Spanning Tree Protocol Inter-VLAN Routing
|
|
|
- Tobias Higgins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spanning Tree Protocol Inter-VLAN Routing Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1
2 Objectives Fundamentals of Spanning Tree Protocol RSTP MSTP EtherChannel Routing between VLANs External route processors CEF-based multilayer switching Internal route processors 2
3 Transparent Bridges Do not modify frames that are forwarded Learns addresses by listening on a port Forwards broadcasts and unknown unicasts on all ports 3
4 Redundant Topologies Layer 2 redundancy improves the availability Implementing alternate paths by adding equipment and cabling Goal to eliminate network outages caused by a single point of failure All networks need redundancy for enhanced reliability Simple Redundant Switched Topology 4
5 Issues with Redundancy Layer 2 loops Broadcast storms Duplicate unicast frames MAC database instability 5
6 Redundant Topologies Layer 2 loops Broadcast storm 6
7 Redundant Topologies Duplicate unicast frames MAC Database Instability 7
8 Explaining a Loop Free Network Loop free network can be achieved manually by shutting down or disconnect redundant links STP runs a Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) to find and block redundant links 8
9 Implementing Spanning Tree With STP, a transparent bridge environment can be redundant STP protect the network against accidental miscabling 9
10 Implementing Spanning Tree STP executes an algorithm called STA. STA chooses a reference point, called a root bridge, and then determines the available paths to that reference point. If more than two paths exists, STA picks the best path and blocks the rest 10
11 Port Roles Root port Switch port closest to the root bridge Designated port All non-root ports that are still permitted to forward traffic Non-designated port All ports configured to be in blocking state to prevent loops 11
12 Spanning-Tree Operation Electing a root bridge Selecting the root port on the non-root bridges Selecting the designated port on each segment How do the switches do this election? 12
13 BPDU Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) is sent between switches to establish and maintain a loop free topology Root ID The lowest BID in the topology Cost of Path Cost of all links from the transmitting switch to the root bridge Bridge ID (BID) of the transmitting switch Port ID Transmitting switch port ID STP timer values Max_Age, Hello Time, Forward Delay 13
14 Bridge PDU (Protocol Data Unit) Each switch in the broadcast domain initially assumes that it is the root bridge 14
15 Bridge ID Lower BID values are preferred Default priority =
16 BPDU Process Electing a root bridge BPDUs are sent in the broadcast domain Compare Bridge IDs One root port is elected on each switch Compares the path costs on all switch ports Lowest overall path cost to the root is automatically assigned the root port role Assign designated and non-designated ports All switch ports in the root bridge will be designated Two switches connected to the same segment sends BPDUs, and the lowest will become designated 16
17 Spanning-Tree Operation 17
18 Spanning Tree Operation One root bridge per network One root port per nonroot bridge One designated port per segment Nondesignated ports are blocking 18
19 Spanning Tree Operation Port states (forward or block) based on: Lowest path cost Lowest sender BID Lowest sender port ID 19
20 Port States 20
21 STP Timers 21
22 STP Port States 22
23 Spanning Tree Enhancements Implementation of : Portfast Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol 802.1w (RSTP) Per VLAN Spanning Tree 802.1q (PVST +) Multiple Spanning Tree 802.1s (MST) Load balancing across links 23
24 PortFast Causes an interface to transition from blocking to forwarding state immediately Do not go through the listening and learning states Configure PortFast on access ports connected to a single server or workstation (or globally on all nontrunking interfaces) Prevents DHCP timeouts 24
25 Rapid Spanning Tree - RSTP STP convergence time = seconds RSTP offers better recovery at layer 2 RSTP requires full-duplex point-to-point connection Alternate and Backup Ports Edge Ports do not participate in STP 25
26 RSTP Port Roles Alternate port Offers an alternate path toward the root bridge Backup port Additional port with a redundant link to the segment 26
27 RSTP Port Roles Edge port A switch port never intended to connect to another switch device Transition to forwarding state immediately If BPDU is received, it becomes a normal spanning-tree port 27
28 RSTP Port States Discarding Prevents the forwarding of data frames Learning Accepts data frames to populate the MAC table, to limit flooding of unknown unicast frames Forwarding Forwarding of data frames in stable active topologies 28
29 Configuring Access Port Macro Use the switchport host macro command on an interface connecting to an end station. Switch(config-if)# switchport host switchport mode will be set to access spanning-tree portfast will be enabled channel group will be disabled Switch(config-if)# end Switch# 29
30 Multiple Spanning Tree - MSTP MST (IEEE 802.1s) extends the IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) algorithm to multiple spanning-trees Main purpose is to reduce the total number of spanning tree instances to match the physical topology Grouping VLANs and associate with spanning tree instances 30
31 MST Use of Extended System ID MST carries the instance number in the 12-bit Extended System ID field of the Bridge ID. 31
32 MST Configuration Example SwitchA(config)# spanning-tree mode mst SwitchA(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration SwitchA(config-mst)# name XYZ SwitchA(config-mst)# revision 1 SwitchA(config-mst)# instance 1 vlan 11, 21, 31 SwitchA(config-mst)# instance 2 vlan 12, 22, 32 SwitchA(config)# spanning-tree mst 1 root primary SwitchB(config)# spanning-tree mode mst SwitchB(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration SwitchB(config-mst)# name XYZ SwitchB(config-mst)# revision 1 SwitchB(config-mst)# instance 1 vlan 11, 21, 31 SwitchB(config-mst)# instance 2 vlan 12, 22, 32 SwitchB(config)# spanning-tree mst 2 root primary 32
33 Spanning Tree Enhancements BPDU guard: Prevents accidental connection of switching devices to PortFast-enabled ports. Connecting switches to PortFast-enabled ports can cause Layer 2 loops or topology changes. BPDU filtering: Restricts the switch from sending unnecessary BPDUs out access ports. Root guard: Prevents switches connected on ports configured as access ports from becoming the root switch. Loop guard: Prevents root ports and alternate ports from moving to forwarding state when they stop receiving BPDUs. 33
34 BPDU Guard BPDU Guard puts an interface configured for STP PortFast in the errdisable state upon receipt of a BPDU. BPDU guard disables interfaces as a preventive step to avoid potential bridging loops. BPDU guard shuts down PortFast-configured interfaces that receive BPDUs, rather than putting them into the STP blocking state (the default behavior). In a valid configuration, PortFast-configured interfaces should not receive BPDUs. Reception of a BPDU by a PortFast-configured interface signals an invalid configuration, such as connection of an unauthorized device. BPDU guard provides a secure response to invalid configurations, because the administrator must manually re-enable the err-disabled interface after fixing the invalid configuration. It is also possible to set up a time-out interval after which the switch automatically tries to reenable the interface. However, if the invalid configuration still exists, the switch err-disables the interface again. 34
