Nondisjunction. Chromosomes may fail to separate during meiosis Resulting gametes may have too few or too many chromosomes Common Disorders:
|
|
|
- Francis Warner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 Chromosomes 2
3 Chromosome Number All cells in the human body (SOMATIC CELLS) have 46 or 23 pairs of chromosomes Called the DIPLOID or 2n number GAMETES (eggs & sperm) have only 23 chromosomes Called the HAPLOID or 1n number 3
4 Nondisjunction Chromosomes may fail to separate during meiosis Resulting gametes may have too few or too many chromosomes Common Disorders: Down Syndrome three 21 st chromosomes Turner Syndrome single X chromosome Klinefelter s Syndrome XXY chromosomes 4
5 5
6 Mutations A mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence of a gene. Mutations in a gene's DNA sequence can alter the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene. How does this happen? Like words in a sentence, the DNA sequence of each gene determines the amino acid sequence for the protein it encodes. The DNA sequence is interpreted in groups of three nucleotide bases, called codons. Each codon specifies a single amino acid in a protein. Gene mutations result from changes in a single gene. Chromosomal mutations involve changes in whole chromosomes. 6
7 Gene Mutations Point Mutations changes in one or a few nucleotides Substitution THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT THE FAT HAT ATE THE RAT Insertion THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT THE FAT CAT XLW ATE THE RAT Deletion THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT THE FAT *** ATE THE RAT 7
8 Gene Mutations Frameshift Mutations shifts the reading frame of the genetic message so that the protein may not be able to perform its function. Insertion THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT THE FAT HCA TAT ETH ERA T Deletion THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT TEF ATC ATA TET GER AT H H
9 Chromosome Mutations Changes in number or structure of entire chromosomes. Such mutations may change the locations of genes on chromosomes, and may even change the number of copies of some genes. Deletions involve the loss of all or parts of a chromosome, while duplication produce extra copies of parts of chromosome. Inversions reverse the direction of parts of chromosomes and translations occur when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another.
10 Chromosome Mutations Original Chromosome Deletion Duplication Inversion Translocation ABC * DEF AC * DEF ABBC * DEF AED * CBF ABC * JKL GHI * DEF 10
11 What Causes Mutations? There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child Mutations can be acquired. Environmental damage Mistakes when DNA is copied
12 Sex-Linked Genes Characteristics that are inherited from genes found on the sex chromosomes. X-linked diseases are those for which the gene is present on the X chromosome. X-linked diseases show inheritance patterns that differ from autosomal diseases. This occurs because males only have one copy of the X chromosome (plus their Y chromosome) and females have two X chromosomes. Because of this, males and females show different patterns of inheritance and severity of manifestation. While there are both dominant and recessive X-linked diseases, there are some characteristics that are common to X-linked disorders in general 12
13 Sex-Linked Traits Sex Determination Females XX Males XY Almost all sex-linked traits are found on the X chromosome Y chromosome contains very few genes and is mainly involved in sex determination
14 Sex-Linked Traits It is possible for a female to be a carrier of an X-linked trait, but not express it Men will express all X- linked traits they inherit X-linked recessive, carrier mother Unaffected father Unaffected Affected Carrier Carrier mother Unaffected son Unaffected daughter Carrier daughter Affected son U.S. National Library of Medicine
