NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
|
|
|
- Emerald Mills
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Non-progressive brain disorders in children and young people: management of spasticity, co-existing motor disorders and their early musculoskeletal complications 1.1 Short title Spasticity in children and young people 2 The remit The Department of Health has asked NICE: To prepare a clinical guideline on the management of spasticity in children with a non-progressive brain injury. 3 Clinical need for the guideline 3.1 Epidemiology a) Spasticity is a sign found in some motor disorders which is characterised by hyperexcitability of the stretch reflex, resulting in a velocity-dependent increase in tonic stretch reflexes (muscle tone) with exaggerated tendon jerk. It is one components of the upper motor neuron syndrome. b) Spasticity is a common and often serious abnormality affecting motor function. Spasticity results in an increased resistance to passive movement of a muscle through hyperactive stretch reflexes causing rapid and strong contraction of the muscle. This dysregulation of tone with movement can result in a wide range of clinical manifestations and functional impairments. Spasticity in children and young people final scope 1
2 c) Spasticity in children and young people is most often seen in cerebral palsy, although it can also occur with other forms of nonprogressive and progressive brain disorders, the latter is outside the remit of this guideline. d) In children and young people with cerebral palsy, the motor disorder can be characterised using the following approaches: Anatomic distribution of motor disorder Unilateral involvement or bilateral involvement Description of involvement of each limb, trunk and oropharynx Nature of motor disorder Spastic, dyskinetic or ataxic as predominat abnormality Dyskinetic further divided into dystonic or choreathetosis Additional tone or movement problems listed as secondary types Functional motor ability Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) used to assess ambulation Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) used to assess hand and arm function Accompanying Impairments This system of classification was developed by the Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe (SCPE) project and replaces the previous classification where the following terms were used to describe anatomic distribution: Hemiplegia one side of body affected, arm usually more severely than leg Diplegia legs predominantly affected, mild to moderate upper limb impairment Quadriplegia sever impairment of arms and legs, often with trunk weakness and oropharyngeal involvement Spasticity in children and young people final scope 2
3 As the guideline will be referring to literature over the last few decades, these terms will still be used in the assessment of the evidence for management of spasticity. e) Cerebral palsy describes a group of permanent disorders of the development of movement and posture, causing activity limitation that are attributed to non-progressive disturbances that occurred in the developing foetal or infant brain. The motor disorders of cerebral palsy are often accompanied by disturbances of sensation, perception, cognition, communication, and behaviour, by epilepsy, and by secondary musculoskeletal problems. f) The prevalence of cerebral palsy in the UK is about 2 per 1000 live births. This figure has not changed significantly in the past 40 years. Around 40% of children with cerebral palsy were born prematurely. In many of these children the precise cause of cerebral palsy is not apparent, but various risk factors can be identified, including maternal illness and postnatal events. g) Although in cerebral palsy the causative brain damage is static, the motor manifestations change over time. Typically, abnormalities of movement and posture are first recognised during infancy or early childhood and progressive disability can occur. h) Up to 80% of children with cerebral palsy have a spastic motor impairment. Other types of motor impairment in cerebral palsy include dyskinetic (with athetosis, dystonia and chorea) and ataxic (with abnormalities of coordination and balance). It is quite common for children with spastic cerebral palsy to also have other motor disorders such as dystonia or ataxia. i) Examples of non-progressive disorders that may affect the brain of a fetus or infant include brain malformations, prenatal vascular events (stroke) and infections (such as cytomegalovirus), perinatal hypoxic or ischaemic encephalopathy, and postnatal head injury or meningitis. When this damage occurs in the developing brains of Spasticity in children and young people final scope 3
4 children under three years of age, it is referred to in this guideline as cerebral palsy. j) Non-progressive disturbances may also occur in older children and young people, for example, from head trauma, encephalitis or meningitis. Non-progressive disturbances affecting movement and posture occurring after this age are defined in this guideline as being acquired. k) Depending on which parts of the motor cortex are damaged, the imbalance between flexor and extensor muscles may lead to abnormal posture of the joints. It is important to distinguish dynamic postural abnormalities (due to muscle spasticity) from fixed contractures (muscles that have become permanently shortened after long-term spasticity). l) The functional abilities of children with spasticity often deteriorate over time. The cause of the progression is not often identified. It may include weakness, posturing, contracture, dystonia, ataxia or other motor disorders. Incorrect diagnosis and high expectations can all lead to functional deterioration. Effective management of spasticity and other motor problems could be important in preventing functional decline. m) The muscular imbalances associated with spasticity often result in abnormal posture, which is initially 'dynamic' with the potential to improve with effective treatment of spasticity. In time the abnormal posturing can become permanent because of contractures, which in turn, may cause fixed joint deformities. Uncorrected deformities in spastic cerebral palsy can cause pain, impair function, reduce mobility and cause difficulties in caring for the child. n) Subluxation or full dislocation of joints arise most commonly in the hips, but shoulder, elbow and ankle dislocations also occur though infrequently. Significant bony deformities can form such as kyphosis and scoliosis of the spine. Spasticity in children and young people final scope 4
