Jon W. Atkinson, B.S., RPSGT
|
|
|
- Delphia Moore
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jon W. Atkinson, B.S., RPSGT
2 State the AASM technical considerations and reporting guidelines Describe normal ECG parameters Understand systematic arrhythmia analysis steps Explain the rule of differing morphology Understand polysomnographic monitoring and recording techniques
3 Modified lead II is recommended Additional leads may be placed if clinically indicated at the discretion of the practitioner Filters: HFF 70 Hz, LFF 0.3 Hz Digital Resolution, 12 bits Sampling rate, desirable 500 Hz, minimal 200 Hz Standard ECG electrodes are suggested rather than gold cups
4 A different lead derivation should be employed if the P wave is not clearly defined or the QRS complex is not of sufficient amplitude If muscle artifact is present, it is appropriate to lower the high frequency filter to 35 or even 15 Hz If slow wave artifact is present (respiratory or sweat), it is appropriate to raise the low frequency filter to as low as 1 Hz Document and changes to derivation or filters
5 Score SINUS TACHYCARDIA during sleep for sustained HR > 90 BPM for adults Score BRADYCARDIA during sleep for sustained HR < 40 BPM, ages 6-adult Score ASYSTOLE for cardiac pauses > 3 seconds duration, ages 6-adult Score WIDE COMPLEX TACHYCARDIA for a rhythm lasting a minimum of 3 consecutive beats at a rate > 100 BPM with a QRS duration > 0.12 seconds
6 Score NARROW COMPLEX TACHYCARDIA for a rhythm lasting a minimum of 3 consecutive beats at a rate > 100 BPM with a QRS duration < 0.12 seconds Score ATRIAL FIBRILLATION if there is an irregularly irregular ventricular rhythm associated with the replacement of consistent P waves by rapid oscillations that vary in size, shape and timing
7 OTHER ARRHYTHMIAS Significant arrhythmias such as BLOCKS should be reported if the quality of the single ECG lead is sufficient for accurate scoring ECTOPIC BEATS should be reported if clinically significant
8 A basic understanding of the normal conduction pathway of the heart and the interrelation of the events in the cardiac cycle is essential prior to discussion of abnormal heart rhythms
9 SA node AV Node Bundle of His Left and Right Bundle Branches Purkinje System
10
11
12 Relationship between anatomy and cardiac cycle events P wave = atrial depolarization QRS complex = ventricular depolarization T wave = ventricular repolarization PR interval (last portion from the end of the P wave) = the pause between atrial and ventricular depolarization
13 Atrial depolarization Ventricular repolarization PR interval QRS interval Ventricular depolarization and Atrial repolarization
14 HR = bpm PR interval = sec QRS interval < 0.12 sec SA node discharge = /min AV node discharge = 40-60/min Ventricular tissue discharge = 20-40/min Rhythm = regular
15 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, each appears the same QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval seconds QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate bpm Rhythm Regular Normal sinus rhythm, 30 second display Normal sinus rhythm, 10 second display
16 An arrhythmia is present if there is: Disturbance of impulse formation Disturbance of impulse conduction Both of the above occur The rate is too fast or too slow
17 Tools for the systematic analysis of cardiac arrhythmias Rule of identical morphology: If the wave form looks the same, it has started from the same location and taken the same pathway Rule of differing morphology: If the wave form looks different, it has started from a different location, taken a different pathway, or both
18 P Wave Absent or present? Morphology the same? QRS Complex Absent or present? Morphology the same?
19 P for every QRS QRS for every P 1:1 relationship Measure the PR interval Normal, too short, too long? Measure the QRS interval Normal or too long?
