PQRI MEASURE CODING AND REPORTING PRINCIPLES
|
|
|
- Martina Hart
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PQRI MEASURE CODING AND REPORTING PRINCIPLES PQRI Measure Denominators and Numerators Each PQRI measure consists of two major components: 1. A denominator that describes the eligible cases for a measure (the eligible patient population associated with a measure s numerator) 2. A numerator that describes the clinical action required by the measure for reporting and performance measure denominators and numerators are further specified by specific codes, usually ICD-9 and CPT Category I codes for denominators and CPT Category II codes or G codes (where CPT Category II codes are not yet available) for numerators. Each measure is unique, so it is important to review and understand each measure s specifications, which provide definitions and specific instructions for coding and reporting measure components. Use of CPT II Modifiers CPT II modifiers are unique to CPT II codes and may be used to report PQRI measures by appending the appropriate modifier to a CPT II code if allowed for a given measure. The modifiers for a code are mutually exclusive and their use is guided by the measure s coding instructions, which are included in the numerator coding section of the PQRI Measure Specifications. Use of the modifiers is unique to CPT II codes and may not be used with other types of CPT codes. Descriptions of each modifier are provided below to help identify circumstances when the use of an exclusion modifier may be appropriate. Note that in a payfor-reporting model, accurate reporting on all selected applicable measures counts the same, whether reporting that the clinical action was performed or not. CPT II code modifiers fall into two categories, exclusion modifiers and the 8P reporting modifier. 1. Exclusion modifiers may be appended to a CPT II code to indicate that an action specified in the measure was not provided due to medical, patient, or system reason(s) documented in the medical record. These modifiers serve as denominator exclusions for the purpose of measuring performance. Some measures do not provide for performance exclusions. Reasons for appending a performance measure exclusion modifier fall into one of three categories: 1P exclusion modifier due to medical reasons Examples include: not indicated (absence of organ/limb, already received/performed); contraindicated (patient allergic history, potential adverse drug interaction) 2P exclusion modifier due to patient reasons Examples include: patient declined; economic, social, or religious reasons 3P exclusion modifier due to system reasons Examples include: resources to perform the services not available; insurance or coverage/payer-related limitations; other reasons attributable to health care delivery system 2. Reporting modifier 8P is available for use only with CPT II codes to facilitate reporting an eligible case when an action described in a measure is not performed and the reason is not specified. Instructions for appending this modifier to CPT Category II codes are included in applicable measures. Use of the 8P reporting modifier indicates that the patient is eligible for the measure; however, there is no indication in the record that the action described in the measure was performed, nor was there any documented reason attributable to the exclusion modifiers. 8P reporting modifier - action not performed, reason not otherwise specified The 8P modifier facilitates reporting an eligible case on a given measure when the clinical action does not apply to a specific encounter. Eligible professionals can use the 5-1
2 8P modifier to receive credit for successful reporting but will not receive credit for performance. For example, a patient with diabetes may present to a clinician for reasons that do not involve glycemic control, hypertension, or cholesterol management. However, the claim for services for that encounter will contain ICD-9 and CPT codes that will draw the patient into the diabetes measures denominator during analysis. The 8P modifier serves to include the patient in the numerator when reporting rates are calculated for PQRI. Reporting Frequency and Performance Timeframes Each measure includes a reporting frequency requirement for each denominator-eligible patient seen during the reporting period. The reporting frequency is described in the instructions: Report one-time only Report once for each procedure performed Report once for each acute episode A measure s performance timeframe is defined in the measure s description and is distinct from the reporting frequency requirement. The performance timeframe, unique to each measure, delineates the timeframe in which the clinical action described in the numerator may be accomplished. Performance timeframes may be stated as within 12 months, or most recent. This means that: 1. The clinical action in the numerator need be performed only once during a 12-month period for each patient seen during the reporting period 2. The quality code need be reported only one time for each patient by each eligible professional caring for the patient who has chosen to report that measure during the reporting period If the measure calls for a clinical test result, then the most recent test result only needs to be obtained, assessed, and reported one time per reporting period. A test does not need to have been performed within the reporting period, nor does it need to have been performed by the same eligible professional. Performance timeframes may also be tied to a specific clinical event that requires reporting each time the event occurs within the reporting period. The following are examples of measures reported each time the clinical action described by the measure numerator is taken: Procedure-related measures require reporting each time the procedure is performed and have distinct performance timeframes tied to them. The date of service is the date that is used to report the measure. Examples are perioperative care or imaging measures. Chronic care measures, such as those that call for prescribing a medication, require the eligible professional to verify whether the medication is current and being taken by the patient. A new prescription is not required to meet the measure requirement unless it is clinically indicated. Acute care measures are tied to specific episodes of acute care and require reporting each time an acute event occurs. Examples are measures related to hospitalizations, fractures and osteoporosis management, or stroke measures. Claims-Based Reporting Principles The following principles apply to the reporting of quality-data codes for PQRI measure The CPT Category II code, which supplies the numerator, must be reported on the same claim form as the payment codes, usually ICD-9 and CPT Category I codes, which supply the denominator. Quality-data codes must be submitted with a line item charge of zero dollars ($0.00) at the time the associated covered service is performed.! The submitted charge field cannot be blank. 5-2
3 ! The line item charge should be $0.00.! If a system does not allow a $0.00 line item charge, use a small amount such as $0.01! Entire claims with a zero charge will be rejected. (Total charge for the claim cannot be $0.00)! Quality data code line items will be denied for payment, but are then passed through the claims processing system for PQRI analysis. Multiple eligible professionals quality-data codes can be reported on the same claim. Multiple CPT Category II codes for multiple measures that are applicable to a patient visit can be reported on the same claim, as long as the corresponding denominator codes are also line items on that claim. The individual NPI of the participating eligible professional(s) must be properly used on the claim. Timeliness of Quality Data Submission Claims processed by the Carrier/MAC must reach the national Medicare claims system data warehouse (National Claims History file) by February 29, 2008 to be included in the analysis. Claims for services furnished toward the end of the reporting period should be filed promptly. Claims that are resubmitted only to add quality-data codes will not be included in the analysis. Successful Reporting The 2007 PQRI incentive payment is an all-or-nothing bonus (subject to cap) based on successful reporting. Eligible professionals need not enroll or file an intent to participate for the PQRI. Eligible professionals can participate by reporting the appropriate quality measure data on claims submitted to their Medicare claims processing contractor. In order to satisfactorily meet the requirements of the program and receive the bonus payment, certain reporting thresholds must be met. When four or more measures are applicable to the services provided by an eligible professional, the 80% threshold must be met on at least three of the measures reported. Good news for those physicians practicing in a group practice, not all physicians in the group must participate in PQRI to be eligible for the bonus payment. Individual analysis will be done using the individual physician s national provider identifier (NPI) to determine satisfactory reporting and the bonus payment calculation. Thus, physicians must bill with an NPI to participate in PQRI. The potential 1.5 percent incentive payment will be paid in mid-2008 as a lump-sum bonus payment made to the practice at the Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) level. According to the CMS website, the NPI is the only unique provider enumerator that can be used by the CMS PQRI analysis contractor to properly identify eligible physicians at the individual-physician level. The performing professional s NPI must be used for the quality-data codes and related services. For claims submitted via the ASC X12N 837 professional health care claim transaction, the group practice NPI is placed in the provider billing segment, loop 2010AA, and the performing professional s NPI is placed in loop 2420A. For claims submitted via the CMS 1500 form, the performing professional s NPI is placed on the individual line item. Placing the performing eligible professional s NPI on the individual line item will allow the analysis of successful reporting and the bonus payment calculation to be performed at the individual level, though payment will be made at the TIN level. Bonus Payment Participating eligible professionals who successfully report may earn a 1.5% bonus, subject to cap. The potential 1.5% bonus will be based on allowed charges for covered professional services: 5-3
4 1. Furnished during the reporting period of July 1 through December 31, 2007, 2. Received into the CMS National Claims History (NCH) file by February 29, 2008 (Joy s comment: claim should be received by the Carrier no later than February 28, 2008), and 3. Paid under the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (Joy s comment: HCPCS J codes for drugs are not subject to the bonus). Because claims processing times may vary by time of the year and Medicare Carrier/Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC), physicians should submit claims from the end of 2007 promptly, so that those claims will reach the NCH file by February 29, Bonuses will be paid as a lump sum in mid There is no beneficiary copayment or notice to the beneficiary regarding the bonus payments. A payment cap that would reduce the potential bonus below 1.5% of allowed charges may apply in situations where a physician reports relatively few instances of quality measure data. The physician s cap will be calculated by multiplying: (1) the physician s total instances of reporting quality data for all measures (not limited only to measures meeting the 80% threshold), by (2) a constant of 300%, and by (3) the national average per measure payment amount. The national average per measure payment amount is one value for all measures and all participants that is calculated by dividing: (1) the total amount of allowed charges under the Physician Fee Schedule for all covered professional services furnished during the reporting period on claims for which quality measures were reported by all participants in the program by (2) the total number of instances for which data were reported by all participants in the program for all measures during the reporting period. (Note that the national average per measure payment amount calculation only takes into account the charges on claims for which quality measures were reported, whereas the individual bonus calculation takes into account charges for all services furnished during the reporting period.) While the purpose of the cap is clear, it is not possible to determine the impact of the cap until the national average per measure payment amount can be calculated after the end of the reporting period. CMS recommends that physicians report on every quality measure that is applicable to their patient populations to: (1) increase the likelihood that they will reach the 80% satisfactorily reporting requirement for the requisite number of measures and (2) increase the likelihood that they will not be affected by the bonus payment cap Physician Quality Reporting Initiative Measures - Not All Inclusive 1) Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control in Type 1 or 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Percentage of patients aged years with diabetes (type 1 or type 2) who had most recent hemoglobin A1c greater than 9.0% - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. The performance period for this measure is 12 months. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide services for the primary management of diabetes mellitus will submit this measure ICD-9: , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit) (office/outpatient visit); (home visit); (nursing facility); (domiciliary); and G0270-G0271 (nutrition therapy) Most recent hemoglobin A1c level > 9.0% (3046F) Most recent hemoglobin A1c level < 7.0% (3044F) Most recent hemoglobin A1c level 7.0% to 9.0% (3045F) Hemoglobin A1c not performed during last 12 months reason not specified (3046F-8P) 2) Low Density Lipoprotein Control in Type 1 or 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Percentage of patients aged years with diabetes (type 1 or type 2) who had most recent LDL-C level in control (less than 100 mg/dl) - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. The performance period for this measure is 12 months. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide services for the primary management of diabetes mellitus will submit this measure. 5-4
5 ICD-9: , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit) (office/outpatient visit); (home visit); (nursing facility); (domiciliary); and G0270-G0271 (nutrition therapy) Most recent LDL-C < 100 mg/dl (3048F) Most recent LDL-C mg/dl (3049F) Most recent LDL-C 130 mg/dl (3050F) LDL-C level not performed during last 12 months reason not specified (3048F-8P) 3) High Blood Pressure Control in Type 1 or 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Percentage of patients aged years with diabetes (type 1 or type 2) who had most recent blood pressure in control (less than 140/80 mm Hg) - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. The performance period for this measure is 12 months. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide services for the primary management of diabetes mellitus will submit this measure. ICD-9: , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit); (home visit); (nursing facility); (domiciliary); and G0270-G0271 (nutrition therapy) Systolic codes Most recent systolic blood pressure < 130 mm Hg (3074F) Most recent systolic blood pressure 130 to 139 mm Hg (3075F) Most recent systolic blood pressure > 140 mm Hg (3077F) AND Diastolic codes Most recent diastolic blood pressure < 80 mm Hg (3078F) Most recent diastolic blood pressure mm Hg (3079F) Most recent diastolic blood pressure > 90 mm Hg (3080F) OR Blood pressure measurement not performed, reason not specified (2000F-8P) 4) Screening for Future Fall Risk - Percentage of patients aged 65 years and older who were screened for future fall risk (patients are considered at risk for future falls if they have had 2 or more falls in the past year or any fall with injury in the past year) at least once within 12 months - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. This measure is appropriate for use in all nonacute settings (excludes emergency departments and acute care hospitals). It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care for the patient will submit this measure. ICD-9: None specified - CPT: (PT eval); (office/outpatient visit), (nursing facility), (domiciliary), (domiciliary), (home visits), and (preventive), (preventive counseling), Definition: A fall is defined as a sudden, unintentional change in position causing an individual to land at a lower level, on an object, the floor, or the ground, other than as a consequence of sudden onset of paralysis, epileptic seizure, or overwhelming external force (Tinetti). Screening for future fall risk; documentation of 2 or more falls in the past year or any fall with injury in the past year (1100F) Screening for future fall risk; documentation of no falls in the past year or only 1 fall without injury in the past year (1101F) Screening for future fall risk not performed for medical reasons (1100F-1P) Screening for future fall risk not performed, reason not specified (1100F-8P) 5) Heart Failure: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy for Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVSD) - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) who were prescribed ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for all heart failure patients seen during the reporting period. The left ventricular systolic dysfunction may be 5-5
6 determined by quantitative or qualitative assessment. Examples of a quantitative or qualitative assessment may include an echocardiogram: 1) that provides a numerical value of left ventricular systolic dysfunction or 2) that uses descriptive terms such as moderately or severely depressed left ventricular dysfunction. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary management of patients with heart failure will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , ; , , , , , ; 428.0, 428.1, , , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), 99238, (discharge), (office/outpatient consult), (nursing facility), (domiciliary), (home visit) OR AND ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy prescribed and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40% or documentation of moderately or severely depressed left ventricular systolic function (4009F and 3021F) ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy not prescribed for medical reason (4009F-1P) ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy not prescribed for patient reasons (4009F-2P) ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy not prescribed for system reasons (4009F-3P) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40% or documentation of moderately or severely depressed left ventricular systolic function (3021F) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) >40% or documentation as normal or mildly depressed left ventricular systolic function (3022F) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was not performed or documented reason not otherwise specified (3021F-8P) OR ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy not prescribed reason not specified and left ventricular ejection fraction <40% or documentation of moderately or severely depressed left ventricular systolic dysfunction (4009F- 8P and 3021F) 6) Oral Antiplatelet Therapy Prescribed for Patients with Coronary Artery Disease - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease who were prescribed oral antiplatelet therapy - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide the primary management of patients with coronary artery disease will submit this measure. - Oral antiplatelet therapy consists of aspirin, clopidogrel/plavix, or combination of aspirin and dipyridamole/aggrenox. ICD-9: , 414.8, 414.9, ; 412, , , V45.81, V45.82 and CPT (office/outpatient visit); 99238, (discharge), (office/outpatient consult), (nursing facility), (domiciliary), (home visit) Oral antiplatelet therapy prescribed (4011F) Documentation of medical reason(s) for not prescribing oral antiplatelet therapy (4011F-1P) Documentation of patient reason(s) for not prescribing oral antiplatelet therapy (4011F-2P) Documentation of system reason(s) for not prescribing oral antiplatelet therapy (4011F-3P) Oral antiplatelet therapy not prescribed reason not specified (4011F-8P) 7) Beta-blocker Therapy for Coronary Artery Disease Patients with Prior Myocardial Infarction (MI) - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease and prior myocardial infarction (MI) who were prescribed beta-blocker therapy - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide the primary management of patients with coronary artery disease with prior myocardial infarction (MI) will submit this measure. ICD-9: , 414.8, 414.9, 411.0, 411.1, , , 413.0, 413.1, 413.9, V45.81, V45.82, *, 412* and Patients who had a prior MI at any time ICD-9: , 412 and CPT (office/outpatient visit), 99238, (discharge), (office/outpatient consult), (nursing facility), (domiciliary), (home visit) *Denominator inclusion for this measure requires the presence of a prior MI diagnosis AND at least one E/M code during the measurement period. Diagnosis codes for Coronary Artery Disease (which include MI diagnosis codes) may also accompany the MI diagnosis code, but are not required for inclusion in the measure. 5-6
7 Beta-blocker therapy prescribed (4006F) Documentation of medical reason(s) for not prescribing beta-blocker therapy (4006F-1P) Documentation of patient reason(s) for not prescribing beta-blocker therapy (4006F-2P) Documentation of system reason(s) for not prescribing beta-blocker therapy (4006F-3P) Beta-blocker therapy not prescribed, reason not specified (4006F-8P) 8) Heart Failure: Beta-blocker Therapy for Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of heart failure who also have left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) and who were prescribed beta-blocker therapy - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for all heart failure patients seen during the reporting period. The left ventricular systolic dysfunction may be determined by quantitative or qualitative assessment. Examples of a quantitative or qualitative assessment may include an echocardiogram: 1) that provides a numerical value of left ventricular systolic dysfunction or 2) that uses descriptive terms such as moderately or severely depressed left ventricular dysfunction. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary management of patients with heart failure will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , ; , , , , , ; 428.0, 428.1, , , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), (home visit), (nursing facility), (domiciliary) Beta blocker therapy prescribed and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40% or documentation of moderately or severely depressed left ventricular systolic function (4006F and 3021F) OR Documentation of medical reason(s) for not prescribing beta-blocker therapy (4006F-1P) Documentation of patient reason(s) for not prescribing beta-blocker therapy (4006F-2P) Documentation of system reason(s) for not prescribing beta-blocker therapy (4006F-3P) AND Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40% or documentation of moderately or severely depressed left ventricular systolic function (3021F) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 40% or documentation as normal or mildly depressed left ventricular systolic function (3022F) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was not performed or documented, reason not otherwise specified (3021F-8P) OR Beta-blocker therapy was not prescribed, reason not otherwise specified and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40% or documentation of moderately or severely depressed left ventricular systolic function (4006F-8P and 3021F) 9) Antidepressant Medication During Acute Phase for Patients with New Episode of Major Depression - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older diagnosed with new episode of major depressive disorder (MDD) and documented as treated with antidepressant medication during the entire 84-day (12 week) acute treatment phase - This measure is to be reported for each occurrence of MDD during the reporting period. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide the primary management of patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , 298.0, 300.4, 309.1, 311 and CPT: (office/outpatient visit); 90801, 90802, , (psychiatry) Definition: A new episode is defined as a patient with major depression who has not been seen or treated for major depression by any practitioner in the prior 4 months. A new episode can either be a recurrence for a patient with prior major depression or a patient with a new onset of major depression. 5-7