15 Example: Color Blindness Various tests for color blindness.
16 Pedigree Charts Pedigree charts show a record of the family of an individual They can be used to study the transmission of a hereditary condition They are particularly useful when there are large families and a good family record over several generations. 16
17 Studying human genetics You cannot make humans of different types breed together Pedigree charts offer an ethical way of studying human genetics Today genetic engineering has new tools to offer doctors studying genetic diseases A genetic counsellor will still use pedigree charts to help determine the distribution of a disease in an affected family
18 Symbols used in pedigree charts Normal male Affected male A marriage with five children, two daughters and three sons. The eldest son is affected by the condition. Normal female Affected female Marriage Eldest child Youngest child
19 A pedigree chart of a family showing 20 individuals
20 Generations are identified by Roman numerals I II III IV
21 Individuals in each generation are identified by Arabic numerals numbered from the left Therefore the affected individuals are II3, IV2 and IV3 I II III IV
22 A DNA fingerprint is a type of restriction map. DNA fingerprints are based on parts of an individual s DNA that can by used for identification. based on noncoding regions of DNA noncoding regions have repeating DNA sequences number of repeats differs between people banding pattern on a gel is a DNA fingerprint
23 DNA fingerprinting is used for identification. DNA fingerprinting depends on the probability of a match. Many people have the same number of repeats in a certain region of DNA. The probability that two people share identical numbers of repeats in several locations is very small. (mother) (child 1) (child 2) (father)
24 Karyotype A picture of chromosomes Arranged in pairs by size Chromosomes #1-22 autosomes Chromosome pair #23 sex chromosomes Ex. XX = female; XY = male
25 Karyotype
26 How is the sex of an individual figured out? X is the symbol for Female and the female carries 2 x chromosomes Y is the symbol for male and it carries both an x and a y chromosome So when conception occurs and cells are divided the end result is X + X = FEMALE Y + X = MALE Now when there is a missing x chromosome (May be present but defective) X + 0 = FEMALE (Turner Syndrome) occurs When an extra X chromosome is found in the cell Y + X + X = MALE (Klinefelter Syndrome) occurs 26
27 What chromosomes do all males have that the females don't have? It s the Y chromosome The Y chromosome is responsible for kick starting the process to create a male. It is the male who determines the sex of the child as he is the only one who carries the Y chromosome. The male inherits a copy of his fathers genetic material. And it is through this that one can determine his lineage King Henry VIII King Henry the Eighth, to six wives he was wedded: One died, one survived, two divorced, two beheaded." 27
28 Normal Male 2n = 46 28
29 Normal Female 2n = 46 29
30 Chromosome Mutations Down Syndrome Chromosome 21 does not separate correctly. They have 47 chromosomes in stead of 46. Children with Down Syndrome develop slower, may have heart and stomach illnesses and vary greatly in their degree of intelligence.
31 Male, Trisomy 21 (Down s) 2n = 47 31
32 Female Down s Syndrome 2n = 47 32
33 Klinefelter s Syndrome 2n = 47 33
34 Klinefelter Syndrome or XXY Syndrome Klinefelter syndrome is one that affects the male sexual development. The characteristics of this disorder include: Small testicles. Infertility. Lower testosterone level, sparse facial and body hair, taller than average height may develop a feminine body shape which is caused by the lower level of testosterone. It happens 1 in every 500 births to 1 in every 1000 births. 34
35
36 Turner s Syndrome 2n = 45 36
37 Turner Syndrome Characteristics They are short in stature. They have webbed necks, low ears, lower hairline, are secondary sex characteristics underdeveloped. Are often treated with hormone replacement therapy to counteract the lost hormones and simulate puberty. Turner syndrome is the absence of an X chromosome or by damaged X chromosome. They may have problems with diabetes, osteoporosis, ear/hearing problems, obesity, kidney and coronary issues. 37
38
39 Making a Karyotype Cut out the chromosomes Arrange in pairs by size Glue the pairs and number the autosomes 1-22 Glue the Sex Chromosomes last Title it Male (Disorder) or Female (Disorder)
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Each person normally has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all. We inherit one chromosome per pair from our mother and one from our father.
 AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE
 SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
BioBoot Camp Genetics
 BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance
 Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
The correct answer is c A. Answer a is incorrect. The white-eye gene must be recessive since heterozygous females have red eyes.
 1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive.
 11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
Fact Sheet 14 EPIGENETICS
 This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
Influence of Sex on Genetics. Chapter Six
 Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009
 MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities
 Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
Gene and Chromosome Mutation Worksheet (reference pgs. 239-240 in Modern Biology textbook)
 Name Date Per Look at the diagrams, then answer the questions. Gene Mutations affect a single gene by changing its base sequence, resulting in an incorrect, or nonfunctional, protein being made. (a) A
Name Date Per Look at the diagrams, then answer the questions. Gene Mutations affect a single gene by changing its base sequence, resulting in an incorrect, or nonfunctional, protein being made. (a) A
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles. Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully
 Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
www.njctl.org PSI Biology Mitosis & Meiosis
 Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2
 Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses
 B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
Genetics Test Biology I
 Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
X Linked Inheritance
 X Linked Inheritance Information for Patients and Families 2 X linked Inheritance The following will give you information about what X linked inheritance means and how X linked conditions are inherited.
X Linked Inheritance Information for Patients and Families 2 X linked Inheritance The following will give you information about what X linked inheritance means and how X linked conditions are inherited.
