Mr. Storie 30S Chemistry Organic Chem - Alkanes. Organic Chemistry
|
|
|
- Amy Powell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Organic Chemistry 1
2 UNIT 5: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY All important vocabulary is in Italics and bold. Compare and contrast inorganic and organic chemistry. Describe the structural characteristics of carbon. Name, draw, and construct structural models of alkanes Include: branched alkanes, structural isomers Compare and contrast the molecular structures of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Include: trends in melting points and boiling points Name, draw, and construct molecular models of alkenes and alkynes Include: branched alkenes and alkynes Outline the transformation of alkanes to alkenes or alkynes and vice versa. Include: dehydrogenation/hydrogenation Compare and contrast the structure of aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Include: molecular models, structural formulas, common uses Write condensed structural formulas for and name common alcohols. Include: uses of common alcohols Write condensed structural formulas for and name organic acids. Include: uses and functions of common organic acids Write condensed structural formulas for and name esters. Include: uses and functions of common esters Write condensed structural formulas for and name alkyl halides. Describe some common organic reactions. Including: esterification, halogenation, hydration, hydrogenation Describe the process of polymerization and identify important natural and synthetic polymers. Additional KEY Terms distillation alkyl group substituent cycloalkanes saturated unsaturated resonance functional group monomer HYDROCARBONS 2
3 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS OF ALKANES: 3
4 1. If an alkane has: a) 6 carbons, how many H atoms will it have? b) 20 H atoms, how many C atoms will it have? c) 25 C atoms, how many H atoms will it have? d) 12 H atoms, how many C atoms will it have? 2. Identify each of the following as organic or inorganic. a) NaHCO 3 d) HCN b) CH 4 e) Ca 2 C c) HC 2 H 3 O 2 f) C 2 H 2 3. Name each of the following: a) C 7 H 16 b) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 4
5 4. Draw the structural formulas for each of the following: a) butane h) 2,2,3,4-tetramethylpentane b) decane i) 3-ethyl-2,2-dimethylhexane c) heptane j) 5-butyl-2,2-dimethylnonane d) 2,3-dimethylpentane k) 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane e) 3-ethylhexane l) 3,3-diethylheptane f) 3-ethylpentane m) 2,3,5-trimethylhexane g) 2,3-dimethybutane n) 3,4-diethyl-2,2,7-trimethyloctane 5. Determine if the is anything wrong with these compound names? Correct the error is found. (Hint: Draw the structures first) a) 5-methylhexane e) 4-methyloctane b) 2-ethyl-2-methylpropane f) 2,3-trimethylheptane c) 1-methylbutane g) 1,4-dimethylpentane d) 3,5-ethyl-2-methylheptane h) 1,3,5-trimethylnonane 5
6 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS OF STRUCTURAL ISOMERS: 1. Draw and name 5 structural isomers of C 6 H Draw and name 9 structural isomers of C 7 H Indicate which straight-chain alkane is a structural isomer of each of the following. a) 4-ethyloctane b) 3-methylpentane c) 2,2,3,3-tetramethylpentane d) 2-methylbutane e) 3-ethylhexane f) 2-methylhexane g) 2,2-dimethylpentane 6
7 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ON ALKENES AND ALKYNES: 1. If you have an alkene with a) 6 carbons, how many H s do you have? b) 12 carbons, how many H s do you have? c) 20 H s, how many carbons do you have? d) 17 carbons, how many H s do you have? e) 6 H s, how many carbons do you have? 2. If you have and alkyne with a) 6 carbons, how many H s do you have? b) 12 carbons, how many H s do you have? c) 20 H s, how many carbons do you have? d) 17 carbons, how many H s do you have? e) 6 H s, how many carbons do you have? 3. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated organic compounds? 4. What properties of hydrocarbons change as the length of the chain increases? 5. Draw the following structures: a) propyne f) 2,3,5-trimethyl-2-hexene b) 4-ethyl-2-nonene g) 3,5-dimethyl-1-heptyne c) 3-decyne h) 4,4-diethyl-7-methyl-2-decene d) 4,4-dimethyl-2-pentyne i) 3-methyl-1-butene e) 3-methyl-1-butyne j) 5-ethyl-2,2,4,6-tetramethyl-4-octene 7
8 6. Name the following compounds. 7. What, if anything, is wrong with the following names? a) 2-methyl-3-butene d) 2,2-dimethyl-1-hexene b) 2,2-dimethyl-3-pentyne e) 3-methyl-1-octyne c) 1-butene f) 5-octyne 8. Write the balanced equation, using structural formulas, for the following reactions. a) hydrogenation of 2-butene b) dehydrogenation of propane c) 4-methyl-2-hexyne + 1 H 2 8
9 KNOW YOUR FATS! Your task is to complete the following research project using the website below as a resource. (Feel free to use and reference any other website you would like, for additional information) 1. Complete the following questions on page : # 67, 68, 69, Complete these questions below on fats: 1. What organic components must a molecule have to be a fat? 2. How are fat types different? 3. What does hydrogenated mean, and why do companies use hydrogenated fats? 4. Why do companies use partially-hydrogenated fats and how are they made? 5. Where do saturated fats come from? 6. What are Omega fats and why are they important? 7. Which geometric isomer is more naturally occurring and which is produced by man? 8. Name some products where you would find trans fats. 9. List the types of fat that are good and bad for you? 10. What are the health risks of eating too much bad fat? NAME: CATEGORY Amount of Information Quality of Information Organization All questions are addressed in complete sentences with proper grammar. Information is NOT copied directly from the website. It includes several supporting details and/or pictures. Information is very organized with wellconstructed paragraphs and subheadings. All questions are addressed, but some are not in complete sentences OR there are grammar mistakes. Information is NOT copied directly from the website, but no addition detail is provided. Information is well organized. Some questions are addressed quickly and in point form. Information is NOT copied; but questions are missing relevant information. No special care was taken to present the information. One or more questions were not addressed. All information is copied directly from the internet. The information appears to be disorganized. 9
