SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS CHEMISTRY ATAR YEAR 11
|
|
|
- Damian Andrews
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS CHEMISTRY ATAR YEAR 11
2 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that the Authority s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with prior written permission of the School Curriculum and Standards Authority. Copying or communication of any third party copyright material can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with permission of the copyright owners. Any content in this document that has been derived from the Australian Curriculum may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 Australia licence Disclaimer Any resources such as texts, websites and so on that may be referred to in this document are provided as examples of resources that teachers can use to support their learning programs. Their inclusion does not imply that they are mandatory or that they are the only resources relevant to the course. 2014/16111v5
3 1 Sample assessment task Chemistry ATAR Year 11 Task 7 Unit 1 Assessment type: Extended response Conditions Period allowed for completion of the task: 3 weeks Task weighting 5% of the school mark for this pair of units Comparing fossil fuels and biofuels (47 marks) Identify the main components (give the name and, where practical, the chemical formula) for the following fossil fuels and biofuels coal petroleum petrodiesel natural gas biogas biodiesel bioethanol. Compare the energy output of these fuels on a gram and mole basis. For fuels that are a mixture, the mole comparison can be based on the most common component or a typical component of the fuel. Assume complete combustion for the comparison. Compare the carbon dioxide produced for complete combustion of each of the fuels on a gram and mole basis. Again for mixtures use the most common component or a typical component of the fuel. For one application of one fossil fuel and one application of one biofuel comment on the validity of assuming complete combustion in determining energy output. Explain your reason for either accepting or rejecting the assumption. Give references for the sources you have used to get information (you must use at least three resources).
4 2 Marking key for sample assessment task 7 Unit 1 1 mark for main components of each fuel coal petroleum petrodiesel natural gas biogas biodiesel bioethanol 1 mark for energy output on a gram basis for each fuel mark for energy output on a mole basis for each fuel mark for CO 2 output on a gram basis for each fuel mark for CO 2 output on a mole basis for each fuel 1 7 Discussion of application of fossil fuel (and recognition that complete combustion is unlikely) description of application discussion of fuel to oxygen ratio in the application statement about validity of assuming complete combustion for energy and CO 2 outputs (linked to discussion about fuel to oxygen ratio) Discussion of application of biofuel (and recognition that complete combustion is unlikely) description of application discussion of fuel to oxygen ratio in the application statement about validity of assuming complete combustion for energy and CO 2 outputs (linked to discussion about fuel to oxygen ratio) References at least three sources 1 mark for each source up to 3 marks 1 mark for referencing style that enables verification Total /47
5 3 Sample assessment task Chemistry ATAR Year 11 Task 8 Unit 1 Assessment type: Test Conditions Time for the task: 50 minutes Task weighting 2% of the school mark for this pair of units Structure of the test: Section ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEST Suggested working time Number of questions ONE Multiple choice 10 minutes TWO Written answers 40 minutes 7 30 DO NOT OPEN THE TEST UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO
6 4 Section 1: Multiple choice questions Which one of the following is not a reason for carbon to be able to form large numbers of compounds? (a) (b) (c) (d) The ability of carbon atoms to form four covalent bonds. The ability of carbon atoms to bond to each other in covalent network structures. The ability of carbon atoms to form multiple (double and triple) covalent bonds. The ability of carbon atoms to bond with each other to form long stable chains. 2. A hydrocarbon with the formula C 6 H 12 could be what type of compound? (a) (b) (c) (d) a straight chain alkane a branched chain alkane an alkene an aromatic hydrocarbon 3. Which one of the following molecules contains a double bond? (a) (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH 3 (b) (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH 3 (c) CH 3 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 2 CH 3 (d) (CH 3 ) 2 CCHCH 3 4. Which one of the following hydrocarbons is unsaturated? (a) CH 4 (b) C 7 H 16 (c) C 4 H 10 (d) C 3 H 6 5. Which one of the following sets of formulae contains only one saturated hydrocarbon? (a) C 2 H 6, C 3 H 6, C 4 H 8 (b) C 3 H 6, C 4 H 8, C 6 H 12 (c) C 2 H 6, C 3 H 6, C 8 H 18 (d) CH 4, C 2 H 6, C 6 H Which one of the following statements about the benzene molecule is false? (a) Benzene has the molecular formula C 6 H 6. (b) Benzene has a planar (flat) structure with all bond angles 120. (c) Benzene will react with Br 2 in an addition reaction similar to addition of Br 2 to alkenes. (d) The pi (double bond) electrons in benzene are delocalised.
