How to Choose a CPU Core for Multi-CPU SOC Designs
|
|
|
- Brett Gaines
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to Choose a CPU Core for Multi-CPU SOC Designs MIPS Technologies, Inc. June 2002 The use of multiple CPUs in SOC designs is becoming increasingly popular. Processor cores being considered for multi-cpu designs should possess several important features, including excellent performance density, efficient inter-processor communications, debug support, and implementation flexibility and configurability. This article examines these features in relation to a core specifically designed for multi-cpu designs, the MIPS32 M4K core. Due to an increasing demand for programmable performance, the use of multiple CPUs is becoming very popular among SOC designers. For many applications, performance requirements are increasing faster than the ability of a single CPU to keep pace. The allocation of performance, and thus response time, for complex real-time systems is often easier with multiple CPUs. And dedicated CPUs in peripherals or special accelerators can offload low-level functionality from a main CPU, allowing it to focus on higher-level functions. Multi-CPU designs are feasible in embedded systems today for various reasons. Embedded applications often have a great deal of partitioning flexibility, which facilitates mapping to multiple CPUs. In some cases, it is much easier to map to multiple separate CPUs than to try to use a single one. Similarly, many embedded applications have obvious parallelism that can be exploited with parallel CPUs. The NPU designers, for instance, have taken advantage of this for routing. And finally, with today s and 0.10-micron processes, multi-cpu SOC systems can be built economically. Multi-CPU designs can be found in many important growing markets. Network routing is one of the leading applications where multi-cpu designs have become popular. Most of the new generation of network processors are based on multi-cpu designs. In addition to these standard NPUs, targeted ASSPs are using multiple processors to build more optimized, application targeted routing solutions. For many, a targeted ASSP is a much more efficient solution than a standard NPU. An ASSP can integrate the right physical interfaces or target the on-chip memory size or provide the best configuration of processors. Related applications such as DSLAMs and base stations, or high-performance networked storage devices, also work well with a divide-and-conquer approach to building high-performance programmable solutions. Even end-user equipment is beginning to utilize multiple CPUs to get
2 the best performance density for cost and/or power reasons. Set-top boxes, residential gateways and even smart mobile devices are being built with multiple CPUs and not just one RISC processor and one DSP, but multiple quantities of each. What Makes a Good CPU Core For a processor core to be a good candidate for multi-cpu designs it must possess a few important features. First and foremost, it must provide excellent performance density. The goal in a multi-cpu design is to attain as much aggregate performance as possible per square millimeter or per watt. The solution that has the most MIPS in the smallest space or the lowest power is preferred. Another requirement is efficient inter-processor communications. Even though many multi-cpu designs are software coherent, there is still a significant amount of inter-processor communication. If a framework for the support of communication between the processors is not provided, then it will have to be developed by the SOC designer. This is not only timeconsuming; it also introduces another level of complexity to the design. Providing support for inter-processor communication simplifies the SOC designer s task and shortens development time. It can also minimize inefficiencies at the partitioning boundaries. Multi-CPU designs can be a challenge to debug. The cores interact with and are dependent upon one another, and it s important to see this interaction when debugging an SOC. This requires that the CPUs have a built-in capability that allows them to be debugged at the same time while also fully interacting. Without this, SOC debug can quickly become a nightmare or, worse, it may be impossible to fully debug. It is also critical that the CPUs be supported with good multi-cpu debug tools that allow the SOC designer to take advantage of the debug capabilities built into the CPUs. Something else to consider is the level of flexibility in configuring and implementing the CPU core. In a multi-cpu design, it is important to minimize area and power consumption while maximizing performance, and a highly configurable, synthesizable CPU enables the designer to target area, power and frequency for the specific application. This is not possible with a hardened core, or one that isn t configurable, which severely limits the implementation options. With these factors in mind, MIPS Technologies recently launched a CPU core specifically designed for multi-cpu designs. The MIPS32 M4K core is high-performance, yet, perhaps surprising to some, is also small and low-power. It is also synthesizable and has a low-latency memory system. Let s examine how the M4K core maps to the requirements listed above. Performance Density In terms of performance density -- the best performance in the smallest space or with the lowest power consumption -- the M4K core provides high performance within tight area and power constraints. It delivers approximately 1.35 Dhrystone MIPS/MHz (without using questionable compiler tricks that might be found with other cores), and it runs at up to 240 MHz (worst case) 2
3 in a generic 0.13-micron process, or up to 300 MHz in a higher performance 0.13-micron process. On the denominator side of the performance density equation, the M4K core is an extremely small, very low-power processor. It can be configured to be as small as 32K gates or less than 0.3 mm 2, while still maintaining full MIPS32 architecture compatibility. Its power consumption is extremely low, as low as 0.10 mw/mhz in a generic 0.13-micron process. The core also includes new MIPS architecture enhancements to improve performance for important application functions. They include prioritized, vectored interrupts and up to four register contexts to minimize interrupt latency and overhead. Bit-field and byte-level instructions are included to provide highly efficient packet handling. User-defined instruction-set extensions have been included for SOC designers who want to implement proprietary, highly focused application optimizations and extend the industrystandard MIPS32 instruction set in the M4K with custom instructions. Any register-to-register or register-immediate instruction can be added. The custom instructions can be single or multicycle and new user state is also supported. These user-defined instructions are supported in the core RTL, synthesis scripts and simulation models, and can be used with industry-standard development tools from companies such as Green Hills, Cygnus and Mentor. 3