20 Rhythm Is R-R interval constant? Is P-P interval constant? How to calculate rate Times 2 method - count the number of beats in a 30 sec screen and multiply by 2 Times 4 method - count the number of beats in 15 seconds and multiply by 4 Times 6 method - count the number of beats in 10 seconds and multiply by 6 Don t rely on the cardiotachometer on the study This rate is usually derived from the pulse oximeter and can be inaccurate
21 PAC s Sinus bradycardia Atrial tachycardias Sinus arrhythmia Sinus pauses Paroxysmal tachycardias Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter Except for atrial fibrillation where the P waves have been replaced by waves of variable size, shape and duration, and atrial flutter where the P waves are replaced by saw-tooth appearing flutter waves, atrial arrhythmias will demonstrate P waves.
22 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, appearance of the P wave of the abnormal beat is different (arises from a different location.) QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval seconds (may vary slightly with the abnormal beat) QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate bpm Rhythm Irregular, P-P and R-R intervals are different Premature atrial contraction, 30 second display Premature atrial contraction, 10 second display
23 Key features: Aberrant P wave associated with a beat occurring earlier than expected (at the arrows) Note that it is more clearly visualized when spread out in a 10 second display, a feature true of viewing almost all arrhythmias
24 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, each appears the same QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval seconds QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate <60 bpm (<40 in sleep) Rhythm Regular Sinus bradycardia, 30 second display Sinus bradycardia, 10 second display
25 Key features: Looks like normal sinus rhythm except the rate is too slow Note that bradycardia in sleep is defined as a sustained rhythm with rate less than 40 beats per minute
26 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, each appears the same; may not be well defined in SVT QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval seconds QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate Rhythm >100 bpm (> 90 bpm in sleep) Regular Atrial tachycardia, 30 second display Atrial tachycardia, 10 second display
27 Key features: Looks like normal sinus rhythm except rate is too fast Note that tachycardia in sleep is defined as a sustained rhythm with rate greater than 90 beats per minute
28 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, each appears the same QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval seconds QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate Usually bpm Rhythm Irregular Sinus arrhythmia, 30 second display Sinus arrhythmia, 10 second display
29 Key features: A usually benign phenomenon where the HR increases with inhalation and slows with exhalation mediated by stimulation of the vagus nerve Often seen in youngsters and athletic individuals Similar shifts in HR can be seen with apnea (slowing) and resumption of breathing (acceleration) This bradytachy phenomenon has been recognized as the most prevalent arrhythmia in patients with sleep disordered breathing
30 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Absent during pause QRS complex Absent during pause PR interval Absent during pause QRS interval Absent during pause P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate bpm, but any rate is possible Rhythm Irregular Sinus pause, 30 second display Sinus pause, 10 second display
31 Key features: Abrupt absence of both P waves and QRS complexes, if lasting longer than 3 seconds, should be scored as asystole per AASM guidelines May be due to sinus arrest or block of sinus excitatory impulse (sinus exit block) This usually cannot be determined on surface ECG and requires an electrophysiological heart study
32 Parameter/waveform P wave QRS complex PR interval Value/characteristic Present, aberrant, often hidden Present, appearance is the same may be aberrant seconds QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate bpm Rhythm Regular during paroxysm Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, 30 second display Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, 10 second display
33 Key features: Abrupt increase in HR and abrupt termination of the increase, typically with normal appearing QRS complexes This abrupt onset and offset is termed a paroxysm These events should be scored as Narrow Complex Tachycardia per AASM guidelines
34 Parameter/waveform P wave QRS complex PR interval QRS interval P:QRS ratio Rate Rhythm Value/characteristic None, fibrillatory wave present Present, appearance is the same Not measurable seconds Not applicable Ventricular rate highly variable Irregularly irregular Atrial fibrillation, 30 second display Atrial fibrillation, 10 second display
