ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 17 Thunderstorms and Tornadoes Dr. DeCaria
|
|
|
- Piers Bryant
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THUNDERSTORMS ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 17 Thunderstorms and Tornadoes Dr. DeCaria A thunderstorm is a storm that produces thunder and lightning. Normally the vertical motion in the atmosphere is very slow, on the order of centimeters per second (about one-tenth of a mile per hour). In a thunderstorm, updrafts can easily exceed 50 mph, and have been observed at over 80 mph. Thunderstorms require some lifting mechanism to start the initial upward motion. This mechanism can be any one of the four lifting mechanisms that we discussed earlier in the semester ο Orographic lifting ο Frontal wedging ο Convergence ο Convective lifting DISTRIBUTION OF THUNDERSTORMS On average there are about 45,000 thunderstorms around the world every day. Most thunderstorms occur over land, and in the Tropics. Each year the U.S. experiences around 100,000 thunderstorms. Florida and the Gulf Coast experience the most thunderstorms in the U.S., because mt air that moves over the hot land is very unstable. Eastern New Mexico and Colorado also experience numerous thunderstorms, due to mt air moving upslope toward the Continental Divide. The fewest thunderstorms occur on the West Coast, because mp air is very stable. AIR MASS THUNDERSTORMS Air mass thunderstorms are associated with mt air. Stages of development of air mass thunderstorms
2 ο Cumulus stage strong updrafts build the storm ο Mature stage precipitation begins. Downdrafts form from both the frictional drag of the precipitation, and due to entrainment of dryer air and evaporation of precipitation. ο Dissipating stage downdrafts have shut off the updrafts that feed the storm. Clouds evaporate as the storm dissipates. Air mass thunderstorms are more likely to occur over mountains or hills, due to differential heating and orographic lifting. The sea-breeze is a common cause of air-mass thunderstorms along Florida s coast. GUST FRONTS AND DOWNBURSTS Thunderstorm downdrafts are cool because of two factors: ο Entrainment of unsaturated, cooler air from outside of the thunderstorm. ο Evaporation of precipitation into the air As the cool downdraft hits the ground it spreads out. The leading edge of the downdraft acts like a miniature cold front, and is called the gust front. As the gust front passes the wind become gusty, and the temperature drops. The lifting of warm, moist air along the gust front can trigger new thunderstorm development. If the downdraft is very strong it is called a downburst. Downbursts can be quite damaging to trees, building, power lines, and airplanes. They are often mistaken for tornadoes by people who experience them. A very narrow downburst is sometimes called a microburst. 2
3 SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS A thunderstorm is classified as severe if any one of the following conditions are met: ο It produces winds in excess of 50 knots (58 mph). ο It produces hail larger than one inch in diameter. 1 ο It produces a tornado Severe thunderstorms are often produced beneath the jet stream or other region of strong upper level winds. OTHER CLASSIFICATIONS OF THUNDERSTORMS Thunderstorms are also classified according to the number and strength of the updrafts, or cells. ο In a single-cell thunderstorm there is only one main updraft and downdraft. Most air mass thunderstorms are of this variety. ο If there is more than one updraft present than we have a multi-cell thunderstorm. ο If there is a single, large updraft that is rotating then we have a super-cell thunderstorm. The vertical profile of the winds determines whether the storm will be single-, multi-, or super-cell. SQUALL LINES Squall lines are narrow, fast moving lines of thunderstorms that occur a hundred or so miles ahead of a cold front. Squall lines sometimes form along the dryline, a boundary between ct and mt air over West Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas. MESOSCALE CONVECTIVE COMPLEX (MCC) 1 Prior to January 5, 2010 the cutoff size was ¾ inch diameter. 3
4 Mesoscale Convective Complexes are very large groups of thunderstorms that form in the late afternoon or evening over the Great Plains, and persist for up to 12 hours or more. MCC s are responsible for a large amount of the rainfall received in the Central U.S. TORNADOES Tornadoes are rotating columns of wind that form beneath some severe thunderstorms. Tornadoes form and sustain themselves due to vortex stretching. ο Vortex stretching refers to what occurs when a column of air that is initially rotating only slowly is stretched along the axis of rotation. As the column of air stretches it also becomes skinnier. Because of conservation of angular momentum, as the column becomes skinnier it begins to spin faster. ο Vortex stretching occurs in your bathtub or sink, and is why a whirlpool often forms in a draining bathtub. This vortex stretching can occur in a thunderstorm updraft, and can cause the vortex to rotate at incredible speeds (over 250 mph!). Small tornadoes can form due to the vertical wind shear near the ground. Initially, the rotation will be along a horizontal axis, but the thunderstorm updraft can tilt the rotation to the vertical, and then stretch it. Tornadoes formed in this manner can spin either clockwise or counterclockwise. The larger, and most devastating tornadoes form from super-cell thunderstorms. The updrafts in super-cell thunderstorms already are slowly spinning in a counterclockwise (cyclonic) direction. This is often referred to as a mesocyclone. The tornado, and vortex stretching, occur within the mesocyclone. Tornadoes formed in this manner always rotate counterclockwise. About 80% of tornadoes spin counterclockwise. ο This is not directly due to the Coriolis force acting on the tornado, because tornadoes are too small to directly feel the effects of the earth s rotation. 4