10 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS OF ALCOHOLS: 1. Compare and contrast the effect of the OH group in organic and inorganic chemistry. 2. What is the IUPAC name of each of the following alcohols? 10
11 3. Draw the structural formula of each alcohol. a) Methanol b) 1-pentanol c) 4-methyl-2-heptanol d) 9,9-dimethyl-6-propyl-4-decanol e) 3-ethyl-2-methyl-1-pentanol f) 2,4,5-trimethyl-2-hexanol g) 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol h) 3,5-diethyl-3-octanol i) phenol j) 2,4-diethylphenol 11
12 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: 1. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following. 2. Draw the structure of each of the following. a) ethanoic acid b) octanoic acid c) 3-methylhexanoic acid d) 4,4-dimethylheptanoic acid e) 3,3-dimethyl-4-propyldecanoic acid f) 2,2,3-trimethylbutanoic acid g) 3-ethylheptanoic acid 12
13 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS OF ESTERS: 1. Write the esterification equation for each of the following. Name and draw the structural formula for each reactant and product formed. a) propanoic acid and 1-butanol b) butanoic acid and 1-hexanol c) pentanoic acid and 1-octanol d) methanoic acid and ethanol e) hexanoic acid and 1-propanol f) butanoic acid and methanol 13
14 2. Draw the condensed formula that completes each of the following equations. Name each reactant and product. 14
15 COMPLETE THIS ASSIGNMENT TO GAIN A STRONGER UNDERSTANDING OF POLYMERS AND THEIR USAGE: 1. GO TO: Macrogalleria of Polymer Fun 2. Go to level 1: a. Go to three or four stores b. List SIX different polymers (skip duplicates) 3. Follow the links for each polymer (level 2) a. Draw polymer and name (draw) monomers b. List each polymers use in life Write a conclusion / summary about what you have learned about polymers, organic chemistry and life. Sample Work: Marks are based on completeness of polymer information, neatness of information and thoughtful conclusion. / 10 15
16 Organic Unit Review 1. Draw complete structural formulas for alkanes with two and six carbons. Name the structures. 2. Draw condensed structural formulas for pentane and heptane. 3. Name the compounds that follow: 4. Draw complete structural formulas for the following compounds: a. 3-ethyl-2,4-dimethyloctane b. 2,2,4-trimethylpentane c. 3-ethylhexane d. 3,5-diethyl-2,3-dimethyl-5-propyldecane e. Propyne f. cyclopentane 5. Draw the structural formulas for the following alkenes. If a compound has geometric isomers, draw both the cis and trans forms. a. 1-pentene b. 2-hexene c. 2-methyl-2-hexene d. 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 16
17 6. Name the following compounds: 7. Why are the following names incorrect? a. 2-dimethylpentane b. 1,3-dimethylpropane c. 3-methylbutane d. 3,4-dimethylbutane 8. Explain the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon compounds. 9. Draw all the possible alkenes with the molecular formula C 4 H 8. Name each compound. 10. Explain why alkenes have cis/trans isomers and alkanes don t. 11. Draw a structure for each compound. a. p diethylbenzene b. 2-methyl-3-phenylpentane c. p-xylene d. toluene 17
18 12. Write a complete balanced equation for the combustion of pentane. 13. Name the following compounds: 14. Name the following compounds: d. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH 15. Give the structural formula for each of the following compounds: a. 2-chloropropane b. 1-iodo-2,2-dimethylpentane c. p-bromobenzene. d. 2-methylphenol e. 1,2-dichlorocyclohexane f. 1,2-ethandiol 18
19 16. Give the name for the following carboxylic acids and esters: a. HCOOH b. CH 3 CH 2 COOH c. CH 3 COOCH 2 CH 3 d. CH 3 COOH e. CH 3 (CH 2 ) 4 COOH f. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 COOCH 2 CH Use the ester from question 16c to show a complete de-esterification reaction. 18. Use 2-butene to show a hydration reaction. 19. Write the structure for the reactants and expected products from each reaction: a. propene + bromine gas b. 2-pentene + iodine gas c. 3-octyne + hydrogen gas d. trans 2-butene + hydrogen gas 20. Explain the difference between addition and condensation polymerization. 19
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Page 1. 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? (1) 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4)
 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test
 Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test 2. Write the IUPAC names for the following organic molecules: a) acetone: propanone d) acetylene: ethyne b) acetic acid: ethanoic acid e)
Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test 2. Write the IUPAC names for the following organic molecules: a) acetone: propanone d) acetylene: ethyne b) acetic acid: ethanoic acid e)
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I
 Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3. Copyright 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 1: Organic Compounds 1.1-1
 Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of carbon based compounds. The structural and genetic materials of living organisms are organic compounds. Many of the substances
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of carbon based compounds. The structural and genetic materials of living organisms are organic compounds. Many of the substances
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch14_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Compounds with the -OH group attached to a saturated alkane-like carbon are known as A)
Ch14_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Compounds with the -OH group attached to a saturated alkane-like carbon are known as A)
Alkanes. Chapter 1.1
 Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS 2010, 2003, 1980, by David A. Katz. All rights reserved.