5 o) These changes may substantially worsen the child's functional disability and impair the ability to walk or sit. Postural management or other specialist equipment may be necessary. Children and young people may avoid walking if it becomes unsafe or uncomfortable or if it requires a large effort. Abnormal posturing of the shoulder, elbow, or hand may greatly impair the function of the upper limb. These functional deteriorations can cause a consequent reduction in the individual's independence, for example in dressing or toileting or in access to education or play. A lack of independence leads to an increased need for support by paid carers or family members. It may also reduce employment opportunities. p) Progressive disability requires acknowledgment, surveillance, prevention and management, especially during the transition to young adulthood when the demands of normal teenage life become more dominant in determining the health of the individual. q) Successful treatment of spasticity might lead to better motor function, reduction or prevention of contractures and other fixed musculoskeletal deformities, enhanced functional abilities and independence, and ultimately an improvement in the person's quality of life. 3.2 Current practice a) The aims of managing spasticity are to minimise the effect that it has on the child to treat pain, improve motor function, improve ease of care, and prevent the consequences of spasticity. In combination with other interventions dealing with the child s associated motor disorders and co-morbidities, the aim is to promote independence and to achieve as complete an integration into society as possible for the affected child or young person. b) Many treatments are used in the management of spasticity, with considerable variation in practice. Spasticity in children and young people final scope 5
6 c) Many physiotherapy regimens are commonly used in children and young people with spasticity. These include passive stretching, muscle strengthening therapeutic exercises, serial casting, using splints and discouraging and preventing postures and movement that lead to disability and deformity, and encouraging postures and movement that improve function. d) Orthoses, aids and appliances are used to manage seating and posture or for example to hold limbs in an advantageous position to improve functionality and to prevent or treat deformity. Ankle foot orthoses of various sorts are frequently used. Similar devices are also used to immobilise the knee or to encourage hip abduction. Upper limb orthoses may be employed. e) Spasticity may be alleviated by a wide range of interventions aimed at modulating the abnormal stretch reflex: Oral anti-spastic medications such as baclofen may be used in those with extensive spasticity. Intrathecal baclofen is administered into the cerebrospinal fluid using an implanted pump. It is used for severe spasticity. Local injection with botulinum toxin A may be effective. This works by temporarily blocking the release of the neuromuscular transmitter acetylcholine. Selective dorsal rhizotomy is used to reduce spasticity in the legs by interruption of the spinal reflex, and is covered by Selective dorsal rhizotomy for spasticity in cerebral palsy, NICE interventional procedure guidance 373 (2010). This procedure has potential adverse effects such as hip instability and spinal deformity. f) Orthopaedic surgery has a major role in the management of early and late consequences of spasticity. Muscle tendon lengthening procedures can both release shortened muscles and weaken spastic muscle, thereby improving the balance of forces influencing Spasticity in children and young people final scope 6
7 joint position. Osteotomy procedures can correct deformities and stabilise hip dislocation. Rotational osteotomy can correct torsional deformities and relieve malaligned muscular forces. Spinal deformities can be treated with fusion and instrumentation techniques. Disorders such as pes equinus and pes varus, scissoring and hip instability can be managed using such techniques. Hip subluxation or dislocation occurs in up to 25% of children with cerebral palsy and surgery can be helpful to stabilise joints. Surgical procedures can alleviate many of the consequences of spasticity, resulting in significant functional improvement. g) Expertise in and access to various types of treatment varies. Bracing techniques may be employed inappropriately or without evidence of benefit. Conversely, in some areas orthoses are not funded. Placement of intrathecal baclofen pumps is available in certain regional centres only. 4 The guideline The guideline development process is described in detail on the NICE website (see section 6, Further information ). This scope defines what the guideline will (and will not) examine, and what the guideline developers will consider. The scope is based on the referral from the Department of Health. The areas that will be addressed by the guideline are described in the following sections. 4.1 Population Groups that will be covered a) Children and young people from birth up to their 19th birthday who have spasticity as a result of a non-progressive brain disorder. It will include those with spasticity resulting from cerebral palsy and Spasticity in children and young people final scope 7
8 those with spasticity resulting from a non-progressive brain injury acquired later in childhood or adolescence. b) Subgroups of this population will be considered in relation to the anatomic distribution of the motor disorder and the nature of the motor disorder Groups that will not be covered a) Adults 19 years and older. b) Children and young people with spasticity resulting from a progressive brain disorder. However, many of the recommendations on the management of spasticity might also apply to these children and young people. c) Children with a pure dystonia or other motor disorders which do not co-exist with spasticity. 4.2 Healthcare setting a) All settings in which NHS care is provided. 4.3 Clinical management Key clinical issues that will be covered Unless otherwise stated, each issue will be considered in relation to the subgroups of people with unilateral spasticity and bilateral spasticity. If clinically appropriate, each issue will also be considered in relation to the severity of the functional impairment using GMFCS and MACS. However, as this classification system has only recently come into general use, we will also use the older classification system (of spastic monoplegia, diplegia, hemiplegia and quadriplegia with severity graded as mild, moderate, or severe) as necessary to describe the reported evidence. a) Physiotherapy and occupational therapy interventions that have a direct effect to reduce spasticity, its musculoskeletal Spasticity in children and young people final scope 8
9 consequences, or accompanying motor disorders for example, muscle shortening. b) Orthoses (for example, ankle-foot orthoses, knee splints, serial casting and upper limb orthoses) for preventing and treating contractures and improving function (such as mobility). c) Oral medications specifically baclofen, benzodiazepines (diazepam, nitrazepam, clonazepam), levodopa, tizanidine and dantrolene d) Long-term use of intramuscular botulinum toxin A and B to reduce spasticity, maintain motor function and prevent secondary complications. e) Whether an effective response to a bolus dose of intrathecal baclofen predicts an effective long-term response in children and young people with moderate to severe spasticity. f) The intrathecal baclofen pump to reduce spasticity, maintain motor function, to improve posture and improve health related quality of life in children and young people with moderate to severe spasticity. g) Orthopaedic surgery specifically (tendon lengthening and transfer procedures, and osteotomy) to prevent and correct deformities and prevent joint dislocations. h) Multilevel surgery (multiple surgical procedures done at the same time) compared with interval surgery (consecutive operations) to improve health related quality of life in children and young people. i) Selective dorsal rhizotomy Clinical issues that will not be covered a) Diagnosis and assessment of spasticity and co-existing motor disorders. Spasticity in children and young people final scope 9