7 5 7. Which one of the following is the correct equation for the complete combustion of butane? (a) 2 C 4 H O 2 8 CO H 2 O (b) 2 C 4 H O 2 8 CO + 10 H 2 O (c) C 4 H O 2 4 CO H 2 O (d) C 4 H O 2 4 CO + 4 H 2 O 8. Which one of the following compounds readily undergoes addition reactions? (a) ethane (C 2 H 6 ) (b) ethene (C 2 H 4 ) (c) methylbenzene (C 7 H 8 ) (d) chloromethane (CH 3 C ) 9. When pent 2 ene is reacted with chlorine water, the most likely product is (a) (b) (c) (d) 2,2 dichloropentane. 2,3 dichloropentene. 2,3 dichloropentane. 1,2 dichloropentane. Consider the reaction of benzene shown below to answer question 10. Cl + C 2 FeC 3 + HC 10. This type of reaction is known as (a) (b) (c) (d) combustion. redox. addition. substitution.
8 6 Section 2: Written answers Complete the following table by writing the IUPAC name of the compound or drawing the structure as appropriate. Show all hydrogen atoms for structures you draw. (4 marks) IUPAC Name Structure CH 3 H 3 C CH 2 CH CH 2 CH 3 (1 mark) 3 chloro 2 methylhexane (1 mark) H 3 C CH 2 CH C CH 3 H 3 C (1 mark) 2,3 dimethyloct 4 ene (1 mark)
9 7 2. Complete the following reaction equations by writing the formula for the missing molecule in the space provided. (3 marks) hv (a) CH 3 CH 3 + C 2 CH 3 CH 2 C + (b) CH 3 Br + Br hv 2 + HBr (c) + HBr CH 3 CH 2 CHBrCH 3 3. Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. Structural formulae can be used to write the equations. (6 marks) (a) Butane reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light. (b) Octane burns in a plentiful supply of oxygen. (c) Pent 2 ene reacts with bromine gas.
10 8 4. It is possible for straight chain and branched alkanes with the molecular formula C 5 H 12 to exist. Draw and name the structural formulae of the 3 possible alkanes with this molecular formula. Show all hydrogen atoms in your structures. (6 marks) (a) name: (b) name: (c) name: 5. For the following pair of compounds describe a chemical test that could be used to distinguish between them. Include the distinguishing observation in your answer. (4 marks) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 and CH 3 CH=CH CH 2 CH 3 Test: Distinguishing observation:
11 9 6. The structure of benzene is represented by two 6 membered rings with double bonds shown in alternate positions and a double headed arrow between the two 6 membered rings (1) or by a single 6 membered ring with a circle in the centre (2). OR 1 2 Explain why benzene is represented by structure 1 or 2 rather than a single 6 membered ring with three single bonds and three double bonds. (3 marks) 7. Propane gas is used in gas cylinders for barbeques. The equation for combustion of propane is shown below with its enthalpy change. C 3 H 8 (g) + 5 O 2 (g) 3 CO 2 (g) + 4 H 2 O(g) kj If a gas cylinder contains 45.0 kg of propane, how much energy (in kilojoules) can be produced by the combustion of the gas? (4 marks)
12 10 Marking key for sample assessment task 8 Unit 1 Section 1: Multiple choice 10 marks Correct Question response 1 b 2 c 3 d 4 d 5 a 6 c 7 a 8 b 9 c 10 d Section 2: Written answers 30 marks 1. Complete the following table by writing the IUPAC name of the compound or drawing the structure as appropriate. Show all hydrogen atoms for structures you draw. (4 marks) IUPAC Name 3 methylpentane (1 mark) Structure CH 3 H 3 C CH 2 CH CH 2 CH 3 3 chloro 2 methylhexane CH 3 H 3 C CH CH CH2 CH2 Cl CH 3 (1 mark) 2 methylpent 2 ene (accept 2 methyl 2 pentene) (1 mark) H 3 C CH 2 CH C CH 3 H 3 C 2,3 dimethyloct 4 ene CH 3 H 3 C CH CH CH CH CH2 CH 2 CH 3 H 3 C (1 mark)
13 11 2. Complete the following reaction equations by writing the formula for the missing molecule in the space provided. (3 marks) hv (a) CH 3 CH 3 + C 2 CH 3 CH 2 C + HC (b) CH 3 Br + Br hv CH 2 Br HBr (c) CH 3 CHCHCH 3 + HBr CH 3 CH 2 CHBrCH 3 OR CH 3 CH 2 CHCH 2 1 mark for each correct molecule 3 3. Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. Structural formulae can be used to write the equations. (6 marks) (a) Butane reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light. hv CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 + C 2 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 C + HC Accept any chlorobutane 1 mark for correct formulae for reactants 1 1 mark for correct formulae for product(s) 1 (b) Octane burns in a plentiful supply of oxygen. 2 C 8 H O 2 16 CO H 2 O 1 mark for correct formulae for reactants and products 1 1 mark for balancing 1 (c) Pent 2 ene reacts with bromine gas. CH 3 CHCHCH 2 CH 3 + Br 2 CH 3 CHBrCHBrCH 2 CH 3 1 mark for correct formulae for reactants 1 1 mark for correct formula for product 1