8 Report G8126: 1) For all patients with a diagnosis of Major Depression, New Episode who were prescribed a full 12 week course of antidepressant medication OR 2) At the completion of a 12 week course of antidepressant medication. Patient with new episode of MDD documented as being treated with antidepressant medication during the entire 12 week acute treatment phase (G8126) Patient with new episode of MDD not documented as being treated with antidepressant medication during the entire 12 week acute treatment phase (G8127) Clinician documented that patient with a new episode of MDD was not an eligible candidate for antidepressant medication treatment or patient did not have a new episode of MDD (G8128) 39) Screening or Therapy for Osteoporosis for Women Aged 65 Years and Older - Percentage of female patients aged 65 years and older who have a central dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement ordered or performed at least once since age 60 or pharmacologic therapy prescribed within 12 months - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once during the reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. Female patients aged 65 years and older should have a central DXA measurement ordered or performed at least once since the time they turned 60 years or have pharmacologic therapy prescribed to prevent or treat osteoporosis. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care or care for treatment of fracture or osteoporosis will submit this measure. ICD-9: No specific diagnosis codes and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), and (preventive), (preventive counseling) Definition: Pharmacologic Therapy: U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved pharmacologic options for osteoporosis prevention and/or treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis include, in alphabetical order: bisphosphonates (alendronate, ibandronate, and risedronate), calcitonin, estrogens (estrogens and/or hormone therapy), parathyroid hormone [PTH (1-34), teriparatide], and selective estrogen receptor modules or SERMs (raloxifene). Central Dual-energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) ordered (3096F) Central Dual-energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) results documented (3095F) Pharmacologic therapy (other than minerals/vitamins) for osteoporosis prescribed (4005F) Documentation of medical reason(s) for not ordering or performing a central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement or not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (3096F-1P) Documentation of patient reason(s) for not ordering or performing central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement or not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (3096F-2P) Documentation of system reason(s) for not ordering or performing central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement or not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (3096F-3P) Central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement was not ordered or performed and a pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis was not prescribed reason not otherwise specified (3096F-8P) 40) Osteoporosis: Management Following Fracture - Percentage of patients aged 50 years and older with fracture of the hip, spine, or distal radius who had a central dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement ordered or performed or pharmacologic therapy prescribed - This measure is to be reported after each occurrence of a fracture during the reporting period. Patients with a fracture of the hip, spine, or distal radius should have a central DXA measurement ordered or performed or pharmacologic therapy prescribed. The management (DXA ordered or performed or pharmacologic therapy prescribed) should occur within three months of the initial visit with the reporting clinician following the fracture. Patients with documentation of prior central DXA measurement or already receiving pharmacologic therapy would automatically meet the intent of this measure. It is anticipated that clinicians who manage the primary or ongoing care for osteoporosis or osteoporosis related fracture(s) will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , , 805.2, 805.4, 805.6, 805.8, , , , , , , , , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office consult) 5-8
9 Definition: Pharmacologic Therapy: U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved pharmacologic options for osteoporosis prevention and/or treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis include, in alphabetical order: bisphosphonates (alendronate, ibandronate, and risedronate), calcitonin, estrogens (estrogens and/or hormone therapy), parathyroid hormone [PTH (1-34), teriparatide], and selective estrogen receptor modules or SERMs (raloxifene). Central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) ordered (3096F) Central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) results documented (3095F) Pharmacologic therapy (other than minerals/vitamins) for osteoporosis prescribed (4005F) Documentation of medical reason(s) for not ordering or performing a central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement or not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (3096F-1P) Documentation of patient reason(s) for not ordering or performing a central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement or not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (3096F-2P) Documentation of system reason(s) for not ordering or performing a central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement or not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (3096F-3P) Central dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement was not ordered or performed and a pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis was not prescribed reason not otherwise specified (3096F-8P) 41) Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy - Percentage of patients aged 50 years and older with a diagnosis of osteoporosis who were prescribed pharmacologic therapy within 12 months - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. Patients with a diagnosis of osteoporosis should be prescribed pharmacologic therapy to treat osteoporosis. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide services for patients with the diagnosis of osteoporosis will submit this measure. ICD-9: , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), and (preventive), (preventive counseling) Definition: Pharmacologic Therapy: U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved pharmacologic options for osteoporosis prevention and/or treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis include, in alphabetical order: bisphosphonates (alendronate, ibandronate, and risedronate), calcitonin, estrogens (estrogens and/or hormone therapy), parathyroid hormone [PTH (1-34), teriparatide], and selective estrogen receptor modules or SERMs (raloxifene). 1P) Pharmacologic therapy (other than minerals/vitamins) for osteoporosis prescribed (4005F) Documentation of medical reason(s) for not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (4005F- Documentation of patient reason(s) for not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (4005F-2P) Documentation of system reason for not prescribing pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis (4005F-3P) Pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis was not prescribed reason not otherwise specified (4005F-8P) 42) Osteoporosis: Counseling for Vitamin D, Calcium Intake, and Exercise - Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of osteoporosis who are either receiving both calcium and vitamin D or have been counseled regarding both calcium and vitamin D intake, and exercise at least once within 12 months - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. Patients with a diagnosis of osteoporosis should be receiving both calcium and vitamin D or had counseling regarding their use and counseled on exercise. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide services for patients with the diagnosis of osteoporosis will submit this measure. ICD-9: , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), and (preventive), (preventive counseling) Documentation of receipt of counseling on exercise AND either both calcium and vitamin D use or counseling regarding both calcium and vitamin D use (4019F) Documentation of medical reason(s) for patient not receiving both calcium and vitamin D or and not needing counseling regarding both calcium and vitamin D intake, and exercise (e.g., patient has dementia and is unable to receive counseling) (4019F-1P) Receipt of counseling on exercise AND either both calcium and vitamin D use or counseling regarding both calcium and vitamin D use was not documented reason not otherwise specified (4019F-8P) 5-9
10 46) Medication Reconciliation - Percentage of patients aged 65 years and older discharged from any inpatient facility (e.g., hospital, skilled nursing facility, or rehabilitation facility) and seen within 60 days following discharge in the office by the physician providing on-going care who had a reconciliation of the discharge medications with the current medication list in the medical record documented - This measure is to be reported at an office visit occurring within 60 days of each inpatient facility discharge during the reporting period. This measure is appropriate for use in the ambulatory setting only. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary on-going care will submit this measure when a patient is seen in the office within 60 days following discharge from any inpatient facility. If a patient has not been discharged within the 60-day timeframe from an inpatient facility, there are no reporting requirements for this measure. ICD-9: No specific diagnosis code and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), and (preventive), (preventive counseling) Patient discharged from an inpatient facility within the last 60 days and discharge medications reconciled with the current medication list in outpatient medical record (1110F and 1111F) Patient discharged from an inpatient facility within the last 60 days and discharge medication not reconciled with current medication list in the medical record, reason not specified (1110F and 1111F-8P) 47) Advance Care Plan - Percentage of patients aged 65 years and older with documentation of a surrogate decision-maker or advance care plan in the medical record - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. This measure is appropriate for use in all healthcare settings. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care services for the patient will submit this measure. ICD-9: No specific diagnosis codes and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (observation services), (initial inpatient), (subsequent inpatient), (admit and discharge on the same day), (ED services), (critical care), (nursing facility), (domiciliary/rest home), (home visits), and (preventive services), (preventive counseling) Surrogate decision maker or advance care plan documented in the medical record (1080F) Surrogate decision maker or advance directive not documented for patient reasons (1080F-2P) Surrogate decision maker or advance directive not documented, reason not specified (1080F-8P) (Joy s Comment: For successful reporting of this measure, primary care physicians will have to report on this measure at least one time for every Medicare patient.) 48) Assessment of Presence or Absence of Urinary Incontinence in Women Aged 65 Years and Older - Percentage of female patients aged 65 years and older who were assessed for the presence or absence of urinary incontinence within 12 months - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. This measure is appropriate for use in the ambulatory setting only. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care for the patient will submit this measure. ICD-9: No specific codes and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), and (preventive), (preventive counseling) Definition: Urinary incontinence is defined as any involuntary leakage of urine. Presence or absence of urinary incontinence assessed (1090F) Presence or absence of urinary incontinence not assessed for medical reasons (1090F-1P) Presence or absence of urinary incontinence not assessed reason not specified (1090F-8P) 49) Characterization of Urinary Incontinence in Women Aged 65 Years and Older - Percentage of female patients aged 65 years and older with a diagnosis of urinary incontinence whose urinary incontinence was characterized at least once within 12 months - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. This measure is appropriate for use in the ambulatory setting only. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide services for patients with the diagnosis of urinary incontinence will submit this measure. ICD-9: 307.6, 625.6, and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), and (preventive), (preventive counseling) 5-10
