Chapter 1: The Science of Rapid Learning
|
|
|
- Sandra Walters
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1: The Science of Rapid Learning Introduction You may have a fear that you aren t cut out for learning science or math. Thinking, I m just not a math person, or I don t have a logical mind I m a creative thinker or even I m just not smart enough. Maybe you haven t been presented these subjects in a way that suits your mind. You can learn these subjects; you just need to work with your mind, not against it. The following sections will teach you how to do that. Optimize Your Learning Mind The Mind is a Meaning Making Machine What does it mean to say, The mind is a meaning making machine.? The primary function of your mind is to take incoming information and attach meaning to it. Sometimes what is presented has no inherent meaning. For instance no one has ever really seen an electron orbital. Yet this is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics. So how is your mind to make meaning out of this concept and others that do not have an inherent or obvious meaning in your life? To find meaning and learn new information it must first be relevant. For instance do you: Like baseball? Play video games? Like music? Follow the political process? If you answered yes to any of these questions, you found something in these topics that made this information relevant. To master any subject especially those that are hard use the mind s quest for relevance to develop meaning. This is done by making these subjects relevant to you. Learning trigonometry is easy when it is relevant: you balance best when you are at 90 o with respect to the floor, at what angle do you topple over? Take Advantage of Patterns In addition to finding relevance, finding patterns in what you are learning also helps creates meaning. In fact, intelligence could simply be described as being able to see and construct patterns from the world around you. Finding patterns is finding a 4
2 relationship between facts or concepts. For example, when learning the amino acids you can group the 20 molecules by non-polar side chains (i.e. glycine CH 3 ), uncharged side chains (i.e. serine CH 2 -OH) and charged (i.e. lysine CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 - CH 2 -NH - 3 ) polar side chains. Use the brains natural tendency to find patterns in any subject you are learning. Emotion is Key in the Learning Process Emotion plays a role in how we learn - if you are anxious about taking a test and haven t eaten or slept, learning the material is made more difficult. However, we also know that being over-relaxed (often as a result of understimulation) can lead to boredom and a lack of motivation. The brain needs a non-threatening environment with enough challenge to evoke an emotional investment in the subject. Use these practical tips to engage your emotions and to evoke an emotional investment: Write out your goals (including why you want to achieve them), stick them by your computer and read them every morning. Journal about what is going on for you emotionally while you are studying. Make time for those things that you know are relaxing, walking the dog, listening to music, exercise. Learning Environment is Vital Craft your environment so that learning is favored eat, sleep, limit the distractions and don t let a little frustration while you are learning get you down; it enhances the whole process. Here are a few tips to enhance your learning environment: Create a study zone away from distractions (library study area, quiet room somewhere). Don t multi-task: turn off your phone and mp3 player or leave them at home or in your car. Lighting, seating and temperature should be comfortable but not overly so. You don t want to become too relaxed. Multi-Modal Learning is Highly Effective Learning is a complex process. Interacting with your environment enhances all aspects of learning. It is a mistake to think that full concentration on the subject 5
3 of interest is what is going to ensure rapid and lasting learning. Countries that require music and art classes have higher overall standardized test scores than countries that do not. Tips to practice incorporating your environment into your study: If you have a hobby, nurture it. Treat it as part of your learning practice not as a reward once you attain a goal. Surround yourself with those things that please and stimulate you, art, music, or your favorite movies. Treat Mind And Body As If They Are Connected Just because the mind and the body seem to be separate from each other, that should not lead you to believe that thinking and movement are independent of each other. Research shows that areas of the brain that are important for movement are also vital for learning. How do you take advantage of that fact? Exercise increases the chemicals in the brain that allow us to respond rapidly to learning challenges. Rapid learning is enhanced by something as simple as exercising 20 min a day. Tips to enhance your actual study time: Make time to incorporate exercise or movement into your daily routine. If you are stuck when trying to learn something new, take 20 min. out to dance or walk or run. Every Brain Registers Information Uniquely Every mind is unique. Accelerate your learning by taking advantage of the unique way in which your mind takes in information. You may have noticed that you learn quite easily if the information is presented to you in a certain format (e.g. outlined before the lecture) and that other formats frustrate and confuse you. You may be the type of person who can learn easily while the teacher is talking and writing on the board, or you might be someone who can t comprehend anything unless you are doodling while someone else is talking. Instead of resisting how you take in information, take advantage of how you learn. 6
4 Example: You are attending a Chemistry laboratory, before the experiment begins the teacher wants to make a couple of points about the experiment. 1). She has written a few notes about the compound you will isolate on the board. 2). She has a model of the compound and is talking about the chemical structure. 3). The instructor has beakers and flasks with the compound at different stages of isolation sitting on the laboratory bench. She demonstrates how to use the ring stand to safely attach the flasks. So what information did everyone in the class absorb? Depending on your learning strengths, different information has been imparted. For the student preferring Kinesthetic learning, the main message imparted was how to physically do the experiment: swish the flasks, attach them to the ring stand and so forth. If you prefer to learn in a Read/Write format, the notes on the board are copied carefully and may be annotated by pictures of the set up. You may, however, have missed the verbal instructions about how to attach the flasks or use the instruments. If your strength is as an Aural learner, her verbal instructions are crystal clear and other aspects such as handouts were missed. The student with a more even balance of modality strengths or preferences (Multimodal) will take a bit of everything that is presented. Depending on their unique combination of learning strengths, a different take home message has been acquired. Each of these four students, if asked to summarize the pre-lab discussion, would undoubtedly come up with a variation on the lecture. When learning strengths and preferences are understood, optimized and utilized, it is easier to compensate for weaker modalities. Once you have determined your learning strengths, you will experience a new level of freedom and power over your ability to learn any subject. The VARK Learning Modalities VARK is an acronym for Visual, Aural, Read/Write and Kinesthetic and used to describe four common learning modalities. VARK is also a method that when applied will help optimize the preferred learning strength of an individual. By knowing, for example, that a person prefers to learn by using pictures, study guides and notes can be created that are heavy in images. This will make learning easier and memory 7