35 BPDU Filtering BPDU filtering prevents a Cisco switch from sending BPDUs on PortFastenabled interfaces, preventing unnecessary BPDUs from being transmitted to host devices. BPDU guard has no effect on an interface if BPDU filtering is enabled. When enabled globally, BPDU filtering has these attributes: It affects all operational PortFast ports on switches that do not have BPDU filtering configured on the individual ports. If BPDUs are seen, the port loses its PortFast status, BPDU filtering is disabled, and STP sends and receives BPDUs on the port as it would with any other STP port on the switch. Upon startup, the port transmits ten BPDUs. If this port receives any BPDUs during that time, PortFast and PortFast BPDU filtering are disabled. When enabled on an interface, BPDU filtering has these attributes: It ignores all BPDUs received. It sends no BPDUs. 35
36 Root Guard Root guard is useful in avoiding Layer 2 loops during network anomalies. The Root guard feature forces an interface to become a designated port to prevent surrounding switches from becoming root bridges. Root guard-enabled ports are forced to be designated ports. If the bridge receives superior STP BPDUs on a Root guard-enabled port, the port moves to a root-inconsistent STP state, which is effectively equivalent to the STP listening state, and the switch does not forward traffic out of that port. As a result, this feature enforces the position of the root bridge. 36
37 Root Guard Motivation Switches A and B comprise the core of the network. Switch A is the root bridge. Switch C is an access layer switch. When Switch D is connected to Switch C, it begins to participate in STP. If the priority of Switch D is 0 or any value lower than that of the current root bridge, Switch D becomes the root bridge. Having Switch D as the root causes the Gigabit Ethernet link connecting the two core switches to block, thus causing all the data to flow via a 100-Mbps link across the access layer. This is obviously a terrible outcome. 37
38 Root Guard Operation After the root guard feature is enabled on a port, the switch does not enable that port to become an STP root port. Cisco switches log the following message when a root guard enabled port receives a superior BPDU: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARDBLOCK: Port 1/1 tried to become nondesignated in VLAN 77. Moved to root-inconsistent state. 38
39 Root Guard Operation The current design recommendation is to enable root guard on all access ports so that a root bridge is not established through these ports. In this configuration, Switch C blocks the port connecting to Switch D when it receives a superior BPDU. The port transitions to the root-inconsistent STP state. No traffic passes through the port while it is in root-inconsistent state. When Switch D stops sending superior BPDUs, the port unblocks again and goes through regular STP transition of listening and learning, and eventually to the forwarding state. Recovery is automatic; no intervention is required. 39
40 Loop Guard The Loop Guard STP feature improves the stability of Layer 2 networks by preventing bridging loops. In STP, switches rely on continuous reception or transmission of BPDUs, depending on the port role. A designated port transmits BPDUs whereas a nondesignated port receives BPDUs. Bridging loops occur when a port erroneously transitions to forwarding state because it has stopped receiving BPDUs. Ports with loop guard enabled do an additional check before transitioning to forwarding state. If a nondesignated port stops receiving BPDUs, the switch places the port into the STP loop-inconsistent blocking state. If a switch receives a BPDU on a port in the loop-inconsistent STP state, the port transitions through STP states according to the received BPDU. As a result, recovery is automatic, and no manual intervention is necessary. 40
41 Loop Guard Messages When the Loop Guard feature places a port into the loop-inconsistent blocking state, the switch logs the following message: SPANTREE-2-LOOPGUARDBLOCK: No BPDUs were received on port 3/2 in vlan 3. Moved to loop-inconsistent state. After recovery, the switch logs the following message: SPANTREE-2-LOOPGUARDUNBLOCK: port 3/2 restored in vlan 3. 41
42 Loop Guard Operation 42
43 Loop Guard Configuration Considerations Configure Loop Guard on a per-port basis, although the feature blocks inconsistent ports on a per-vlan basis; for example, on a trunk port, if BPDUs are not received for only one particular VLAN, the switch blocks only that VLAN (that is, moves the port for that VLAN to the loop-inconsistent STP state). In the case of an EtherChannel interface, the channel status goes into the inconsistent state for all the ports belonging to the channel group for the particular VLAN not receiving BPDUs. Enable Loop Guard on all nondesignated ports. Loop guard should be enabled on root and alternate ports for all possible combinations of active topologies. Loop Guard is disabled by default on Cisco switches. 43
44 Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) The link between Switches B and C becomes unidirectional. Switch B can receive traffic from Switch C, but Switch C cannot receive traffic from Switch B. On the segment between Switches B and C, Switch B is the designated bridge sending the root BPDUs and Switch C expects to receive the BPDUs. Switch C waits until the max-age timer (20 seconds) expires before it takes action. When this timer expires, Switch C moves through the listening and learning states and then to the forwarding state. At this moment, both Switch B and Switch C are forwarding to each other and there is no blocking port in the network. 44
45 UDLD Modes Normal Mode UDLD detects unidirectional links due to misconnected interfaces on fiber-optic connections. UDLD changes the UDLDenabled port to an undetermined state if it stops receiving UDLD messages from its directly connected neighbor. Aggressive Mode (Preferred) When a port stops receiving UDLD packets, UDLD tries to reestablish the connection with the neighbor. After eight failed retries, the port state changes to the err-disable state. Aggressive mode UDLD detects unidirectional links due to oneway traffic on fiber-optic and twisted-pair links and due to misconnected interfaces on fiber-optic links. 45
46 Flex Links Flex Links is a Layer 2 availability feature that provides an alternative solution to STP and allows users to turn off STP and still provide basic link redundancy. Flex Links can coexist with spanning tree on the distribution layer switches; however, the distribution layer switches are unaware of the Flex Links feature. Flex Links enables a convergence time of less than 50 milliseconds. In addition, this convergence time remains consistent regardless of the number of VLANs or MAC addresses configured on switch uplink ports. Flex Links is based on defining an active/standby link pair on a common access switch. Flex Links are a pair of Layer 2 interfaces, either switchports or port channels, that are configured to act as backup to other Layer 2 interfaces. 46
47 EtherChannel Bundles individual Ethernet links into a single logical link Up to 8 physical links can be bundle together Usually used for trunk links Provides high bandwidth Load balancing Automatic failover Simplifies subsequent logical configuration (does not need to configure each physical link) 47
48 EtherChannel - Protocols PAgP Port Aggregation Protocol Cisco proprietary PAgP packets sent between ports to negotiate the forming of a channel Ensures that all ports have the same type of configuration LACP Link Aggregation Protocol IEEE 802.3ad standard Allows several physical ports to be bundled together to form a single logical channel 48
49 PAgP Modes Mode Auto Desirable On Nonsilent Purpose Places an interface in a passive negotiating state in which the interface responds to the PAgP packets that it receives but does not initiate PAgP negotiation (default). Places an interface in an active negotiating state in which the interface initiates negotiations with other interfaces by sending PAgP packets. Interfaces configured in the on mode do not exchange PAgP packets. Forces the interface to channel without PAgP. If a switch is connected to a partner that is PAgP-capable, configure the switch interface for non-silent operation. The non-silent keyword is always used with the auto or desirable mode. If you do not specify non-silent with the auto or desirable mode, silent is assumed. The silent setting is for connections to file servers or packet analyzers; this setting enables PAgP to operate, to attach the interface to a channel group, and to use the interface for transmission. 49
50 LACP Modes Mode Passive Active On Purpose Places a port in a passive negotiating state. In this state, the port responds to the LACP packets that it receives but does not initiate LACP packet negotiation (default). Places a port in an active negotiating state. In this state, the port initiates negotiations with other ports by sending LACP packets. Forces the interface to the channel without PAgP or LACP. 50
51 Inter-VLAN Routing Options External router with a separate interface for each VLAN. External router trunked to Layer 2 switch (router-on-a-stick). Multilayer switch (pictured). 51
52 Inter-VLAN routing with external router L3 capability is needed to communicate between VLANs Trunk between switch and router Sub-interfaces configured on the router for all VLANs 52
53 Inter-VLAN routing with external router Advantages: Implementation is simple Layer 3 services not required on the switch Router provides communication between VLANs Disadvantages: The router is a single point of failure Traffic path between switch and router may become congested Latency is higher than on Layer 3 switch 53
54 Multilayer switching - MLS Combines the functionality of a switch and a router into one device Software based routing process (packet re-writing) to specialized ASIC hardware Optimized for campus LAN When MLS s own MAC address is in Layer 2 header Destined for the MLS or Destination IP address is compared against Layer 3 forwarding table 54
55 High-Speed Memory Tables Multilayer switches build routing, bridging, QoS, and ACL tables for centralized or distributed switching. Switches perform lookups in these tables to make decisions, such as to determine whether a packet with a specific destination IP address is supposed to be dropped according to an ACL. These tables support high-performance lookups and search algorithms to maintain line-rate performance. Multilayer switches deploy these memory tables using specialized memory architectures, referred to as content addressable memory (CAM), and ternary content addressable memory (TCAM). 55
56 Tables CAM table: Primary table used to make Layer 2 forwarding decisions. The table is built by recording the source address and inbound port of all frames. When a frame arrives at the switch with a destination MAC address of an entry in the CAM table, the frame is forwarded out only through the port associated with that specific MAC address. TCAM table: Stores ACL, QoS, and other information generally associated with upper-layer processing. TCAM is most useful for building tables for searching on the longest match, such as IP routing tables organized by IP prefixes. 56
57 Switch Virtual Interface - SVI Virtual Layer 3 interface configured for any VLAN Acts as a default gateway for a VLAN and traffic can be routed between VLANs Provide Layer 3 IP connectivity to the switch Support routing protocols 57
58 Routed ports on a multilayer switch Physical switch port capable of Layer 3 packet processing Not associated with a particular VLAN Switch port functionality is removed Behaves like a regular router interface, but does not support subinterfaces 58
59 Routed ports on a multilayer switch 59
60 Distributed Hardware Forwarding Layer 3 switching software employs a distributed architecture in which the control path and data path are relatively independent. The control path code, such as routing protocols, runs on the route processor. Each interface module includes a microcoded processor that handles all packet forwarding. The Ethernet interface module and the switching fabric forward most of the data packets. 60
61 Cisco Switching Methods Process Switching Fast Switching Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) 61
62 Cisco Switching Methods Process Switching Router strips off the Layer 2 header for each incoming frame Looks up the Layer 3 destination network address in the routing table for each packet, and then sends the frame with rewritten Layer 2 header, including computed cyclic redundancy check (CRC), to the outgoing interface. All these operations are done by software running on the CPU for each individual frame. Process switching is the most CPU-intensive method available in Cisco routers. It can greatly degrade performance and is generally used only as a last resort or during troubleshooting. 62
63 Cisco Switching Methods Fast Switching After the lookup of the first packet destined for a particular IP network, the router initializes the fast-switching cache used by the fast switching mode. When subsequent frames arrive, the destination is found in this fastswitching cache. The frame is rewritten with corresponding link addresses and is sent over the outgoing interface. 63
64 Cisco Switching Methods - CEF The default-switching mode. CEF is less CPU-intensive than fast switching or process switching. A router with CEF enabled uses information from tables built by the CPU, such as the routing table and ARP table, to build hardware-based tables known as the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) and adjacency tables. These tables are then used to make hardware-based forwarding decisions for all frames in a data flow Although CEF is the fastest switching mode, there are limitations, such as other features that are not compatible with CEF or rare instances in which CEF functions can actually degrade performance, such as CEF polarization in a topology using load-balanced Layer 3 paths. 64
65 Cisco Forwarding Decision Methods Route caching: Also known as flow-based or demand-based switching, a Layer 3 route cache is built within hardware functions as the switch sees traffic flow into the switch. This is functionally equivalent to Fast Switching in the Cisco router IOS. Topology-based switching: Information from the routing table is used to populate the route cache, regardless of traffic flow. The populated route cache is called the FIB. CEF is the facility that builds the FIB. This is functionally equivalent to CEF in the Cisco router IOS. 65
66 Route Caching First packet in a stream is switched in software by the route processor. Information is stored in cache table as a flow. All subsequent packets are switched in hardware. 66
67 Topology-Based Switching Faster than route caching. Even first packet forwarded by hardware. CEF populates FIB with information from routing table. 67
68 CEF Processing CEF uses special strategies to switch data packets to their destinations expediently. It caches the information generated by the Layer 3 routing engine even before the switch encounters any data flows. CEF caches routing information in one table (FIB) and caches Layer 2 next-hop addresses and frame header rewrite information for all FIB entries in another table, called the adjacency table (AT). 68
69 Forwarding Information Base (FIB) Derived from the IP routing table. Arranged for maximum lookup throughput. IP destination prefixes stored in TCAM, from most-specific to leastspecific entry. FIB lookup based on Layer 3 destination address prefix (longest match) matches structure of CEF entries within the TCAM. When TCAM full, wildcard entry redirects frames to the Layer 3 engine. Updated after each network change but only once. Each change in the IP routing table triggers a similar change in the FIB. Contains all known routes. Contains all next-hop addresses associated with all destination networks. 69
