Gastric MALT lymphoma
|
|
|
- Quentin Skinner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
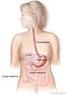
1 Produced Due for revision Gastric MALT lymphoma In this article we are aiming to: explain what MALT lymphoma is and how it develops describe the symptoms you could have and the tests you will need outline how gastric MALT lymphoma is treated, how you are followed up after treatment and what the outlook is with this type of lymphoma. What is MALT lymphoma? A lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which consists of lymph vessels and lymph glands (nodes) and other organs including the spleen. The lymphatic system is part of our immune system and one vital component of it is the lymphocyte, a special white blood cell that helps us fight off infections. When lymphocytes grow in a way that is out of control, they build up and a lymphoma develops. MALT lymphomas are one type of lymphoma. MALT lymphoma is a low-grade (indolent) type of B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma. Unlike many other types of lymphoma it occurs at sites that are outside the spleen and lymph nodes. These are known as extra-nodal sites. It was first recognised as a specific type of lymphoma in 1983 and this was an important development because it behaves quite differently from other non-hodgkin lymphomas and is also treated differently. How did it get its name? When viewed under a microscope, the way that the lymphoma cells are organised resembles the lymphoid tissue that is normally found in the gut. This type of tissue is called mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue or MALT, where mucosa is a soft, moist, protective tissue that covers or lines many different parts of the body. MALT lymphoma only seems to arise within this special type of lymphoid tissue after it has formed as part of a reaction to an infection or to inflammation. How common is MALT lymphoma and where does it occur? Although MALT lymphoma is the third most common type of non-hodgkin lymphoma, it accounts for fewer than 1 in 10 of these tumours, so it is not a common lymphoma. Although this form of lymphoma can occur at any age, it is most common in late middle-aged and elderly people. It is roughly equally common in men and women. 1
2 MALT lymphomas have been found at almost all extra-nodal sites, including the gut, the salivary glands, the lung, the thyroid gland and around the eye. The most common site, however, is the gut. The most common site in the gut for MALT lymphoma to be found is the stomach and stomach (gastric) MALT lymphomas account for roughly a third of all MALT lymphomas. How do MALT lymphomas develop? As mentioned above, MALT lymphomas arise at sites that have acquired some MALT-type lymphoid tissue as a result of some other disorder or infection. For some MALT lymphomas this underlying condition remains a mystery. For others, more is known about the factors that might have played a part in the build-up of this kind of lymphoid tissue. For example, in the thyroid gland MALT lymphomas can develop as a result of an autoimmune inflammatory condition known as Hashimoto s thyroiditis (where autoimmune means an immune reaction against your own body tissues). Similarly, in the salivary gland MALT lymphoma can develop as a result of another autoimmune condition called Sjögren s syndrome. However, most is known about gastric MALT lymphoma, as the stomach is the commonest site for these lymphomas to develop. In the stomach, the majority of these lymphomas are associated with infection with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter infection causes inflammation of the mucosa or lining of the stomach and MALT-type lymphoid tissue develops as part of this inflammatory reaction. Once this MALT-type tissue has formed, there is continuous stimulation of the lymphocytes within it to divide and increase in number as a result of the constant presence of bacteria. This is a normal immune reaction. However, in a small number of people this constant stimulation results in a mistake occurring within the genetic material of a lymphoid cell. These faulty cells go on to multiply and they do not die off as they would normally. This eventually leads to a build-up of cells and the development of a lymphoma. What is Helicobacter pylori? Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium that we know has been around for many centuries. It is unusual in that it has become adapted to survive in the acid conditions found in the stomach, conditions that would destroy most other organisms. The bacterium is thought to be passed on from person to person and close personal contact appears to make this infection spread more easily. Infection normally happens in childhood and most people will then have it for their whole life unless it is treated with special eradication therapies. 2
