POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
|
|
|
- Polly Copeland
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Issue Date (Created): November 26, 2013 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): November 26, 2013 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY I. POLICY Whole exome sequencing is considered investigational for all indications. There is insufficient evidence to support a conclusion concerning the health outcomes or benefits associated with this procedure. Cross-reference: II. PRODUCT VARIATIONS [N] = No product variation, policy applies as stated [Y] = Standard product coverage varies from application of this policy, see below [N] Capital Cares 4 Kids [N] PPO [N] HMO [N] SeniorBlue HMO [N] SeniorBlue PPO [N] Indemnity [N] SpecialCare [N] POS [Y] FEP PPO* *The FEP program dictates that all drugs, devices or biological products approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) may not be considered investigational. Therefore, FDA-approved drugs, devices or biological products may be assessed on the basis of medical necessity. Page 1
2 III. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND Whole exome sequencing (WES) is defined as targeted sequencing of the subset of the human genome that contains functionally important sequences of protein-coding DNA. WES has been proposed to be more efficient than traditional sequencing methods in discovering the genetic causes of diseases. Currently available clinical assays designed for the molecular diagnosis of rare Mendelian diseases are incomplete. This is due to genetic heterogeneity, the presence of unknown causative genes, and because only a portion of the known genes and mutations can be efficiently tested using conventional molecular methods. Recently, next-generation sequencing technologies have become more accessible in terms of cost and speed and have been adopted by a growing number of molecular genetic clinical laboratories. Depending on the disorder and the degree of genetic and clinical heterogeneity, the current diagnostic pathway for patients with suspected genetic disorders accompanied by multiple anomalies may depend on various combinations of low-yield radiographic, electrophysiological, biochemical, biopsy, and targeted genetic evaluations. (1) The search for a diagnosis may thus become a time-consuming and expensive process. When a disease-causing gene(s) is established, assays based on polymerase chain reaction technology, for example, can be designed to specifically detect known mutations for clinical diagnosis. When many different point mutations in a gene are possible, Sanger sequencing, the current gold standard for detecting unknown point mutations, can be employed to determine the entire sequence of the coding and intron/exon splice sites of gene regions where mutations are most likely to be found. However, when genes are large and mutations are possible in many or all exons (protein-coding regions of the gene), and when there is genetic (locus) heterogeneity, comprehensive Sanger sequencing may be prohibitively laborious and costly. Whole exome sequencing (WES) using next-generation sequencing technology is a relatively new approach to obtaining a genetic diagnosis in patients more efficiently compared with traditional methods. Exome sequencing has the capacity to determine an individual s exomic variation profile in a single assay. This profile is limited to most of the protein coding sequence of an individual (approximately 85%), is composed of about 20,000 genes, and 180,000 exons (protein-coding segments of a gene), and constitutes approximately 1% of the whole genome. It is believed that the exome contains about 85% of heritable disease-causing mutations. Published exome sequencing studies show that the technology can be used to detect previously annotated pathogenic mutations and reveal new likely pathogenic mutations in known and unknown genes. The diagnostic yield, based on a limited number of studies, appears to be significantly increased above that of traditional Sanger sequencing, and exome sequencing has the advantage of speed and efficiency relative to Sanger sequencing of multiple genes. Page 2
3 Limitations of WES At this time, the limitations of WES include technical and implementation challenges. There are issues of error rates due to uneven sequencing coverage, gaps in exon capture prior to sequencing, and difficulties with narrowing the large initial number of variants to manageable numbers without losing likely candidate mutations. It is difficult to filter and interpret potential causative variants from the large number of variants of unknown significance generated for each patient. Variant databases are poorly annotated, and algorithms for annotating variants will need to be automated. Existing databases that catalog variants and putative disease associations are known to have significant entry error rates. Approaches for characterizing the functional impact of rare and novel variants (i.e., achieving full-genome clinical interpretations that are scientifically sound and medically relevant) have to be improved. The variability contributed by the different platforms and procedures used by different clinical laboratories offering exome sequencing as a clinical service is unknown, and detailed guidance from regulatory and professional organizations is still under development. Finally, exome sequencing has some similar limitations as Sanger sequencing; e.g., it will not identify the following: intronic sequences or gene regulatory regions; chromosomal changes; large deletions, duplications or rearrangements within genes; nucleotide repeats; or epigenetic changes. There are also ethical questions about reporting incidental findings, such as identifying medically relevant mutations in genes unrelated to the diagnostic question, sex chromosome abnormalities and non-paternity when family studies are performed. Results of testing with WES (2) 1) A variant known to cause human disease is identified. This is a sequence variant that has been shown through prior genetic and clinical research to cause a disease. 2) A variant suspected to cause human disease is identified. Most variants detected by WES sequencing are uncharacterized and some are novel (i.e., never known to have been observed in a human sample). Some variants allow for relatively easy and accurate clinical interpretation; however, for most there is little data upon which to base an assessment of causality. Tools to facilitate the assessment of causality include bioinformatic analyses, predicted structural changes and others. While these tools may be useful, their predictive power is highly variable. 3) A variant of uncertain significance is identified, Among the known 30,000-40,000 variants that reside in the protein-coding portions of the genome, the typical subject will have 3 to 8 actionable variants. (Most of these relate to reproductive risks, that is, heterozygous carrier alleles.) But the remaining thousands are either highly likely to be benign or of uncertain clinical significance. It can be equally as Page 3
