Using VLANs with Cisco Aironet Wireless Equipment
|
|
|
- Hilary Sutton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using VLANs with Cisco Aironet Wireless Equipment Document ID: In order to get Cisco Aironet drivers, firmware and utility software, use this link to the Cisco Wireless Downloads. Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions VLANs Significance of Native VLAN VLANs on Access Points Concepts with Access Points Access Point Configuration VLANs on Bridges Concepts on Bridges Bridge Configuration Use a RADIUS Server to Assign Users to VLANs Use a RADIUS Server for Dynamic Mobility Group Assignment Bridge Group Configuration on Access Points and Bridges Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) Interaction with Related Switches Switch ConfigurationCatalyst OS Switch ConfigurationIOS Based Catalyst Switches Switch ConfigurationCatalyst 2900XL/3500XL Verify Verify the Wireless Equipment Verify the Switch Troubleshoot Related Information Introduction This document provides a sample configuration to use virtual LANs (VLANs) with Cisco Aironet wireless equipment. Prerequisites Requirements Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration: Familiarity with Cisco Aironet wireless equipment
2 Familiarity with LAN switching concepts of VLANs and VLAN trunking Components Used The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions: Cisco Aironet Access Points and Wireless Bridges Cisco Catalyst Switches The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command. Related Products You can use the switch side of this configuration with any of these hardware or software: Catalyst 6x00/5x00/4x00 that runs CatOS or IOS Catalyst 35x0/37x0/29xx that runs IOS Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL that runs IOS Conventions Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions. VLANs A VLAN is a switched network that is logically segmented by functions, project teams, or applications rather than on a physical or geographical basis. For example, all workstations and servers used by a particular workgroup team can be connected to the same VLAN, regardless of their physical connections to the network or the fact that they can be intermingled with other teams. Use VLANs to reconfigure the network through software rather than physically unplug or move the devices or wires. A VLAN can be thought of as a broadcast domain that exists within a defined set of switches. A VLAN consists of a number of end systems, either hosts or network equipment (such as bridges and routers), connected by a single bridging domain. The bridging domain is supported on various pieces of network equipment, such as LAN switches, that operate bridging protocols between them with a separate group for each VLAN. When you connect a device to a Cisco Catalyst switch, the port where the device is connected is a member of VLAN 1. The MAC address of that device is a part of VLAN 1. You can define multiple VLANs on a single switch, and you can configure a switch port on most Catalyst models as a member of multiple VLANs.
3 When the number of ports in a network exceeds the port capacity of the switch, you must cross connect multiple switch chassis, which defines a trunk. The trunk is not a member of any VLAN, but a conduit over which traffic passes for one or more VLANs. In fundamental terms, the key in the configuration of an access point to connect to a specific VLAN is to configure its SSID to recognize that VLAN. Because VLANs are identified by a VLAN ID or name, it follows that, if the SSID on an access point is configured to recognize a specific VLAN ID or name, a connection to the VLAN is established. When this connection is made, associated wireless client devices that have the same SSID can access the VLAN through the access point. The VLAN processes data to and from the clients the same way that it processes data to and from wired connections. You can configure up to 16 SSIDs on your access point, so you can support up to 16 VLANs. You can assign only one SSID to a VLAN. You extend VLANs into a wireless LAN when you add IEEE Q tag awareness to the access point. Frames destined for different VLANs are transmitted by the access point wirelessly on different SSIDs with different WEP keys. Only the clients associated with that VLAN receive those packets. Conversely, packets that come from a client associated with a certain VLAN are Q tagged before they are forwarded onto the wired network. For example, employees and guests can access the wireless network of a company at the same time and be administratively separate. A VLAN maps to an SSID, and the wireless client attaches to the appropriate SSID. In networks with wireless bridges, you can pass multiple VLANs across the wireless link in order to provide connectivity to a VLAN from separate locations. If 802.1q is configured on the FastEthernet interface of an access point, the access point always sends keepalives on VLAN1 even if VLAN 1 is not defined on the access point. As a result, the Ethernet switch connects to the access point and generates a warning message. There is no loss of function on either the access point or the switch, but the switch log contains meaningless messages that can cause more important messages to be wrapped and not seen. This behavior creates a problem when all SSIDs on an access point are associated to mobility networks. If all SSIDs are associated to mobility networks, the Ethernet switch port to which the access point is connected can be configured as an access port. The access port is normally assigned to the native VLAN of the access point, which is not necessarily VLAN1. This causes the Ethernet switch to generate warning messages noting that traffic with an 802.1q tag is sent from the access point. You can eliminate the excessive messages on the switch if you disable the keepalive function. If you ignore minor points in these concepts when you deploy VLANs with Cisco Aironet wireless equipment, you can experience unexpected performance, for example:
4 The failure to limit allowed VLANs on the trunk to those defined on the wireless device If VLANs 1, 10, 20, 30 and 40 are defined on the switch, but only VLANs 1, 10 and 30 are defined on the wireless equipment, you must remove the others from the trunk switchport. Misuse of the designation of infrastructure SSID When you install access points, only assign the infrastructure SSID when you use an SSID on: workgroup bridge devices repeater access points non root bridges It is a misconfiguration to designate the infrastructure SSID for an SSID with only wireless laptop computers for clients, and causes unpredictable results. In bridge installations, you can only have one infrastructure SSID. The infrastructure SSID must be the SSID that correlates to the Native VLAN. Misuse or incorrect design of guest mode SSID designation When you define multiple SSIDs/VLANs on Cisco Aironet wireless equipment, one (1) SSID can be assigned as guest mode SSID with the SSID broadcast in radio beacons. The other SSIDs are not broadcast. The client devices must indicate which SSID to connect. Failure to recognize that multiple VLANs and SSIDs indicate multiple OSI Model Layer 3 subnets Deprecated versions of Cisco Aironet software permit binding multiple SSIDs to one VLAN. Current versions do not. OSI Model Layer 3 routing failures or incorrect designs Each SSID and its linked VLAN must have a routing device and some source to address clients, for example a DHCP server or the scope on a DHCP server. Misunderstand or incorrectly configure Native VLAN The routers and switches that make up the physical infrastructure of a network are managed in a different method than the client PCs that attach to that physical infrastructure. The VLAN these router and switch interfaces are members of is called the Native VLAN (by default, VLAN 1). Client PCs are members of a different VLAN, just as IP telephones are members of yet another VLAN. The administrative interface of the access point or bridge (interface BVI1) are considered and numbered a part of the Native VLAN regardless of what VLANs or SSIDs pass through that wireless device. Significance of Native VLAN When you use an IEEE 802.1Q trunk port, all frames are tagged except those on the VLAN configured as the "native VLAN" for the port. Frames on the native VLAN are always transmitted untagged and are normally received untagged. Therefore, when an AP is connected to the switchport, the native VLAN configured on the AP must match the native VLAN configured on the switchport. Note: If there is a mismatch in the native VLANs, the frames are dropped. This scenario is better explained with an example. If the native VLAN on the switchport is configured as VLAN 12 and on the AP, the native VLAN is configured as VLAN 1, then when the AP sends a frame on its native VLAN to the switch, the switch considers the frame as belonging to VLAN 12 since the frames from the native VLAN of the AP are untagged. This causes confusion in the network and results in connectivity problems. The same happens when the switchport forwards a frame from its native VLAN to the AP.