3 It can be quite difficult to treat this infection and eradication (complete removal) of the bacterium normally involves the use of a combination of antibiotics, together with a drug that cuts down the amount of acid that is secreted in the stomach (such as a proton-pump inhibitor or PPI). The exact combination used varies between treatment centres. In some people initial attempts to eradicate the organism can fail and different drug combinations might have to be tried before eradication is successful. How are gastric MALT lymphomas detected? Many people with a Helicobacter pylori infection have no symptoms. Some people experience the symptoms you would get with various types of gastric and duodenal disease, such as symptoms of duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, gastritis, gastric carcinoma (cancer of the stomach lining cells) or gastric lymphoma. In the majority of people gastric MALT lymphoma is found during tests for persistent indigestion although only a very small percentage of people with this symptom have lymphoma. The indigestion is probably more related to the presence of the Helicobacter infection than to the actual lymphoma and patients often feel better after they have had treatment to eradicate the bacterium, whether or not the lymphoma is regressing (decreasing). How is gastric MALT lymphoma diagnosed? Gastric MALT lymphoma is usually discovered unexpectedly during an endoscopy examination of the stomach (where an optical instrument is passed down through the mouth to look inside the gut). The lining of the stomach might just look generally inflamed or swollen and the diagnosis might only come to light after biopsies taken at the time are examined under the microscope. In other people, ulceration or a nodular (lumpy) mass might be seen in the stomach during endoscopy. It is very difficult, and often impossible, to tell the difference between lymphoma and carcinoma on the basis of inspection of these ulcers or nodules during the endoscopy examination. Sometimes, reaching a diagnosis can even be difficult when the samples are examined under the microscope. While trying to make a diagnosis the pathologist will assess: the size and shape of the lymphoid cells where the cells are positioned within the stomach lining how the cells interact with the other components that make up the stomach wall. 3
4 In the past, patients often required several examinations of the stomach before a confident diagnosis of lymphoma could be made. More recently, pathologists have become better at recognising the subtle features that are characteristic of this lymphoma. However, there will still be instances when it is not possible to distinguish confidently between a lymphoma and inflammation, meaning that more than one endoscopic examination could be required. Will any other tests be needed after a MALT lymphoma is diagnosed? Once a diagnosis of MALT lymphoma has been made, you might require several further tests. Firstly, because the diagnosis is usually unsuspected, not enough samples may have been taken during the first endoscopy. If this is the case, another endoscopy might be required so that further biopsies can be taken from the area of lymphoma. It is very important that the presence of the Helicobacter organism is confirmed so that a firm diagnosis can be made. In many cases this will have been possible at the time of the initial diagnostic investigation, but sometimes there are very few organisms and they are difficult to find. If this is the case you might have a sample of blood taken to look for evidence of infection. Research has shown that the response of gastric MALT lymphoma to treatment depends very much on how deeply the tumour is situated within the stomach wall. This is best assessed by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). In this examination a tiny ultrasound probe at the tip of the endoscope tube uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the stomach wall. These images can be used to measure how far the lymphoma has spread through the stomach wall. Alternatively, computed tomography (CT) scanning can be used, although this is not considered to be as good as EUS for assessing the thickness of the stomach wall. As with all lymphomas, it is important to assess whether the lymphoma has spread through the body this is known as staging. You will have a full physical examination and blood tests, including a full blood count. Staging would also usually involve a CT scan to find out if any lymph nodes in the chest, abdomen or pelvis have become involved. These scans use a special kind of X-ray machine that takes pictures from different angles around your body a computer then combines these into an image of your internal organs. The bone marrow is rarely involved in MALT lymphoma (this only occurs in about 1 in 10 people with this type of lymphoma), but a bone marrow biopsy is usually performed to check for this. In this test a sample of bone marrow is removed using a special needle. 4
5 This is usually inserted through your skin, into your pelvis (hip bone) using a local anaesthetic. Unlike lymphomas that arise within the lymph node system, MALT lymphomas tend to spread to other extra-nodal sites rather than to other lymph nodes. It can spread to the thyroid gland, for example. These other extra-nodal sites would normally be studied as part of your general assessment and the staging of the lymphoma. Lastly, there are some alterations within the lymphoma cells that can have a bearing on how well the lymphoma responds to therapy. These include alterations in genes that may underlie the change from normal lymphocytes to abnormal lymphoma cells. These can normally be detected in the laboratory using the original biopsies, but the techniques are quite sophisticated and frequently take some time to