4 In addition and perhaps most importantly the M4K core features all of this while maintaining complete MIPS32 compatibility and working with the wide range of software and tools available for MIPS CPUs. This core is, in fact, the only available configurable processor with custom instruction extensions, based on a well-supported, industry-standard architecture. Inter-Processor Communication In multi-cpu designs, the processors have to communicate with each other to control access to shared resources. In most of the multi-cpu designs being built today, memory coherence is managed completely in software, so the normal cache coherency mechanisms for communication are not available. The M4K core includes support for multi-cpu semaphores by externalizing the behavior of the Load Linked (LL) and the Store Conditional (SC) instructions in the MIPS architecture to allow the system logic to maintain the necessary monitoring. In addition, the behavior of the SYNC instruction, which provides a memory ordering barrier to ensure correct ordering semantics, is also brought out to the signal interface to give the system design maximum control and flexibility. As shown in Figure 2, when a typical semaphore access code sequence is executed, the LL and SC instructions provide the behavior of an atomic Read Modify Write sequence without the need to propagate a lock through the system. 4
5 For example, in a test-and-set spin-lock, an LL instruction generates a read on the signal interface that is identified as an LL to the system. The system then sets a monitor on that address. If another processor writes to the monitored address, the monitor s pass/fail flag is cleared. When the CPU executes the SC instruction, the system logic conditionally executes the store to memory depending on the state of the monitor. The pass/fail indication is returned to the processor, where the software typically repeats a failed sequence until it succeeds. Similarly, the semantics of the SYNC instruction are externalized to allow the system to ensure the correct behavior of the memory barrier. As shown in the example in Figure 3, a SYNC is placed between the last store to a shared buffer and the store that releases a controlling semaphore. When the SYNC instruction is executed, the CPU signals to the system logic that the CPU is waiting for a synch response. Once the system is sure that ordering can be guaranteed, it signals it back to the CPU, allowing subsequent loads or stores to issue. A simple system may wait for all outstanding transactions to complete; or, a more complex system that can maintain order in its queues and buffers may respond more quickly. Either way, the CPU software and hardware mechanism is the same. The inter-processor communications features on the M4K are an elegant solution, fully supported by industry-standard development tools. A designer implementing a multi-cpu design 5
6 using the M4K core can use these features to quickly and easily communicate between cores, reducing design time and lowering implementation risk. Debug Support Debugging a multi-cpu design can be a challenge. The interactions between multiple processors can create scenarios that are difficult or impossible to identify and resolve unless debugging can be performed on all of the cores at the same time. The M4K core has features in its EJTAG-based debug logic to ease this challenge. First, the EJTAG interface on the M4K core can be daisy-chained with all of the cores on an SOC to allow a single debug probe and host to debug all of the cores simultaneously. This also enables support of independent or synchronous start, stop and single step control. Another nice feature for multi-cpu debug supported on the M4K core is cross CPU breakpoints. The core supports the ability for a breakpoint in one CPU to force a breakpoint in one or more of the other CPUs within a few clocks. This is software controlled through a small logic block that defines which CPU can cross break any other CPU. This capability is very useful for debugging problems that involve CPU interactions. These debug features on the M4K core reduce design time and risk by offering the user a fully supported, easy-to-use debug environment for multi-cpu SOC designs. Configurability Since efficiency is critical in multi-cpu systems, implementation flexibility and configurability are crucial to building the optimal solution for the particular application problem being solved. The M4K core is the most configurable core MIPS Technologies has ever developed. As shown in Figure 4, most of the CPU blocks are optional or configurable. 6
7 The multiplier can be targeted for high performance or for minimal area. As mentioned previously, the number of register contexts can be configured. The MIPS16e code compression decoder can be removed if not needed. Multiple tradeoffs in debug support can be made with either minimal support, and different numbers of hardware breakpoints can be defined. Even the TAP controller is optional. For program and data trace, an on-chip capture buffer can be included or excluded, and trace support can be configured out. The coprocessor interface logic can be configured in or out. User-defined custom instruction extensions can be added, as mentioned previously, and clock gating (to reduce power consumption) can be included or excluded. In addition to this internal core configurability, the M4K core supports considerable flexibility in the memory system design. It can support Harvard-type systems with separate instruction and data memory spaces using a very low-latency synchronous SRAM style interface for highly efficient memory access. This interface supports single-cycle and multi-cycle transactions and supports connecting 8-, 16-, or 32-bit peripherals. Or, it can be built for a shared memory system with a combined instruction and data space using the same low latency interface. In addition, a bridge from the SRAM-style interface to EC-based system logic supports use of existing peripherals built for systems based on MIPS32 4K, 4KE, or MIPS64 5K cores. 7
