Cardiac Pacemakers (Effective April 30, 2004)
|
|
|
- Garry Cain
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 governing Category B IDE clinical trials. CMS determines that coverage of intracranial PTA and stenting is reasonable and necessary under these circumstances. C. Nationally Non-Covered Indications All other indications for PTA with or without stenting to treat obstructive lesions of the vertebral and cerebral arteries remain non-covered. The safety and efficacy of these procedures are not established. All other indications for PTA without stenting for which CMS has not specifically indicated coverage remain non-covered. D. Other Coverage of PTA with stenting not specifically addressed or discussed in this NCD is at local Medicare contractor discretion Cardiac Pacemakers (Effective April 30, 2004) (Rev. 16, ) Cardiac pacemakers are self-contained, battery-operated units that send electrical stimulation to the heart. They are generally implanted to alleviate symptoms of decreased cardiac output related to abnormal heart rate and/or rhythm. Pacemakers are generally used for persistent, symptomatic second- or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block and symptomatic sinus bradycardia. Cardiac pacemakers are covered as prosthetic devices under the Medicare program, subject to the following conditions and limitations. While cardiac pacemakers have been covered under Medicare for many years, there were no specific guidelines for their use other than the general Medicare requirement that covered services be reasonable and necessary for the treatment of the condition. Services rendered for cardiac pacing on or after the effective dates of this instruction are subject to these guidelines, which are based on certain assumptions regarding the clinical goals of cardiac pacing. While some uses of pacemakers are relatively certain or unambiguous, many other uses require considerable expertise and judgment. Consequently, the medical necessity for permanent cardiac pacing must be viewed in the context of overall patient management. The appropriateness of such pacing may be conditional on other diagnostic or therapeutic modalities having been undertaken. Although significant complications and adverse side effects of pacemaker use are relatively rare, they cannot be ignored when considering the use of pacemakers for dubious medical conditions, or marginal clinical benefit. These guidelines represent current concepts regarding medical circumstances in which permanent cardiac pacing may be appropriate or necessary. As with other areas of medicine, advances in knowledge and techniques in cardiology are expected. Consequently, judgments about the medical necessity and acceptability of new uses for
2 cardiac pacing in new classes of patients may change as more conclusive evidence becomes available. This instruction applies only to permanent cardiac pacemakers, and does not address the use of temporary, non-implanted pacemakers. The two groups of conditions outlined below deal with the necessity for cardiac pacing for patients in general. These are intended as guidelines in assessing the medical necessity for pacing therapies, taking into account the particular circumstances in each case. However, as a general rule, the two groups of current medical concepts may be viewed as representing: Group I: Single-Chamber Cardiac Pacemakers a) conditions under which single chamber pacemaker claims may be considered covered without further claims development; and b) conditions under which single-chamber pacemaker claims would be denied unless further claims development shows that they fall into the covered category, or special medical circumstances exist of the sufficiency to convince the contractor that the claim should be paid. Group II: Dual-Chamber Cardiac Pacemakers - a) conditions under which dual-chamber pacemaker claims may be considered covered without further claims development, and b) conditions under which dual-chamber pacemaker claims would be denied unless further claims development shows that they fall into the covered categories for single- and dualchamber pacemakers, or special medical circumstances exist sufficient to convince the contractor that the claim should be paid. The CMS opened the NCD on Cardiac Pacemakers to afford the public an opportunity to comment on the proposal to revise the language contained in the instruction. The revisions transfer the focus of the NCD from the actual pacemaker implantation procedure itself to the reasonable and necessary medical indications that justify cardiac pacing. This is consistent with our findings that pacemaker implantation is no longer considered routinely harmful or an experimental procedure. Group I: Single-Chamber Cardiac Pacemakers (Effective March 16, 1983) A. Nationally Covered Indications Conditions under which cardiac pacing is generally considered acceptable or necessary, provided that the conditions are chronic or recurrent and not due to transient causes such as acute myocardial infarction, drug toxicity, or electrolyte imbalance. (In cases where there is a rhythm disturbance, if the rhythm disturbance is chronic or recurrent, a single episode of a symptom such as syncope or seizure is adequate to establish medical necessity.) 1. Acquired complete (also referred to as third-degree) AV heart block. 2. Congenital complete heart block with severe bradycardia (in relation to age), or significant physiological deficits or significant symptoms due to the bradycardia.