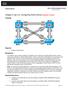
5 The configuration of native VLAN becomes even more important when you have a Repeater AP setup in your wireless network. You cannot configure multiple VLANs on the Repeater APs. Repeater APs support only the native VLAN. Therefore, the native VLAN configuration on the root AP, the switch port to which the AP is connected, and the Repeater AP, must be the same. Otherwise traffic through the switch does not pass to and from the Repeater AP. An example for the scenario where the mismatch in the Repeater AP's native VLAN configuration can create problems is when there is a DHCP server behind the switch to which the root AP is connected. In this case the clients associated with the Repeater AP do not receive an IP address from the DHCP server because the frames (DHCP requests in our case) from the Repeater AP's native VLAN (which is not the same as root AP and the switch) are dropped. Also, when you configure the switch port, ensure that all the VLANs that are configured on the APs are allowed on the switchport. For example, if VLANs 6, 7, and 8 exist on the AP (Wireless Network) the VLANs have to be allowed on the switchport. This can be done using this command in the switch: switchport trunk allowed vlan add 6,7,8 By default, a switchport configured as a trunk allows all VLANs to pass through the trunk port. Refer to Interaction with Related Switches for more information on how to configure the switchport. Note: Allowing all VLANs on the AP can also become a problem in some cases, specifically if it is a large network. This can result in high CPU utilization on the APs. Prune the VLANs at the switch so that only the VLAN traffic that the AP is interested in passes through the AP to avoid high CPU. VLANs on Access Points In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document. Note: In order to find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool ( registered customers only). Concepts with Access Points This section discusses concepts about how to deploy VLANs on access points and refers to this network diagram. In this sample network, VLAN 1 is the Native VLAN, and VLANs 10, 20, 30 and 40 exist, and are trunked to another switch chassis. Only VLANs 10 and 30 are extended into the wireless domain. The Native VLAN is required to provide management capability and client authentications.
6 Access Point Configuration In order to configure the access point for VLANs, complete these steps: 1. From the AP GUI, click Services > VLAN to navigate to the Services: VLAN page. a. The first step is to configure the native VLAN. From the Current VLAN List, select New. b. Enter the VLAN number of the Native VLAN in the VLAN ID box. The VLAN number must match the Native VLAN configured on the switch. c. Because interface BVI 1 is associated to the subinterface of the Native VLAN, the IP address assigned to interface BVI 1 must be in the same IP subnet as other infrastructure devices on the network (that is, the interface SC0 on a Catalyst switch that runs CatOS.) d. Select the checkbox for the Native VLAN. e. Select check boxes for the radio interface or interfaces where this VLAN applies. f. Click Apply.
7 Or, from the CLI, issue these commands: AP# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. AP(config)# interface Dot11Radio0.1 AP(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native AP(config subif)# interface FastEthernet0.1 AP(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native AP(config subif)# end AP# write memory 2. In order to configure other VLANs, follow these steps: a. From the Current VLAN List, select New. b. Enter the VLAN number of the desired VLAN in the VLAN ID box. The VLAN number must match a VLAN configured on the switch. c. Select check boxes for the radio interface or interfaces where this VLAN applies. d. Click Apply.
8 e. Or, from the CLI, issue these commands: AP# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. AP(config)# interface Dot11Radio0.10 AP(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10 AP(config subif)# interface FastEthernet0.10 AP(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10 AP(config subif)# end AP# write memory Repeat steps 2a through 2d for each VLAN desired or enter these commands from the CLI with appropriate changes to the subinterface and VLAN numbers: AP# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. AP(config)# interface Dot11Radio0.30 AP(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 30 AP(config subif)# interface FastEthernet0.30 AP(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 30 AP(config subif)# end AP# write memory 3. The next step is to associate the configured VLANs to the SSIDs. In order to do this, click Security > SSID Manager.