14 12 4. It is possible for straight chain and branched alkanes with the molecular formula C 5 H 12 to exist. Draw and name the structural formulae of 3 possible alkanes with this molecular formula. Show all hydrogen atoms in your structures. (6 marks) (a) H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 name: pentane (b) CH 3 H 3 C CH CH 2 CH 3 name: methylbutane (accept 2 methylbutane) (c) CH 3 H 3 C C CH 3 CH 3 name: 2,2 dimethylpropane 1 mark for each correct structure 3 1 mark for each IUPAC name 3 5. For the following pair of compounds describe a chemical test that could be used to distinguish between them. Include the distinguishing observation in your answer. (4 marks) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 and CH 3 CH=CH CH 2 CH 3 Test: Shake each hydrocarbon with about 10 drops of bromine water in the absence of UV light (or in dark). Quantity of bromine water used should not be in excess. (excess Br 2 water will mean orange colour will remain even if reaction occurs) Distinguishing observation: The bromine water will decolourise rapidly when shaken with the alkene. The bromine water will not decolourise (or very slowly decolourise) with the alkane. Recognition that hydrocarbons are shaken with bromine water (recognition of quantity not needed to get mark) Recognition that reaction is done in absence of UV light 1 Recognition that alkene decolourises bromine water 1 Recognition that alkane does not decolourise bromine water 1 1
15 13 6. The structure of benzene is represented by two 6 membered rings with double bonds shown in alternate positions and a double headed arrow between the two 6 membered rings (1) or by a single 6 membered ring with a circle in the centre (2). OR 1 2 Explain why benzene is represented by structure 1 or 2 rather than a 6 membered ring with three single bonds and three double bonds. (3 marks) Recognition that benzene does not have 3 single bonds and 3 double bonds 1 Recognition that the C to C bonds are all the same with same bond length intermediate of the typical C to C single bond and C to C double bond Recognition that benzene has 6 delocalized electrons Propane gas is used in gas cylinders for barbeques. The equation for combustion of propane is shown below with its enthalpy change. C 3 H 8 (g) + 5 O 2 (g) 3 CO 2 (g) + 4 H 2 O(g) kj If a gas cylinder contains 45.0 kg of propane, how much energy (in kilojoules) can be produced by the combustion of the gas? (4 marks) M(C 3 H 8 ) = g mol 1 1 m(c 3 H 8 ) = 45.0 kg = g 1 n(c 3 H 8 ) = mol Energy = = kj 1
16 14 Sample assessment task Chemistry ATAR Year 11 Task 17 Unit 2 Assessment type: Practical investigation Conditions Period allowed for completion of the task: 1.5 weeks Task weighting 5% of the school mark for this pair of units Determine which acid is the most reactive when reacted with metal carbonates. (24 marks) The effect of acid rain on statues made from calcium carbonate is well documented. The aim of this investigation is to determine if there is any difference in the reaction rate of different acids with metal carbonates. Task description 1. Research what reaction rate means and how you could measure it in a school laboratory (Suggestions: rate of mass loss during evolution of carbon dioxide, rate of evolution of carbon dioxide). 2. Brainstorm or discuss what most reactive might mean. For example, it may mean the fastest reaction with another agent. Write down what you have decided most reactive means and explain why you chose that way to define it. 3. Design a way to measure the reaction rates of the samples provided. Write a detailed description of your design, including the equipment and acids you intend to use, the dependent and independent variables, the measurements or observations you intend to make and how you propose to process your data. 4. Carry out your experimental work in your group. 5. Process the data on an individual basis. Show all working. 6. Write your report. This should include an introduction describing what reaction rate and most reactive mean; details of experimental designs; all raw measurements, calculations and observations in the Results section; your conclusions; and evidence of the ways you minimised errors and uncertainties.