5 Instead, it is because the storms that spawn the tornadoes (the mesocylones) are large enough to feel the effects of rotation. A tornado may have multiple suction vortices. Although the visible part of the tornado usually extends from the cloud and moves toward the ground, the suction in the tornado is actually upwards. The cloud forms in the vortex because pressures are low enough to cause the air to adiabatically cool to saturation. In order to be classified as a tornado, the vortex must reach the ground. Otherwise, it is just reported as a funnel cloud. A tornado that occurs over water is called a waterspout. TORNADO CLIMATOLOGY Tornadoes can occur during any month of the year. Tornadoes have been reported in every state of the U.S. Most tornadoes, however, occur during the Spring, and over the Great Plains. this is because the conditions for forming severe thunderstorms (the collision of mt air with cp air) often occur in this region at this time of year. Since most tornadoes form in the mt air ahead of a cold front, where the prevailing flow is southwesterly, most tornadoes move toward the northeast. THE F-SCALE OF TORNADO INTENSITY Tornado intensity is measured on a scale created by Dr. Ted Fujita, a noted tornado researcher. It is referred to as the F-scale. Since tornado winds cannot be measured directly, the F-scale is based on the damage caused by the tornado. The F-scale goes from F0 to F5, with F0 being light damage, and F5 being incredible damage. 5
6 TORNADO SAFETY Pay attention to the TV or radio when thunderstorms are in your area, and listen for the issuance of Tornado Watches or Tornado Warnings. Keep a battery operated AM or FM radio available. You may want to purchase a weather-band radio. The National Atmospheric and Oceanic Administration (NOAA), the parent organization of the National Weather Service, operates radio stations that continually broadcast weather information. Radios that can receive these broadcasts are relatively inexpensive, and can be bought at most electronic stores. Some of these radios even have alarms on them that will sound if a tornado watch or warning has been issued. TORNADO WATCHES AND WARNINGS A Tornado Watch means that the conditions are ripe for tornado formation, and that tornadoes are possible. A Tornado Warning means that a tornado has been spotted. If a Tornado Warning has been issued ο Seek shelter immediately! ο Go to the lowest level of your building. ο If possible, get into the basement, or into an interior room (but away from any windows or doors to the outside). ο Look around to make sure there are no heavy or glass objects near or above you. ο If possible, cover yourself with pillow, blankets, or a mattress. ο Keep monitoring the radio or TV for updated information. 6
Storms Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
WEATHER THEORY Temperature, Pressure And Moisture
 WEATHER THEORY Temperature, Pressure And Moisture Air Masses And Fronts Weather Theory- Page 77 Every physical process of weather is a result of a heat exchange. The standard sea level temperature is 59
WEATHER THEORY Temperature, Pressure And Moisture Air Masses And Fronts Weather Theory- Page 77 Every physical process of weather is a result of a heat exchange. The standard sea level temperature is 59
Basics of weather interpretation
 Basics of weather interpretation Safety at Sea Seminar, April 2 nd 2016 Dr. Gina Henderson Oceanography Dept., USNA ghenders@usna.edu Image source: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/naturalhazards/view.php?id=80399,
Basics of weather interpretation Safety at Sea Seminar, April 2 nd 2016 Dr. Gina Henderson Oceanography Dept., USNA ghenders@usna.edu Image source: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/naturalhazards/view.php?id=80399,
2. The map below shows high-pressure and low-pressure weather systems in the United States.
 1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
Severe Weather Information
 Severe Weather Information TORNADO FACTS Canada gets more tornadoes than any other country with the exception of the United States. Tornadoes are rotating columns of high winds. Sometimes they move quickly
Severe Weather Information TORNADO FACTS Canada gets more tornadoes than any other country with the exception of the United States. Tornadoes are rotating columns of high winds. Sometimes they move quickly
WeatherBug Vocabulary Bingo
 Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Evaluating components of the water cycle. LAB: Experimenting with porosity and permeability.
SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Evaluating components of the water cycle. LAB: Experimenting with porosity and permeability.
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Mid latitude Cyclonic Storm System. 08 _15 ab. jpg
 Mid latitude Cyclonic Storm System 08 _15 ab. jpg Mid Latitude Cyclone Storm System (MLCSS) It has several names. Cyclone, Cyclonic Storm, Cyclonic System, Depression. Cyclonic Storms are the weather maker
Mid latitude Cyclonic Storm System 08 _15 ab. jpg Mid Latitude Cyclone Storm System (MLCSS) It has several names. Cyclone, Cyclonic Storm, Cyclonic System, Depression. Cyclonic Storms are the weather maker
Tornadoes Answer Sheet
 LEVEL 1 None LEVEL 2 Definitions for A Tornado Is Born anvil cloud: the upper portion of a cumulonimbus cloud that flattens spreads out, sometimes for hundreds of miles atmosphere: the mass of air surrounding
LEVEL 1 None LEVEL 2 Definitions for A Tornado Is Born anvil cloud: the upper portion of a cumulonimbus cloud that flattens spreads out, sometimes for hundreds of miles atmosphere: the mass of air surrounding
Clouds for pilots. Ed Williams. http://williams.best.vwh.net/
 Clouds for pilots Ed Williams http://williams.best.vwh.net/ Clouds are important to pilots! Many of our weather problems are associated with clouds: Fog Thunderstorms Cloud In flight icing Cloud physics
Clouds for pilots Ed Williams http://williams.best.vwh.net/ Clouds are important to pilots! Many of our weather problems are associated with clouds: Fog Thunderstorms Cloud In flight icing Cloud physics
Air Masses and Fronts
 Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Convective Clouds. Convective clouds 1
 Convective clouds 1 Convective Clouds Introduction Convective clouds are formed in vertical motions that result from the instability of the atmosphere. This instability can be caused by: a. heating at
Convective clouds 1 Convective Clouds Introduction Convective clouds are formed in vertical motions that result from the instability of the atmosphere. This instability can be caused by: a. heating at
Chapter Overview. Seasons. Earth s Seasons. Distribution of Solar Energy. Solar Energy on Earth. CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen
THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen
Hurricanes. Characteristics of a Hurricane
 Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: WEATHER BASICS: STATION MODELS: MOISTURE: PRESSURE AND WIND: Weather
 Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6
 Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain
 Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain Terminal Learning Objective Action: Analyze weather of cold regions and mountainous terrain Condition: Given a training mission that involves a specified
Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain Terminal Learning Objective Action: Analyze weather of cold regions and mountainous terrain Condition: Given a training mission that involves a specified
Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development. Atmospheric Stability
 Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development Atmospheric Stability 1 Cloud Development - stable environment Stable air (parcel) - vertical motion is inhibited if clouds form, they will be shallow, layered
Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development Atmospheric Stability 1 Cloud Development - stable environment Stable air (parcel) - vertical motion is inhibited if clouds form, they will be shallow, layered
A.4 SEVERE WEATHER PLAN
 Page 1 of 5 A.4 SEVERE WEATHER PLAN 1.0 Purpose 1.1 The purpose of this Severe Weather Response Plan is to minimize the impact on the University from a severe weather incident 2.0 Applicability 2.1 This
Page 1 of 5 A.4 SEVERE WEATHER PLAN 1.0 Purpose 1.1 The purpose of this Severe Weather Response Plan is to minimize the impact on the University from a severe weather incident 2.0 Applicability 2.1 This
The Atmosphere and Winds
 Oceanography 10, T. James Noyes, El Camino College 8A-1 The Atmosphere and Winds We need to learn about the atmosphere, because the ocean and atmosphere are tightly interconnected with one another: you
Oceanography 10, T. James Noyes, El Camino College 8A-1 The Atmosphere and Winds We need to learn about the atmosphere, because the ocean and atmosphere are tightly interconnected with one another: you
UNIT VII--ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND INSTABILITY
 UNIT VII--ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND INSTABILITY The stability or instability of the atmosphere is a concern to firefighters. This unit discusses how changes in the atmosphere affect fire behavior, and
UNIT VII--ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND INSTABILITY The stability or instability of the atmosphere is a concern to firefighters. This unit discusses how changes in the atmosphere affect fire behavior, and
Supercell Thunderstorm Structure and Evolution
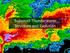 Supercell Thunderstorm Structure and Evolution Supercellular Convection Most uncommon, but most dangerous storm type Produces almost all instances of very large hail and violent (EF4-EF5) tornadoes Highly
Supercell Thunderstorm Structure and Evolution Supercellular Convection Most uncommon, but most dangerous storm type Produces almost all instances of very large hail and violent (EF4-EF5) tornadoes Highly
7613-1 - Page 1. Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions
 Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms?