9 Note: You do not need to associate every VLAN defined on the access point with an SSID. For example, for security reasons, most access point installations do not associate an SSID with the Native VLAN. a. In order to create a new SSID, choose New. b. Enter the desired SSID (case sensitive) in the SSID box. c. Select the desired VLAN number to associate this SSID with from the dropdown list. Note: In order to keep this document within its intended scope, security for an SSID is not addressed. d. Click Apply RadioX to create the SSID on the selected radio, or Apply all to create it on all radios. Or from the CLI, issue these commands:
10 4. AP# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. AP(config)# interface Dot11Radio0 AP(config if)# ssid Red AP(config if ssid)# vlan 10 AP(config if ssid)# end AP# write memory Repeat steps 3a through 3d for each SSID desired or enter these commands from the CLI with appropriate changes to the SSID. AP# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. AP(config)# interface Dot11Radio0 AP(config if)# ssid Green AP(config if ssid)# vlan 30 AP(config if ssid)# end AP# write memory Note: These examples do not include authentication. Some form of authentication (Open, Network EAP) is required for clients to associate. VLANs on Bridges Concepts on Bridges This section discusses concepts related to how to deploy VLANs on bridges and refers to this network diagram. In this sample network, VLAN 1 is the Native VLAN, and VLANs 10, 20, 30 and 40 exist. Only VLANs 10 and 30 are extended to the other side of the link. The wireless link is encrypted. In order to encrypt data that passes over the radio link, apply encryption to only the SSID of the Native VLAN. That encryption applies to all other VLANs. When you bridge, there is no need to associate a separate SSID with each VLAN. VLAN configurations is the same on both the root and non root bridges.
11 Bridge Configuration In order to configure the bridge for VLANs, like the sample network diagram, complete these steps: 1. From the AP GUI, click Services > VLAN to navigate to the Services: VLAN page. a. The first step is to configure the Native VLAN. In order to do this, choose <New> from the Current VLAN List. b. Enter the VLAN number of the Native VLAN in the VLAN ID box. This must match the Native VLAN configured on the switch. c. Because interface BVI 1 is associated to the subinterface of the Native VLAN, the IP address assigned to interface BVI 1 must be in the same IP subnet as other infrastructure devices on the network (i.e. interface SC0 on a Catalyst switch that runs CatOS.) d. Select the checkbox for the Native VLAN. e. Click Apply. Or, from the CLI, issue these commands: bridge# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. bridge(config)# interface Dot11Radio0.1 bridge(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native bridge(config subif)# interface FastEthernet0.1 bridge(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native bridge(config subif)# end bridge# write memory 2. In order to configure other VLANs, follow these steps: a. From the Current VLAN List, select New.
12 b. Enter the VLAN number of the desired VLAN in the VLAN ID box. The VLAN number must match a VLAN configured on the switch. c. Click Apply. Or, from the CLI, issue these commands: bridge# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. bridge(config)# interface Dot11Radio0.10 bridge(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10 bridge(config subif)# interface FastEthernet0.10 bridge(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10 bridge(config subif)# end bridge# write memory d. Repeat steps 2a through 2c for each VLAN desired or enter the commands from the CLI with appropriate changes to the subinterface and VLAN numbers. AP# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. bridge(config)# interface Dot11Radio0.30 bridge(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 30 bridge(config subif)# interface FastEthernet0.30 bridge(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 30 bridge(config subif)# end bridge# write memory 3. From the SSID Manager (under the Security > SSID Manager menu item,) associate the Native VLAN with an SSID.
13 Note: When you bridge, the only SSID that you must associate with a VLAN is the one that correlates to the Native VLAN. You must designate this SSID as the Infrastructure SSID. a. From the Current SSID List, select New. b. Enter the desired SSID (case sensitive) in the SSID box. c. Select the VLAN number that correlates to the Native VLAN from the dropdown list. Note: In order to keep this document within its intended scope, security for an SSID is not addressed. d. Click Apply to create the SSID on the radio and associate it to the Native VLAN. e. Scroll back down to the bottom of the page, and under Global Radio G SSID Properties select the SSID from the Set Infrastructure SSID dropdown list. Click Apply. Or from the CLI, issue these commands: AP# configure terminal
14 Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. AP(config)# interface Dot11Radio0 AP(config if)# ssid Black AP(config if ssid)# vlan 1 AP(config if ssid)# infrastructure ssid AP(config if ssid)# end AP# write memory Note: When VLANs are in use, SSIDs are configured under the physical Dot11Radio interface, not under any logical subinterface. Note: This example does not include authentication. The root and non root bridges require some form of authentication (Open, Network EAP, etc.) in order to associate. Use a RADIUS Server to Assign Users to VLANs You can configure your RADIUS authentication server to assign users or groups of users to a specific VLAN when they authenticate to the network. For information on this feature, refer to the section Using a RADIUS Server to Assign Users to VLANs of the document Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points, 12.4(3g)JA & 12.3(8)JEB. Use a RADIUS Server for Dynamic Mobility Group Assignment You can also configure a RADIUS server to dynamically assign mobility groups to users or user groups. This eliminates the need to configure multiple SSIDs on the access point. Instead, you need to configure only one SSID per access point. For information on this feature, refer to the section Using a RADIUS Server for Dynamic Mobility Group Assignment of the document Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points, 12.4(3g)JA & 12.3(8)JEB. Bridge Group Configuration on Access Points and Bridges In general, bridge groups create segmented switching domains. Traffic is confined to hosts within each bridge group, but not between the bridge groups. The switch forwards traffic only among the hosts that make up the bridge group, which restricts broadcast and multicast traffic (flooding) to only those hosts. Bridge groups relieve network congestion and provide additional network security when they segment traffic to certain areas of the network. Refer to Bridging Overview for detailed information. In a wireless network, bridge groups are configured on the wireless access points and bridges in order for the data traffic of a VLAN to be transmitted from wireless media to the wired side and vice versa. Perform this step from the AP CLI in order to enable bridge groups globally on the access point/bridge. This example uses the bridge group number 1. Ap(configure)#bridge 1 Note: You can number your bridge groups from 1 to 255. Configure the radio interface and the Fast Ethernet interface of the wireless device to be in the same bridge group. This creates a path between these two different interfaces, and they are in the same VLAN for tagging purposes. As a result, the data transmitted from the wireless side through the radio interface is transmitted to the Ethernet interface to which the wired network is connected and vice versa. In other words, radio and