5 or retention of the information better. By learning how to learn anyone can be a good student and you will have the satisfaction of knowing more about your self. Visual Learning 1. Visual learning is characterized by a holistic approach to learning subject as opposed to reducing the subject to its smallest parts and reconstructing. The appearance of the subject its color, texture and design are interesting and drawing comes naturally. 2. Student prefers to learn material as a series of images. 3. Image types include: diagrams, symbols, flow charts and graphs. 4. Text is made more like an image by underlining with different color pens or highlighting. As an example a chemical symbol may be drawn to look like the atom or molecule. 5. Symbols and spaces are used in place of words. 6. Optimal lectures would include gestures and language that is image driven. 7. Textbooks and handouts having concepts displayed as diagrams, pictures and graphs are preferred. If a course text book does not have adequate images look at other books and on the internet for images of the topic. 8
6 8. To prepare for exams, which are usually written, translate materials such as lecture notes, text books and hand outs into diagrams, images, flow charts etc. 9. Practice turning visual clues back into written words for exams. Aural Learning 1. Learners with strong aural abilities prefer hearing something to reading it. 2. Effective learning is enhanced by explaining what they have heard and being asked questions verbally. 3. Lectures are enjoyable experiences. 4. Discussions with other students, teachers and presenters have high impact and learning value. 5. Can remember what is spoken more easily then what is read. 6. Often taking notes of a spoken lecture is secondary to listening so notes may have to be augmented by listening to tape recordings of the lecture or speaking to others. 7. Information mastery is acquired by teaching or speaking about it to others. 9
7 8. Reading your notes out loud, even just to yourself is an excellent method to again hear the material. 9. To answer exam questions it is helpful to imagine that you are talking to the teacher or examiner and verbally giving the answer. Listen to the answer in your mind and write it down. This can be practiced by going over previous exams and practicing listening to your inner voice and writing it down. Read / Write Learning 1. Read / Write learning is characterized by preferring to read about a topic and then to write or take notes. Lectures and pictures are fine but you prefer to read about what you are learning. 2. Schools and colleges mostly require students to demonstrate learning in written form usual emphasizing reading. 3. If you prefer to learn by reading you benefit by: making lists, outlines, and writing definitions. 4. Learning material include: textbooks, dictionaries, and handouts. 10
8 5. Mastery of the material is by writing what has been read. This would include writing definitions, cycles and sequences, changing reactions, augmenting diagrams and pictures with words. 6. To prepare for tests it is useful to rearrange lists and notes into questions, multiple choice and essay and to write the answer. Lists and descriptions written should be rewritten. Words and concepts should be arranged into primary points and hierarchies. Kinesthetic Learning 1. Kinesthetic learners like to experience learning and exams. 2. The preferred method of learning is by doing something. A subject is only meaningful if it feels practical, and relevant. 3. To acquire information and to master it an activity must be done. 4. Hands On Method of learning is beneficial, e.g. performing experiments, building models and test taking. 5. It is helpful to review a subject while exercising, standing, writing, or drawing and role playing. 11
9 Multimodal Learning Most individuals are multimodal learners. That is they do not show an exclusive preference to one learning modality but blend their preferred methods. For example a person who prefers to listen (aural learner) but is also visual may record a lecture and draw pictures or schematics of the topic. The blend may include 2, 3 or all four methods of learning. To maximize your time learning it is useful to use as many as the modalities as possible in the process. For example by listening to a taped lecture and rewriting notes to images, three styles, aural, visual, read/write are incorporated into the activity. This is useful for the multimodal learner. Critical Thinking: How Critical is it Anyway? Critical thinking is a process where a subject is conceptualized. This typically requires the breakdown of the information into its components. The components are then reassembled into a format that is relevant to the student in the preferred modality. There are many advantages to critical thinking. First it removes the need to memorize the material because the topic is understood. Additionally the material can now be applied to different situations. An example of this is an organic synthesis. A student can memorize each step of a synthesis A B C D. Alternatively or by critically analyzing the process identify reactive bonds and 12
10 reaction products and apply this knowledge to the formation of compounds in each step. In science and math critically analysis allows real mastery, allowing the student to make inferences, conclusions and predictions. Strategies in Critical Thinking: Group all the relevant facts together. Break the facts into component parts and draw out implications of each. Verify that each fact is internally consistent and doesn t contradict another fact. Step By Step Process What is the objective of the lesson, method, function? Is the conclusion supported by the facts? Does this make sense? What are the main concepts: theories, laws, principles? What facts are provided? What are the inferences, interpretations, conclusions or solutions? Are there assumptions about the facts I need to know? How would the conclusion change if I am wrong? Cognitive or concept maps are one method of breaking down and grouping information. There are many formats and rarely one right way to create a concept map. A concept, instead, displays a person s unique understanding and interrelations of concepts. In this method the facts are diagramed or charted. Ideas, words, process, etc. are linked or grouped to represent the information. Variations on the mapping of information can be done to fit visual, read/write, aural and kinesthetic learner. Example of a Cognitive Map: Spectroscopy is a technique used in physics, chemistry and biology. Mathematics is used to analyze information. Imagine that you have been presented with a series of lectures on spectroscopy. Using critical thinking how you would breakdown a subject that encompasses so many fields of science and math? Diagram or write out the major components of spectroscopy. Instrumentation: used to acquire data in the laboratory. 13
11 Analysis: equations described in lecture, reading and lab. assignments. Description (image) of what a spectrum actually consists of. Major aspects of spectrums e.g. energy, frequency, radiation etc. Construct a learning tool. This can be a list of equations or theories, a concept map or diagram that reflects what you are trying to systematically learn (critical thinking). Goal Definition & Critical Thinking: refine the diagram or flow chart by asking your self what the goal of that series of lectures on spectroscopy is. Enhance or edit your diagram to incorporate the goal(s), objectives, facts and theories that were presented. Using your critical thinking and learning aid(s) work some problems. See if these aids help in problem solving, does it work? The actual format will depend on you. Perhaps instead of pictures in the above example, a Read/Write learner would have texts and lists of items in each segment. The point is to apply the step of critical thinking to breakdown the topic into logical groupings. 14
VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire
 Student Services Study Skills Student Development and Counselling VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to
Student Services Study Skills Student Development and Counselling VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to
VAK Learning Styles. Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions:
 What is Your Learning Preference? VAK Learning Styles Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions: Some people like to see what you
What is Your Learning Preference? VAK Learning Styles Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions: Some people like to see what you
Learning Styles. The VARK Categories. What is a Learning Style?
