day-old male infant with congestive heart failure, hepatomegaly and skin hemangiomas. The abdominal radiograph (Figure 1A) demonstrates hepatomegaly; the chest radiograph (Figure 1B) demonstrates cardiomegaly with vascular congestion. The supine longitudinal B- scan (Figure 1C) demonstrates an enlarged liver with a dilated hepatic vein draining into the inferior vena cava. Real-time sonography (Figure 1D) demonstrates an enlarged liver with multiple areas of decreased echogenicity. These relatively anechoic areas do contain internal echoes in contrast to the enlarged vascular structures which are echo free. Notice the enlarged hepatic vein draining into the inferior vena cava. In this clinical context, this patient was thought most likely to have hepatic hemangiomas resulting in hepatomegaly with high output cardiac failure. Hepatic CT scan (Figure 1E) demonstrated areas of decreased density on the unenhanced study. Subsequent aortography (Figure if) demonstrated venous pooling indicative of diffuse hepatic hemangiomata. The clinical triad consists of hepatomegaly, congestive heart failure, and cutaneous hemangiomas in one-third of patients with hepatic hemangioendotheliomatosis. Bruits may be heard over the liver and there may be liver calcifications. Complications include congestive heart failure, hyperconsumptive coagulopathy, and hepatic rupture (1). Treatment usually consists of steroids when there is diffuse involvement; radiation or surgery may be used with local involvement. These lesions regress in approximately 6-12 months. r -#{149}#{149}#{149} - ;T#{149}= #{149} A F J= * -=.- -SI Figure 1A Hepatomegaly. Figure lb Cardiomegaly, vascular congestion. 30 RadioGraphics November 1981 Volume 1, Number 3
3 Sumner, et al. Case 1 #{149} : :;ii:t#{149}#{149}- * _#{149},,4 4..-#{149}= #{149} #{149} : i...l I V #{149}#{149}J #{149},,.- ;T -,-. i;-.,j :..#{149} 1C Figure Longitudinal supine hepatic B-scan: varying sized, relatively anechoic areas. IVC: inferior vena cava, HV: large hepatic vein. Figure ld Longitudinal supine hepatic real-time sonogram showing multiple relatively anechoic areas (arrowheads), enlarged hepatic vein [V] drains into inferior vena cava [IVC]. H heart. _,...eir Liver CT (uninfused): hepatomegaly with multiple areas of Figure if decreased density. Aortogram: diffuse hepatic venous pooling. Volume 1, Number 3 November 1981 RadioGraphics 31
4 Sumner, et al. Calcified Thrombus Inferior Vena Cava in Case 2 Case 2 is a 1,600-gram premature infant delivered by cesarean section because of fetal distress. Initial abdominal radiographs (Figures 2A & B) demonstrated a right upper quadrant calcification. The ovoid or bulletshaped calcification is in the region of the inferior vena cava. This radiological appearance is typical of calcified thrombus within the inferior vena cava. Transverse supine B-scan of the liver (Figure 2C) demonstrates a highly echogenic focus in the region of the inferior vena cava; the longitudinal supine B-scan (Figure 2D) demonstrates the dense echo collection to be within the inferior vena cava. Real-time abdominal sonography (Figures 2E & F) localized the calcification within the inferior vena cava and established the patency of the inferior vena cava and the renal veins. Further invasive angiographic studies were precluded, real-time sonography having established the diagnosis. Calcification of a thrombus within the inferior vena cava has been reported in 20 case reports since 1961 (2). The age at which the lesion is detected ranges from the first day of life to late adulthood, and the typical radiographic appearance is that of a bullet-shaped or ovoid calcification to the right of T11-12 in the region of the inferior vena cava. The patients are usually asymptomatic, but there may be extension of the inferior vena cava thrombus into the renal veins. Therefore, it is important to establish the patency of the renal veins. Diagnosis previously depended on inferior vena cavagraphy and radionuclide venography. We now advocate real-time sonography not only to establish this diagnosis, but also to exclude intrahepatic calcification or calcification in a right upper quadrant mass such as a neuroblastoma. #{149}#{149}t#{149} I. 5. *4 : %#{149}#{149} I A : _.a_ B..... Figures 2A & B Bullet-shaped right upper quadrant calcification (arrowheads). 32 RadioGraphics November 1981 Volume 1, Number 3
