Overview. Fetal heart rates. Electrocardiogram. Recognition and Treatment of
|
|
|
- Geraldine Nichols
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recognition and Treatment of Fetal and Neonatal Arrhythmias Matthew Egan, MD 41 st Regional Perinatal Symposium September 12, 2014 Overview Review normal fetal heart rates and electrocardiogram Irregular rhythms Tachycardias Heart Block Fetal heart rates Electrocardiogram Normal range 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm) Less than 100 bpm is bradycardia di Great than 180 bpm is tachycardia Expect variation Fetal arrhythmias 1-3% of pregnancies
2 Normal ranges vary with age Normal Electrocardiogram 0-1d 1-3d 3-7d d mo mo mo Heart rate (122) R amplitude 5-26 V1 R amplitude 0-10 (4) V6 158 (122) 166 (128) 182 (149) 179 (149) 185 (141) 169 (131) QRS axis (135) (134) (133) (109) (75) (60) 6-98 (55) (13) (15) (12) (10) (10) (10) (9) ( ) (5) (5) (8) (12) (13) (13) Table adapted from Moss and Adams Heart Disease in infants, children and adolescents, 7 th edition, page 257. Irregular rhythms: Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) ECG of PAC Most common arrhythmia during fetal and neonatal time period Can be conducted or blocked at AV node Well tolerated and considered benign Less than 1% risk of progressing to supraventricular tachycardia Usually resolve spontaneously in first few months of life
3 Blocked PAC Fetal PAC Heart rate 77 beats per minute in newborn infant Fetal PAC M-mode Doppler Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Premature beat with different QRS morphology from baseline Rarely seen prenatally More concerning if polymorphic Terminology Couplet = two consecutive PVCs Bigeminy = alternating with sinus beat Trigeminy = every third beat is PVC Typically benign with structurally normal heart and usually no treatment required
4 Premature Ventricular Contractions Tachycardias: Sinus tachycardia Heart rates exceeding upper limits it for age, greater than 180 bpm in fetus 11 1:1 atrial ti to ventricular ti conduction Gradual onset and cessation Secondary to other stimulus Fetus- hypoxia, maternal fever, infection Neonate- fever, dehydration, pain, anemia, hyperthyroidism Sinus tachycardia Sinus tachycardia- Fetus Heart rate 180 bpm
5 Supraventricular tachycardia Most common tachycardia in fetus and infants (1/250 to 1/1000) Rapid, regular tachycardia Abrupt onset and termination Atrioventricular (AV) re-entrant tachycardia most common in infants AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia predominates in older children 90% spontaneously resolve in first year of life SVT Associated anomalies Typically structurally normal heart 9-32% have congenital heart disease Many defects described but most common is Ebstein s anomaly of the tricuspid valve Also hypertrophic p cardiomyopathy, y, rhabdomyomas Genetics Typically sporadic Three fold higher h risk in WPW in 1 st degree relatives Non WPW 7% have first degree relative with SVT Re-entry mechanism Requires 2 pathways around insulated core (AV valve annulus) Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Accessory Connection Preexcitation ti on baseline ECG Connection allows for conduction from atrium ti to ventricle til (antegrade) and usually ventricle to atrium (retrograde) May allow rapid transmission to ventricle (i.e. atrial fibrillation)
6 WPW ECG Fetal SVT Delta wave and short PR interval Fetal SVT M mode Fetal SVT - Hydrops Heart rate 250 bpm
7 Neonatal SVT EKG SVT Management Heart rate = 276 beats per minute Acute management Vagal maneuvers Ice to face, Valsalva, gag reflex Adenosine rapid bolus, then flush Short half life 0.1 mg/kg (max 6 mg) Repeat 0.2 mg/kg (max 12 mg) Unstable, no IV access then cardioversion Sedation when possible 0.5 to 1 J/kg, can repeat 2 J/kg If tachycardia recurs start anti-arrhythmic therapy Medical Therapy Digoxin Mechanism: inhibits Na-K ATPase Slows down AV node conduction Positive inotropic effects First line for SVT, especially in infants Contraindicated in WPW Studies suggest it can increase conductivity in accessory pathway or increase risk sudden death
8 Medical Therapy Beta blocker Inhibition of sinus node, AV node conduction Esmolol- IV form with short half life Propranolol- non selective beta 1 and beta 2 adrenergic receptor blocker Atenolol- selective beta 1 blocker Medical Therapy- Second line Flecainide Na channel blocker Risk of proarrhythmia, widens QRS Sotalol K channel blocking and beta blocker effects Can lead to QTc prolongation, proarrhythmia Amiodarone K channel blocking + multiple other actions, potent Long half life Photosensitivity, thyroid dysfunction, pulmonary fibrosis, elevation of liver enzymes Treatment- Fetal SVT Intermittent SVT less than 50% of time observation Sustained tachycardia Digoxin Digoxin + Flecainide Sotalol +/- Digoxin We initiate therapy as inpatient, monitor maternal telemetry after initial electrocardiogram Fetal strip of SVT conversion Sudden decrease in heart rate with increased variability post conversion