70 Adjacency Table (AT) Derived from ARP table and contains Layer 2 header rewrite (MAC) information for each next hop contained in the FIB. Nodes in network are said to be adjacent if they are within a single hop from each other. Maintains Layer 2 next-hop addresses and link-layer header information for all FIB entries. Populated as adjacencies are discovered. Each time adjacency entry created (such as via ARP), a Layer 2 header for that adjacent node is pre-computed and stored in the adjacency table. When the adjacency table is full, a CEF TCAM entry points to the Layer 3 engine to redirect the adjacency. 70
71 CEF-based multilayer switches Packets not processed in hardware: IP packets that use IP header options Packets forwarded to a tunnel interface Packets with non-supported encapsulation types Packet that exceed the maximum transmission unit (MTU) 71
72 CEF-based MLS Operation Step 1: Host A sends a packet to Host B. The switch recognizes the frame as a Layer 3 packet because the destination MAC (MAC-M) matches the Layer 3 engine MAC 72
73 CEF-based MLS Operation Step 2: The switch performs a CEF lookup based on the destination IP address (IP-B). The packets hits the CEF entry for the connected network (VLAN20) and is redirected to the Layer 3 engine 73
74 CEF-based MLS Operation Step 3: The Layer 3 engine installs an ARP adjacency in the switch for Host B IP address Step 4: The Layer 3 engine sends ARP requests for Host B on VLAN20 74
75 CEF-based MLS Operation Step 5: Host B sends an ARP response to the Layer 3 engine Step 6: The Layer 3 engine installs the resolved adjacency in the switch 75
76 CEF-based MLS Operation Step 7: The switch forwards the packet to Host B Step 8: The switch receives a subsequent packet for Host B (IP-B) 76
77 CEF-based MLS Operation Step 9: The switch performs a Layer 3 lookup and finds a CEF entry for Host B. The entry points to the adjacency with rewrite information for Host B 77
78 CEF-based MLS Operation Step 10: The switch rewrites packet per the adjacency information and forwards the packet to Host B on VLAN20 78
79 Summary STP protects the network from loops RSTP quickly adapts to network topology transitions MSTP reduces the burden of STP traffic and CPU processing EtherChannel adds redundancy and creates high-bandwidth connections between switches 79
80 Summary An external router can be configured to route packets between the VLANs on a Layer 2 switch Multilayer switches allow routing and the configuration of interfaces to pass packets between VLANs CEF-based multilayer switching facilitates packet switching in hardware 80
Objectives. The Role of Redundancy in a Switched Network. Layer 2 Loops. Broadcast Storms. More problems with Layer 2 loops
 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
CHAPTER 10 LAN REDUNDANCY. Scaling Networks
 CHAPTER 10 LAN REDUNDANCY Scaling Networks CHAPTER 10 10.0 Introduction 10.1 Spanning Tree Concepts 10.2 Varieties of Spanning Tree Protocols 10.3 Spanning Tree Configuration 10.4 First-Hop Redundancy
CHAPTER 10 LAN REDUNDANCY Scaling Networks CHAPTER 10 10.0 Introduction 10.1 Spanning Tree Concepts 10.2 Varieties of Spanning Tree Protocols 10.3 Spanning Tree Configuration 10.4 First-Hop Redundancy
Chapter 3. Enterprise Campus Network Design
 Chapter 3 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1 Overview The network foundation hosting these technologies for an emerging enterprise should be efficient, highly available, scalable, and manageable. This
Chapter 3 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1 Overview The network foundation hosting these technologies for an emerging enterprise should be efficient, highly available, scalable, and manageable. This
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks. Chapter 5: Ethernet
 CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching
 CCNP 3 v5 - Chapter 4 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing VLANs VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks Network devices in different
CCNP 3 v5 - Chapter 4 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing VLANs VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks Network devices in different
- Spanning Tree Protocol -
 1 Switching Loops - Spanning Tree Protocol - A Layer-2 switch belongs to only one broadcast domain, and will forward both broadcasts and multicasts out every port but the originating port. When a switching
1 Switching Loops - Spanning Tree Protocol - A Layer-2 switch belongs to only one broadcast domain, and will forward both broadcasts and multicasts out every port but the originating port. When a switching
IMPLEMENTING CISCO SWITCHED NETWORKS V2.0 (SWITCH)
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO SWITCHED NETWORKS V2.0 (SWITCH) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Switched Networks (SWITCH) v2.0 is a five-day instructor-led training course developed to help students prepare for
IMPLEMENTING CISCO SWITCHED NETWORKS V2.0 (SWITCH) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Switched Networks (SWITCH) v2.0 is a five-day instructor-led training course developed to help students prepare for
RESILIENT NETWORK DESIGN
 Matěj Grégr RESILIENT NETWORK DESIGN 1/36 2011 Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology, Matěj Grégr, igregr@fit.vutbr.cz Campus Best Practices - Resilient network design Campus
Matěj Grégr RESILIENT NETWORK DESIGN 1/36 2011 Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology, Matěj Grégr, igregr@fit.vutbr.cz Campus Best Practices - Resilient network design Campus
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Objectives. Explain the Role of Redundancy in a Converged Switched Network. Explain the Role of Redundancy in a Converged Switched Network
 Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged network Summarize how STP works to eliminate Layer 2 loops in a converged
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged network Summarize how STP works to eliminate Layer 2 loops in a converged
Configuring EtherChannels
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional)
 Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional) CCNP Route (642-902) EIGRP Chapter: EIGRP Overview and Neighbor Relationships EIGRP Neighborships Neighborship over WANs EIGRP Topology, Routes,
Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional) CCNP Route (642-902) EIGRP Chapter: EIGRP Overview and Neighbor Relationships EIGRP Neighborships Neighborship over WANs EIGRP Topology, Routes,
Switching in an Enterprise Network
 Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
- EtherChannel - Port Aggregation
 1 Port Aggregation - EtherChannel - A network will often span across multiple switches. Trunk ports are usually used to connect switches together. There are two issues with using only a single physical
1 Port Aggregation - EtherChannel - A network will often span across multiple switches. Trunk ports are usually used to connect switches together. There are two issues with using only a single physical
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
hp ProLiant network adapter teaming
 hp networking june 2003 hp ProLiant network adapter teaming technical white paper table of contents introduction 2 executive summary 2 overview of network addressing 2 layer 2 vs. layer 3 addressing 2
hp networking june 2003 hp ProLiant network adapter teaming technical white paper table of contents introduction 2 executive summary 2 overview of network addressing 2 layer 2 vs. layer 3 addressing 2
High Availability Failover Optimization Tuning HA Timers PAN-OS 6.0.0
 High Availability Failover Optimization Tuning HA Timers PAN-OS 6.0.0 Revision C 2013, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Passive Link State Auto Configuration (A/P)...
