A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Pre-Lab Exercises
|
|
|
- Neil Mathews
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Pre-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be looking at the brain & cranial nerves. This should be done before lab, so we don't waste time in lab! This guide should only be attempted after reading the correct sections in either the lab or lecture book, or watching any videos that have been assigned.. The Steps found in this first "Pre-lab Guide" do NOT have to be done in the order they are found. However, please do all the questions within a step before moving on to another step!
2 2 Step 1. Key Concepts on the Cranial Nerves (from the book and videos) #1 Answer these questions after reading the appropriate text in your book, or watching any video your instructor has assigned. Q1. List the cranial nerves in order, starting with the anterior-most. Give yourself some room, because you'll be adding text under each name: Q2. Under each cranial nerve name, write a short descriptive phrase explaining what each nerve does. There is a list on the next page that will allow you to check your list; however, you should try to make your list on your own. Q3. Now, check your table with the list on the following page. (Darned! You mean there was a list on the next page??!! Why don't I read ahead?) More on next page
3 3 Cranial Nerve Organization Table Cranial Nerve: Major Functions: I Olfactory II Optic III Oculomotor IV Trochlear V Trigeminal VI Abducens VII Facial VIII Vestibulocochlear (auditory) IX Glossopharyngeal X Vagus XI Accessory (spinal accessory) XII Hypoglossal Sensory only: smell Sensory only: vision Mainly Motor: eyelid and eyeball movement Mainly Motor: eyeball movement Motor & Sensory: chewing most face & mouth senses of touch & pain Mainly Motor: eyeball movement laterally Motor & Sensory: controls most facial expressions taste Mainly Sensory: hearing equilibrium sensation Motor & Sensory (only sense listed here): taste senses blood pressure Motor & Sensory: senses blood pressure slows heart rate stimulates most thoracic and abdominal visceral organs Mainly Motor: controls swallowing movements Mainly Motor: controls tongue movements
4 4 #2 Make a mnemonic device to remember the cranial nerves. Read Me Read Me A mnemonic (or "mnemonic device"), is any learning technique that aids memory. To improve long term memory, mnemonic systems are used to make memorization easier. They do so by increasing the efficiency of the process of consolidation. This process involves the conversion of short term memory to long term memory. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often verbal, such as a very short poem or a special word used to help a person remember something, particularly lists, but a mnemonic may instead be visual, kinesthetic or auditory. Mnemonics rely on associations between easy-to-remember constructs which can be related back to the data that are to be remembered. This is based on the observation that the human mind much more easily remembers spatial, personal, surprising, physical, sexual, humorous, or otherwise meaningful information, as compared to retrieving arbitrary sequences. Therefore, it is better to come up with your own, rather than memorizing someone else's. And make it as funny as you can. Read Me A common way to do this is to take the first letter of each word you need to remember, and come up with some humorous phrase that uses the first letter. On our list that follows, we wrote out an example of a mnemonic for the cranial nerves Example of a "not funny" mnemonic device: Mnemonic: Oh, oh, oh, to touch and feel very good velvet...ah, heaven Q4. Write down, in the space below, the mnemonic device you'll be using to remember the nerves in order.