MUTATION, DNA REPAIR AND CANCER
 MUTATION, DNA REPAIR AND CANCER 1 Mutation A heritable change in the genetic material Essential to the continuity of life Source of variation for natural selection New mutations are more likely to be harmful
MUTATION, DNA REPAIR AND CANCER 1 Mutation A heritable change in the genetic material Essential to the continuity of life Source of variation for natural selection New mutations are more likely to be harmful
14.3 Studying the Human Genome
 14.3 Studying the Human Genome Lesson Objectives Summarize the methods of DNA analysis. State the goals of the Human Genome Project and explain what we have learned so far. Lesson Summary Manipulating
14.3 Studying the Human Genome Lesson Objectives Summarize the methods of DNA analysis. State the goals of the Human Genome Project and explain what we have learned so far. Lesson Summary Manipulating
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
LAB : PAPER PET GENETICS. male (hat) female (hair bow) Skin color green or orange Eyes round or square Nose triangle or oval Teeth pointed or square
 Period Date LAB : PAPER PET GENETICS 1. Given the list of characteristics below, you will create an imaginary pet and then breed it to review the concepts of genetics. Your pet will have the following
Period Date LAB : PAPER PET GENETICS 1. Given the list of characteristics below, you will create an imaginary pet and then breed it to review the concepts of genetics. Your pet will have the following
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3
 Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities
 Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
Heredity. Sarah crosses a homozygous white flower and a homozygous purple flower. The cross results in all purple flowers.
 Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name: 4. A typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross is a) 9:1 b) 3:4 c) 9:3:3:1 d) 1:2:1:2:1 e) 6:3:3:6
 Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome.
 Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Umm AL Qura University MUTATIONS. Dr Neda M Bogari
 Umm AL Qura University MUTATIONS Dr Neda M Bogari CONTACTS www.bogari.net http://web.me.com/bogari/bogari.net/ From DNA to Mutations MUTATION Definition: Permanent change in nucleotide sequence. It can
Umm AL Qura University MUTATIONS Dr Neda M Bogari CONTACTS www.bogari.net http://web.me.com/bogari/bogari.net/ From DNA to Mutations MUTATION Definition: Permanent change in nucleotide sequence. It can
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1
 Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
somatic cell egg genotype gamete polar body phenotype homologous chromosome trait dominant autosome genetics recessive
 CHAPTER 6 MEIOSIS AND MENDEL Vocabulary Practice somatic cell egg genotype gamete polar body phenotype homologous chromosome trait dominant autosome genetics recessive CHAPTER 6 Meiosis and Mendel sex
CHAPTER 6 MEIOSIS AND MENDEL Vocabulary Practice somatic cell egg genotype gamete polar body phenotype homologous chromosome trait dominant autosome genetics recessive CHAPTER 6 Meiosis and Mendel sex
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
7A The Origin of Modern Genetics
 Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
Marrying a relative. Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other?
 Marrying a relative Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other? The simple answer to this question is Yes, there is an increased chance.
Marrying a relative Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other? The simple answer to this question is Yes, there is an increased chance.
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Academic Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Test
 Academic Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Each organism has a unique combination
Academic Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Each organism has a unique combination
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Certain human genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia, result from single base-pair mutations in DNA. (a) Explain how a single base-pair mutation
AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Certain human genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia, result from single base-pair mutations in DNA. (a) Explain how a single base-pair mutation
Mutations and Genetic Variability. 1. What is occurring in the diagram below?
 Mutations and Genetic Variability 1. What is occurring in the diagram below? A. Sister chromatids are separating. B. Alleles are independently assorting. C. Genes are replicating. D. Segments of DNA are
Mutations and Genetic Variability 1. What is occurring in the diagram below? A. Sister chromatids are separating. B. Alleles are independently assorting. C. Genes are replicating. D. Segments of DNA are
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis
 BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
17. A testcross A.is used to determine if an organism that is displaying a recessive trait is heterozygous or homozygous for that trait. B.