10 b) Management of spasticity and co-existing motor disorders caused by a progressive brain disorder or a spinal cord injury. c) Management of motor disorders which do not co-exist with spasticity. d) Holistic management of cerebral palsy or other non-progressive brain disorders. e) Play therapy. f) Complementary and alternative therapies. g) Management of the following complications: kyphosis scoliosis. h) Management of comorbidities, including: 4.4 Main outcomes cognitive and learning disabilities visual, hearing and speech impairments epilepsy feeding difficulties (including enteral tube feeding) disorders of nutrition and growth impaired bone mineralisation (osteoporosis) pressure sores urological disorders (voiding difficulties or incontinence) gastrointestinal disorders (including gastro-oesophageal reflux and constipation) respiratory disorders (including apnoea, airway obstruction and chronic aspiration). a) Reduction of spasticity. b) Optimisation of movement and function. Spasticity in children and young people final scope 10
11 c) Reduction of pain. d) Adverse effects of interventions. e) Acceptability and tolerability in children and young people. f) Health related quality of life. 4.5 Economic aspects Developers will take into account both clinical and cost effectiveness when making recommendations involving a choice between alternative interventions. A review of the economic evidence will be conducted and analyses will be carried out as appropriate. The preferred unit of effectiveness is the quality-adjusted life year (QALY), and the costs considered will usually only be from an NHS and personal social services (PSS) perspective. Further detail on the methods can be found in 'The guidelines manual' (see Further information ). 4.6 Status Scope This is the final scope Timing The development of the guideline recommendations will begin in July Related NICE guidance 5.1 Published guidance Selective dorsal rhizotomy for spasticity in cerebral palsy. NICE interventional procedure guidance 373 (2010). Available from Spasticity in children and young people final scope 11
12 6 Further information Information on the guideline development process is provided in: How NICE clinical guidelines are developed: an overview for stakeholders' the public and the NHS The guidelines manual. These are available from the NICE website ( Information on the progress of the guideline will also be available from the NICE website ( Spasticity in children and young people final scope 12
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy. Jenny Wilson, MD wilsjen@ohsu.edu OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015
 Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD wilsjen@ohsu.edu OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD wilsjen@ohsu.edu OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
Cerebral Palsy. www.teachinngei.org p. 1
 Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity
 Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
Long-term implications of cerebral palsy in an aging population
 ACPIN Conference 2014 Long-term implications of cerebral palsy in an aging population Stephanie Cawker Clinical Specialist Physiotherapist Neuro-disabilities Great Ormond Street Children s Hospital Stephanie.cawker@gosh.nhs.uk
ACPIN Conference 2014 Long-term implications of cerebral palsy in an aging population Stephanie Cawker Clinical Specialist Physiotherapist Neuro-disabilities Great Ormond Street Children s Hospital Stephanie.cawker@gosh.nhs.uk
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Managing Spasticity. Spasticity Service
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
Cerebral palsy, neonatal death and stillbirth rates Victoria, 1973-1999
 Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
What is the Spasticity Clinic?
 The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy. Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay.
 Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
Other Common Names Palsy; Little s Disease; Infantile Cerebral Paralysis; Static Encephalopathy.
 1 CEREBRAL PALSY Other Common Names Palsy; Little s Disease; Infantile Cerebral Paralysis; Static Encephalopathy. Definition/Description Cerebral Palsy (CP) is an umbrella term that covers a group of non-progressive,
1 CEREBRAL PALSY Other Common Names Palsy; Little s Disease; Infantile Cerebral Paralysis; Static Encephalopathy. Definition/Description Cerebral Palsy (CP) is an umbrella term that covers a group of non-progressive,
Changing Perspectives in Cerebral Palsy. Dr Owen Hensey
 Changing Perspectives in Cerebral Palsy Dr Owen Hensey Definition Cerebral Palsy A persistent, but not unchanging, disorder of movement and posture due to a non-progressive lesion in the immature brain
Changing Perspectives in Cerebral Palsy Dr Owen Hensey Definition Cerebral Palsy A persistent, but not unchanging, disorder of movement and posture due to a non-progressive lesion in the immature brain
ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY. www.almirall.com. Solutions with you in mind
 ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY www.almirall.com Solutions with you in mind WHAT IS SPASTICITY? The muscles of the body maintain what is called normal muscle tone, a level of muscle tension that allows us to hold
ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY www.almirall.com Solutions with you in mind WHAT IS SPASTICITY? The muscles of the body maintain what is called normal muscle tone, a level of muscle tension that allows us to hold
Cerebral Palsy: Intervention Methods for Young Children. Emma Zercher. San Francisco State University
 RUNNING HEAD: Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods, 1 Cerebral Palsy: Intervention Methods for Young Children Emma Zercher San Francisco State University May 21,
RUNNING HEAD: Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods Cerebral Palsy & Intervention Methods, 1 Cerebral Palsy: Intervention Methods for Young Children Emma Zercher San Francisco State University May 21,
Classification of Cerebral Palsy and Major Causes Physiologic Topographic Etiologic Function. trauma, infection)
 Cerebral palsy (CP) It is a diagnostic term used to describe a group of motor syndromes. a static encephalopathy, a term previously used, is now inaccurate because of the recognition that the neurologic
Cerebral palsy (CP) It is a diagnostic term used to describe a group of motor syndromes. a static encephalopathy, a term previously used, is now inaccurate because of the recognition that the neurologic
Cerebral Palsy. Causes
 Cerebral Palsy Cerebral Palsy (sera brul PAUL zee) (CP) is an injury or abnormality of the developing brain that affects movement. This means that something happened to the brain or the brain did not develop
Cerebral Palsy Cerebral Palsy (sera brul PAUL zee) (CP) is an injury or abnormality of the developing brain that affects movement. This means that something happened to the brain or the brain did not develop
CEREBRAL PALSY CLASSIFICATION BY SEVERITY LEVEL
 Patient Name: Today s Date: CAUSE OF CEREBRAL PALSY Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) or Intrapartum Asphyxia - Brain injury Lack of oxygen to the brain or asphyxia. Intracranial Hemorrhage (IVH) Brain
Patient Name: Today s Date: CAUSE OF CEREBRAL PALSY Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) or Intrapartum Asphyxia - Brain injury Lack of oxygen to the brain or asphyxia. Intracranial Hemorrhage (IVH) Brain
Cerebral Palsy Ages: 0-3 What kinds of physicians will my child need?