High Availability Failover Optimization Tuning HA Timers PAN-OS 6.0.0 Revision C 2013, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Passive Link State Auto Configuration (A/P)...
Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide
 Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide Overview A virtual PortChannel (vpc) allows links that are physically connected to two different Cisco Nexus 5000 Series devices to appear as a single PortChannel
Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide Overview A virtual PortChannel (vpc) allows links that are physically connected to two different Cisco Nexus 5000 Series devices to appear as a single PortChannel
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example
 Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000
 Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
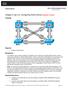 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
IP SAN BEST PRACTICES
 IP SAN BEST PRACTICES PowerVault MD3000i Storage Array www.dell.com/md3000i TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 OVERVIEW ISCSI... 3 IP SAN DESIGN... 4 BEST PRACTICE - IMPLEMENTATION...
IP SAN BEST PRACTICES PowerVault MD3000i Storage Array www.dell.com/md3000i TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 OVERVIEW ISCSI... 3 IP SAN DESIGN... 4 BEST PRACTICE - IMPLEMENTATION...
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
AT-S60 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8400 Series Switch. Software Release Notes
 AT-S60 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8400 Series Switch Supported Platforms Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S60 management software. The AT-S60
AT-S60 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8400 Series Switch Supported Platforms Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S60 management software. The AT-S60
AlliedWare Plus OS How To Configure interoperation between PVST+ and RSTP or MSTP
 AlliedWare Plus OS How To Configure interoperation between PVST+ and RSTP or MSTP Introduction Spanning trees that protect networks from loops can provide better traffic load balancing if traffic in different
AlliedWare Plus OS How To Configure interoperation between PVST+ and RSTP or MSTP Introduction Spanning trees that protect networks from loops can provide better traffic load balancing if traffic in different
- Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers -
 1 Layered Communication - Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers - Network communication models are generally organized into layers. The OSI model specifically consists of seven layers, with each layer representing
1 Layered Communication - Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers - Network communication models are generally organized into layers. The OSI model specifically consists of seven layers, with each layer representing
Fundamentals of Switching
 1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
6/8/2011. Document ID: 12023. Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used. Conventions. Introduction
 Page 1 of 9 Products & Services Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
Page 1 of 9 Products & Services Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1
 640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1 Course Introduction Course Introduction Chapter 01 - Small Network Implementation Introducing the Review Lab Cisco IOS User Interface Functions
640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1 Course Introduction Course Introduction Chapter 01 - Small Network Implementation Introducing the Review Lab Cisco IOS User Interface Functions
The ABCs of Spanning Tree Protocol
 The ABCs of Spanning Tree Protocol INTRODUCTION In an industrial automation application that relies heavily on the health of the Ethernet network that attaches all the controllers and computers together,
The ABCs of Spanning Tree Protocol INTRODUCTION In an industrial automation application that relies heavily on the health of the Ethernet network that attaches all the controllers and computers together,
Port Trunking. Contents
 13 Port Trunking Contents Overview.................................................... 13-2 Port Trunk Features and Operation........................... 13-4 Trunk Configuration Methods................................
13 Port Trunking Contents Overview.................................................... 13-2 Port Trunk Features and Operation........................... 13-4 Trunk Configuration Methods................................
Abstract. MEP; Reviewed: GAK 10/17/2005. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2005 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Dell PowerVault MD Series Storage Arrays: IP SAN Best Practices
 Dell PowerVault MD Series Storage Arrays: IP SAN Best Practices A Dell Technical White Paper Dell Symantec THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND MAY CONTAIN TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS AND
Dell PowerVault MD Series Storage Arrays: IP SAN Best Practices A Dell Technical White Paper Dell Symantec THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND MAY CONTAIN TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS AND
Zarząd (7 osób) F inanse (13 osób) M arketing (7 osób) S przedaż (16 osób) K adry (15 osób)
 QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
June 2006. Bridge & Switch. Pietro Nicoletti Piero[at]studioreti.it. Bridge-Switch-Engl - 1 P. Nicoletti: see note pag. 2
![June 2006. Bridge & Switch. Pietro Nicoletti Piero[at]studioreti.it. Bridge-Switch-Engl - 1 P. Nicoletti: see note pag. 2 June 2006. Bridge & Switch. Pietro Nicoletti Piero[at]studioreti.it. Bridge-Switch-Engl - 1 P. Nicoletti: see note pag. 2](/thumbs/22/1747267.jpg) Bridge & Switch Pietro Nicoletti Piero[at]studioreti.it Bridge-Switch-Engl - P. Nicoletti: see note pag. Copyright note These slides are protected by copyright and international treaties. The title and
Bridge & Switch Pietro Nicoletti Piero[at]studioreti.it Bridge-Switch-Engl - P. Nicoletti: see note pag. Copyright note These slides are protected by copyright and international treaties. The title and
How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE
 How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE Summary This document attempts to standardize the methods used to configure Intrauve in situations where there is little or no understanding of
How To Understand and Configure Your Network for IntraVUE Summary This document attempts to standardize the methods used to configure Intrauve in situations where there is little or no understanding of
Management Software. Web Browser User s Guide AT-S106. For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch. Version 1.0.0. 613-001339 Rev.
 Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
How To Balance On A Cisco Catalyst Switch With The Etherchannel On A Fast Ipv2 (Powerline) On A Microsoft Ipv1 (Powergen) On An Ipv3 (Powergadget) On Ipv4
 Cisco - Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switch...Page 1 of 10 Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents
Cisco - Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switch...Page 1 of 10 Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 6 DESIGNING A NETWORK TOPOLOGY
 CHAPTER 6 DESIGNING A NETWORK TOPOLOGY Expected Outcomes Able to identify terminology that will help student discuss technical goals with customer. Able to introduce a checklist that can be used to determine
CHAPTER 6 DESIGNING A NETWORK TOPOLOGY Expected Outcomes Able to identify terminology that will help student discuss technical goals with customer. Able to introduce a checklist that can be used to determine
Port Trunking. Contents
 12 Port Trunking Contents Overview..................................................... 12-2................................... 12-2 Port Connections and Configuration.......................... 12-3 Link
12 Port Trunking Contents Overview..................................................... 12-2................................... 12-2 Port Connections and Configuration.......................... 12-3 Link
CCNP SWITCH: Implementing High Availability and Redundancy in a Campus Network
 CCNP SWITCH: Implementing High Availability and Redundancy in a Campus Network Olga Torstensson SWITCHv6 1 Components of High Availability Redundancy Technology (including hardware and software features)
CCNP SWITCH: Implementing High Availability and Redundancy in a Campus Network Olga Torstensson SWITCHv6 1 Components of High Availability Redundancy Technology (including hardware and software features)
How To Switch In Sonicos Enhanced 5.7.7 (Sonicwall) On A 2400Mmi 2400Mm2 (Solarwall Nametra) (Soulwall 2400Mm1) (Network) (
 You can read the recommendations in the user, the technical or the installation for SONICWALL SWITCHING NSA 2400MX IN SONICOS ENHANCED 5.7. You'll find the answers to all your questions on the SONICWALL
You can read the recommendations in the user, the technical or the installation for SONICWALL SWITCHING NSA 2400MX IN SONICOS ENHANCED 5.7. You'll find the answers to all your questions on the SONICWALL
Howstuffworks "How LAN Switches Work" Click here to go back to the normal view!
 Page 1 of 17 Search ComputerStuff AutoStuff ElectronicsStuff ScienceStuff HomeStuff EntertainmentStuff MoneyStuff TravelStuff Main > Computer > Hardware Click here to go back to the normal view! How LAN
Page 1 of 17 Search ComputerStuff AutoStuff ElectronicsStuff ScienceStuff HomeStuff EntertainmentStuff MoneyStuff TravelStuff Main > Computer > Hardware Click here to go back to the normal view! How LAN
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R
 VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH
 16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH User s Manual (DN-95312) - 0 - Content Web Smart Switch Configure login ---------------------------------- 2 Administrator Authentication Configuration ---------------------------------------------
16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH User s Manual (DN-95312) - 0 - Content Web Smart Switch Configure login ---------------------------------- 2 Administrator Authentication Configuration ---------------------------------------------
Data Networking and Architecture. Delegates should have some basic knowledge of Internet Protocol and Data Networking principles.
 Data Networking and Architecture The course focuses on theoretical principles and practical implementation of selected Data Networking protocols and standards. Physical network architecture is described
Data Networking and Architecture The course focuses on theoretical principles and practical implementation of selected Data Networking protocols and standards. Physical network architecture is described
OVERLAYING VIRTUALIZED LAYER 2 NETWORKS OVER LAYER 3 NETWORKS
 OVERLAYING VIRTUALIZED LAYER 2 NETWORKS OVER LAYER 3 NETWORKS Matt Eclavea (meclavea@brocade.com) Senior Solutions Architect, Brocade Communications Inc. Jim Allen (jallen@llnw.com) Senior Architect, Limelight
OVERLAYING VIRTUALIZED LAYER 2 NETWORKS OVER LAYER 3 NETWORKS Matt Eclavea (meclavea@brocade.com) Senior Solutions Architect, Brocade Communications Inc. Jim Allen (jallen@llnw.com) Senior Architect, Limelight
"Charting the Course...
 Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
A New Approach to Developing High-Availability Server
 A New Approach to Developing High-Availability Server James T. Yu, Ph.D. School of Computer Science, Telecommunications, and Information Systems DePaul University jyu@cs.depaul.edu ABSTRACT This paper
A New Approach to Developing High-Availability Server James T. Yu, Ph.D. School of Computer Science, Telecommunications, and Information Systems DePaul University jyu@cs.depaul.edu ABSTRACT This paper
Chapter 4: Spanning Tree Design Guidelines for Cisco NX-OS Software and Virtual PortChannels
 Design Guide Chapter 4: Spanning Tree Design Guidelines for Cisco NX-OS Software and Virtual PortChannels 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Design Guide Chapter 4: Spanning Tree Design Guidelines for Cisco NX-OS Software and Virtual PortChannels 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Securing end devices
 Securing end devices Securing the network edge is already covered. Infrastructure devices in the LAN Workstations Servers IP phones Access points Storage area networking (SAN) devices. Endpoint Security
Securing end devices Securing the network edge is already covered. Infrastructure devices in the LAN Workstations Servers IP phones Access points Storage area networking (SAN) devices. Endpoint Security
Fast Fault Recovery in Switched Networks for Carrying IP Telephony Traffic
 Technical report, IDE1002, February 2010 Fast Fault Recovery in Switched Networks for Carrying IP Telephony Traffic Master s Thesis in Computer Network Engineering ALI AKBAR EISAZADEH & NORA ESPAHBODI
Technical report, IDE1002, February 2010 Fast Fault Recovery in Switched Networks for Carrying IP Telephony Traffic Master s Thesis in Computer Network Engineering ALI AKBAR EISAZADEH & NORA ESPAHBODI
TRILL for Data Center Networks
 24.05.13 TRILL for Data Center Networks www.huawei.com enterprise.huawei.com Davis Wu Deputy Director of Switzerland Enterprise Group E-mail: wuhuajun@huawei.com Tel: 0041-798658759 Agenda 1 TRILL Overview
24.05.13 TRILL for Data Center Networks www.huawei.com enterprise.huawei.com Davis Wu Deputy Director of Switzerland Enterprise Group E-mail: wuhuajun@huawei.com Tel: 0041-798658759 Agenda 1 TRILL Overview
IP SAN Best Practices
 IP SAN Best Practices A Dell Technical White Paper PowerVault MD3200i Storage Arrays THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND MAY CONTAIN TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS AND TECHNICAL INACCURACIES.
IP SAN Best Practices A Dell Technical White Paper PowerVault MD3200i Storage Arrays THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND MAY CONTAIN TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS AND TECHNICAL INACCURACIES.