3 3. Second-degree AV heart block of Type II (i.e., no progressive prolongation of P-R interval prior to each blocked beat. P-R interval indicates the time taken for an impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles on an electrocardiogram). 4. Second-degree AV heart block of Type I (i.e., progressive prolongation of P-R interval prior to each blocked beat) with significant symptoms due to hemodynamic instability associated with the heart block. 5. Sinus bradycardia associated with major symptoms (e.g., syncope, seizures, congestive heart failure); or substantial sinus bradycardia (heart rate less than 50) associated with dizziness or confusion. The correlation between symptoms and bradycardia must be documented, or the symptoms must be clearly attributable to the bradycardia rather than to some other cause. 6. In selected and few patients, sinus bradycardia of lesser severity (heart rate 50-59) with dizziness or confusion. The correlation between symptoms and bradycardia must be documented, or the symptoms must be clearly attributable to the bradycardia rather than to some other cause. 7. Sinus bradycardia is the consequence of long-term necessary drug treatment for which there is no acceptable alternative when accompanied by significant symptoms (e.g., syncope, seizures, congestive heart failure, dizziness or confusion). The correlation between symptoms and bradycardia must be documented, or the symptoms must be clearly attributable to the bradycardia rather than to some other cause. 8. Sinus node dysfunction with or without tachyarrhythmias or AV conduction block (i.e., the bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome, sino-atrial block, sinus arrest) when accompanied by significant symptoms (e.g., syncope, seizures, congestive heart failure, dizziness or confusion). 9. Sinus node dysfunction with or without symptoms when there are potentially lifethreatening ventricular arrhythmias or tachycardia secondary to the bradycardia (e.g., numerous premature ventricular contractions, couplets, runs of premature ventricular contractions, or ventricular tachycardia). 10. Bradycardia associated with supraventricular tachycardia (e.g., atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, or paroxysmal atrial tachycardia) with high-degree AV block which is unresponsive to appropriate pharmacological management and when the bradycardia is associated with significant symptoms (e.g., syncope, seizures, congestive heart failure, dizziness or confusion). 11. The occasional patient with hypersensitive carotid sinus syndrome with syncope due to bradycardia and unresponsive to prophylactic medical measures.
4 12. Bifascicular or trifascicular block accompanied by syncope which is attributed to transient complete heart block after other plausible causes of syncope have been reasonably excluded. 13. Prophylactic pacemaker use following recovery from acute myocardial infarction during which there was temporary complete (third-degree) and/or Mobitz Type II seconddegree AV block in association with bundle branch block. 14. In patients with recurrent and refractory ventricular tachycardia, "overdrive pacing" (pacing above the basal rate) to prevent ventricular tachycardia. (Effective May 9, 1985) 15. Second-degree AV heart block of Type I with the QRS complexes prolonged. B. Nationally Noncovered Indications Conditions which, although used by some physicians as a basis for permanent cardiac pacing, are considered unsupported by adequate evidence of benefit and therefore should not generally be considered appropriate uses for single-chamber pacemakers in the absence of the above indications. Contractors should review claims for pacemakers with these indications to determine the need for further claims development prior to denying the claim, since additional claims development may be required. The object of such further development is to establish whether the particular claim actually meets the conditions in a) above. In claims where this is not the case or where such an event appears unlikely, the contractor may deny the claim 1. Syncope of undetermined cause. 2. Sinus bradycardia without significant symptoms. 3. Sino-atrial block or sinus arrest without significant symptoms. 4. Prolonged P-R intervals with atrial fibrillation (without third-degree AV block) or with other causes of transient ventricular pause. 5. Bradycardia during sleep. 6. Right bundle branch block with left axis deviation (and other forms of fascicular or bundle branch block) without syncope or other symptoms of intermittent AV block). 7. Asymptomatic second-degree AV block of Type I unless the QRS complexes are prolonged or electrophysiological studies have demonstrated that the block is at or beyond the level of the His bundle (a component of the electrical conduction system of the heart).