17 15 Time plan Step Day Step In class/homework 1 1 Submit definition of most reactive 20 min brainstorm/discussion Group discussion of research ideas followed by individual submission of research design Carry out procedure and collect data (group) Carry out procedure and collect data (group) Entire period Entire period Entire period 4 5 Process data (individual) Entire period and homework 5 6 Submit report (individual) Entire period
18 16 Marking key for sample assessment task 17 Unit 2 Research and submit research design evidence of individual research identification of variables viable experimental design Carry out procedure and collect data selection of appropriate equipment safety precautions used during procedure all raw measurements recorded in an appropriate format evidence of fair testing Processing data calculations and observations evaluation of data conclusions Submit report information from research in introduction details of experimental design evidence of the ways you minimised errors and uncertainties report presented using appropriate format use of scientific terminology as appropriate Subtotal / Subtotal / Subtotal / Subtotal /10 Total /24
Alkanes. Chapter 1.1
 Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 (adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
(adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I
 Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
CHEM 203 Exam 1. KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
Stoichiometry. Lecture Examples Answer Key
 Stoichiometry Lecture Examples Answer Key Ex. 1 Balance the following chemical equations: 3 NaBr + 1 H 3 PO 4 3 HBr + 1 Na 3 PO 4 2 C 3 H 5 N 3 O 9 6 CO 2 + 3 N 2 + 5 H 2 O + 9 O 2 2 Ca(OH) 2 + 2 SO 2
Stoichiometry Lecture Examples Answer Key Ex. 1 Balance the following chemical equations: 3 NaBr + 1 H 3 PO 4 3 HBr + 1 Na 3 PO 4 2 C 3 H 5 N 3 O 9 6 CO 2 + 3 N 2 + 5 H 2 O + 9 O 2 2 Ca(OH) 2 + 2 SO 2
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Page 1. 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? (1) 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4)
 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3. Copyright 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 1: Organic Compounds 1.1-1
 Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2
 MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
IB Chemistry. DP Chemistry Review
 DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test
 Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test 2. Write the IUPAC names for the following organic molecules: a) acetone: propanone d) acetylene: ethyne b) acetic acid: ethanoic acid e)
Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test 2. Write the IUPAC names for the following organic molecules: a) acetone: propanone d) acetylene: ethyne b) acetic acid: ethanoic acid e)
Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
CHM220 Addition lab. Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes*
 CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
Unit 2: Quantities in Chemistry
 Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
1. What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula PO and a gram-molecular mass of 284 grams?
 Name: Tuesday, May 20, 2008 1. What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula PO and a gram-molecular mass of 284 grams? 2 5 1. P2O 5 3. P10O4 2. P5O 2 4. P4O10 2. Which substance
Name: Tuesday, May 20, 2008 1. What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula PO and a gram-molecular mass of 284 grams? 2 5 1. P2O 5 3. P10O4 2. P5O 2 4. P4O10 2. Which substance
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS
 Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4
 ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4 1) Write an equation to describe the initiation step in the chlorination of methane. 2) Reaction intermediates that have unpaired electrons are called. 3) When
ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4 1) Write an equation to describe the initiation step in the chlorination of methane. 2) Reaction intermediates that have unpaired electrons are called. 3) When
Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula
 Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula Alkanes have the molecular formula C n. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons because each member of the family has the maximum
Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula Alkanes have the molecular formula C n. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons because each member of the family has the maximum
Chemical Calculations: Formula Masses, Moles, and Chemical Equations
 Chemical Calculations: Formula Masses, Moles, and Chemical Equations Atomic Mass & Formula Mass Recall from Chapter Three that the average mass of an atom of a given element can be found on the periodic
Chemical Calculations: Formula Masses, Moles, and Chemical Equations Atomic Mass & Formula Mass Recall from Chapter Three that the average mass of an atom of a given element can be found on the periodic
Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked.
 GCSE CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Chemistry 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed). Instructions Answer all
GCSE CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Chemistry 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed). Instructions Answer all
Name Date Class STOICHIOMETRY. SECTION 12.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358)
 Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
e. What are the compositions and uses of fractions of crude oil? f. How are further fractions lubricationg oils and waxes obtained?
 CRUDE OIL AND ITS COMPOSITION 1. Use a textbook to answer the following questions: a. How was crude oil formed? b. What is crude oil chemically? c. How can the components of crude oil be separated? d.
CRUDE OIL AND ITS COMPOSITION 1. Use a textbook to answer the following questions: a. How was crude oil formed? b. What is crude oil chemically? c. How can the components of crude oil be separated? d.