8 This bridge supports low latency memory to maintain high-performance access to local memory while connecting to a traditional MIPS-based CPU subsystem. Multi-CPU Systems What can systems do with multiple CPU cores? As shown in Figure 5, a network storage system can use multiple cores to offload specialized functions from a host processor, a MIPS64 20Kc core, for instance. By putting a CPU at network interfaces, higher level functions like filtering, L2 or L3 protocol response and segmentation and reassembly can be done locally by the peripheral device, freeing up the host CPU for higher level protocol and management functions. Similarly, using one or more M4K cores in an accelerator, like the TCP offload in this example, allows the partitioning of special high-performance functions away from the host processor, while still maintaining the advantages of a standard reprogrammable device. Another common example of a multi-cpu system design is a line card. This may be for a network router, a DSLAM, or a wireless base station. In these cases, parallel CPU subsystems, sometimes called micro-engines, are used to provide a tremendous amount of aggregate performance for highly parallel applications, such as level 2 processing, packet classification, filtering, or tag management. In this case, the host processor is used primarily for exception processing. There are many variations of this approach using not only parallel processing but also pipelines of processors or pipelines of parallel processors. 8
9 Multi-CPU design is becoming increasingly popular with chip designers because it provides scalable, programmable performance and fits the natural partitioning of many networking and other embedded system designs. As with most SOC design today, multi-cpu design is not without challenges, but those challenges are lessened considerably when using a CPU core like the MIPS32 M4K that is optimized to handle the job. David Courtight is director of product strategy at MIPS Technologies, Inc. Copyright , MIPS Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. MIPS is a registered trademark and MIPS32, M4K, MIPS16e, 4K, 4KE, MIPS64, 5K, 20Kc and MIPS-based are trademarks of MIPS Technologies, Inc. All other trademarks used herein are the property of their respective owners. 9
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Five Families of ARM Processor IP
 ARM1026EJ-S Synthesizable ARM10E Family Processor Core Eric Schorn CPU Product Manager ARM Austin Design Center Five Families of ARM Processor IP Performance ARM preserves SW & HW investment through code
ARM1026EJ-S Synthesizable ARM10E Family Processor Core Eric Schorn CPU Product Manager ARM Austin Design Center Five Families of ARM Processor IP Performance ARM preserves SW & HW investment through code
A Lab Course on Computer Architecture
 A Lab Course on Computer Architecture Pedro López José Duato Depto. de Informática de Sistemas y Computadores Facultad de Informática Universidad Politécnica de Valencia Camino de Vera s/n, 46071 - Valencia,
A Lab Course on Computer Architecture Pedro López José Duato Depto. de Informática de Sistemas y Computadores Facultad de Informática Universidad Politécnica de Valencia Camino de Vera s/n, 46071 - Valencia,
Achieving Nanosecond Latency Between Applications with IPC Shared Memory Messaging
 Achieving Nanosecond Latency Between Applications with IPC Shared Memory Messaging In some markets and scenarios where competitive advantage is all about speed, speed is measured in micro- and even nano-seconds.
Achieving Nanosecond Latency Between Applications with IPC Shared Memory Messaging In some markets and scenarios where competitive advantage is all about speed, speed is measured in micro- and even nano-seconds.
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers
 ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
A Generic Network Interface Architecture for a Networked Processor Array (NePA)
 A Generic Network Interface Architecture for a Networked Processor Array (NePA) Seung Eun Lee, Jun Ho Bahn, Yoon Seok Yang, and Nader Bagherzadeh EECS @ University of California, Irvine Outline Introduction
A Generic Network Interface Architecture for a Networked Processor Array (NePA) Seung Eun Lee, Jun Ho Bahn, Yoon Seok Yang, and Nader Bagherzadeh EECS @ University of California, Irvine Outline Introduction
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY
 İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGİNEERİNG SOFTWARE ENGINEERING THE PROJECT OF THE INSTRUCTION SET COMPUTER ORGANIZATION GÖZDE ARAS B1205.090015 Instructor: Prof. Dr. HASAN HÜSEYİN BALIK DECEMBER
İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGİNEERİNG SOFTWARE ENGINEERING THE PROJECT OF THE INSTRUCTION SET COMPUTER ORGANIZATION GÖZDE ARAS B1205.090015 Instructor: Prof. Dr. HASAN HÜSEYİN BALIK DECEMBER
Implementation Details
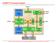 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation
 Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Which ARM Cortex Core Is Right for Your Application: A, R or M?
 Which ARM Cortex Core Is Right for Your Application: A, R or M? Introduction The ARM Cortex series of cores encompasses a very wide range of scalable performance options offering designers a great deal
Which ARM Cortex Core Is Right for Your Application: A, R or M? Introduction The ARM Cortex series of cores encompasses a very wide range of scalable performance options offering designers a great deal
A Survey on ARM Cortex A Processors. Wei Wang Tanima Dey
 A Survey on ARM Cortex A Processors Wei Wang Tanima Dey 1 Overview of ARM Processors Focusing on Cortex A9 & Cortex A15 ARM ships no processors but only IP cores For SoC integration Targeting markets:
A Survey on ARM Cortex A Processors Wei Wang Tanima Dey 1 Overview of ARM Processors Focusing on Cortex A9 & Cortex A15 ARM ships no processors but only IP cores For SoC integration Targeting markets:
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines
 Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada ken@unb.ca Micaela Serra
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada ken@unb.ca Micaela Serra
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield
 DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
Achieving Mainframe-Class Performance on Intel Servers Using InfiniBand Building Blocks. An Oracle White Paper April 2003
 Achieving Mainframe-Class Performance on Intel Servers Using InfiniBand Building Blocks An Oracle White Paper April 2003 Achieving Mainframe-Class Performance on Intel Servers Using InfiniBand Building
Achieving Mainframe-Class Performance on Intel Servers Using InfiniBand Building Blocks An Oracle White Paper April 2003 Achieving Mainframe-Class Performance on Intel Servers Using InfiniBand Building
White Paper. Real-time Capabilities for Linux SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux
 White Paper Real-time Capabilities for Linux SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux Abstract This white paper describes the real-time capabilities provided by SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux. software. REACT enables
White Paper Real-time Capabilities for Linux SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux Abstract This white paper describes the real-time capabilities provided by SGI REACT Real-Time for Linux. software. REACT enables
Programmable Logic IP Cores in SoC Design: Opportunities and Challenges
 Programmable Logic IP Cores in SoC Design: Opportunities and Challenges Steven J.E. Wilton and Resve Saleh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia Vancouver, B.C.,