5 Effective October 1, Asymptomatic bradycardia in post-mycardial infarction patients about to initiate longterm beta-blocker drug therapy. C. Other All other indications for single-chamber cardiac pacing for which CMS has not specifically indicated coverage remain nationally noncovered, except for Category B Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) clinical trials, or as routine costs of singlechamber cardiac pacing associated with clinical trials, in accordance with section of the NCD Manual. Group II: Dual-Chamber Cardiac Pacemakers (Effective May 9, 1985) A. Nationally Covered Indications Conditions under dual-chamber cardiac pacing are considered acceptable or necessary in the general medical community unless conditions 1 and 2 under Group II. B., are present: 1. Patients in who single-chamber (ventricular pacing) at the time of pacemaker insertion elicits a definite drop in blood pressure, retrograde conduction, or discomfort. 2. Patients in whom the pacemaker syndrome (atrial ventricular asynchrony), with significant symptoms, has already been experienced with a pacemaker that is being replaced. 3. Patients in whom even a relatively small increase in cardiac efficiency will importantly improve the quality of life, e.g., patients with congestive heart failure despite adequate other medical measures. 4. Patients in whom the pacemaker syndrome can be anticipated, e.g., in young and active people, etc. Dual-chamber pacemakers may also be covered for the conditions, as listed in Group I. A., if the medical necessity is sufficiently justified through adequate claims development. Expert physicians differ in their judgments about what constitutes appropriate criteria for dual-chamber pacemaker use. The judgment that such a pacemaker is warranted in the patient meeting accepted criteria must be based upon the individual needs and characteristics of that patient, weighing the magnitude and likelihood of anticipated benefits against the magnitude and likelihood of disadvantages to the patient. B. Nationally Noncovered Indications Whenever the following conditions (which represent overriding contraindications) are present, dual-chamber pacemakers are not covered:
6 1. Ineffective atrial contractions (e.g., chronic atrial fibrillation or flutter, or giant left atrium. 2. Frequent or persistent supraventricular tachycardias, except where the pacemaker is specifically for the control of the tachycardia. 3. A clinical condition in which pacing takes place only intermittently and briefly, and which is not associated with a reasonable likelihood that pacing needs will become prolonged, e.g., the occasional patient with hypersensitive carotid sinus syndrome with syncope due to bradycardia and unresponsive to prophylactic medical measures. 4. Prophylactic pacemaker use following recovery from acute myocardial infarction during which there was temporary complete (third-degree) and/or Type II second-degree AV block in association with bundle branch block. C. Other All other indications for dual-chamber cardiac pacing for which CMS has not specifically indicated coverage remain nationally noncovered, except for Category B IDE clinical trials, or as routine costs of dual-chamber cardiac pacing associated with clinical trials, in accordance with section of the NCD Manual. (This NCD last reviewed June 2004.) Cardiac Pacemaker Evaluation Services (Rev. 1, ) CIM 50-1 Medicare covers a variety of services for the post-implant follow-up and evaluation of implanted cardiac pacemakers. The following guidelines are designed to assist contractors in identifying and processing claims for such services. NOTE: These new guidelines are limited to lithium battery-powered pacemakers, because mercury-zinc battery-powered pacemakers are no longer being manufactured and virtually all have been replaced by lithium units. Contractors still receiving claims for monitoring such units should continue to apply the guidelines published in 1980 to those units until they are replaced. There are two general types of pacemakers in current use - single-chamber pacemakers which sense and pace the ventricles of the heart, and dual-chamber pacemakers which sense and pace both the atria and the ventricles. These differences require different monitoring patterns over the expected life of the units involved. One fact of which contractors should be aware is that many dual-chamber units may be programmed to pace only the ventricles; this may be done either at the time the pacemaker is implanted or at some time afterward. In such cases, a dual-chamber unit, when programmed or
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Billing and Coding Guide
 2014 Billing and Coding Guide Contents Links to sections are clickable. To return to the place last viewed: alt+left arrow or right click mouse and select previous view. Introduction Letter to the User
2014 Billing and Coding Guide Contents Links to sections are clickable. To return to the place last viewed: alt+left arrow or right click mouse and select previous view. Introduction Letter to the User
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
GuidePoint. Physician Reimbursement Primer for Cardiac Rhythm Management. With Clinical Case Examples. GuidePoint is simplifying reimbursement.