 Learning Styles What is a Learning Style? Learning styles focus on how your brain receives information. No one else learns or processes information exactly the way you do! If you discover how you process
Learning Styles What is a Learning Style? Learning styles focus on how your brain receives information. No one else learns or processes information exactly the way you do! If you discover how you process
xxx Lesson 19 how memory works and techniques to improve it, and (2) appreciate the importance of memory skills in education and in his or her life.
 xxx Lesson 19 Memory Skills! Overview: This lesson provides a basic look at how our memory works and how it can be improved by using some simple techniques. Objectives: The objective of this lesson is
xxx Lesson 19 Memory Skills! Overview: This lesson provides a basic look at how our memory works and how it can be improved by using some simple techniques. Objectives: The objective of this lesson is
It is vital that you understand the rationale behind the correct answer(s) as wel as the incorrect answer options.
 Getting the Most out of ATI www.atitesting.com What is ATI? ATI is an online resource that will be used throughout the nursing program to help you learn about nursing practice as well as help prepare you
Getting the Most out of ATI www.atitesting.com What is ATI? ATI is an online resource that will be used throughout the nursing program to help you learn about nursing practice as well as help prepare you
Learning Style Inventory
 Learning Style Inventory To better understand how you prefer to learn and process information, place a check in the appropriate space after each statement below, then use the scoring directions at the
Learning Style Inventory To better understand how you prefer to learn and process information, place a check in the appropriate space after each statement below, then use the scoring directions at the
Pamper yourself. Plan ahead. Remember it s important to eat and sleep well. Don t. Don t revise all the time
 Plan ahead Do Have your own revision timetable start planning well before exams begin. Your teacher should be able to help. Make your books, notes and essays user-friendly. Use headings, highlighting and
Plan ahead Do Have your own revision timetable start planning well before exams begin. Your teacher should be able to help. Make your books, notes and essays user-friendly. Use headings, highlighting and
Communication Process
 Welcome and Introductions Lesson 7 Communication Process Overview: This lesson teaches learners to define the elements of effective communication and its process. It will focus on communication as the
Welcome and Introductions Lesson 7 Communication Process Overview: This lesson teaches learners to define the elements of effective communication and its process. It will focus on communication as the
TYPES OF LEARNERS. Visual Learners. Auditory Learners
 utilize a variety of teaching modalities, such as small group process, lecture, and experiential activities be flexible and meet each learner s needs provide information that will overlap with information
utilize a variety of teaching modalities, such as small group process, lecture, and experiential activities be flexible and meet each learner s needs provide information that will overlap with information
INFORMATION FOR LEARNING: MAKING IT YOUR OWN
 INFORMATION FOR LEARNING: MAKING IT YOUR OWN Active listening: notetaking in lectures DCU Student Learning Resources Office of the Vice-President for Learning Innovation and Registrar 2 INFORMATION FOR
INFORMATION FOR LEARNING: MAKING IT YOUR OWN Active listening: notetaking in lectures DCU Student Learning Resources Office of the Vice-President for Learning Innovation and Registrar 2 INFORMATION FOR
What s Your Learning Style?
 What s Your Learning Style? Different people have different learning styles. Style refers to a student s specific learning preferences and actions. One student may learn more effectively from listening
What s Your Learning Style? Different people have different learning styles. Style refers to a student s specific learning preferences and actions. One student may learn more effectively from listening
LESSON 7: LEARNING MODELS
 LESSON 7: LEARNING MODELS INTRODUCTION mobility motivation persistence sociological Think about your favorite class. Does the teacher lecture? Do you do experiments or go on field trips? Does the teacher
LESSON 7: LEARNING MODELS INTRODUCTION mobility motivation persistence sociological Think about your favorite class. Does the teacher lecture? Do you do experiments or go on field trips? Does the teacher
Learn How to Revise 1
 Learn How to Revise 1 SCHOOL EXAM DATES 2016 END OF YEAR EXAMS FOR YEARS 7-9 BEGIN ON MONDAY 6 TH JUNE THEY WILL TAKE PLACE IN LESSONS DURING THIS WEEK AND IF NECESSARY THE WEEK AFTER. Some subjects are
Learn How to Revise 1 SCHOOL EXAM DATES 2016 END OF YEAR EXAMS FOR YEARS 7-9 BEGIN ON MONDAY 6 TH JUNE THEY WILL TAKE PLACE IN LESSONS DURING THIS WEEK AND IF NECESSARY THE WEEK AFTER. Some subjects are
Reading and Taking Notes on Scholarly Journal Articles
 Reading and Taking Notes on Scholarly Journal Articles Set aside enough time in your schedule to read material thoroughly and repeatedly, until you understand what the author is studying, arguing, or discussing.
Reading and Taking Notes on Scholarly Journal Articles Set aside enough time in your schedule to read material thoroughly and repeatedly, until you understand what the author is studying, arguing, or discussing.
INDEX OF LEARNING STYLES *
 INDEX OF LEARNING STYLES * DIRECTIONS Enter your answers to every question on the ILS scoring sheet. Please choose only one answer for each question. If both a and b seem to apply to you, choose the one
INDEX OF LEARNING STYLES * DIRECTIONS Enter your answers to every question on the ILS scoring sheet. Please choose only one answer for each question. If both a and b seem to apply to you, choose the one
Handouts for teachers
 ASKING QUESTIONS THAT ENCOURAGE INQUIRY- BASED LEARNING How do we ask questions to develop scientific thinking and reasoning? Handouts for teachers Contents 1. Thinking about why we ask questions... 1
ASKING QUESTIONS THAT ENCOURAGE INQUIRY- BASED LEARNING How do we ask questions to develop scientific thinking and reasoning? Handouts for teachers Contents 1. Thinking about why we ask questions... 1
Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave.
 VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to complete the questionnaire before reading the accompanying explanation.)
VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to complete the questionnaire before reading the accompanying explanation.)
