From Addr To Addr. Hdr len. Service class. Packet Length Fragment Number. Destination Port. Error Check. Source Port
|
|
|
- Stephanie George
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4 4 IP version Recall the TCP packet format... Hdr len TCP packet Packet Number Service class Packet Length Fragment Number TTL Protocol Error Check Source Port From Addr To Addr Sequence Number Acknowledgement Number Destination Port Hdr Len Flags Receiver Window Error Check 8 DATA 16 Urgent Pointer
2 Sequence and Acknowledgment Numbers Seg. # 1 Seg. # 1 Ack. # 1 Ack. # 1 Seg. # 1 Seg. # 2 Ack. # 1 Ack. # 2 Loss Case No Loss Case and the basic idea of using acknowledgment and retransmissions to ensure reliable delivery.
3 Maintaining Transmission Efficiency Ack 8 Ack Since they knew segments would overlap on the wire, the designers of TCP did something tricky. Acknowledgments are cumulative. Whenever a packet arrives, the receiver sends an acknowledgment containing the number of the last packet (actally byte) that was received in order. That is, if the sender sees 2, it knows that segments 1-12 all got through Ok.
4 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
5 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
6 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
7 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
8 0 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
9 0 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
10 0 1 2 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
11 0 1 2 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
12 This means that if one packet of a sequence gets lost in transit, the receiver will respond to each packet that arrives after the lost packet by acknowledging the last message received before the loss. It also means that the sender may not receive an acknowledgment for every packet sent. When a lost packet is retransmitted, completing a sequence of packets, the receiver can acknowledge the receipt of the entire sequence by sending an acknowledgment for the last packet.
13 0 1 2 Ack 8 Ack Cumulative acknowledgments also makes it unnecessary to retransmit lost acknowledgments in some cases. As long as the acknowledgment that is lost is not for the last packet in a sequence, the cummulative acknowledgment sent for a later packet will assure the sender that the earlier packet was received.
14 Slow Segments == Confused Conversations GET /index.html 1 Retransmission of GET /index.html 1 Contents of index.html 1 Contents of index.html 1 GET /main.html 1 If every conversation numbers packets starting with #1, it would be easy for packets from two different connections to become confused. On the other hand, if every connection started with a random sequence number, how would one know that there had not been an earlier packet that was missed?
15 In an ongoing TCP connection, one cannot really distinguish the sender from the receiver. Both sides are allowed to send and receive data. Both side need to associate sequence numbers with the packets they send so that the other side can send appropriate acknowledgments. Therefore, both sides pick a random inital sequence number, both sides send this number in a special packet called a SYN, and both sides send acknowledments of the receipt The Connection Start 3-Way Handshake SYN (seq # = x) Ack y+1 Ack x+1 & SYN (seq # = y) GET /index.html x+1 Ack x+2 Contents of index.html (seq = y+1) To avoid having packets from two different connections look the same (i.e., have the same sequence numbers), choose initial sequence numbers RANDOMLY and send special start conversation segments to tell the other side of the choice.
16 TCP Segment Format Source Port Destination Port Sequence (Segment) Number Acknowledgment Number Hdr Len Flags Receiver window Error Check Urgent Pointer DATA The Flags field of the TCP packet is used to distinguish special packets like the starting SYN packets.
17 Flags (nothing) SYN FIN ACK RESET Here s some data Connect Disconnect I got segment # I m confused and want to hang up URG By the way,... PUSH Send data now The Flags field is also used to indicate a) whether a packet contains an acknowledgment (they almost all do), b) whether the sender would like to terminate the connection normally (FIN), c) whether the sender would like to terminate the connection abnormally (RESET).
18 FIN (seq # = z) Connection Termination Ack z=1 & FIN (seq # = W) Ack W+1 Closing is complicated because both sides are allowed to send data. Closing one side means that that side has nothing more to send...but there might still be more data to receive! Therefore, each side has to send its own FIN packet (and acknowledge receipt of a FIN from the other side). Let s use TCPCapture to actually see what happens at the application level and at the TCP level when two programs try to communicate using HTTP
Computer Networks. Chapter 5 Transport Protocols
 Computer Networks Chapter 5 Transport Protocols Transport Protocol Provides end-to-end transport Hides the network details Transport protocol or service (TS) offers: Different types of services QoS Data
Computer Networks Chapter 5 Transport Protocols Transport Protocol Provides end-to-end transport Hides the network details Transport protocol or service (TS) offers: Different types of services QoS Data
Transport Layer Protocols
 Transport Layer Protocols Version. Transport layer performs two main tasks for the application layer by using the network layer. It provides end to end communication between two applications, and implements
Transport Layer Protocols Version. Transport layer performs two main tasks for the application layer by using the network layer. It provides end to end communication between two applications, and implements
Computer Networks UDP and TCP
 Computer Networks UDP and TCP Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York I m a system programmer specializing in TCP/IP communication protocol on UNIX systems. How can I explain a thing
Computer Networks UDP and TCP Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York I m a system programmer specializing in TCP/IP communication protocol on UNIX systems. How can I explain a thing
Transport Layer. Chapter 3.4. Think about
 Chapter 3.4 La 4 Transport La 1 Think about 2 How do MAC addresses differ from that of the network la? What is flat and what is hierarchical addressing? Who defines the IP Address of a device? What is
Chapter 3.4 La 4 Transport La 1 Think about 2 How do MAC addresses differ from that of the network la? What is flat and what is hierarchical addressing? Who defines the IP Address of a device? What is
COMP 3331/9331: Computer Networks and Applications. Lab Exercise 3: TCP and UDP (Solutions)
 COMP 3331/9331: Computer Networks and Applications Lab Exercise 3: TCP and UDP (Solutions) AIM To investigate the behaviour of TCP and UDP in greater detail. EXPERIMENT 1: Understanding TCP Basics Tools
COMP 3331/9331: Computer Networks and Applications Lab Exercise 3: TCP and UDP (Solutions) AIM To investigate the behaviour of TCP and UDP in greater detail. EXPERIMENT 1: Understanding TCP Basics Tools
Visualizations and Correlations in Troubleshooting
 Visualizations and Correlations in Troubleshooting Kevin Burns Comcast kevin_burns@cable.comcast.com 1 Comcast Technology Groups Cable CMTS, Modem, Edge Services Backbone Transport, Routing Converged Regional
Visualizations and Correlations in Troubleshooting Kevin Burns Comcast kevin_burns@cable.comcast.com 1 Comcast Technology Groups Cable CMTS, Modem, Edge Services Backbone Transport, Routing Converged Regional
IP Network Layer. Datagram ID FLAG Fragment Offset. IP Datagrams. IP Addresses. IP Addresses. CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP
 CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming TCP/IP IP Network Layer Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina IP Datagrams IP is the network layer packet delivery
Solution of Exercise Sheet 5
 Foundations of Cybersecurity (Winter 15/16) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes CISPA / Saarland University saarland university computer science Protocols = {????} Client Server IP Address =???? IP Address =????
