General Surgery Clerkship Learning Activity Objectives Cases/Discussion Questions
|
|
|
- Bonnie French
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General Surgery Clerkship Learning Activity Objectives Cases/Discussion Questions Abdominal Distention (Clinical Case Study) 1. List the differential diagnosis of intestinal obstruction. 2. Identify signs and symptoms of a large bowel obstruction 3. Identify signs and symptoms of a small bowel obstruction 4. Differentiate a small bowel obstruction from a large bowel obstruction 5. Discuss the diagnostic studies available for large bowel obstruction 6. List the known risk factors for colon carcinoma 7. Identify the common symptoms of carcinoma of the colon, rectum, and anus 8. List the appropriate laboratory and radiologic studies for the diagnosis of carcinoma of the colon, rectum, and anus 9. Outline specific preoperative and postoperative management issues 10. Discuss the surgical treatment of colon carcinoma, including anatomic relationships 11. Discuss the indications for adjuvant medical treatment of carcinoma of the colon, rectum, and anus, i.e., chemotherapy and radiation therapy 12. Discuss the role of CEA in the management of colorectal carcinoma 13. Discuss the staging of colorectal carcinoma and their associated five-year survival 14. Discuss the effect of obstruction or perforation on the prognosis of colorectal carcinoma 15. Develop a cohesive post-operative care plan and follow-up surveillance plan in a patient with colorectal carcinoma. 16. Discuss the treatment of liver metastases. Acute Abdomen 1. List the major categories of disease which cause pain in the abdomen. 2. Discuss the characteristics of the major types of acute abdominal pain especially their character, time course, and location. 3. Describe the clinical signs and significance of peritonitis. 4. Discuss common diagnostic tests (laboratory and radiological) used to help diagnose the acute abdomen. Include the following: WBC + differential, amylase, urinalysis, chest x- ray, plain abdominal film, abdominal series (plain abdominal film, lateral decubitus of the abdomen and chest x-ray), right upper quadrant ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) of the abdomen. 5. Identify the common causes of severe abdominal pain that do not require surgery. 6. Discuss the differential diagnosis of a patient who presents with shock and acute abdomen. Benign Perianal Disease 1. Discuss the anatomy of hemorrhoids. 2. Differentiate between internal and external hemorrhoids. 3. Describe the role of the anal sphincters in maintaining fecal continence. 4. State common causes of hemorrhoidal disease. Include the following in your discussion: heredity, diet, pregnancy, and occupation. 5. Outline the principles of managing patients with symptomatic external hemorrhoids.
2 6. Describe the symptoms and physical findings of patients with internal hemorrhoids. 7. Outline the principles of managing patients with symptomatic internal hemorrhoids. 8. Discuss the role of anal crypts in perianal infection. 9. Describe the various types of perianal infections, including perianal, perirectal, ischiorectal, and pelvirectal infection. 10. Outline the symptoms and physical findings of patients with perianal infections. 11. Outline the principles of managing patients with perianal infections and their sequelae (i.e. perianal fistulas). 12. Define fissure-in-ano. Describe the symptoms and physical findings of patients with fissure-in-ano and outline the principles of management. Biliary Disease 1. List the common types of gallstones and describe the pathophysiology involved in their formation. 2. List several diseases known to predispose to gallstones. 3. Describe the signs and symptoms in a patient with biliary colic. Contrast these symptoms with those of acute cholecystitis. 4. List the tests commonly used to diagnose calculus biliary tract disease. Describe the indications for, limitations of, and potential complications of each. 5. Describe the likely natural history of a young patient with asymptomatic gallstones. 6. List the complications which can occur from biliary calculi. 7. Outline the medical and surgical management of a patient with acute cholecystitis. 8. Describe the symptoms and signs of choledocholithiasis; describe the management of this problem. 9. Contrast the liver enzyme abnormalities in obstructive jaundice and viral hepatitis. 10. List the most common bacteria which cause cholecystitis and cholangitis. Breast Cancer Differentiate between benign and malignant diseases of the breast; include their presentation, physical examination findings, and treatment. 2. Outline the diagnosis and management of a patient with nipple discharge. 3. List the major risk factors for breast cancer. 4. Describe the current recommendations for screening mammography. 5. Outline the fundamentals for diagnosing and managing a breast mass. 6. List the diagnostic modalities and their sequence in working up a patient with a breast mass. 7. Describe the categories of malignant breast disease and the differences in their management. 8. Outline the presentation and management of a patient with inflammatory breast cancer. 9. Describe the staging for breast cancer. 10. Outline current treatment options for a patient with non-invasive breast cancer. 11. Outline current treatment options for a patient with invasive breast cancer. 12. Outline the need for lymph node removal and its risks and benefits. 13. Describe the rationale for adjuvant chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and radiation therapy for breast cancer.