11 Definition: Characterization includes, but is not limited to, (frequency, volume, timing, type of symptoms, how bothersome) Urinary incontinence characterized (1091F) Urinary incontinence not characterized reason not specified (1091F-8P) 50) Plan of Care for Urinary Incontinence in Women Aged 65 Years and Older - Percentage of female patients aged 65 years and older with a diagnosis of urinary incontinence with a documented plan of care for urinary incontinence at least once within 12 months - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. This measure is appropriate for use in the ambulatory setting only. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide services for patients with the diagnosis of urinary incontinence will submit this measure. ICD-9: 307.6, 625.6, and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), and (preventive), (preventive counseling) Definition: Plan of care may include behavioral interventions (e.g., bladder training, pelvic floor muscle training, prompted voiding), referral to specialist, surgical treatment, reassess at follow-up visit, lifestyle interventions, addressing co-morbid factors, modification or discontinuation of medications contributing to urinary incontinence, or pharmacologic therapy. Urinary incontinence plan of care documented (0509F) Plan of care for urinary incontinence not documented reason not specified (0509F-8P) 51) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Spirometry Evaluation - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of COPD who had spirometry evaluation results documented - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period using the most recent spirometry results in the patient record for patients seen during the reporting period. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care services for the patient will submit this measure. ICD-9: 491.0, 491.1, , 491.8, 491.9, 492.0, 492.8, 496 and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), , (preventive), (preventive counseling) Instructions: Look for most recent documentation of spirometry evaluation results in the medical record; do not limit the search to the reporting period. Spirometry results documented and reviewed (3023F) Spirometry results not documented medical reason(s) (3023F-1P) Spirometry results not documented for patient reasons (3023F-2P) Spirometry results not documented for system reasons (3023F-3P) Spirometry results not documented, reason not specified (3023F-8P) 52) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Bronchodilator Therapy - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of COPD and who have an FEV1/FVC less than 70% and have symptoms who were prescribed an inhaled bronchodilator - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for all COPD patients seen during the reporting period. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care services for the patient will submit this measure. ICD-9: 491.0, 491.1, , 491.8, 491.9, 492.0, 492.8, 496 and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), , (preventive), (preventive counseling) Inhaled bronchodilator prescribed and spirometry test results demonstrate FEV 1 /FVC < 70% with COPD symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, cough/sputum, wheezing) (4025F and 3025F) Documentation of medical reason(s) for not prescribing an inhaled bronchodilator and spirometry test results demonstrate FEV 1 /FVC < 70% with COPD symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, cough/sputum, wheezing) (4025F-1P and 3025F) Documentation of patient reason(s) for not prescribing an inhaled bronchodilator and spirometry test results demonstrate FEV 1 /FVC < 70% with COPD symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, cough/sputum, wheezing) (4025F-2P and 3025F) 5-11
12 Documentation of system reason(s) for not prescribing an inhaled bronchodilator and spirometry test results demonstrate FEV 1 /FVC < 70% with COPD symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, cough/sputum, wheezing) (4025F-3P and 3025F) Spirometry results demonstrate FEV 1 /FVC 70% or patient does not have COPD symptoms (3027F) Spirometry test not performed or documented (3025F-8P) Inhaled bronchodilator not prescribed, reason not specified and spirometry test results demonstrate FEV 1 /FVC < 70% with COPD symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, cough/sputum, wheezing) (4025F-8P and 3025F) 53) Asthma: Pharmacologic Therapy - Percentage of patients aged 5 to 40 years with a diagnosis of mild, moderate, or severe persistent asthma who were prescribed either the preferred long-term control medication (inhaled corticosteroid) or an acceptable alternative treatment - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for all asthma patients seen during the reporting period. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care services for the patient will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , , , , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), , (preventive), (preventive counseling) Definition: acceptable alternative treatment (leukotriene modifiers, cromolyn sodium, nedocromil sodium, or sustained-released methylxanthines) Persistent asthma (mild, moderate, or severe) and preferred long term control medication or acceptable alternative treatment prescribed (4015F and 1038F) Persistent asthma (mild, moderate, or severe) and preferred long-term control medication or acceptable alternative treatment not prescribed for patient reasons (4015F-2P and 1038F) Intermittent asthma (1039F) Persistent asthma (mild, moderate, or severe) and preferred long-term control medication or acceptable alternative treatment not prescribed, reason not specified (4015F-8P and 1038F) 60) Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Assessment for Alarm Symptoms - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, who were assessed for the presence or absence of the following alarm symptoms: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding - This measure is to be reported once for all GERD patients seen during the reporting period. Patients seen for an initial evaluation of GERD should have documentation in the medical record of the presence or absence of alarm symptoms. If the initial evaluation of GERD occurred prior to the reporting period, report the proper CPT Category II code with modifier indicated in the numerator coding indicating this is not the initial evaluation. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide care for patients with GERD will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult) Definition: Patients assessed for the presence or absence of the following alarm symptoms: involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding Alarm symptoms assessed; none present (1070F) Alarm symptoms assessed; one or more present (1071F) Patient does not meet denominator inclusion because the initial evaluation of GERD occurred prior to the reporting period (1070F-8P) Alarm symptoms not assessed for medical reasons (1070F-1P) Alarm symptoms not assessed, reason not specified (1071F-8P) (Joy s Comment: For successful reporting of this measure, physicians will have to report on this measure at least one time for every Medicare patient with GERD.) 61) Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Upper Endoscopy for Patients with Alarm Symptoms - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, with at least one alarm symptom who were either referred for upper endoscopy or had an upper endoscopy performed - This measure is to be reported once for all GERD patients seen during the reporting period. Patients seen for an initial evaluation of GERD and at least one alarm symptom will be referred for upper endoscopy or have an upper endoscopy performed. If the initial evaluation of GERD occurred prior to the reporting period, 5-12
13 report the proper CPT II Category II code with modifier indicated in the numerator coding indicating this is not the initial evaluation. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide care for patients with GERD will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult) Definition: Alarm symptoms for GERD include involuntary weight loss, dysphagia, and GI bleeding. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy performed (3130F) Documentation of referral for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (3132F and 1071F) Patient does not have alarm symptoms (1070F) Initial evaluation of GERD occurred prior to the reporting period (1071F-8P) Upper endoscopy not performed or patient not referred for upper endoscopy for medical reasons (e.g., patient has already had the procedure) (3130F-1P and 1071F) Upper endoscopy not performed or patient not referred for upper endoscopy for patient reasons (3130F-2P and 1071F) Upper endoscopy not performed or patient not referred for upper endoscopy for system reasons (3130F-3P and 1071F) Upper endoscopy not performed or patient not referred for upper endoscopy, reason not specified (3130F- 8P and 1071F) (Joy s Comment: For successful reporting of this measure, physicians will have to report on this measure and measure #60 at least one time for every Medicare patient with GERD.) 63) Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Barium Swallow- Inappropriate Use - Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of GERD, seen for an initial evaluation, who did not have a Barium swallow test ordered - This measure is to be reported once for all GERD patients seen during the reporting period. Patients being seen for an initial evaluation of GERD should not receive a barium swallow test. If the initial evaluation of GERD occurred prior to the reporting period, report the proper CPT Category II with modifier indicated in the numerator coding indicating this is not the initial evaluation. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide care for patients with GERD will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult) Definitions: This is an overuse measure. For performance, the numerator will be calculated as the difference between patients in the denominator and patients for whom a CPT Category II code was reported for barium swallow test ordered. A higher score indicates appropriate treatment of patients with GERD (i.e., the proportion for whom a barium swallow test was not ordered). Barium swallow test ordered (3142F) Patient does not meet denominator inclusion because the initial evaluation of GERD occurred prior to the reporting period (3200F-8P) Barium swallow test ordered for medical reasons (3142F-1P) Barium swallow test not ordered (3200F) (Joy s Comment: For successful reporting of this measure, physicians will have to report on this measure and measure #60 at least one time for every Medicare patient with GERD.) 64) Asthma Assessment - Percentage of patients aged 5 to 40 years with a diagnosis of asthma who were evaluated during at least one office visit within 12 months for the frequency (numeric) of daytime and nocturnal asthma symptoms - This measure is to be reported a minimum of once per reporting period for patients seen during the reporting period. It is anticipated that clinicians who provide primary care services for the patient with a diagnosis of asthma will submit this measure. ICD-9: , , , , , , and CPT: (office/outpatient visit), (office/outpatient consult), , (preventive), (preventive counseling) Definitions: To be counted in calculations of this measure, symptom frequency must be numerically quantified. Measure may also be met by clinician documentation or patient completion of an asthma assessment 5-13
2013 ACO Quality Measures
 ACO 1-7 Patient Satisfaction Survey Consumer Assessment of HealthCare Providers Survey (CAHPS) 1. Getting Timely Care, Appointments, Information 2. How well Your Providers Communicate 3. Patient Rating
ACO 1-7 Patient Satisfaction Survey Consumer Assessment of HealthCare Providers Survey (CAHPS) 1. Getting Timely Care, Appointments, Information 2. How well Your Providers Communicate 3. Patient Rating
Clinical Quality Measure Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW
 Clinical Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW NQF 0105 PQRS 9 NQF 0002 PQRS 66 Antidepressant Medication Management Appropriate Testing for Children with Pharyngitis (2-18 years)