Chapter 3! Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations. Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3! : Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Anatomy of a Chemical Equation CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (g) Anatomy of a Chemical Equation CH 4 (g) + 2 O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2
Chapter 3! : Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Anatomy of a Chemical Equation CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (g) Anatomy of a Chemical Equation CH 4 (g) + 2 O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1. A chemical equation. (C-4.4)
 Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter 1: Moles and equations. Learning outcomes. you should be able to:
 Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2015. M33 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 16 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions
2015. M33 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 16 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY. 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions:
 SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY ANSWER SCHEME UPS 2004/2005 SK027 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions: Enthalpy change ΔH (kj/mol) Atomization energy
SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY ANSWER SCHEME UPS 2004/2005 SK027 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions: Enthalpy change ΔH (kj/mol) Atomization energy
Calculating Atoms, Ions, or Molecules Using Moles
 TEKS REVIEW 8B Calculating Atoms, Ions, or Molecules Using Moles TEKS 8B READINESS Use the mole concept to calculate the number of atoms, ions, or molecules in a sample TEKS_TXT of material. Vocabulary
TEKS REVIEW 8B Calculating Atoms, Ions, or Molecules Using Moles TEKS 8B READINESS Use the mole concept to calculate the number of atoms, ions, or molecules in a sample TEKS_TXT of material. Vocabulary
Molecular Formula Determination
 Molecular Formula Determination Classical Approach Qualitative elemental analysis Quantitative elemental analysis Determination of empirical formula Molecular weight determination Molecular formula determination
Molecular Formula Determination Classical Approach Qualitative elemental analysis Quantitative elemental analysis Determination of empirical formula Molecular weight determination Molecular formula determination
20.2 Chemical Equations
 All of the chemical changes you observed in the last Investigation were the result of chemical reactions. A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms in one or more reactants to form one or more
All of the chemical changes you observed in the last Investigation were the result of chemical reactions. A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms in one or more reactants to form one or more
1. How many hydrogen atoms are in 1.00 g of hydrogen?
 MOLES AND CALCULATIONS USING THE MOLE CONCEPT INTRODUCTORY TERMS A. What is an amu? 1.66 x 10-24 g B. We need a conversion to the macroscopic world. 1. How many hydrogen atoms are in 1.00 g of hydrogen?
MOLES AND CALCULATIONS USING THE MOLE CONCEPT INTRODUCTORY TERMS A. What is an amu? 1.66 x 10-24 g B. We need a conversion to the macroscopic world. 1. How many hydrogen atoms are in 1.00 g of hydrogen?
7-5.5. Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including:
 7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
17.2 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS
 17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Chapter 3. Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies
 Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
Summer Holidays Questions
 Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
The Mole and Molar Mass
 The Mole and Molar Mass 1 Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. Molar mass is numerically equal to atomic mass, molecular mass, or formula mass. However the units of molar mass are g/mol.
The Mole and Molar Mass 1 Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. Molar mass is numerically equal to atomic mass, molecular mass, or formula mass. However the units of molar mass are g/mol.
STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION
 STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION FUNDAMENTALS: moles and kilomoles Atomic unit mass: 1/12 126 C ~ 1.66 10-27 kg Atoms and molecules mass is defined in atomic unit mass: which is defined in relation to the 1/12
STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION FUNDAMENTALS: moles and kilomoles Atomic unit mass: 1/12 126 C ~ 1.66 10-27 kg Atoms and molecules mass is defined in atomic unit mass: which is defined in relation to the 1/12
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro. Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley Hills, Maqqwertd ygoijpk[l
 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
CHEMISTRY II FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 Name Period CHEMISTRY II FINAL EXAM REVIEW Final Exam: approximately 75 multiple choice questions Ch 12: Stoichiometry Ch 5 & 6: Electron Configurations & Periodic Properties Ch 7 & 8: Bonding Ch 14: Gas
Name Period CHEMISTRY II FINAL EXAM REVIEW Final Exam: approximately 75 multiple choice questions Ch 12: Stoichiometry Ch 5 & 6: Electron Configurations & Periodic Properties Ch 7 & 8: Bonding Ch 14: Gas
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ARMATIC CMPUNDS 1. Name benzene derivatives given the structures, and draw the structures given the names. This includes: Monosubstituted benzenes named as derivatives of benzene:
A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ARMATIC CMPUNDS 1. Name benzene derivatives given the structures, and draw the structures given the names. This includes: Monosubstituted benzenes named as derivatives of benzene:
Suggested solutions for Chapter 7
 s for Chapter 7 7 PRBLEM 1 Are these molecules conjugated? Explain your answer in any reasonable way. C Et C Et C Et Revision of the basic kinds of conjugation and how to show conjugation with curly arrows.
s for Chapter 7 7 PRBLEM 1 Are these molecules conjugated? Explain your answer in any reasonable way. C Et C Et C Et Revision of the basic kinds of conjugation and how to show conjugation with curly arrows.