3 Breast Skills Workshop Identify and describe the major types of breast lumps (fibroadenoma, fibrocystic disease, carcinoma, and cysts). Describe the typical age range for each. 1. Discuss the most anatomical location for breast cancer to occur. 2. List signs associated with malignant breast lesions. 3. Describe common risk factors associated with breast cancer. 4. Demonstrate the ability to perform a breast examination. 5. Demonstrate the ability to find a lump upon breast examination. 6. Demonstrate the ability to predict whether a breast mass is benign or malignant based upon physical examination findings and radiologic studies. 7. Accurately interpret a mammogram of a patient with a benign appearing breast mass. 8. Accurately interpret a mammogram of a patient with a carcinoma of the breast. 9. Given a case study discuss the most appropriate study for confirming diagnosis of a malignant versus benign breast lesion. Include the following studies in your discussion: a. Fine needle aspiration. b. CORE needle biopsy c. Surgery excisional biopsy d. Mammography e. Mammatome f. Ultrasound Diverticular Disease 1. Discuss the major etiologies of diverticular disease including age, diet, and vascular anatomy of the colon. 2. Describe the clinical signs and symptoms of diverticular disease. Differentiate between the signs and symptoms of diverticulitis and diverticulosis including signs of inflammation and bleeding. 3. Discuss the complications of diverticular disease including bleeding, obstruction, perforation, and fistula formation. 4. Describe the management of symptomatic but uncomplicated diverticulosis. Esophageal Disease 1. Differentiate between structural esophageal disease vs functional esophageal disease. 2. Describe typical and atypical symptoms of esophageal disease. 3. List the functions of the Upper Esophageal Sphincter, Lower Esophageal Sphincter, and the Esophageal body. 4. Describe two important tests for diagnosing structural problems in the esophagus and two tests for identifying functional disease. 5. List the relative merits of medical and surgical treatment of common benign esophageal diseases such as GERD and achalasia 6. Discuss the diagnostic work-up and treatment plan for a patient with Barrett s esophagus and gastroesophageal reflux disease. 7. How are esophageal tumors diagnosed and how are they staged? 8. Describe the surgical treatments for esophageal cancer
4 Fluid and Blood Resuscitation 1. Describe how the length and radius of an intravenous catheter influences delivery rate. 2. Discuss various intravenous placement sites and note the pros and cons of each of the following: a. Femoral b. Internal jugular c. Superior vena cava d. Intraosseous 3. Differentiate between the following fluids and their use in resuscitation. a. Ringer s Lactate b. Normal Saline c. Hypertonic Saline d. Colloids 4. Discuss the indications for the following blood products. Include: a. Packed red blood cells b. Fresh frozen plasma c. Platelets d. Cryoprecipitate e. Factor VII Hemodynamic Monitoring 1. Describe the purpose of the pulmonary artery catheter. 2. Describe how the pulmonary artery catheter is placed. 3. Discuss the purpose of each lumen of the pulmonary artery catheter. 4. Discuss potential complications of the pulmonary artery catheter. 5. Discuss the importance of the pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP) and how it is measured. 6. Describe the difference between a cardiac output (CO) and cardiac index (CI) and discuss how they are measured. 7. Discuss the clinical maneuvers that can be done to improve a patient s CO/CI. 8. Define oxygen delivery (DO 2 ), oxygen consumption (VO 2 ), oxygen extraction ratio (O 2 ER), and systemic venous oxygen content (SVO 2 ). 9. List the interventions that may increase DO List two interventions that are commonly manipulated to increase the DO List the etiologies of shock and their effects on CI, SVR, PAWP, CVP, SVO 2, and HR. 12. Discuss common therapies used to decrease VO 2. ICU Tutorial (No objectives available.) Liver and Portal Hypertension For Hypertension : 1. Define portal hypertension and classify its etiology. 2. Review the portal circulation and describe the changes that occur in portal hypertension.
5 3. Describe five clinical manifestations of portal hypertension. 4. List four complications associated with portal hypertension. 5. Outline the diagnostic methods appropriate for each complication of portal hypertension. 6. Outline the treatment methods available for variceal hemorrhage, including the principles for reduction of portal pressure. 7. Describe the medical and surgical treatment of a patient with ascites. 8. Describe the prognosis for patients with portal hypertension. For Liver: 1. What is the initial diagnostic radiologic test for a suspected liver mass? 2. Compare the etiologies of the various types of cystic masses in the liver. 3. What are the preferred methods for treating different types of liver abscesses? 4. List a differential diagnosis for a solid liver mass. 5. What radiologic tests can be used to distinguish the type of solid mass? 6. Describe the treatment modalities available for hepatic neoplasms. Mechanical Ventilation 1. Describe the goals of mechanical ventilation. 2. Differentiate between volume cycled and pressure cycled breaths. 3. Identify the parameters that need to be set on a ventilator. 4. Describe the various modes of ventilation and provide indications for each. Include the following: a. Assist Control Pressure and Volume b. Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation Pressure and Volume c. Pressure Regulated Volume Control d. Airway Pressure Release Ventilation e. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure 5. Discuss the use of the following ventilator adjuncts: a. Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) b. Pressure Support 6. List benefits and potential complications of PEEP. 7. Discuss weaning criteria for mechanical ventilation. 8. Discuss the primary cause and prevention of oxygen toxicity. 9. Using a mechanical ventilator discuss which settings are used to change the paco 2 and pao 2. Pancreas 1. Discuss the diagnostic approach to patients with acute abdominal pain. 2. Create a differential diagnosis for acute epigastric abdominal pain. 3. List the five most common etiologies of acute pancreatitis. 4. Discuss the definition of acute versus chronic pancreatitis. 5. Discuss the prognostic criteria for acute pancreatitis. 6. List the most common complications of acute pancreatitis.
6 Skin & Soft Tissue For Skin: 1. Describe several kinds of benign nevi and pigmented lesions. 2. Describe the gross morphologic and pathologic differences between benign and malignant nevi and discuss the approach to diagnosis. 3. List predisposing factors for melanoma. 4. Describe the major prognostic variables of melanoma; include a discussion of Clark s level and Breslow depth. 5. Identify possible areas of metastasis of melanoma and outline steps to determine the extent of disease. 6. Outline local, regional, and systemic therapy for melanoma. 7. Distinguish gross pathologic differences between basal and squamous cell carcinomas and list predisposing causes and likely areas of clinical sites. 8. Distinguish the natural history, the curability, and the propensity to metastasize of basal and squamous cell carcinomas. 9. Describe medical and surgical therapies available for both types of skin cancer. For Sarcoma: 1. Describe the clinical features of a sarcoma presenting in the head or neck, the trunk and the extremity. 2. Describe the techniques to diagnose and adequately stage a soft tissue tumor of the extremity. 3. Outline medical, surgical, and radiotherapy modalities which can be applied to soft tissue tumors. 4. List factors that are associated with a poorer prognosis for soft tissue sarcomas. 5. Identify four clinical features of nevi suggesting malignancy and a need for biopsy. 6. Identify non-pigmented ulcerative and non-ulcerative lesions requiring biopsy. Stomach & Duodenum For Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers: 1. Describe the pathogenesis of gastric and duodenal ulcer. 2. Discuss the role of helicobacter pylori in ulcer formation. 3. Identify the pathophysiology of ulcers and discuss the significance of their anatomic location (e.g., anterior duodenal risk for perforation; posterior duodenal risk for penetration and hemorrhage; pyloric channel risk for obstruction; gastric risk malignancy). 4. Identify the differences between gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers. 5. List the main symptoms of peptic ulcer disease. 6. Describe the value of each of the following diagnostic studies in a patient with suspected peptic ulcer disease: upper gastrointestinal x-rays, endoscopy and biopsy, gastric analysis and serum gastrin. 7. Outline the medical treatment of peptic ulcer disease include the following: a. Antacids b. H2 blockers c. Proton pump inhibitors d. Surface coating agents e. Diet
7 f. Contraindicated medications (steroids, aspirin), g. Treatment of heliocobacter pylori 8. List the clinical features of the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. 9. List the complications of peptic ulcer disease that require surgical treatment. 10. Describe the clinical presentation of each complication of peptic ulcer disease and outline diagnostic plans in appropriate sequence for each. 11. Define intractability of peptic ulcers. 12. Name the common and newer operations for duodenal and gastric ulcers and discuss the physiologic rational, risks, and effectiveness of each. 13. Discuss the side effects of the common operations for duodenal and gastric ulcers including a description of the dumping syndrome. For Gastric Neoplasms: 1. Identify the premalignant conditions and epidemiology of gastric cancers. 2. Classify the common gastric neoplasms (adenocarcinoma, lymphoma, carcinoid, and leiomyosarcoma). 3. List diagnostic modalities for gastric neoplasms. 4. List the general principles of curative and palliative surgical procedures for gastric neoplasms and discuss the role of adjunctive/alternative treatment (chemotherapy and radiation therapy). Surgical Infections 1. List the factors which contribute to infection following a surgical procedure. 2. List the types of surgical infections. 3. Describe the diagnostic features and indicated treatment for common skin infections. 4. Discuss four common hand infections and describe the treatment for each. 5. Describe the clinical features and treatment of anaerobic and synergistic gangrene. 6. List the causes of postoperative fever and discuss the diagnostic steps for evaluation. 7. Describe the indication and method for providing routine and reverse isolation. 8. Describe the diagnostic evaluation for intra abdominal abscess. 9. Identify the antibiotic of choice for acute cholecystitis, perforated sigmoid diverticulitis, empyema of the lung and a vascular graft infection. Surgical Nutrition 1. Identify surgical patients who require nutritional support. 2. Calculate nutritional requirements using a variety of methods. 3. Determine what type (enteral vs. parenteral) of nutritional support is appropriate for surgical patients. 4. List advantages and disadvantages of enteral nutrition. 5. List advantages and disadvantages of parenteral nutrition. 6. Design and implement a plan to evaluate and follow a patient s nutritional status. Trauma Overview 1. Identify the criteria for a Trauma Team Activation (TTA) at LAC+USC Medical Center. 2. Identify the correct initial sequence of priorities to be followed in assessing the multipleinjured patient.
8 3. Outline the primary and secondary evaluation surveys used to assess the trauma patient. 4. Identify diagnostic and therapeutic actions for treating specific traumatic injuries as outlined in the Assessment and Management of Trauma ( Red Book). 5. Discuss the protocols for treating trauma patients as outlined in the Assessment and Management of Trauma (Red Book). Vascular - see Vascular Handbook in Surgery Clerkship Office Wound Healing 1. Describe the sequential steps of wound healing and the approximate time course associated with each. 2. Describe the differences in healing by: primary closure delayed primary closure secondary intention 3. Describe the appearance of a non-healing or inflamed wound and its management. 4. Describe clinical factors that may retard wound healing. 5. Describe the use of closed suction drainage of wounds. 6. List the causes of postoperative fever and discuss the diagnostic steps for evaluation. 7. Contrast dehiscence and evisceration and describe their clinical presentations.
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives
 Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA. Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005
 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
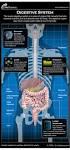 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal Impairment
 Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
The Anorexic Cat For this reason, any cat that stops eating for any reason is considered an emergency situation.
 The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
United States Department of Transportation National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Paramedic: National Standard Curriculum 1
 UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
Colocutaneous Fistula. Disclosures
 Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
GI Bleeding. Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics
 GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
Common Pathology Diagnoses: ICD-9 to ICD-10 Mapping
 PERFORMANCE THAT MATTERS NUMBER OF CODES 14,000 69,000 ICD-9 DIAGNOSIS CODES ICD-10 DIAGNOSIS CODES CODE STRUCTURE ICD-9-CM CODE FORMAT ICD-10-CM CODE FORMAT X X X X X X X X X X X X CATEGORY ETIOLOGY,
PERFORMANCE THAT MATTERS NUMBER OF CODES 14,000 69,000 ICD-9 DIAGNOSIS CODES ICD-10 DIAGNOSIS CODES CODE STRUCTURE ICD-9-CM CODE FORMAT ICD-10-CM CODE FORMAT X X X X X X X X X X X X CATEGORY ETIOLOGY,
Nicole Kounalakis, MD
 Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
understanding GI bleeding
 understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
Chronic abdominal pain of childhood
 Chronic abdominal pain of childhood Sandra I. Escalera, M.D. ProHealth Physicians Associate Clinical Professor Department of Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine Objectives Brief overview of approach
Chronic abdominal pain of childhood Sandra I. Escalera, M.D. ProHealth Physicians Associate Clinical Professor Department of Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine Objectives Brief overview of approach
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Oncology. Objectives. Cancer Nomenclature. Cancer is a disease of the cell Cancer develops when certain cells begin to grow out of control
 Oncology Objectives Describe the etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms of cancer Discuss medical and family history findings relevant to cancer Identify general signs and symptoms associated with
Oncology Objectives Describe the etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms of cancer Discuss medical and family history findings relevant to cancer Identify general signs and symptoms associated with
The Top 20 ICD-10 Documentation Issues That Cause DRG Changes
 7th Annual Association for Clinical Documentation Improvement Specialists Conference The Top 20 ICD-10 Documentation Issues That Cause DRG Changes Donna Smith, RHIA Project Manager, Consulting Services
7th Annual Association for Clinical Documentation Improvement Specialists Conference The Top 20 ICD-10 Documentation Issues That Cause DRG Changes Donna Smith, RHIA Project Manager, Consulting Services
The Whipple Procedure. Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain
 The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Appendix G - Identification and Selection of Studies
 FINAL Emergency framework for rationing of blood for massively bleeding patients during a red phase of a Appendix G - Identification and Selection of Studies Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria We included studies
FINAL Emergency framework for rationing of blood for massively bleeding patients during a red phase of a Appendix G - Identification and Selection of Studies Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria We included studies
Billing Guideline. Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16
 Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer
 Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Colorectal cancer. A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment
 Colorectal cancer A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Colorectal cancer 4 i. What is colorectal cancer? 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 4 iii.
Colorectal cancer A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Colorectal cancer 4 i. What is colorectal cancer? 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 4 iii.
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Pancreatic Cancer. The Killer that must be discovered early. Dr Alfred Kow Wei Chieh
 Pancreatic Cancer The Killer that must be discovered early 27 th June 2015 Dr Alfred Kow Wei Chieh Consultant Department of Surgery Division of HPB Surgery & Liver Transplantation & Assistant Dean (Education)
Pancreatic Cancer The Killer that must be discovered early 27 th June 2015 Dr Alfred Kow Wei Chieh Consultant Department of Surgery Division of HPB Surgery & Liver Transplantation & Assistant Dean (Education)
Goals and Objectives for the General Surgery Rotation Resident PGY1 Hamilton Health Sciences or St. Joseph Healthcare (2 four-week rotational blocks)
 Goals and Objectives for the General Surgery Rotation Resident PGY1 Hamilton Health Sciences or St. Joseph Healthcare (2 four-week rotational blocks) Overview During the first year of their residency training
Goals and Objectives for the General Surgery Rotation Resident PGY1 Hamilton Health Sciences or St. Joseph Healthcare (2 four-week rotational blocks) Overview During the first year of their residency training
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS)
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
General Thoracic Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks. C34.11 Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe, right bronchus or lung
 ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
Treatment of Hepatic Neoplasm
 I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A multidisciplinary approach to the prevention and early detection of invasive pancreatic cancer.
 This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
NP/PA Clinical Hepatology Fellowship Summary of Year-Long Curriculum
 OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Carbohydrate antigen 19 9 (CA 19 9) (serum, plasma)
 Carbohydrate antigen 19 9 (CA 19 9) (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Carbohydrate antigen 19 9 (CA 19 9) 1.2 Alternative names Cancer antigen 19 9, cancer antigen GI
Carbohydrate antigen 19 9 (CA 19 9) (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Carbohydrate antigen 19 9 (CA 19 9) 1.2 Alternative names Cancer antigen 19 9, cancer antigen GI
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein
 Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Other Names/Abbreviations AFP 190.25 - Alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring the response of certain
Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects
 Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects This document lists sample learning objectives by subject matter The numerical ranking in parenthesis following
Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects This document lists sample learning objectives by subject matter The numerical ranking in parenthesis following
Medical Surgical Nursing (Elsevier)
 1 of 6 I. The Musculoskeletal System Medical Surgical Nursing (Elsevier) 1. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: The Comprehensive Health History 2. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: A Nursing Approach to
1 of 6 I. The Musculoskeletal System Medical Surgical Nursing (Elsevier) 1. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: The Comprehensive Health History 2. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: A Nursing Approach to
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests
 LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests Applicable CPT Code(s): 86692 Antibody; Hepatitis, Delta Agent 86704 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); Total 86705 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); IgM Antibody
LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests Applicable CPT Code(s): 86692 Antibody; Hepatitis, Delta Agent 86704 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); Total 86705 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); IgM Antibody
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Digestive System (continued) Digestive System. Stomach. Peptic Ulcer Disease
 Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Breast Cancer. Presentation by Dr Mafunga
 Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners
 Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
APPENDIX B SAMPLE PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
 APPENDIX B SAMPLE PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The critical care nurse practitioner orientation is an individualized process based on one s previous experiences and should
APPENDIX B SAMPLE PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The critical care nurse practitioner orientation is an individualized process based on one s previous experiences and should
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
The Sepsis Puzzle: Identification, Monitoring and Early Goal Directed Therapy
 The Sepsis Puzzle: Identification, Monitoring and Early Goal Directed Therapy Cindy Goodrich RN, MS, CCRN Content Description Sepsis is caused by widespread tissue injury and systemic inflammation resulting
The Sepsis Puzzle: Identification, Monitoring and Early Goal Directed Therapy Cindy Goodrich RN, MS, CCRN Content Description Sepsis is caused by widespread tissue injury and systemic inflammation resulting
What is Barrett s esophagus? How does Barrett s esophagus develop?
 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology)
 STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
GI Bleed. Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System. Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital
 October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
NEOPLASMS C00 D49. Presented by Jan Halloran CCS
 NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations. Chapter. Grade. CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma
 Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases. Premed 2 Pathophysiology
 Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements
 Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA
 Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass. Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003
 Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003 Common Presentations of Breast Disease Breast Mass Abnormal
Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003 Common Presentations of Breast Disease Breast Mass Abnormal
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System
 Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
PATIENT INFORMATION ABOUT ADJUVANT THERAPY AFTER THE WHIPPLE OPERATION FOR ADENOCARCINOMA ( CANCER ) OF THE PANCREAS AND RELATED SITES.
 PATIENT INFORMATION ABOUT ADJUVANT THERAPY AFTER THE WHIPPLE OPERATION FOR ADENOCARCINOMA ( CANCER ) OF THE PANCREAS AND RELATED SITES. Radiation Oncology Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins Last
PATIENT INFORMATION ABOUT ADJUVANT THERAPY AFTER THE WHIPPLE OPERATION FOR ADENOCARCINOMA ( CANCER ) OF THE PANCREAS AND RELATED SITES. Radiation Oncology Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins Last
How common is bowel cancer?
 information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
Cervical lymphadenopathy
 Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery
 Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano. Background
 Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
Certified Clinical Documentation Specialist Examination Content Outline - 2016
 Certified Clinical Documentation Specialist Examination Content Outline - 2016 1. Healthcare Regulations, Reimbursement, and Documentation Requirements Related to the Inpatient Prospective Payment System
Certified Clinical Documentation Specialist Examination Content Outline - 2016 1. Healthcare Regulations, Reimbursement, and Documentation Requirements Related to the Inpatient Prospective Payment System
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
 Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Summary Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn s disease can appear in any part of a person s digestive
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Summary Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn s disease can appear in any part of a person s digestive
GI Assessment, Diagnosis and Case Studies. Jami Windhorn, RN BSN SOAR Session #6
 GI Assessment, Diagnosis and Case Studies Jami Windhorn, RN BSN SOAR Session #6 Abdominal Assessment 4 Quadrants: * Right Upper * Right Lower * Left Upper * Left Lower Abdominal Assessment 9 Regions: Abdominal
GI Assessment, Diagnosis and Case Studies Jami Windhorn, RN BSN SOAR Session #6 Abdominal Assessment 4 Quadrants: * Right Upper * Right Lower * Left Upper * Left Lower Abdominal Assessment 9 Regions: Abdominal
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS
 YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
The recommendations made throughout this book are by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC).
 INTRODUCTION This book has been prepared for people with bowel cancer, their families and friends. The first section is for people with bowel cancer, and is intended to help you understand what bowel cancer
INTRODUCTION This book has been prepared for people with bowel cancer, their families and friends. The first section is for people with bowel cancer, and is intended to help you understand what bowel cancer
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