5 5 #3 Look for trends among the cranial nerves, to help make your life easier by answering some questions. Answer these questions after reading the appropriate text in your book, or watching any video your instructor has assigned. Q5. How many of the cranial nerves are involved with eye movement? List them: Q6. How many of the cranial nerves are involved with chewing, moving the tongue, or swallowing? Name them: Q7. How many are purely or mainly sensory? List their names here:
6 Q8. How many of the cranial nerves do you think have a completely obvious name, given their function? Below is a list of the nerves, plus a brief description of what their names mean (in mostly Latin). Place a check next to any name you think is obvious: I Olfactory - "of smell" II Optic - "of vision" III Oculomotor - "eye mover" IV Trochlear - "pulley" (what is being "pulled"?) V Trigeminal - "3 bodies" (it has 3 big branches) VI Abducens - "to cause abduction" (think about what is being abducted!) VII Facial - "of the face" VIII Vestibulocochlear - "from the vestibule and cochlea" IX Glossopharyngeal - "tongue and throat" X Vagus - "wandering" (ask yourself: why does it have this name??) XI Accessory - "helper" XII Hypoglossal - "below the tongue" 6 Q9. In Anatomy & Physiology class, you are going to hear a lot about the "vagal tone" of many visceral organs. What do you suppose this means? If you don't know, ask your instructor in lab, and write it down here:
7 7 Step 2. Key Concepts on the Brain Anatomy (from the book and videos) #1 Answer these questions, after reading your book or watching the online videos your instructor assigns you: Q10. There are 4 commonly referred to subdivisions of the adult brain. Name them here: Different instructors will have you know different names for regions, or may divide the brain differently, so you should check with him or her after making this list. For now, write down what you see in your book or online videos: A. B. C. D. More on next page
8 8 Q2. Of course, all the subdivisions can be further subdivided into more specific regions. Different instructors will have you know different subregions, so you should check with him or her after making this list. For now, write down what you see in your book or online videos: A. Cerebrum (telencephalon) B. Diencephalon C. Brain Stem D. Cerebellum More on next page
9 9 Q3. Here is what your final list should look like. Bring this to lab on a separate sheet of paper, as we'll be adding to it there. Use a separate sheet of paper to make this final list, and bring it to lab: A. Cerebrum (telencephalon) 1. cerebral cortex (outer gray matter) 2. inner white matter (inner tracts, nuclei, etc.) B. Diencephalon 1. epithalamus 2. thalamus 3. hypothalamus C. Brain Stem 1. midbrain 2. pons 3. medulla oblongata D. Cerebellum 1. arbor vitae (inner white matter) 2. folia (outer gray matter)
10 10 Step 3 Make a key #1 On the image below, indicate the 4 main regions of the brain (A, B, C & D on the outline we just made) by outlining them.
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Ventral Surface. The Cranial Nerves 4/5/2010. Review: Spinal Nerves
 The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
Angela Wilkin May 2013
 Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
Cranial Nerves. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve
 Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services
 Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Lecture 2, Human cognition
 Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
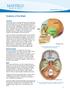 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Directions for construction used with permission from Pacific Science Center - Brain Power
 Directions for construction used with permission from Pacific Science Center - Brain Power The Vestibular System The vestibular system within the inner ear detects both the position and motion of the head
Directions for construction used with permission from Pacific Science Center - Brain Power The Vestibular System The vestibular system within the inner ear detects both the position and motion of the head
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain
 Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd.
 About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Schneps, Leila; Colmez, Coralie. Math on Trial : How Numbers Get Used and Abused in the Courtroom. New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p i.
 New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p i. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=2 New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p ii. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=3 New
New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p i. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=2 New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p ii. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=3 New
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function
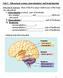 Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Problem-Based Group Activities for a Sensation & Perception Course. David S. Kreiner. University of Central Missouri
 -Based Group Activities for a Course David S. Kreiner University of Central Missouri Author contact information: David Kreiner Professor of Psychology University of Central Missouri Lovinger 1111 Warrensburg
-Based Group Activities for a Course David S. Kreiner University of Central Missouri Author contact information: David Kreiner Professor of Psychology University of Central Missouri Lovinger 1111 Warrensburg
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire
 Student Services Study Skills Student Development and Counselling VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to
Student Services Study Skills Student Development and Counselling VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
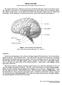 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Vertebrobasilar Disease
 The Vascular Surgery team at the University of Michigan is dedicated to providing exceptional treatments for in the U-M Cardiovascular Center (CVC), our new state-of-the-art clinical facility. Treatment
The Vascular Surgery team at the University of Michigan is dedicated to providing exceptional treatments for in the U-M Cardiovascular Center (CVC), our new state-of-the-art clinical facility. Treatment
Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014
 Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014 Richard Webster, Paediatric Neurologist Children s Hospital at Westmead Typical history Unilateral LMN facial weakness Acute onset over a day or
Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014 Richard Webster, Paediatric Neurologist Children s Hospital at Westmead Typical history Unilateral LMN facial weakness Acute onset over a day or
Discuss risk factors and characteristics of various levels of brain injury from mild to severe
 Understanding Brain Injury and Effective Strategies for Communication Kristin A. King, PhD, CCC-SLP University of Tennessee kking29@uthsc.edu Objectives Participants will be able to: Discuss risk factors
Understanding Brain Injury and Effective Strategies for Communication Kristin A. King, PhD, CCC-SLP University of Tennessee kking29@uthsc.edu Objectives Participants will be able to: Discuss risk factors
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child
 O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child April 3, 2008 Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its related
O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child April 3, 2008 Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its related
Stress Psychophysiology. Introduction. The Brain. Chapter 2
 Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
It s All in the Brain!