Programmable Logic IP Cores in SoC Design: Opportunities and Challenges Steven J.E. Wilton and Resve Saleh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia Vancouver, B.C.,
All Programmable Logic. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems. Zürcher Fachhochschule
 All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
A New Chapter for System Designs Using NAND Flash Memory
 A New Chapter for System Designs Using Memory Jim Cooke Senior Technical Marketing Manager Micron Technology, Inc December 27, 2010 Trends and Complexities trends have been on the rise since was first
A New Chapter for System Designs Using Memory Jim Cooke Senior Technical Marketing Manager Micron Technology, Inc December 27, 2010 Trends and Complexities trends have been on the rise since was first
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler
 ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
Figure 1 FPGA Growth and Usage Trends
 White Paper Avoiding PCB Design Mistakes in FPGA-Based Systems System design using FPGAs is significantly different from the regular ASIC and processor based system design. In this white paper, we will
White Paper Avoiding PCB Design Mistakes in FPGA-Based Systems System design using FPGAs is significantly different from the regular ASIC and processor based system design. In this white paper, we will
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000. ILP Execution
 EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000 Lecture #11: Wednesday, 3 May 2000 Lecturer: Ben Serebrin Scribe: Dean Liu ILP Execution
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000 Lecture #11: Wednesday, 3 May 2000 Lecturer: Ben Serebrin Scribe: Dean Liu ILP Execution
White Paper. S2C Inc. 1735 Technology Drive, Suite 620 San Jose, CA 95110, USA Tel: +1 408 213 8818 Fax: +1 408 213 8821 www.s2cinc.com.
 White Paper FPGA Prototyping of System-on-Chip Designs The Need for a Complete Prototyping Platform for Any Design Size, Any Design Stage with Enterprise-Wide Access, Anytime, Anywhere S2C Inc. 1735 Technology
White Paper FPGA Prototyping of System-on-Chip Designs The Need for a Complete Prototyping Platform for Any Design Size, Any Design Stage with Enterprise-Wide Access, Anytime, Anywhere S2C Inc. 1735 Technology
Tensilica Software Development Toolkit (SDK)
 Tensilica Datasheet Tensilica Software Development Toolkit (SDK) Quickly develop application code Features Cadence Tensilica Xtensa Xplorer Integrated Development Environment (IDE) with full graphical
Tensilica Datasheet Tensilica Software Development Toolkit (SDK) Quickly develop application code Features Cadence Tensilica Xtensa Xplorer Integrated Development Environment (IDE) with full graphical
Synchronization. Todd C. Mowry CS 740 November 24, 1998. Topics. Locks Barriers
 Synchronization Todd C. Mowry CS 740 November 24, 1998 Topics Locks Barriers Types of Synchronization Mutual Exclusion Locks Event Synchronization Global or group-based (barriers) Point-to-point tightly
Synchronization Todd C. Mowry CS 740 November 24, 1998 Topics Locks Barriers Types of Synchronization Mutual Exclusion Locks Event Synchronization Global or group-based (barriers) Point-to-point tightly
Introduction to RISC Processor. ni logic Pvt. Ltd., Pune
 Introduction to RISC Processor ni logic Pvt. Ltd., Pune AGENDA What is RISC & its History What is meant by RISC Architecture of MIPS-R4000 Processor Difference Between RISC and CISC Pros and Cons of RISC
Introduction to RISC Processor ni logic Pvt. Ltd., Pune AGENDA What is RISC & its History What is meant by RISC Architecture of MIPS-R4000 Processor Difference Between RISC and CISC Pros and Cons of RISC
VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF INTERNET CHECKSUM CALCULATION FOR 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET
 VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF INTERNET CHECKSUM CALCULATION FOR 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET Tomas Henriksson, Niklas Persson and Dake Liu Department of Electrical Engineering, Linköpings universitet SE-581 83 Linköping
VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF INTERNET CHECKSUM CALCULATION FOR 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET Tomas Henriksson, Niklas Persson and Dake Liu Department of Electrical Engineering, Linköpings universitet SE-581 83 Linköping
BY STEVE BROWN, CADENCE DESIGN SYSTEMS AND MICHEL GENARD, VIRTUTECH
 WHITE PAPER METRIC-DRIVEN VERIFICATION ENSURES SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT QUALITY BY STEVE BROWN, CADENCE DESIGN SYSTEMS AND MICHEL GENARD, VIRTUTECH INTRODUCTION The complexity of electronic systems is rapidly
WHITE PAPER METRIC-DRIVEN VERIFICATION ENSURES SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT QUALITY BY STEVE BROWN, CADENCE DESIGN SYSTEMS AND MICHEL GENARD, VIRTUTECH INTRODUCTION The complexity of electronic systems is rapidly
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1 9NJ, UK. *peter.harrod@arm.com
 Serial Wire Debug and the CoreSight TM Debug and Trace Architecture Eddie Ashfield, Ian Field, Peter Harrod *, Sean Houlihane, William Orme and Sheldon Woodhouse ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1
Serial Wire Debug and the CoreSight TM Debug and Trace Architecture Eddie Ashfield, Ian Field, Peter Harrod *, Sean Houlihane, William Orme and Sheldon Woodhouse ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1
- Nishad Nerurkar. - Aniket Mhatre
 - Nishad Nerurkar - Aniket Mhatre Single Chip Cloud Computer is a project developed by Intel. It was developed by Intel Lab Bangalore, Intel Lab America and Intel Lab Germany. It is part of a larger project,
- Nishad Nerurkar - Aniket Mhatre Single Chip Cloud Computer is a project developed by Intel. It was developed by Intel Lab Bangalore, Intel Lab America and Intel Lab Germany. It is part of a larger project,
Outline. Introduction. Multiprocessor Systems on Chip. A MPSoC Example: Nexperia DVP. A New Paradigm: Network on Chip
 Outline Modeling, simulation and optimization of Multi-Processor SoCs (MPSoCs) Università of Verona Dipartimento di Informatica MPSoCs: Multi-Processor Systems on Chip A simulation platform for a MPSoC
Outline Modeling, simulation and optimization of Multi-Processor SoCs (MPSoCs) Università of Verona Dipartimento di Informatica MPSoCs: Multi-Processor Systems on Chip A simulation platform for a MPSoC
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors
 Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors White paper Joseph Yiu January 2013 Overview Finite state machines (FSM) are commonly used in electronic designs. FSM can be used
Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors White paper Joseph Yiu January 2013 Overview Finite state machines (FSM) are commonly used in electronic designs. FSM can be used
ARM Webinar series. ARM Based SoC. Abey Thomas