15 Ethernet interfaces that belong to the same bridge group actually bridge the data between them. In an access point/bridge, you need to have one bridge group per VLAN so that traffic can pass from the wire to the wireless and vice versa. The more VLAN you have that need to pass traffic across the wireless, the more bridge groups that are needed. For example, if you have only one VLAN to pass traffic across the wireless to wired side of your network, configure only one bridge group from the CLI of the AP/bridge. If you have multiple VLANs to pass traffic from the wireless to wired side and vice versa, configure bridge groups for each VLAN at the radio sub interface, as well as the Fast Ethernet sub interface. 1. Configure the bridge group in the wireless interface with the bridge group dot11radio interface command. This is an example. AP# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. AP(config)# interface Dot11Radio0.1 Ap(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native Ap(config subif)# bridge group 1! Here "1" represents the bridge group number. ap(config subif)# exit 2. Configure the bridge group with the same bridge group number ("1" in this example) in the Fast Ethernet interface so that VLAN 1 traffic is passed across the wireless interface to this wired side and vice versa. Ap(config)# interface fastethernet0.1 Ap(config subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native Ap(config subif)# bridge group 1! Here "1" represents the bridge group number. Ap(config subif)# exit Note: When you configure a bridge group on the radio interface, these commands are set automatically. bridge group 1 subscriber loop control bridge group 1 block unknown source no bridge group 1 source learning no bridge group 1 unicast flooding bridge group 1 spanning disabled Note: When you configure a bridge group on the Fast Ethernet interface, these commands are set automatically. no bridge group 1 source learning bridge group 1 spanning disabled Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) Integrated routing and bridging makes it possible to route a specific protocol between routed interfaces and bridge groups, or route a specific protocol between bridge groups. Local or unroutable traffic can be bridged
16 among the bridged interfaces in the same bridge group, while routable traffic can be routed to other routed interfaces or bridge groups With integrated routing and bridging, you can do this: Switch packets from a bridged interface to a routed interface Switch packets from a routed interface to a bridged interface Switch packets within the same bridge group Enable IRB on the wireless access points and bridges in order to route your traffic between bridge groups or between routed interfaces and bridge groups. You need an external router or a Layer 3 switch in order to route between bridge groups or between bridge groups and routed interfaces. Issue this command in order to enable IRB in the AP/bridge. AP(configure)#bridge irb Integrated routing and bridging uses the concept of a Bridge Group Virtual Interface (BVI) in order to route traffic between routed interfaces and bridge groups or between bridge groups. A BVI is a virtual interface within the Layer 3 switch router that acts like a normal routed interface. A BVI does not support bridging but actually represents the correspondent bridge group to routed interfaces within the Layer 3 switch router. It has all the network layer attributes (such as a network layer address and filters) that apply to the correspondent bridge group. The interface number assigned to this virtual interface corresponds to the bridge group that this virtual interface represents. This number is the link between the virtual interface and the bridge group. Perform these steps in order to configure the BVI on access points and bridges. 1. Configure the BVI and assign the correspondent number of the bridge group to the BVI. This example assigns bridge group number 1 to the BVI. Ap(configure)#interface BVI 1 AP(config if)#ip address ! Assign an IP address to the BVI. Ap(config if)#no shut 2. Enable a BVI to accept and route routable packets received from its correspondent bridge group. Ap(config)# bridge 1 route ip!! This example enables the BVI to accept and route the IP packet. It is important to understand that you only need a BVI for the management/native VLAN in which the AP is located (in this example, VLAN 1). You do not need a BVI for any other subinterface, irrespective of how many VLANs and bridge groups you configure on your AP/bridge. This is because you tag the traffic in all other VLANs (except the native VLAN) and send it out to the switch though a dot1q trunked interface onto the wired side. For example, if you have 2 VLANs on your network, you need two bridge groups, but only one BVI correspondent to the management VLAN is sufficient in your wireless network.
17 When you enable routing for a given protocol on the bridge group virtual interface, packets that come from a routed interface, but are destined for a host in a bridged domain, are routed to the bridge group virtual interface and are forwarded to the correspondent bridged interface. All traffic that is routed to the bridge group virtual interface is forwarded to the correspondent bridge group as bridged traffic. All routable traffic received on a bridged interface is routed to other routed interfaces as if it comes directly from the bridge group virtual interface. Refer to Configure Bridging for more detailed information on bridging and IRB. Interaction with Related Switches In this section, you are presented with the information to configure, or verify the configuration of the Cisco switches that connect to Cisco Aironet wireless equipment. Note: In order to find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool ( registered customers only). Switch ConfigurationCatalyst OS In order to configure a switch that runs Catalyst OS to trunk VLANs to an access point, the command syntax is set trunk <module #/port #> on dot1q and set trunk <module #/port #> <vlan list>. An example from to the sample network diagram, is: set trunk 2/1 on dot1q set trunk 2/1 1,10,30 Switch ConfigurationIOS Based Catalyst Switches From interface configuration mode, enter these commands, if you want to: Configure the switchport to trunk VLANs to an access point On a Catalyst switch that runs IOS The CatIOS includes but is not limited to: 6x00 4x00 35x0 295x switchport mode trunk switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport nonegotiate switchport trunk native vlan 1 switchport trunk allowed vlan add 1,10,30 Note: IOS based Cisco Aironet wireless equipment does not support Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), so the switch must not try to negotiate it. Switch ConfigurationCatalyst 2900XL/3500XL From interface configuration mode, enter these commands, if you want to configure the switchport to trunk VLANs to an access point on a Catalyst 2900XL or 3500XL switch that runs IOS:
18 Verify switchport mode trunk switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 1 switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,10,30 Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly. Verify the Wireless Equipment show vlandisplays all VLANs currently configured on the access point, and their status ap#show vlan Virtual LAN ID: 1 (IEEE 802.1Q Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interfaces: FastEthernet0.1 Dot11Radio0.1 Virtual Dot11Radio0.1 This is configured as native Vlan for the following interface(s) : FastEthernet0 Dot11Radio0 Virtual Dot11Radio0 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: Bridging Bridge Group Bridging Bridge Group Virtual LAN ID: 10 (IEEE 802.1Q Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interfaces: FastEthernet0.10 Dot11Radio0.10 Virtual Dot11Radio0.10 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: Bridging Bridge Group Bridging Bridge Group Bridging Bridge Group Virtual LAN ID: 30 (IEEE 802.1Q Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interfaces: FastEthernet0.30 Dot11Radio0.30 Virtual Dot11Radio0.30 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: Bridging Bridge Group Bridging Bridge Group Bridging Bridge Group ap# show dot11 associationsdisplays information about associated clients, per SSID/VLAN ap#show dot11 associations Client Stations on Dot11Radio0: SSID [Green] : SSID [Red] :