What Have I Learned In This Class?
 xxx Lesson 26 Learning Skills Review What Have I Learned In This Class? Overview: The Learning Skills review focuses on what a learner has learned during Learning Skills. More importantly this lesson gives
xxx Lesson 26 Learning Skills Review What Have I Learned In This Class? Overview: The Learning Skills review focuses on what a learner has learned during Learning Skills. More importantly this lesson gives
Online Courses: During the Course
 Online Courses: During the Course Keep up Keeping up is essential to your success in an online course. Without weekly lectures, online courses can easily be put on the back burner. It is critical to stay
Online Courses: During the Course Keep up Keeping up is essential to your success in an online course. Without weekly lectures, online courses can easily be put on the back burner. It is critical to stay
CHIPPEWA STUDY SKILLS. Helpful Hints for Test and. Exam Preparation. Brought to you by Chippewa Resource and Student Success
 CHIPPEWA STUDY SKILLS Helpful Hints for Test and Exam Preparation Brought to you by Chippewa Resource and Student Success The Raider 5 Step Study Method & Other Tidbits Step 1: Organize Your Notebook Your
CHIPPEWA STUDY SKILLS Helpful Hints for Test and Exam Preparation Brought to you by Chippewa Resource and Student Success The Raider 5 Step Study Method & Other Tidbits Step 1: Organize Your Notebook Your
Index. Section 1 - Characteristics of the Successful Online Student... 4. Section 2 Course Navigation... 8. Appendix A Reading Tips...
 Page 1 Index Section 1 - Characteristics of the Successful Online Student... 4 Section 2 Course Navigation... 8 Appendix A Reading Tips... 12 Appendix B Writing Tips... 13 Appendix C Study Tips... 14 Appendix
Page 1 Index Section 1 - Characteristics of the Successful Online Student... 4 Section 2 Course Navigation... 8 Appendix A Reading Tips... 12 Appendix B Writing Tips... 13 Appendix C Study Tips... 14 Appendix
Preparing and Revising for your GCSE Exams
 Preparing and Revising for your GCSE Exams Preparing and Revising for GCSEs Page 2 Contents Introduction 3 Effective Learning and Revision 4 What you need to Revise 5 Revision Notes and Practice 6 Getting
Preparing and Revising for your GCSE Exams Preparing and Revising for GCSEs Page 2 Contents Introduction 3 Effective Learning and Revision 4 What you need to Revise 5 Revision Notes and Practice 6 Getting
Lesson Plan for Note Taking
 Lesson Plan for Note Taking Goals: To prepare students to take pertinent notes form lecture, books and activities. Expose students to different styles of note-taking. Give students an opportunity to practice
Lesson Plan for Note Taking Goals: To prepare students to take pertinent notes form lecture, books and activities. Expose students to different styles of note-taking. Give students an opportunity to practice
Math: Study Skills, Note Taking Skills, And Test Taking Strategies
 Math: Study Skills, Note Taking Skills, And Test Taking Strategies Math Study Skill Active Study vs. Passive Study Be actively involved in managing the learning process, the mathematics and your study
Math: Study Skills, Note Taking Skills, And Test Taking Strategies Math Study Skill Active Study vs. Passive Study Be actively involved in managing the learning process, the mathematics and your study
Language, Learning, and Content Instruction
 CHAPTER 2 Language, Learning, and Content Instruction WHAT DO YOU KNOW WHEN YOU KNOW A LANGUAGE? Have you ever thought about what you know when you know a language? Most people s first reaction is to say,
CHAPTER 2 Language, Learning, and Content Instruction WHAT DO YOU KNOW WHEN YOU KNOW A LANGUAGE? Have you ever thought about what you know when you know a language? Most people s first reaction is to say,
STEP 1: IDENTIFY A BEHAVIOR TO CHANGE
 Establishing Healthy Behaviors Worksheet The Establishing Healthy Behaviors Worksheet is designed to carry you through a series of steps that will guide and assist you in establishing healthy lifestyle
Establishing Healthy Behaviors Worksheet The Establishing Healthy Behaviors Worksheet is designed to carry you through a series of steps that will guide and assist you in establishing healthy lifestyle
An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment
 An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment Dr. David Seiler, Assistant Professor, Department of Adult and Career Education, Valdosta State University,
An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment Dr. David Seiler, Assistant Professor, Department of Adult and Career Education, Valdosta State University,
Pamper yourself. Remember it s important to eat and sleep well. Don t revise all the time
 Plan ahead Do Have your own revision timetable start planning well before exams begin. Your teacher should be able to help. Make your books, notes and essays user-friendly. Use headings, highlighting and
Plan ahead Do Have your own revision timetable start planning well before exams begin. Your teacher should be able to help. Make your books, notes and essays user-friendly. Use headings, highlighting and
Writing learning objectives
 Writing learning objectives This material was excerpted and adapted from the following web site: http://www.utexas.edu/academic/diia/assessment/iar/students/plan/objectives/ What is a learning objective?
Writing learning objectives This material was excerpted and adapted from the following web site: http://www.utexas.edu/academic/diia/assessment/iar/students/plan/objectives/ What is a learning objective?
How to Study Mathematics Written by Paul Dawkins
 How to Study Mathematics Written by Paul Dawkins Before I get into the tips for how to study math let me first say that everyone studies differently and there is no one right way to study for a math class.
How to Study Mathematics Written by Paul Dawkins Before I get into the tips for how to study math let me first say that everyone studies differently and there is no one right way to study for a math class.
V.A.R.K. LEARNING STYLES TEST
 V.A.R.K. LEARNING STYLES TEST This test is to find out something about your preferred learning method. Choose the answer that best explains your preference and circle the letter (V, A,R or K). 1. You are
V.A.R.K. LEARNING STYLES TEST This test is to find out something about your preferred learning method. Choose the answer that best explains your preference and circle the letter (V, A,R or K). 1. You are
Section 15 Revision Techniques
 Section 15 Revision Techniques Introduction This section in your Study Skills manual will consolidate information relating to revision techniques. This section will consider how to prepare for examinations
Section 15 Revision Techniques Introduction This section in your Study Skills manual will consolidate information relating to revision techniques. This section will consider how to prepare for examinations