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
Chemical Calculations: The Mole Concept and Chemical Formulas. AW Atomic weight (mass of the atom of an element) was determined by relative weights.
 1 Introduction to Chemistry Atomic Weights (Definitions) Chemical Calculations: The Mole Concept and Chemical Formulas AW Atomic weight (mass of the atom of an element) was determined by relative weights.
1 Introduction to Chemistry Atomic Weights (Definitions) Chemical Calculations: The Mole Concept and Chemical Formulas AW Atomic weight (mass of the atom of an element) was determined by relative weights.
Studying an Organic Reaction. How do we know if a reaction can occur? And if a reaction can occur what do we know about the reaction?
 Studying an Organic Reaction How do we know if a reaction can occur? And if a reaction can occur what do we know about the reaction? Information we want to know: How much heat is generated? How fast is
Studying an Organic Reaction How do we know if a reaction can occur? And if a reaction can occur what do we know about the reaction? Information we want to know: How much heat is generated? How fast is
Sample Problem: STOICHIOMETRY and percent yield calculations. How much H 2 O will be formed if 454 g of. decomposes? NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + 2 H 2 O
 STOICHIOMETRY and percent yield calculations 1 Steps for solving Stoichiometric Problems 2 Step 1 Write the balanced equation for the reaction. Step 2 Identify your known and unknown quantities. Step 3
STOICHIOMETRY and percent yield calculations 1 Steps for solving Stoichiometric Problems 2 Step 1 Write the balanced equation for the reaction. Step 2 Identify your known and unknown quantities. Step 3
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
 Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
IB Chemistry 1 Mole. One atom of C-12 has a mass of 12 amu. One mole of C-12 has a mass of 12 g. Grams we can use more easily.
 The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION. 37 74 20 40 60 80 m/e
 CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual
 Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
Question (3): What are the different types of covalent bonds found in carbons compounds? Briefly explain with examples.
 CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) Chemistry: For Class 10 Page : 1 Question (1): What is organic chemistry? Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds of living matter i.e., plants and animals (CO 2, carbonates,
CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) Chemistry: For Class 10 Page : 1 Question (1): What is organic chemistry? Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds of living matter i.e., plants and animals (CO 2, carbonates,
NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS 2010, 2003, 1980, by David A. Katz. All rights reserved.
 NMENCLATURE F RGANIC CMPUNDS 2010, 2003, 1980, by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. rganic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to bond with itself to form long chains
NMENCLATURE F RGANIC CMPUNDS 2010, 2003, 1980, by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. rganic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to bond with itself to form long chains
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry CHEM 1021 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
Chemical Proportions in Compounds
 Chapter 6 Chemical Proportions in Compounds Solutions for Practice Problems Student Textbook page 201 1. Problem A sample of a compound is analyzed and found to contain 0.90 g of calcium and 1.60 g of
Chapter 6 Chemical Proportions in Compounds Solutions for Practice Problems Student Textbook page 201 1. Problem A sample of a compound is analyzed and found to contain 0.90 g of calcium and 1.60 g of
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols
 F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 13_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In organic chemistry, the term unsaturated means a molecule A) which contains one or more
Ch 13_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In organic chemistry, the term unsaturated means a molecule A) which contains one or more
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CHEM 150 - COLLEGE CHEMISTRY I
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CHEM 150 - COLLEGE CHEMISTRY I PREPARED BY: NICOLE HELDT SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH, AND PROFESSIONAL STUDIES SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CHEM 150 - COLLEGE CHEMISTRY I PREPARED BY: NICOLE HELDT SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH, AND PROFESSIONAL STUDIES SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
Candidate Style Answer
 Candidate Style Answer Chemistry A Unit F321 Atoms, Bonds and Groups High banded response This Support Material booklet is designed to accompany the OCR GCE Chemistry A Specimen Paper F321 for teaching
Candidate Style Answer Chemistry A Unit F321 Atoms, Bonds and Groups High banded response This Support Material booklet is designed to accompany the OCR GCE Chemistry A Specimen Paper F321 for teaching
83 to 87% carbon 11-15% hydrogen 0.1-7% sulphur 0.06-1.5% oxygen 0.1-0.5% nitrogen
 Petroleum chemistry rude is the name for a liquid mixture of different hydrocarbon connections found in the earth. Petroleum, strictly speaking is crude oil, but it is used to describe all kinds of hydrocarbons.