19 Others: (not related to any ssid) ap# Verify the Switch On a Catalyst OS based switch, show trunk <module #/port #>displays the status of a trunk on a given port Console> (enable) show trunk 2/1 * indicates vtp domain mismatch Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan 2/1 on dot1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk 2/1 1,10,30 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain 2/1 1,10,30 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned 2/1 1,10,30 Console> (enable) On a IOS based switch, show interface fastethernet <module #/port #> trunk displays the status of a trunk on a given interface 2950g#show interface fastethernet 0/22 trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/22 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/22 1,10,30 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/22 1,10,30 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/22 1,10, gA# On a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL switch, show interface fastethernet <module #/port #> switchport displays the status of a trunk on a given interface cat3524xl#show interface fastethernet 0/22 switchport Name: Fa0/22 Switchport: Enabled Administrative mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: Disabled Access Mode VLAN: 0 ((Inactive)) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking VLANs Enabled: 1,10,30, Trunking VLANs Active: 1,10,30 Pruning VLANs Enabled: Priority for untagged frames: 0 Override vlan tag priority: FALSE
20 Troubleshoot Voice VLAN: none Appliance trust: none Self Loopback: No wlan cat3524xl a# There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration. Related Information Configuring VLANs (Access Point Configuration Guide) Configuring VLANs (Bridge Configuration Guide) Trunking Technical Support Interaction with Related Switches System Requirements to Implement Trunking Overview of Bridging Wireless Authentication Types on a Fixed ISR Configuration Example Wireless Authentication Types on Fixed ISR Through SDM Configuration Example Wireless LAN Connectivity Using an ISR with WEP Encryption and LEAP Authentication Configuration Example Basic Wireless LAN Connection Configuration Example Technical Support & Documentation Cisco Systems Contacts & Feedback Help Site Map Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions Privacy Statement Cookie Policy Trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. Updated: Oct 15, 2009 Document ID: 46141
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example
 Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Table of Contents. Cisco Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example
 Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Cisco Aironet Wireless Bridges FAQ
 Cisco Aironet Wireless Bridges FAQ Document ID: 16041 Contents Introduction What is the Cisco Aironet Wireless Bridge? What are the different platforms of wireless bridges that Cisco offers? Where can
Cisco Aironet Wireless Bridges FAQ Document ID: 16041 Contents Introduction What is the Cisco Aironet Wireless Bridge? What are the different platforms of wireless bridges that Cisco offers? Where can
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router
 Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Overview of Routing between Virtual LANs
 Overview of Routing between Virtual LANs This chapter provides an overview of virtual LANs (VLANs). It describes the encapsulation protocols used for routing between VLANs and provides some basic information
Overview of Routing between Virtual LANs This chapter provides an overview of virtual LANs (VLANs). It describes the encapsulation protocols used for routing between VLANs and provides some basic information
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R
 VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
Web Authentication Proxy on a Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Example
 Web Authentication Proxy on a Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Example Document ID: 113151 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Web Authentication Proxy on
Web Authentication Proxy on a Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Example Document ID: 113151 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Web Authentication Proxy on
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Management Software. Web Browser User s Guide AT-S106. For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch. Version 1.0.0. 613-001339 Rev.
 Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
Network Detector Setup and Configuration
 339 N. Bernardo Avenue, Suite 200 Mountain View, CA 94043 www.airtightnetworks.net MODE SYST RPS MASTR STAT SPEDUPLX STACK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91 0 11 12 1X 2X 11X 12X 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 2122 23 24 13X
339 N. Bernardo Avenue, Suite 200 Mountain View, CA 94043 www.airtightnetworks.net MODE SYST RPS MASTR STAT SPEDUPLX STACK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91 0 11 12 1X 2X 11X 12X 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 2122 23 24 13X
Enabling Multiple Wireless Networks on RV320 VPN Router, WAP321 Wireless-N Access Point, and Sx300 Series Switches
 print email Article ID: 4941 Enabling Multiple Wireless Networks on RV320 VPN Router, WAP321 Wireless-N Access Point, and Sx300 Series Switches Objective In an ever-changing business environment, your
print email Article ID: 4941 Enabling Multiple Wireless Networks on RV320 VPN Router, WAP321 Wireless-N Access Point, and Sx300 Series Switches Objective In an ever-changing business environment, your
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Switching in an Enterprise Network
 Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)
 4 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Contents Overview...................................................... 4-3 Configuration Options: Normal Versus Advanced Mode.............. 4-4 Normal Mode Configuration..................................
4 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Contents Overview...................................................... 4-3 Configuration Options: Normal Versus Advanced Mode.............. 4-4 Normal Mode Configuration..................................
VLANs. Application Note
 VLANs Application Note Table of Contents Background... 3 Benefits... 3 Theory of Operation... 4 IEEE 802.1Q Packet... 4 Frame Size... 5 Supported VLAN Modes... 5 Bridged Mode... 5 Static SSID to Static
VLANs Application Note Table of Contents Background... 3 Benefits... 3 Theory of Operation... 4 IEEE 802.1Q Packet... 4 Frame Size... 5 Supported VLAN Modes... 5 Bridged Mode... 5 Static SSID to Static
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
LANs and VLANs A Simplified Tutorial
 Application Note LANs and VLANs A Simplified Tutorial Version 3.0 May 2002 COMPAS ID 90947 Avaya Labs 1 Companion document IP Addressing: A Simplified Tutorial COMPAS ID 92962 2 Introduction As the name
Application Note LANs and VLANs A Simplified Tutorial Version 3.0 May 2002 COMPAS ID 90947 Avaya Labs 1 Companion document IP Addressing: A Simplified Tutorial COMPAS ID 92962 2 Introduction As the name
FSM73xx GSM73xx GMS72xxR Shared access to the Internet across Multiple routing VLANs using a Prosafe Firewall
 FSM73xx GSM73xx GMS72xxR Shared access to the Internet across Multiple routing VLANs using a Prosafe Firewall This document describes how to: - Create multiple routing VLANs - Obtain Internet access on
FSM73xx GSM73xx GMS72xxR Shared access to the Internet across Multiple routing VLANs using a Prosafe Firewall This document describes how to: - Create multiple routing VLANs - Obtain Internet access on
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Configuring DHCP Snooping
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
What is VLAN Routing?
 Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
How To Balance On A Cisco Catalyst Switch With The Etherchannel On A Fast Ipv2 (Powerline) On A Microsoft Ipv1 (Powergen) On An Ipv3 (Powergadget) On Ipv4
 Cisco - Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switch...Page 1 of 10 Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents
Cisco - Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switch...Page 1 of 10 Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000
 Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
How to Create VLANs Within a Virtual Switch in VMware ESXi
 How to Create VLANs Within a Virtual Switch in VMware ESXi I am not responsible for your actions or their outcomes, in any way, while reading and/or implementing this tutorial. I will not provide support
How to Create VLANs Within a Virtual Switch in VMware ESXi I am not responsible for your actions or their outcomes, in any way, while reading and/or implementing this tutorial. I will not provide support
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice
 BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Securing end devices
 Securing end devices Securing the network edge is already covered. Infrastructure devices in the LAN Workstations Servers IP phones Access points Storage area networking (SAN) devices. Endpoint Security
Securing end devices Securing the network edge is already covered. Infrastructure devices in the LAN Workstations Servers IP phones Access points Storage area networking (SAN) devices. Endpoint Security
Basic Wireless Configuration
 Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Abstract. Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Sample Configuration for using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) with Cisco Catalyst 4500 or 3750 Switches for VLAN Assignment for Avaya 9600 and 1600 Series
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Sample Configuration for using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) with Cisco Catalyst 4500 or 3750 Switches for VLAN Assignment for Avaya 9600 and 1600 Series
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing
 Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Abstract. MEP; Reviewed: GAK 10/17/2005. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2005 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer
 Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer Objectives Organize the CCENT objectives by which layer or layers they address. Background / Preparation In this lab, you associate the objectives of
Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer Objectives Organize the CCENT objectives by which layer or layers they address. Background / Preparation In this lab, you associate the objectives of
GregSowell.com. Mikrotik Basics
 Mikrotik Basics Terms Used Layer X When I refer to something being at layer X I m referring to the OSI model. VLAN 802.1Q Layer 2 marking on traffic used to segment sets of traffic. VLAN tags are applied
Mikrotik Basics Terms Used Layer X When I refer to something being at layer X I m referring to the OSI model. VLAN 802.1Q Layer 2 marking on traffic used to segment sets of traffic. VLAN tags are applied
BLADE PVST+ Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco
 BLADE PVST+ Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco Technical Brief Industry-standard PVST+ Spanning Tree Protocol with Cisco interoperability Introduction...1 Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1d)...1
BLADE PVST+ Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco Technical Brief Industry-standard PVST+ Spanning Tree Protocol with Cisco interoperability Introduction...1 Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1d)...1
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Microsoft Windows 2003 DNS Server for Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) Discovery Configuration Example
 Microsoft Windows 2003 DNS Server for Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) Discovery Configuration Example Document ID: 107606 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Wireless
Microsoft Windows 2003 DNS Server for Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) Discovery Configuration Example Document ID: 107606 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Wireless
VLAN 802.1Q. 1. VLAN Overview. 1. VLAN Overview. 2. VLAN Trunk. 3. Why use VLANs? 4. LAN to LAN communication. 5. Management port
 1. VLAN Overview 2. VLAN Trunk 3. Why use VLANs? 4. LAN to LAN communication 5. Management port 6. Applications 6.1. Application 1 6.2. Application 2 6.3. Application 3 6.4. Application 4 6.5. Application
1. VLAN Overview 2. VLAN Trunk 3. Why use VLANs? 4. LAN to LAN communication 5. Management port 6. Applications 6.1. Application 1 6.2. Application 2 6.3. Application 3 6.4. Application 4 6.5. Application
Apple Airport Extreme Base Station V4.0.8 Firmware: Version 5.4
 1. APPLE AIRPORT EXTREME 1.1 Product Description The following are device specific configuration settings for the Apple Airport Extreme. Navigation through the management screens will be similar but may
1. APPLE AIRPORT EXTREME 1.1 Product Description The following are device specific configuration settings for the Apple Airport Extreme. Navigation through the management screens will be similar but may
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
Syslog Server Configuration on Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs)
 Syslog Server Configuration on Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs) Document ID: 107252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Syslog Server Support on Wireless LAN Controllers
Syslog Server Configuration on Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs) Document ID: 107252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Syslog Server Support on Wireless LAN Controllers
Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional)
 Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional) CCNP Route (642-902) EIGRP Chapter: EIGRP Overview and Neighbor Relationships EIGRP Neighborships Neighborship over WANs EIGRP Topology, Routes,
Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional) CCNP Route (642-902) EIGRP Chapter: EIGRP Overview and Neighbor Relationships EIGRP Neighborships Neighborship over WANs EIGRP Topology, Routes,
Interlink Networks Secure.XS and Cisco Wireless Deployment Guide
 Overview Interlink Networks Secure.XS and Cisco Wireless Deployment Guide (An AVVID certification required document) This document is intended to serve as a guideline to setup Interlink Networks Secure.XS
Overview Interlink Networks Secure.XS and Cisco Wireless Deployment Guide (An AVVID certification required document) This document is intended to serve as a guideline to setup Interlink Networks Secure.XS
Configuring Redundancy
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure redundancy and contains these sections: Configuring Fault Tolerance, page 7-1 Configuring HSRP, page 7-5 Configuring Interface and Device Tracking, page
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure redundancy and contains these sections: Configuring Fault Tolerance, page 7-1 Configuring HSRP, page 7-5 Configuring Interface and Device Tracking, page
Layer 2 / Layer 3 switches and multi-ssid multi-vlan network with traffic separation
 Layer 2 / Layer 3 switches and multi-ssid multi-vlan network with traffic separation This document describes the steps to undertake in configuring a Layer 2/Layer 3 switch (in this document a FMS7382S