 How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms? Objective In the summer, over the Great Plains, weather predictions often call for afternoon thunderstorms. While most of us use weather forecasts to help pick
How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms? Objective In the summer, over the Great Plains, weather predictions often call for afternoon thunderstorms. While most of us use weather forecasts to help pick
MiSP WEATHER WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION Teacher Guide, L1 L3. Introduction
 MiSP WEATHER WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION Teacher Guide, L1 L3 Introduction This MiSP unit can be included in a standard weather and climate unit. Some teachers may like it as part of the introduction. Others
MiSP WEATHER WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION Teacher Guide, L1 L3 Introduction This MiSP unit can be included in a standard weather and climate unit. Some teachers may like it as part of the introduction. Others
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource
 Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Satellite Weather And Climate (SWAC) Satellite and cloud interpretation
 Satellite Weather And Climate (SWAC) Satellite and cloud interpretation Vermont State Climatologist s Office University of Vermont Dr. Lesley-Ann Dupigny-Giroux Vermont State Climatologist ldupigny@uvm.edu
Satellite Weather And Climate (SWAC) Satellite and cloud interpretation Vermont State Climatologist s Office University of Vermont Dr. Lesley-Ann Dupigny-Giroux Vermont State Climatologist ldupigny@uvm.edu
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind
 Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms
 Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Chapter 6 - Cloud Development and Forms. Interesting Cloud
 Chapter 6 - Cloud Development and Forms Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Interesting Cloud 1 Mechanisms that Lift Air Orographic lifting Frontal Lifting Convergence Localized convective
Chapter 6 - Cloud Development and Forms Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Interesting Cloud 1 Mechanisms that Lift Air Orographic lifting Frontal Lifting Convergence Localized convective
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test
 WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
Description: This competition will test the student's knowledge of meteorological terms, techniques, and events.
 Weather or Not Description: This competition will test the student's knowledge of meteorological terms, techniques, and events. Number of Participants: 2 Approximate Time: 45 minutes The Competition: 1.
Weather or Not Description: This competition will test the student's knowledge of meteorological terms, techniques, and events. Number of Participants: 2 Approximate Time: 45 minutes The Competition: 1.
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Evalua&ng Downdra/ Parameteriza&ons with High Resolu&on CRM Data
 Evalua&ng Downdra/ Parameteriza&ons with High Resolu&on CRM Data Kate Thayer-Calder and Dave Randall Colorado State University October 24, 2012 NOAA's 37th Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Convective
Evalua&ng Downdra/ Parameteriza&ons with High Resolu&on CRM Data Kate Thayer-Calder and Dave Randall Colorado State University October 24, 2012 NOAA's 37th Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Convective
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775
 Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775 LEVELED BOOK T SEVERE WEATHER Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrated by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775 LEVELED BOOK T SEVERE WEATHER Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrated by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and
6 th Grade Science Assessment: Weather & Water Select the best answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this test.
 Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
Hazardous Weather Primer. CERT Basic Training Unit 0
 Hazardous Weather Primer Unit 0 Topic Overview: CERT Activation Basic Weather Weather Hazards: Flooding, Winter Weather, Extreme temperatures, severe thunderstorms, tornados Weather Safety Personal Preparedness
Hazardous Weather Primer Unit 0 Topic Overview: CERT Activation Basic Weather Weather Hazards: Flooding, Winter Weather, Extreme temperatures, severe thunderstorms, tornados Weather Safety Personal Preparedness
Severe Weather. www.readinga-z.com. Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
 Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,801 LEVELED READER T Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrations by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,801 LEVELED READER T Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrations by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Meteorology: Weather and Climate
 Meteorology: Weather and Climate Large Scale Weather Systems Lecture 1 Tropical Cyclones: Location and Structure Prof. Roy Thompson Crew building Large-scale Weather Systems Tropical cyclones (1-2) Location,
Meteorology: Weather and Climate Large Scale Weather Systems Lecture 1 Tropical Cyclones: Location and Structure Prof. Roy Thompson Crew building Large-scale Weather Systems Tropical cyclones (1-2) Location,
CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate
 Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Emergency Management is responsible for coordinating the City of Houston s preparation for and response to emergency situations.