 It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
WHAT IS NLP: A MODEL OF COMMUNICATION AND PERSONALITY
 WHAT IS NLP: A MODEL OF COMMUNICATION AND PERSONALITY By Tad James, M.S., Ph.D. Neuro Linguistic Programming (NLP) began as a model of how we communicate to ourselves and others which was developed by
WHAT IS NLP: A MODEL OF COMMUNICATION AND PERSONALITY By Tad James, M.S., Ph.D. Neuro Linguistic Programming (NLP) began as a model of how we communicate to ourselves and others which was developed by
Homework Help Stroke
 The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
PAGE OVERVIEW: PATIENT ASSESSMENT, BODY SYSTEMS AND SYSTEM
 PATIENT ASSESSMENT SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOL TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE INTRODUCTION......................... 5 FORMAT........................... 5 APPROACH.......................... 6 SECTION I.....................
PATIENT ASSESSMENT SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOL TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE INTRODUCTION......................... 5 FORMAT........................... 5 APPROACH.......................... 6 SECTION I.....................
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
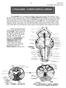 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) According to the IDEA, (2004), traumatic brain injury is defined by as:
 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) DEFINITION: According to the IDEA, (2004), traumatic brain injury is defined by as: An acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force, resulting in total
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) DEFINITION: According to the IDEA, (2004), traumatic brain injury is defined by as: An acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force, resulting in total
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT
 PURDUE UNIVERSITY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Crawford County A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Developed by Carol Judd Description: Brain architecture is a process that begins early in life and continues
PURDUE UNIVERSITY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Crawford County A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Developed by Carol Judd Description: Brain architecture is a process that begins early in life and continues
M. Gallucci S. Capoccia A. Catalucci, Radiographic Atlas of Skull and Brain Anatomy
 M. Gallucci S. Capoccia A. Catalucci, Radiographic Atlas of Skull and Brain Anatomy Massimo Gallucci Silvia Capoccia Alessia Catalucci Radiographic Atlas of Skull and Brain Anatomy With 794 Figures Springer
M. Gallucci S. Capoccia A. Catalucci, Radiographic Atlas of Skull and Brain Anatomy Massimo Gallucci Silvia Capoccia Alessia Catalucci Radiographic Atlas of Skull and Brain Anatomy With 794 Figures Springer
Narrative Writing Conference Planner
 Narrative Writing Conference Planner Name Class Before our conference on your narrative piece, read the list of questions and directions after the trait(s) that I ve highlighted on this sheet. We ll review
Narrative Writing Conference Planner Name Class Before our conference on your narrative piece, read the list of questions and directions after the trait(s) that I ve highlighted on this sheet. We ll review
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Lecture One: Brain Basics
 Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Link: University of Canberra http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/learning/oralpres.html#preparing
 6. Voice, speech and body language: The way you speak, the way you act and the way you move around can be very important to succeed in your presentation. Here you will find some useful advices and links
6. Voice, speech and body language: The way you speak, the way you act and the way you move around can be very important to succeed in your presentation. Here you will find some useful advices and links
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
Behavior & Sensory Strategies for Individuals with ASD
 Behavior & Sensory Strategies for Individuals with ASD Kathleen Mo Taylor, OTR/L The Autism Programs Center for Development and Disability University of New Mexico This presentation is made possible, in
Behavior & Sensory Strategies for Individuals with ASD Kathleen Mo Taylor, OTR/L The Autism Programs Center for Development and Disability University of New Mexico This presentation is made possible, in
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave.
 VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to complete the questionnaire before reading the accompanying explanation.)
VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to complete the questionnaire before reading the accompanying explanation.)
Amazing AmMy Brain! DID YOU KNOW..
 My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system
 Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Math: Study Skills, Note Taking Skills, And Test Taking Strategies
 Math: Study Skills, Note Taking Skills, And Test Taking Strategies Math Study Skill Active Study vs. Passive Study Be actively involved in managing the learning process, the mathematics and your study
Math: Study Skills, Note Taking Skills, And Test Taking Strategies Math Study Skill Active Study vs. Passive Study Be actively involved in managing the learning process, the mathematics and your study
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Meditation for Stress Management
 What is? Meditation is the focusing of attention on one thing to the exclusion of all other thoughts. Often, people are able to relieve their stress through meditation, because by focusing on only one
What is? Meditation is the focusing of attention on one thing to the exclusion of all other thoughts. Often, people are able to relieve their stress through meditation, because by focusing on only one
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