9 Fetal SVT with hydrops resolution after anti-arrhythmic therapy Atrial Flutter Regular, rapid narrow complex tachycardia As much as 30% fetal tachycardia Atrial rates 300 to 500 bpm prenatally, typically 240 to 360 in neonates Usually 2:1 or 3:1 AV conduction Adenosine can be diagnostic if flutter waves difficult to see Fetal Atrial Flutter Fetal Atrial Flutter
10 Fetal Atrial Flutter Fetal atrial flutter 1:1 Atrial Flutter EKG- 2:1 block Treatment fetal atrial flutter If near term, consider delivery First line therapy- Digoxin or Sotalol Second line - Amiodarone ** This article provides treatment and dosing recommendations for fetal arrhythmias
11 Treatment neonatal atrial flutter Synchronized DC cardioversion 0.5 to 1 Joule/kg Antiarrhythmic medication, such as digoxin, can be given Controversial need for maintenance therapy after cardioversion due to low recurrence risk Typically will continue digoxin for 6-9 months AV Block Abnormal conduction from atria to ventricles 1 st degree- PR prolonged 2 nd degree Type I (Wenkebach)- progressive PR prolongation Type II abrupt failure of conduction 3 rd degree (Complete) AV dissociation Complete AV Block Congenital heart block 40% associated with maternal autoimmune disease (Lupus, Sjogren) Anti-Ro and Anti-La antibodies Cross react with fetal conduction system ~50% associated with complex congenital heart disease Heterotaxy common (Polysplenia or left isomerism) May be asymptomatic or associated with heart failure, such as hydrops Worse outcome Hydrops, structurally heart disease, ventricular rate less than 55
12 Fetal heart block Fetal heart block Congenital heart block Treatment Observation for structurally normal heart, normal function Immune associated variant Steroids (dexamethasone) have been effective in some studies at preventing progression to complete block Consider IVIG Both have side effects Not effective in those with structural heart disease Congenital heart block Treatment Sympathomimetics ti (terbutaline) t when ventricular rates less than 55 bpm Fetal pacing not been effective
13 Class 1 Indications for pacemaker placement Congenital 3 rd degree block with ventricular dysfunction or wide complex escape With rate less than 50 bpm and a structurally normal heart With rate less than 70 bpm with congenital heart defect Thank you Sonographers: Maureen, Margaret and Sue Colleagues at Pediatric Cardiology Dr. Atallah, Dr. Smith, Dr. Kveselis, Dr. Byrum Neonatology and Perinatology Services Resources Allen et al. Moss and Adams Heart Disease in Infants, Children, and Adolescents. 8 th Edition; 2013, Donofrio M et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Fetal Cardiac Disease. Circulation Gregoratos G et al. ACC/AHA Guidelines for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia h Devices (Committee on Pacemaker implantation) Circulation. 1998; 97: Killen S and Fish F. Fetal and Neonatal Arrhythmias. Neoreviews 2008:9:e242-e252. Lai et al. Echocardiography in Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease from Fetus to Adult Lopes, L et al. Perinatal Outcome of Fetal AV Block. Circulation. 2008;118. Skinner J and Sharland G. Detection and management of life threatening arrhythmias in the perinatal period. Early Human Development. 2008; 84, Zaidi A and Ro P. Treatment of Fetal and Neonatal Arrhythmias. Touch briefings 2008;
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
Trust Guideline for the Management of New-born Babies with abnormal heart rhythm
 A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
TOP 5. The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac. Arrhythmias in Dogs & Cats. Sinus Arrhythmia. TOP 5 Arrhythmias Seen in Dogs & Cats
 Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
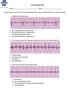 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls
 Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient
 Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
Atrial Fibrillation The High Risk Obese Patient Frederick Schaller, D.O.,F.A.C.O.I. Professor and Vice Dean Touro University Nevada A 56 year old male with a history of hypertension and chronic stable
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT. Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
Electrolyte Physiology. Something in the way she moves
 Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY
 Care Pathway Triage category ATRIAL FIBRILLATION PATHWAY ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY AF/ FLUTTER IS PRIMARY REASON FOR PRESENTATION YES NO ONSET SYMPTOMS OF AF./../ TIME DURATION OF AF
Care Pathway Triage category ATRIAL FIBRILLATION PATHWAY ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT/CARDIOLOGY AF/ FLUTTER IS PRIMARY REASON FOR PRESENTATION YES NO ONSET SYMPTOMS OF AF./../ TIME DURATION OF AF
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Introduction. Sinus Rhythms. Premature Beats. Secondary article. John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
 John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect. Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015
 Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
Atrial Fibrillation: Drugs, Ablation, or Benign Neglect Robert Kennedy, MD October 10, 2015 Definitions 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary.