 NMENCLATURE F RGANIC CMPUNDS 2010, 2003, 1980, by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. rganic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to bond with itself to form long chains
NMENCLATURE F RGANIC CMPUNDS 2010, 2003, 1980, by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. rganic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to bond with itself to form long chains
CHEM 203 Exam 1. KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
IUPAC System of Nomenclature
 IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Chemistry 1110 Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
 hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
Worksheets for Organic Chemistry
 Worksheets for Organic Chemistry Worksheet 1 Alkanes Question 1. Provide IUPAC names for the following structures a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Chemistry of Natural Substances Organic Chemistry Worksheets 1
Worksheets for Organic Chemistry Worksheet 1 Alkanes Question 1. Provide IUPAC names for the following structures a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Chemistry of Natural Substances Organic Chemistry Worksheets 1
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 (adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
(adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
e. What are the compositions and uses of fractions of crude oil? f. How are further fractions lubricationg oils and waxes obtained?
 CRUDE OIL AND ITS COMPOSITION 1. Use a textbook to answer the following questions: a. How was crude oil formed? b. What is crude oil chemically? c. How can the components of crude oil be separated? d.
CRUDE OIL AND ITS COMPOSITION 1. Use a textbook to answer the following questions: a. How was crude oil formed? b. What is crude oil chemically? c. How can the components of crude oil be separated? d.
Question (3): What are the different types of covalent bonds found in carbons compounds? Briefly explain with examples.
 CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) Chemistry: For Class 10 Page : 1 Question (1): What is organic chemistry? Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds of living matter i.e., plants and animals (CO 2, carbonates,
CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) Chemistry: For Class 10 Page : 1 Question (1): What is organic chemistry? Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds of living matter i.e., plants and animals (CO 2, carbonates,
1. The functional group present in carboxylic acids is called a A) carbonyl group. B) carboxyl group. C) carboxylate group. D) carbohydroxyl group.
 Name: Date: 1. The functional group present in carboxylic acids is called a A) carbonyl group. B) carboxyl group. C) carboxylate group. D) carbohydroxyl group. 2. Which of the following statements concerning
Name: Date: 1. The functional group present in carboxylic acids is called a A) carbonyl group. B) carboxyl group. C) carboxylate group. D) carbohydroxyl group. 2. Which of the following statements concerning
Ch17_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch17_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which molecule is a carboxylic acid? A) 1) B) C) D) E) CH3 CH2 CH2 NH2 2) Which molecule
Ch17_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which molecule is a carboxylic acid? A) 1) B) C) D) E) CH3 CH2 CH2 NH2 2) Which molecule
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 13_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In organic chemistry, the term unsaturated means a molecule A) which contains one or more
Ch 13_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In organic chemistry, the term unsaturated means a molecule A) which contains one or more
UNIT 5: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 onour hemistry Unit 5: rganic hemistry hapter 5: ydrocarbon ompounds 5.: ydrocarbons UNIT 5: RGANI EMISTRY ydrocarbons: - compounds that contains hydrogen and carbon atoms. - it may contain oxygen, nitrogen
onour hemistry Unit 5: rganic hemistry hapter 5: ydrocarbon ompounds 5.: ydrocarbons UNIT 5: RGANI EMISTRY ydrocarbons: - compounds that contains hydrogen and carbon atoms. - it may contain oxygen, nitrogen
Basic definitions for organic chemistry
 rganic Chemistry - Introduction F 1 Basic definitions for organic chemistry Scope rganic chemistry is a vast subject so is split it into small sections for study. This is done by studying compounds which
rganic Chemistry - Introduction F 1 Basic definitions for organic chemistry Scope rganic chemistry is a vast subject so is split it into small sections for study. This is done by studying compounds which
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Naming Organic Compounds
 Nomenclature Naming Organic Compounds The increasingly large number of organic compounds identified with each passing day, together with the fact that many of these compounds are isomers of other compounds,
Nomenclature Naming Organic Compounds The increasingly large number of organic compounds identified with each passing day, together with the fact that many of these compounds are isomers of other compounds,
Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a benzene ring.
 Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
CH 102 Practice Exam 2 PCC-Sylvania
 CH 102 Practice Exam 2 PCC-Sylvania True/False Indicate if the statement is true or false. 1.Tertiary alcohols are not easily oxidized. 2.Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes. 3.Primary alcohols
CH 102 Practice Exam 2 PCC-Sylvania True/False Indicate if the statement is true or false. 1.Tertiary alcohols are not easily oxidized. 2.Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes. 3.Primary alcohols
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 Introduction to rganic Chemistry Theory Manual Written by Judy Gordon & Lara Passlow p Table of Contents An Introduction to rganic Chemistry... 3 Functional Groups... 6 Chemical Formulae and the Structures
Introduction to rganic Chemistry Theory Manual Written by Judy Gordon & Lara Passlow p Table of Contents An Introduction to rganic Chemistry... 3 Functional Groups... 6 Chemical Formulae and the Structures
Chapter 18: Organic Chemistry
 h 18 Page 1 hapter 18: rganic hemistry rganic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that focuses on compounds that contain carbon (Exceptions:, 2, 3 2-, and N - ) Even though organic compounds only contain
h 18 Page 1 hapter 18: rganic hemistry rganic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that focuses on compounds that contain carbon (Exceptions:, 2, 3 2-, and N - ) Even though organic compounds only contain
Alcohols. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH 1-propanol OH
 Chapter 12 rganic Compounds with xygen and Sulfur 12.1 Alcohols, Thiols, and Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( ) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( )
Chapter 12 rganic Compounds with xygen and Sulfur 12.1 Alcohols, Thiols, and Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( ) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( )
Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391)
 NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
UNIT (9) CARBOXYLIC ACIDS, ESTERS, AMINES, AND AMIDES
 UNIT (9) CARBXYLIC ACIDS, ESTERS, AMINES, AND AMIDES 9.1 Carboxylic Acids The functional group in carboxylic acids is called the carboxyl group. A carboxyl group is a carbonyl group (C = ) with a hydroxyl
UNIT (9) CARBXYLIC ACIDS, ESTERS, AMINES, AND AMIDES 9.1 Carboxylic Acids The functional group in carboxylic acids is called the carboxyl group. A carboxyl group is a carbonyl group (C = ) with a hydroxyl
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Fourteen 1
 An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
Organic chemistry. Bridge course
 Organic chemistry Nomenclature of Organic compounds Bridge course Nomenclature of organic compounds There are two systems of naming 1. Trivial system 2. IUPAC system Trivial system: When a few organic
Organic chemistry Nomenclature of Organic compounds Bridge course Nomenclature of organic compounds There are two systems of naming 1. Trivial system 2. IUPAC system Trivial system: When a few organic
HOMEWORK PROBLEMS: IR SPECTROSCOPY AND 13C NMR. The peak at 1720 indicates a C=O bond (carbonyl). One possibility is acetone:
 HMEWRK PRBLEMS: IR SPECTRSCPY AND 13C NMR 1. You find a bottle on the shelf only labeled C 3 H 6. You take an IR spectrum of the compound and find major peaks at 2950, 1720, and 1400 cm -1. Draw a molecule
HMEWRK PRBLEMS: IR SPECTRSCPY AND 13C NMR 1. You find a bottle on the shelf only labeled C 3 H 6. You take an IR spectrum of the compound and find major peaks at 2950, 1720, and 1400 cm -1. Draw a molecule
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur
 Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur 1 Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) that replaces a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur 1 Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) that replaces a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached
GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS
 Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
BASIC NOMENCLATURE. The names of the groups you must be able to recognize and draw are:
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: BASI NOMENLATURE 1. Give examples of, and recognize when given the structure, representatives of the following classes of compounds. Alkyl halides (1, 2, 3 ) Alcohols (1, 2,
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: BASI NOMENLATURE 1. Give examples of, and recognize when given the structure, representatives of the following classes of compounds. Alkyl halides (1, 2, 3 ) Alcohols (1, 2,
ORGANIC NOMENCLATURE
 hemistry 121 Winter 2001 ourse otes Principles of hemistry II Introduction RGAI MELATURE onfusion can arise in organic chemistry because of the variety of names that have been applied to compounds; common
hemistry 121 Winter 2001 ourse otes Principles of hemistry II Introduction RGAI MELATURE onfusion can arise in organic chemistry because of the variety of names that have been applied to compounds; common
Chemistry Grade 11 Year and weekly plan 2015
 Chemistry Grade 11 Year and weekly plan 2015 TERM1 Content Curriculum Statement Teaching Method Atomic combinations: molecular structure chemical bond (is seen as the net electrostatic force two atoms
Chemistry Grade 11 Year and weekly plan 2015 TERM1 Content Curriculum Statement Teaching Method Atomic combinations: molecular structure chemical bond (is seen as the net electrostatic force two atoms
CHM220 Addition lab. Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes*
 CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility
 Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
12.4 FUNCTIONAL-GROUP INFRARED ABSORPTIONS
 552 APTER 12 INTRODUTION TO SPETROSOPY. INFRARED SPETROSOPY AND MASS SPETROMETRY PROBLEM 12.9 Which of the following vibrations should be infrared-active and which should be infrared-inactive (or nearly
552 APTER 12 INTRODUTION TO SPETROSOPY. INFRARED SPETROSOPY AND MASS SPETROMETRY PROBLEM 12.9 Which of the following vibrations should be infrared-active and which should be infrared-inactive (or nearly
Laboratory 22: Properties of Alcohols
 Introduction Alcohols represent and important class of organic molecules. In this experiment you will study the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. Solubility in water, and organic solvents,
Introduction Alcohols represent and important class of organic molecules. In this experiment you will study the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. Solubility in water, and organic solvents,
PTAC: Applied Chemistry COURSE OUTLINE & OBJECTIVES ESC Approved November 19, 2004
 INTRODUCTION PTAC: Applied Chemistry COURSE OUTLINE & OBJECTIVES ESC Approved November 19, 2004 A. Introduction to Chemistry Terms 1. Define basic terms associated with chemistry: Organic/inorganic/biochemistry/physical
INTRODUCTION PTAC: Applied Chemistry COURSE OUTLINE & OBJECTIVES ESC Approved November 19, 2004 A. Introduction to Chemistry Terms 1. Define basic terms associated with chemistry: Organic/inorganic/biochemistry/physical
Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula
 Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula Alkanes have the molecular formula C n. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons because each member of the family has the maximum
Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula Alkanes have the molecular formula C n. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons because each member of the family has the maximum
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry CHEM 1021 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry Terms and Background Information
 Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry Terms and Background Information Basic rganic Chemistry rganic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. rganic compounds are compounds
Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry Terms and Background Information Basic rganic Chemistry rganic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. rganic compounds are compounds
Curso: FUNDAMENTOS DE QUIMICA ORGANICA Y BIOLOGICA FUNDAMENTALS OF ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
 UNIVERSIDAD DEL TURABO ESCUELA DE CIENCIAS Y TECNOLOGIA DEPARTAMENTO DE FISICA & QUIMICA GURABO, PUERTO RICO Curso: FUNDAMENTOS DE QUIMICA ORGANICA Y BIOLOGICA FUNDAMENTALS OF ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
UNIVERSIDAD DEL TURABO ESCUELA DE CIENCIAS Y TECNOLOGIA DEPARTAMENTO DE FISICA & QUIMICA GURABO, PUERTO RICO Curso: FUNDAMENTOS DE QUIMICA ORGANICA Y BIOLOGICA FUNDAMENTALS OF ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A.
 Lesson Element Keyword activities Instructions for teachers These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A. Just a minute! To run this activity you will need a set
Lesson Element Keyword activities Instructions for teachers These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A. Just a minute! To run this activity you will need a set
the double or triple bond. If the multiple bond is CH 3 C CCHCCH 3
 Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic ompounds Alkenes and Alkynes Unsaturated contain carbon-carbon double and triple bond to which more hydrogen atoms can be added. Alkenes: carbon-carbon double bonds Alkynes:
Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic ompounds Alkenes and Alkynes Unsaturated contain carbon-carbon double and triple bond to which more hydrogen atoms can be added. Alkenes: carbon-carbon double bonds Alkynes:
ALKENES AND ALKYNES REACTIONS A STUDENT WHO HAS MASTERED THE MATERIAL IN THIS SECTION SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 ALKENES AND ALKYNES REACTINS A STUDENT W AS MASTERED TE MATERIAL IN TIS SECTIN SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Given the starting materials and reaction conditions, predict the products of the following reactions of
ALKENES AND ALKYNES REACTINS A STUDENT W AS MASTERED TE MATERIAL IN TIS SECTIN SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Given the starting materials and reaction conditions, predict the products of the following reactions of
Subject : Chemistry GET IT FREE FROM WBSITE www.tekoclasses.com CONTENTS CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
 Subject : Chemistry GET IT FREE FROM WBSITE www.tekoclasses.com CONTENTS PART II S.No. Topics Page No. 1. Carbon & Its Compounds 1 44 2. Periodic Table & Periodicity in Properties. 45-62 Class : X (CBSE)
Subject : Chemistry GET IT FREE FROM WBSITE www.tekoclasses.com CONTENTS PART II S.No. Topics Page No. 1. Carbon & Its Compounds 1 44 2. Periodic Table & Periodicity in Properties. 45-62 Class : X (CBSE)
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols
 F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
Infrared Spectroscopy
 Infrared Spectroscopy 1 Chap 12 Reactions will often give a mixture of products: OH H 2 SO 4 + Major Minor How would the chemist determine which product was formed? Both are cyclopentenes; they are isomers.
Infrared Spectroscopy 1 Chap 12 Reactions will often give a mixture of products: OH H 2 SO 4 + Major Minor How would the chemist determine which product was formed? Both are cyclopentenes; they are isomers.
*0500/402* 0500/402. CHEMISTRY STANDARD GRADE Credit Level. Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre
 FOR OFFIIL USE 0500/402 NTIONL QULIFITIONS 2009 MONDY, MY 0.50 M 2.20 PM Total HEMISTRY STNDRD GRDE redit Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
FOR OFFIIL USE 0500/402 NTIONL QULIFITIONS 2009 MONDY, MY 0.50 M 2.20 PM Total HEMISTRY STNDRD GRDE redit Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
Chapter 13 Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines, and Amides. Carboxylic Acids. Names and Sources of Some Carboxylic Acids. IUPAC Names
 Chapter 13 Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines, and Amides 13.1 Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid contains a carboxyl group, which is a carbonyl group (C=) attached to a hydroxyl group (
Chapter 13 Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines, and Amides 13.1 Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid contains a carboxyl group, which is a carbonyl group (C=) attached to a hydroxyl group (
Identification of Unknown Organic Compounds
 Identification of Unknown Organic Compounds Introduction The identification and characterization of the structures of unknown substances are an important part of organic chemistry. Although it is often
Identification of Unknown Organic Compounds Introduction The identification and characterization of the structures of unknown substances are an important part of organic chemistry. Although it is often
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum
 Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition
 Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
DUI Stations. Do some research to fill in the chemistry table. Some examples have been completed for you: IUPAC name Methanol Methanal Methanoic acid
 DUI Stations Station 1: Introduction to alcohol chemistry Introduction: Molecules of alcohols, aldehydes and organic acids all have characteristic functional groups. Functional groups are groups of a few
DUI Stations Station 1: Introduction to alcohol chemistry Introduction: Molecules of alcohols, aldehydes and organic acids all have characteristic functional groups. Functional groups are groups of a few
4.5 Physical Properties: Solubility
 4.5 Physical Properties: Solubility When a solid, liquid or gaseous solute is placed in a solvent and it seems to disappear, mix or become part of the solvent, we say that it dissolved. The solute is said
4.5 Physical Properties: Solubility When a solid, liquid or gaseous solute is placed in a solvent and it seems to disappear, mix or become part of the solvent, we say that it dissolved. The solute is said
Q.1 Draw structures for, and name, all carboxylic acids with formula :-
 arboxylic acids F4 1 ARBXYLI AIDS Structure contain the carboxyl functional group includes a carbonyl (=) group and a hydroxyl (-) group the bonds are in a planar arrangement are isomeric with esters :-
arboxylic acids F4 1 ARBXYLI AIDS Structure contain the carboxyl functional group includes a carbonyl (=) group and a hydroxyl (-) group the bonds are in a planar arrangement are isomeric with esters :-
How to Quickly Solve Spectrometry Problems
 How to Quickly Solve Spectrometry Problems You should be looking for: Mass Spectrometry (MS) Chemical Formula DBE Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) Important Functional Groups o Alcohol O-H o Carboxylic Acid
How to Quickly Solve Spectrometry Problems You should be looking for: Mass Spectrometry (MS) Chemical Formula DBE Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) Important Functional Groups o Alcohol O-H o Carboxylic Acid
Carbon: The Element of Life from the six-part. Elements of Chemistry Series
 Carbon: The Element of Life from the six-part Elements of Chemistry Series Produced by Algonquin Educational Productions Distributed by... 800.323.9084 FAX 847.328.6706 www.unitedlearning.com This video
Carbon: The Element of Life from the six-part Elements of Chemistry Series Produced by Algonquin Educational Productions Distributed by... 800.323.9084 FAX 847.328.6706 www.unitedlearning.com This video
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Part 4 Nomenklatur -konformation
 MULTIPLE COICE QUESTIONS Part 4 Nomenklatur -konformation (Answers on pages 21-22) Topic: Nomenclature 1. The IUPAC name for A) 6-Ethyl-3,4-dimethylheptane B) 2-Ethyl-4,5-dimethylheptane C) 3,4,6-Trimethyloctane
MULTIPLE COICE QUESTIONS Part 4 Nomenklatur -konformation (Answers on pages 21-22) Topic: Nomenclature 1. The IUPAC name for A) 6-Ethyl-3,4-dimethylheptane B) 2-Ethyl-4,5-dimethylheptane C) 3,4,6-Trimethyloctane
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Synthesis of Isopentyl Acetate
 Experiment 8 Synthesis of Isopentyl Acetate Objectives To prepare isopentyl acetate from isopentyl alcohol and acetic acid by the Fischer esterification reaction. Introduction Esters are derivatives of
Experiment 8 Synthesis of Isopentyl Acetate Objectives To prepare isopentyl acetate from isopentyl alcohol and acetic acid by the Fischer esterification reaction. Introduction Esters are derivatives of
MOLECULAR REPRESENTATIONS AND INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY
 MLEULAR REPRESENTATINS AND INFRARED SPETRSPY A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Given a Lewis (dash or dot), condensed, bond-line, or wedge formula of a compound draw the other representations. 2. Give examples
MLEULAR REPRESENTATINS AND INFRARED SPETRSPY A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Given a Lewis (dash or dot), condensed, bond-line, or wedge formula of a compound draw the other representations. 2. Give examples
CONFORMATIONAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE EXERCISES. 1) Draw a Newman projection of the most stable conformation of 2-methylpropane.
 CONFORMATIONAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE EXERCISES 1) Draw a Newman projection of the most stable conformation of 2-methylpropane. 2) The structures below are: C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 A) not isomers. B) conformational
CONFORMATIONAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE EXERCISES 1) Draw a Newman projection of the most stable conformation of 2-methylpropane. 2) The structures below are: C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 A) not isomers. B) conformational
FIRE HAZARD PROPERTIES. Acetaldehyde IA -38 (-39) 347 (175) 4.0 60 0.8 1.5 70 (21) Yes 1 2 4 2 CH 3
 Acetaldehyde IA -38 (-3947 (17) 4.0 60 0.8 1. 70 (21) Yes 1 2 4 2 CHO (Acetic Aldehyde) (Ethanal) 7-07-0 Note: Polymerizes. See NFPA 49 contained in Fire Protection Guide to Hazardous Materials. Acetone
Acetaldehyde IA -38 (-3947 (17) 4.0 60 0.8 1. 70 (21) Yes 1 2 4 2 CHO (Acetic Aldehyde) (Ethanal) 7-07-0 Note: Polymerizes. See NFPA 49 contained in Fire Protection Guide to Hazardous Materials. Acetone
Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols
 Introduction Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols As has been mentioned before, over 20 million organic compounds have been identified. If each substance had to be studied as an entity completely
Introduction Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols As has been mentioned before, over 20 million organic compounds have been identified. If each substance had to be studied as an entity completely
17.2 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS
 17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
How to Interpret an IR Spectrum
 How to Interpret an IR Spectrum Don t be overwhelmed when you first view IR spectra or this document. We have simplified the interpretation by having you only focus on 4/5 regions of the spectrum. Do not
How to Interpret an IR Spectrum Don t be overwhelmed when you first view IR spectra or this document. We have simplified the interpretation by having you only focus on 4/5 regions of the spectrum. Do not
Chapter 10. Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems. Class Notes. B. The allyl group is both a common name and an accepted IUPAC name
 Chapter 10 Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems Chapter 10 suggested problems: I. The allyl group Class Notes A. B. The allyl group is both a common name and an accepted IUPAC name 1. Allyl alcohol
Chapter 10 Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems Chapter 10 suggested problems: I. The allyl group Class Notes A. B. The allyl group is both a common name and an accepted IUPAC name 1. Allyl alcohol
Fuel Oil and Home Heating Oil Produce from Polystyrene and Polypropylene Waste Plastics Mixture
 Research article Fuel Oil and Home Heating Oil Produce from Polystyrene and Polypropylene Waste Plastics Mixture Mohammad Mamunor Rashid, Moinuddin Sarker * Natural State Research, Inc., Department of
Research article Fuel Oil and Home Heating Oil Produce from Polystyrene and Polypropylene Waste Plastics Mixture Mohammad Mamunor Rashid, Moinuddin Sarker * Natural State Research, Inc., Department of
PRACTICE PROBLEMS, CHAPTERS 1-3
 PRATIE PRBLEMS, APTERS 1-3 (overed from h. 3: Alkane and Alkyl alide nomenclature only) 1. The atomic number of boron is 5. The correct electronic configuration of boron is: A. 1s 2 2s 3 B. 1s 2 2p 3.
PRATIE PRBLEMS, APTERS 1-3 (overed from h. 3: Alkane and Alkyl alide nomenclature only) 1. The atomic number of boron is 5. The correct electronic configuration of boron is: A. 1s 2 2s 3 B. 1s 2 2p 3.
ALCOHOLS: Properties & Preparation
 ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: R-, where R is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol.
ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: R-, where R is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol.