5 Sumner, et at. Case 2 I r#{149}-; Sb. #{149}.#{149}.,( q. =. _ hka :b. t - p C D Figures 2C & D Transverse supine (C) and longitudinal supine (D) hepatic B-scan: dense echo collection (arrowheads) within inferior vena cava (IVC) with posterior acoustic shadowing (open arrows). Figures 2E & F Transverse supine (E) and longitudinal supine (F) hepatic real-time sonogram: dense echo collection 1+] representing calcification within inferior vena cava [IVC] with posterior acoustic shadowing (open arrows). L liver. Volume 1, Number S November 1981 RadioGraphics 33
6 Sumner, et at. Multicystic Kidney- Potter Type II Case 3 Case 3 is a 2-day-old infant with a right-sided abdominal mass. Intravenous urography (Figure 3A) demonstrated non-visualization of the right kidney. The differential diagnosis included multicystic kidney and a severely hydronephrotic right kidney, possibly due to ureteropelvic junction obstruction. B-scan sonography in the region of the right kidney (Figures SB & C) demonstrated multiple echo-free areas separated by linear echo collections having the appearance of septa. Real-time sonography (Figure 3D) demonstrated a similar appearance. In differentiating multicystic kidney from severe hydronephrosis, one looks for a dilated pelvis located medially (3). In this case a medial hydropelvis was not identified. Neither ureteral dilatation nor a bladder abnormality such as a ureterocele was detected. Further evaluation with technetium glucoheptonate (Figures SE & F) demonstrated a photopenic (photon deficient) region in the area of the right kidney on the early scan. The 31/2 hour delayed scan had a similar appearance. This finding suggested a multicystic kidney rather than a hydronephrotic kidney secondary to ureteropelvic junction obstruction. (A hydronephrotic kidney would not be expected to remain photopenic on an isotope study if renal function existed.) At surgery, a multicystic right kidney with no vascular supply and no ureteral drainage was identified (Figure 3G). Histologic diagnosis was multicystic kidney, Potter Type II. Figure 3A - Non-opacified right kidney, normal cystogram. 34 RadioGraphics November 1981 Volume 1, Number 3
7 Sumner, et at. Neonatal abdominal.real-time sonography Case 3 Figures 3B, C & D Supine transverse (B) and longitudinal (C) B-scans: right kidney replaced by multiple anechoic compartments separated by echogenic septations. Transverse supine real-time sonogram (D): right kidney replaced by multiple anechoic compartments [C] separated by echogenic septations. -.. #{149} $#{149} ;.,-#{149} - - #{149} ) #{149} -#{149}... Figures 3E, F & G Early (E) and delayed (F) technetium glucoheptonate scans showing non-function on right [R], POST = posterior. Surgical specimen (G): multicystic kidney without vascular supply or ureter. Volume 1, Number 3 November 1981 RadioGraphics 35
8 Sumner, et at. Polycystic Kidneys- Potter Type I Case 4 Case 4 is a one-day-old male infant with bilateral flank masses. Intravenous urography (Figure 4A) demonstrated the typical appearance of infantile polycystic kidney disease with contrast material radiating perpendicularly and extending to the peripheral cortex within ectatic tubules. Contact B-scan in the prone longitudinal position (Figure 4B) demonstrated enlarged highly echogenic kidneys. Real-time sonography in the longitudinal supine position using the liver as an acoustic window (Figure 4C) demonstrated an enlarged highly echogenic right kidney. Its echogenicity is greater than that of the adjacent liver parenchyma which is the reverse of normal. This appearance has been described in various types of polycystic disease of the kidneys (4). The typical appearance of this patient s intravenous urogram as well as the sonographic appearance is consistent with the infantile form of polycystic disease or Potter Type I. This patient s liver sonogram was normal. I, *. #{149} - =#{149}#{149} - #{149},- 4 - f #{149}#{149}#{149} * \#{149}) :- #{149}:#{149} Figure 4A Classical urographic appearance of renal tubular ectasia. 36 RadioGraphics November 1981 Volume 1, Number 3