 CITY OF HOUSTON Office of Emergency Management October 2004 Emergency Management is responsible for coordinating the City of Houston s preparation for and response to emergency situations. Houston is exposed
CITY OF HOUSTON Office of Emergency Management October 2004 Emergency Management is responsible for coordinating the City of Houston s preparation for and response to emergency situations. Houston is exposed
INTRODUCTION STORM CHRONOLOGY AND OBSERVATIONS
 THE MESOCYCLONE EVOLUTION OF THE WARREN, OKLAHOMA TORNADOES By Timothy P. Marshall and Erik N. Rasmussen (Reprinted from the 12th Conference on Severe Local Storms, American Meteorological Society, San
THE MESOCYCLONE EVOLUTION OF THE WARREN, OKLAHOMA TORNADOES By Timothy P. Marshall and Erik N. Rasmussen (Reprinted from the 12th Conference on Severe Local Storms, American Meteorological Society, San
This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air. 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development
 Stability & Cloud Development This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development Stability & Movement A rock,
Stability & Cloud Development This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development Stability & Movement A rock,
The Nature of Storms. What You ll Learn How thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes
 13 What You ll Learn How thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes form. What the effects of severe weather are. How repetitive weather patterns can cause droughts, floods, and other hazards. The Nature
13 What You ll Learn How thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes form. What the effects of severe weather are. How repetitive weather patterns can cause droughts, floods, and other hazards. The Nature
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools
 Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Weather: 4.H.3 Weather and Classical Instruments Grade
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Weather: 4.H.3 Weather and Classical Instruments Grade
BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE
 NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF
NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF
FOURTH GRADE WEATHER
 FOURTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different reservoirs of water. LAB: Experimenting with surface tension and capillary
FOURTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different reservoirs of water. LAB: Experimenting with surface tension and capillary
Texas Department of Public Safety Texas Division of Emergency Management. Texas State Operations Center
 Texas Department of Public Safety Texas Division of Emergency Management Texas State Operations Center Situation Awareness Brief Saturday, July 20 th 2013 As of 0900 CDT Tropical Weather Outlook For the
Texas Department of Public Safety Texas Division of Emergency Management Texas State Operations Center Situation Awareness Brief Saturday, July 20 th 2013 As of 0900 CDT Tropical Weather Outlook For the
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form?
 Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Four Ways
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Four Ways
Humidity, Condensation, Clouds, and Fog. Water in the Atmosphere
 Humidity, Condensation, Clouds, and Fog or Water in the Atmosphere The Hydrologic Cycle Where the Water Exists on Earth Evaporation From the Oceans and Land The Source of Water Vapor for the Atmosphere
Humidity, Condensation, Clouds, and Fog or Water in the Atmosphere The Hydrologic Cycle Where the Water Exists on Earth Evaporation From the Oceans and Land The Source of Water Vapor for the Atmosphere
5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words
 5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words abiotic factor A nonliving part of an ecosystem. acceleration Change in velocity with respect to time. action The force one object applies to a second, as in Newton
5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words abiotic factor A nonliving part of an ecosystem. acceleration Change in velocity with respect to time. action The force one object applies to a second, as in Newton
Thunderstorm Basics. Updraft Characteristics (Rising Air) Downdraft Characteristics (Air Descends to the Ground)
 Thunderstorm Basics Updraft Characteristics (Rising Air) Cumulus Tower Upward Cloud Motion Updraft Dominant Downdraft/Updraft Downdraft Dominant Rain-Free Base Downdraft Characteristics (Air Descends to
Thunderstorm Basics Updraft Characteristics (Rising Air) Cumulus Tower Upward Cloud Motion Updraft Dominant Downdraft/Updraft Downdraft Dominant Rain-Free Base Downdraft Characteristics (Air Descends to
Hurricanes: Nature's Wildest Storms by Erin Ryan
 Name: : Nature's Wildest Storms by Erin Ryan You may already know that hurricanes are major tropical storms that can cause devastating waves, wind, and rain. They happen during Hurricane Season, which
Name: : Nature's Wildest Storms by Erin Ryan You may already know that hurricanes are major tropical storms that can cause devastating waves, wind, and rain. They happen during Hurricane Season, which
Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air
 LESSON 4 Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air INTRODUCTION How can a hang glider stay up in the air for hours without a motor? How can a bird soar over an open field without flapping its wings? They can
LESSON 4 Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air INTRODUCTION How can a hang glider stay up in the air for hours without a motor? How can a bird soar over an open field without flapping its wings? They can
8.5 Comparing Canadian Climates (Lab)
 These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
ATMS 310 Jet Streams
 ATMS 310 Jet Streams Jet Streams A jet stream is an intense (30+ m/s in upper troposphere, 15+ m/s lower troposphere), narrow (width at least ½ order magnitude less than the length) horizontal current
ATMS 310 Jet Streams Jet Streams A jet stream is an intense (30+ m/s in upper troposphere, 15+ m/s lower troposphere), narrow (width at least ½ order magnitude less than the length) horizontal current
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms
 Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Four Ways
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Four Ways
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents
 How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
Stability and Cloud Development. Stability in the atmosphere AT350. Why did this cloud form, whereas the sky was clear 4 hours ago?