Petroleum chemistry rude is the name for a liquid mixture of different hydrocarbon connections found in the earth. Petroleum, strictly speaking is crude oil, but it is used to describe all kinds of hydrocarbons.
Formulas, Equations and Moles
 Chapter 3 Formulas, Equations and Moles Interpreting Chemical Equations You can interpret a balanced chemical equation in many ways. On a microscopic level, two molecules of H 2 react with one molecule
Chapter 3 Formulas, Equations and Moles Interpreting Chemical Equations You can interpret a balanced chemical equation in many ways. On a microscopic level, two molecules of H 2 react with one molecule
How To Calculate Mass In Chemical Reactions
 We have used the mole concept to calculate mass relationships in chemical formulas Molar mass of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH)? Molar mass = 2 x 12.011 + 6 x 1.008 + 1 x15.999 = 46.069 g/mol Mass percentage of
We have used the mole concept to calculate mass relationships in chemical formulas Molar mass of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH)? Molar mass = 2 x 12.011 + 6 x 1.008 + 1 x15.999 = 46.069 g/mol Mass percentage of
Chapter 4. Chemical Energy
 hapter 4 hemical Energy Perhaps the most convenient form in which to store energy is chemical energy. The foods we eat, combined with the oxygen we breathe, store energy that our bodies extract and convert
hapter 4 hemical Energy Perhaps the most convenient form in which to store energy is chemical energy. The foods we eat, combined with the oxygen we breathe, store energy that our bodies extract and convert
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
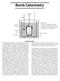 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Mole Notes.notebook. October 29, 2014
 1 2 How do chemists count atoms/formula units/molecules? How do we go from the atomic scale to the scale of everyday measurements (macroscopic scale)? The gateway is the mole! But before we get to the
1 2 How do chemists count atoms/formula units/molecules? How do we go from the atomic scale to the scale of everyday measurements (macroscopic scale)? The gateway is the mole! But before we get to the
Atomic Masses. Chapter 3. Stoichiometry. Chemical Stoichiometry. Mass and Moles of a Substance. Average Atomic Mass
 Atomic Masses Chapter 3 Stoichiometry 1 atomic mass unit (amu) = 1/12 of the mass of a 12 C atom so one 12 C atom has a mass of 12 amu (exact number). From mass spectrometry: 13 C/ 12 C = 1.0836129 amu
Atomic Masses Chapter 3 Stoichiometry 1 atomic mass unit (amu) = 1/12 of the mass of a 12 C atom so one 12 C atom has a mass of 12 amu (exact number). From mass spectrometry: 13 C/ 12 C = 1.0836129 amu
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Theory (Core) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Theory (Core) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour
CHEMICAL FORMULA COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSCRIPTS. Chapter 3: Molecular analysis 3O 2 2O 3
 Chapter 3: Molecular analysis Read: BLB 3.3 3.5 H W : BLB 3:21a, c, e, f, 25, 29, 37,49, 51, 53 Supplemental 3:1 8 CHEMICAL FORMULA Formula that gives the TOTAL number of elements in a molecule or formula
Chapter 3: Molecular analysis Read: BLB 3.3 3.5 H W : BLB 3:21a, c, e, f, 25, 29, 37,49, 51, 53 Supplemental 3:1 8 CHEMICAL FORMULA Formula that gives the TOTAL number of elements in a molecule or formula
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions
 Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Molar Mass of Butane
 Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
IUPAC System of Nomenclature
 IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Other Stoich Calculations A. mole mass (mass mole) calculations. GIVEN mol A x CE mol B. PT g A CE mol A MOLE MASS :
 Chem. I Notes Ch. 12, part 2 Using Moles NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. 1 MOLE = 6.02 x 10 23 representative particles (representative particles
Chem. I Notes Ch. 12, part 2 Using Moles NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. 1 MOLE = 6.02 x 10 23 representative particles (representative particles
Unit 3 Notepack Chapter 7 Chemical Quantities Qualifier for Test
 Unit 3 Notepack Chapter 7 Chemical Quantities Qualifier for Test NAME Section 7.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter A. What is a mole? 1. Chemistry is a quantitative science. What does this term mean?