35 Key features: Irregularly irregular rhythm P waves are replaced by rapid oscillations of varying size, shape and duration Presence of A Fib should be scored per AASM guidelines
36 Parameter/waveform P wave QRS complex PR interval QRS interval P:QRS ratio Rate Rhythm Value/characteristic None, saw tooth appearance flutter waves present Present, appearance is the same Not measurable seconds Variable 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, etc Atrial , ventricular depends on degree of block Regular or irregular dependent on variability of block Atrial flutter, 30 second display Atrial flutter, 10 second display
37 Key Features: Distinct, regular, rapid flutter waves with saw tooth appearance Ventricular rhythm can be regular or irregular Atrial flutter should be note under other significant arrhythmias
38 Premature junctional contraction Junctional rhythm Accelerated junctional rhythm Junctional tachycardia
39 Key features: Junctional arrhythmias may have inverted P waves due to retrograde conduction or the P wave may not be seen as it occurs in concert with the QRS complex and is buried If the P wave is inverted, the PR interval is shorter than normal or the P wave may even occur after the QRS complex
40 Parameter/waveform P wave: QRS complex: PR Interval: QRS Interval: P to QRS Ratio: Rhythm: Rate: Value/characteristic Premature and abnormal configuration, will be inverted; can be before (with shortened PR interval), after or hidden in the QRS Present, appearance is the same Shorter than normal; < 0.12 seconds seconds?; < 1:1 if hidden; 1:1 if inverted P is seen Irregular Usually normal but can occur in sinus tachycardia or sinus bradycardia Premature junctional contraction, 30 second display Premature junctional contraction, 10 second display
41 Key features: Normal appearing QRS complex occurring earlier than expected No P wave or inverted P wave
42 Parameter/waveform P wave: QRS complex: PR Interval: QRS Interval: P to QRS Ratio: Rhythm: Rate: Value/characteristic If seen, abnormal configuration, will be inverted; can be before (with shortened PR interval), after or hidden in the QRS Present, appearance is the same Shorter than normal; < 0.12 seconds seconds?; < 1:1 if hidden; 1:1 if inverted P is seen Regular bpm Junctional (nodal) rhythm, 30 second display Junctional (nodal) rhythm, 10 second display
43 Key features: In the sample on the previous slide the P wave is inverted and occurs before the QRS complex with abbreviated PR interval the rhythm is regular and the rate is within the normal range for junctional tissue (40-60 beats per minute) Report as a significant arrhythmia if the single lead recording is quality of the single ECG lead is sufficient for accurate scoring
44 Parameter/waveform P wave: QRS complex: PR Interval: QRS Interval: P to QRS Ratio: Rhythm: Rate: Value/characteristic If seen, abnormal configuration, will be inverted; can be before (with shortened PR interval), after or hidden in the QRS Present, appearance is the same Shorter than normal; < 0.12 seconds seconds?; < 1:1 if hidden; 1:1 if inverted P is seen Regular bpm Accelerated junctional (nodal) rhythm, 30 second display Accelerated junctional (nodal) rhythm, 10 second display
45 Key features: In the sample on the previous slide no P wave is seen but it could be inverted before or after QRS complex rate is beats per minute and looks like normal sinus rhythm except for the absence or inversion of the P wave Report as a significant arrhythmia if the single lead recording is quality of the single ECG lead is sufficient for accurate scoring
46 Parameter/waveform P wave: QRS complex: PR Interval: QRS Interval: P to QRS Ratio: Rhythm: Rate: Value/characteristic If seen, abnormal configuration, will be inverted; can be before (with shortened PR interval), after or hidden in the QRS Present, appearance is the same Shorter than normal; < 0.12 seconds seconds?; < 1:1 if hidden; 1:1 if inverted P is seen Regular >100 bpm Junctional Tachycardia, 30 second display Junctional Tachycardia, 10 second display
47 Key features: In the sample on the previous slide note the inverted P wave following the QRS complex (arrow) rhythm is regular and rate is greater than 100 per minute Report as a significant arrhythmia if the single lead recording is quality of the single ECG lead is sufficient for accurate scoring
48 1 st degree AV block 2 nd degree AV block, Mobitz type I 2 nd degree AV block, Mobitz type 2 3 rd degree AV block As the name implies, there is a problem with the conduction of the electrical impulse between the atria and the ventricles. The impulse transmission is either delayed or totally blocked.