9 Sumner, et al. Case 4 Figure 4B Prone longitudinal renal B-scan: increased echogenicity of kidney parenchyma with loss of central pelvocalyceal echoes. Normal liver [L} ultrasonograrn. Figure 4C Supine longitudinal real-time sonogram: enlarged kidney (arrowheads) with kidney echogenicity exceeding liver echogenicity. K kidney; L liver. Volume 1, Number 3 November 1981 RadioGraphics 37
10 Sumner, et at. Polycystic Case 5 Kidneys- Potter Type III Case 5 is a one-day-old female infant with suspected bilateral nephromegaly. Intravenous urography (Figure 5A) demonstrated enlarged kidneys bilaterally with slight calyceal spreading and without marked infundibular narrowing. B-scan renal sonography in the longitudinal supine position on the right (Figure SB) demonstrated an enlarged, highly echogenic kidney whose echogenicity exceeded that of adjacent normal liver parenchyma. Real-time sonography (Figure 5C) demonstrated similar findings. This sonographic appearance is highly suggestive of cystic disease of the kidney, and we believe the radiographic appearance combined with the sonographic appearance in this patient indicates the adult form of polycystic kidney disease, Potter Type III. Liver and pancreatic sonography were normal. Bilateral flank masses (Cases 4 & 5), may result from polycystic disease of the kidney. Adult and infantile varieties, inherited as autosomal dominant and recessive traits, respectively, cannot be easily distinguished during infancy by ultrasonography alone (5). Neonatal ultrasonography reveals enlarged kidneys with diffusely increased echogenicity, poor definition and/or distortion of renal outlines and loss of definition of the central pelvocalyceal echo complex (6). Patients with infantile polycystic disease may have increased liver echogenicity because of hepatic fibrosis (7,8); whereas, hepatic and pancreatic cysts may be detected in older patients with adult polycystic disease. Intravenous urography and a detailed family history help to establish the correct diagnosis in these two conditions. Figure 5A Enlarged kidneys with slight calyceal spreading. 38 RadioGraphics November 1981 Volume 1, Number 3
11 Sumner, et al. Case 5 Figure 5B Supine longitudinal renal B-scan: enlarged highly echogenic kidney [K], renal echogenicity exceeds liver [LI. Figure SC Supine longitudinal real-time sonogram: enlarged highly echogenic right kidney [K] with normal liver [L]. Volume 1, Number S November 1981 RadioGraphics 39
12 Sumner, et al. Conclusion This exhibit urges application of real-time sonography in the evaluation of the neonatal abdomen. Normal vascular anatomy is easily delineated; vascular patency is established by the dynamic aspects of real-time scanning. Size, configuration and tissue characteristics of abdominal viscera are similarly rapidly determined. The advantages of diagnostic utility, speed of examination and portability of equipment make real-time sonography particularly suited for the detection of neonatal abdominal masses. Detection of renal pathology is especially important because renal or perirenal abnormalities account for most neonatal abdominal or flank masses. If hydronephrosis is detected, the course of the ureter should be scanned to identify ureterectasis. Ureterectasis indicates obstruction distal to the ureteropelvic junction and/or vesicoureteral reflux. Possible obstructive etiologies include ureteroceles (simple and ectopic) and posterior urethral valves. The bladder should be examined for a ureterocele that sonographically simulates an intravesical cystic mass (9). If no ureterocele is identified, cystography is warranted to exclude a refluxing megaureter or posterior urethral valves in the male infant. If renal sonography indicates cystic disease of the kidney, intravenous urography and detailed family history may confirm congenital cystic renal disease. Additional confirmatory findings may be supplied by liver and pancreatic scanning. References 1. Slovis TL, Berdon WE, Halter JO, et al Hemangiomas of the liver in infants. Am J Roentgenol 123: , Apr Kassner EG, Baumstark A, Kinkhabwala MN, et at: Calcified thrombus in the inferior vena cava in infants and children. Pediatr Radiol 4: , Apr Ralls PW, Esensten ML, Boger D, et al: Severe hydronephrosis and severe renal cystic disease: ultrasonic differentiation. Am J Roentgenol 134: , Mar Boal DK, Teele RL: Sonography of infantile