 Cerebral Palsy Ages: 0-3 What kinds of physicians will my child need? What other conditions may affect my child? Primary Care Physician - addresses general health needs of your child Orthopedic Surgeon/neuromusculoskeletal
Cerebral Palsy Ages: 0-3 What kinds of physicians will my child need? What other conditions may affect my child? Primary Care Physician - addresses general health needs of your child Orthopedic Surgeon/neuromusculoskeletal
Cerebral Palsy Information
 Cerebral Palsy Information The following information was extracted from the Mayo Clinic s website Definition: "Cerebral palsy" is a general term for a group of disorders that appear during the first few
Cerebral Palsy Information The following information was extracted from the Mayo Clinic s website Definition: "Cerebral palsy" is a general term for a group of disorders that appear during the first few
Surgery of the Upper Extremity in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy
 Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities
 Penn Comprehensive Neuroscience Center Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities Penn Neuro-Orthopaedics Service 1 Table of Contents Overview Overview 1 Treatment 2 Procedures 4 Achilles Tendon Lengthening
Penn Comprehensive Neuroscience Center Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities Penn Neuro-Orthopaedics Service 1 Table of Contents Overview Overview 1 Treatment 2 Procedures 4 Achilles Tendon Lengthening
1. What is Cerebral Palsy?
 1. What is Cerebral Palsy? Introduction Cerebral palsy refers to a group of disorders that affect movement. It is a permanent, but not unchanging, physical disability caused by an injury to the developing
1. What is Cerebral Palsy? Introduction Cerebral palsy refers to a group of disorders that affect movement. It is a permanent, but not unchanging, physical disability caused by an injury to the developing
What is cerebral palsy?
 What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
In recent years some doctors have treated spasticity in children with Botox, the musclerelaxing agent used cosmetically for wrinkles.
 The following excerpt has been taken from the Christopher & Dana Reeve Foundation Paralysis Resource Center website. http://www.christopherreeve.org/site/c.mtkzkgmwkwg/b.4453419/k.3757/spasticity.h tm
The following excerpt has been taken from the Christopher & Dana Reeve Foundation Paralysis Resource Center website. http://www.christopherreeve.org/site/c.mtkzkgmwkwg/b.4453419/k.3757/spasticity.h tm
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010
 Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
CEREBRAL PALSY WHAT IS CP REFERS TO THE BRAIN; REFERS TO THE LOSS OR IMPAIRMENT OF MOTOR FUNCTION MOTOR TYPES
 CEREBRAL REFERS TO THE BRAIN; PALSY REFERS TO THE LOSS OR IMPAIRMENT OF MOTOR FUNCTION WHAT IS CP FIGURE 1 Spasticity Cerebral palsy (CP) describes a group of permanent disorders of the development of
CEREBRAL REFERS TO THE BRAIN; PALSY REFERS TO THE LOSS OR IMPAIRMENT OF MOTOR FUNCTION WHAT IS CP FIGURE 1 Spasticity Cerebral palsy (CP) describes a group of permanent disorders of the development of
The Road to Rehabilitation
 The Road to Rehabilitation Part 7 Traveling Toward Relief: Dealing with Spasticity & Brain Injury Written by Cindy Ivanhoe, MD Elie Elovic, MD Content reveiwed by Gregory O Shanick, MD Brain Injury Association
The Road to Rehabilitation Part 7 Traveling Toward Relief: Dealing with Spasticity & Brain Injury Written by Cindy Ivanhoe, MD Elie Elovic, MD Content reveiwed by Gregory O Shanick, MD Brain Injury Association
C CS. California Children Services Alameda County
 C CS California Children Services Alameda County The California Children Services (CCS) Program strives to assure access to medical services essential to the health and well-being of children with catastrophic
C CS California Children Services Alameda County The California Children Services (CCS) Program strives to assure access to medical services essential to the health and well-being of children with catastrophic
Cerebral Palsy. 1 - Introduction. An informative Booklet for families in the Children and Teens program
 Cerebral Palsy 1 - Introduction An informative Booklet for families in the Children and Teens program Centre de réadaptation Estrie, 2008 Preface Dear parents, It is with great pleasure that we present
Cerebral Palsy 1 - Introduction An informative Booklet for families in the Children and Teens program Centre de réadaptation Estrie, 2008 Preface Dear parents, It is with great pleasure that we present
A Rapidly Growing Population with. - Murray Goldstein, DO, MPH Chairman, Cerebral Palsy International Research CPIRF
 Adults with Cerebral Palsy A Rapidly Growing Population with Complex Health Issues - Murray Goldstein, DO, MPH Chairman, Cerebral Palsy International Research Foundation Scientific Advisory Council CPIRF
Adults with Cerebral Palsy A Rapidly Growing Population with Complex Health Issues - Murray Goldstein, DO, MPH Chairman, Cerebral Palsy International Research Foundation Scientific Advisory Council CPIRF
Cerebral Palsy Road Map: What to Expect As Your Child Grows
 a Cerebral Palsy Road Map: What to Expect As Your Child Grows A To help you understand what having cerebral palsy means for your child, we at Gillette Children s Specialty Healthcare created the Cerebral
a Cerebral Palsy Road Map: What to Expect As Your Child Grows A To help you understand what having cerebral palsy means for your child, we at Gillette Children s Specialty Healthcare created the Cerebral
Specialist Children s Service
 Specialist Children s Service Information and Guidelines for Referrers March 2009, Version 3.0 Contents CONTENTS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 3 TEAMS BASED AT THE WOOD STREET HEALTH CENTRE:... 3 TEAMS BASED ELSEWHERE
Specialist Children s Service Information and Guidelines for Referrers March 2009, Version 3.0 Contents CONTENTS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 3 TEAMS BASED AT THE WOOD STREET HEALTH CENTRE:... 3 TEAMS BASED ELSEWHERE
Cerebral Palsy The ABC s of CP
 Cerebral Palsy The ABC s of CP Toni Benton, M.D. Continuum of Care Project UNM HSC School of Medicine April 20, 2006 Cerebral Palsy Outline I. Definition II. Incidence, Epidemiology and Distribution III.