 ARM Webinar series ARM Based SoC Verification Abey Thomas Agenda About ARM and ARM IP ARM based SoC Verification challenges Verification planning and strategy IP Connectivity verification Performance verification
ARM Webinar series ARM Based SoC Verification Abey Thomas Agenda About ARM and ARM IP ARM based SoC Verification challenges Verification planning and strategy IP Connectivity verification Performance verification
Design Cycle for Microprocessors
 Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
What is a bus? A Bus is: Advantages of Buses. Disadvantage of Buses. Master versus Slave. The General Organization of a Bus
 Datorteknik F1 bild 1 What is a bus? Slow vehicle that many people ride together well, true... A bunch of wires... A is: a shared communication link a single set of wires used to connect multiple subsystems
Datorteknik F1 bild 1 What is a bus? Slow vehicle that many people ride together well, true... A bunch of wires... A is: a shared communication link a single set of wires used to connect multiple subsystems
Meeting the Five Key Needs of Next-Generation Cloud Computing Networks with 10 GbE
 White Paper Meeting the Five Key Needs of Next-Generation Cloud Computing Networks Cloud computing promises to bring scalable processing capacity to a wide range of applications in a cost-effective manner.
White Paper Meeting the Five Key Needs of Next-Generation Cloud Computing Networks Cloud computing promises to bring scalable processing capacity to a wide range of applications in a cost-effective manner.
Accelerating High-Speed Networking with Intel I/O Acceleration Technology
 White Paper Intel I/O Acceleration Technology Accelerating High-Speed Networking with Intel I/O Acceleration Technology The emergence of multi-gigabit Ethernet allows data centers to adapt to the increasing
White Paper Intel I/O Acceleration Technology Accelerating High-Speed Networking with Intel I/O Acceleration Technology The emergence of multi-gigabit Ethernet allows data centers to adapt to the increasing
Chapter 13 Embedded Operating Systems
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 13 Embedded Operating Systems Eighth Edition By William Stallings Embedded System Refers to the use of electronics and software within a product
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 13 Embedded Operating Systems Eighth Edition By William Stallings Embedded System Refers to the use of electronics and software within a product
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs
 Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
A White Paper By: Dr. Gaurav Banga SVP, Engineering & CTO, Phoenix Technologies. Bridging BIOS to UEFI
 A White Paper By: Dr. Gaurav Banga SVP, Engineering & CTO, Phoenix Technologies Bridging BIOS to UEFI Copyright Copyright 2007 by Phoenix Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
A White Paper By: Dr. Gaurav Banga SVP, Engineering & CTO, Phoenix Technologies Bridging BIOS to UEFI Copyright Copyright 2007 by Phoenix Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501. Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2
 Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
Infrastructure Matters: POWER8 vs. Xeon x86
 Advisory Infrastructure Matters: POWER8 vs. Xeon x86 Executive Summary This report compares IBM s new POWER8-based scale-out Power System to Intel E5 v2 x86- based scale-out systems. A follow-on report
Advisory Infrastructure Matters: POWER8 vs. Xeon x86 Executive Summary This report compares IBM s new POWER8-based scale-out Power System to Intel E5 v2 x86- based scale-out systems. A follow-on report
Using VMWare VAAI for storage integration with Infortrend EonStor DS G7i
 Using VMWare VAAI for storage integration with Infortrend EonStor DS G7i Application Note Abstract: This document describes how VMware s vsphere Storage APIs (VAAI) can be integrated and used for accelerating
Using VMWare VAAI for storage integration with Infortrend EonStor DS G7i Application Note Abstract: This document describes how VMware s vsphere Storage APIs (VAAI) can be integrated and used for accelerating
- An Essential Building Block for Stable and Reliable Compute Clusters
 Ferdinand Geier ParTec Cluster Competence Center GmbH, V. 1.4, March 2005 Cluster Middleware - An Essential Building Block for Stable and Reliable Compute Clusters Contents: Compute Clusters a Real Alternative
Ferdinand Geier ParTec Cluster Competence Center GmbH, V. 1.4, March 2005 Cluster Middleware - An Essential Building Block for Stable and Reliable Compute Clusters Contents: Compute Clusters a Real Alternative
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19
 Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas
 Technology Trend MSP432 TM microcontrollers: Bringing high performance to low-power applications The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas Instruments leverages its more than 20 years of lowpower leadership
Technology Trend MSP432 TM microcontrollers: Bringing high performance to low-power applications The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas Instruments leverages its more than 20 years of lowpower leadership
Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs
 Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs William Orme September 2008 Abstract As SoC designs become ever more complex
Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs William Orme September 2008 Abstract As SoC designs become ever more complex
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet
 Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics
 Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Client/Server Computing Distributed Processing, Client/Server, and Clusters
 Client/Server Computing Distributed Processing, Client/Server, and Clusters Chapter 13 Client machines are generally single-user PCs or workstations that provide a highly userfriendly interface to the
Client/Server Computing Distributed Processing, Client/Server, and Clusters Chapter 13 Client machines are generally single-user PCs or workstations that provide a highly userfriendly interface to the
ZigBee Technology Overview
 ZigBee Technology Overview Presented by Silicon Laboratories Shaoxian Luo 1 EM351 & EM357 introduction EM358x Family introduction 2 EM351 & EM357 3 Ember ZigBee Platform Complete, ready for certification
ZigBee Technology Overview Presented by Silicon Laboratories Shaoxian Luo 1 EM351 & EM357 introduction EM358x Family introduction 2 EM351 & EM357 3 Ember ZigBee Platform Complete, ready for certification
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR 1. What is the purpose of segment registers
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR 1. What is the purpose of segment registers
System Considerations
 System Considerations Interfacing Performance Power Size Ease-of Use Programming Interfacing Debugging Cost Device cost System cost Development cost Time to market Integration Peripherals Different Needs?