polycystic kidney disease. Am J Roentgenol 135: , Sept Kendall AR, Pollack HM, Karafin L: Congenital cystic disease of kidney. Urology 4: , Dec Kelsey JA, Bowie JD: Gray-scale ultrasonography in the diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease. Radiology 122: , Mar Rosenfield AT, Siegel NJ, Kappelman NB, et al: Gray scale ultrasonography in medullary cystic disease of the kidney and congenital hepatic fibrosis with tubular ectasia: new observations. Am J Roentgenol 129: , Aug Thomas JL, Sumner TE, Crowe JE: Neonatal detection and evaluation of infantile polycystic disease by gray scale echography. J Clin Ultrasound 6: , Oct Sumner TE, Crowe JE, Resnick MI: Diagnosis of ectopic ureterocele using ultrasound. Urology 15:82-85, Jan RadioGraphics November 1981 Volume 1, Number 3
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Basic Abdominal Sonographic Anatomy and Protocol
 Basic Abdominal Sonographic Anatomy and Protocol Sandra Hagen-Ansert, M.S., RDMS, RDCS Ultrasound Education Specialist and Clinical Consultant Charleston, South Carolina Table of Contents 1. Objectives
Basic Abdominal Sonographic Anatomy and Protocol Sandra Hagen-Ansert, M.S., RDMS, RDCS Ultrasound Education Specialist and Clinical Consultant Charleston, South Carolina Table of Contents 1. Objectives
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Radiographic Findings and Comments
 642 Abdomen (Cont.) Differential Diagnosis of Abdominal s E. Focal parenchymal calcification of the kidney Tuberculosis (Fig. 27.19) Adenocarcinoma (Fig. 27.20) Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor) (Fig. 27.21)
642 Abdomen (Cont.) Differential Diagnosis of Abdominal s E. Focal parenchymal calcification of the kidney Tuberculosis (Fig. 27.19) Adenocarcinoma (Fig. 27.20) Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor) (Fig. 27.21)
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
Preparation iagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview"
 Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
ESPR-Meeting, Barcelona/Spain, June 2007
 Imaging recommendations in paediatric uroradiology: Minutes of the ESPR workgroup session on urinary tract infection, fetal hydronephrosis, urinary tract ultrasonography and voiding cystourethrography
Imaging recommendations in paediatric uroradiology: Minutes of the ESPR workgroup session on urinary tract infection, fetal hydronephrosis, urinary tract ultrasonography and voiding cystourethrography
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF HYPOECHOIC AND ANECHOIC MASSES WITH GRAY SCALE SONOGRAPHY: NEW OBSERVATIONS
 J Cliri Ultrasound 7:249-254. August 1979 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF HYPOECHOIC AND ANECHOIC MASSES WITH GRAY SCALE SONOGRAPHY: NEW OBSERVATIONS Robert L. Bree, M.D., and Terry M. Silver, M.D. With the
J Cliri Ultrasound 7:249-254. August 1979 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF HYPOECHOIC AND ANECHOIC MASSES WITH GRAY SCALE SONOGRAPHY: NEW OBSERVATIONS Robert L. Bree, M.D., and Terry M. Silver, M.D. With the
US for Detecting Renal Calculi with Nonenhanced CT as a Reference Standard 1
 Genitourinary Imaging Keir A. B. Fowler, MD Julie A. Locken, MD Joshua H. Duchesne Michael R. Williamson, MD Index terms: Kidney, calculi, 811.811, 813.811 Kidney, CT, 81.12111, 81.12115 Kidney, US, 81.1298
Genitourinary Imaging Keir A. B. Fowler, MD Julie A. Locken, MD Joshua H. Duchesne Michael R. Williamson, MD Index terms: Kidney, calculi, 811.811, 813.811 Kidney, CT, 81.12111, 81.12115 Kidney, US, 81.1298
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors
 Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Assessment and Management of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Article urology Assessment and Management of Fetal Hydronephrosis William A. Kennedy II, MD* Objectives After completing this article, the reader should be able to: 1. Differentiate genitourinary abnormalities
Article urology Assessment and Management of Fetal Hydronephrosis William A. Kennedy II, MD* Objectives After completing this article, the reader should be able to: 1. Differentiate genitourinary abnormalities
thirteen, it was more marked and here one could see a certain degree of beading along the lines which radiated out from the calyx.