 GuidePoint GuidePoint is simplifying reimbursement. Physician Reimbursement Primer for Cardiac Rhythm Management With Clinical Case Examples DISCLAIMER Reimbursement information provided by Boston Scientific
GuidePoint GuidePoint is simplifying reimbursement. Physician Reimbursement Primer for Cardiac Rhythm Management With Clinical Case Examples DISCLAIMER Reimbursement information provided by Boston Scientific
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians
 Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
MEDICAL POLICY No. 91104-R7 DETOXIFICATION I. POLICY/CRITERIA
 DETOXIFICATION MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: January 7, 2013 Review Dates: 1/93, 2/97, 4/99, 2/01, 12/01, 2/02, 2/03, 1/04, 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11, 12/12, 12/13, 11/14 Date
DETOXIFICATION MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: January 7, 2013 Review Dates: 1/93, 2/97, 4/99, 2/01, 12/01, 2/02, 2/03, 1/04, 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11, 12/12, 12/13, 11/14 Date
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013
 Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI
 Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Pacemaker Counter and Histogram Operation and Interpretation. Percentage of total count. Figure 2. Detailed ALTRUA Paced and Sensed Event Counters
 A Closer Look SUMMARY This article provides information regarding the operation and interpretation of Event Counters and Histograms available in ALTRUA, INSIGNIA, PULSAR MAX II, and DISCOVERY II pacemakers.
A Closer Look SUMMARY This article provides information regarding the operation and interpretation of Event Counters and Histograms available in ALTRUA, INSIGNIA, PULSAR MAX II, and DISCOVERY II pacemakers.
MRI Case Study MRI Cervical Spine
 MRI Case Study MRI Cervical Spine Jewish Hospital Louisville, KY The Revo MRI SureScan pacing system is MR Conditional designed to allow patients to undergo MRI under the specified conditions for use.
MRI Case Study MRI Cervical Spine Jewish Hospital Louisville, KY The Revo MRI SureScan pacing system is MR Conditional designed to allow patients to undergo MRI under the specified conditions for use.
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
2015 Billing and Coding Guide. Rhythm Management
 2015 Billing and Coding Guide Rhythm Management Links to sections are clickable. Introduction Letter to the User i Disclaimer ii GuidePoint Reimbursement Resources at a Glance Intro 1 Medicare Payment
2015 Billing and Coding Guide Rhythm Management Links to sections are clickable. Introduction Letter to the User i Disclaimer ii GuidePoint Reimbursement Resources at a Glance Intro 1 Medicare Payment
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
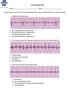 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Addendum to the Guideline on antiarrhythmics on atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter
 22 July 2010 EMA/CHMP/EWP/213056/2010 Addendum to the Guideline on antiarrhythmics on atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter Draft Agreed by Efficacy Working Party July 2008 Adoption by CHMP for release
22 July 2010 EMA/CHMP/EWP/213056/2010 Addendum to the Guideline on antiarrhythmics on atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter Draft Agreed by Efficacy Working Party July 2008 Adoption by CHMP for release
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery
 Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
School of Health Sciences
 School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
510(k) Summary May 7, 2012
 510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
TOP 5. The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac. Arrhythmias in Dogs & Cats. Sinus Arrhythmia. TOP 5 Arrhythmias Seen in Dogs & Cats
 Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect. Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation
 The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Adult Cardiac Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks
 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter
 Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY. Charles Jazra
 RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
RATE VERSUS RHYTHM CONTROL OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: SPECIAL CONSIDERATION IN ELDERLY Charles Jazra NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Age Prevalence, percent
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona
 Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
Ch. 138 CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES 28 138.1 CHAPTER 138. CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES GENERAL PROVISIONS
 Ch. 138 CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES 28 138.1 CHAPTER 138. CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES Sec. 138.1 Principle. 138.2. Definitions. GENERAL PROVISIONS PROGRAM, SERVICE, PERSONNEL AND AGREEMENT REQUIREMENTS
Ch. 138 CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES 28 138.1 CHAPTER 138. CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION SERVICES Sec. 138.1 Principle. 138.2. Definitions. GENERAL PROVISIONS PROGRAM, SERVICE, PERSONNEL AND AGREEMENT REQUIREMENTS
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Introduction. Sinus Rhythms. Premature Beats. Secondary article. John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
 John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol
 Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
What Are Arrhythmias?