1. Adult behavior can be changed to some extent. 2. Adult education should be designed to help people mature and grow.
 Handout 1: A Philosophy for Adult Education * Adapted from Bergevin, P. (1967). A Philosophy for Adult Education. New York: The Seabury Press, pp. 3-5.* It is important to preserve the uniqueness of individuals
Handout 1: A Philosophy for Adult Education * Adapted from Bergevin, P. (1967). A Philosophy for Adult Education. New York: The Seabury Press, pp. 3-5.* It is important to preserve the uniqueness of individuals
IMPROVE YOUR LEARNING SKILLS
 IMPROVE YOUR LEARNING SKILLS Riitta Aikkola Vaasa University of Applied Sciences 1 IMPROVE YOUR LEARNING SKILLS Learning is a skill and it can be improved. Everyone has the opportunity to develop their
IMPROVE YOUR LEARNING SKILLS Riitta Aikkola Vaasa University of Applied Sciences 1 IMPROVE YOUR LEARNING SKILLS Learning is a skill and it can be improved. Everyone has the opportunity to develop their
PIANOWEB.com ( 800 ) 327-4266
 Mission Statement: Jazz Piano Lessons To Teach, in their home, on their own piano/keyboard, anywhere in the world, students how to play jazz piano, through a Non Traditional approach which emphasizes Musical
Mission Statement: Jazz Piano Lessons To Teach, in their home, on their own piano/keyboard, anywhere in the world, students how to play jazz piano, through a Non Traditional approach which emphasizes Musical
Thinking Skills. Lesson Plan. Introduction
 xxx Lesson 18 Thinking Skills Overview: This lesson provides basic foundational information about two types of thinking skills: critical and creative. Students have used critical and creative skills each
xxx Lesson 18 Thinking Skills Overview: This lesson provides basic foundational information about two types of thinking skills: critical and creative. Students have used critical and creative skills each
This Is. My Teen s Notebook
 This Is My Teen s Notebook 1 I know it s here somewhere! 2 Practical Personal Portable 3 Recipe for a Simple System 5-6 Dividers 1 Notebook (3 ring binder) File Clipart goes here! I.E.P (Individual Education
This Is My Teen s Notebook 1 I know it s here somewhere! 2 Practical Personal Portable 3 Recipe for a Simple System 5-6 Dividers 1 Notebook (3 ring binder) File Clipart goes here! I.E.P (Individual Education
Developing Critical Thinking Skills Saundra Yancy McGuire. Slide 1 TutorLingo On Demand Tutor Training Videos
 Developing Critical Thinking Skills Saundra Yancy McGuire Slide 1 TutorLingo On Demand Tutor Training Videos To view Closed Captioning, click on the Notes tab to the left. For screen reader accessible
Developing Critical Thinking Skills Saundra Yancy McGuire Slide 1 TutorLingo On Demand Tutor Training Videos To view Closed Captioning, click on the Notes tab to the left. For screen reader accessible
COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY IN TEACHING READING
 Лю Пэн COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY IN TEACHING READING Effective Elementary Reading Program Effective approach must contain the following five components: 1. Phonemic awareness instruction to help children learn
Лю Пэн COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY IN TEACHING READING Effective Elementary Reading Program Effective approach must contain the following five components: 1. Phonemic awareness instruction to help children learn
Study Strategies Used By Successful Students
 Study Strategies Used By Successful Students Test performance not only reflects how much one studied in the hours and days right before the test but also how well the person has been studying throughout
Study Strategies Used By Successful Students Test performance not only reflects how much one studied in the hours and days right before the test but also how well the person has been studying throughout
Mental Health Role Plays
 Mental Health Role Plays Goals: To discuss various mental health issues and mental illnesses. To discuss stigma, support and treatment options surrounding mental health issues and mental illnesses. Requirements:
Mental Health Role Plays Goals: To discuss various mental health issues and mental illnesses. To discuss stigma, support and treatment options surrounding mental health issues and mental illnesses. Requirements:
To download the script for the listening go to: http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/sites/teacheng/files/learning-stylesaudioscript.
 Learning styles Topic: Idioms Aims: - To apply listening skills to an audio extract of non-native speakers - To raise awareness of personal learning styles - To provide concrete learning aids to enable
Learning styles Topic: Idioms Aims: - To apply listening skills to an audio extract of non-native speakers - To raise awareness of personal learning styles - To provide concrete learning aids to enable
SI Coordinator Handbook. Information, Resources and Forms
 SI Coordinator Handbook Information, Resources and Forms Updated November 2010 1 2 Table of Contents SI Coordinator Job Description... 5 Observations and Evaluations... 9 Initial Contacts... 10 Informal
SI Coordinator Handbook Information, Resources and Forms Updated November 2010 1 2 Table of Contents SI Coordinator Job Description... 5 Observations and Evaluations... 9 Initial Contacts... 10 Informal
A Step By Step Guide On How To Attract Your Dream Life Now
 A Step By Step Guide On How To Attract Your Dream Life Now This guide is about doing things in a step by step fashion every day to get the results you truly desire. There are some techniques and methods
A Step By Step Guide On How To Attract Your Dream Life Now This guide is about doing things in a step by step fashion every day to get the results you truly desire. There are some techniques and methods
Planning and preparing presentations Giving presentations Features of a good presentation Poster presentations
 Presentations What is a presentation? Planning and preparing presentations Giving presentations Features of a good presentation Poster presentations For further information and the full range of study
Presentations What is a presentation? Planning and preparing presentations Giving presentations Features of a good presentation Poster presentations For further information and the full range of study
Arkansas State PIRC/ Center for Effective Parenting
 Increasing Your Child s Motivation to Learn In order to be successful in school and to learn, students must stay involved in the learning process. This requires students to do many different activities
Increasing Your Child s Motivation to Learn In order to be successful in school and to learn, students must stay involved in the learning process. This requires students to do many different activities
Modifying Curriculum and Instruction
 Modifying Curriculum and Instruction Purpose of Modification: The purpose of modification is to enable an individual to compensate for intellectual, behavioral, or physical disabi1ities. Modifications
Modifying Curriculum and Instruction Purpose of Modification: The purpose of modification is to enable an individual to compensate for intellectual, behavioral, or physical disabi1ities. Modifications
SUGGESTIONS FOR WORKING WITH STUDENTS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS (ASD) Provided for Information and sharing only
 SUGGESTIONS FOR WORKING WITH STUDENTS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS (ASD) Provided for Information and sharing only 1. I have attached an informational handout about autism spectrum disorders and the
SUGGESTIONS FOR WORKING WITH STUDENTS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS (ASD) Provided for Information and sharing only 1. I have attached an informational handout about autism spectrum disorders and the
-----------------------------2008 Farmer Mentor Handbook----------------------------- Adult Learning Styles. Adult Learning Styles
 Learning Styles Primer for Farmer Mentors You are now considering the possibility of mentoring a future farmer; taking an intern under your wing; and inviting someone to come to your farm to observe, listen
Learning Styles Primer for Farmer Mentors You are now considering the possibility of mentoring a future farmer; taking an intern under your wing; and inviting someone to come to your farm to observe, listen
Difficult Tutoring Situations
 Difficult Tutoring Situations At some time or other, all tutors will find themselves faced with difficult situations in a tutoring session. The following information will provide you with some common categories