complete. How is gastric MALT lymphoma treated? Until the early 1990s surgery was probably the most commonly used treatment for gastric MALT lymphoma. Since then, however, the link between gastric MALT lymphoma and Helicobacter infection has become increasingly apparent. This, together with the results of laboratory studies on cells derived from lymphomas, suggested that eradication of the Helicobacter bacterium alone might be an effective treatment for gastric MALT lymphoma. Further studies, some of which have now followed up patients for well over 10 years, have confirmed this, showing that eradication of Helicobacter infection alone can lead to regression of the tumour in 50 70% of cases. The best results with this treatment occur when the tumour has not extended very far through the gastric wall and has not spread to the lymph nodes. You would normally be prescribed an initial antibiotic-based regime for Helicobacter eradication clarithromycin and either amoxicillin or metronidazole, usually together with a PPI drug such as omeprazole. You will be followed up by repeat endoscopies and biopsies to confirm that the infection has been eradicated and to assess whether the lymphoma is regressing. The interval of time between eradication of the Helicobacter and regression of the tumour is highly variable between patients. In some people the lymphoma might be found to have regressed at the first follow-up biopsy (ie after about 4 8 weeks). In other people full regression can take a year or more. There have even been reports of patients whose lymphoma has regressed many years after Helicobacter eradication, despite their having had no other therapies. 5
6 Can we tell in advance whether Helicobacter eradication will be successful? It is impossible to predict with 100% accuracy whether a lymphoma will or will not respond to Helicobacter eradication therapy. Also, as we have seen, it is not possible to predict how long the lymphoma will take to decrease in size or disappear altogether if the therapy is successful. There are, however, certain features that make it less likely that the lymphoma will respond well to eradication therapy. In general, eradication therapy is usually less successful when: the Helicobacter organism cannot be identified and there is no evidence of previous infection the lymphoma has extended deeply through the stomach wall there is spread to local or distant lymph nodes. What happens if Helicobacter eradication doesn t work? Some patients therefore do not respond to Helicobacter eradication therapy alone and if this was the case you might have to have more conventional anti-lymphoma therapies such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Chemotherapy using only one drug (single-agent chemotherapy) is the most usual treatment. You might be prescribed an alkylating agent such as cyclophosphamide or chlorambucil, which treat cancers by damaging the cancer cell s DNA (the genetic material in the cell) and stopping these abnormal cells from multiplying. Another type of drug that your doctor might prescribe is a nucleoside analogue such as cladribine, which prevents DNA working properly so curbs the growth of lymphoma cells. These drugs appear to work equally well. Another treatment, a monoclonal antibody drug called rituximab (MabThera ) is currently being assessed in clinical trials. This works by attaching itself to the abnormal lymphoma cells (but not to normal cells) this helps the abnormal cells to die and also helps your own immune system to attack them. When rituximab is used it is usually given with other chemotherapy drugs such as chlorambucil. Less is known about how effective it is to use a combination of chemotherapy drugs for MALT lymphoma. It is generally believed, however, that multiple drugs should probably not be used in the first instance unless you have a more aggressive diffuse large B-cell type of lymphoma as well. If you are prescribed combination chemotherapy to treat gastric 6
7 lymphoma, it should be combined with a PPI drug to reduce the amount of acid secretion in the stomach. Some people who don t respond to anti-helicobacter treatment will be treated with radiotherapy and this has been found to be just as effective as chemotherapy. How are people with gastric MALT lymphoma monitored and what is the outlook? The most important investigation in the follow-up of patients with gastric MALT lymphoma is inspection of the gastric wall through an endoscope, together with close examination of any abnormal areas and of the area previously involved by lymphoma. How often these follow-up endoscopies should be done remains controversial. After confirmation of Helicobacter eradication, assessment endoscopies would normally be done every 3 4 months at first, then every 6 months and eventually once a year. The exact regime will depend on many factors, including how long it has taken for the lymphoma to regress completely in terms of both the appearance at endoscopy and the results of biopsies. In a small proportion of people who are initially treated by Helicobacter eradication, relapse is detected at follow-up endoscopies. In some patients this is associated with recurrent Helicobacter infection and this usually responds to further antibiotic-based therapy. In a few cases, relapse detected on microscopic examination of a biopsy clears