 CONGENITAL CYSTIC DILATATION OF THE RENAL COLLECTING TUBULES A NEW DISEASE ENTITY* VINCENT VERMOOTEN** In 1943, while I was in the U. S. Army, a young soldier was referred to me because of gross, painless,
CONGENITAL CYSTIC DILATATION OF THE RENAL COLLECTING TUBULES A NEW DISEASE ENTITY* VINCENT VERMOOTEN** In 1943, while I was in the U. S. Army, a young soldier was referred to me because of gross, painless,
Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology
 1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension
 Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology)
 STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015
 Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
Benign liver diseases Geir Folvik, MD Division of Gastroenterology Department of Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital Bergen, Norway 30.11.2015 1 Agenda Benign focal liver lesions Fatty liver disease
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery. Torbjørn Dahl
 Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
Spleen. Anatomy. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Normal. Related Anatomy Anterior to spleen. Medial border. Posteriorly
 Spleen (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy Normal Intraperitoneal, except hilum Left hypochondrium Left hemidiaphragm superior generally considered to be ovoid, with a convex superior and a concave
Spleen (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy Normal Intraperitoneal, except hilum Left hypochondrium Left hemidiaphragm superior generally considered to be ovoid, with a convex superior and a concave
surg urin Surgery: Urinary System 1
 Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Administrative. Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality
 CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
Radiologic Evaluation of Renal Cysts
 Eugene K. Cha, HMS III November 2004 Radiologic Evaluation of Renal Cysts Eugene K. Cha, Harvard Medical School III Renal Anatomy Netter FH. Atlas of Human Anatomy, Second Edition. 2001, p 313. 2 HPI:
Eugene K. Cha, HMS III November 2004 Radiologic Evaluation of Renal Cysts Eugene K. Cha, Harvard Medical School III Renal Anatomy Netter FH. Atlas of Human Anatomy, Second Edition. 2001, p 313. 2 HPI:
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation
 Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
renal transplantation: A single-center comparative study
 Impact of posterior urethral valves on pediatric renal transplantation: A single-center comparative study BY Mohamed Kamal Gheith, MD Oberarzt die Urologie, Universitätsmedizin Mainz Ass. Prof. of Urology,
Impact of posterior urethral valves on pediatric renal transplantation: A single-center comparative study BY Mohamed Kamal Gheith, MD Oberarzt die Urologie, Universitätsmedizin Mainz Ass. Prof. of Urology,
Breast Ultrasound: Benign vs. Malignant Lesions
 October 25-November 19, 2004 Breast Ultrasound: Benign vs. Malignant Lesions Jill Steinkeler,, Tufts University School of Medicine IV Breast Anatomy Case Presentation-Patient 1 62 year old woman with a
October 25-November 19, 2004 Breast Ultrasound: Benign vs. Malignant Lesions Jill Steinkeler,, Tufts University School of Medicine IV Breast Anatomy Case Presentation-Patient 1 62 year old woman with a
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein
 Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments
 PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC
 Department of Radiology Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC Jennifer Johnston MSIII, Wayne State Medical School Stage 4 Metastatic
Department of Radiology Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC Jennifer Johnston MSIII, Wayne State Medical School Stage 4 Metastatic
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes
 Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
 In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
Soft Tissue Diffuse Neurofibromas
 ase Series Soft Tissue Diffuse Neurofibromas Sonographic Findings Wen hen, MD, Jian-Wen Jia, MD, Jin-Rui Wang, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to describe the sonographic findings of soft tissue
ase Series Soft Tissue Diffuse Neurofibromas Sonographic Findings Wen hen, MD, Jian-Wen Jia, MD, Jin-Rui Wang, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to describe the sonographic findings of soft tissue
Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography
 Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient
 Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient Upper GI Series Thought to be malrotation, no evidence of midgut volvulus Needed to repeat UGI Series WHY? Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series No
Pediatric Upper GI Series New Patient Upper GI Series Thought to be malrotation, no evidence of midgut volvulus Needed to repeat UGI Series WHY? Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series No
SCREENING COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND FOR LOWER EXTREMITY DVT
 SCREENING COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND FOR LOWER EXTREMITY DVT R. Eugene Zierler, M.D. The D. E. Strandness, Jr. Vascular Laboratory University of Washington Medical Center Division of Vascular Surgery University
SCREENING COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND FOR LOWER EXTREMITY DVT R. Eugene Zierler, M.D. The D. E. Strandness, Jr. Vascular Laboratory University of Washington Medical Center Division of Vascular Surgery University
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in General Surgery
 Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in General Surgery 2010 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation of the
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in General Surgery 2010 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation of the
Emergency Ultrasound Course
 Emergency Ultrasound Course Dr Justin Bowra ED Course Manual 2: EFAST Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma JUSTIN BOWRA 1 The Questions: 1. Is there free fluid (FF) a. In the pleural space?