Difficult Tutoring Situations At some time or other, all tutors will find themselves faced with difficult situations in a tutoring session. The following information will provide you with some common categories
New Faculty Orientation 2012 CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT & LEARNING STYLES
 New Faculty Orientation 2012 CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT & LEARNING STYLES LEARNING AND TEACHING This student-centered perspective is a hallmark of the CSUDH approach to teaching. We strive to empower instructors
New Faculty Orientation 2012 CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT & LEARNING STYLES LEARNING AND TEACHING This student-centered perspective is a hallmark of the CSUDH approach to teaching. We strive to empower instructors
Classroom Behavior Management Plan
 Haffner 1 Classroom Behavior Management Plan Daniel Haffner November 20, 2009 EDUC 348 Haffner 2 Philosophy of Classroom Management Classroom management is a course taught at every teacher college across
Haffner 1 Classroom Behavior Management Plan Daniel Haffner November 20, 2009 EDUC 348 Haffner 2 Philosophy of Classroom Management Classroom management is a course taught at every teacher college across
STEP 5: Giving Feedback
 STEP 5: Giving Feedback Introduction You are now aware of the responsibilities of workplace mentoring, the six step approach to teaching skills, the importance of identifying the point of the lesson, and
STEP 5: Giving Feedback Introduction You are now aware of the responsibilities of workplace mentoring, the six step approach to teaching skills, the importance of identifying the point of the lesson, and
Supplemental Activity
 Materials: Test-Taking Skills Assessment on page 80 in this workbook (page 19 in the student workbook) Test-Taking Tips on page 81 in this workbook (page 20 in the student workbook) Tactics for Studying
Materials: Test-Taking Skills Assessment on page 80 in this workbook (page 19 in the student workbook) Test-Taking Tips on page 81 in this workbook (page 20 in the student workbook) Tactics for Studying
F O C U S Challenge? Reaction? Insight? Action Chapter Seven Engaging, Listening, and Note Taking in Class
 F O C U S Challenge? Reaction? Insight? Action Chapter Seven Engaging, Listening, and Note Taking in Class Reading Assignments Chapter 7, pages 151-174 PowerPoint Presentations Chapter 7 FOCUS on Community
F O C U S Challenge? Reaction? Insight? Action Chapter Seven Engaging, Listening, and Note Taking in Class Reading Assignments Chapter 7, pages 151-174 PowerPoint Presentations Chapter 7 FOCUS on Community
Active Learning Strategies ORCHESTRATING LEARNER PARTICIPATION IN EDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES
 Active Learning Strategies ORCHESTRATING LEARNER PARTICIPATION IN EDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES The overall goal of this presentation is to provide faculty with information and strategies to enhance learner participation
Active Learning Strategies ORCHESTRATING LEARNER PARTICIPATION IN EDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES The overall goal of this presentation is to provide faculty with information and strategies to enhance learner participation
P-4: Differentiate your plans to fit your students
 What Makes a Differentiated Classroom Different From a Traditional Classroom? In the chart below, you ll notice the ways in which a differentiated classroom differs from a traditional classroom. You may
What Makes a Differentiated Classroom Different From a Traditional Classroom? In the chart below, you ll notice the ways in which a differentiated classroom differs from a traditional classroom. You may
GMAT SYLLABI. Types of Assignments - 1 -
 GMAT SYLLABI The syllabi on the following pages list the math and verbal assignments for each class. Your homework assignments depend on your current math and verbal scores. Be sure to read How to Use
GMAT SYLLABI The syllabi on the following pages list the math and verbal assignments for each class. Your homework assignments depend on your current math and verbal scores. Be sure to read How to Use
HOW DOES EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPACT YOUR GIFTED AND/OR TWICE EXCEPTIONAL CHILD?
 HOW DOES EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPACT YOUR GIFTED AND/OR TWICE EXCEPTIONAL CHILD? Results Learning Presented by Cyle A. Feingold Founder and Director Results Learning, LLC AGENDA Overview of Executive Function
HOW DOES EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPACT YOUR GIFTED AND/OR TWICE EXCEPTIONAL CHILD? Results Learning Presented by Cyle A. Feingold Founder and Director Results Learning, LLC AGENDA Overview of Executive Function
Exam Preparation and Memory Strategies
 Counselling & Learning Support North Vancouver Campus Student Success Workshops Exam Preparation and Memory Strategies BR 267 604.984.1744 www.capilanou.ca/services Prepared by: Alison Parry, Learning
Counselling & Learning Support North Vancouver Campus Student Success Workshops Exam Preparation and Memory Strategies BR 267 604.984.1744 www.capilanou.ca/services Prepared by: Alison Parry, Learning
STUDENT SUPPORT SERVICES PRESENTS SCHEDULING TIME FOR STUDY
 STUDENT SUPPORT SERVICES PRESENTS SCHEDULING TIME FOR STUDY 1. PLAN ENOUGH TIME FOR STUDY. A college expects a student to average about two hours in studying (including library work, term papers, themes,
STUDENT SUPPORT SERVICES PRESENTS SCHEDULING TIME FOR STUDY 1. PLAN ENOUGH TIME FOR STUDY. A college expects a student to average about two hours in studying (including library work, term papers, themes,
Force and Motion: Ramp It Up
 Force and Motion: Grade Level: 4-5 Time: 3 class periods By: Carrie D. Perry (Bedford County Public Schools) Overview After watching an engaging video on Olympic alpine skiers, students then participate
Force and Motion: Grade Level: 4-5 Time: 3 class periods By: Carrie D. Perry (Bedford County Public Schools) Overview After watching an engaging video on Olympic alpine skiers, students then participate
Facilitating Adult Learning
 Facilitating Adult Learning How to Teach so People Learn Prepared by: Dr. Lela Vandenberg Senior Leadership & Professional Development Specialist 11 Agriculture Hall East Lansing, MI 48824-1039 (517) 353-1898
Facilitating Adult Learning How to Teach so People Learn Prepared by: Dr. Lela Vandenberg Senior Leadership & Professional Development Specialist 11 Agriculture Hall East Lansing, MI 48824-1039 (517) 353-1898
MATHEMATICS: REPEATING AND GROWING PATTERNS First Grade. Kelsey McMahan. Winter 2012 Creative Learning Experiences
 MATHEMATICS: REPEATING AND GROWING PATTERNS Kelsey McMahan Winter 2012 Creative Learning Experiences Without the arts, education is ineffective. Students learn more and remember it longer when they are
MATHEMATICS: REPEATING AND GROWING PATTERNS Kelsey McMahan Winter 2012 Creative Learning Experiences Without the arts, education is ineffective. Students learn more and remember it longer when they are
Decomposing Numbers (Operations and Algebraic Thinking)
 Decomposing Numbers (Operations and Algebraic Thinking) Kindergarten Formative Assessment Lesson Designed and revised by Kentucky Department of Education Mathematics Specialists Field-tested by Kentucky
Decomposing Numbers (Operations and Algebraic Thinking) Kindergarten Formative Assessment Lesson Designed and revised by Kentucky Department of Education Mathematics Specialists Field-tested by Kentucky
GED Language Arts, Writing Lesson 1: Noun Overview Worksheet
 CLN Televised Courses Nina Beegle, Instructor Lesson 1: Noun Overview Worksheet NOUNS: DEFINITION A NOUN can be a person, a place, a thing, or an idea. EXAMPLES: man, children, store, a dream There are
CLN Televised Courses Nina Beegle, Instructor Lesson 1: Noun Overview Worksheet NOUNS: DEFINITION A NOUN can be a person, a place, a thing, or an idea. EXAMPLES: man, children, store, a dream There are
TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed)
 TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed) Table 1 Major categories in the cognitive domain of the taxonomy of educational objectives
TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed) Table 1 Major categories in the cognitive domain of the taxonomy of educational objectives
Time management, study plans, and exams
 Time management, study plans, and exams The best strategy for avoiding stress and anxiety about homework, assignments and exams is an effective and consistent study plan teamed with good time management.