 Stability and Cloud Development AT350 Why did this cloud form, whereas the sky was clear 4 hours ago? Stability in the atmosphere An Initial Perturbation Stable Unstable Neutral If an air parcel is displaced
Stability and Cloud Development AT350 Why did this cloud form, whereas the sky was clear 4 hours ago? Stability in the atmosphere An Initial Perturbation Stable Unstable Neutral If an air parcel is displaced
Convection Currents in the Air
 LESSON 5 Convection Currents in the Air Hold on to your hat! Whether you are walking along a beach or flying a kite in an open field, a really windy day can make you feel like you are about to be swept
LESSON 5 Convection Currents in the Air Hold on to your hat! Whether you are walking along a beach or flying a kite in an open field, a really windy day can make you feel like you are about to be swept
If wispy, no significant icing or turbulence. If dense or in bands turbulence is likely. Nil icing risk. Cirrocumulus (CC)
 Cirrus (CI) Detached clouds in the form of delicate white filaments or white patches or narrow bands. These clouds have a fibrous or hair like appearance, or a silky sheen or both. with frontal lifting
Cirrus (CI) Detached clouds in the form of delicate white filaments or white patches or narrow bands. These clouds have a fibrous or hair like appearance, or a silky sheen or both. with frontal lifting
State Of Wisconsin Department of Military Affairs
 State Of Wisconsin Department of Military Affairs Division of Emergency Management Brian M. Satula Administrator Scott Walker Governor For more information contact: Tod Pritchard Office: 608-242-3324 Cell:
State Of Wisconsin Department of Military Affairs Division of Emergency Management Brian M. Satula Administrator Scott Walker Governor For more information contact: Tod Pritchard Office: 608-242-3324 Cell:
Weather Radar Basics
 Weather Radar Basics RADAR: Radio Detection And Ranging Developed during World War II as a method to detect the presence of ships and aircraft (the military considered weather targets as noise) Since WW
Weather Radar Basics RADAR: Radio Detection And Ranging Developed during World War II as a method to detect the presence of ships and aircraft (the military considered weather targets as noise) Since WW
A SEVERE WEATHER CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE WILMINGTON, NC WFO COUNTY WARNING AREA
 A SEVERE WEATHER CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE WILMINGTON, NC WFO COUNTY WARNING AREA Carl R. Morgan National Weather Service Wilmington, NC 1. INTRODUCTION The National Weather Service (NWS) Warning Forecast Office
A SEVERE WEATHER CLIMATOLOGY FOR THE WILMINGTON, NC WFO COUNTY WARNING AREA Carl R. Morgan National Weather Service Wilmington, NC 1. INTRODUCTION The National Weather Service (NWS) Warning Forecast Office
Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds
 Name: Pd: Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a large collection of very tiny droplets of water or ice crystals. The
Name: Pd: Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a large collection of very tiny droplets of water or ice crystals. The
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE!
 FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
CLIMATE OF RWANDA. Overview. Linked to other lessons
 Geography S6 GENERAL PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF RWANDA Lesson 75 Developed by (Niwagaba Innocent) Subtopic Climate and factors influencing it in Rwanda Specific Objectives The learners must be able to: Describe
Geography S6 GENERAL PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF RWANDA Lesson 75 Developed by (Niwagaba Innocent) Subtopic Climate and factors influencing it in Rwanda Specific Objectives The learners must be able to: Describe
6. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows the average monthly temperature of two cities A and B.