Layer 2 / Layer 3 switches and multi-ssid multi-vlan network with traffic separation This document describes the steps to undertake in configuring a Layer 2/Layer 3 switch (in this document a FMS7382S
- Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP -
 1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting
 Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
Implementation of Virtual Local Area Network using network simulator
 1060 Implementation of Virtual Local Area Network using network simulator Sarah Yahia Ali Department of Computer Engineering Techniques, Dijlah University College, Iraq ABSTRACT Large corporate environments,
1060 Implementation of Virtual Local Area Network using network simulator Sarah Yahia Ali Department of Computer Engineering Techniques, Dijlah University College, Iraq ABSTRACT Large corporate environments,
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Abstract. Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Sample Configuration for using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) with Cisco Catalyst 4500 or 3750 Switches for VLAN assignment to Avaya 4600 Series IP Telephones
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Sample Configuration for using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) with Cisco Catalyst 4500 or 3750 Switches for VLAN assignment to Avaya 4600 Series IP Telephones
Objectives. The Role of Redundancy in a Switched Network. Layer 2 Loops. Broadcast Storms. More problems with Layer 2 loops
 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide. Revised February 28, 2013 2:32 pm Pacific
 Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide Revised February 28, 2013 2:32 pm Pacific Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide
Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide Revised February 28, 2013 2:32 pm Pacific Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide
Lab 8.4.5.1 Configuring LEAP/EAP using Local RADIUS Authentication
 Lab 8.4.5.1 Configuring LEAP/EAP using Local RADIUS Authentication Objective Topology Estimated Time: 40 minutes Number of Team Members: Students can work in teams of two. In this lab, the student will
Lab 8.4.5.1 Configuring LEAP/EAP using Local RADIUS Authentication Objective Topology Estimated Time: 40 minutes Number of Team Members: Students can work in teams of two. In this lab, the student will
Installing Windows 95 Drivers and Utilities for the Cisco Aironet 340/350 Series Client Adapters
 Installing Windows 95 Drivers and Utilities for the Cisco Aironet 340/350 Series Client Adapters Document ID: 12134 You need a valid Cisco.com account in order to download Cisco Aironet drivers, firmware,
Installing Windows 95 Drivers and Utilities for the Cisco Aironet 340/350 Series Client Adapters Document ID: 12134 You need a valid Cisco.com account in order to download Cisco Aironet drivers, firmware,
Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point
 Article ID: 5036 Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point Objective The Workgroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless
Article ID: 5036 Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point Objective The Workgroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless
6/8/2011. Document ID: 12023. Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used. Conventions. Introduction
 Page 1 of 9 Products & Services Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
Page 1 of 9 Products & Services Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
Configuring EtherChannels
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
hp ProLiant network adapter teaming
 hp networking june 2003 hp ProLiant network adapter teaming technical white paper table of contents introduction 2 executive summary 2 overview of network addressing 2 layer 2 vs. layer 3 addressing 2
hp networking june 2003 hp ProLiant network adapter teaming technical white paper table of contents introduction 2 executive summary 2 overview of network addressing 2 layer 2 vs. layer 3 addressing 2
Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network
 Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 9 Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright Cisco
Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 9 Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright Cisco
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Configuration Management: Best Practices White Paper
 Configuration Management: Best Practices White Paper Document ID: 15111 Contents Introduction High Level Process Flow for Configuration Management Create Standards Software Version Control and Management
Configuration Management: Best Practices White Paper Document ID: 15111 Contents Introduction High Level Process Flow for Configuration Management Create Standards Software Version Control and Management
IP Addressing and Subnetting. 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
VLAN Interoperability
 PowerConnect Application Note #4 November 2003 VLAN Interoperability This Application Notes relates to the following Dell PowerConnect products: PowerConnect 33xx PowerConnect 52xx Abstract This Application
PowerConnect Application Note #4 November 2003 VLAN Interoperability This Application Notes relates to the following Dell PowerConnect products: PowerConnect 33xx PowerConnect 52xx Abstract This Application
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Cisco 12 CCNA Certification
 Cisco 12 CCNA Certification Application for Board Authorization of Courses District: Chilliwack School District 33 Developed by: John Murtha Date: May7, 2004 School: Sardis Secondary Principal: Bob Patterson
Cisco 12 CCNA Certification Application for Board Authorization of Courses District: Chilliwack School District 33 Developed by: John Murtha Date: May7, 2004 School: Sardis Secondary Principal: Bob Patterson
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM
 Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM A Dell technical white paper Version 1.1 Victor Teeter Network Solutions Engineer This document is for informational purposes
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM A Dell technical white paper Version 1.1 Victor Teeter Network Solutions Engineer This document is for informational purposes
How To Configure Voice Vlan On An Ip Phone
 1 VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is used to logically divide a physical network into several broadcast domains. VLAN membership can be configured through software instead of physically relocating devices
1 VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is used to logically divide a physical network into several broadcast domains. VLAN membership can be configured through software instead of physically relocating devices
Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline
 www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
Exhibit n.2: The layers of a hierarchical network
 3. Advanced Secure Network Design 3.1 Introduction You already know that routers are probably the most critical equipment piece in today s networking. Without routers, internetwork communication would
3. Advanced Secure Network Design 3.1 Introduction You already know that routers are probably the most critical equipment piece in today s networking. Without routers, internetwork communication would
Cisco Networking Professional-6Months Project Based Training
 Cisco Networking Professional-6Months Project Based Training Core Topics Cisco Certified Networking Associate (CCNA) 1. ICND1 2. ICND2 Cisco Certified Networking Professional (CCNP) 1. CCNP-ROUTE 2. CCNP-SWITCH