Foundations of Cybersecurity (Winter 15/16) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes CISPA / Saarland University saarland university computer science Protocols = {????} Client Server IP Address =???? IP Address =????
[Prof. Rupesh G Vaishnav] Page 1
![[Prof. Rupesh G Vaishnav] Page 1 [Prof. Rupesh G Vaishnav] Page 1](/thumbs/26/7709048.jpg) Basics The function of transport layer is to provide a reliable end-to-end communications service. It also provides data transfer service for the user layers above and shield the upper layers from the
Basics The function of transport layer is to provide a reliable end-to-end communications service. It also provides data transfer service for the user layers above and shield the upper layers from the
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio).
 Client App Network Server App 25-May-13 15:32 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio). TCP is an end to end protocol which
Client App Network Server App 25-May-13 15:32 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio). TCP is an end to end protocol which
ICOM 5026-090: Computer Networks Chapter 6: The Transport Layer. By Dr Yi Qian Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering Fall 2006 UPRM
 ICOM 5026-090: Computer Networks Chapter 6: The Transport Layer By Dr Yi Qian Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering Fall 2006 Outline The transport service Elements of transport protocols A
ICOM 5026-090: Computer Networks Chapter 6: The Transport Layer By Dr Yi Qian Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering Fall 2006 Outline The transport service Elements of transport protocols A
Chapter 5. Transport layer protocols
 Chapter 5. Transport layer protocols This chapter provides an overview of the most important and common protocols of the TCP/IP transport layer. These include: User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Transmission
Chapter 5. Transport layer protocols This chapter provides an overview of the most important and common protocols of the TCP/IP transport layer. These include: User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Transmission
B-2 Analyzing TCP/IP Networks with Wireshark. Ray Tompkins Founder of Gearbit www.gearbit.com
 B-2 Analyzing TCP/IP Networks with Wireshark June 15, 2010 Ray Tompkins Founder of Gearbit www.gearbit.com SHARKFEST 10 Stanford University June 14-17, 2010 TCP In this session we will examine the details
B-2 Analyzing TCP/IP Networks with Wireshark June 15, 2010 Ray Tompkins Founder of Gearbit www.gearbit.com SHARKFEST 10 Stanford University June 14-17, 2010 TCP In this session we will examine the details
TCP Performance Management for Dummies
 TCP Performance Management for Dummies Nalini Elkins Inside Products, Inc. Monday, August 8, 2011 Session Number 9285 Our SHARE Sessions Orlando 9285: TCP/IP Performance Management for Dummies Monday,
TCP Performance Management for Dummies Nalini Elkins Inside Products, Inc. Monday, August 8, 2011 Session Number 9285 Our SHARE Sessions Orlando 9285: TCP/IP Performance Management for Dummies Monday,
TCP Flow Control. TCP Receiver Window. Sliding Window. Computer Networks. Lecture 30: Flow Control, Reliable Delivery
 TCP Flow Control Computer Networks The receiver side of a TCP connection maintains a receiver buffer: Lecture : Flow Control, eliable elivery application process may be slow at reading from the buffer
TCP Flow Control Computer Networks The receiver side of a TCP connection maintains a receiver buffer: Lecture : Flow Control, eliable elivery application process may be slow at reading from the buffer
How do I get to www.randomsite.com?
 Networking Primer* *caveat: this is just a brief and incomplete introduction to networking to help students without a networking background learn Network Security. How do I get to www.randomsite.com? Local
Networking Primer* *caveat: this is just a brief and incomplete introduction to networking to help students without a networking background learn Network Security. How do I get to www.randomsite.com? Local
Outline. TCP connection setup/data transfer. 15-441 Computer Networking. TCP Reliability. Congestion sources and collapse. Congestion control basics
 Outline 15-441 Computer Networking Lecture 8 TCP & Congestion Control TCP connection setup/data transfer TCP Reliability Congestion sources and collapse Congestion control basics Lecture 8: 09-23-2002
Outline 15-441 Computer Networking Lecture 8 TCP & Congestion Control TCP connection setup/data transfer TCP Reliability Congestion sources and collapse Congestion control basics Lecture 8: 09-23-2002
NetView for z/os V6.1 Packet Trace Analysis
 NetView for z/os V6.1 Packet Trace Analysis Introduction This paper provides insights into the Packet Trace Analysis feature delivered in IBM Tivoli NetView for z/os V6.1, including an explanation of the
NetView for z/os V6.1 Packet Trace Analysis Introduction This paper provides insights into the Packet Trace Analysis feature delivered in IBM Tivoli NetView for z/os V6.1, including an explanation of the
TCP over Multi-hop Wireless Networks * Overview of Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Internet Protocol (IP)
 TCP over Multi-hop Wireless Networks * Overview of Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) *Slides adapted from a talk given by Nitin Vaidya. Wireless Computing and Network Systems Page
TCP over Multi-hop Wireless Networks * Overview of Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) *Slides adapted from a talk given by Nitin Vaidya. Wireless Computing and Network Systems Page
La couche transport dans l'internet (la suite TCP/IP)
 La couche transport dans l'internet (la suite TCP/IP) C. Pham Université de Pau et des Pays de l Adour Département Informatique http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham Congduc.Pham@univ-pau.fr Cours de C. Pham,
La couche transport dans l'internet (la suite TCP/IP) C. Pham Université de Pau et des Pays de l Adour Département Informatique http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham Congduc.Pham@univ-pau.fr Cours de C. Pham,
CPS221 Lecture: Layered Network Architecture
 CPS221 Lecture: Layered Network Architecture Objectives last revised 9/10/12 1. To discuss the OSI layered architecture model 2. To discuss the specific implementation of this model in TCP/IP Materials:
CPS221 Lecture: Layered Network Architecture Objectives last revised 9/10/12 1. To discuss the OSI layered architecture model 2. To discuss the specific implementation of this model in TCP/IP Materials:
Outline. CSc 466/566. Computer Security. 18 : Network Security Introduction. Network Topology. Network Topology. Christian Collberg
 Outline Network Topology CSc 466/566 Computer Security 18 : Network Security Introduction Version: 2012/05/03 13:59:29 Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@gmail.com Copyright
Outline Network Topology CSc 466/566 Computer Security 18 : Network Security Introduction Version: 2012/05/03 13:59:29 Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@gmail.com Copyright
TCP for Wireless Networks
 TCP for Wireless Networks Outline Motivation TCP mechanisms Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP Fast retransmit/recovery Transmission freezing Selective retransmission Transaction oriented TCP Adapted
TCP for Wireless Networks Outline Motivation TCP mechanisms Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP Fast retransmit/recovery Transmission freezing Selective retransmission Transaction oriented TCP Adapted
Access Control: Firewalls (1)
 Access Control: Firewalls (1) World is divided in good and bad guys ---> access control (security checks) at a single point of entry/exit: in medieval castles: drawbridge in corporate buildings: security/reception
Access Control: Firewalls (1) World is divided in good and bad guys ---> access control (security checks) at a single point of entry/exit: in medieval castles: drawbridge in corporate buildings: security/reception
TCP in Wireless Mobile Networks
 TCP in Wireless Mobile Networks 1 Outline Introduction to transport layer Introduction to TCP (Internet) congestion control Congestion control in wireless networks 2 Transport Layer v.s. Network Layer
TCP in Wireless Mobile Networks 1 Outline Introduction to transport layer Introduction to TCP (Internet) congestion control Congestion control in wireless networks 2 Transport Layer v.s. Network Layer
IP address format: Dotted decimal notation: 10000000 00001011 00000011 00011111 128.11.3.31
 IP address format: 7 24 Class A 0 Network ID Host ID 14 16 Class B 1 0 Network ID Host ID 21 8 Class C 1 1 0 Network ID Host ID 28 Class D 1 1 1 0 Multicast Address Dotted decimal notation: 10000000 00001011
IP address format: 7 24 Class A 0 Network ID Host ID 14 16 Class B 1 0 Network ID Host ID 21 8 Class C 1 1 0 Network ID Host ID 28 Class D 1 1 1 0 Multicast Address Dotted decimal notation: 10000000 00001011
Networking Overview. (as usual, thanks to Dave Wagner and Vern Paxson)
 Networking Overview (as usual, thanks to Dave Wagner and Vern Paxson) Focus For This Lecture Sufficient background in networking to then explore security issues in next few lectures Networking = the Internet
Networking Overview (as usual, thanks to Dave Wagner and Vern Paxson) Focus For This Lecture Sufficient background in networking to then explore security issues in next few lectures Networking = the Internet
Overview of TCP/IP. TCP/IP and Internet
 Overview of TCP/IP System Administrators and network administrators Why networking - communication Why TCP/IP Provides interoperable communications between all types of hardware and all kinds of operating
Overview of TCP/IP System Administrators and network administrators Why networking - communication Why TCP/IP Provides interoperable communications between all types of hardware and all kinds of operating
Networking Test 4 Study Guide
 Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
Effect of Packet-Size over Network Performance
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 762 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN: 2277-1956 Effect of Packet-Size over Network Performance Abhi U. Shah 1, Daivik H. Bhatt
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 762 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN: 2277-1956 Effect of Packet-Size over Network Performance Abhi U. Shah 1, Daivik H. Bhatt
Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks
 Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks for TCP/IP Networks June 16, 2011 Laura Chappell Founder Chappell University/Wireshark University laura@chappellu.com SHARKFEST 11 Stanford University June 13 16, 2011 The
Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks for TCP/IP Networks June 16, 2011 Laura Chappell Founder Chappell University/Wireshark University laura@chappellu.com SHARKFEST 11 Stanford University June 13 16, 2011 The
Ethernet. Ethernet. Network Devices
 Ethernet Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design Ethernet Ethernet is a term used to refer to a diverse set of frame based networking
Ethernet Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design Ethernet Ethernet is a term used to refer to a diverse set of frame based networking
Host Fingerprinting and Firewalking With hping
 Host Fingerprinting and Firewalking With hping Naveed Afzal National University Of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan Email: 1608@nu.edu.pk Naveedafzal gmail.com Abstract: The purpose
Host Fingerprinting and Firewalking With hping Naveed Afzal National University Of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan Email: 1608@nu.edu.pk Naveedafzal gmail.com Abstract: The purpose
Network Security TCP/IP Refresher
 Network Security TCP/IP Refresher What you (at least) need to know about networking! Dr. David Barrera Network Security HS 2014 Outline Network Reference Models Local Area Networks Internet Protocol (IP)
Network Security TCP/IP Refresher What you (at least) need to know about networking! Dr. David Barrera Network Security HS 2014 Outline Network Reference Models Local Area Networks Internet Protocol (IP)
CS155 - Firewalls. Simon Cooper <sc@sgi.com> CS155 Firewalls 22 May 2003
 CS155 - Firewalls Simon Cooper CS155 Firewalls 22 May 2003 1 Why Firewalls? Need for the exchange of information; education, business, recreation, social and political Need to do something
CS155 - Firewalls Simon Cooper CS155 Firewalls 22 May 2003 1 Why Firewalls? Need for the exchange of information; education, business, recreation, social and political Need to do something
La couche transport dans l'internet (la suite TCP/IP)
 La couche transport dans l'internet (la suite TCP/IP) C. Pham RESO-LIP/INRIA Université Lyon 1 http://www.ens-lyon.fr/~cpham Basé sur les transparent de Shivkumar Kalyanaraman La couche transport dans
La couche transport dans l'internet (la suite TCP/IP) C. Pham RESO-LIP/INRIA Université Lyon 1 http://www.ens-lyon.fr/~cpham Basé sur les transparent de Shivkumar Kalyanaraman La couche transport dans
Hands-on Network Traffic Analysis. 2015 Cyber Defense Boot Camp
 Hands-on Network Traffic Analysis 2015 Cyber Defense Boot Camp What is this about? Prerequisite: network packet & packet analyzer: (header, data) Enveloped letters inside another envelope Exercises Basic
Hands-on Network Traffic Analysis 2015 Cyber Defense Boot Camp What is this about? Prerequisite: network packet & packet analyzer: (header, data) Enveloped letters inside another envelope Exercises Basic
CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks. Exam 2 Solutions. Your name: 10/31/2013
 CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Jon Turner Exam Solutions Your name: 0/3/03. (0 points). Consider a circular DHT with 7 nodes numbered 0,,...,6, where the nodes cache key-values pairs for 60
CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks Jon Turner Exam Solutions Your name: 0/3/03. (0 points). Consider a circular DHT with 7 nodes numbered 0,,...,6, where the nodes cache key-values pairs for 60
DO NOT REPLICATE. Analyze IP. Given a Windows Server 2003 computer, you will use Network Monitor to view and analyze all the fields of IP.
 Advanced TCP/IP Overview There is one primary set of protocols that runs networks and the Internet today. In this lesson, you will work with those protocols: the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and
Advanced TCP/IP Overview There is one primary set of protocols that runs networks and the Internet today. In this lesson, you will work with those protocols: the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and
Computer Networks Practicum 2015
 Computer Networks Practicum 2015 Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, The Netherlands http://acropolis.cs.vu.nl/ spyros/cnp/ 1 Overview This practicum consists of two parts. The first is to build a TCP implementation
Computer Networks Practicum 2015 Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, The Netherlands http://acropolis.cs.vu.nl/ spyros/cnp/ 1 Overview This practicum consists of two parts. The first is to build a TCP implementation
Overview. Securing TCP/IP. Introduction to TCP/IP (cont d) Introduction to TCP/IP
 Overview Securing TCP/IP Chapter 6 TCP/IP Open Systems Interconnection Model Anatomy of a Packet Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) Web Security (HTTP over TLS, Secure-HTTP) Lecturer: Pei-yih Ting 1 2
Overview Securing TCP/IP Chapter 6 TCP/IP Open Systems Interconnection Model Anatomy of a Packet Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) Web Security (HTTP over TLS, Secure-HTTP) Lecturer: Pei-yih Ting 1 2
Network Security: Workshop. Dr. Anat Bremler-Barr. Assignment #2 Analyze dump files Solution Taken from www.chrissanders.org
 1.pcap - File download Network Security: Workshop Dr. Anat Bremler-Barr Assignment #2 Analyze dump files Solution Taken from www.chrissanders.org Downloading a file is a pretty basic function when described
1.pcap - File download Network Security: Workshop Dr. Anat Bremler-Barr Assignment #2 Analyze dump files Solution Taken from www.chrissanders.org Downloading a file is a pretty basic function when described
Defending Computer Networks Lecture 6: TCP and Scanning. Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science
 Defending Computer Networks Lecture 6: TCP and Scanning Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science Logis;cs HW1 due tomorrow First quiz will be Tuesday September 23 rd. Half hour quiz at start
Defending Computer Networks Lecture 6: TCP and Scanning Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science Logis;cs HW1 due tomorrow First quiz will be Tuesday September 23 rd. Half hour quiz at start
2057-15. First Workshop on Open Source and Internet Technology for Scientific Environment: with case studies from Environmental Monitoring
 2057-15 First Workshop on Open Source and Internet Technology for Scientific Environment: with case studies from Environmental Monitoring 7-25 September 2009 TCP/IP Networking Abhaya S. Induruwa Department
2057-15 First Workshop on Open Source and Internet Technology for Scientific Environment: with case studies from Environmental Monitoring 7-25 September 2009 TCP/IP Networking Abhaya S. Induruwa Department
Kap. 2. Transport - Schicht
 Kap. 2 Transport - Schicht 2-2 Transport-Schicht Transport-Schicht: bietet eine logische Kommunikation zw. Anwendungen TCP: - Verbindungsorientiert mittels 3-Way-Handshake - zuverlässiger Datentransport
Kap. 2 Transport - Schicht 2-2 Transport-Schicht Transport-Schicht: bietet eine logische Kommunikation zw. Anwendungen TCP: - Verbindungsorientiert mittels 3-Way-Handshake - zuverlässiger Datentransport
TCP/IP Optimization for Wide Area Storage Networks. Dr. Joseph L White Juniper Networks
 TCP/IP Optimization for Wide Area Storage Networks Dr. Joseph L White Juniper Networks SNIA Legal Notice The material contained in this tutorial is copyrighted by the SNIA. Member companies and individuals
TCP/IP Optimization for Wide Area Storage Networks Dr. Joseph L White Juniper Networks SNIA Legal Notice The material contained in this tutorial is copyrighted by the SNIA. Member companies and individuals
Prefix AggregaNon. Company X and Company Y connect to the same ISP, and they are assigned the prefixes:
 Data Transfer Consider transferring an enormous file of L bytes from Host A to B using a MSS of 1460 bytes and a 66 byte header. What is the maximum value of L such that TCP sequence numbers are not exhausted?
Data Transfer Consider transferring an enormous file of L bytes from Host A to B using a MSS of 1460 bytes and a 66 byte header. What is the maximum value of L such that TCP sequence numbers are not exhausted?
CMPE 150 Winter 2009
 CMPE 150 Winter 2009 Lecture 6 January 22, 2009 P.E. Mantey CMPE 150 -- Introduction to Computer Networks Instructor: Patrick Mantey mantey@soe.ucsc.edu http://www.soe.ucsc.edu/~mantey/ / t / Office: Engr.
CMPE 150 Winter 2009 Lecture 6 January 22, 2009 P.E. Mantey CMPE 150 -- Introduction to Computer Networks Instructor: Patrick Mantey mantey@soe.ucsc.edu http://www.soe.ucsc.edu/~mantey/ / t / Office: Engr.
NETI@home: A Distributed Approach to Collecting End-to-End Network Performance Measurements
 NETI@home: A Distributed Approach to Collecting End-to-End Network Performance Measurements Charles Robert Simpson, Jr. and George F. Riley Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech), Atlanta Georgia,
NETI@home: A Distributed Approach to Collecting End-to-End Network Performance Measurements Charles Robert Simpson, Jr. and George F. Riley Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech), Atlanta Georgia,
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio).
 This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio). Here we explore the sequence of interactions in a typical FTP (File Transfer Protocol) session.
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio). Here we explore the sequence of interactions in a typical FTP (File Transfer Protocol) session.
Mobile Communications Chapter 9: Mobile Transport Layer
 Mobile Communications Chapter 9: Mobile Transport Layer Motivation TCP-mechanisms Classical approaches Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP PEPs in general Additional optimizations Fast retransmit/recovery
Mobile Communications Chapter 9: Mobile Transport Layer Motivation TCP-mechanisms Classical approaches Indirect TCP Snooping TCP Mobile TCP PEPs in general Additional optimizations Fast retransmit/recovery
COMP 361 Computer Communications Networks. Fall Semester 2003. Midterm Examination
 COMP 361 Computer Communications Networks Fall Semester 2003 Midterm Examination Date: October 23, 2003, Time 18:30pm --19:50pm Name: Student ID: Email: Instructions: 1. This is a closed book exam 2. This
COMP 361 Computer Communications Networks Fall Semester 2003 Midterm Examination Date: October 23, 2003, Time 18:30pm --19:50pm Name: Student ID: Email: Instructions: 1. This is a closed book exam 2. This
Networking Attacks: Link-, IP-, and TCP-layer attacks. CS 161: Computer Security Prof. David Wagner
 Networking Attacks: Link-, IP-, and TCP-layer attacks CS 161: Computer Security Prof. David Wagner February 28, 2013 General Communication Security Goals: CIA! Confidentiality: No one can read our data
Networking Attacks: Link-, IP-, and TCP-layer attacks CS 161: Computer Security Prof. David Wagner February 28, 2013 General Communication Security Goals: CIA! Confidentiality: No one can read our data
Firewall Implementation
 CS425: Computer Networks Firewall Implementation Ankit Kumar Y8088 Akshay Mittal Y8056 Ashish Gupta Y8410 Sayandeep Ghosh Y8465 October 31, 2010 under the guidance of Prof. Dheeraj Sanghi Department of
CS425: Computer Networks Firewall Implementation Ankit Kumar Y8088 Akshay Mittal Y8056 Ashish Gupta Y8410 Sayandeep Ghosh Y8465 October 31, 2010 under the guidance of Prof. Dheeraj Sanghi Department of
Layer 7 Load Balancing and Content Customization
 C H A P T E R 4 Layer 7 Load Balancing and Content Customization This chapter will discuss the methods and protocols involved in accomplishing a Layer 7 load-balancing solution. The reasons for and benefits
C H A P T E R 4 Layer 7 Load Balancing and Content Customization This chapter will discuss the methods and protocols involved in accomplishing a Layer 7 load-balancing solution. The reasons for and benefits
Life of a Packet CS 640, 2015-01-22
 Life of a Packet CS 640, 2015-01-22 Outline Recap: building blocks Application to application communication Process to process communication Host to host communication Announcements Syllabus Should have
Life of a Packet CS 640, 2015-01-22 Outline Recap: building blocks Application to application communication Process to process communication Host to host communication Announcements Syllabus Should have
TCP and Wireless Networks Classical Approaches Optimizations TCP for 2.5G/3G Systems. Lehrstuhl für Informatik 4 Kommunikation und verteilte Systeme
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Chapter 4 Mobility on the
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Chapter 4 Mobility on the
Configuring TCP Intercept (Preventing Denial-of-Service Attacks)
 Configuring TCP Intercept (Preventing Denial-of-Service Attacks) This chapter describes how to configure your router to protect TCP servers from TCP SYN-flooding attacks, a type of denial-of-service attack.
Configuring TCP Intercept (Preventing Denial-of-Service Attacks) This chapter describes how to configure your router to protect TCP servers from TCP SYN-flooding attacks, a type of denial-of-service attack.
What is a DoS attack?
 CprE 592-YG Computer and Network Forensics Log-based Signature Analysis Denial of Service Attacks - from analyst s point of view Yong Guan 3216 Coover Tel: (515) 294-8378 Email: guan@ee.iastate.edu October
CprE 592-YG Computer and Network Forensics Log-based Signature Analysis Denial of Service Attacks - from analyst s point of view Yong Guan 3216 Coover Tel: (515) 294-8378 Email: guan@ee.iastate.edu October
NetFlow/IPFIX Various Thoughts
 NetFlow/IPFIX Various Thoughts Paul Aitken & Benoit Claise 3 rd NMRG Workshop on NetFlow/IPFIX Usage in Network Management, July 2010 1 B #1 Application Visibility Business Case NetFlow (L3/L4) DPI Application
NetFlow/IPFIX Various Thoughts Paul Aitken & Benoit Claise 3 rd NMRG Workshop on NetFlow/IPFIX Usage in Network Management, July 2010 1 B #1 Application Visibility Business Case NetFlow (L3/L4) DPI Application
DDoS Protecion Total AnnihilationD. DDoS Mitigation Lab
 DDoS Protecion Total AnnihilationD A Industry body formed to foster synergy among stakeholders to promote advancement in DDoS defense knowledge. Independent academic R&D division of Nexusguard building
DDoS Protecion Total AnnihilationD A Industry body formed to foster synergy among stakeholders to promote advancement in DDoS defense knowledge. Independent academic R&D division of Nexusguard building
(Refer Slide Time: 02:17)
 Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #06 IP Subnetting and Addressing (Not audible: (00:46)) Now,
Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #06 IP Subnetting and Addressing (Not audible: (00:46)) Now,
Network Security I: Overview
 Network Security I: Overview April 13, 2015 Lecture by: Kevin Chen Slides credit: Vern Paxson, Dawn Song 1 network security 2 Today s Lecture Networking overview + security issues Keep in mind, networking
Network Security I: Overview April 13, 2015 Lecture by: Kevin Chen Slides credit: Vern Paxson, Dawn Song 1 network security 2 Today s Lecture Networking overview + security issues Keep in mind, networking
Networks: IP and TCP. Internet Protocol
 Networks: IP and TCP 11/1/2010 Networks: IP and TCP 1 Internet Protocol Connectionless Each packet is transported independently from other packets Unreliable Delivery on a best effort basis No acknowledgments
Networks: IP and TCP 11/1/2010 Networks: IP and TCP 1 Internet Protocol Connectionless Each packet is transported independently from other packets Unreliable Delivery on a best effort basis No acknowledgments
Multipath TCP in Practice (Work in Progress) Mark Handley Damon Wischik Costin Raiciu Alan Ford
 Multipath TCP in Practice (Work in Progress) Mark Handley Damon Wischik Costin Raiciu Alan Ford The difference between theory and practice is in theory somewhat smaller than in practice. In theory, this
Multipath TCP in Practice (Work in Progress) Mark Handley Damon Wischik Costin Raiciu Alan Ford The difference between theory and practice is in theory somewhat smaller than in practice. In theory, this
Network and Services Discovery
 A quick theorical introduction to network scanning January 8, 2016 Disclaimer/Intro Disclaimer/Intro Network scanning is not exact science When an information system is able to interact over the network
A quick theorical introduction to network scanning January 8, 2016 Disclaimer/Intro Disclaimer/Intro Network scanning is not exact science When an information system is able to interact over the network
Innominate mguard Version 6
 Innominate mguard Version 6 Application Note: Firewall Logging mguard smart mguard PCI mguard blade mguard industrial RS EAGLE mguard mguard delta Innominate Security Technologies AG Albert-Einstein-Str.
Innominate mguard Version 6 Application Note: Firewall Logging mguard smart mguard PCI mguard blade mguard industrial RS EAGLE mguard mguard delta Innominate Security Technologies AG Albert-Einstein-Str.
CS 5480/6480: Computer Networks Spring 2012 Homework 3 Due by 1:25 PM MT, Monday March 5 th 2012
 CS 5480/6480: Computer Networks Spring 2012 Homework 3 Due by 1:25 PM MT, Monday March 5 th 2012 Important: No cheating will be tolerated. No Late Submission will be allowed. Total points for 5480 = 37
CS 5480/6480: Computer Networks Spring 2012 Homework 3 Due by 1:25 PM MT, Monday March 5 th 2012 Important: No cheating will be tolerated. No Late Submission will be allowed. Total points for 5480 = 37
Secure Network Access System (SNAS) Indigenous Next Generation Network Security Solutions
 Secure Network Access System (SNAS) Indigenous Next Generation Network Security Solutions Gigi Joseph, Computer Division,BARC. Gigi@barc.gov.in Intranet Security Components Network Admission Control (NAC)
Secure Network Access System (SNAS) Indigenous Next Generation Network Security Solutions Gigi Joseph, Computer Division,BARC. Gigi@barc.gov.in Intranet Security Components Network Admission Control (NAC)
We will give some overview of firewalls. Figure 1 explains the position of a firewall. Figure 1: A Firewall
 Chapter 10 Firewall Firewalls are devices used to protect a local network from network based security threats while at the same time affording access to the wide area network and the internet. Basically,
Chapter 10 Firewall Firewalls are devices used to protect a local network from network based security threats while at the same time affording access to the wide area network and the internet. Basically,
Understanding Layer 2, 3, and 4 Protocols
 2 Understanding Layer 2, 3, and 4 Protocols While many of the concepts well known to traditional Layer 2 and Layer 3 networking still hold true in content switching applications, the area introduces new
2 Understanding Layer 2, 3, and 4 Protocols While many of the concepts well known to traditional Layer 2 and Layer 3 networking still hold true in content switching applications, the area introduces new
Pig Laboratory. Additional documentation for the laboratory. Exercises and Rules. Tstat Data
 Pig Laboratory This laboratory is dedicated to Hadoop Pig and consists of a series of exercises: some of them somewhat mimic those in the MapReduce laboratory, others are inspired by "real-world" problems.
Pig Laboratory This laboratory is dedicated to Hadoop Pig and consists of a series of exercises: some of them somewhat mimic those in the MapReduce laboratory, others are inspired by "real-world" problems.
UNDERSTANDING FIREWALLS TECHNICAL NOTE 10/04
 UNDERSTANDING FIREWALLS TECHNICAL NOTE 10/04 REVISED 23 FEBRUARY 2005 This paper was previously published by the National Infrastructure Security Co-ordination Centre (NISCC) a predecessor organisation
UNDERSTANDING FIREWALLS TECHNICAL NOTE 10/04 REVISED 23 FEBRUARY 2005 This paper was previously published by the National Infrastructure Security Co-ordination Centre (NISCC) a predecessor organisation
The Transport Layer and Implica4ons for Network Monitoring. CS 410/510 Spring 2014
 The Transport Layer and Implica4ons for Network Monitoring CS 410/510 Spring 2014 Review Preliminaries: Three Principles of Informa4on Security The Three A s Review: Network Protocol Stacks Review: Network
The Transport Layer and Implica4ons for Network Monitoring CS 410/510 Spring 2014 Review Preliminaries: Three Principles of Informa4on Security The Three A s Review: Network Protocol Stacks Review: Network
Firewalls. configuring a sophisticated GNU/Linux firewall involves understanding
 Firewalls slide 1 configuring a sophisticated GNU/Linux firewall involves understanding iptables iptables is a package which interfaces to the Linux kernel and configures various rules for allowing packets
Firewalls slide 1 configuring a sophisticated GNU/Linux firewall involves understanding iptables iptables is a package which interfaces to the Linux kernel and configures various rules for allowing packets
Port Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment. ECE4893 Internetwork Security Georgia Institute of Technology
 Port Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment ECE4893 Internetwork Security Georgia Institute of Technology Agenda Reconnaissance Scanning Network Mapping OS detection Vulnerability assessment Reconnaissance
Port Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment ECE4893 Internetwork Security Georgia Institute of Technology Agenda Reconnaissance Scanning Network Mapping OS detection Vulnerability assessment Reconnaissance
TCP/IP and the Internet
 TCP/IP and the Internet Computer networking today is becoming more and more entwined with the internet. By far the most popular protocol set in use is TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol).
TCP/IP and the Internet Computer networking today is becoming more and more entwined with the internet. By far the most popular protocol set in use is TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol).
ACHILLES CERTIFICATION. SIS Module SLS 1508
 ACHILLES CERTIFICATION PUBLIC REPORT Final DeltaV Report SIS Module SLS 1508 Disclaimer Wurldtech Security Inc. retains the right to change information in this report without notice. Wurldtech Security
ACHILLES CERTIFICATION PUBLIC REPORT Final DeltaV Report SIS Module SLS 1508 Disclaimer Wurldtech Security Inc. retains the right to change information in this report without notice. Wurldtech Security
CSMA/CA. Information Networks p. 1
 Information Networks p. 1 CSMA/CA IEEE 802.11 standard for WLAN defines a distributed coordination function (DCF) for sharing access to the medium based on the CSMA/CA protocol Collision detection is not
Information Networks p. 1 CSMA/CA IEEE 802.11 standard for WLAN defines a distributed coordination function (DCF) for sharing access to the medium based on the CSMA/CA protocol Collision detection is not
TCP/IP Networking for Wireless Systems. Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology
 TCP/IP Networking for Wireless Systems Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Content Internet Protocol Suite Link Layer: Ethernet, PPP, ARP, MAC Addressing Network Layer:
TCP/IP Networking for Wireless Systems Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Content Internet Protocol Suite Link Layer: Ethernet, PPP, ARP, MAC Addressing Network Layer:
NAT & IP Masquerade. Internet NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION INTRODUCTION. NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5. Internal PC 192.168.0.25
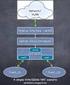 NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
NAT & IP Masquerade Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Pre-requisites TCP/IP IP Address Space NAT & IP Masquerade Protocol version 4 uses a 32 bit IP address. In theory, a 32 bit address space should provide addresses
Algorithms and Techniques Used for Auto-discovery of Network Topology, Assets and Services
 Algorithms and Techniques Used for Auto-discovery of Network Topology, Assets and Services CS4983 Senior Technical Report Brian Chown 0254624 Faculty of Computer Science University of New Brunswick Canada
Algorithms and Techniques Used for Auto-discovery of Network Topology, Assets and Services CS4983 Senior Technical Report Brian Chown 0254624 Faculty of Computer Science University of New Brunswick Canada
Improving the Performance of TCP Using Window Adjustment Procedure and Bandwidth Estimation
 Improving the Performance of TCP Using Window Adjustment Procedure and Bandwidth Estimation R.Navaneethakrishnan Assistant Professor (SG) Bharathiyar College of Engineering and Technology, Karaikal, India.
Improving the Performance of TCP Using Window Adjustment Procedure and Bandwidth Estimation R.Navaneethakrishnan Assistant Professor (SG) Bharathiyar College of Engineering and Technology, Karaikal, India.