Emergency Ultrasound Course Dr Justin Bowra ED Course Manual 2: EFAST Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma JUSTIN BOWRA 1 The Questions: 1. Is there free fluid (FF) a. In the pleural space?
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Diuretic Renography in Children
 Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Diuretic Renography in Children version 2.0, approved February 7, 1999 Authors: Gerald A. Mandell, MD (DuPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, DE);
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Diuretic Renography in Children version 2.0, approved February 7, 1999 Authors: Gerald A. Mandell, MD (DuPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, DE);
AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of the Focused Assessment With Sonography for Trauma (FAST) Examination
 AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of the Focused Assessment With Sonography for Trauma (FAST) Examination 2007 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine The American Institute of Ultrasound
AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of the Focused Assessment With Sonography for Trauma (FAST) Examination 2007 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine The American Institute of Ultrasound
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
06/10/09. 64 Slice BODY CT PROTOCOLS. Table of Contents
 06/10/09 64 Slice BODY CT PROTOCOLS Table of Contents General CT Comments 1 Protocol Routine Abdomen/Pelvis.. Routine Chest, Abdomen and Pelvis Retroperitoneal Hemorrhage Trauma. CT Cystography... Triple
06/10/09 64 Slice BODY CT PROTOCOLS Table of Contents General CT Comments 1 Protocol Routine Abdomen/Pelvis.. Routine Chest, Abdomen and Pelvis Retroperitoneal Hemorrhage Trauma. CT Cystography... Triple
Squamous cell carcinoma located in the renal caliceal system: A case report and review of the literature
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.32/ No. 1/2002 Squamous cell carcinoma located in the renal caliceal system: A case report and review of the literature AYHAN KARABULUT 1, LEVENT EMİR 1, MEHMET GÖNÜLTAŞ 2,
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.32/ No. 1/2002 Squamous cell carcinoma located in the renal caliceal system: A case report and review of the literature AYHAN KARABULUT 1, LEVENT EMİR 1, MEHMET GÖNÜLTAŞ 2,
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Diagnostic Medical Sonography 130 Diagnostic Medical Sonography Location: Trenholm Campus - Bldg. H Program Information Diagnostic Medical Sonography (DMS) is a diagnostic procedure that uses high frequency
Diagnostic Medical Sonography 130 Diagnostic Medical Sonography Location: Trenholm Campus - Bldg. H Program Information Diagnostic Medical Sonography (DMS) is a diagnostic procedure that uses high frequency
Something Old, Something New.