Time management, study plans, and exams The best strategy for avoiding stress and anxiety about homework, assignments and exams is an effective and consistent study plan teamed with good time management.
Learning Styles and the Writing Process
 Learning Styles and the Writing Process Gathering Information Look at Model Papers Both student writing and professional papers will give you useful ideas about structure and organization. List Important
Learning Styles and the Writing Process Gathering Information Look at Model Papers Both student writing and professional papers will give you useful ideas about structure and organization. List Important
INTRODUCTION TO COACHING TEACHING SKILLS TEACHING/LEARNING. September 2007 Page 1
 TEACHING SKILLS September 2007 Page 1 TEACHING SKILLS Being a teacher is one of the main roles a coach fulfils for their players. The ability to teach effectively, especially the technical skills of ice
TEACHING SKILLS September 2007 Page 1 TEACHING SKILLS Being a teacher is one of the main roles a coach fulfils for their players. The ability to teach effectively, especially the technical skills of ice
As tutors, we are responsible for improving the skills of our peers.
 Tutor s Creed As tutors, we are responsible for improving the skills of our peers. As tutors, we will consider the body of work presented at the session in the following manner: First, we will impart to
Tutor s Creed As tutors, we are responsible for improving the skills of our peers. As tutors, we will consider the body of work presented at the session in the following manner: First, we will impart to
Metacognition. Complete the Metacognitive Awareness Inventory for a quick assessment to:
 Metacognition Metacognition is essential to successful learning because it enables individuals to better manage their cognitive skills and to determine weaknesses that can be corrected by constructing
Metacognition Metacognition is essential to successful learning because it enables individuals to better manage their cognitive skills and to determine weaknesses that can be corrected by constructing
Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
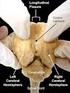 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 12, December-2011 1 Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 12, December-2011 1 Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
How Can Teachers Teach Listening?
 3 How Can Teachers Teach Listening? The research findings discussed in the previous chapter have several important implications for teachers. Although many aspects of the traditional listening classroom
3 How Can Teachers Teach Listening? The research findings discussed in the previous chapter have several important implications for teachers. Although many aspects of the traditional listening classroom
Practical Study Tips
 Please read and inform student-athletes about this information Practical Study Tips Set Goals Setting goals helps you decide what is important, gives you a plan for success, and keeps you focused. Setting
Please read and inform student-athletes about this information Practical Study Tips Set Goals Setting goals helps you decide what is important, gives you a plan for success, and keeps you focused. Setting
100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success. Some Great Tips To Boost Your Sales
 100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success Some Great Tips To Boost Your Sales 100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success By Sean Mcpheat, Managing Director Of The Sales Training Consultancy What makes a successful
100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success Some Great Tips To Boost Your Sales 100 Ways To Improve Your Sales Success By Sean Mcpheat, Managing Director Of The Sales Training Consultancy What makes a successful
2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment).
 2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment). Criteria Oral Presentation- Group project Poster Presentation display/ visual aids 1 - Attempts the standard use the
2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment). Criteria Oral Presentation- Group project Poster Presentation display/ visual aids 1 - Attempts the standard use the
NETWORKING GUIDE CONTRIBUTOR: CAREERS SERVICE, ANNA PERSSON
 NETWORKING GUIDE CONTRIBUTOR: CAREERS SERVICE, ANNA PERSSON NETWORK YOUR WAY TO A JOB Networking is an important part of any job search. It s the process of establishing contacts for the purpose of gathering
NETWORKING GUIDE CONTRIBUTOR: CAREERS SERVICE, ANNA PERSSON NETWORK YOUR WAY TO A JOB Networking is an important part of any job search. It s the process of establishing contacts for the purpose of gathering
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI)
 Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
How To Teach A Class
 Scientists Teaching Science Barbara Houtz January 13, 2014 Instructional Design The systematic design of materials, activities, and interactive environments for learning. Broadly informed by educational
Scientists Teaching Science Barbara Houtz January 13, 2014 Instructional Design The systematic design of materials, activities, and interactive environments for learning. Broadly informed by educational
When I think about using an advanced scientific or graphing calculator, I feel:
 Slide 2.11, 2.14 & 3.2 MATH HISTORY QUESTION EXERCISE ONE My last math course was (course, year, and school): I would say that my experience in that course was: A math course I especially remember was:
Slide 2.11, 2.14 & 3.2 MATH HISTORY QUESTION EXERCISE ONE My last math course was (course, year, and school): I would say that my experience in that course was: A math course I especially remember was:
Get Ready for IELTS Writing. About Get Ready for IELTS Writing. Part 1: Language development. Part 2: Skills development. Part 3: Exam practice
 About Collins Get Ready for IELTS series has been designed to help learners at a pre-intermediate level (equivalent to band 3 or 4) to acquire the skills they need to achieve a higher score. It is easy
About Collins Get Ready for IELTS series has been designed to help learners at a pre-intermediate level (equivalent to band 3 or 4) to acquire the skills they need to achieve a higher score. It is easy
Stress management for presentations and interviews
 Learning Development Stress management for presentations and interviews This guide aims to help you recognise and understand anxiety and nervousness which may arise during presentations or interviews.