Cerebral Palsy The ABC s of CP Toni Benton, M.D. Continuum of Care Project UNM HSC School of Medicine April 20, 2006 Cerebral Palsy Outline I. Definition II. Incidence, Epidemiology and Distribution III.
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy. Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego
 Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal hygiene problems
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal hygiene problems
Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario
 Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY?
 WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
P U T T I N G T H E P I E C E S T O G E T H E R
 MEDICAL THERAPY PROGRAM P U T T I N G T H E P I E C E S T O G E T H E R CALIFORNIA CHILDREN SERVICES CCS is a statewide program providing medical care and rehabilitation to children with physical disabilities.
MEDICAL THERAPY PROGRAM P U T T I N G T H E P I E C E S T O G E T H E R CALIFORNIA CHILDREN SERVICES CCS is a statewide program providing medical care and rehabilitation to children with physical disabilities.
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Supporting children and young people with cerebral palsy to fulfil their potential through sport
 Supporting children and young people with cerebral palsy to fulfil their potential through sport About this toolkit For pupils The aim of the pack is to give children and young people information about
Supporting children and young people with cerebral palsy to fulfil their potential through sport About this toolkit For pupils The aim of the pack is to give children and young people information about
CP Factsheet An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy
 An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy The concept of ageing and cerebral palsy is now becoming more recognised and more research is being undertaken. However many people, including some professionals,
An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy The concept of ageing and cerebral palsy is now becoming more recognised and more research is being undertaken. However many people, including some professionals,
Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006. SUBJECT: Changes Conforming to CR3648 for Therapy Services
 CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006 Change
CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 55 Date: MAY 5, 2006 Change
The surgical management of cerebral palsy
 The surgical management of cerebral palsy T. DUCKWORTH University Department of Orthopaedics, Sheffield Cerebral palsy more than any other paralytic condition presents some of the most difficult and challenging
The surgical management of cerebral palsy T. DUCKWORTH University Department of Orthopaedics, Sheffield Cerebral palsy more than any other paralytic condition presents some of the most difficult and challenging
Staying Mobile & Active Post Stroke. Kevin Lockette PT Ohana Pacific Rehab Services, LLC Honoulu- Kailua www.ohanapacificrehab.
 Staying Mobile & Active Post Stroke Kevin Lockette PT Ohana Pacific Rehab Services, LLC Honoulu- Kailua www.ohanapacificrehab.com 808 262 1118 Aging Process Changes in body composition Loss of muscle tissue/increase
Staying Mobile & Active Post Stroke Kevin Lockette PT Ohana Pacific Rehab Services, LLC Honoulu- Kailua www.ohanapacificrehab.com 808 262 1118 Aging Process Changes in body composition Loss of muscle tissue/increase
Classification Policy and Procedures
 Classification Policy and Procedures The purpose of the Classification Policy and Procedures is to clearly define the systems of classification adopted by Athletics Australia and recognise the role of
Classification Policy and Procedures The purpose of the Classification Policy and Procedures is to clearly define the systems of classification adopted by Athletics Australia and recognise the role of
Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1)
 Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1) What is RSMD1? The congenital muscular dystrophies are a group of conditions which share early presentation
Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1) What is RSMD1? The congenital muscular dystrophies are a group of conditions which share early presentation
9th International Congress on Cerebral Palsy
 Medimond - Monduzzi Editore International Proceedings Division 9th International Congress on Cerebral Palsy Mental and Physical Activity are Imperative Bled, Slovenia, 15-18 May 2013 Editor Milivoj Velickovic
Medimond - Monduzzi Editore International Proceedings Division 9th International Congress on Cerebral Palsy Mental and Physical Activity are Imperative Bled, Slovenia, 15-18 May 2013 Editor Milivoj Velickovic
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Rehabilitation for movement difficulties after stroke bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online.
Rehabilitation for movement difficulties after stroke bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online.