 1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
Formation & Classification
 CLOUDS Formation & Classification DR. K. K. CHANDRA Department of forestry, Wildlife & Environmental Sciences, GGV, Bilaspur What is Cloud It is mass of tiny water droplets or ice crystals or both of size
CLOUDS Formation & Classification DR. K. K. CHANDRA Department of forestry, Wildlife & Environmental Sciences, GGV, Bilaspur What is Cloud It is mass of tiny water droplets or ice crystals or both of size
Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow
 AS/A2-Level Geography Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow Learning Objectives: To describe and explain the weather associated with high and low pressure systems and their links to extreme
AS/A2-Level Geography Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow Learning Objectives: To describe and explain the weather associated with high and low pressure systems and their links to extreme
Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns
 Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you should
Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you should
Perth Academy. Geography Department
 Perth Academy Geography Department Natural Hazards Tropical Storms Natural Hazards Natural Hazards affect a large percentage of the world s population. Despite the damage and destruction caused, there
Perth Academy Geography Department Natural Hazards Tropical Storms Natural Hazards Natural Hazards affect a large percentage of the world s population. Despite the damage and destruction caused, there
-ma, we see that the acceleration of a falling object (g) is g=g*m
 Forces of Motion And Sir Isaac Newton Sir Isaac Newton, the father of mechanics, is one of the most important scientists who ever lived, changing the standards by which scientists think. His genius in
Forces of Motion And Sir Isaac Newton Sir Isaac Newton, the father of mechanics, is one of the most important scientists who ever lived, changing the standards by which scientists think. His genius in
Wind shear - poses challenges and dangers at the most critical stages of flight
 Wind shear - poses challenges and dangers at the most critical stages of flight Authored and illustrated by Sari Jay June 2009 Introduction Over 40 years ago, in the 1960s, low level wind shear was just
Wind shear - poses challenges and dangers at the most critical stages of flight Authored and illustrated by Sari Jay June 2009 Introduction Over 40 years ago, in the 1960s, low level wind shear was just
Anyone Else Notice That Its Been Windy Lately?
 National Weather Service Aberdeen, South Dakota January 2014 Inside this issue: Has it Been Windy Lately or What? 2013 Year in Review 2013 Year in Review (cont.) 1 2 3 Has it Been Windy Lately or What?
National Weather Service Aberdeen, South Dakota January 2014 Inside this issue: Has it Been Windy Lately or What? 2013 Year in Review 2013 Year in Review (cont.) 1 2 3 Has it Been Windy Lately or What?
UNIT IV--TEMPERATURE-MOISTURE RELATIONSHIP
 UNIT IV--TEMPERATURE-MOISTURE RELATIONSHIP Weather is the most variable and often the most critical determinant of fire behavior. This is the first of several units that will deal with weather and its
UNIT IV--TEMPERATURE-MOISTURE RELATIONSHIP Weather is the most variable and often the most critical determinant of fire behavior. This is the first of several units that will deal with weather and its
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Clouds. A simple scientific explanation for the weather-curious. By Kira R. Erickson
 Clouds A simple scientific explanation for the weather-curious By Kira R. Erickson Table of Contents 1 3 4 INTRO 2 Page 3 How Clouds Are Formed Types of Clouds Clouds and Weather More Information Page
Clouds A simple scientific explanation for the weather-curious By Kira R. Erickson Table of Contents 1 3 4 INTRO 2 Page 3 How Clouds Are Formed Types of Clouds Clouds and Weather More Information Page
Cover Photo - Alan Moller
 Cover Photo - Alan Moller The Spotter s Role I. INTRODUCTION The National Weather Service (NWS) has a number of devices for detecting severe thunderstorms. Included in these are radar, satellite, and lightning
Cover Photo - Alan Moller The Spotter s Role I. INTRODUCTION The National Weather Service (NWS) has a number of devices for detecting severe thunderstorms. Included in these are radar, satellite, and lightning
Water & Climate Review
 Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
Chapter 2. Aviation Weather Hazards. Icing. Introduction
 LAKP-Ontario and Quebec 9 Chapter 2 Aviation Weather Hazards Introduction Throughout its history, aviation has had an intimate relationship with the weather. Time has brought improvements - better aircraft,
LAKP-Ontario and Quebec 9 Chapter 2 Aviation Weather Hazards Introduction Throughout its history, aviation has had an intimate relationship with the weather. Time has brought improvements - better aircraft,
Chapter 3: Weather Map. Weather Maps. The Station Model. Weather Map on 7/7/2005 4/29/2011
 Chapter 3: Weather Map Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described weather conditions. Local weathers are affected by weather pattern. We need to see all the numbers describing weathers at many
Chapter 3: Weather Map Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described weather conditions. Local weathers are affected by weather pattern. We need to see all the numbers describing weathers at many
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist. Introduction. Climatic controls
 Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Temperature affects water in the air.