 ch04 Student: 1. Which of the following does not inactivate an X chromosome? A. Mammals B. Drosophila C. C. elegans D. Humans 2. Who originally identified a highly condensed structure in the interphase
ch04 Student: 1. Which of the following does not inactivate an X chromosome? A. Mammals B. Drosophila C. C. elegans D. Humans 2. Who originally identified a highly condensed structure in the interphase
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
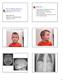 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE. Section B: Sex Chromosomes
 CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA
 Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling. Chapter 20
 Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling Chapter 20 What is Gene Therapy? Treating a disease by replacing, manipulating or supplementing a gene The act of changing an individual s DNA sequence to fix a non-functional
Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling Chapter 20 What is Gene Therapy? Treating a disease by replacing, manipulating or supplementing a gene The act of changing an individual s DNA sequence to fix a non-functional
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism
 Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
Basic Concepts Recombinant DNA Use with Chapter 13, Section 13.2
 Name Date lass Master 19 Basic oncepts Recombinant DN Use with hapter, Section.2 Formation of Recombinant DN ut leavage Splicing opyright lencoe/mcraw-hill, a division of he Mcraw-Hill ompanies, Inc. Bacterial
Name Date lass Master 19 Basic oncepts Recombinant DN Use with hapter, Section.2 Formation of Recombinant DN ut leavage Splicing opyright lencoe/mcraw-hill, a division of he Mcraw-Hill ompanies, Inc. Bacterial
Protein Synthesis. Page 41 Page 44 Page 47 Page 42 Page 45 Page 48 Page 43 Page 46 Page 49. Page 41. DNA RNA Protein. Vocabulary
 Protein Synthesis Vocabulary Transcription Translation Translocation Chromosomal mutation Deoxyribonucleic acid Frame shift mutation Gene expression Mutation Point mutation Page 41 Page 41 Page 44 Page
Protein Synthesis Vocabulary Transcription Translation Translocation Chromosomal mutation Deoxyribonucleic acid Frame shift mutation Gene expression Mutation Point mutation Page 41 Page 41 Page 44 Page
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Genetics for the Novice
 Genetics for the Novice by Carol Barbee Wait! Don't leave yet. I know that for many breeders any article with the word genetics in the title causes an immediate negative reaction. Either they quickly turn
Genetics for the Novice by Carol Barbee Wait! Don't leave yet. I know that for many breeders any article with the word genetics in the title causes an immediate negative reaction. Either they quickly turn
Bob Jesberg. Boston, MA April 3, 2014
 DNA, Replication and Transcription Bob Jesberg NSTA Conference Boston, MA April 3, 2014 1 Workshop Agenda Looking at DNA and Forensics The DNA, Replication i and Transcription i Set DNA Ladder The Double
DNA, Replication and Transcription Bob Jesberg NSTA Conference Boston, MA April 3, 2014 1 Workshop Agenda Looking at DNA and Forensics The DNA, Replication i and Transcription i Set DNA Ladder The Double
Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele.
 Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations. Chapters 12-13.3
 DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations Chapters 12-13.3 1A)Identify the components of DNA and explain its role in heredity. DNA s Role in heredity: Contains the genetic information of a cell that can
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations Chapters 12-13.3 1A)Identify the components of DNA and explain its role in heredity. DNA s Role in heredity: Contains the genetic information of a cell that can
Meiosis is a special form of cell division.
 Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number
 Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Cancer Genomics: What Does It Mean for You?
 Cancer Genomics: What Does It Mean for You? The Connection Between Cancer and DNA One person dies from cancer each minute in the United States. That s 1,500 deaths each day. As the population ages, this
Cancer Genomics: What Does It Mean for You? The Connection Between Cancer and DNA One person dies from cancer each minute in the United States. That s 1,500 deaths each day. As the population ages, this
DRAGON GENETICS LAB -- Principles of Mendelian Genetics
 DragonGeneticsProtocol Mendelian Genetics lab Student.doc DRAGON GENETICS LAB -- Principles of Mendelian Genetics Dr. Pamela Esprivalo Harrell, University of North Texas, developed an earlier version of
DragonGeneticsProtocol Mendelian Genetics lab Student.doc DRAGON GENETICS LAB -- Principles of Mendelian Genetics Dr. Pamela Esprivalo Harrell, University of North Texas, developed an earlier version of
*Please consult the online schedule for this course for the definitive date and time for this lecture.