Unit 3 Notepack Chapter 7 Chemical Quantities Qualifier for Test NAME Section 7.1 The Mole: A Measurement of Matter A. What is a mole? 1. Chemistry is a quantitative science. What does this term mean?
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses
 Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses B. Calculations of moles C. Calculations of number of atoms from moles/molar masses 1. Avagadro
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses B. Calculations of moles C. Calculations of number of atoms from moles/molar masses 1. Avagadro
2. The percent yield is the maximum amount of product that can be produced from the given amount of limiting reactant.
 UNIT 6 stoichiometry practice test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. moles F 1. The mole ratio is a comparison of how many grams of one substance are required to participate in
UNIT 6 stoichiometry practice test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. moles F 1. The mole ratio is a comparison of how many grams of one substance are required to participate in
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum
 Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
Chapter 3. Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions This chapter uses the concepts of conservation of mass to assist the student in gaining an understanding of chemical changes. Upon completion of Chapter
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions This chapter uses the concepts of conservation of mass to assist the student in gaining an understanding of chemical changes. Upon completion of Chapter
87 16 70 20 58 24 44 32 35 40 29 48 (a) graph Y versus X (b) graph Y versus 1/X
 HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter
 Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter 6. Substances that cannot be decomposed into two or more simpler substances by chemical means are called a. pure substances. b. compounds. c. molecules. d. elements.
Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter 6. Substances that cannot be decomposed into two or more simpler substances by chemical means are called a. pure substances. b. compounds. c. molecules. d. elements.
CP Chemistry Review for Stoichiometry Test
 CP Chemistry Review for Stoichiometry Test Stoichiometry Problems (one given reactant): 1. Make sure you have a balanced chemical equation 2. Convert to moles of the known substance. (Use the periodic
CP Chemistry Review for Stoichiometry Test Stoichiometry Problems (one given reactant): 1. Make sure you have a balanced chemical equation 2. Convert to moles of the known substance. (Use the periodic
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound
 EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
Stoichiometry. What is the atomic mass for carbon? For zinc?
 Stoichiometry Atomic Mass (atomic weight) Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams We use atomic mass units an atomic mass unit (AMU) is one twelfth the mass of the catbon-12
Stoichiometry Atomic Mass (atomic weight) Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams We use atomic mass units an atomic mass unit (AMU) is one twelfth the mass of the catbon-12
Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations
 Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations 1 Submicroscopic Macroscopic 2 Chapter Outline 1. Formula Masses (Ch 6.1) 2. Percent Composition (supplemental material) 3. The Mole & Avogadro s Number (Ch 6.2) 4. Molar
Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations 1 Submicroscopic Macroscopic 2 Chapter Outline 1. Formula Masses (Ch 6.1) 2. Percent Composition (supplemental material) 3. The Mole & Avogadro s Number (Ch 6.2) 4. Molar
Unit 5 Practice Test. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The internal energy of a system is always increased by. A) adding
Name: Class: Date: Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The internal energy of a system is always increased by. A) adding
Getting the most from this book...4 About this book...5
 Contents Getting the most from this book...4 About this book....5 Content Guidance Topic 1 Atomic structure and the periodic table...8 Topic 2 Bonding and structure...14 Topic 2A Bonding....14 Topic 2B
Contents Getting the most from this book...4 About this book....5 Content Guidance Topic 1 Atomic structure and the periodic table...8 Topic 2 Bonding and structure...14 Topic 2A Bonding....14 Topic 2B
Stoichiometry Review
 Stoichiometry Review There are 20 problems in this review set. Answers, including problem set-up, can be found in the second half of this document. 1. N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) --------> 2NH 3 (g) a. nitrogen
Stoichiometry Review There are 20 problems in this review set. Answers, including problem set-up, can be found in the second half of this document. 1. N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) --------> 2NH 3 (g) a. nitrogen
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3)
 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3) Chemical Compounds 1. Classification of Elements and Compounds Types of Pure Substances (Figure 3.4) Elements -- made up of only one type of atom
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3) Chemical Compounds 1. Classification of Elements and Compounds Types of Pure Substances (Figure 3.4) Elements -- made up of only one type of atom
Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes (The Mole Continues)
 Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes (The Mole Continues) is a big word for a process that chemist s use to calculate amounts in reactions. It makes use of the coefficient ratio set up by balanced reaction equations
Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes (The Mole Continues) is a big word for a process that chemist s use to calculate amounts in reactions. It makes use of the coefficient ratio set up by balanced reaction equations
Standard Free Energies of Formation at 298 K. Average Bond Dissociation Energies at 298 K
 1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