Ethernet Storage Best Practices
 Technical Report Ethernet Storage Best Practices David Klem, Trey Layton, Frank Pleshe, NetApp January 2010 TR-3802 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 2 USING VLANS FOR TRAFFIC SEPARATION... 3 2.1 VLAN
Technical Report Ethernet Storage Best Practices David Klem, Trey Layton, Frank Pleshe, NetApp January 2010 TR-3802 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 2 USING VLANS FOR TRAFFIC SEPARATION... 3 2.1 VLAN
VXLAN: Scaling Data Center Capacity. White Paper
 VXLAN: Scaling Data Center Capacity White Paper Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) Overview This document provides an overview of how VXLAN works. It also provides criteria to help determine when and where
VXLAN: Scaling Data Center Capacity White Paper Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) Overview This document provides an overview of how VXLAN works. It also provides criteria to help determine when and where
BLADE PVST+ Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco
 BLADE PVST+ Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco Technical Brief Industry-standard PVST+ Spanning Tree Protocol with Cisco interoperability Introduction...1 Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1d)...1
BLADE PVST+ Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco Technical Brief Industry-standard PVST+ Spanning Tree Protocol with Cisco interoperability Introduction...1 Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1d)...1
Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network
 Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 9 Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright Cisco
Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 9 Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright Cisco
How To Learn Cisco Cisco Ios And Cisco Vlan
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Expert Reference Series of White Papers. Planning for the Redeployment of Technical Personnel in the Modern Data Center
 Expert Reference Series of White Papers Planning for the Redeployment of Technical Personnel in the Modern Data Center info@globalknowledge.net www.globalknowledge.net Planning for the Redeployment of
Expert Reference Series of White Papers Planning for the Redeployment of Technical Personnel in the Modern Data Center info@globalknowledge.net www.globalknowledge.net Planning for the Redeployment of
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
IP Routing Features. Contents
 7 IP Routing Features Contents Overview of IP Routing.......................................... 7-3 IP Interfaces................................................ 7-3 IP Tables and Caches........................................
7 IP Routing Features Contents Overview of IP Routing.......................................... 7-3 IP Interfaces................................................ 7-3 IP Tables and Caches........................................
CISCO STUDY GUIDE. Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) 640-504 Edition 2
 CISCO STUDY GUIDE Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) 640-504 Edition 2 Congratulations!! You have purchased a Testkiller, Ltd Study Guide. This study guide is a selection of keypoints
CISCO STUDY GUIDE Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) 640-504 Edition 2 Congratulations!! You have purchased a Testkiller, Ltd Study Guide. This study guide is a selection of keypoints
LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide
 LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide This document provides guidance on how to design a local area network (LAN) for a Business Ready Branch or autonomous Business Ready
LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide This document provides guidance on how to design a local area network (LAN) for a Business Ready Branch or autonomous Business Ready
Expert Reference Series of White Papers. The Evolution of Cisco Switching
 Expert Reference Series of White Papers The Evolution of Cisco Switching 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com The Evolution of Cisco Switching Joe Rinehart, MBA, CCIE #14256, CCNP/DP/VP Introduction Cisco
Expert Reference Series of White Papers The Evolution of Cisco Switching 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com The Evolution of Cisco Switching Joe Rinehart, MBA, CCIE #14256, CCNP/DP/VP Introduction Cisco
Fiber Channel Over Ethernet (FCoE)
 Fiber Channel Over Ethernet (FCoE) Using Intel Ethernet Switch Family White Paper November, 2008 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
Fiber Channel Over Ethernet (FCoE) Using Intel Ethernet Switch Family White Paper November, 2008 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks Volume 1
 Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks Volume 1 Course Introduction Learner Skills and Knowledge Course Goal and E Learning Goal and Course Flow Additional Cisco Glossary of Terms Your Training
Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks Volume 1 Course Introduction Learner Skills and Knowledge Course Goal and E Learning Goal and Course Flow Additional Cisco Glossary of Terms Your Training
Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes
 Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Table of Contents Description... 3 Benefits... 4 Theory of Operation... 4 Interaction with Other Features... 7
Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Table of Contents Description... 3 Benefits... 4 Theory of Operation... 4 Interaction with Other Features... 7
Juniper Networks EX Series/ Cisco Catalyst Interoperability Test Results. May 1, 2009
 Juniper Networks EX Series/ Cisco Catalyst Interoperability Test Results May 1, 2009 Executive Summary Juniper Networks commissioned Network Test to assess interoperability between its EX4200 and EX8208
Juniper Networks EX Series/ Cisco Catalyst Interoperability Test Results May 1, 2009 Executive Summary Juniper Networks commissioned Network Test to assess interoperability between its EX4200 and EX8208
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
- Switch Port Configuration -
 1 Cisco Operating Systems - Switch Port Configuration - Cisco offers two brands of network switches: Catalyst Cisco s flagship switching platform, with a large selection of models spanning access, distribution,
1 Cisco Operating Systems - Switch Port Configuration - Cisco offers two brands of network switches: Catalyst Cisco s flagship switching platform, with a large selection of models spanning access, distribution,
ANZA Formación en Tecnologías Avanzadas
 INTRODUCING CISCO DATA CENTER NETWORKING (DCICN) Temario This new assoicate level course has been designed to introduce delegates to the three primary technologies that are used in the Cisco Data Center.
INTRODUCING CISCO DATA CENTER NETWORKING (DCICN) Temario This new assoicate level course has been designed to introduce delegates to the three primary technologies that are used in the Cisco Data Center.