Spina Bifida Occulta. Lo-Call 1890 20 22 60. Occulta Means Hidden
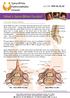 Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Cerebral Palsy. Distributed By: Maine Parent Federation PO Box 2067 Augusta, Maine 04338. 1-800-870-7746 (Maine Only) 207-588-1933
 Distributed By: Maine Parent Federation PO Box 2067 Augusta, Maine 04338 (Maine Only) 207-588-1933 Email: parentconnect@mpf.org Online community: Original: 01/2000 Updated: Information Disclaimer The purpose
Distributed By: Maine Parent Federation PO Box 2067 Augusta, Maine 04338 (Maine Only) 207-588-1933 Email: parentconnect@mpf.org Online community: Original: 01/2000 Updated: Information Disclaimer The purpose
Children with cerebral palsy in Europe: figures and disability
 Children with cerebral palsy in Europe: figures and disability on behalf of SCPE Collaborative Group Coordinator: Christine Cans, Grenoble Javier de la Cruz, Hosp Univ 12 de Octubre, Madrid Surveillance
Children with cerebral palsy in Europe: figures and disability on behalf of SCPE Collaborative Group Coordinator: Christine Cans, Grenoble Javier de la Cruz, Hosp Univ 12 de Octubre, Madrid Surveillance
Muscle Spasms and Stiffness
 Muscle Spasms and Stiffness Practical living for everyday life with MS Contents 02 What do we mean by spasms, stiffness and spasticity? 03 The effects of spasms and stiffness 04 What causes spasms and
Muscle Spasms and Stiffness Practical living for everyday life with MS Contents 02 What do we mean by spasms, stiffness and spasticity? 03 The effects of spasms and stiffness 04 What causes spasms and
The Child With Cerebral Palsy
 The Child With Cerebral Palsy Lisa Thornton, MD Medical Director, KidsRehab LaRabida Children's Hospital Schwab Rehabilitation Hospital University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Cerebral Palsy
The Child With Cerebral Palsy Lisa Thornton, MD Medical Director, KidsRehab LaRabida Children's Hospital Schwab Rehabilitation Hospital University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Cerebral Palsy
Orthopaedic Issues in Adults with CP: If I Knew Then, What I Know Now
 Orthopaedic Issues in Adults with CP: If I Knew Then, What I Know Now Laura L. Tosi, MD Director, Bone Health Program Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC Epidemiology 87-93% of children born
Orthopaedic Issues in Adults with CP: If I Knew Then, What I Know Now Laura L. Tosi, MD Director, Bone Health Program Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC Epidemiology 87-93% of children born
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University
 Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury*
 ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
REHABILITATION MEDICINE by PROFESSOR ANTHONY WARD
 REHABILITATION MEDICINE by PROFESSOR ANTHONY WARD What is Rehabilitation Medicine? Rehabilitation Medicine (RM) is the medical specialty with rehabilitation as its primary strategy. It provides services
REHABILITATION MEDICINE by PROFESSOR ANTHONY WARD What is Rehabilitation Medicine? Rehabilitation Medicine (RM) is the medical specialty with rehabilitation as its primary strategy. It provides services
A Note to Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapists
 D Page 1 of 5 A Note to Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapists Treating Children with Hurler Syndrome Because Hurler syndrome is such a rare disease, we have provided some basic information to assist
D Page 1 of 5 A Note to Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapists Treating Children with Hurler Syndrome Because Hurler syndrome is such a rare disease, we have provided some basic information to assist
A Range of Treatment Options Individualizes Spasticity Management
 VOLUME 21, NUMBER 2 2012 A Range of Treatment Options Individualizes Spasticity Management by Angela Sinner, D.O., pediatric rehabilitation medicine specialist and Debbie Song, M.D., pediatric neurosurgeon
VOLUME 21, NUMBER 2 2012 A Range of Treatment Options Individualizes Spasticity Management by Angela Sinner, D.O., pediatric rehabilitation medicine specialist and Debbie Song, M.D., pediatric neurosurgeon
Developmental Pediatrics Rehabilitation Learner Orientation Package
 Spasticity Clinic Follow Up Assessment Template This letter should be directed to the family, and copied to the involved family physician, any specialists that are involved of the care and also the relevant
Spasticity Clinic Follow Up Assessment Template This letter should be directed to the family, and copied to the involved family physician, any specialists that are involved of the care and also the relevant
REHABILITATION SERVICES
 REHABILITATION SERVICES Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS... 2 PRIOR AUTHORIZATION REQUIREMENTS FOR MEDICAID REIMBURSEMENT OF INPATIENT REHABILITATION SERVICES (Updated 4/1/11)...
REHABILITATION SERVICES Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS... 2 PRIOR AUTHORIZATION REQUIREMENTS FOR MEDICAID REIMBURSEMENT OF INPATIENT REHABILITATION SERVICES (Updated 4/1/11)...
Jellow. for the Cerebral Palsy. Antara Hazarika, Kumar Anchal, Priti Thankar, Samraat Sardesai. a study by
 Jellow for the Cerebral Palsy a study by Antara Hazarika, Kumar Anchal, Priti Thankar, Samraat Sardesai Index Understanding the world of CP Modes of communication The need for the product ( product rational)
Jellow for the Cerebral Palsy a study by Antara Hazarika, Kumar Anchal, Priti Thankar, Samraat Sardesai Index Understanding the world of CP Modes of communication The need for the product ( product rational)
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015
 Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
12. Physical Therapy (PT)
 1 2. P H Y S I C A L T H E R A P Y ( P T ) 12. Physical Therapy (PT) Clinical presentation Interventions Precautions Activity guidelines Swimming Generally, physical therapy (PT) promotes health with a
1 2. P H Y S I C A L T H E R A P Y ( P T ) 12. Physical Therapy (PT) Clinical presentation Interventions Precautions Activity guidelines Swimming Generally, physical therapy (PT) promotes health with a
Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity
 Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity Last Review Date: November 13, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.31bC5 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity Last Review Date: November 13, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.31bC5 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
How To Cover Occupational Therapy
 Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
CEREBRAL PALSY. Who Owns Your Body? What is Cerebral Palsy?
 SOUTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR FAMILIES AND CHILDREN WITH SPECIAL NEEDS CEREBRAL PALSY Inside This Issue: Correct Terms 2 Types of CP 4 Spasticity 5 Establish A Bowel Routine Special Other Topics of Interest
SOUTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR FAMILIES AND CHILDREN WITH SPECIAL NEEDS CEREBRAL PALSY Inside This Issue: Correct Terms 2 Types of CP 4 Spasticity 5 Establish A Bowel Routine Special Other Topics of Interest
Dr. Enas Elsayed. Brunnstrom Approach
 Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CEREBRAL PALSY. A Comparison between Elongation of the Tendo Calcaneus and Gastrocnemius Recession
 EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CEREBRAL PALSY A Comparison between Elongation of the Tendo Calcaneus and Gastrocnemius Recession W. J. W. SHARRARD and S. BERNSTEIN,* SHEFFIELD, ENGLAND From the Children s Hospital,
EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CEREBRAL PALSY A Comparison between Elongation of the Tendo Calcaneus and Gastrocnemius Recession W. J. W. SHARRARD and S. BERNSTEIN,* SHEFFIELD, ENGLAND From the Children s Hospital,
A Capstone Project for PTY 768 Presented to the Faculty of the Department of Physical Therapy Sage Graduate School
 Use of modified core strengthening and stabilization exercises in conjunction with Dynamic Movement Orthoses (DMO) to increase trunk control and grasp control in a 12 year old boy with Spastic Diplegic
Use of modified core strengthening and stabilization exercises in conjunction with Dynamic Movement Orthoses (DMO) to increase trunk control and grasp control in a 12 year old boy with Spastic Diplegic
The Taxi Program provides services only to residents of the City of Napa.
 The NCTPA Taxi Program is a valuable taxpayer funded component of our agency s transportation services. While not intended as a primary means of transportation, this program was created to provide a lifeline
The NCTPA Taxi Program is a valuable taxpayer funded component of our agency s transportation services. While not intended as a primary means of transportation, this program was created to provide a lifeline
W SITTING, KNEELING, LONG LEG & SIDE SITTING Perils, Problems, & Prevention
 W SITTING, KNEELING, LONG LEG & SIDE SITTING Perils, Problems, & Prevention Tema Stein B.P.T., D.O (mp) Paediatric Physical Therapist Osteopathic Manual Practitioner Toddlers, preschoolers and children
W SITTING, KNEELING, LONG LEG & SIDE SITTING Perils, Problems, & Prevention Tema Stein B.P.T., D.O (mp) Paediatric Physical Therapist Osteopathic Manual Practitioner Toddlers, preschoolers and children
Extended Disability Income. Fixed cease age. Extended Disability Income. Whole Life UP TO 24 MONTHS. Pre-retirement.
 For intermediaries Sanlam Risk Cover January 2015 Temporary Disability Income benefit (OIT3) Primary Income Protector benefits Waiting period Sickness Temporary Disability Income Including fixed payment
For intermediaries Sanlam Risk Cover January 2015 Temporary Disability Income benefit (OIT3) Primary Income Protector benefits Waiting period Sickness Temporary Disability Income Including fixed payment
How To Become A Physio And Rehabilitation Medicine Specialist
 EUROPEAN BOARD OF PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE LOGBOOK EUROPEAN UNION OF MEDICAL SPECIALISTS UEMS IDENTIFICATION... 2 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 3 THE TRAINING COURSE... 3 TRAINING PROGRAMME... 4
EUROPEAN BOARD OF PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE LOGBOOK EUROPEAN UNION OF MEDICAL SPECIALISTS UEMS IDENTIFICATION... 2 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 3 THE TRAINING COURSE... 3 TRAINING PROGRAMME... 4
How To Manage Cerebral Palsy In General Practice
 Disability Cerebral palsy in Dinah Reddihough childhood Background Cerebral palsy is the most common cause of physical disability in childhood. While some children have only a motor disorder, others have
Disability Cerebral palsy in Dinah Reddihough childhood Background Cerebral palsy is the most common cause of physical disability in childhood. While some children have only a motor disorder, others have
Life Care Plan. Amir Kumar. Projected Evaluations. Per Unit $5000 - $6000
 Projected Evaluations Rehabilitation Long-Term Needs Assessment 1 11/17/07 21 2027 4 X Only (1 X already accomplished.) Assess Handicapping Conditions $5000 - $6000 One time already conducted as of 11/17/07
Projected Evaluations Rehabilitation Long-Term Needs Assessment 1 11/17/07 21 2027 4 X Only (1 X already accomplished.) Assess Handicapping Conditions $5000 - $6000 One time already conducted as of 11/17/07
Clinical Guidelines for Stroke Management
 Stop stroke. Save lives. End suffering. Clinical Guidelines for Stroke Management quick guide for physiotherapy This summary is an implementation tool designed to raise the awareness of the recommendations
Stop stroke. Save lives. End suffering. Clinical Guidelines for Stroke Management quick guide for physiotherapy This summary is an implementation tool designed to raise the awareness of the recommendations
Statement for the Record. Mr. Chairman and Members of the Committee:
 The Need For National Cerebral Palsy Surveillance - Testimony before the House Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies - Committee on Appropriations Dr. Janice
The Need For National Cerebral Palsy Surveillance - Testimony before the House Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies - Committee on Appropriations Dr. Janice
12/15/2008. Image from: http://www.emedicine.com/neuro/topic533.htm
 A non-progressive disorder Caused by brain injury pre (70-80%), peri, or post natally Injure occurs before CNS reaches maturity Patients often have great potential masked by their condition Image from:
A non-progressive disorder Caused by brain injury pre (70-80%), peri, or post natally Injure occurs before CNS reaches maturity Patients often have great potential masked by their condition Image from:
Therapeutic Canine Massage
 Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
Cerebral Palsy Neurogenic Bladder, Outcomes of Lifetime Care
 Cerebral Palsy Neurogenic, Outcomes of Lifetime Care Kevin P Murphy MD Gillette Lifetime Specialty Healthcare St. Paul Minnesota Cerebral Palsy 1 Disclosure Information AACPDM 67 th Annual Meeting, October
Cerebral Palsy Neurogenic, Outcomes of Lifetime Care Kevin P Murphy MD Gillette Lifetime Specialty Healthcare St. Paul Minnesota Cerebral Palsy 1 Disclosure Information AACPDM 67 th Annual Meeting, October
Substandard Underwriting Structured Settlements
 Substandard Underwriting Structured Settlements Structures 101-Back to Basics February 20-22, 2013 Las Vegas, Nevada Rosemary Brindamour BSN CSSC Chief Medical Underwriter Structured Settlement Underwriting
Substandard Underwriting Structured Settlements Structures 101-Back to Basics February 20-22, 2013 Las Vegas, Nevada Rosemary Brindamour BSN CSSC Chief Medical Underwriter Structured Settlement Underwriting
Cerebral Palsy. IHSS Training Academy 1
 Cerebral Palsy What is Cerebral Palsy? Doctors use the term cerebral palsy to refer to any one of a number of neurological disorders that appear in infancy or early childhood and permanently affect body
Cerebral Palsy What is Cerebral Palsy? Doctors use the term cerebral palsy to refer to any one of a number of neurological disorders that appear in infancy or early childhood and permanently affect body
What types of scoliosis are there?