Cisco Networking Professional-6Months Project Based Training Core Topics Cisco Certified Networking Associate (CCNA) 1. ICND1 2. ICND2 Cisco Certified Networking Professional (CCNP) 1. CCNP-ROUTE 2. CCNP-SWITCH
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Installing Cable Modem Software Drivers
 Configuration Installing Cable Modem Software Drivers Windows 98SE Operating System Windows Me Operating System Windows 2000 Operating System Windows XP Operating System Wireless LAN Configuration Telnet
Configuration Installing Cable Modem Software Drivers Windows 98SE Operating System Windows Me Operating System Windows 2000 Operating System Windows XP Operating System Wireless LAN Configuration Telnet
Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT)
 8 Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) Contents Overview...................................................... 8-3 Translating Between an Inside and an Outside Network........... 8-3 Local and
8 Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) Contents Overview...................................................... 8-3 Translating Between an Inside and an Outside Network........... 8-3 Local and
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuration of Cisco Autonomous Access Point with 802.1x Authentication for Avaya 3631 Wireless Telephone
 Configuration of Cisco Autonomous Access Point with 802.1x Authentication for Avaya 3631 Wireless Telephone Product Summary Manufacturer: Cisco Systems: www.cisco.com Access Point: Cisco Aironet 1130AG
Configuration of Cisco Autonomous Access Point with 802.1x Authentication for Avaya 3631 Wireless Telephone Product Summary Manufacturer: Cisco Systems: www.cisco.com Access Point: Cisco Aironet 1130AG
Design and Implementation Guide. Apple iphone Compatibility
 Design and Implementation Guide Apple iphone Compatibility Introduction Security in wireless LANs has long been a concern for network administrators. While securing laptop devices is well understood, new
Design and Implementation Guide Apple iphone Compatibility Introduction Security in wireless LANs has long been a concern for network administrators. While securing laptop devices is well understood, new
Chapter 3 Management. Remote Management
 Chapter 3 Management This chapter describes how to use the management features of your ProSafe 802.11a/g Dual Band Wireless Access Point WAG102. To access these features, connect to the WAG102 as described
Chapter 3 Management This chapter describes how to use the management features of your ProSafe 802.11a/g Dual Band Wireless Access Point WAG102. To access these features, connect to the WAG102 as described
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide
 MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
Virtual LAN Configuration Guide Version 9
 Virtual LAN Configuration Guide Version 9 Document version 96-1.0-12/05/2009 2 IMPORTANT NOTICE Elitecore has supplied this Information believing it to be accurate and reliable at the time of printing,
Virtual LAN Configuration Guide Version 9 Document version 96-1.0-12/05/2009 2 IMPORTANT NOTICE Elitecore has supplied this Information believing it to be accurate and reliable at the time of printing,
Cisco on Cisco Best Practices Cisco Wireless LAN Design
 Cisco on Cisco Best Practices All contents are Copyright 1992 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Contents 1. Overview...4 2. Architecture...4 2.1.
Cisco on Cisco Best Practices All contents are Copyright 1992 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Contents 1. Overview...4 2. Architecture...4 2.1.
Easy Smart Configuration Utility
 Easy Smart Configuration Utility REV1.1.0 1910010977 CONTENTS Chapter 1 About this Guide...1 1.1 Intended Readers... 1 1.2 Conventions... 1 1.3 Overview of This Guide... 1 Chapter 2 Getting Started...4
Easy Smart Configuration Utility REV1.1.0 1910010977 CONTENTS Chapter 1 About this Guide...1 1.1 Intended Readers... 1 1.2 Conventions... 1 1.3 Overview of This Guide... 1 Chapter 2 Getting Started...4
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide
 LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide This document provides guidance on how to design a local area network (LAN) for a Business Ready Branch or autonomous Business Ready
LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide This document provides guidance on how to design a local area network (LAN) for a Business Ready Branch or autonomous Business Ready
Configuring QoS in a Wireless Environment
 12 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) on your Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). With this feature, you can provide preferential treatment to certain traffic
12 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) on your Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). With this feature, you can provide preferential treatment to certain traffic
Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery
 Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery, page 1 Restrictions for Configuring the Device
Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery, page 1 Restrictions for Configuring the Device
Security Considerations in IP Telephony Network Configuration
 Security Considerations in IP Telephony Network Configuration Abstract This Technical Report deals with fundamental security settings in networks to provide secure VoIP services. Example configurations
Security Considerations in IP Telephony Network Configuration Abstract This Technical Report deals with fundamental security settings in networks to provide secure VoIP services. Example configurations
TotalCloud Phone System
 TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
UTM10 in multi-ssid, multi-vlan network with WMS5316. Network diagram
 UTM10 in multi-ssid, multi-vlan network with WMS5316 This document describes how to use the UTM10 (unified threat management system) and WMS5316 (wireless management system) to create a multi-vlan, multi-ssid
UTM10 in multi-ssid, multi-vlan network with WMS5316 This document describes how to use the UTM10 (unified threat management system) and WMS5316 (wireless management system) to create a multi-vlan, multi-ssid
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 4 Management. Viewing the Activity Log
 Chapter 4 Management This chapter describes how to use the management features of your NETGEAR WG102 ProSafe 802.11g Wireless Access Point. To get to these features, connect to the WG102 as described in
Chapter 4 Management This chapter describes how to use the management features of your NETGEAR WG102 ProSafe 802.11g Wireless Access Point. To get to these features, connect to the WG102 as described in
Deployment Guide: Cisco Guest Access Using the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
 Deployment Guide: Cisco Guest Access Using the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller August 2006 Contents Overview section on page 1 Configuring Guest Access on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller section on page
Deployment Guide: Cisco Guest Access Using the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller August 2006 Contents Overview section on page 1 Configuring Guest Access on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller section on page
Felix Rohrer. PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N. Topology Diagram
 Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