 Something Old, Something New. Michelle A. Fajardo, D.O. Loma Linda University Medical Center Clinical Presentation 6 year old boy, presented with hematuria Renal mass demonstrated by ultrasound & CT scan
Something Old, Something New. Michelle A. Fajardo, D.O. Loma Linda University Medical Center Clinical Presentation 6 year old boy, presented with hematuria Renal mass demonstrated by ultrasound & CT scan
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa
 ED Visits Related to Bariatric Surgery: Review of Normal Post-Surgical Anatomy as Well as Complications Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa Disclosures Background Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
ED Visits Related to Bariatric Surgery: Review of Normal Post-Surgical Anatomy as Well as Complications Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Ottawa Disclosures Background Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Three-dimensional Ultrasound Imaging
 NELSON - 3D/4D ULTRASOUND IMAGING - UIA ANNUAL MEETING, 3/2006 1 Three-dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Thomas R. Nelson, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego La Jolla, California Abstract Three-dimensional
NELSON - 3D/4D ULTRASOUND IMAGING - UIA ANNUAL MEETING, 3/2006 1 Three-dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Thomas R. Nelson, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego La Jolla, California Abstract Three-dimensional
Vascular Technology (VT) Content Outline Anatomy & physiology 20% Cerebrovascular Cerebrovascular normal anatomy Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels
 Vascular Technology (VT) Content Outline Anatomy & physiology 20% normal anatomy Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels hemodynamics Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels for normal perfusion normal anatomy
Vascular Technology (VT) Content Outline Anatomy & physiology 20% normal anatomy Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels hemodynamics Evaluate the cerebrovascular vessels for normal perfusion normal anatomy
Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed Tomography (CT) Scan of the Chest Performed for Reasons Other than Thyroid Disease
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
Sonographic Demonstration of Galenic Arteriovenous Malformations in the Neonate
 435 Sonographic Demonstration of Galenic Arteriovenous Malformations in the Neonate Don A. Cubberley 1 Richard B. Jaffe 2 George W. Nixon 2 Cerebral arteriovenous malformation with aneurysmal dilatation
435 Sonographic Demonstration of Galenic Arteriovenous Malformations in the Neonate Don A. Cubberley 1 Richard B. Jaffe 2 George W. Nixon 2 Cerebral arteriovenous malformation with aneurysmal dilatation
Running head: OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 1. Obesity and Medical Imaging. November 13, 2012
 Running head: OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 1 Obesity and Medical Imaging November 13, 2012 OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 2 Abstract Obesity is a growing problem in the United States, and it affects the health
Running head: OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 1 Obesity and Medical Imaging November 13, 2012 OBESITY AND MEDICAL IMAGING 2 Abstract Obesity is a growing problem in the United States, and it affects the health
Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
Patient information on soft markers
 Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
Case III. Disscussion. the UHP ultrasound protocol. Novel Ultrasound Approach to the Empiric Evaluation of the Undifferentiated Hypotensive Patient
 The UHP Ultrasound Protocol: A Novel Ultrasound Approach to the Empiric Evaluation of the Undifferentiated Hypotensive Patient JOHN S. ROSE, MD,* AARON E. BAIR, MD,* DIKU MANDAVIA, MD, AND DONNA J. KINSER,
The UHP Ultrasound Protocol: A Novel Ultrasound Approach to the Empiric Evaluation of the Undifferentiated Hypotensive Patient JOHN S. ROSE, MD,* AARON E. BAIR, MD,* DIKU MANDAVIA, MD, AND DONNA J. KINSER,
Measure #405: Appropriate Follow-up Imaging for Incidental Abdominal Lesions National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #405: Appropriate Follow-up Imaging for Incidental Abdominal Lesions National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION:
Measure #405: Appropriate Follow-up Imaging for Incidental Abdominal Lesions National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION:
Sonography. 1. Introduction. 2. Documentation of Compliance. 3. Didactic Competency Requirements. 4. Clinical Competency Requirements
 PRIMARY CERTIFICATION Sonography 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet the Professional Education Requirements specified in the ARRT Rules and Regulations.
PRIMARY CERTIFICATION Sonography 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet the Professional Education Requirements specified in the ARRT Rules and Regulations.