 Patient and Family Education Scoliosis About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment This handout covers the most common type of scoliosis, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Other types of scoliosis may
Patient and Family Education Scoliosis About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment This handout covers the most common type of scoliosis, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Other types of scoliosis may
CEREBRAL PALSY AND MENTAL RETARDATION DEFINITION
 CEREBRAL PALSY AND MENTAL RETARDATION DEFINITION It is a disorder of posture movement and tone due to a static encephalopathy acquired during brain growth in fetal life infancy or early childhood. Though
CEREBRAL PALSY AND MENTAL RETARDATION DEFINITION It is a disorder of posture movement and tone due to a static encephalopathy acquired during brain growth in fetal life infancy or early childhood. Though
Treatment of hip dysplasia in children with. Terje Terjesen Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Oslo University Hospital, Rikshospitalet
 Treatment of hip dysplasia in children with cerebral palsy Terje Terjesen Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Oslo University Hospital, Rikshospitalet Oslo, Norway Why do CP children have problems in the
Treatment of hip dysplasia in children with cerebral palsy Terje Terjesen Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Oslo University Hospital, Rikshospitalet Oslo, Norway Why do CP children have problems in the
Range of Injury Scale Values
 Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
Competency Based Goals and Objectives:
 PEDIATRIC SPORTS MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES & OVERALL EDUCATIONAL GOALS Competency Based Goals and Objectives: Mission: Train fellows to become sports medicine physicians
PEDIATRIC SPORTS MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES & OVERALL EDUCATIONAL GOALS Competency Based Goals and Objectives: Mission: Train fellows to become sports medicine physicians
Musculoskeletal System SMA CARE SERIES
 Musculoskeletal System SMA CARE SERIES SMA CARE SERIES - Musculoskeletal System Contents Introduction 3 Contractures in Children with SMA 5 Bone Health in Children with SMA 7 The Hips in Children with
Musculoskeletal System SMA CARE SERIES SMA CARE SERIES - Musculoskeletal System Contents Introduction 3 Contractures in Children with SMA 5 Bone Health in Children with SMA 7 The Hips in Children with
FAMILY GUIDE TO MANAGEMENT OF SPASTICITY
 FAMILY GUIDE TO MANAGEMENT OF SPASTICITY DONNA L. NIMEC, M.D. DIRECTOR, PEDIATRIC PHYSICAL MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION SPAULDING REHABILITATION HOSPITAL Table of Contents Page I. Introduction 3 II. Physical
FAMILY GUIDE TO MANAGEMENT OF SPASTICITY DONNA L. NIMEC, M.D. DIRECTOR, PEDIATRIC PHYSICAL MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION SPAULDING REHABILITATION HOSPITAL Table of Contents Page I. Introduction 3 II. Physical
TRADIES NATIONAL HEALTH MONTH HEALTH SNAPSHOT
 TRADIES NATIONAL HEALTH month AUGUST 2016 TRADIES NATIONAL HEALTH MONTH HEALTH SNAPSHOT Prepared by the Australian Physiotherapy Association ABOUT THE TRADIES NATIONAL HEALTH MONTH SNAPSHOT Marcus Dripps,
TRADIES NATIONAL HEALTH month AUGUST 2016 TRADIES NATIONAL HEALTH MONTH HEALTH SNAPSHOT Prepared by the Australian Physiotherapy Association ABOUT THE TRADIES NATIONAL HEALTH MONTH SNAPSHOT Marcus Dripps,
The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy
 MARIANJOY Rehabilitation Hospital Wheaton Franciscan Healthcare The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating Even the Smallest Steps, One Step at a Time The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating
MARIANJOY Rehabilitation Hospital Wheaton Franciscan Healthcare The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating Even the Smallest Steps, One Step at a Time The Pediatric Program at Marianjoy Celebrating
Chiari malformations
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain. History
 A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
First Year. PT7040- Clinical Skills and Examination II
 First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
Case: Cerebral Palsy
 Case: Cerebral Palsy A.W. is a 48 y.o. AA female with diplegic Cerebral Palsy(CP) Dysphagia, coughing, with solid foods X 3 mo. Vague generalized abdominal pain intermittently, 3 lb wt loss Seizure disorder
Case: Cerebral Palsy A.W. is a 48 y.o. AA female with diplegic Cerebral Palsy(CP) Dysphagia, coughing, with solid foods X 3 mo. Vague generalized abdominal pain intermittently, 3 lb wt loss Seizure disorder