 What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Atrial Fibrillation and Ablation Therapy: A Patient s Guide
 Atrial Fibrillation and Ablation Therapy: A Patient s Guide ATRIAL FIBRILLATION CENTER AT UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER www.heart.urmc.edu 585-275-4775 INTRODUCTION Our goal at the Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation and Ablation Therapy: A Patient s Guide ATRIAL FIBRILLATION CENTER AT UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER www.heart.urmc.edu 585-275-4775 INTRODUCTION Our goal at the Atrial Fibrillation
2013 Medicare Physician Coding and Reimbursement Changes
 2013 Medicare Physician Coding and Reimbursement Changes Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent of Medtronic s Economic Strategies
2013 Medicare Physician Coding and Reimbursement Changes Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent of Medtronic s Economic Strategies
Karen Bain James Cook University Hospital Middlesbrough
 Karen Bain James Cook University Hospital Middlesbrough Electrophysiology Electrophysiology... Is the study of the heart s electrical system Assesses the function of each component of cardiac conduction
Karen Bain James Cook University Hospital Middlesbrough Electrophysiology Electrophysiology... Is the study of the heart s electrical system Assesses the function of each component of cardiac conduction
Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA
 Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA Intrinsic Conduction Automaticity-cardiac cells ability to spontaneously depolarize and initiate impulse Depolarization-cardiac cells go to a+ intracellular and
Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA Intrinsic Conduction Automaticity-cardiac cells ability to spontaneously depolarize and initiate impulse Depolarization-cardiac cells go to a+ intracellular and
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Reimbursement Information For Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Service Procedures 1
 GE Healthcare Information For Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Procedures 1 2011 Update www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage, and payment for electrophysiology procedures
GE Healthcare Information For Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Procedures 1 2011 Update www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage, and payment for electrophysiology procedures
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
Advances in the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation At VCU Medical Center
 Contact Us For additional information or to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists, please call: Ken Ellenbogen, M.D. Cardiology/Electrophysiology 804-828-7565 or 804-628-0147 You can also
Contact Us For additional information or to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists, please call: Ken Ellenbogen, M.D. Cardiology/Electrophysiology 804-828-7565 or 804-628-0147 You can also
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm
 Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, ARRHYTHMIAS AND PACING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
2320-6691 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 ISSN 2347-954X
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3B):1132-1136 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation
 Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
The Heart Rhythm Charity
 The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2006 Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rhythm)
The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2006 Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rhythm)
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Atrial fibrillation. Quick reference guide. Issue date: June 2006. The management of atrial fibrillation
 Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
HEART RHYTHM DISORDERS CRAIG A. McPHERSON, M.D., AND LYNDA E. ROSENFELD, M.D.
 HEART RHYTHM DISORDERS CRAIG A. McPHERSON, M.D., AND LYNDA E. ROSENFELD, M.D. INTRODUCTION Heart rhythm disorders, called arrhythmias, pose one of the paradoxes of medicine. Almost anyone s heart will
HEART RHYTHM DISORDERS CRAIG A. McPHERSON, M.D., AND LYNDA E. ROSENFELD, M.D. INTRODUCTION Heart rhythm disorders, called arrhythmias, pose one of the paradoxes of medicine. Almost anyone s heart will
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
Electrolyte Physiology. Something in the way she moves
 Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
A randomized, controlled trial comparing the efficacy of carvedilol vs. metoprolol in the treatment of atrial fibrillation
 A randomized, controlled trial comparing the efficacy of carvedilol vs. metoprolol in the treatment of atrial fibrillation Gabriel Sayer Lay Abstract: Atrial fibrillation is a common form of irregular,
A randomized, controlled trial comparing the efficacy of carvedilol vs. metoprolol in the treatment of atrial fibrillation Gabriel Sayer Lay Abstract: Atrial fibrillation is a common form of irregular,
Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information
 AF A Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
AF A Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
Local Coverage Article: NCD Coding Article for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans Used for Non- Oncologic Conditions (A53134)
 Local Coverage Article: NCD Coding Article for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans Used for Non- Oncologic Conditions (A53134) Contractor Information Contractor Name Novitas Solutions, Inc. Article
Local Coverage Article: NCD Coding Article for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans Used for Non- Oncologic Conditions (A53134) Contractor Information Contractor Name Novitas Solutions, Inc. Article
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD
 92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