Clinical Crosswalk: HEDIS, Meaningful Use, PQRS, PCMH, Beacon, 10 SOW NQF 0105 PQRS 9 NQF 0002 PQRS 66 Antidepressant Medication Management Appropriate Testing for Children with Pharyngitis (2-18 years)
Mar. 31, 2011 (202) 690-6145. Improving Quality of Care for Medicare Patients: Accountable Care Organizations
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Room 352-G 200 Independence Avenue, SW Washington, DC 20201 Office of Media Affairs MEDICARE FACT SHEET FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Room 352-G 200 Independence Avenue, SW Washington, DC 20201 Office of Media Affairs MEDICARE FACT SHEET FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
Demonstrating Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements for Eligible Providers Using Certified EMR Technology
 Demonstrating Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements for Eligible Providers Using Certified EMR Technology The chart below lists the measures (and specialty exclusions) that eligible providers must demonstrate
Demonstrating Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements for Eligible Providers Using Certified EMR Technology The chart below lists the measures (and specialty exclusions) that eligible providers must demonstrate
Ohio Health Homes Learning Community Meeting. Overview of Health Homes Measures
 Ohio Health Homes Learning Community Meeting Overview of Health Homes Measures Tuesday, March 5, 2013 Presenter: Amber Saldivar, MHSM Associate Director, Informatics Analysis Health Services Advisory Group,
Ohio Health Homes Learning Community Meeting Overview of Health Homes Measures Tuesday, March 5, 2013 Presenter: Amber Saldivar, MHSM Associate Director, Informatics Analysis Health Services Advisory Group,
Performance Measurement for the Medicare and Medicaid Eligible (MME) Population in Connecticut Survey Analysis
 Performance Measurement for the Medicare and Medicaid Eligible (MME) Population in Connecticut Survey Analysis Methodology: 8 respondents The measures are incorporated into one of four sections: Highly
Performance Measurement for the Medicare and Medicaid Eligible (MME) Population in Connecticut Survey Analysis Methodology: 8 respondents The measures are incorporated into one of four sections: Highly
HEdis Code Quick Reference Guide Disease Management Services
 HEdis Code Quick Reference Guide Disease Management Services Respiratory Conditions Appropriate Testing for Children With Pharyngitis (ages 2-18) [Commercial, Medicaid] Appropriate Treatment (no antibiotic)
HEdis Code Quick Reference Guide Disease Management Services Respiratory Conditions Appropriate Testing for Children With Pharyngitis (ages 2-18) [Commercial, Medicaid] Appropriate Treatment (no antibiotic)
ACO Program: Quality Reporting Requirements. Jennifer Faerberg Mary Wheatley April 28, 2011
 ACO Program: Quality Reporting Requirements Jennifer Faerberg Mary Wheatley April 28, 2011 Agenda for Today s Call Overview Quality Reporting Requirements Benchmarks/Thresholds Scoring Model Scoring Methodology
ACO Program: Quality Reporting Requirements Jennifer Faerberg Mary Wheatley April 28, 2011 Agenda for Today s Call Overview Quality Reporting Requirements Benchmarks/Thresholds Scoring Model Scoring Methodology
Chapter Three Accountable Care Organizations
 Chapter Three Accountable Care Organizations One of the most talked-about changes in health care delivery in recent decades is Accountable Care Organizations, or ACOs. Having gained the attention of both
Chapter Three Accountable Care Organizations One of the most talked-about changes in health care delivery in recent decades is Accountable Care Organizations, or ACOs. Having gained the attention of both
OBJECTIVES AGING POPULATION AGING POPULATION AGING IMPACT ON MEDICARE AGING POPULATION
 OBJECTIVES Kimberly S. Hodge, PhDc, MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN- K Director, ACO Care Management & Clinical Nurse Specialist Franciscan ACO, Inc. Central Indiana Region Indianapolis, IN By the end of this session
OBJECTIVES Kimberly S. Hodge, PhDc, MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN- K Director, ACO Care Management & Clinical Nurse Specialist Franciscan ACO, Inc. Central Indiana Region Indianapolis, IN By the end of this session
2012 Physician Quality Reporting System (Physician Quality Reporting) Implementation Guide
 2012 Physician Quality Reporting System (Physician Quality Reporting) Implementation Guide CPT only copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 26 Table of Contents Introduction
2012 Physician Quality Reporting System (Physician Quality Reporting) Implementation Guide CPT only copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 26 Table of Contents Introduction
Radiology Business Management Association Technology Task Force. Sample Request for Proposal
 Technology Task Force Sample Request for Proposal This document has been created by the RBMA s Technology Task Force as a guideline for use by RBMA members working with potential suppliers of Electronic
Technology Task Force Sample Request for Proposal This document has been created by the RBMA s Technology Task Force as a guideline for use by RBMA members working with potential suppliers of Electronic
Psychiatrists and Reporting on Meaningful Use Stage 1. August 6, 2012
 Psychiatrists and Reporting on Meaningful Use Stage 1 August 6, 2012 Quick Overview Functional Measures Providers (tracked by NPI) must report on 15 core objectives and associated measures and 5 objectives
Psychiatrists and Reporting on Meaningful Use Stage 1 August 6, 2012 Quick Overview Functional Measures Providers (tracked by NPI) must report on 15 core objectives and associated measures and 5 objectives
Medicare Shared Savings Program Quality Measure Benchmarks for the 2014 Reporting Year
 Medicare Shared Savings Program Quality Measure Benchmarks for the 2014 Reporting Year Release Notes/Summary of Changes (February 2015): Issued correction of 2014 benchmarks for ACO-9 and ACO-10 quality
Medicare Shared Savings Program Quality Measure Benchmarks for the 2014 Reporting Year Release Notes/Summary of Changes (February 2015): Issued correction of 2014 benchmarks for ACO-9 and ACO-10 quality
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements Summary. http://www.cms.gov/ehrincentiveprograms/
 Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements Summary 2010 What are the Requirements of Stage 1 Meaningful Use? Basic Overview of Stage 1 Meaningful Use: Reporting period
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements Summary 2010 What are the Requirements of Stage 1 Meaningful Use? Basic Overview of Stage 1 Meaningful Use: Reporting period
2012 Physician Quality Reporting System:
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services R Official CMS Information for Medicare Fee-For-Service Providers 2012 Physician Quality : Medicare Electronic Health Record
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services R Official CMS Information for Medicare Fee-For-Service Providers 2012 Physician Quality : Medicare Electronic Health Record
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS) Measure Specification and Measure Flow Guide for Claims and Registry Reporting of Individual Measures
 2016 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS) Measure Specification and Measure Flow Guide for Claims and Registry Reporting of Individual Measures Utilized by Individual Eligible Professionals for Claims
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS) Measure Specification and Measure Flow Guide for Claims and Registry Reporting of Individual Measures Utilized by Individual Eligible Professionals for Claims
Improving Quality of Care for Medicare Patients: Accountable Care Organizations
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Improving Quality of Medicare Patients: Overview The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (), an agency within the Department
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Improving Quality of Medicare Patients: Overview The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (), an agency within the Department
Improving Quality of Care for Medicare Patients: Accountable Care Organizations
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Improving Quality of Care for Medicare Patients: FACT SHEET Overview http://www.cms.gov/sharedsavingsprogram On October
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Improving Quality of Care for Medicare Patients: FACT SHEET Overview http://www.cms.gov/sharedsavingsprogram On October
Overview of Clinical Quality Measures Reporting in the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Final Rule on Meaningful Use
 Overview of Clinical Quality Measures Reporting in the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Final Rule on Meaningful Use Clinical Quality Measures Clinical quality measures have been defined
Overview of Clinical Quality Measures Reporting in the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Final Rule on Meaningful Use Clinical Quality Measures Clinical quality measures have been defined
2010 QARR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Adults
 2010 QARR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Adults ADULT MEASURES (19 through 64 years) GUIDELINE HEDIS COMPLIANT CPT/ICD9 CODES DOCUMENTATION TIPS Well Care Access to Ambulatory Care Ensure a preventive or other
2010 QARR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Adults ADULT MEASURES (19 through 64 years) GUIDELINE HEDIS COMPLIANT CPT/ICD9 CODES DOCUMENTATION TIPS Well Care Access to Ambulatory Care Ensure a preventive or other
Stage 2 June 13, 2014
 Stage 2 June 13, 2014 1 General Overview of Idaho Medicaid s EHR Incentive Program Stage 2 Meaningful Use (MU) Overview 2014 Reporting Helpful Resources 2 3 Medicaid can pay certain providers an incentive
Stage 2 June 13, 2014 1 General Overview of Idaho Medicaid s EHR Incentive Program Stage 2 Meaningful Use (MU) Overview 2014 Reporting Helpful Resources 2 3 Medicaid can pay certain providers an incentive
MEASURING CARE QUALITY
 MEASURING CARE QUALITY Region November 2015 For Clinical Effectiveness of Care Measures of Performance From: Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS ) HEDIS is a set of standardized performance
MEASURING CARE QUALITY Region November 2015 For Clinical Effectiveness of Care Measures of Performance From: Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS ) HEDIS is a set of standardized performance
Aligning Incentives for Quality: Pharmacy's Role in Achieving Hospital and National Goals. Objectives. National Organizations: Key Linkages
 Aligning Incentives for Quality: Pharmacy's Role in Achieving Hospital and National Goals Kasey K. Thompson, Pharm.D. Director, Practice Standards and Quality Division Director, Patient Safety American
Aligning Incentives for Quality: Pharmacy's Role in Achieving Hospital and National Goals Kasey K. Thompson, Pharm.D. Director, Practice Standards and Quality Division Director, Patient Safety American
Explanation of CMS Proposed Performance Measurement Framework for ACOs and Comparison with IHA P4P Measure Set April 2011
 Explanation of CMS Proposed Performance ment Framework for ACOs and Comparison with IHA P4P Set April 2011 This briefing outlines Section II E ( and Other Reporting Requirements) of the Shared Savings
Explanation of CMS Proposed Performance ment Framework for ACOs and Comparison with IHA P4P Set April 2011 This briefing outlines Section II E ( and Other Reporting Requirements) of the Shared Savings
DENOMINATOR: All female patients aged 65 years and older with a diagnosis of urinary incontinence
 Measure #50: Urinary Incontinence: Plan of Care for Urinary Incontinence in Women Aged 65 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Person and Caregiver-Centered Experience and Outcomes 2016 PQRS
Measure #50: Urinary Incontinence: Plan of Care for Urinary Incontinence in Women Aged 65 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Person and Caregiver-Centered Experience and Outcomes 2016 PQRS
2013 MEDICARE FEE-FOR-SERVICE QUALITY AND RESOURCE USE REPORT
 2013 MEDICARE FEE-FOR-SERVICE QUALITY AND RESOURCE USE REPORT Sample Medical Practice Last Four Digits of Your Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): 1530 ABOUT THIS REPORT FROM MEDICARE WHAT This Quality
2013 MEDICARE FEE-FOR-SERVICE QUALITY AND RESOURCE USE REPORT Sample Medical Practice Last Four Digits of Your Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): 1530 ABOUT THIS REPORT FROM MEDICARE WHAT This Quality
ABELMed EHR-EMR/PM version 12, an ONC HIT 2014 Edition Complete EHR, has been certified for the following 42 clinical quality measures (CQMs).
 ABELMed EHR-EMR/PM version 12, an ONC HIT 2014 Edition Complete EHR, has been certified for the following 42 clinical quality measures (CQMs). The information contained in this document is also available
ABELMed EHR-EMR/PM version 12, an ONC HIT 2014 Edition Complete EHR, has been certified for the following 42 clinical quality measures (CQMs). The information contained in this document is also available
2013 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): Implementation Guide Claims-Based Reporting for Incentive
 2013 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): Implementation Guide Claims-Based Reporting for Incentive CPT only copyright 2012 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 28 Table of
2013 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): Implementation Guide Claims-Based Reporting for Incentive CPT only copyright 2012 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 28 Table of
Accountable Care Organizations: Notice of Proposed Rulemaking
 Accountable Care Organizations: Notice of Proposed Rulemaking Presentation by: Pam Silberman, JD, DrPH North Carolina Institute of Medicine April 15, 2011 1 Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) An ACO
Accountable Care Organizations: Notice of Proposed Rulemaking Presentation by: Pam Silberman, JD, DrPH North Carolina Institute of Medicine April 15, 2011 1 Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) An ACO
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis
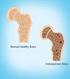 Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Achieving Quality and Value in Chronic Care Management
 The Burden of Chronic Disease One of the greatest burdens on the US healthcare system is the rapidly growing rate of chronic disease. These statistics illustrate the scope of the problem: Nearly half of
The Burden of Chronic Disease One of the greatest burdens on the US healthcare system is the rapidly growing rate of chronic disease. These statistics illustrate the scope of the problem: Nearly half of
Medicare Shared Savings Program Quality Measure Benchmarks for the 2015 Reporting Year
 Medicare Shared Savings Program Quality Measure Benchmarks for the 2015 Reporting Year Release Notes/Summary of Changes (February 2015): Issued correction of 2015 benchmarks for ACO-9 and ACO-10 quality
Medicare Shared Savings Program Quality Measure Benchmarks for the 2015 Reporting Year Release Notes/Summary of Changes (February 2015): Issued correction of 2015 benchmarks for ACO-9 and ACO-10 quality
2014 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Proposed Rule Quality Provisions
 2014 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Proposed Rule Quality Provisions The 2014 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) was published in the Federal Register on July
2014 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Proposed Rule Quality Provisions The 2014 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) was published in the Federal Register on July
We're Ready for MU2...Are You?
 Meaningful Use Are you considering purchasing an Electronic Health Record (EHR) or moving from your current vendor? Is your goal to attain Meaningful Use status in order to receive EHR incentive dollars?
Meaningful Use Are you considering purchasing an Electronic Health Record (EHR) or moving from your current vendor? Is your goal to attain Meaningful Use status in order to receive EHR incentive dollars?
ACO Name and Location Allina Health Minneapolis, Minnesota
 ACO Name and Location Allina Health Minneapolis, Minnesota ACO Primary Contact Patrick Flesher Director, Payer Contracting & Pioneer ACO Program Email: Patrick.Flesher@allina.com Phone: 612-262-4865 Composition
ACO Name and Location Allina Health Minneapolis, Minnesota ACO Primary Contact Patrick Flesher Director, Payer Contracting & Pioneer ACO Program Email: Patrick.Flesher@allina.com Phone: 612-262-4865 Composition
PTE Pediatric Asthma Metrics Reporting Updated January 2015
 PTE Pediatric Asthma Metrics Reporting Updated January 20 Introduction: The Maine Health Management Coalition s (MHMC) Pathways to Excellence (PTE) Program is preparing for its next round of PTE Pediatric
PTE Pediatric Asthma Metrics Reporting Updated January 20 Introduction: The Maine Health Management Coalition s (MHMC) Pathways to Excellence (PTE) Program is preparing for its next round of PTE Pediatric
SUMMARY OF CHANGES TO QOF 2015/16 - ENGLAND CLINICAL
 SUMMARY OF CHANGES TO QOF 2015/1 - ENGLAND KEY No change Retired/replaced Wording and/or change Point or threshold change Indicator ID change 14/15 QOF ID 15/1 QOF ID NICE ID Indicator wording Changes
SUMMARY OF CHANGES TO QOF 2015/1 - ENGLAND KEY No change Retired/replaced Wording and/or change Point or threshold change Indicator ID change 14/15 QOF ID 15/1 QOF ID NICE ID Indicator wording Changes
The Role of Health Information Technology in Improving Health Care
 The Role of Health Information Technology in Improving Health Care The HIT Symposium Massachusetts Institute of Technology July 1, 2009 Michael T. Rapp, MD, JD, FACEP Director, Quality Measurement and
The Role of Health Information Technology in Improving Health Care The HIT Symposium Massachusetts Institute of Technology July 1, 2009 Michael T. Rapp, MD, JD, FACEP Director, Quality Measurement and
ATTACHMENT B Care Management Organization (CMO) Quality Incentive Payment Methodology
 This attachment describes the CMO program period cost reduction guarantees as follows: 1. Fees-at-Risk; 2. Reconciliation Methodology and Holdback Calculation; 3. Operational and Reconciliation Data Requirements;
This attachment describes the CMO program period cost reduction guarantees as follows: 1. Fees-at-Risk; 2. Reconciliation Methodology and Holdback Calculation; 3. Operational and Reconciliation Data Requirements;
Physician and other health professional services
 O n l i n e A p p e n d i x e s 4 Physician and other health professional services 4-A O n l i n e A p p e n d i x Access to physician and other health professional services 4 a1 Access to physician care
O n l i n e A p p e n d i x e s 4 Physician and other health professional services 4-A O n l i n e A p p e n d i x Access to physician and other health professional services 4 a1 Access to physician care
SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES
 Summary Table of Measures, Product Lines and Changes 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES General Guidelines for Data Collection and Reporting Guidelines for Calculations and Sampling
Summary Table of Measures, Product Lines and Changes 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES General Guidelines for Data Collection and Reporting Guidelines for Calculations and Sampling
SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURE CHANGES
 Summary Table of Measure 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURE CHANGES Guidelines for Physician Measurement Effectiveness of Preventive Care Guidelines for Physician Effectiveness of Care Adult BMI Assessment Weight
Summary Table of Measure 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURE CHANGES Guidelines for Physician Measurement Effectiveness of Preventive Care Guidelines for Physician Effectiveness of Care Adult BMI Assessment Weight
Clinical Quality Measures. for 2014
 Clinical Quality Measures for 2014 Mission of OFMQHIT To advance the implementation and use of vital health information technology to improve healthcare quality, efficiency and safety by assisting physician
Clinical Quality Measures for 2014 Mission of OFMQHIT To advance the implementation and use of vital health information technology to improve healthcare quality, efficiency and safety by assisting physician
11/2/2015 Domain: Care Coordination / Patient Safety
 11/2/2015 Domain: Care Coordination / Patient Safety 2014 CT Commercial Medicaid Compared to 2012 all LOB Medicaid Quality Compass Benchmarks 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Documentation of Current Medications in
11/2/2015 Domain: Care Coordination / Patient Safety 2014 CT Commercial Medicaid Compared to 2012 all LOB Medicaid Quality Compass Benchmarks 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Documentation of Current Medications in
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #317: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for High Blood Pressure and Follow-Up Documented National Quality Strategy Domain: Community / Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #317: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for High Blood Pressure and Follow-Up Documented National Quality Strategy Domain: Community / Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Allscripts CQS Planning for 2014 Webinar: FAQs
 Allscripts CQS Planning for 2014 Webinar: FAQs Listed below are questions asked by attendees based on the CQS Planning for 2014 Webinars, held on May 8, May 28, and May 30, 2014. Answers are provided below.
Allscripts CQS Planning for 2014 Webinar: FAQs Listed below are questions asked by attendees based on the CQS Planning for 2014 Webinars, held on May 8, May 28, and May 30, 2014. Answers are provided below.