System Considerations Interfacing Performance Power Size Ease-of Use Programming Interfacing Debugging Cost Device cost System cost Development cost Time to market Integration Peripherals Different Needs?
Vorlesung Rechnerarchitektur 2 Seite 178 DASH
 Vorlesung Rechnerarchitektur 2 Seite 178 Architecture for Shared () The -architecture is a cache coherent, NUMA multiprocessor system, developed at CSL-Stanford by John Hennessy, Daniel Lenoski, Monica
Vorlesung Rechnerarchitektur 2 Seite 178 Architecture for Shared () The -architecture is a cache coherent, NUMA multiprocessor system, developed at CSL-Stanford by John Hennessy, Daniel Lenoski, Monica
Instruction Set Design
 Instruction Set Design Instruction Set Architecture: to what purpose? ISA provides the level of abstraction between the software and the hardware One of the most important abstraction in CS It s narrow,
Instruction Set Design Instruction Set Architecture: to what purpose? ISA provides the level of abstraction between the software and the hardware One of the most important abstraction in CS It s narrow,
Performance Comparison of RTOS
 Performance Comparison of RTOS Shahmil Merchant, Kalpen Dedhia Dept Of Computer Science. Columbia University Abstract: Embedded systems are becoming an integral part of commercial products today. Mobile
Performance Comparison of RTOS Shahmil Merchant, Kalpen Dedhia Dept Of Computer Science. Columbia University Abstract: Embedded systems are becoming an integral part of commercial products today. Mobile
Scaling Networking Applications to Multiple Cores
 Scaling Networking Applications to Multiple Cores Greg Seibert Sr. Technical Marketing Engineer Cavium Networks Challenges with multi-core application performance Amdahl s Law Evaluates application performance
Scaling Networking Applications to Multiple Cores Greg Seibert Sr. Technical Marketing Engineer Cavium Networks Challenges with multi-core application performance Amdahl s Law Evaluates application performance
Multi-Threading Performance on Commodity Multi-Core Processors
 Multi-Threading Performance on Commodity Multi-Core Processors Jie Chen and William Watson III Scientific Computing Group Jefferson Lab 12000 Jefferson Ave. Newport News, VA 23606 Organization Introduction
Multi-Threading Performance on Commodity Multi-Core Processors Jie Chen and William Watson III Scientific Computing Group Jefferson Lab 12000 Jefferson Ave. Newport News, VA 23606 Organization Introduction
REMOTE DEVELOPMENT OPTION
 Leading the Evolution DATA SHEET MICRO FOCUS SERVER EXPRESS TM REMOTE DEVELOPMENT OPTION Executive Overview HIGH PRODUCTIVITY DEVELOPMENT FOR LINUX AND UNIX DEVELOPERS Micro Focus Server Express is the
Leading the Evolution DATA SHEET MICRO FOCUS SERVER EXPRESS TM REMOTE DEVELOPMENT OPTION Executive Overview HIGH PRODUCTIVITY DEVELOPMENT FOR LINUX AND UNIX DEVELOPERS Micro Focus Server Express is the
Applying the Benefits of Network on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design
 Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
Business Process Management The Must Have Enterprise Solution for the New Century
 Business Process Management The Must Have Enterprise Solution for the New Century 15200 Weston Parkway, Suite 106 Cary, NC 27513 Phone: (919) 678-0900 Fax: (919) 678-0901 E-Mail: info@ultimus.com WWW:
Business Process Management The Must Have Enterprise Solution for the New Century 15200 Weston Parkway, Suite 106 Cary, NC 27513 Phone: (919) 678-0900 Fax: (919) 678-0901 E-Mail: info@ultimus.com WWW:
Reducing Cost and Complexity with Industrial System Consolidation
 WHITE PAPER Multi- Virtualization Technology Industrial Automation Reducing Cost and Complexity with Industrial System Consolidation Virtualization on multi-core Intel vpro processors helps lower overall
WHITE PAPER Multi- Virtualization Technology Industrial Automation Reducing Cost and Complexity with Industrial System Consolidation Virtualization on multi-core Intel vpro processors helps lower overall
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
FPGA Prototyping Primer
 FPGA Prototyping Primer S2C Inc. 1735 Technology Drive, Suite 620 San Jose, CA 95110, USA Tel: +1 408 213 8818 Fax: +1 408 213 8821 www.s2cinc.com What is FPGA prototyping? FPGA prototyping is the methodology
FPGA Prototyping Primer S2C Inc. 1735 Technology Drive, Suite 620 San Jose, CA 95110, USA Tel: +1 408 213 8818 Fax: +1 408 213 8821 www.s2cinc.com What is FPGA prototyping? FPGA prototyping is the methodology
SPARC64 VIIIfx: CPU for the K computer
 SPARC64 VIIIfx: CPU for the K computer Toshio Yoshida Mikio Hondo Ryuji Kan Go Sugizaki SPARC64 VIIIfx, which was developed as a processor for the K computer, uses Fujitsu Semiconductor Ltd. s 45-nm CMOS
SPARC64 VIIIfx: CPU for the K computer Toshio Yoshida Mikio Hondo Ryuji Kan Go Sugizaki SPARC64 VIIIfx, which was developed as a processor for the K computer, uses Fujitsu Semiconductor Ltd. s 45-nm CMOS
CISC, RISC, and DSP Microprocessors
 CISC, RISC, and DSP Microprocessors Douglas L. Jones ECE 497 Spring 2000 4/6/00 CISC, RISC, and DSP D.L. Jones 1 Outline Microprocessors circa 1984 RISC vs. CISC Microprocessors circa 1999 Perspective:
CISC, RISC, and DSP Microprocessors Douglas L. Jones ECE 497 Spring 2000 4/6/00 CISC, RISC, and DSP D.L. Jones 1 Outline Microprocessors circa 1984 RISC vs. CISC Microprocessors circa 1999 Perspective:
Making Multicore Work and Measuring its Benefits. Markus Levy, president EEMBC and Multicore Association
 Making Multicore Work and Measuring its Benefits Markus Levy, president EEMBC and Multicore Association Agenda Why Multicore? Standards and issues in the multicore community What is Multicore Association?
Making Multicore Work and Measuring its Benefits Markus Levy, president EEMBC and Multicore Association Agenda Why Multicore? Standards and issues in the multicore community What is Multicore Association?
Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin
 BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
VHDL DESIGN OF EDUCATIONAL, MODERN AND OPEN- ARCHITECTURE CPU
 VHDL DESIGN OF EDUCATIONAL, MODERN AND OPEN- ARCHITECTURE CPU Martin Straka Doctoral Degree Programme (1), FIT BUT E-mail: strakam@fit.vutbr.cz Supervised by: Zdeněk Kotásek E-mail: kotasek@fit.vutbr.cz
VHDL DESIGN OF EDUCATIONAL, MODERN AND OPEN- ARCHITECTURE CPU Martin Straka Doctoral Degree Programme (1), FIT BUT E-mail: strakam@fit.vutbr.cz Supervised by: Zdeněk Kotásek E-mail: kotasek@fit.vutbr.cz
LTE Release 10 Small Cell Physical Layer Evolution Issues and Challenges Facing Small Cell Product Developers in Multi- Core Environments
 LTE Release 10 Small Cell Physical Layer Evolution Issues and Challenges Facing Small Cell Product Developers in Multi- Core Environments By Brian Meads, Director of Software Sales, CommAgility LTE Industry
LTE Release 10 Small Cell Physical Layer Evolution Issues and Challenges Facing Small Cell Product Developers in Multi- Core Environments By Brian Meads, Director of Software Sales, CommAgility LTE Industry
Migrating Application Code from ARM Cortex-M4 to Cortex-M7 Processors
 Migrating Application Code from ARM Cortex-M4 to Cortex-M7 Processors Joseph Yiu and Robert Boys January 2015 Version 1.1 The latest version of this document is here: /appnotes/docs/apnt_270.asp 1 Cortex
Migrating Application Code from ARM Cortex-M4 to Cortex-M7 Processors Joseph Yiu and Robert Boys January 2015 Version 1.1 The latest version of this document is here: /appnotes/docs/apnt_270.asp 1 Cortex
KeyStone Training. Multicore Navigator Overview. Overview Agenda
 KeyStone Training Multicore Navigator Overview What is Navigator? Overview Agenda Definition Architecture Queue Manager Sub System (QMSS) Packet DMA (PKTDMA) Descriptors and Queuing What can Navigator
KeyStone Training Multicore Navigator Overview What is Navigator? Overview Agenda Definition Architecture Queue Manager Sub System (QMSS) Packet DMA (PKTDMA) Descriptors and Queuing What can Navigator
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems
 ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network on Chip. Presenter: YUAN Zheng
 Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS. A step change in speed
 HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed NAME OF REPORT SECTION 3 HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed Faster is more profitable in the front office
HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed NAME OF REPORT SECTION 3 HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed Faster is more profitable in the front office
Highly Available Mobile Services Infrastructure Using Oracle Berkeley DB
 Highly Available Mobile Services Infrastructure Using Oracle Berkeley DB Executive Summary Oracle Berkeley DB is used in a wide variety of carrier-grade mobile infrastructure systems. Berkeley DB provides
Highly Available Mobile Services Infrastructure Using Oracle Berkeley DB Executive Summary Oracle Berkeley DB is used in a wide variety of carrier-grade mobile infrastructure systems. Berkeley DB provides
Performance analysis and comparison of virtualization protocols, RDP and PCoIP
 Performance analysis and comparison of virtualization protocols, RDP and PCoIP Jiri Kouril, Petra Lambertova Department of Telecommunications Brno University of Technology Ustav telekomunikaci, Purkynova
Performance analysis and comparison of virtualization protocols, RDP and PCoIP Jiri Kouril, Petra Lambertova Department of Telecommunications Brno University of Technology Ustav telekomunikaci, Purkynova
An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture
 An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture Trevor Martin CEng, MIEE Technical Director This article gives an overview of the ARM 7 architecture and a description of its major features for a developer new
An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture Trevor Martin CEng, MIEE Technical Director This article gives an overview of the ARM 7 architecture and a description of its major features for a developer new
FLIX: Fast Relief for Performance-Hungry Embedded Applications
 FLIX: Fast Relief for Performance-Hungry Embedded Applications Tensilica Inc. February 25 25 Tensilica, Inc. 25 Tensilica, Inc. ii Contents FLIX: Fast Relief for Performance-Hungry Embedded Applications...