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
IDENTIFICATION OF ALCOHOLS
 IDENTIFICATION OF ALCOHOLS Alcohols are organic compounds that which considered as derivatives of water. One of the hydrogen atoms of water molecule (H-O-H) has been replaced by an alkyl or substituted
IDENTIFICATION OF ALCOHOLS Alcohols are organic compounds that which considered as derivatives of water. One of the hydrogen atoms of water molecule (H-O-H) has been replaced by an alkyl or substituted
for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency of the vibration
 ! = 1 2"c k (m + M) m M wavenumbers! =!/c = 1/" wavelength frequency! units: cm 1 for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency
! = 1 2"c k (m + M) m M wavenumbers! =!/c = 1/" wavelength frequency! units: cm 1 for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency
Module 2 Alcohols, halogenoalkanes and analysis
 UNIT Module 2 Alcohols, halogenoalkanes and analysis 2 Introduction Throughout the centuries, chemists have synthesised new substances and investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials.
UNIT Module 2 Alcohols, halogenoalkanes and analysis 2 Introduction Throughout the centuries, chemists have synthesised new substances and investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials.
 2814 hains, Rings and Spectroscopy June 2003 Mark Scheme 2814 Mark Scheme June 2003 The following annotations may be used when marking: X = incorrect response (errors may also be underlined) ^ = omission
2814 hains, Rings and Spectroscopy June 2003 Mark Scheme 2814 Mark Scheme June 2003 The following annotations may be used when marking: X = incorrect response (errors may also be underlined) ^ = omission
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Molecular Formula Determination
 Molecular Formula Determination Classical Approach Qualitative elemental analysis Quantitative elemental analysis Determination of empirical formula Molecular weight determination Molecular formula determination
Molecular Formula Determination Classical Approach Qualitative elemental analysis Quantitative elemental analysis Determination of empirical formula Molecular weight determination Molecular formula determination
ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4
 ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4 1) Write an equation to describe the initiation step in the chlorination of methane. 2) Reaction intermediates that have unpaired electrons are called. 3) When
ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4 1) Write an equation to describe the initiation step in the chlorination of methane. 2) Reaction intermediates that have unpaired electrons are called. 3) When
a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler units
 Chemical Bonds 1. Which of the following is NOT a true compound? a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
Chemical Bonds 1. Which of the following is NOT a true compound? a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7. Alcohols, Ethers and More
 Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Boston University Dresden Science Program ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CAS CH 203 Lecture
 Boston University Dresden Science Program ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CAS CH 203 Lecture Instructor: Professor Wolf D. Habicher, Professor Claus Rüger Meeting Times Lectures: twice a week at 90 minutes each Discussions:
Boston University Dresden Science Program ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CAS CH 203 Lecture Instructor: Professor Wolf D. Habicher, Professor Claus Rüger Meeting Times Lectures: twice a week at 90 minutes each Discussions:
Suggested solutions for Chapter 3
 s for Chapter PRBLEM Assuming that the molecular ion is the base peak (00% abundance) what peaks would appear in the mass spectrum of each of these molecules: (a) C5Br (b) C60 (c) C64Br In cases (a) and
s for Chapter PRBLEM Assuming that the molecular ion is the base peak (00% abundance) what peaks would appear in the mass spectrum of each of these molecules: (a) C5Br (b) C60 (c) C64Br In cases (a) and
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
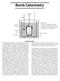 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Lipids. There are 2 types of lipids; those that contain the structural component of a fatty acid; and
 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but not in water. named for the Greek word lipos, which means fat. extracted from cells using
Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but not in water. named for the Greek word lipos, which means fat. extracted from cells using
Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
cyclohexane cyclopentane Nomenclature Follows same rules as for stright-chain alkanes. Examples: name the following
 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-10- 3-16 Study Problems: 3-43, 3-44, 3-45, 3-46 Key oncepts and Skills: ompare the energies of cycloalkanes, and explain ring
Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-10- 3-16 Study Problems: 3-43, 3-44, 3-45, 3-46 Key oncepts and Skills: ompare the energies of cycloalkanes, and explain ring
Name Lab #3: Solubility of Organic Compounds Objectives: Introduction: soluble insoluble partially soluble miscible immiscible
 Lab #3: Solubility of rganic Compounds bjectives: - Understanding the relative solubility of organic compounds in various solvents. - Exploration of the effect of polar groups on a nonpolar hydrocarbon
Lab #3: Solubility of rganic Compounds bjectives: - Understanding the relative solubility of organic compounds in various solvents. - Exploration of the effect of polar groups on a nonpolar hydrocarbon
Predicting Phase Equilibria of Oxygenated Compounds Using Molecular Models Results from the MEMOBIOL Project.
 Renewable energies Eco-friendly production Innovative transport Eco-efficient processes Sustainable resources Predicting Phase Equilibria of Oxygenated Compounds Using Molecular Models Results from the
Renewable energies Eco-friendly production Innovative transport Eco-efficient processes Sustainable resources Predicting Phase Equilibria of Oxygenated Compounds Using Molecular Models Results from the
1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule?
 Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2210, rganic Chem I 1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule? A. sp 3 B. sp 2 C. sp D. not hybridized 2. Name the functional groups in
Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2210, rganic Chem I 1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule? A. sp 3 B. sp 2 C. sp D. not hybridized 2. Name the functional groups in