Configuring Traffic Storm Control
 39 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the traffic storm control feature on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
39 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the traffic storm control feature on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Redundancy and load balancing at L3 in Local Area Networks. Fulvio Risso Politecnico di Torino
 Redundancy and load balancing at L3 in Local Area Networks Fulvio Risso Politecnico di Torino 1 Default gateway redundancy (1) H1 DG: R1 H2 DG: R1 H3 DG: R1 R1 R2 ISP1 ISP2 Internet 3 Default gateway redundancy
Redundancy and load balancing at L3 in Local Area Networks Fulvio Risso Politecnico di Torino 1 Default gateway redundancy (1) H1 DG: R1 H2 DG: R1 H3 DG: R1 R1 R2 ISP1 ISP2 Internet 3 Default gateway redundancy
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
Virtual PortChannels: Building Networks without Spanning Tree Protocol
 . White Paper Virtual PortChannels: Building Networks without Spanning Tree Protocol What You Will Learn This document provides an in-depth look at Cisco's virtual PortChannel (vpc) technology, as developed
. White Paper Virtual PortChannels: Building Networks without Spanning Tree Protocol What You Will Learn This document provides an in-depth look at Cisco's virtual PortChannel (vpc) technology, as developed
- Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP -
 1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
Configuring Link Bundling on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Configuring Link Bundling on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes the configuration of link bundle interfaces on the Cisco CRS Router. A link bundle is a group of one or more ports that are aggregated
Configuring Link Bundling on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes the configuration of link bundle interfaces on the Cisco CRS Router. A link bundle is a group of one or more ports that are aggregated
Level 2 Routing: LAN Bridges and Switches
 Level 2 Routing: LAN Bridges and Switches Norman Matloff University of California at Davis c 2001, N. Matloff September 6, 2001 1 Overview In a large LAN with consistently heavy traffic, it may make sense
Level 2 Routing: LAN Bridges and Switches Norman Matloff University of California at Davis c 2001, N. Matloff September 6, 2001 1 Overview In a large LAN with consistently heavy traffic, it may make sense
CORPORATE NETWORKING
 CORPORATE NETWORKING C. Pham Université de Pau et des Pays de l Adour Département Informatique http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham Congduc.Pham@univ-pau.fr Typical example of Ethernet local networks Mostly based
CORPORATE NETWORKING C. Pham Université de Pau et des Pays de l Adour Département Informatique http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham Congduc.Pham@univ-pau.fr Typical example of Ethernet local networks Mostly based
Redundancy and load balancing at L3 in Local Area Networks. Fulvio Risso Politecnico di Torino
 Redundancy and load balancing at L3 in Local Area Networks Fulvio Risso Politecnico di Torino 1 Problem: the router is a single point of failure H1 H2 H3 VLAN4 H4 VLAN4 Corporate LAN Corporate LAN R1 R2
Redundancy and load balancing at L3 in Local Area Networks Fulvio Risso Politecnico di Torino 1 Problem: the router is a single point of failure H1 H2 H3 VLAN4 H4 VLAN4 Corporate LAN Corporate LAN R1 R2
ALL8894WMP. User s Manual. 8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4-port PoE. Web Management Switch
 ALL8894WMP 8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4-port PoE Web Management Switch User s Manual Content Content I Introduction..3 Product Overview.3 Web Management Feature.3 Specification..4 Mechanical...4 Performance...5
ALL8894WMP 8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4-port PoE Web Management Switch User s Manual Content Content I Introduction..3 Product Overview.3 Web Management Feature.3 Specification..4 Mechanical...4 Performance...5
LAN Switching and VLANs
 26 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the relationship of LAN switching to legacy internetworking devices such as bridges and routers. Understand the advantages of VLANs. Know the difference between access
26 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the relationship of LAN switching to legacy internetworking devices such as bridges and routers. Understand the advantages of VLANs. Know the difference between access
Cisco Data Centre: Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking
 coursemonster.com/uk Cisco Data Centre: Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking View training dates» Overview In the Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking training course, delegates will learn to:â
coursemonster.com/uk Cisco Data Centre: Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking View training dates» Overview In the Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking training course, delegates will learn to:â
Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching
 CCNP3 v5 - Chapter 5 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing High Availability in a Campus Environment Routing issues Hosts rely on a router to find the best path Issues with established
CCNP3 v5 - Chapter 5 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing High Availability in a Campus Environment Routing issues Hosts rely on a router to find the best path Issues with established
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
 SFWR 4C03: Computer Networks and Computer Security January 19-22 2004 Lecturer: Kartik Krishnan Lectures 7-9 RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol When a system with a local disk is bootstrapped it
SFWR 4C03: Computer Networks and Computer Security January 19-22 2004 Lecturer: Kartik Krishnan Lectures 7-9 RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol When a system with a local disk is bootstrapped it
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Topology A map of an internetwork that indicates network segments, interconnection points,
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Topology A map of an internetwork that indicates network segments, interconnection points,
Campus Network for High Availability Design Guide
 Campus Network for High Availability Design Guide Cisco Validated Design May 21, 2008 Introduction This document is the first in a series of two documents describing the best way to design campus networks
Campus Network for High Availability Design Guide Cisco Validated Design May 21, 2008 Introduction This document is the first in a series of two documents describing the best way to design campus networks
Expert Reference Series of White Papers. VMware vsphere Distributed Switches
 Expert Reference Series of White Papers VMware vsphere Distributed Switches info@globalknowledge.net www.globalknowledge.net VMware vsphere Distributed Switches Rebecca Fitzhugh, VCAP-DCA, VCAP-DCD, VCAP-CIA,
Expert Reference Series of White Papers VMware vsphere Distributed Switches info@globalknowledge.net www.globalknowledge.net VMware vsphere Distributed Switches Rebecca Fitzhugh, VCAP-DCA, VCAP-DCD, VCAP-CIA,
Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart 8-Port Switch 2 Combo SFP Open Slot
 Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart 8-Port Switch 2 Combo SFP Open Slot User s Manual (DN-80201) Content Introduction ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4 Product
Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart 8-Port Switch 2 Combo SFP Open Slot User s Manual (DN-80201) Content Introduction ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4 Product
Internet Working 5 th lecture. Chair of Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2004
 5 th lecture Chair of Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2004 1 43 Last lecture Lecture room hopefully all got the message lecture on tuesday and thursday same
5 th lecture Chair of Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2004 1 43 Last lecture Lecture room hopefully all got the message lecture on tuesday and thursday same
Networking Test 4 Study Guide
 Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
Networking Test 4 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. IPX/SPX is considered the protocol suite of the Internet, and it is the most widely used protocol suite in LANs.
Network security includes the detection and prevention of unauthorized access to both the network elements and those devices attached to the network.
 By: Ziad Zubidah CCNP Security IT Security Officer National Information Technology Center Network security includes the detection and prevention of unauthorized access to both the network elements and
By: Ziad Zubidah CCNP Security IT Security Officer National Information Technology Center Network security includes the detection and prevention of unauthorized access to both the network elements and
TechBrief Introduction
 TechBrief Introduction Leveraging Redundancy to Build Fault-Tolerant Networks The high demands of e-commerce and Internet applications have required networks to exhibit the same reliability as the public
TechBrief Introduction Leveraging Redundancy to Build Fault-Tolerant Networks The high demands of e-commerce and Internet applications have required networks to exhibit the same reliability as the public
TRILL for Service Provider Data Center and IXP. Francois Tallet, Cisco Systems
 for Service Provider Data Center and IXP Francois Tallet, Cisco Systems 1 : Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links overview How works designs Conclusion 2 IETF standard for Layer 2 multipathing Driven
for Service Provider Data Center and IXP Francois Tallet, Cisco Systems 1 : Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links overview How works designs Conclusion 2 IETF standard for Layer 2 multipathing Driven
SSVP SIP School VoIP Professional Certification
 SSVP SIP School VoIP Professional Certification Exam Objectives The SSVP exam is designed to test your skills and knowledge on the basics of Networking and Voice over IP. Everything that you need to cover
SSVP SIP School VoIP Professional Certification Exam Objectives The SSVP exam is designed to test your skills and knowledge on the basics of Networking and Voice over IP. Everything that you need to cover