FLIX: Fast Relief for Performance-Hungry Embedded Applications Tensilica Inc. February 25 25 Tensilica, Inc. 25 Tensilica, Inc. ii Contents FLIX: Fast Relief for Performance-Hungry Embedded Applications...
GSM/GPRS PHYSICAL LAYER ON SANDBLASTER DSP
 GSM/GPRS PHYSICAL LAYER ON SANDBLASTER DSP Raghunath Kalavai, Murugappan Senthilvelan, Sitij Agrawal, Sanjay Jinturkar, John Glossner Sandbridge Technologies, 1 North Lexington Avenue, White Plains, NY
GSM/GPRS PHYSICAL LAYER ON SANDBLASTER DSP Raghunath Kalavai, Murugappan Senthilvelan, Sitij Agrawal, Sanjay Jinturkar, John Glossner Sandbridge Technologies, 1 North Lexington Avenue, White Plains, NY
Advanced Core Operating System (ACOS): Experience the Performance
 WHITE PAPER Advanced Core Operating System (ACOS): Experience the Performance Table of Contents Trends Affecting Application Networking...3 The Era of Multicore...3 Multicore System Design Challenges...3
WHITE PAPER Advanced Core Operating System (ACOS): Experience the Performance Table of Contents Trends Affecting Application Networking...3 The Era of Multicore...3 Multicore System Design Challenges...3
The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers
 The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers Ravi Arimilli IBM RISC System/6000 Division 1 Agenda. Server Background. Cache Heirarchy Performance Study. RS/6000 Value Server System Structure.
The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers Ravi Arimilli IBM RISC System/6000 Division 1 Agenda. Server Background. Cache Heirarchy Performance Study. RS/6000 Value Server System Structure.
ANNEX. to the. Commission Delegated Regulation
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 12.10.2015 C(2015) 6823 final ANNEX 1 PART 6/11 ANNEX to the Commission Delegated Regulation amending Council Regulation (EC) No 428/2009 setting up a Community regime for
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 12.10.2015 C(2015) 6823 final ANNEX 1 PART 6/11 ANNEX to the Commission Delegated Regulation amending Council Regulation (EC) No 428/2009 setting up a Community regime for
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications
 Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
RTP Performance Enhancing Proxy
 PACE RTP Performance Enhancing Proxy V2 Whilst the above information has been prepared by Inmarsat in good faith, and all reasonable efforts have been made to ensure its accuracy, Inmarsat makes no warranty
PACE RTP Performance Enhancing Proxy V2 Whilst the above information has been prepared by Inmarsat in good faith, and all reasonable efforts have been made to ensure its accuracy, Inmarsat makes no warranty
Enhance Service Delivery and Accelerate Financial Applications with Consolidated Market Data
 White Paper Enhance Service Delivery and Accelerate Financial Applications with Consolidated Market Data What You Will Learn Financial market technology is advancing at a rapid pace. The integration of
White Paper Enhance Service Delivery and Accelerate Financial Applications with Consolidated Market Data What You Will Learn Financial market technology is advancing at a rapid pace. The integration of
Web of Things Architecture
 Web of Things Architecture 1. Introduction This document is an explanation about the architecture of Web Of Things (WoT). The purpose of this document is to provide (a) a guideline of the mapping between
Web of Things Architecture 1. Introduction This document is an explanation about the architecture of Web Of Things (WoT). The purpose of this document is to provide (a) a guideline of the mapping between
Building Blocks for PRU Development
 Building Blocks for PRU Development Module 1 PRU Hardware Overview This session covers a hardware overview of the PRU-ICSS Subsystem. Author: Texas Instruments, Sitara ARM Processors Oct 2014 2 ARM SoC
Building Blocks for PRU Development Module 1 PRU Hardware Overview This session covers a hardware overview of the PRU-ICSS Subsystem. Author: Texas Instruments, Sitara ARM Processors Oct 2014 2 ARM SoC
Introduction to Cloud Computing
 Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
Operating Systems 4 th Class
 Operating Systems 4 th Class Lecture 1 Operating Systems Operating systems are essential part of any computer system. Therefore, a course in operating systems is an essential part of any computer science
Operating Systems 4 th Class Lecture 1 Operating Systems Operating systems are essential part of any computer system. Therefore, a course in operating systems is an essential part of any computer science