4 challenging to prove that a variant is benign as it is to prove it is pathogenic. Currently, nearly all of the variants among the tens of thousands must be considered of uncertain significance. Regulatory Status No U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-cleared genotyping tests were found. Thus, genotyping is offered as a laboratory-developed test. Clinical laboratories may develop and validate tests in-house ( home-brew ) and market them as a laboratory service; such tests must meet the general regulatory standards of the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act (CLIA). The laboratory offering the service must be licensed by CLIA for high-complexity testing. Examples of laboratories offering exome sequencing as a clinical service Laboratory Ambry Genetics, Aliso Viejo, CA GeneDx, Gaithersburg, MD Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX University of California Los Angeles Health System EdgeBio, Gaithersburg, MD Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City Emory Genetics Laboratory, Atlanta, GA. Laboratory indications for testing The patient's clinical presentation is unclear/atypical disease and there are multiple genetic conditions in the differential diagnosis. a patient with a diagnosis that suggests the involvement of one or more of many different genes, which would, if even available and sequenced individually, be prohibitively expensive used when a patient s medical history and physical exam findings strongly suggest that there is an underlying genetic etiology. In some cases, the patient may have had an extensive evaluation consisting of multiple genetic tests, without identifying an etiology. This test is intended for use in conjunction with the clinical presentation and other markers of disease progression for the management of patients with rare genetic disorders. Recommended In situations where there has been a diagnostic failure with no discernible path... In situations where there are currently no available tests to determine the status of a potential genetic disease... In situations with atypical findings indicative of multiple disease[s] Provided as a service to families with children who have had an extensive negative work-up for a genetic disease; also used to identify novel disease genes. Indicated when there is a suspicion of a genetic etiology contributing to the proband s manifestations. IV. RATIONALE The policy was created in August 2013 with review of the literature covering the period through August 27, Literature Review Analytic validity Whole exome sequencing (WES) has not yet been well-standardized for the clinical laboratory and has not been fully characterized in publicly available documents with regard to the analytic validity for the various types of relevant mutations. The few existing professional guidelines give only high-level direction. Technical limitations include error rates due to uneven sequencing coverage and gaps in exon capture prior to sequencing, and the variability contributed by the Page 4
5 different platforms and procedures used by different clinical laboratories offering exome sequencing as a clinical service is unknown. Clinical utility The clinical utility of exome sequencing lies in the influence of the results on medical decision making and patient outcomes. There are several ways in which clinical utility can be demonstrated. WES may detect additional mutations that are missed by other testing methods, thus leading to a definitive diagnosis. o If the establishment of a definitive diagnosis leads to management changes that improve outcomes, then clinical utility has been established. o If the establishment of a definitive diagnosis leads to avoidance of other tests that are unnecessary, then this is another example of clinical utility. If WES is at least as accurate as other methods of sequencing, then an improvement in the efficiency of workup (diagnosis obtained more quickly and/or at less cost), then clinical utility has been established. WES in characterizing Mendelian disorders Typically, when a phenotype/history suggests a genetic etiology, microdeletions/duplications should be excluded by chromosomal microarray analysis and, if clinically appropriate, other possible disorders like inborn errors of metabolism should also be excluded. If these tests are negative, the potential uses of WES include facilitating the accurate diagnosis of individuals with a suspected monogenic (Mendelian) disorder that presents with an atypical presentation or multiple congenital anomalies, is difficult to confirm with clinical or laboratory criteria alone (e.g., when disease characteristics are shared among multiple disorders, leading to potentially overlapping differential diagnoses [clinical heterogeneity]), and when there is a long list of possible candidate genes. (3) An additional potential use of WES is when a clinical presentation is suggestive of a specific genetic condition, but targeted testing is negative or unavailable. In this situation, the yield of a definitive diagnosis can be used to evaluate the clinical utility of WES, also considering whether management changes occur that improve outcomes. As cited in a 2013 TEC Special Report, currently there are no published studies that systematically examine potential outcomes of interest such as changes in medical management (including revision of initial diagnoses), and changes in reproductive decision making after a diagnosis of a Mendelian disorder by WES. (4) A small number of studies of patient series, and a larger number of very small series or family studies report anecdotal examples of medical management and reproductive decision-making outcomes of exome sequencing in patients who were not diagnosed by traditional methods. These studies show that over and above traditional molecular and conventional diagnostic testing, exome sequencing can lead to a diagnosis that influences patient care and/or reproductive decisions, but give no indication of the proportion of patients for which this is true. The publication of a large number of small diagnostic studies with Page 5