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
RUSSELLS HALL HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT
 RUSSELLS HALL HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE ATRIAL FIBRILLATION March 2011 For quick links to AF algorithms: UNSTABLE PATIENT STABLE PATIENT - 1 - Introduction Atrial fibrillation is
RUSSELLS HALL HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE ATRIAL FIBRILLATION March 2011 For quick links to AF algorithms: UNSTABLE PATIENT STABLE PATIENT - 1 - Introduction Atrial fibrillation is
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. in general practice. 22 BPJ Issue 39
 Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
School of Health Sciences
 School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, ARRHYTHMIAS AND PACING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Guidelines for the interpretation of the neonatal electrocardiogram
 European Heart Journal (2002) 23, 1329 1344 doi:10.1053/euhj.2002.3274, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Task Force Report Guidelines for the interpretation of the neonatal electrocardiogram
European Heart Journal (2002) 23, 1329 1344 doi:10.1053/euhj.2002.3274, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Task Force Report Guidelines for the interpretation of the neonatal electrocardiogram
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines. Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center
 Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND ANAESTHESIA
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND ANAESTHESIA Dr AD Theron, SHO in Anaesthesia, Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Exeter, UK. E-mail: drabrietheron@yahoo.co.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the commonest arrhythmias.
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND ANAESTHESIA Dr AD Theron, SHO in Anaesthesia, Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Exeter, UK. E-mail: drabrietheron@yahoo.co.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the commonest arrhythmias.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways. for the primary care physicians
 Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
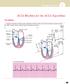 ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
Introduction 2/9/2015
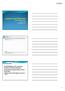 Thomas Haffey, D.O. FACC, FACOI, FNLA, CSOM February, 2015 Atrial Tachycardias Diagram summarizing types of atrial tachycardias often encountered in patients with a history of AF, including those seen
Thomas Haffey, D.O. FACC, FACOI, FNLA, CSOM February, 2015 Atrial Tachycardias Diagram summarizing types of atrial tachycardias often encountered in patients with a history of AF, including those seen
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier
 Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Syncope. enough to include disorders such as epileptic seizures and concussion. January 14-15, 2011 SCA Conference 1
 Syncope and Atypical Seizures Ravi Mandapati, M.D., FACC.; FHRS Director, Specialized Program for Arrhythmias in Congenital Heart Disease UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center David Geffen School of Medicine
Syncope and Atypical Seizures Ravi Mandapati, M.D., FACC.; FHRS Director, Specialized Program for Arrhythmias in Congenital Heart Disease UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center David Geffen School of Medicine
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome
 Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide
 Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Chest Pain in Young Athletes. Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.
 Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
TABLE 1 Clinical Classification of AF. New onset AF (first detected) Paroxysmal (<7 days, mostly < 24 hours)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist
 Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
JAPI VOL. 52 NOVEMBER 2004 www.japi.org 883
 Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers
 1 Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. All students were awarded 2 points for question #2 due to no appropriate responses for
1 Quiz 4 Arrhythmias summary statistics and question answers The correct answers to questions are indicated by *. All students were awarded 2 points for question #2 due to no appropriate responses for
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
ACUTE ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TREATMENT IN THE SURGICAL PATIENT
 DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Atrial fibrillation. Quick reference guide. Issue date: June 2006. The management of atrial fibrillation
 Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Quick reference guide Issue date: June 2006 Atrial fibrillation The management of atrial fibrillation Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Contents Contents Patient-centred
Anti Arrhythmic Agents
 Introduction to Antiarrhythmic Agents Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Anti Arrhythmic Agents Introduction to anti arrhythmic agents Mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis Management
Introduction to Antiarrhythmic Agents Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Anti Arrhythmic Agents Introduction to anti arrhythmic agents Mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis Management
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI
 Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Atrial Fibrillation and Cardiac Device Therapy RAKESH LATCHAMSETTY, MD DIVISION OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITAL ANN ARBOR, MI Outline Atrial Fibrillation What is it? What are the associated
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response
 Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
Question 1: Interpret the rhythm strip above (comment on regularity, rate, P wave, PR interval and QRS)?
 It is your first month on your NICU rotation and you are prerounding on your patients. The nurse takes you aside and says she s been seeing something funny on the cardiac monitor. You walk to the bedside
It is your first month on your NICU rotation and you are prerounding on your patients. The nurse takes you aside and says she s been seeing something funny on the cardiac monitor. You walk to the bedside
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias
 Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation
 The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
Ngaire has Palpitations
 Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being
 Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. danjcohen@optonline.net
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. danjcohen@optonline.net
Official Online ACLS Exam
 \ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
\ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD
 92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