49 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, each appears the same QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval >0.20 seconds QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio 1:1 Rate Usually normal Rhythm Regular st degree AV block, 30 second display 1 st st degree AV block, 10 second display 1 st
50 Key features: Resembles normal sinus rhythm Prolonged PR interval (greater than 0.20 seconds)
51 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, normal sinus P, some not followed by QRS QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval Progressively lengthening QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio >1:1 Rate Usually slow to normal Rhythm Irregular 2nd degree AV block, type I, Wenkebach, 30 second display nd degree AV block, type I, Wenkebach, 10 second display 2 nd
52 Key features: Progressively increasing PR interval until there is a P wave without corresponding QRS complex (see the arrows on the previous slide) Note a 10 second window is necessary for adequate assessment P to QRS ratio is greater than 1:1 This is the Wenkebach phenomenon Report as a significant arrhythmia if the single lead recording is quality of the single ECG lead is sufficient for accurate scoring
53 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, normal sinus P, some not followed by QRS complex, often >= 2 P waves before QRS complex QRS complex Present, each appears the same PR interval Constant PR interval before dropped QRS, may be normal or prolonged PR interval QRS interval seconds P:QRS ratio >1:1 Rate Usually slow to normal Rhythm Irregular 2nd degree AV block, type II, 30 second display nd degree AV block, type II, 10 second display 2 nd
54 Key features: Non-conducted P wave PR interval is constant before the dropped QRS complex Several non-conducted P waves may occur in a row This is the Hayes phenomenon Report as a significant arrhythmia if the single lead recording is quality of the single ECG lead is sufficient for accurate scoring
55 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave Present, normal sinus P, some not followed by QRS complex, often >= 2 P waves before QRS complex QRS complex Present, appearance is the same PR interval Highly variable QRS interval <0.12 if block is high conducting system (bundle of His) or >0.12 if lower conducting system (bundle branches) P:QRS ratio >1:1 Rate Ventricular rate if block is high, <40 if block is lower Rhythm Regular P-P and regular R-R intervals but not the same rate 3rd degree AV block, 30 second display rd degree AV block, 10 second display 3 rd
56 Key features: The P to P interval is constant and the R to R interval is constant but they do not occur at the same rate The atria and the ventricles are functioning independently This is also known as AV dissociation Report as a significant arrhythmia if the single lead recording is quality of the single ECG lead is sufficient for accurate scoring
57 Premature Ventricular Contractions Unifocal PVC s Multifocal PVC s Ventricular Trigeminy Ventricular Bigeminy Ventricular couplets Idioventricular Rhythm Accelerated Ventricular Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia Runs of ventricular tachycardia Sustained ventricular tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation
58 Key Features Ventricular arrhythmias are void of P waves prior to the abnormal beat(s) The QRS complexes are prolonged (greater than 0.12 seconds) and often bizarre in appearance
59 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present with abnormal beat(s) QRS complex: Occurs earlier than expected and appears widened and bizarre compared to sinus originated beats PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > 0.12 sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Usually but can occur with faster or slower rates Unifocal PVC s, 30 second display Unifocal PVC s, 10 second display
60 Key features: No P wave prior to the abnormal beat occurring earlier than expected The QRS complex duration is greater than 0.12 seconds and bizarre appearing Unifocal PVC s all look alike (originate from the same focus and take the same pathway) Rule of identical morphology Report as a significant arrhythmia if clinically significant (frequency >???)
61 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present with abnormal beat(s) QRS complex: Occurs earlier than expected and appears widened and bizarre compared to sinus originated beats. QRS complexes have different morphology PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > 0.12 sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Usually but can occur with faster or slower rates Multifocal PVC s, 30 second display Multifocal PVC s, 10 second display
62 Key features: No P wave prior to the abnormal beats occurring earlier than expected The QRS complex duration is greater than 0.12 seconds and bizarre appearing Multifocal PVC s look different from each other (originate from a different focus and take a different pathway) Rule of differing morphology Report as clinically significant ectopy
63 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present with abnormal beat(s) QRS complex: Occurs earlier than expected and appears widened and bizarre compared to sinus originated beats. Every other beat is abnormal PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Usually but can occur with faster or slower rates Ventricular bigeminy, 30 second display Ventricular bigeminy, 10 second display
64 Key features: No P wave prior to the abnormal beat occurring earlier than expected The QRS complex duration is greater than 0.12 seconds and bizarre appearing Bigeminy refers to a pattern of every other beat being abnormal Atrial and junctional bigeminy patterns can occur, hence it is important to identify the origin as well as the pattern Report as clinically significant ectopy
65 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present with abnormal beat(s) QRS complex: Occurs earlier than expected and appears widened and bizarre compared to sinus originated beats. Every third beat is abnormal PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Usually but can occur with faster or slower rates Ventricular trigeminy, 30 second display Ventricular trigeminy, 10 second display
66 Key features: No P wave prior to the abnormal beat occurring earlier than expected The QRS complex duration is greater than 0.12 seconds and bizarre appearing Trigeminy refers to a pattern of every third beat being abnormal Atrial and junctional trigeminy patterns can occur, hence it is important to identify the origin as well as the pattern Report as clinically significant ectopy
67 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present with abnormal beat(s) QRS complex: Occurs earlier than expected and appears widened and bizarre compared to sinus originated beats. Ventricular beats are paired, may be multifocal PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > 0.12 sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Usually but can occur with faster or slower rates Ventricular couplets, 30 second display Ventricular couplets, 10 second display
68 Key features: These are paired ventricular beats (occurring back to back) They may be unifocal as in the example on the previous slide Multifocal ventricular look different from each other Report as clinically significant ectopy
69 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present QRS complex: Widened and bizarre PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > 0.12 sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Regular Rate: < 40 bpm Ventricular rhythm, 30 second display Ventricular rhythm, 10 second display
70 Key features: No P wave and wide, bizarre QRS complex The rhythm is regular and the rate is normal for ventricular impulses (20-40 beats per minute)
71 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present QRS complex: Widened and bizarre PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > 0.12 sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm Accelerated ventricular rhythm, 30 second display Accelerated ventricular rhythm, 10 second display
72 Key features: No P wave and wide, bizarre QRS complex Rhythm is regular and the rate is too fast for normal for ventricular impulses ( beats per minute) Report as clinically significant ectopy
73 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present QRS complex: Widened and bizarre PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm during the run Accelerated ventricular rhythm, 30 second display Runs of ventricular tachycardia, 30 second display Runs of ventricular tachycardia, 10 second display
74 Key features: No P wave and wide, bizarre QRS complex Rhythm is regular and the rate is greater than 100 beats per minute Report as wide complex tachycardia
75 Parameter/waveform Value/characteristic P wave: Not present QRS complex: Widened and bizarre PR Interval: None QRS Interval: > 0.12 sec P to QRS Ratio: < 1:1 Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm Sustained ventricular tachycardia, 30 second display Sustained ventricular tachycardia, 10 second display
76 Key features: No P wave and wide, bizarre QRS complex Rhythm is regular and the rate is greater than 100 beats per minute Sustained - defined as exceeding 30 seconds duration This is an emergency arrhythmia Assess the patient and follow your institution s emergency protocol Report as wide complex tachycardia
77 Parameter/waveform P wave: QRS complex: PR Interval: QRS Interval: P to QRS Ratio: Rhythm: Rate: Value/characteristic Not present None, wave forms are chaotic and disorganized, variable size and morphology None Not measurable None Chaotic Not measurable Ventricular fibrillation, 30 second display Ventricular fibrillation, 10 second display
78 Key features: No identifiable P waves or QRS complexes This is an emergency situation Assess the patient and then activate the emergency medical response system according to your protocols Report as clinically significant ectopy
79 This presentation has reviewed: AASM guidelines for recording and reporting arrhythmias Basic anatomy and pathways of the cardiac conducting system Basic ECG waveforms and their relation to the cardiac cycle Presentation of normal ECGPresentation of a systematic way to analyze cardiac arrhythmias Examples of atrial, junctional, and ventricular arrhythmias and AV blocks
80 Atkinson JW. Cardiac Arrhythmias. in Mattice C, Brooks R, Lee-Chiong T, (Eds.), Fundamentals of Sleep Technology 2 nd Edition, pp Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Berry RB, Brooks R, Gamaldo CE, Harding SM, Marcus CL and Vaughn BV for the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, Version 2.0, pp Darien, Illinois: American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 2012.