6 positive results but few with negative results, raise the possibility of publication bias the impact of which is unknown. Summary Whole exome sequencing (WES) using next-generation sequencing has been recently introduced as a laboratory-developed diagnostic clinical laboratory test. A potential major indication for use is molecular diagnosis of patients with a phenotype that is suspicious for a genetic disorder or for patients with known genetic disorders that have a large degree of genetic heterogeneity involving substantial gene complexity. Such patients may be left without a clinical diagnosis of their disorder, despite a lengthy diagnostic work-up involving a variety of traditional molecular and other types of conventional diagnostic tests. For some of these patients, WES, after initial conventional testing has failed to make the diagnosis, may return a likely pathogenic variant. However, at this time, there are many technical limitations to WES that prohibit its use in routine clinical care. The limited experience with WES on a population level leads to gaps in understanding and interpreting ancillary information and variants of uncertain significance. As a result, the risk/benefit ratio of WES testing is poorly defined. Therefore, the use of WES is considered investigational for all indications. Practice Guidelines and Position Statements The American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) states that diagnostic testing with WES (and whole genome sequencing [WGS]) should be considered In the clinical diagnostic assessment of a phenotypically affected individual when: a. The phenotype or family history data strongly implicate a genetic etiology, but the phenotype does not correspond with a specific disorder for which a genetic test targeting a specific gene is available on a clinical basis. b. A patient presents with a defined genetic disorder that demonstrates a high degree of genetic heterogeneity, making WES or WGS analysis of multiple genes simultaneously a more practical approach. c. A patient presents with a likely genetic disorder but specific genetic tests available for that phenotype have failed to arrive at a diagnosis. d. A fetus with a likely genetic disorder in which specific genetic tests, including targeted sequencing tests, available for that phenotype have failed to arrive at a diagnosis. The ACMG states that for screening purposes: WGS/WES may be considered in preconception carrier screening, using a strategy to focus on genetic variants known to be associated with significant phenotypes in homozygous or hemizygous progeny. Page 6
7 ACMG states that WGS/WES should not be used at this time as an approach to prenatal screening, or as a first-tier approach for newborn screening. Available online at: In March 2013, an ACMG board finalized approval of their recommends for reporting incidental findings in whole genome and whole exome sequencing. (5) A working group determined that reporting some incidental findings would likely have medical benefit for the patients and families of patients undergoing clinical sequencing and recommended that when a report is issued for clinically indicated exome and genome sequencing, a minimum list of conditions, genes and variants should be routinely evaluated and reported to the ordering clinician. A full list of the specified conditions can be found online at: Anticipated_Recommendations_on_Incidental_Findings_in_Clinical_Exome_and_Genome_Seq uencing.pdf V. DEFINITIONS NA VI. BENEFIT VARIATIONS The existence of this medical policy does not mean that this service is a covered benefit under the member's contract. Benefit determinations should be based in all cases on the applicable contract language. Medical policies do not constitute a description of benefits. A member s individual or group customer benefits govern which services are covered, which are excluded, and which are subject to benefit limits and which require preauthorization. Members and providers should consult the member s benefit information or contact Capital for benefit information. VII. DISCLAIMER Capital s medical policies are developed to assist in administering a member s benefits, do not constitute medical advice and are subject to change. Treating providers are solely responsible for medical advice and treatment of members. Members should discuss any medical policy related to their coverage or condition with their provider and consult their benefit information to determine if the service is covered. If there is a discrepancy between this medical policy and a member s benefit information, the benefit information will govern. Capital considers the information contained in this medical policy to be proprietary and it may only be disseminated as permitted by law. Page 7
8 VIII. CODING INFORMATION Note: This list of codes may not be all-inclusive, and codes are subject to change at any time. The identification of a code in this section does not denote coverage as coverage is determined by the terms of member benefit information. In addition, not all covered services are eligible for separate reimbursement. There are no specific CPT codes for whole exome sequencing. Investigational therefore not covered: When used to report whole exome sequencing. CPT Codes Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) copyrighted by American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. IX. REFERENCES 1. Dixon-Salazar TJ, Silhavy JL, Udpa N et al. Exome sequencing can improve diagnosis and alter patient management. Sci Transl Med 2012; 4(138):138ra Biesecker LG. Opportunities and challenges for the integration of massively parallel genomic sequencing into clinical practice: lessons from the ClinSeq project. Genet Med 2012; 14(4): Bamshad MJ, Ng SB, Bigham AW et al. Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery. Nat Rev Genet 2011; 12(11): Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Technology Evaluation Center (TEC). Special Report: Exome Sequencing for Clinical Diagnosis of Patients with Suspected Genetic Disorders. TEC Assessments 2013; Volume 28 Tab TBD. 5. Green RC, Berg JS, Grody WW et al. ACMG recommendations for reporting of incidental findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing. Genet Med 2013; 15(7): X. POLICY HISTORY MP CAC 11/26/13 New policy adopting BCBSA. Previously silent, now investigational. Page 8
9 Top Health care benefit programs issued or administered by Capital BlueCross and/or its subsidiaries, Capital Advantage Insurance Company, Capital Advantage Assurance Company and Keystone Health Plan Central. Independent licensees of the BlueCross BlueShield Association. Communications issued by Capital BlueCross in its capacity as administrator of programs and provider relations for all companies. Page 9
Whole Exome and Whole Genome Sequencing for Diagnosis of Genetic Disorders
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Whole Exome and Whole Genome Sequencing for Diagnosis of Genetic
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Whole Exome and Whole Genome Sequencing for Diagnosis of Genetic
Information leaflet. Centrum voor Medische Genetica. Version 1/20150504 Design by Ben Caljon, UZ Brussel. Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel
 Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY TITLE POLICY NUMBER ACUTE INPATIENT REHABILITATION MP-8.003
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: May 27, 2008 May 1, 2008- RETIRED I. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND Inpatient rehabilitation hospitals provide an
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: May 27, 2008 May 1, 2008- RETIRED I. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND Inpatient rehabilitation hospitals provide an
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY TITLE DIABETIC SELF-MANAGEMENT TRAINING PROGRAM POLICY NUMBER MP- 2.076
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2005 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: May 24, 2011 August 31, 2011- RETIRED I. POLICY Initial diabetic self-management training (DSMT) may be considered
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2005 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: May 24, 2011 August 31, 2011- RETIRED I. POLICY Initial diabetic self-management training (DSMT) may be considered
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): October 25, 2011 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 27, 2015 Effective Date: April 1, 2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS
Original Issue Date (Created): October 25, 2011 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 27, 2015 Effective Date: April 1, 2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY TITLE DENTAL AND ORAL SURGERY SERVICES AFTER AN ACCIDENT POLICY NUMBER MP- 1.108
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2005 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: June 29, 2010 May 25, 2011- RETIRED I. POLICY II. Dental and/or oral surgery services (on a limited basis)
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2005 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: June 29, 2010 May 25, 2011- RETIRED I. POLICY II. Dental and/or oral surgery services (on a limited basis)
MEDICAL POLICY I. POLICY OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY (OUTPATIENT) MP-8.004 POLICY TITLE POLICY NUMBER
 Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 3/24/2015 Effective Date: 11/2/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 3/24/2015 Effective Date: 11/2/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine
 Micronova 20.11.2012 Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine Kristiina Assoc. professor, Director of Genetic Department HUSLAB, Helsinki University Central Hospital The Human Genome Packed
Micronova 20.11.2012 Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine Kristiina Assoc. professor, Director of Genetic Department HUSLAB, Helsinki University Central Hospital The Human Genome Packed
Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform
 Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform NextCODE Health is bringing the full power of the world s largest and most successful genomics platform to everyday clinical care NextCODE
Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform NextCODE Health is bringing the full power of the world s largest and most successful genomics platform to everyday clinical care NextCODE
Leading Genomics. Diagnostic. Discove. Collab. harma. Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik
 Leading Genomics Diagnostic harma Discove Collab Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik Global leadership for using the genome to create better medicine WuXi NextCODE provides a uniquely proven and integrated
Leading Genomics Diagnostic harma Discove Collab Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik Global leadership for using the genome to create better medicine WuXi NextCODE provides a uniquely proven and integrated
Just the Facts: A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
 1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
MEDICAL POLICY I. POLICY POLICY TITLE HOME HEALTH POLICY NUMBER MP-3.002
 Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 1/27/2015 Effective Date: 6/1/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 1/27/2015 Effective Date: 6/1/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 1/27/2015 Effective Date: 6/1/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 1/27/2015 Effective Date: 6/1/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
The National Institute of Genomic Medicine (INMEGEN) was
 Genome is...... the complete set of genetic information contained within all of the chromosomes of an organism. It defines the particular phenotype of an individual. What is Genomics? The study of the
Genome is...... the complete set of genetic information contained within all of the chromosomes of an organism. It defines the particular phenotype of an individual. What is Genomics? The study of the
MEDICAL POLICY HIGH-DOSE CHEMOTHERAPY WITH OR WITHOUT AUTOLOGOUS STEM CELL RESCUE FOR AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES, INCLUDING MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS MP-9.
 Original Issue Date (Created): August 23, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: June 17, 2008 July 1, 2009- RETIRED I. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND High dose chemotherapy (HDC) involves the
Original Issue Date (Created): August 23, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: June 17, 2008 July 1, 2009- RETIRED I. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND High dose chemotherapy (HDC) involves the
Human Genome Organization: An Update. Genome Organization: An Update
 Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Professional Practice Medical Record Documentation Guidelines
 Professional Practice Medical Record Documentation Guidelines INTRODUCTION Consistent and complete documentation in the medical record is an essential component of quality patient care. All Participating
Professional Practice Medical Record Documentation Guidelines INTRODUCTION Consistent and complete documentation in the medical record is an essential component of quality patient care. All Participating
Genetic testing. The difference diagnostics can make. The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association
 6 Genetic testing The difference diagnostics can make The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association Genetic INTRODUCTION testing The Department of Health published Our Inheritance, Our Future - Realising
6 Genetic testing The difference diagnostics can make The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association Genetic INTRODUCTION testing The Department of Health published Our Inheritance, Our Future - Realising
Targeted. sequencing solutions. Accurate, scalable, fast TARGETED
 Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
A leader in the development and application of information technology to prevent and treat disease.