Learning Development Stress management for presentations and interviews This guide aims to help you recognise and understand anxiety and nervousness which may arise during presentations or interviews.
California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3
 California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3 Words were selected using the following established frequency lists: (1) Dolch 220 (2) Fry 100 (3) American Heritage Top 150 Words in English
California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3 Words were selected using the following established frequency lists: (1) Dolch 220 (2) Fry 100 (3) American Heritage Top 150 Words in English
ADD/ADHD in the Classroom
 ADD/ADHD in the Classroom TIPS FOR TEACHERS AND PARENTS At any given time, a teacher can expect to have at least one student with ADHD. The impulsive and hyperactive behavior of such students can be distracting
ADD/ADHD in the Classroom TIPS FOR TEACHERS AND PARENTS At any given time, a teacher can expect to have at least one student with ADHD. The impulsive and hyperactive behavior of such students can be distracting
Days. Day 1. Reflection Teacher Responsibilities. Lesson Plans
 Days Day 1 Lesson Plans Call the students to the carpet by the number of letters in their names. If your name has less than 5 letters, come to the carpet. If your name has more than 5 letters, come to
Days Day 1 Lesson Plans Call the students to the carpet by the number of letters in their names. If your name has less than 5 letters, come to the carpet. If your name has more than 5 letters, come to
How to teach listening 2012
 How to teach listening skills "Great speakers are not born, they re trained." - Dale Carnegie (1921) Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) To enhance deeper understanding of the process of listening as a communicative
How to teach listening skills "Great speakers are not born, they re trained." - Dale Carnegie (1921) Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) To enhance deeper understanding of the process of listening as a communicative
Social Return on Investment
 Social Return on Investment Valuing what you do Guidance on understanding and completing the Social Return on Investment toolkit for your organisation 60838 SROI v2.indd 1 07/03/2013 16:50 60838 SROI v2.indd
Social Return on Investment Valuing what you do Guidance on understanding and completing the Social Return on Investment toolkit for your organisation 60838 SROI v2.indd 1 07/03/2013 16:50 60838 SROI v2.indd
NOTE-TAKING. Rutgers School of Nursing
 NOTE-TAKING Rutgers School of Nursing WHEN TO TAKE NOTES BEFORE DURING AFTER I. Before Class: Preparation (mental and physical) Read Textbook BEFORE Class Start Taking Notes BEFORE Class The SQ3R Method
NOTE-TAKING Rutgers School of Nursing WHEN TO TAKE NOTES BEFORE DURING AFTER I. Before Class: Preparation (mental and physical) Read Textbook BEFORE Class Start Taking Notes BEFORE Class The SQ3R Method
Chapter 3. Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions This chapter uses the concepts of conservation of mass to assist the student in gaining an understanding of chemical changes. Upon completion of Chapter
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions This chapter uses the concepts of conservation of mass to assist the student in gaining an understanding of chemical changes. Upon completion of Chapter
ORIENTATIONS INVENTORY
 ORIENTATIONS INVENTORY Instructions for questions (1-18 and 20-26): Place a check mark in the blank next to the statement that is more true for you or true most of the time. 1. When planning the activities
ORIENTATIONS INVENTORY Instructions for questions (1-18 and 20-26): Place a check mark in the blank next to the statement that is more true for you or true most of the time. 1. When planning the activities
Mindset: The New Psychology of Success Carol S. Dweck, Ph.D.
 Mindset: The New Psychology of Success Carol S. Dweck, Ph.D. Chapter 1: The Mindsets Chapter 1 presents the two different mindsets fixed and growth. Ms. Dweck reveals that she came upon the idea of researching
Mindset: The New Psychology of Success Carol S. Dweck, Ph.D. Chapter 1: The Mindsets Chapter 1 presents the two different mindsets fixed and growth. Ms. Dweck reveals that she came upon the idea of researching
FIREFIGHTER APPLICANT APTITUDE TEST OVERVIEW
 FIRE DEPARTMENT RECRUITMENT SECTION PAGE 1 FIREFIGHTER APPLICANT APTITUDE TEST OVERVIEW The following four categories have been provided to help you identify the types of questions that are asked on the
FIRE DEPARTMENT RECRUITMENT SECTION PAGE 1 FIREFIGHTER APPLICANT APTITUDE TEST OVERVIEW The following four categories have been provided to help you identify the types of questions that are asked on the
SUPPORTING STUDENTS WITH WORKING MEMORY DIFFICULTIES
 SUPPORTING STUDENTS WITH WORKING MEMORY DIFFICULTIES No matter how motivated you are, it is hard to learn and retrieve key knowledge and skills if you can only hold on to a limited amount of information
SUPPORTING STUDENTS WITH WORKING MEMORY DIFFICULTIES No matter how motivated you are, it is hard to learn and retrieve key knowledge and skills if you can only hold on to a limited amount of information
Module Five Critical Thinking
 Module Five Critical Thinking Introduction Critical thinking is often perceived as a difficult skill separate from the thinking process as a whole. In fact, it is the essence of thinking. It is not enough
Module Five Critical Thinking Introduction Critical thinking is often perceived as a difficult skill separate from the thinking process as a whole. In fact, it is the essence of thinking. It is not enough
Fun for all the Family 3- Quite a few games for articles and determiners
 Fun for all the Family 3- Quite a few games for articles and determiners Articles in English is one of those grammar points that are fairly easy to explain the fundamentals of, but even Advanced learners
Fun for all the Family 3- Quite a few games for articles and determiners Articles in English is one of those grammar points that are fairly easy to explain the fundamentals of, but even Advanced learners
Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss. A Guide to Services for Students with a
 Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss A Guide to Services for Students with a Learning Disability (Revised 4.28.14) Do I Have A Learning
Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss A Guide to Services for Students with a Learning Disability (Revised 4.28.14) Do I Have A Learning