Report on comparing quality among Medicare Advantage plans and between Medicare Advantage and fee-for-service Medicare
 O N L I N E A P P E N D I X E S 6 Report on comparing quality among Medicare Advantage plans and between Medicare Advantage and fee-for-service Medicare 6-A O N L I N E A P P E N D I X Current quality
O N L I N E A P P E N D I X E S 6 Report on comparing quality among Medicare Advantage plans and between Medicare Advantage and fee-for-service Medicare 6-A O N L I N E A P P E N D I X Current quality
Stage 1 Meaningful Use for Specialists. NYC REACH Primary Care Information Project NYC Department of Health & Mental Hygiene
 Stage 1 Meaningful Use for Specialists NYC REACH Primary Care Information Project NYC Department of Health & Mental Hygiene 1 Today s Agenda Meaningful Use Overview Meaningful Use Measures Resources Primary
Stage 1 Meaningful Use for Specialists NYC REACH Primary Care Information Project NYC Department of Health & Mental Hygiene 1 Today s Agenda Meaningful Use Overview Meaningful Use Measures Resources Primary
Re: CMS-1345-P; Medicare Program; Medicare Shared Savings Program: Accountable Care Organizations; Proposed Rule
 Department of Health and Human Services Attention: CMS 1345 P P.O. Box 8013, Baltimore, MD 21244 8013 Re: CMS-1345-P; Medicare Program; Medicare Shared Savings Program: Accountable Care Organizations;
Department of Health and Human Services Attention: CMS 1345 P P.O. Box 8013, Baltimore, MD 21244 8013 Re: CMS-1345-P; Medicare Program; Medicare Shared Savings Program: Accountable Care Organizations;
ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATION QUICK-REFERENCE SETUP GUIDE
 ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATION QUICK-REFERENCE SETUP GUIDE V 9.0 eclinicalworks, 2013. All rights reserved Contents CONTENTS ACO SETUP 3 Demographics 3 ACO 12 4 ACO 13 6 ACO 14 7 ACO 15 8 ACO 16 9 ACO 17
ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATION QUICK-REFERENCE SETUP GUIDE V 9.0 eclinicalworks, 2013. All rights reserved Contents CONTENTS ACO SETUP 3 Demographics 3 ACO 12 4 ACO 13 6 ACO 14 7 ACO 15 8 ACO 16 9 ACO 17
with implementing care management
 EHR Systems Promote Quality Improvement and Practice Efficiencies Andrew Miller, MD, MPH In 2004, the US Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) released an outline for a 10-year plan to transform
EHR Systems Promote Quality Improvement and Practice Efficiencies Andrew Miller, MD, MPH In 2004, the US Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) released an outline for a 10-year plan to transform
SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES
 Summary Table of Measures, Product Lines and Changes 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES General Guidelines for Data Collection and Reporting Guidelines for Calculations and Sampling
Summary Table of Measures, Product Lines and Changes 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES General Guidelines for Data Collection and Reporting Guidelines for Calculations and Sampling
Summary of QOF indicators
 Summary of QOF indicators Clinical domain Atrial fibrillation (AF) AF001. The contractor establishes and maintains a register of patients with atrial fibrillation AF002. The percentage of patients with
Summary of QOF indicators Clinical domain Atrial fibrillation (AF) AF001. The contractor establishes and maintains a register of patients with atrial fibrillation AF002. The percentage of patients with
See page 331 of HEDIS 2013 Tech Specs Vol 2. HEDIS specs apply to plans. RARE applies to hospitals. Plan All-Cause Readmissions (PCR) *++
 Hospitalizations Inpatient Utilization General Hospital/Acute Care (IPU) * This measure summarizes utilization of acute inpatient care and services in the following categories: Total inpatient. Medicine.
Hospitalizations Inpatient Utilization General Hospital/Acute Care (IPU) * This measure summarizes utilization of acute inpatient care and services in the following categories: Total inpatient. Medicine.
Medicare EHR Incentive Program - Meaningful Use
 EHR Incentive Programs A program administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) An Introduction to the Medicare EHR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals cms.gov/ehrincentiveprograms
EHR Incentive Programs A program administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) An Introduction to the Medicare EHR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals cms.gov/ehrincentiveprograms
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 SPECIFICATION F MEASURES GROUP REPTING ONLY INFLAMMATY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPTING OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: REGISTRY ONLY 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPTING
SPECIFICATION F MEASURES GROUP REPTING ONLY INFLAMMATY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPTING OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: REGISTRY ONLY 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPTING
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Programs. Specifics of the Program for Eligible Professionals
 Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Programs Specifics of the Program for Eligible Professionals Today s Session This training will cover the following topics: EHR Incentive Programs a Background Who Is
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Programs Specifics of the Program for Eligible Professionals Today s Session This training will cover the following topics: EHR Incentive Programs a Background Who Is
Under section 1899 of the Act, CMS has established the Medicare Shared Savings
 CMS-1612-FC 848 M. Medicare Shared Savings Program Under section 1899 of the Act, CMS has established the Medicare Shared Savings program (Shared Savings Program) to facilitate coordination and cooperation
CMS-1612-FC 848 M. Medicare Shared Savings Program Under section 1899 of the Act, CMS has established the Medicare Shared Savings program (Shared Savings Program) to facilitate coordination and cooperation
ANALYSIS OF THE CMS PROPOSED RULE FOR THE MEDICARE SHARED SAVINGS PROGRAM AND ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATIONS (2011)
 Occupational Therapy: Living Life To Its Fullest ANALYSIS OF THE CMS PROPOSED RULE FOR THE MEDICARE SHARED SAVINGS PROGRAM AND ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATIONS (2011) The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid
Occupational Therapy: Living Life To Its Fullest ANALYSIS OF THE CMS PROPOSED RULE FOR THE MEDICARE SHARED SAVINGS PROGRAM AND ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATIONS (2011) The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid
January 2014 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): What s New for 2014 Purpose Important Changes for 2014 PQRS PQRS Incentive Individual EPs
 January 2014 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): What s New for 2014 Purpose This fact sheet includes important information about changes to the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS) for 2014.
January 2014 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): What s New for 2014 Purpose This fact sheet includes important information about changes to the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS) for 2014.
"2015 ACO quality measures- What's new? How can we be successful?"
 "2015 ACO quality measures- What's new? How can we be successful?" ACO Announcements Reminders: ACO Notifications, Requests for Tax ID information from PECOS, Upcoming Boardline Upcoming Specialty Initiative
"2015 ACO quality measures- What's new? How can we be successful?" ACO Announcements Reminders: ACO Notifications, Requests for Tax ID information from PECOS, Upcoming Boardline Upcoming Specialty Initiative
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
 Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
Test Procedure for 170.304 (j) Calculate and Submit Clinical Quality Measures
 Test Procedure for 170.304 (j) Calculate and Submit Clinical Quality Measures This document describes the draft test procedure for evaluating conformance of complete EHRs or EHR modules 1 to the certification
Test Procedure for 170.304 (j) Calculate and Submit Clinical Quality Measures This document describes the draft test procedure for evaluating conformance of complete EHRs or EHR modules 1 to the certification
2014 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): Implementation Guide 12/13/2013
 2014 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): Implementation Guide 12/13/2013 CPT only copyright 2013 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 41 Table of Contents Page Introduction
2014 Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS): Implementation Guide 12/13/2013 CPT only copyright 2013 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 41 Table of Contents Page Introduction
Core Set of Objectives and Measures Must Meet All 15 Measures Stage 1 Objectives Stage 1 Measures Reporting Method
 Stage 1 Meaningful Use Criteria Physicians must meet all 15 Core Set objectives and measures and five of the 10 Menu Set objectives and measures. They also must report clinical quality measures (see separate
Stage 1 Meaningful Use Criteria Physicians must meet all 15 Core Set objectives and measures and five of the 10 Menu Set objectives and measures. They also must report clinical quality measures (see separate
Medical Billing Requirements - Medicaid Incentive Checklist
 AAP Meaningful Use: Becoming a Meaningful User An Outpatient Checklist On July 13, 2010, the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released a Final Rule establishing the criteria with which
AAP Meaningful Use: Becoming a Meaningful User An Outpatient Checklist On July 13, 2010, the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released a Final Rule establishing the criteria with which
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Specifics of the Program for Eligible Professionals. August 10, 2010
 Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Specifics of the Program for Eligible Professionals August 10, 2010 Today s Session This training will cover the following topics: EHR Incentive Programs a Background
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Specifics of the Program for Eligible Professionals August 10, 2010 Today s Session This training will cover the following topics: EHR Incentive Programs a Background
An Introduction to the Medicare EHR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals
 EHR Incentive Programs A program administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) An Introduction to the Medicare EHR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals cms.gov/ehrincentiveprograms
EHR Incentive Programs A program administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) An Introduction to the Medicare EHR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals cms.gov/ehrincentiveprograms
8/14/2012 California Dual Demonstration DRAFT Quality Metrics
 Stakeholder feedback is requested on the following: 1) metrics 69 through 94; and 2) withhold measures for years 1, 2, and 3. Steward/ 1 Antidepressant medication management Percentage of members 18 years
Stakeholder feedback is requested on the following: 1) metrics 69 through 94; and 2) withhold measures for years 1, 2, and 3. Steward/ 1 Antidepressant medication management Percentage of members 18 years
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements Overview. http://www.cms.gov/ehrincentiveprograms/
 Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements Overview 2010 What is Meaningful Use? Meaningful Use is using certified EHR technology to Improve quality, safety, efficiency,
Medicare & Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Meaningful Use Stage 1 Requirements Overview 2010 What is Meaningful Use? Meaningful Use is using certified EHR technology to Improve quality, safety, efficiency,
Welcome The AAMC, UHC and FPSC Web Conference on 2014 PQRS Proposed Changes will begin shortly.
 Welcome The AAMC, UHC and FPSC Web Conference on 2014 PQRS Proposed Changes will begin shortly. Please do not place your phones on hold. If you need to leave the event, hang up and dial back into the conference.
Welcome The AAMC, UHC and FPSC Web Conference on 2014 PQRS Proposed Changes will begin shortly. Please do not place your phones on hold. If you need to leave the event, hang up and dial back into the conference.
Initial Preventive Physical Examination
 Initial Preventive Physical Examination Overview The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act (MMA) of 2003 expanded Medicare's coverage of preventive services. Central to the Centers
Initial Preventive Physical Examination Overview The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act (MMA) of 2003 expanded Medicare's coverage of preventive services. Central to the Centers
Coventry Health Care of Florida, Inc. Coventry Health Plan of Florida, Inc. Coventry Health and Life Insurance Company Commercial Lines of Business
 Coventry Health Care of Florida, Inc. Coventry Health Plan of Florida, Inc. Coventry Health and Life Insurance Company Commercial Lines of Business Quality Management Program 2012 Overview Quality Improvement
Coventry Health Care of Florida, Inc. Coventry Health Plan of Florida, Inc. Coventry Health and Life Insurance Company Commercial Lines of Business Quality Management Program 2012 Overview Quality Improvement
Table 1 Performance Measures. Quality Monitoring P4P Yr1 Yr2 Yr3. Specification Source. # Category Performance Measure
 Table 1 Performance Measures # Category Performance Measure 1 Behavioral Health Risk Assessment and Follow-up 1) Behavioral Screening/ Assessment within 60 days of enrollment New Enrollees who completed
Table 1 Performance Measures # Category Performance Measure 1 Behavioral Health Risk Assessment and Follow-up 1) Behavioral Screening/ Assessment within 60 days of enrollment New Enrollees who completed
MaineCare Value Based Purchasing Initiative
 MaineCare Value Based Purchasing Initiative The Accountable Communities Strategy Jim Leonard, Deputy Director, MaineCare Peter Kraut, Acting Accountable Communities Program Manager Why Value-Based Purchasing
MaineCare Value Based Purchasing Initiative The Accountable Communities Strategy Jim Leonard, Deputy Director, MaineCare Peter Kraut, Acting Accountable Communities Program Manager Why Value-Based Purchasing
ProviderReport. Message from the CEO. Provider Relations adds Provider Partnership team
 ProviderReport Message from the CEO We recognize the important role our providers play in ensuring member access to high quality services. Our success is built on the philosophy that quality healthcare
ProviderReport Message from the CEO We recognize the important role our providers play in ensuring member access to high quality services. Our success is built on the philosophy that quality healthcare
Medicare 2015 QI Program Evaluation
 Color Code: Red does not meet 5 star threshold, or target. Green meets or exceeds 5 star threshold/target. Improving or Maintaining Physical Health (HOS) Improving or Maintaining Mental Health (HOS) Diabetes
Color Code: Red does not meet 5 star threshold, or target. Green meets or exceeds 5 star threshold/target. Improving or Maintaining Physical Health (HOS) Improving or Maintaining Mental Health (HOS) Diabetes
ATLANTIC and OPTIMUS ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATIONs CMS QUALITY MEASURES
 CARE / PATIENT SAFETY ATLANTIC and OPTIMUS ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATIONs CMS QUALITY MEASURES This tool is for REFERENCE USE ONLY and serves as an Emergency Backup Documentation Tool (downtime procedure
CARE / PATIENT SAFETY ATLANTIC and OPTIMUS ACCOUNTABLE CARE ORGANIZATIONs CMS QUALITY MEASURES This tool is for REFERENCE USE ONLY and serves as an Emergency Backup Documentation Tool (downtime procedure
Hospital Quality Initiative Overview CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES December 2005
 Hospital Quality Initiative Overview CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES December 2005 Background Quality health care is a high priority for the Bush administration, the Department of Health and Human
Hospital Quality Initiative Overview CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES December 2005 Background Quality health care is a high priority for the Bush administration, the Department of Health and Human
convey the clinical quality measure's title, number, owner/developer and contact
 CMS-0033-P 153 convey the clinical quality measure's title, number, owner/developer and contact information, and a link to existing electronic specifications where applicable. TABLE 20: Proposed Clinical
CMS-0033-P 153 convey the clinical quality measure's title, number, owner/developer and contact information, and a link to existing electronic specifications where applicable. TABLE 20: Proposed Clinical
Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage of patients
Measure #236 (NQF 0018): Controlling High Blood Pressure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage of patients
Total Health Quality Indicators For Providers 2015
 Total Health Quality Indicators For Providers 2015 Adult- Preventive Measure Test/Procedure Parameters Frequency CPT/HCPCS CPT II ICD-9 BMI Assessment BMI Recording 18-74 yrs Yearly G8417, G8418, G8420
Total Health Quality Indicators For Providers 2015 Adult- Preventive Measure Test/Procedure Parameters Frequency CPT/HCPCS CPT II ICD-9 BMI Assessment BMI Recording 18-74 yrs Yearly G8417, G8418, G8420
12/15/2010. EMR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals
 12/15/2010 EMR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals Topics for Today Meaningful Use Program Overview Who is eligible What is Meaningful Use (MU) How do you qualify How do you sign up How to determine
12/15/2010 EMR Incentive Program for Eligible Professionals Topics for Today Meaningful Use Program Overview Who is eligible What is Meaningful Use (MU) How do you qualify How do you sign up How to determine
Many of the changes that have been made to this final rule were directly responsive to CMA s comments.
 On July 13, 2010, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released the final rule defining meaningful use of an electronic health record (EHR) system. The original version of this rule was released
On July 13, 2010, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released the final rule defining meaningful use of an electronic health record (EHR) system. The original version of this rule was released
SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES
 Summary Table of Measures, Product Lines and Changes 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES General Guidelines for Data Collection and Reporting Guidelines for Calculations and Sampling
Summary Table of Measures, Product Lines and Changes 1 SUMMARY TABLE OF MEASURES, PRODUCT LINES AND CHANGES General Guidelines for Data Collection and Reporting Guidelines for Calculations and Sampling
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #326 (NQF 1525): Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: Chronic Anticoagulation Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS,
Measure #326 (NQF 1525): Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: Chronic Anticoagulation Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS,
A Detailed Data Set From the Year 2011
 2012 HEDIS 2012 A Detailed Data Set From the Year 2011 Commercial Product We are pleased to present the AvMed HEDIS 2012 Report, a detailed data set designed to give employers and consumers an objective
2012 HEDIS 2012 A Detailed Data Set From the Year 2011 Commercial Product We are pleased to present the AvMed HEDIS 2012 Report, a detailed data set designed to give employers and consumers an objective
The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery
 Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Physician Quality Reporting System What Neurosurgeons Need to Know for 2015
 Physician Quality System What Neurosurgeons Need to Know for 2015 Prepared by the: American Association of Neurological Surgeons Congress of Neurological Surgeons For More Information Contact: Rachel Groman,
Physician Quality System What Neurosurgeons Need to Know for 2015 Prepared by the: American Association of Neurological Surgeons Congress of Neurological Surgeons For More Information Contact: Rachel Groman,
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis
 Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P
 James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P Chairman, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center Chair, General Internal Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University Associate Medical Director, Hospice
James F. Kravec, M.D., F.A.C.P Chairman, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center Chair, General Internal Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University Associate Medical Director, Hospice
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
CPT Coding Update And Other Issues
 CPT Coding Update And Other Issues Robert E. Smith, M.D. Alison Lynch, M.D. November 13, 2013 1 Disclaimer This information is for educational and informational purposes only, and represents the understanding
CPT Coding Update And Other Issues Robert E. Smith, M.D. Alison Lynch, M.D. November 13, 2013 1 Disclaimer This information is for educational and informational purposes only, and represents the understanding
Effective ACO Compliance
 Effective ACO Compliance HCCA Compliance Institute April 21, 2013 Margaret Hambleton, MBA, CHC, CHPC Sr. Vice President, Chief Compliance Officer St. Joseph Health System 1 Objectives Understand Accountable
Effective ACO Compliance HCCA Compliance Institute April 21, 2013 Margaret Hambleton, MBA, CHC, CHPC Sr. Vice President, Chief Compliance Officer St. Joseph Health System 1 Objectives Understand Accountable
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working
 GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
Meaningful Use: Stage 1: Functional Measures Eligible Professionals (EPs)
 Meaningful Use: Stage 1: Functional Measures Eligible Professionals (EPs) What is Meaningful Use? American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009/Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical
Meaningful Use: Stage 1: Functional Measures Eligible Professionals (EPs) What is Meaningful Use? American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009/Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical