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems
 CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting 5. Vulnerability Scanning
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting 5. Vulnerability Scanning
Stop And Wait. ACK received; transmit frame 2 CS 455 3
 Data Link Layer, Part 5 Sliding Window Protocols These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable
Data Link Layer, Part 5 Sliding Window Protocols These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable
Lab Exercise SSL/TLS. Objective. Step 1: Open a Trace. Step 2: Inspect the Trace
 Lab Exercise SSL/TLS Objective To observe SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer / Transport Layer Security) in action. SSL/TLS is used to secure TCP connections, and it is widely used as part of the secure web:
Lab Exercise SSL/TLS Objective To observe SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer / Transport Layer Security) in action. SSL/TLS is used to secure TCP connections, and it is widely used as part of the secure web:
Distinct. Network Monitor. User s Guide
 Distinct Network Monitor Version 4.2 User s Guide Distinct Corporation 3315 Almaden Expressway San Jose, CA 95118 USA Phone: +1 408-445-3270 Fax: +1 408-445-3274 Email: sales@distinct.com WWW: http://www.distinct.com
Distinct Network Monitor Version 4.2 User s Guide Distinct Corporation 3315 Almaden Expressway San Jose, CA 95118 USA Phone: +1 408-445-3270 Fax: +1 408-445-3274 Email: sales@distinct.com WWW: http://www.distinct.com
How To Understand The Internet Of S (Netware)
 Summer Workshop on Cyber Security Computer s Security (Part 1) Dr. Hamed Mohsenian-Rad University of California at Riverside and Texas Tech University August 12-16, 2013 Supported by National Science Foundation
Summer Workshop on Cyber Security Computer s Security (Part 1) Dr. Hamed Mohsenian-Rad University of California at Riverside and Texas Tech University August 12-16, 2013 Supported by National Science Foundation
There s nothing like a Firewall. Olivier Paul, GET/INT MONAM 07, Toulouse, France
 There s nothing like a Firewall Olivier Paul, GET/INT MONAM 07, Toulouse, France How does this relate to risk? From wikipedia Risk = (probability of incident) * (Cost of incident) From risk evaluation
There s nothing like a Firewall Olivier Paul, GET/INT MONAM 07, Toulouse, France How does this relate to risk? From wikipedia Risk = (probability of incident) * (Cost of incident) From risk evaluation
Internet Protocols. Background CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 3 Internet Protocols Background The Internet protocols are the world s most popular open-system (nonproprietary) protocol suite because they can be used to communicate across any set of interconnected
CHAPTER 3 Internet Protocols Background The Internet protocols are the world s most popular open-system (nonproprietary) protocol suite because they can be used to communicate across any set of interconnected
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET CRAFTING
 CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET CRAFTING Protect your FOSS-based IT infrastructure from packet crafting by learning more about it. In the previous articles in this series, we explored common infrastructure
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET CRAFTING Protect your FOSS-based IT infrastructure from packet crafting by learning more about it. In the previous articles in this series, we explored common infrastructure
1 An application in BPC: a Web-Server
 1 An application in BPC: a Web-Server We briefly describe our web-server case-study, dwelling in particular on some of the more advanced features of the BPC framework, such as timeouts, parametrized events,
1 An application in BPC: a Web-Server We briefly describe our web-server case-study, dwelling in particular on some of the more advanced features of the BPC framework, such as timeouts, parametrized events,
2 TCP-like Design. Answer
 Homework 3 1 DNS Suppose you have a Host C, a local name server L, and authoritative name servers A root, A com, and A google.com, where the naming convention A x means that the name server knows about
Homework 3 1 DNS Suppose you have a Host C, a local name server L, and authoritative name servers A root, A com, and A google.com, where the naming convention A x means that the name server knows about
IP Subnetting and Addressing
 Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur IP Subnetting and Addressing Prof Indranil Sengupta Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture 6: IP Subnetting and Addressing
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur IP Subnetting and Addressing Prof Indranil Sengupta Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture 6: IP Subnetting and Addressing
Introduction to TCP/IP
 Introduction to TCP/IP Raj Jain The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Nayna Networks Milpitas, CA 95035 Email: Jain@ACM.Org http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview! Internetworking Protocol
Introduction to TCP/IP Raj Jain The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Nayna Networks Milpitas, CA 95035 Email: Jain@ACM.Org http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview! Internetworking Protocol
Firewalls. Basic Firewall Concept. Why firewalls? Firewall goals. Two Separable Topics. Firewall Design & Architecture Issues
 CS 155 May 20, 2004 Firewalls Basic Firewall Concept Separate local area net from internet Firewall John Mitchell Credit: some text, illustrations from Simon Cooper Router All packets between LAN and internet
CS 155 May 20, 2004 Firewalls Basic Firewall Concept Separate local area net from internet Firewall John Mitchell Credit: some text, illustrations from Simon Cooper Router All packets between LAN and internet
The present and the future of TCP/IP
 The present and the future of TCP/IP David Espina Project in Electronics dea09001@student.mdh.com Dariusz Baha Computer science dba04002@student.mdh.se ABSTRACT The Transport Control Protocol (TCP) and
The present and the future of TCP/IP David Espina Project in Electronics dea09001@student.mdh.com Dariusz Baha Computer science dba04002@student.mdh.se ABSTRACT The Transport Control Protocol (TCP) and
Improving DNS performance using Stateless TCP in FreeBSD 9
 Improving DNS performance using Stateless TCP in FreeBSD 9 David Hayes, Mattia Rossi, Grenville Armitage Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures, Technical Report 101022A Swinburne University of Technology
Improving DNS performance using Stateless TCP in FreeBSD 9 David Hayes, Mattia Rossi, Grenville Armitage Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures, Technical Report 101022A Swinburne University of Technology
q Connection establishment (if connection-oriented) q Data transfer q Connection release (if conn-oriented) q Addressing the transport user
 Transport service characterization The Transport Layer End-to-End Protocols: UDP and TCP Connection establishment (if connection-oriented) Data transfer Reliable ( TCP) Unreliable / best effort ( UDP)
Transport service characterization The Transport Layer End-to-End Protocols: UDP and TCP Connection establishment (if connection-oriented) Data transfer Reliable ( TCP) Unreliable / best effort ( UDP)
Network Fundamentals. 2010 Carnegie Mellon University
 Network Fundamentals What We Will Cover Introduction Your Network Fundamentals of networks, flow, and protocols Malicious traffic External Events & Trends Malware Networks in the Broad Working Together
Network Fundamentals What We Will Cover Introduction Your Network Fundamentals of networks, flow, and protocols Malicious traffic External Events & Trends Malware Networks in the Broad Working Together