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
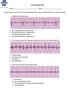 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Electrolyte Physiology. Something in the way she moves
 Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias
 Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
ECG Filtering. Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903
 ECG Filtering Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903 ECG Filtering Three common noise sources q Baseline wander q Power line interference q Muscle noise When filtering any biomedical signal care should be
ECG Filtering Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903 ECG Filtering Three common noise sources q Baseline wander q Power line interference q Muscle noise When filtering any biomedical signal care should be
School of Health Sciences
 School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Detecting Atrial-ventricular blocks Arrhythmia based on RR-intervals on ECG Signals
 Detecting Atrial-ventricular blocks Arrhythmia based on -intervals on ECG Signals Makki Akasha abikier, Ibrahim Musa Ishag, Mohammed Izzeldin, Dong Gyu Lee, Gyoyong shon, Keun Ho Ryu Database/ioinformatics
Detecting Atrial-ventricular blocks Arrhythmia based on -intervals on ECG Signals Makki Akasha abikier, Ibrahim Musa Ishag, Mohammed Izzeldin, Dong Gyu Lee, Gyoyong shon, Keun Ho Ryu Database/ioinformatics
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide
 Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
TOP 5. The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac. Arrhythmias in Dogs & Cats. Sinus Arrhythmia. TOP 5 Arrhythmias Seen in Dogs & Cats
 Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1
 Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms
 Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation
 Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response
 Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
2 ECG basics. Leads and planes. Leads. Planes. from different perspectives, which are called leads and planes.
 558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation
 The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
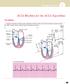 ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
Trust Guideline for the Management of New-born Babies with abnormal heart rhythm
 A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
Short Duration High-Level Exposure to Halon Substitutes: Potential Cardiovascular Effects
 Short Duration High-Level Exposure to Halon Substitutes: Potential Cardiovascular Effects Halon Alternatives Technical Working Conference 1993 Reva Rubenstein, Ph.D. U.S.Environmenta1 Protection Agency
Short Duration High-Level Exposure to Halon Substitutes: Potential Cardiovascular Effects Halon Alternatives Technical Working Conference 1993 Reva Rubenstein, Ph.D. U.S.Environmenta1 Protection Agency
Rigel 333 Multi Parameter Patient Simulator Version 2.0
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Rigel 333 Multi Parameter Patient Simulator Version 2.0 Rigel Medical Seaward Group 18 Bracken Hill Peterlee, County Durham SR8 2SW England www.rigelmedical.com Dear User: We appreciate
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Rigel 333 Multi Parameter Patient Simulator Version 2.0 Rigel Medical Seaward Group 18 Bracken Hill Peterlee, County Durham SR8 2SW England www.rigelmedical.com Dear User: We appreciate
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm
 Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal
 How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
 Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus Rhythm. P-Waves: PRInterval:
 EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus. : 60-100 beats per minute r Rhythrn: Atrial - - o Pwaves: Uniform in appearance Upright w/ normal shape One Preceding each QRS Nor more than.10 second o PR interval:
EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus. : 60-100 beats per minute r Rhythrn: Atrial - - o Pwaves: Uniform in appearance Upright w/ normal shape One Preceding each QRS Nor more than.10 second o PR interval:
ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL
 Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
1 Meet Your AliveCor Heart Monitor
 GETTING STARTED HOW TO RECORD YOUR FIRST ECG 1 Meet Your AliveCor Heart Monitor UNPACK Take your AliveCor out of the box. The device is already connected to an attachment plate that can adhere to the back
GETTING STARTED HOW TO RECORD YOUR FIRST ECG 1 Meet Your AliveCor Heart Monitor UNPACK Take your AliveCor out of the box. The device is already connected to an attachment plate that can adhere to the back
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
PSIO 603/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 2007 MRB 422; 626-6833 jburt@u.arizona.edu. MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle
 SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers. Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012
 QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012 Agenda ECG ICH E14 Thorough QT/QTc study Role of Statistical Programmer References
QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012 Agenda ECG ICH E14 Thorough QT/QTc study Role of Statistical Programmer References
Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring
 Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring By Sanjeev Kumar, Applications Engineer, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Heart rate is one of the most frequently measured parameters of the human body and plays an important
Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring By Sanjeev Kumar, Applications Engineer, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Heart rate is one of the most frequently measured parameters of the human body and plays an important
#AS148 - Automated ECG Analysis
 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino Goleta, Ca 93117 Ph (805)685-0066 Fax (805)685-0067 www.biopac.com info@biopac.com #AS148 - Automated ECG Analysis An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical recording
BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino Goleta, Ca 93117 Ph (805)685-0066 Fax (805)685-0067 www.biopac.com info@biopac.com #AS148 - Automated ECG Analysis An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical recording
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome
 Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Table of Contents Error! Bookmark not defined.
 Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Electrophysiology study (EPS)
 Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
510(k) Summary May 7, 2012
 510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Detection of Heart Diseases by Mathematical Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Using Phonocardiogram Signals
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
An ECG Primer. Quick Look. I saw it, but I did not realize it. Elizabeth Peabody
 4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds
 Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds An introduction to the recording and analysis of electrocardiograms, and the sounds of the heart. Written by Staff of ADInstruments Introduction The beating of the heart
Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds An introduction to the recording and analysis of electrocardiograms, and the sounds of the heart. Written by Staff of ADInstruments Introduction The beating of the heart
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
For more information about the use of the Propaq monitor, refer to the Propaq Directions For Use.
 Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
ECG Measurement and Interpretation
 ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics. The Myocardial Cell. Chapter 1- Thaler
 Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Key Medical Terms Associated with the Cardiovascular System
 1 Key Medical Terms Associated with the Cardiovascular System Aneurysm: A thin, weakened section of the wall of an artery or vein that bulges outward, forming a balloon-like sac. Common causes are atherosclerosis,
1 Key Medical Terms Associated with the Cardiovascular System Aneurysm: A thin, weakened section of the wall of an artery or vein that bulges outward, forming a balloon-like sac. Common causes are atherosclerosis,
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs
 ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
Premature Ventricular Contractions. Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS
 Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Introduction. Sinus Rhythms. Premature Beats. Secondary article. John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
 John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol
 Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery
 Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Introduction to Cardiac Electrophysiology, the Electrocardiogram, and Cardiac Arrhythmias INTRODUCTION
 Introduction to Cardiac Electrophysiology, the Electrocardiogram, and Cardiac Arrhythmias Alfred E. Buxton, M.D., Kristin E. Ellison, M.D., Malcolm M. Kirk, M.D., Gregory F. Michaud, M.D. INTRODUCTION
Introduction to Cardiac Electrophysiology, the Electrocardiogram, and Cardiac Arrhythmias Alfred E. Buxton, M.D., Kristin E. Ellison, M.D., Malcolm M. Kirk, M.D., Gregory F. Michaud, M.D. INTRODUCTION
The EasySense unit can detect that the Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor is connected and the range it is set to.
 Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
The Heart Rhythm Charity
 The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2006 Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rhythm)
The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2006 Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rhythm)