 KEY CONCEPT Most clouds form as air rises and cools. BEFORE, you learned Water vapor circulates from Earth to the atmosphere Warm air is less dense than cool air and tends to rise NOW, you will learn How
KEY CONCEPT Most clouds form as air rises and cools. BEFORE, you learned Water vapor circulates from Earth to the atmosphere Warm air is less dense than cool air and tends to rise NOW, you will learn How
In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. aero quarterly qtr_01 10
 In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. 22 avoiding convective Weather linked to Ice-crystal Icing engine events understanding
In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. 22 avoiding convective Weather linked to Ice-crystal Icing engine events understanding
GEOLOGY 10 Extended Notes #6 The Atmosphere (LT Chapter 11)
 GEOLOGY 10 Extended Notes #6 The Atmosphere (LT Chapter 11) Weather vs. climate? Composition of Air Major Gases Mostly N and O (Fig. 11.2 on p. 283). Additives Water vapor the source of clouds and precipitation
GEOLOGY 10 Extended Notes #6 The Atmosphere (LT Chapter 11) Weather vs. climate? Composition of Air Major Gases Mostly N and O (Fig. 11.2 on p. 283). Additives Water vapor the source of clouds and precipitation
Regional Forecast Center Timişoara 15. Gh. Adam St., Timişoara, Romania, e-mail: cristi_nichita2004@yahoo.com
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Seria Geografie Tom XX, no. 2/2010 (December), pp 197-203 ISSN 1221-1273, E-ISSN 2065-3409 Article no. 202106-492 SOME DOPPLER RADAR FEATURES OF SEVERE WEATHER IN SUPERCELLS
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Seria Geografie Tom XX, no. 2/2010 (December), pp 197-203 ISSN 1221-1273, E-ISSN 2065-3409 Article no. 202106-492 SOME DOPPLER RADAR FEATURES OF SEVERE WEATHER IN SUPERCELLS
Climate Extremes Research: Recent Findings and New Direc8ons
 Climate Extremes Research: Recent Findings and New Direc8ons Kenneth Kunkel NOAA Cooperative Institute for Climate and Satellites North Carolina State University and National Climatic Data Center h#p://assessment.globalchange.gov
Climate Extremes Research: Recent Findings and New Direc8ons Kenneth Kunkel NOAA Cooperative Institute for Climate and Satellites North Carolina State University and National Climatic Data Center h#p://assessment.globalchange.gov
ENVIRONMENTAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: CLIMATE SYSTEM Vol. II - Low-Latitude Climate Zones and Climate Types - E.I. Khlebnikova
 LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
The Official Newsletter of the National Weather Service in Amarillo
 The Dryline The Official Newsletter of the National Weather Service in Amarillo TEXAS COUNTY EARNS STORMREADY RECOGNITION FROM TORNADOES TO FLOODS, TEXAS COUNTY IS PREPARED By Steve Drillette, Warning
The Dryline The Official Newsletter of the National Weather Service in Amarillo TEXAS COUNTY EARNS STORMREADY RECOGNITION FROM TORNADOES TO FLOODS, TEXAS COUNTY IS PREPARED By Steve Drillette, Warning
Clouds, Fog, & Precipitation
 firecatching.blogspot.com Kids.brittanica.com Clouds and fog are physically the same just location is different Fog is considered a stratus cloud at or near the surface What does one see when looking at
firecatching.blogspot.com Kids.brittanica.com Clouds and fog are physically the same just location is different Fog is considered a stratus cloud at or near the surface What does one see when looking at
Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE)
 Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Basic Lesson 3: Using Microsoft Excel to Analyze Weather Data: Topography and Temperature Introduction This lesson uses NCDC data to compare
Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Basic Lesson 3: Using Microsoft Excel to Analyze Weather Data: Topography and Temperature Introduction This lesson uses NCDC data to compare
Pressure. Curriculum for Excellence. Weather and Climate Cross-curricular project Section 2. Background Information:
 Curriculum for Excellence Weather and Climate Cross-curricular project Section 2 Pressure Background Information: Air pressure is the force exerted by air particles. The air around us pushes on us and
Curriculum for Excellence Weather and Climate Cross-curricular project Section 2 Pressure Background Information: Air pressure is the force exerted by air particles. The air around us pushes on us and
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
Floods are too much water on normally dry land. Rivers can flood after heavy rain has fallen over a long period of time. River flooding can last
 Floods are too much water on normally dry land. Rivers can flood after heavy rain has fallen over a long period of time. River flooding can last weeks or longer. River floods usually occur slowly enough
Floods are too much water on normally dry land. Rivers can flood after heavy rain has fallen over a long period of time. River flooding can last weeks or longer. River floods usually occur slowly enough
Atmospheric Stability & Cloud Development
 Atmospheric Stability & Cloud Development Stable situations a small change is resisted and the system returns to its previous state Neutral situations a small change is neither resisted nor enlarged Unstable
Atmospheric Stability & Cloud Development Stable situations a small change is resisted and the system returns to its previous state Neutral situations a small change is neither resisted nor enlarged Unstable