 CHROMOSOMES AND DISEASE Date: September 29, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am- 8:50 am * Room: G-202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Jim Evans 4200A Biomolecular Building jpevans@med.unc.edu Office Hours: by appointment
CHROMOSOMES AND DISEASE Date: September 29, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am- 8:50 am * Room: G-202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Jim Evans 4200A Biomolecular Building jpevans@med.unc.edu Office Hours: by appointment
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
The sequence of bases on the mrna is a code that determines the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide being synthesized:
 Module 3F Protein Synthesis So far in this unit, we have examined: How genes are transmitted from one generation to the next Where genes are located What genes are made of How genes are replicated How
Module 3F Protein Synthesis So far in this unit, we have examined: How genes are transmitted from one generation to the next Where genes are located What genes are made of How genes are replicated How
LECTURE 6 Gene Mutation (Chapter 16.1-16.2)
 LECTURE 6 Gene Mutation (Chapter 16.1-16.2) 1 Mutation: A permanent change in the genetic material that can be passed from parent to offspring. Mutant (genotype): An organism whose DNA differs from the
LECTURE 6 Gene Mutation (Chapter 16.1-16.2) 1 Mutation: A permanent change in the genetic material that can be passed from parent to offspring. Mutant (genotype): An organism whose DNA differs from the
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Heredity Grade Ten
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Causes of Birth Defects
 Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES 1. Margaret has just learned that she has adult polycystic kidney disease. Her mother also has the disease, as did her maternal grandfather and his younger
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES 1. Margaret has just learned that she has adult polycystic kidney disease. Her mother also has the disease, as did her maternal grandfather and his younger
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
The Human Genome Project
 The Human Genome Project Brief History of the Human Genome Project Physical Chromosome Maps Genetic (or Linkage) Maps DNA Markers Sequencing and Annotating Genomic DNA What Have We learned from the HGP?
The Human Genome Project Brief History of the Human Genome Project Physical Chromosome Maps Genetic (or Linkage) Maps DNA Markers Sequencing and Annotating Genomic DNA What Have We learned from the HGP?
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES. Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD
 LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men Information for men from families with a known alteration in the BRCA1/2 gene Introduction BRCA1 and BRCA2
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men Information for men from families with a known alteration in the BRCA1/2 gene Introduction BRCA1 and BRCA2
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance. Ch. 3
 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
Terms: The following terms are presented in this lesson (shown in bold italics and on PowerPoint Slides 2 and 3):
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Genetics 1. Defective enzyme that does not make melanin. Very pale skin and hair color (albino)
 Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
Name Class Date. Figure 13 1. 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13 1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d.
 13 Multiple Choice RNA and Protein Synthesis Chapter Test A Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following are found in both
13 Multiple Choice RNA and Protein Synthesis Chapter Test A Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following are found in both
Genetics Part 1: Inheritance of Traits
 Genetics Part 1: Inheritance of Traits Genetics is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. Offspring usually show some traits of each parent. For a long time, scientists did not understand
Genetics Part 1: Inheritance of Traits Genetics is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. Offspring usually show some traits of each parent. For a long time, scientists did not understand
Genetic information (DNA) determines structure of proteins DNA RNA proteins cell structure 3.11 3.15 enzymes control cell chemistry ( metabolism )
 Biology 1406 Exam 3 Notes Structure of DNA Ch. 10 Genetic information (DNA) determines structure of proteins DNA RNA proteins cell structure 3.11 3.15 enzymes control cell chemistry ( metabolism ) Proteins
Biology 1406 Exam 3 Notes Structure of DNA Ch. 10 Genetic information (DNA) determines structure of proteins DNA RNA proteins cell structure 3.11 3.15 enzymes control cell chemistry ( metabolism ) Proteins
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2)
 Single Gene Disorders Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2) Some Definitions Alleles variants of a given DNA sequence at a particular location (locus) in the genome. Often used more narrowly to describe alternative
Single Gene Disorders Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2) Some Definitions Alleles variants of a given DNA sequence at a particular location (locus) in the genome. Often used more narrowly to describe alternative
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P2 FEBRUARY/MARCH 2015 MEMORANDUM MARKS: 150 This memorandum consists of 12 pages. Life Sciences/P2 2 DBE/Feb. Mar. 2015 PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P2 FEBRUARY/MARCH 2015 MEMORANDUM MARKS: 150 This memorandum consists of 12 pages. Life Sciences/P2 2 DBE/Feb. Mar. 2015 PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING
4 SEX CHROMOSOMES AND SEX DETERMINATION
 4 SEX CHROMOSOMES AND SEX DETERMINATION 4.1 Sex chromosomes and Sex Determination Sex- chromosomes. If present, sex chromosomes may not have the same size, shape, or genetic potential. In humans, females
4 SEX CHROMOSOMES AND SEX DETERMINATION 4.1 Sex chromosomes and Sex Determination Sex- chromosomes. If present, sex chromosomes may not have the same size, shape, or genetic potential. In humans, females
A test your patients can trust.
 A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Genetic engineering is possible
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Genetic engineering is possible