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
CHAPTER 13 Pediatric Urologic Diseases
 CHAPTER 13 Pediatric Urologic Diseases Urinary Incontinence Hypospadias Ureterocele Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction Posterior Urethral Valves Vesicoureteral Reflux Disease Upper Urinary Tract Stones
CHAPTER 13 Pediatric Urologic Diseases Urinary Incontinence Hypospadias Ureterocele Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction Posterior Urethral Valves Vesicoureteral Reflux Disease Upper Urinary Tract Stones
Percutaneous drainage as the treatment of choice for neonatal ovarian cysts
 Pediatr Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00247-006-0240-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ada Kessler. Hagith Nagar. Moshe Graif. Liat Ben-Sira. Elka Miller. Drora Fisher. Irith Hadas-Halperin Percutaneous drainage as the treatment
Pediatr Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00247-006-0240-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ada Kessler. Hagith Nagar. Moshe Graif. Liat Ben-Sira. Elka Miller. Drora Fisher. Irith Hadas-Halperin Percutaneous drainage as the treatment
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Cystic Lung Diseases. Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008
 Cystic Lung Diseases Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008 How do we define a cyst of the lung? Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon
Cystic Lung Diseases Melissa Price Gillian Lieberman, MD Advanced Radiology Clerkship Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center November, 2008 How do we define a cyst of the lung? Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon
Emergency Medicine Sonography POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine Sonography POCKET GUIDE to Sonographic Anatomy and Pathology, MPH, PA-C, RDMS Physician Assistant, Department of Surgery, Division of Urology Lincoln Hospital and Medical Center, Bronx,
Emergency Medicine Sonography POCKET GUIDE to Sonographic Anatomy and Pathology, MPH, PA-C, RDMS Physician Assistant, Department of Surgery, Division of Urology Lincoln Hospital and Medical Center, Bronx,
Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts
 Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
Interventional Radiology
 Nationwide Children s Hospital Department of Radiology is recognized as a pioneering center for research and innovation, and a renowned leader in diagnostic and interventional pediatric radiology. Our
Nationwide Children s Hospital Department of Radiology is recognized as a pioneering center for research and innovation, and a renowned leader in diagnostic and interventional pediatric radiology. Our
Model Answer: Australasian College of Phlebology > Ultrasound in Phlebology > Advanced Course > Topic 4
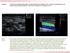 Ques?on 1: Compression sonography (lee image) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of DVT. Are there any advantages of color Doppler ultrasound (right image) over compression sonography in the diagnosis
Ques?on 1: Compression sonography (lee image) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of DVT. Are there any advantages of color Doppler ultrasound (right image) over compression sonography in the diagnosis
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
3D Ultrasound. Outline. What is 3D US? Volume Sonography. 3D Ultrasound in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential. Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
 in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential Outline What is 3D US? What are obvious advantages of 3D US? What is the future of 3D US? Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 2D US
in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential Outline What is 3D US? What are obvious advantages of 3D US? What is the future of 3D US? Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 2D US
Ultrasound of the Thorax (Noncardiac)
 Ultrasound of the Thorax (Noncardiac) Martha Moon Larson, DVM, MS KEYWORDS Ultrasound Thorax Pleural effusion Mediastinum Lung Ultrasound of the noncardiac thorax is an important supplemental imaging modality
Ultrasound of the Thorax (Noncardiac) Martha Moon Larson, DVM, MS KEYWORDS Ultrasound Thorax Pleural effusion Mediastinum Lung Ultrasound of the noncardiac thorax is an important supplemental imaging modality
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
EFSUMB EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR ULTRASOUND IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY Building a European Ultrasound Community
 MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 8: Vascular Ultrasound Level 1 Training and Practice Practical training should involve at least two half day ultrasound
MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 8: Vascular Ultrasound Level 1 Training and Practice Practical training should involve at least two half day ultrasound
Torsed Appendix Testis
 Article Torsed Appendix Testis Gray Scale and Color Doppler Sonographic Findings Compared With Normal Appendix Testis Dal Mo Yang, MD, Joo Won Lim, MD, Jee Eun Kim, MD, Ji Hye Kim, MD, Hyuni Cho, MD Objective.
Article Torsed Appendix Testis Gray Scale and Color Doppler Sonographic Findings Compared With Normal Appendix Testis Dal Mo Yang, MD, Joo Won Lim, MD, Jee Eun Kim, MD, Ji Hye Kim, MD, Hyuni Cho, MD Objective.
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD
 Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
Hemorrhagic venous infarction Heather Borders, MD 12/13/2010 History 16 year old female with four day history of headache and acute change in mental status. History of two days of oral contraceptive use
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA. Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005
 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
Leading the New Standards
 Samsung Merdison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer, in 110
Samsung Merdison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer, in 110