 A leader in the development and application of information technology to prevent and treat disease. About MOLECULAR HEALTH Molecular Health was founded in 2004 with the vision of changing healthcare. Today
A leader in the development and application of information technology to prevent and treat disease. About MOLECULAR HEALTH Molecular Health was founded in 2004 with the vision of changing healthcare. Today
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Proteomics-based Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: proteomics_based_testing_related_to_ovarian_cancer 7/2010
Corporate Medical Policy Proteomics-based Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: proteomics_based_testing_related_to_ovarian_cancer 7/2010
Genetic Testing: Scientific Background for Policymakers
 Genetic Testing: Scientific Background for Policymakers Amanda K. Sarata Specialist in Health Policy December 19, 2011 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress Congressional
Genetic Testing: Scientific Background for Policymakers Amanda K. Sarata Specialist in Health Policy December 19, 2011 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress Congressional
G E N OM I C S S E RV I C ES
 GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
School of Nursing. Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD
 Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Quantitative Electroencephalography as a Diagnostic Aid for Attention File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: quantitative_electroencephalography_as_a_diagnostic_aid_for_adhd
Corporate Medical Policy Quantitative Electroencephalography as a Diagnostic Aid for Attention File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: quantitative_electroencephalography_as_a_diagnostic_aid_for_adhd
European registered Clinical Laboratory Geneticist (ErCLG) Core curriculum
 (February 2015; updated from paper issued by the European Society of Human Genetics Ad hoc committee for the accreditation of clinical laboratory geneticists, published in February 2012) Speciality Profile
(February 2015; updated from paper issued by the European Society of Human Genetics Ad hoc committee for the accreditation of clinical laboratory geneticists, published in February 2012) Speciality Profile
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE Q5B
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
GENETIC TESTING FOR INHERITED MUTATIONS OR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CANCER OR OTHER CONDITIONS MED207.110
 GENETIC TESTING FOR INHERITED MUTATIONS OR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CANCER OR OTHER CONDITIONS MED207.110 COVERAGE: Pre- and post-genetic test counseling may be eligible for coverage in addition to the genetic
GENETIC TESTING FOR INHERITED MUTATIONS OR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CANCER OR OTHER CONDITIONS MED207.110 COVERAGE: Pre- and post-genetic test counseling may be eligible for coverage in addition to the genetic
European Medicines Agency
 European Medicines Agency July 1996 CPMP/ICH/139/95 ICH Topic Q 5 B Quality of Biotechnological Products: Analysis of the Expression Construct in Cell Lines Used for Production of r-dna Derived Protein
European Medicines Agency July 1996 CPMP/ICH/139/95 ICH Topic Q 5 B Quality of Biotechnological Products: Analysis of the Expression Construct in Cell Lines Used for Production of r-dna Derived Protein
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing?
 Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
How To Change Medicine
 P4 Medicine: Personalized, Predictive, Preventive, Participatory A Change of View that Changes Everything Leroy E. Hood Institute for Systems Biology David J. Galas Battelle Memorial Institute Version
P4 Medicine: Personalized, Predictive, Preventive, Participatory A Change of View that Changes Everything Leroy E. Hood Institute for Systems Biology David J. Galas Battelle Memorial Institute Version
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
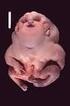 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING
 REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3
 Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES
 PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES BRCA GENETIC TESTING The purpose of this document is to provide guidance to providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance Program (CMAP) on the requirements for
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES BRCA GENETIC TESTING The purpose of this document is to provide guidance to providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance Program (CMAP) on the requirements for
Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care. Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America
 Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America Personalized Medicine Personalized health care is a broad term for interventions
Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America Personalized Medicine Personalized health care is a broad term for interventions
The Future of the Electronic Health Record. Gerry Higgins, Ph.D., Johns Hopkins
 The Future of the Electronic Health Record Gerry Higgins, Ph.D., Johns Hopkins Topics to be covered Near Term Opportunities: Commercial, Usability, Unification of different applications. OMICS : The patient
The Future of the Electronic Health Record Gerry Higgins, Ph.D., Johns Hopkins Topics to be covered Near Term Opportunities: Commercial, Usability, Unification of different applications. OMICS : The patient
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Heredity Grade Ten
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Bioinformatics Resources at a Glance
 Bioinformatics Resources at a Glance A Note about FASTA Format There are MANY free bioinformatics tools available online. Bioinformaticists have developed a standard format for nucleotide and protein sequences
Bioinformatics Resources at a Glance A Note about FASTA Format There are MANY free bioinformatics tools available online. Bioinformaticists have developed a standard format for nucleotide and protein sequences
Diagnostic Scoring System for LQTS
 Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
SNPbrowser Software v3.5
 Product Bulletin SNP Genotyping SNPbrowser Software v3.5 A Free Software Tool for the Knowledge-Driven Selection of SNP Genotyping Assays Easily visualize SNPs integrated with a physical map, linkage disequilibrium
Product Bulletin SNP Genotyping SNPbrowser Software v3.5 A Free Software Tool for the Knowledge-Driven Selection of SNP Genotyping Assays Easily visualize SNPs integrated with a physical map, linkage disequilibrium
Practice Guidelines. Professional Practice Medical Record Documentation Guidelines
 Practice Guidelines 2010 Professional Practice Medical Record Documentation Guidelines Health care benefit programs issued or administered by Capital BlueCross and/or its subsidiaries, Capital Advantage
Practice Guidelines 2010 Professional Practice Medical Record Documentation Guidelines Health care benefit programs issued or administered by Capital BlueCross and/or its subsidiaries, Capital Advantage
Automated DNA sequencing 20/12/2009. Next Generation Sequencing
 DNA sequencing the beginnings Ghent University (Fiers et al) pioneers sequencing first complete gene (1972) first complete genome (1976) Next Generation Sequencing Fred Sanger develops dideoxy sequencing
DNA sequencing the beginnings Ghent University (Fiers et al) pioneers sequencing first complete gene (1972) first complete genome (1976) Next Generation Sequencing Fred Sanger develops dideoxy sequencing
Patient Information. Ordering Physician Information. Indication for Testing (REQUIRED)
 EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Executive summary. Current prenatal screening
 Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
Algorithms in Computational Biology (236522) spring 2007 Lecture #1
 Algorithms in Computational Biology (236522) spring 2007 Lecture #1 Lecturer: Shlomo Moran, Taub 639, tel 4363 Office hours: Tuesday 11:00-12:00/by appointment TA: Ilan Gronau, Taub 700, tel 4894 Office
Algorithms in Computational Biology (236522) spring 2007 Lecture #1 Lecturer: Shlomo Moran, Taub 639, tel 4363 Office hours: Tuesday 11:00-12:00/by appointment TA: Ilan Gronau, Taub 700, tel 4894 Office
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
The Human Genome Project
 The Human Genome Project Brief History of the Human Genome Project Physical Chromosome Maps Genetic (or Linkage) Maps DNA Markers Sequencing and Annotating Genomic DNA What Have We learned from the HGP?
The Human Genome Project Brief History of the Human Genome Project Physical Chromosome Maps Genetic (or Linkage) Maps DNA Markers Sequencing and Annotating Genomic DNA What Have We learned from the HGP?
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics
 G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
Applications of comprehensive clinical genomic analysis in solid tumors: obstacles and opportunities
 Applications of comprehensive clinical genomic analysis in solid tumors: obstacles and opportunities Vincent A. Miller, M.D. Foundation Medicine, Inc. AACR Annual Meeting 2012 Current Concepts session
Applications of comprehensive clinical genomic analysis in solid tumors: obstacles and opportunities Vincent A. Miller, M.D. Foundation Medicine, Inc. AACR Annual Meeting 2012 Current Concepts session
escience and Post-Genome Biomedical Research
 escience and Post-Genome Biomedical Research Thomas L. Casavant, Adam P. DeLuca Departments of Biomedical Engineering, Electrical Engineering and Ophthalmology Coordinated Laboratory for Computational
escience and Post-Genome Biomedical Research Thomas L. Casavant, Adam P. DeLuca Departments of Biomedical Engineering, Electrical Engineering and Ophthalmology Coordinated Laboratory for Computational
Downstream Outcomes of New Molecular Diagnostics CPT Coding System Codes
 Downstream Outcomes of New Molecular Diagnostics CPT Coding System Codes Michael Watson, MS, PhD, FACMG Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders of Newborns and Children April 9, 2014 Disclosures As Executive
Downstream Outcomes of New Molecular Diagnostics CPT Coding System Codes Michael Watson, MS, PhD, FACMG Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders of Newborns and Children April 9, 2014 Disclosures As Executive
Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data
 Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data The Illumina TopHat Alignment and Cufflinks Assembly and Differential Expression apps make RNA data analysis accessible to any user, regardless
Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data The Illumina TopHat Alignment and Cufflinks Assembly and Differential Expression apps make RNA data analysis accessible to any user, regardless
OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Summer Semester, 2015 CLASS SYLLABUS
 OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Summer Semester, 2015 CLASS SYLLABUS Instructor: E-mail: Web site: Virtual Office: Office Hours: Avis Gibons agibons@oakton.edu www.oakton.edu/~agibons online through Desire2Learn
OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Summer Semester, 2015 CLASS SYLLABUS Instructor: E-mail: Web site: Virtual Office: Office Hours: Avis Gibons agibons@oakton.edu www.oakton.edu/~agibons online through Desire2Learn
Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay. June 17, 2016
 Dear Health Care Provider: Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay June 17, 2016 The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency
Dear Health Care Provider: Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers: Interpreting Results from the Aptima Zika Virus Assay June 17, 2016 The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency
Disease gene identification with exome sequencing
 Disease gene identification with exome sequencing Christian Gilissen Dept. of Human Genetics Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre c.gilissen@antrg.umcn.nl Contents Infrastructure Exome sequencing
Disease gene identification with exome sequencing Christian Gilissen Dept. of Human Genetics Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre c.gilissen@antrg.umcn.nl Contents Infrastructure Exome sequencing
RETRIEVING SEQUENCE INFORMATION. Nucleotide sequence databases. Database search. Sequence alignment and comparison
 RETRIEVING SEQUENCE INFORMATION Nucleotide sequence databases Database search Sequence alignment and comparison Biological sequence databases Originally just a storage place for sequences. Currently the
RETRIEVING SEQUENCE INFORMATION Nucleotide sequence databases Database search Sequence alignment and comparison Biological sequence databases Originally just a storage place for sequences. Currently the
Appendix 2 Molecular Biology Core Curriculum. Websites and Other Resources
 Appendix 2 Molecular Biology Core Curriculum Websites and Other Resources Chapter 1 - The Molecular Basis of Cancer 1. Inside Cancer http://www.insidecancer.org/ From the Dolan DNA Learning Center Cold
Appendix 2 Molecular Biology Core Curriculum Websites and Other Resources Chapter 1 - The Molecular Basis of Cancer 1. Inside Cancer http://www.insidecancer.org/ From the Dolan DNA Learning Center Cold
MUTATION, DNA REPAIR AND CANCER
 MUTATION, DNA REPAIR AND CANCER 1 Mutation A heritable change in the genetic material Essential to the continuity of life Source of variation for natural selection New mutations are more likely to be harmful
MUTATION, DNA REPAIR AND CANCER 1 Mutation A heritable change in the genetic material Essential to the continuity of life Source of variation for natural selection New mutations are more likely to be harmful
TECHNOLOGIES, PRODUCTS & SERVICES for MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS, MDx ABA 298
 DIAGNOSTICS BUSINESS ANALYSIS SERIES: TECHNOLOGIES, PRODUCTS & SERVICES for MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS, MDx ABA 298 By ADAMS BUSINESS ASSOCIATES MAY 2014. May 2014 ABA 298 1 Technologies, Products & Services
DIAGNOSTICS BUSINESS ANALYSIS SERIES: TECHNOLOGIES, PRODUCTS & SERVICES for MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS, MDx ABA 298 By ADAMS BUSINESS ASSOCIATES MAY 2014. May 2014 ABA 298 1 Technologies, Products & Services
Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia
 Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia XIII Corso di Formazione Malformazioni Congenite dalla Diagnosi Prenatale alla Terapia Postnatale unipv.eu Carrara, 24 ottobre 2014 Legend:Bluebars
Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia XIII Corso di Formazione Malformazioni Congenite dalla Diagnosi Prenatale alla Terapia Postnatale unipv.eu Carrara, 24 ottobre 2014 Legend:Bluebars
Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research. March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage
 Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage Presentation Overview Core Technology Review Sequence Enrichment Application
Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage Presentation Overview Core Technology Review Sequence Enrichment Application
Guidance on the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act: Implications for Investigators and Institutional Review Boards
 Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP) Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Guidance on the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act: Implications for Investigators and Institutional Review
Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP) Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Guidance on the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act: Implications for Investigators and Institutional Review
Commonly Used STR Markers
 Commonly Used STR Markers Repeats Satellites 100 to 1000 bases repeated Minisatellites VNTR variable number tandem repeat 10 to 100 bases repeated Microsatellites STR short tandem repeat 2 to 6 bases repeated
Commonly Used STR Markers Repeats Satellites 100 to 1000 bases repeated Minisatellites VNTR variable number tandem repeat 10 to 100 bases repeated Microsatellites STR short tandem repeat 2 to 6 bases repeated
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY TITLE POLICY NUMBER SURGICAL TREATMENT OF ACNE AND DERMABRASION MP-1.102
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 26, 2004 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: December 21, 2010 August 31, 2011- RETIRED I. POLICY Surgical Treatment of Acne The surgical excision or
Original Issue Date (Created): July 26, 2004 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: December 21, 2010 August 31, 2011- RETIRED I. POLICY Surgical Treatment of Acne The surgical excision or
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing
 Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Regulatory Issues in Genetic Testing and Targeted Drug Development
 Regulatory Issues in Genetic Testing and Targeted Drug Development Janet Woodcock, M.D. Deputy Commissioner for Operations Food and Drug Administration October 12, 2006 Genetic and Genomic Tests are Types
Regulatory Issues in Genetic Testing and Targeted Drug Development Janet Woodcock, M.D. Deputy Commissioner for Operations Food and Drug Administration October 12, 2006 Genetic and Genomic Tests are Types
If you are signing for a minor child, you refers to your child throughout the consent document.
 CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Adult Patient or Parent, for Minor Patient INSTITUTE: National Cancer Institute PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Raffit Hassan, M.D. STUDY TITLE: Tissue Procurement
CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Adult Patient or Parent, for Minor Patient INSTITUTE: National Cancer Institute PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Raffit Hassan, M.D. STUDY TITLE: Tissue Procurement
Why Disruptive Innovations Matter in Laboratory Diagnostics
 Article: S. Nam.. Clin Chem 2015;61:935-937. http://www.clinchem.org/content/61/7/935.extract Guest: Spencer Nam is a Research Fellow specializing in healthcare at the Clayton Christensen Institute for
Article: S. Nam.. Clin Chem 2015;61:935-937. http://www.clinchem.org/content/61/7/935.extract Guest: Spencer Nam is a Research Fellow specializing in healthcare at the Clayton Christensen Institute for
ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing
 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics ACMG Practice Guidelines ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing Heidi L. Rehm, PhD 1,2, Sherri J. Bale, PhD 3, Pinar Bayrak-Toydemir,
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics ACMG Practice Guidelines ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing Heidi L. Rehm, PhD 1,2, Sherri J. Bale, PhD 3, Pinar Bayrak-Toydemir,
Enhancing Functionality of EHRs for Genomic Research, Including E- Phenotying, Integrating Genomic Data, Transportable CDS, Privacy Threats
 Enhancing Functionality of EHRs for Genomic Research, Including E- Phenotying, Integrating Genomic Data, Transportable CDS, Privacy Threats Genomic Medicine 8 meeting Alexa McCray Christopher G Chute Rex
Enhancing Functionality of EHRs for Genomic Research, Including E- Phenotying, Integrating Genomic Data, Transportable CDS, Privacy Threats Genomic Medicine 8 meeting Alexa McCray Christopher G Chute Rex
Agenda. Regulatory Success. Regulatory Success. Regulatory Success. Antiquated Reimbursement Methodology. Coding Transparency Initiatives
 VALUE-BASED REIMBURSEMENT FOR PERSONALIZED MEDICINE: WHERE DO WE STAND? overview US health care value-based purchasing reforms, explore implications for diagnostics and personalized medicines Michael Longacre,
VALUE-BASED REIMBURSEMENT FOR PERSONALIZED MEDICINE: WHERE DO WE STAND? overview US health care value-based purchasing reforms, explore implications for diagnostics and personalized medicines Michael Longacre,
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation
 PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
patient guide BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer
 patient guide BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer What is hereditary cancer? Cancer affects many people in the U.S.: breast cancer affects 1 in 8 women and ovarian
patient guide BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer What is hereditary cancer? Cancer affects many people in the U.S.: breast cancer affects 1 in 8 women and ovarian
IMMEDIATE HOT LINE: Effective March 2, 2015
 MEDICARE COVERAGE OF LABORATORY TESTING Please remember when ordering laboratory tests that are billed to Medicare/Medicaid or other federally funded programs, the following requirements apply: 1. Only
MEDICARE COVERAGE OF LABORATORY TESTING Please remember when ordering laboratory tests that are billed to Medicare/Medicaid or other federally funded programs, the following requirements apply: 1. Only
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Nazneen Aziz, PhD. Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation Program Office
 2013 Laboratory Accreditation Program Audioconferences and Webinars Implementing Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) as a Clinical Tool in the Laboratory Nazneen Aziz, PhD Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation
2013 Laboratory Accreditation Program Audioconferences and Webinars Implementing Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) as a Clinical Tool in the Laboratory Nazneen Aziz, PhD Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation
EXHIBIT COORDINATING PROVISIONS-STATE/FEDERAL LAW, ACCREDITATION STANDARDS AND GEOGRAPHIC EXCEPTIONS MARYLAND
 EXHIBIT COORDINATING PROVISIONS-STATE/FEDERAL LAW, ACCREDITATION STANDARDS AND GEOGRAPHIC EXCEPTIONS MARYLAND I. INTRODUCTION: Scope. To the extent of any conflict between the Agreement and this State
EXHIBIT COORDINATING PROVISIONS-STATE/FEDERAL LAW, ACCREDITATION STANDARDS AND GEOGRAPHIC EXCEPTIONS MARYLAND I. INTRODUCTION: Scope. To the extent of any conflict between the Agreement and this State
14.3 Studying the Human Genome
 14.3 Studying the Human Genome Lesson Objectives Summarize the methods of DNA analysis. State the goals of the Human Genome Project and explain what we have learned so far. Lesson Summary Manipulating
14.3 Studying the Human Genome Lesson Objectives Summarize the methods of DNA analysis. State the goals of the Human Genome Project and explain what we have learned so far. Lesson Summary Manipulating
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE. Section B: Sex Chromosomes
 CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Markers in Fine Needle Aspirates of the Thyroid
 Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Markers in Fine Needle Aspirates of the Thyroid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_markers_in_fine_needle_aspirates_of_the_thyroid
Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Markers in Fine Needle Aspirates of the Thyroid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_markers_in_fine_needle_aspirates_of_the_thyroid
FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE
 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Genomic Medicine Education Initiatives of the College of American Pathologists
 Genomic Medicine Education Initiatives of the College of American Pathologists Debra G.B. Leonard, MD, PhD, FCAP Chair, Personalized Healthcare Committee, CAP Professor of Pathology, Weill Cornell Medical
Genomic Medicine Education Initiatives of the College of American Pathologists Debra G.B. Leonard, MD, PhD, FCAP Chair, Personalized Healthcare Committee, CAP Professor of Pathology, Weill Cornell Medical
User guide for referring samples to the IBGRL Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory
 International Blood Group Reference Laboratory (IBGRL) IBGRL provides specialist diagnostic services to NHS Blood and Transplant. The Molecular Diagnostics department is a CPA accredited laboratory and
International Blood Group Reference Laboratory (IBGRL) IBGRL provides specialist diagnostic services to NHS Blood and Transplant. The Molecular Diagnostics department is a CPA accredited laboratory and
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE
 AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
Heritability: Twin Studies. Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait
 TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
Overview of testing for Lynch syndrome/hnpcc
 Overview of testing for Lynch syndrome/hnpcc This overview provides detailed information about interpreting MSI/IHC testing and genetic testing for Lynch syndrome/hnpcc. It is intended to be a reference
Overview of testing for Lynch syndrome/hnpcc This overview provides detailed information about interpreting MSI/IHC testing and genetic testing for Lynch syndrome/hnpcc. It is intended to be a reference
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells
 Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review cord_blood_as_a_source_of_stem_cells 2/2001 3/2015 3/2016 3/2015 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review cord_blood_as_a_source_of_stem_cells 2/2001 3/2015 3/2016 3/2015 Description
Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice. Supplementary Guidelines
 Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice Next-generation Sequencing: Standardization of Clinical Testing (Nex-StoCT) Workgroup Principles and Guidelines Supplementary
Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice Next-generation Sequencing: Standardization of Clinical Testing (Nex-StoCT) Workgroup Principles and Guidelines Supplementary
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY TITLE
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: April 15, 2008 July 1, 2009- RETIRED I. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND High dose chemotherapy (HDC) involves the administration
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: April 15, 2008 July 1, 2009- RETIRED I. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND High dose chemotherapy (HDC) involves the administration