spontaneously with no further treatment. In patients where there is a clear relapse of gastric MALT lymphoma, this can be treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in the same way as for those patients who do not respond to eradication therapy, with a similar success rate. Transformation of the lymphoma into a more aggressive form (a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma) occurs in fewer than 1 in 10 people with gastric MALT lymphoma and when this does happen it would normally be treated with intravenous chemotherapy using a combination of drugs, with the aim of curing this more aggressive disease. The outlook for people with gastric MALT lymphoma is usually good, with about 80% of people surviving beyond the 5-year milestone and nearly as many people (77%) being free of the disease 10 years after being diagnosed. 7
8 More information This article has been adapted from our information leaflet, Gastric MALT lymphoma. For a copy of this article or for more information about lymphoma or the treatments for lymphoma, visit our website at or telephone the Lymphoma Association s freephone helpline Talk to your key worker if you have any concerns about your health or treatment. The Lymphoma Association cannot provide information about individual diagnosis or treatment. The information provided by the Lymphoma Association is not a substitute for advice from your health professionals. About our publications: The Lymphoma Association is committed to the provision of high quality information for people with lymphoma, their families and friends. We produce our information in accordance with nationally recognised guidelines. These include the DISCERN tool for information about treatments, the NHS Toolkit for producing patient information, and the Campaign for Plain English guidelines. Our publications are written by experienced medical writers, in close collaboration with medical advisers with expertise in the appropriate field. Textbooks and professional journals are consulted to ensure that information is as up to date as possible. References are provided where they have been used. Some publications are written by professionals themselves, acting on guidance provided by the Lymphoma Association. Our publications are reviewed every two years and updated as necessary. Our publications are reviewed by a panel of volunteers with experience of lymphoma. Publications are also reviewed by members of the Lymphoma Association helpline team, who have many years collective experience of supporting those with lymphoma. In some instances, our publications are funded by educational grants from pharmaceutical companies. These sponsors do not have any involvement in the content of a publication. They are not invited to see the content and have no editorial input. Lymphoma Association Views expressed in this publication are those of the contributors. The Lymphoma Association does not necessarily agree with or endorse the comments included here. 8
Treatment of low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma
 Produced 28.02.2011 Due for revision 28.02.2013 Treatment of low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Lymphomas are described as low grade if the cells appear to be dividing slowly. There are several kinds of low-grade
Produced 28.02.2011 Due for revision 28.02.2013 Treatment of low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Lymphomas are described as low grade if the cells appear to be dividing slowly. There are several kinds of low-grade
Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma
 Produced 28.02.2011 Revision due 28.02.2013 Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer of cells called lymphocytes. These cells are part of our immune system, which helps us to fight off infections.
Produced 28.02.2011 Revision due 28.02.2013 Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer of cells called lymphocytes. These cells are part of our immune system, which helps us to fight off infections.
Lymphomas after organ transplantation
 Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
Produced 21.03.2011 Revision due 21.03.2011 Lymphomas after organ transplantation People who have undergone an organ transplant are more at risk of developing lymphoma known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Leukaemia and lymphoma what s the difference?
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk Leukaemia and lymphoma what s the difference? This is a difficult question to answer simply but it is one that is often
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk Leukaemia and lymphoma what s the difference? This is a difficult question to answer simply but it is one that is often
RADIATION THERAPY FOR LYMPHOMA. Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending
Low grade non-hodgkin Lymphoma
 Low grade non-hodgkin Lymphoma www.lymphomas.org.uk The knowledge to challenge lymphatic cancers The Lymphoma Association provides: freephone helpline emotional support for those affected by lymphomas
Low grade non-hodgkin Lymphoma www.lymphomas.org.uk The knowledge to challenge lymphatic cancers The Lymphoma Association provides: freephone helpline emotional support for those affected by lymphomas
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
How do I find the best place to get treatment for my lymphoma?
 Produced November 2010 Next revision due November 2012 How do I find the best place to get treatment for my lymphoma? Introduction Fortunately this is not a question that patients with cancers of the blood
Produced November 2010 Next revision due November 2012 How do I find the best place to get treatment for my lymphoma? Introduction Fortunately this is not a question that patients with cancers of the blood
Aggressive lymphomas. Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital
 Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners
 Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Many people with non-hodgkin lymphoma have found an educational support group helpful. Support
 Track 2: Treatment Options [Narrator] Many people with non-hodgkin lymphoma have found an educational support group helpful. Support groups take many forms: some meet the needs of people with all kinds
Track 2: Treatment Options [Narrator] Many people with non-hodgkin lymphoma have found an educational support group helpful. Support groups take many forms: some meet the needs of people with all kinds
Who is affected by HCL and what causes it?
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk Hairy cell leukaemia Hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) is a rare and very distinctive cancer of blood cells called B lymphocytes
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk Hairy cell leukaemia Hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) is a rare and very distinctive cancer of blood cells called B lymphocytes
Treating Melanoma S kin Cancer A Quick Guide
 Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
An overview of CLL care and treatment. Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham
 An overview of CLL care and treatment Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham What is CLL? CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too
An overview of CLL care and treatment Dr Dean Smith Haematology Consultant City Hospital Nottingham What is CLL? CLL (Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer
 Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Skin cancer Patient information
 Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Breast Cancer. Presentation by Dr Mafunga
 Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
How To Plan A Staging Investigation For Cancer Of The Oesophagus Or Stomach
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Understanding your diagnosis
 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Understanding your diagnosis Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Understanding your diagnosis Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the
How common is bowel cancer?
 information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
Ovarian cancer. Patient information from the BMJ Group. What is ovarian cancer? What are the symptoms?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
The causes of kidney cancer are unknown. However, there are several factors that may increase your risk including:
 Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
SARCOIDOSIS. Signs and symptoms associated with specific organ involvement can include the following:
 SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
Follicular lymphoma. What is follicular lymphoma? Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk is a cancer of the lymphatic system, a type of non-hodgkin lymphoma. Even though more than 12,000 people are diagnosed
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk is a cancer of the lymphatic system, a type of non-hodgkin lymphoma. Even though more than 12,000 people are diagnosed
Inflammatory breast cancer
 april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have had surgery for
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have had surgery for
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
A 32 year old woman comes to your clinic with neck masses for the last several weeks. Masses are discrete, non matted, firm and rubbery on
 A 32 year old woman comes to your clinic with neck masses for the last several weeks. Masses are discrete, non matted, firm and rubbery on examination. She also has fever, weight loss, and sweats. What
A 32 year old woman comes to your clinic with neck masses for the last several weeks. Masses are discrete, non matted, firm and rubbery on examination. She also has fever, weight loss, and sweats. What
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H. pylori even be good for us?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Helicobacter pylori? What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H.
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Helicobacter pylori? What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H.
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lymphoma. Starting Point. Diagnosed with Lymphoma?
 ESSENTIALS Lymphoma Diagnosed with Lymphoma? It s important to understand everything you can about your diagnosis, treatment options, and places to go for support. This will help you make treatment decisions
ESSENTIALS Lymphoma Diagnosed with Lymphoma? It s important to understand everything you can about your diagnosis, treatment options, and places to go for support. This will help you make treatment decisions
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
Estimated New Cases of Leukemia, Lymphoma, Myeloma 2014
 ABOUT BLOOD CANCERS Leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are types of cancer that can affect the
ABOUT BLOOD CANCERS Leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are types of cancer that can affect the
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Breast cancer affects one in eight Australian women. It is the most common cancer for Victorian women, with almost 3,700 diagnoses in 2012.
 Breast cancer Summary Breast cancer affects one in nine Australian women. It is important for all women to get to know the normal look and feel of their breasts. Although most breast changes aren t caused
Breast cancer Summary Breast cancer affects one in nine Australian women. It is important for all women to get to know the normal look and feel of their breasts. Although most breast changes aren t caused
This factsheet aims to outline the characteristics of some rare lung cancers, and highlight where each type of lung cancer may be different.
 There are several different kinds of lung cancer, often referred to as lung cancer subtypes. Some of these occur more often than others. In this factsheet we will specifically look at the subtypes of cancers
There are several different kinds of lung cancer, often referred to as lung cancer subtypes. Some of these occur more often than others. In this factsheet we will specifically look at the subtypes of cancers
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists
 Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
The recommendations made throughout this book are by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC).
 INTRODUCTION This book has been prepared for people with bowel cancer, their families and friends. The first section is for people with bowel cancer, and is intended to help you understand what bowel cancer
INTRODUCTION This book has been prepared for people with bowel cancer, their families and friends. The first section is for people with bowel cancer, and is intended to help you understand what bowel cancer
Breast Cancer. CSC Cancer Experience Registry Member, breast cancer
 ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer
 Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus)
 The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus) The link between cervical cancer and HPV Key facts: HPV is a virus (the human papillomavirus). Almost all abnormal Pap smear results are
The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus) The link between cervical cancer and HPV Key facts: HPV is a virus (the human papillomavirus). Almost all abnormal Pap smear results are
Your Immune System & Lung Cancer Treatment
 Your Immune System & Lung Cancer Treatment Immunotherapy and Lung Cancer Immunotherapy is quickly developing as an important approach to treating many forms of cancer, including lung cancer. Immunotherapy
Your Immune System & Lung Cancer Treatment Immunotherapy and Lung Cancer Immunotherapy is quickly developing as an important approach to treating many forms of cancer, including lung cancer. Immunotherapy
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
 Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org
 Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
What are peptic ulcers?
 Information about Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are the symptoms? What are the causes? What are peptic ulcers? When should I consult a doctor? What will the doctor do? How should I treat peptic
Information about Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are the symptoms? What are the causes? What are peptic ulcers? When should I consult a doctor? What will the doctor do? How should I treat peptic
Understanding Metastatic Disease
 Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet
 U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
Your bladder cancer diary. WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network
 Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options. John Kuruvilla
 Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Understanding your pathology report
 Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Goiter. This reference summary explains goiters. It covers symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system?
 Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Tumour Markers. What are Tumour Markers? How Are Tumour Markers Used?
 Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant
 Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer
 Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
It can be devastating to be diagnosed with a cancer like multiple myeloma. But there are treatments that can help you live longer and feel better.
 Patient information from the BMJ Group It can be devastating to be diagnosed with a cancer like multiple myeloma. But there are treatments that can help you live longer and feel better. What is multiple
Patient information from the BMJ Group It can be devastating to be diagnosed with a cancer like multiple myeloma. But there are treatments that can help you live longer and feel better. What is multiple
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families
 Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS
 INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
targeted therapy a guide for the patient
 targeted therapy FOR LUNG CANCER a guide for the patient TABLE OF CONTENTS lung cancer basics... 2-3 Gene changes... 4-5 Testing... 7-8 Targeted therapy... 9-11 Drugs Targeting EGFR... 12 Drugs Targeting
targeted therapy FOR LUNG CANCER a guide for the patient TABLE OF CONTENTS lung cancer basics... 2-3 Gene changes... 4-5 Testing... 7-8 Targeted therapy... 9-11 Drugs Targeting EGFR... 12 Drugs Targeting
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
What is Cancer? Section 2 - What Is Cancer? - 1 -
 What is Cancer? Normal Growth The human body is made up of many millions of tiny building blocks called cells. Each organ of the body (eg. brain, liver, muscle) contains its own special types of cells,
What is Cancer? Normal Growth The human body is made up of many millions of tiny building blocks called cells. Each organ of the body (eg. brain, liver, muscle) contains its own special types of cells,
Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis
 Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT
 OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre National Cancer Plan May 2015 Contents About this booklet 1 The Ovaries
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre National Cancer Plan May 2015 Contents About this booklet 1 The Ovaries
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML),
 1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
1 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML), ALSO KNOWN AS ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA WHAT IS CANCER? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly
