Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates. Atoms in Carbohydrates 4/7/09. Functional Groups in Carbohydrates. Chapter 22
|
|
|
- Janis Watson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Carbohydrates Chapter 22 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter 22 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are a class of molecules that includes Simple sugars Starch Cellulose (Insoluble Fiber) Glycogen (animal starch) Chitin (Lobster Shells) Heparin (Anti coagulate) Glycoproteins Others? 4/7/09 2 Atoms in Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have the general formula C n H (2xn) O n Functional Groups in Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Polyhydroxy refers to the numerous OH
2 General Classes of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates can be: Monosaccharide - One single sugar molecule. (glucose, fructose) Disaccharides Two sugar molecules (table sugar) Polysaccharides Many Sugar Molecules (starch, fiber, pectin) Some Monosaccharides Simple sugars 3 to 7 carbon atoms Similarities and differences? Aldose or Ketose? 5 Glucose Ribose Glyceraldehyde 4/7/09 6 Chirality of Simple Sugars How Many Chiral Centers? Which carbon, or carbons, are chiral? Ketotriose Erythrose Fructose 7 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
3 How Many Stereo Isomers? Ketotriose Erythrose Fructose Sterioisomers Isomers that depend on the arrangement of the atoms in space, not just their connections. Types of Stereoisomers Stereoisomers Diasteriomers Enatiomers # of Stereoisomers = 2N, where N= # of chiral centers 9 Stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other Stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other. 10 Naming Stereoisomers Pairs of Enantiomers are Named D or L The position of the OH on the chiral carbon atom furthest from the CHO or -CO group determines the D or L nature. L-Glucose D-Glucose* 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
4 When an aldehyde or ketone reacts with alcohol hemiacetals are formed. Cyclic Stuctures Most of the time sugars are not in straight chains. Instead the atoms in each simple sugar are arranged to form a ring. The key to recognizing the hemiacetals is the presence of a carbon atom bound to both an -OH and a -OR group Sugars contain an aldehyde or ketone and an alcoholic group on the same molecule and they form an internal hemiacetal Such cyclic structures are called Hayworth projections. In these structures the OH groups on the left of the open chain structure always point up and the OH group on the right point down. The carbon that had the C=O bond, is called the anomeric carbon
5 The cyclic form of the simple sugars adds another level of complexity to naming the sugars. When the OH is on the side opposite of the - CH 2 OH, it is labeled an α-sugar, and when it is on the same side as the CH2OH it is labeled β-sugar. 17 The crystaline form of D-Glucose is entirely in its alpha form. Once crystalline D-Glucose is dissolved in water beta-dglucose is seen. This shift is gradual. In the end the glucose maintains the same % of each type. (What determines the relative amounts, and why is the interconversion slow? 18 D-Glucose Some important monosaccharides: Glucose Galactose Fructose Ribose and deoxyribose 4/6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter D-Glucose, sometimes called dextrose or blood sugar, is the most widely occurring of all monosaccharides. In nearly all living organisms, D-glucose serves as a source of energy for all biochemical reactions. It is the final stage in carbohydrate digestion and is easily converted to acetyl-scoa. D-glucose is stored in polymeric form as starch in plants and as glycogen in animals.. 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
6 D-Galactose It is found in plant gums and pectins and is one of the sugars in lactose. Galactose is easily converted to Glucose. They differ only is the orientation of the atoms at one of the carbons in the carbon chain. In some people conversion of galactose to glucose is impaired. In these cases patients must eat a diet low in galactose. (No dairy, caution with vitamins and medicines, no organ meets or garbanzo beans.) D-Fructose A 6 carbon sugar, that forms a 6 member as well as a 5 member ring. 4/7/ Cyclic Forms of D-Fructose D-Ribose 5 Carbon sugar that forms a 5 member ring. Ribose is part of many other important molecules (Coenzyme A and ATP, oxidizing and reducing coenzymes.) Ribose is found in its Oxy and Deoxy forms 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
7 Reducing Sugars Aldehydes can reduce other substances and themselves be oxidized to form a carbocylic acid. In basic solution ketoses can also reduce other substances and be oxidized to a carbocylic acid The fact that these can reduce other substances is used as a common way to test for monosacharides 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter Disacchrides 26 Reactions with alcohols (glycoside and disaccharide formation) Hemiacetals and Alcohols A hemiacetal An alcohol An acetal Hemiacteal : An alcohol and an -OR l group attached to a carbon atom. (The R stands a carbon atom with 3 other things attached to it. Acetal : Two OR groups attached to a carbon atom. (acetyl group : CH 3 CO-). Hemiacteal : An alcohol and an OR group attached to a carbon atom. (The R stands a carbon atom with 3 other things attached to it. Acetal : Two OR groups attached to a carbon atom. Monosaccharides react with alcohols to form acetals, which are called glycosides. 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter /7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
8 Glycosides Monosaccharides react with alcohols to form acetals, which are called glycosides. Glycoside Bonds The type of bond formed between and alcohol and monosaccharide can occur between to monosaccharides. The bond between the anomeric carbon atom and the oxygen atom of the OR group is known as glycosidic bond. The bonds between to monosaccharides are glycosidic bonds In polysaccharides the monosaccharides are connected to each other by glycosidic bond. Linking Monosaccharides 4/6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter The anomeric carbon (C1) is reacting with the C4 to for a glycosidic bond. In this case the bond is between two D-Glusose sugar molecules. The anomeric carbon is in the α form and this link would be called a α-1,4 link 8
9 Glycoside Hydrolysis Since the glycosides no longer contain the hemiacetal group that is etablished equilibria with open chain form they are not reducing sugars. The reverse reaction is the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond. This takes place during digestion of all carbohydrates. 4/6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter /7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter Maltose Made from 2 α-dglucose molecules Joined by a α 1,4 link 2 D-Glucose molecules can join in many ways they do not all give maltose. Present in fermenting grains, it is produced when the enzyme amylase breaks down starches. (What type of enzyme is amylase?) It is hydolyzed to glucose by another enzyme. 35 Lactose Made from β-dglucose and β-d galactose Joined by a β 1,4 link This glycoside link requires lactase in order to by hydrolyzed If it is not broken down it can draw water into the intestines and cause bloating. If not broken down it can be fermented by bacteria in the gut to CO 2, CH 4, and lactate and H 2. The result is pretty miserable. 36 9
10 Sucrose Made from D-glucose and D-fructose Joined by a 1,2 anomeric link This involves the 5 carbon ring form of fructose Derivatives of Monosaccharides The enzyme invertase breaks the glycoside bond and forms a D-glucose D-fructose solution Sucrose is table sugar. 37 The OH groups provide many opportunities to form derivatives of simple sugars. These derivatives are important in the function of many polysaccharides as well as in glucose metabolism. 38 Variations on Carbohydrates: Chitin Many carbohydrates have additional functional groups. These groups can be carboxylic, amino and acetyl groups. Chitin: is a polysaccharide composed of N acetyl D- glucosamine. Connective Tissue: Blood vessels, cartilage and tendons are made of protein fibers that are embedded in a syrupy unbranched polysaccharide mucopolysaccharide.this jell like substance works as a shock absorber in the joints and extra-cellular space. 4/6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter Chitin: is a polysaccharide composed of N acetyl D- glucosamine. It is tough and somewhat rigid. It forms the outside of lobsters, shrimps,and many bugs. It is the 2 nd most abundant polysaccharide. 4/7/
11 Connective Tissue Connective Tissue: Carbohydrates form a syrupy unbranched polysaccharide mucopolysaccharide.this jell like substance works as a shock absorber in the joints and extra-cellular space Hyaluronate Along polysaccharide composed of 25,000 disaccharide units. It is a very rigid polysaccharide that makes a viscous solution with H 2 O. -It is made with sugar derivatives that have carboxyl groups ( CO2 - ). Water is held next to the charged group so this rigid molecule can act as a lubricant for joints Chondroitin 6 sulfate is present in tendons and cartilage where it is linked to proteins. Glucosaminesulfate, as well as chondroitin-6-sulfate is sold to help with joint conditions. Heparin Heparin: This is a polysaccharide associated with connective tissue. It is an anticoagulant. It is composed of variety of monosaccharides many of which contain sulfate groups. 4/7/ /7/09 42 Heparin Highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule It large density of negative charge causes it to binds strongly to blood clotting factors and this prevents clot formation. Its natural utility in animals is not known. It seems to have a role in healing from an injury. Glycoproteins Glycoproteins: Proteins containing short carbohydrate chains are known as glycoproteins. Many uses organism, in some cases they are used to protect a protein from digestion. Some glycoproteins are present at the surface of cells. The protein part of the molecule lies embedded in the cell membrane and the hydrophilic carbohydrate portion extends into the surrounding fluid. It is obtained from slaughtered pigs and cows. 4/7/ /6/
12 4/7/09 Polysaccharides On the Surface of Cells Polysaccharides on Cell Surfaces The oligosaccharide chains function as the receptors for molecular messengers, other cells, pathogens, or drugs. They are also responsible for the A, B and O typing of blood. 4/6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter /6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter Storage Polysaccharides Stach and Glysogen 4/6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter /7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
13 4/7/09 Starch Amylose Starch is a polymer of α D glucose joined by α 1,4 linkage, not a 1,4 linkage as is cellulose. Starch is the way that energy is stored in plants. Starch is fully digestible to humans Starch digestion begins in the mouth where the enzyme amylase can break the starch down into maltose. In the small intestine, amylase is released from the pancreas and finishes off the digestion Starch has two forms- Amylose and amylopectin. 4/7/09 49 Amylose accounts for about 20 % of the starch. It is soluble in water.. The amylose oligosaccharide is a chain, that is often coiled. 4/7/09 Amylopectin 50 Glycogen-Structure Glycogen: Also called animal starch. Glycogen is structurally similar to starch as it is a polymer of α-d-glucose. Glycogen is much more branched than the starch molecule and has a much larger molecular weight up to a million glucose units per molecule. Very similar to amylose but it is branched, and made up of very long polymers 4/7/ /6/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
14 Glycogen-Uses Glycogen is concentrated in the liver and in muscles. In muscles it can be quickly converted to glucose and used to make ATP. In the liver it can be converted to glucose when blood sugar becomes low Cellulose Cellulose β-d glucose units joined by β-1.4 linkage. The seemingly minor difference between the α and β units of glucose in starch and cellulose accounts for the inability in digestion of cellulose. In grazing animals and termites and moths there are microorganisms that reside in the digestive tracts. These produce enzymes that can hydrolyze the β glycosidic bonds in cellulose. Cellulose is the fiber that we need in our diet, but we can not digest it. (What other example have we seen of needing enzymes in bacteria in the gut in order to digest a food.) 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter /6/09 54 Cellulose vs. Starch Cellulose Overall Structure Similar link different anomers. 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter Hydrogen bonds between chains are one of the reasons for cellulose s strength. 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
15 Summary Overview of the Structure and Function of Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides 4/7/09 Satyamurti/ Chapter
CHEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) Page 1
 CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
3) How many monosaccharides are connected to each other in a disaccharide? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 2e (Frost) HOMEWORK Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Life s Sweet Molecules 6.1 Multiple-Choice 1) Which of the following is a polysaccharide? Glucose Sucrose C) Starch D) Maltose
General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 2e (Frost) HOMEWORK Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Life s Sweet Molecules 6.1 Multiple-Choice 1) Which of the following is a polysaccharide? Glucose Sucrose C) Starch D) Maltose
CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1
 CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1 Chiral centers: Asymmetric carbons, i.e carbon atom with four different substituents Enantiomers : Mirror images Stereoisomers MONOSACCHARIDE
CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1 Chiral centers: Asymmetric carbons, i.e carbon atom with four different substituents Enantiomers : Mirror images Stereoisomers MONOSACCHARIDE
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
Catalysis by Enzymes. Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction.
 Catalysis by Enzymes Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction. Enzymatic Reaction Specificity Enzyme Cofactors Many enzymes are conjugated proteins that require nonprotein portions
Catalysis by Enzymes Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction. Enzymatic Reaction Specificity Enzyme Cofactors Many enzymes are conjugated proteins that require nonprotein portions
Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells
 Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Biochemistry of Cells
 Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Macromolecules 1 Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids
 VEA Bringing Learning to Life Program Support Notes Macromolecules 1 Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids Grades 10 - College 25mins Teacher Notes by Sue Wright, B. Sc., Dip. Ed. Produced by VEA Pty Ltd
VEA Bringing Learning to Life Program Support Notes Macromolecules 1 Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids Grades 10 - College 25mins Teacher Notes by Sue Wright, B. Sc., Dip. Ed. Produced by VEA Pty Ltd
How To Understand The Chemistry Of Organic Molecules
 CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
4. Which carbohydrate would you find as part of a molecule of RNA? a. Galactose b. Deoxyribose c. Ribose d. Glucose
 1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
Chapter 5. The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s
 Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
The Molecules of Cells
 The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
I. Chapter 5 Summary. II. Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids. III. Lipids
 I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2
 Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2 Objectives -Know the difference between a reducing sugar and a non-reducing sugar. -Distinguish Monosaccharides from Disaccharides and Polysaccharides -Understand
Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2 Objectives -Know the difference between a reducing sugar and a non-reducing sugar. -Distinguish Monosaccharides from Disaccharides and Polysaccharides -Understand
The Chemistry of Carbohydrates
 The Chemistry of Carbohydrates Experiment #5 Objective: To determine the carbohydrate class of an unknown by carrying out a series of chemical reactions with the unknown and known compounds in each class
The Chemistry of Carbohydrates Experiment #5 Objective: To determine the carbohydrate class of an unknown by carrying out a series of chemical reactions with the unknown and known compounds in each class
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates
 Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Organic Compounds. Essential Questions: What is Organic? What are the 4 major Organic Compounds? How are they made? What are they used for?
 Organic Compounds Essential Questions: What is Organic? What are the 4 major Organic Compounds? How are they made? What are they used for? Aristotle: Francesco Redi: What do we already know? Spontaneous
Organic Compounds Essential Questions: What is Organic? What are the 4 major Organic Compounds? How are they made? What are they used for? Aristotle: Francesco Redi: What do we already know? Spontaneous
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Elements in Biological Molecules
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Worksheet 13.1. Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary
 Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Carbon-organic Compounds
 Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbon The element of life! All living things contain the element carbon. Organic means it contains carbon The reason for this is because of carbon s ability
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbon The element of life! All living things contain the element carbon. Organic means it contains carbon The reason for this is because of carbon s ability
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
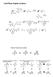 Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance
 Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Chapter 2 Chemical Principles
 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles I. Chemistry. [Students should read this section on their own]. a. Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. b. The atom is the smallest unit
Chapter 2 Chemical Principles I. Chemistry. [Students should read this section on their own]. a. Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. b. The atom is the smallest unit
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1
 Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins
 Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chapter 2. The Chemistry of Life Worksheets
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Enzymes. A. a lipid B. a protein C. a carbohydrate D. a mineral
 Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Name Date Period. Keystone Review Enzymes
 Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
WATER CHAPTER 3 - BIOCHEMISTRY "THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE" POLARITY HYDROGEN BONDING
 CHAPTER 3 - BIOCHEMISTRY "THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE" WATER Compare the body of the jellyfish with our own bodies. The jellyfish will die if it is removed from its water environment, yet we can live in the
CHAPTER 3 - BIOCHEMISTRY "THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE" WATER Compare the body of the jellyfish with our own bodies. The jellyfish will die if it is removed from its water environment, yet we can live in the
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes
 Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes Enzymes: as a catalyst, an enzyme increases the rate of a reaction by changing the way a reaction takes place, but is itself not changed at the end of the reaction. An
Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes Enzymes: as a catalyst, an enzyme increases the rate of a reaction by changing the way a reaction takes place, but is itself not changed at the end of the reaction. An
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Twenty Three 1
 23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Photo Cell Resp Practice. A. ATP B. oxygen C. DNA D. water. The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants.
 Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
Enzymes. Chapter 3. 3.1 Enzymes and catalysts. Vital mistake. What is an enzyme?
 Chapter 3 Enzymes Vital mistake We may not be able to see them, but enzymes are absolutely crucial to the lives of ourselves and all other living organisms. The Quarter Horse (Figure 3.1) is a breed of
Chapter 3 Enzymes Vital mistake We may not be able to see them, but enzymes are absolutely crucial to the lives of ourselves and all other living organisms. The Quarter Horse (Figure 3.1) is a breed of
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch
 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch Introduction Enzymes are proteins composed of amino acid building blocks. Enzymes catalyze or increase the rate of metabolic
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch Introduction Enzymes are proteins composed of amino acid building blocks. Enzymes catalyze or increase the rate of metabolic
3120-1 - Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which series is arranged in correct order according to decreasing size of structures? A) DNA, nucleus, chromosome, nucleotide, nitrogenous base B) chromosome, nucleus, nitrogenous base, nucleotide,
Name: 1) Which series is arranged in correct order according to decreasing size of structures? A) DNA, nucleus, chromosome, nucleotide, nitrogenous base B) chromosome, nucleus, nitrogenous base, nucleotide,
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
BIOMOLECULES. reflect
 reflect A child s building blocks are relatively simple structures. When they come together, however, they can form magnifi cent structures. The elaborate city scene to the right is made of small, simple
reflect A child s building blocks are relatively simple structures. When they come together, however, they can form magnifi cent structures. The elaborate city scene to the right is made of small, simple
Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein
 Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein Biology Leaving Cert Experiments Materials/Equipment Starch solution (1%) Iodine Solution Glucose Solution (1%) 100 C) Benedict s
Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein Biology Leaving Cert Experiments Materials/Equipment Starch solution (1%) Iodine Solution Glucose Solution (1%) 100 C) Benedict s
pathway that involves taking in heat from the environment at each step. C.
 Study Island Cell Energy Keystone Review 1. Cells obtain energy by either capturing light energy through photosynthesis or by breaking down carbohydrates through cellular respiration. In both photosynthesis
Study Island Cell Energy Keystone Review 1. Cells obtain energy by either capturing light energy through photosynthesis or by breaking down carbohydrates through cellular respiration. In both photosynthesis
008 Chapter 8. Student:
 008 Chapter 8 Student: 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of
008 Chapter 8 Student: 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of
1.1.2. thebiotutor. AS Biology OCR. Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport. Module 1.2 Cell Membranes. Notes & Questions.
 thebiotutor AS Biology OCR Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport Module 1.2 Cell Membranes Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. The main
thebiotutor AS Biology OCR Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport Module 1.2 Cell Membranes Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. The main
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion
 Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
Cellular Energy. 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following?
 Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline
 AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
What happens to the food we eat? It gets broken down!
 Enzymes Essential Questions: What is an enzyme? How do enzymes work? What are the properties of enzymes? How do they maintain homeostasis for the body? What happens to the food we eat? It gets broken down!
Enzymes Essential Questions: What is an enzyme? How do enzymes work? What are the properties of enzymes? How do they maintain homeostasis for the body? What happens to the food we eat? It gets broken down!
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Todays Outline. Metabolism. Why do cells need energy? How do cells acquire energy? Metabolism. Concepts & Processes. The cells capacity to:
 and Work Metabolic Pathways Enzymes Features Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Membrane Transport Diffusion Osmosis Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Todays Outline -Releasing Pathways
and Work Metabolic Pathways Enzymes Features Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Membrane Transport Diffusion Osmosis Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Todays Outline -Releasing Pathways
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
2. Which type of macromolecule contains high-energy bonds and is used for long-term energy storage?
 Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Qualitative Testing for Carbohydrates
 R E A 446 modular laboratory program in chemistry program editor:. A. Neidig Qualitative Testing for arbohydrates prepared by James. Schreck, University of Northern olorado, and William M. Loffredo, East
R E A 446 modular laboratory program in chemistry program editor:. A. Neidig Qualitative Testing for arbohydrates prepared by James. Schreck, University of Northern olorado, and William M. Loffredo, East
Water. Definition: A mole (or mol ) Water can IONIZE transiently. NONpolar covalent molecules do not dissolve in water + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +
 Today s Topics Polar Covalent Bonds ydrogen bonding Properties of water p Water C bonds are Nonpolar Will these molecules dissolve in water? Start Macromolecules Carbohydrates & Lipids Sept 4, 05 Why are
Today s Topics Polar Covalent Bonds ydrogen bonding Properties of water p Water C bonds are Nonpolar Will these molecules dissolve in water? Start Macromolecules Carbohydrates & Lipids Sept 4, 05 Why are
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions
 7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions Multiple choice questions 1 B 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 A 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 B Structured questions 11 a i Maintenance of a constant internal environment within set limits i Concentration
7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions Multiple choice questions 1 B 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 A 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 B Structured questions 11 a i Maintenance of a constant internal environment within set limits i Concentration
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM. Section B: Enzymes
 CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
chapter 5 Carbohydrates
 part two The Energy-Yielding Nutrients and Alcohol chapter 5 Carbohydrates Chapter utline Carbohydrates An Introduction Structures and Functions of Simple Carbohydrates Monosaccharides: Glucose, Fructose,
part two The Energy-Yielding Nutrients and Alcohol chapter 5 Carbohydrates Chapter utline Carbohydrates An Introduction Structures and Functions of Simple Carbohydrates Monosaccharides: Glucose, Fructose,
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
 reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
Chapter 4. Carbohydrates: Bountiful Sources of Energy and Nutrients
 hapter 4 arbohydrates: Bountiful Sources of Energy and Nutrients hapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Describe the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates,
hapter 4 arbohydrates: Bountiful Sources of Energy and Nutrients hapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Describe the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates,
Get It Right. Answers. Chapter 1: The Science of Life. A biologist studies all living things.
 Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
What affects an enzyme s activity? General environmental factors, such as temperature and ph. Chemicals that specifically influence the enzyme.
 CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration
 1 of 5 11/9/2011 8:11 PM Name: Hour: Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration Energy in General 1. Differentiate an autotroph from a hetertroph as it relates to obtaining energy and the processes
1 of 5 11/9/2011 8:11 PM Name: Hour: Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration Energy in General 1. Differentiate an autotroph from a hetertroph as it relates to obtaining energy and the processes
Topic 3: Nutrition, Photosynthesis, and Respiration
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
The correct answer is d C. Answer c is incorrect. Reliance on the energy produced by others is a characteristic of heterotrophs.
 1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis
 Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
Lab 2 Biochemistry. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Lipid Structure and Role in Food. The lab has the following learning objectives.
 1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
Macromolecules in my food!!
 Macromolecules in my food!! Name Notes/Background Information Food is fuel: All living things need to obtain fuel from something. Whether it is self- made through the process of photosynthesis, or by ingesting
Macromolecules in my food!! Name Notes/Background Information Food is fuel: All living things need to obtain fuel from something. Whether it is self- made through the process of photosynthesis, or by ingesting
- Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells.
![- Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells. - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells.](/thumbs/40/21014327.jpg) Cellular respiration - how cells make energy - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - ATP - this is provided by the lungs - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood
Cellular respiration - how cells make energy - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - ATP - this is provided by the lungs - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood
CHEM 2353 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. Carbohydrates. Organic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R.
 hapter 7 Notes EM 2353 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry hapter 7 arbohydrates rganic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R. Slabaugh Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux Angelo State University
hapter 7 Notes EM 2353 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry hapter 7 arbohydrates rganic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R. Slabaugh Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux Angelo State University
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
How To Understand The Human Body
 Introduction to Biology and Chemistry Outline I. Introduction to biology A. Definition of biology - Biology is the study of life. B. Characteristics of Life 1. Form and size are characteristic. e.g. A
Introduction to Biology and Chemistry Outline I. Introduction to biology A. Definition of biology - Biology is the study of life. B. Characteristics of Life 1. Form and size are characteristic. e.g. A
CHAPTER 4: Enzyme Structure ENZYMES
 CHAPTER 4: ENZYMES Enzymes are biological catalysts. There are about 40,000 different enzymes in human cells, each controlling a different chemical reaction. They increase the rate of reactions by a factor
CHAPTER 4: ENZYMES Enzymes are biological catalysts. There are about 40,000 different enzymes in human cells, each controlling a different chemical reaction. They increase the rate of reactions by a factor
lt\ Nutrition a-glncose www.cambridge.org in this web service Cambridge University Press Glucose+ fructose Glucose+ galactose
 P. T. Marshall and G. M. ughes 1 Nutrition 1.1 The basic biochemistry of mammalian metabolites The mammals are heterotrophic, that is to say they derive their essential nutrients, via food chains, from
P. T. Marshall and G. M. ughes 1 Nutrition 1.1 The basic biochemistry of mammalian metabolites The mammals are heterotrophic, that is to say they derive their essential nutrients, via food chains, from
How To Eat Healthily
 Pierce College Putman/NUTR& 101 Unit 04 Practice Exam: Carbohydrates 1. Which is not a monosaccharide? a. lactose b. glucose c. fructose d. galactose 2. Used for immediate energy in the body: a. carbohydrates
Pierce College Putman/NUTR& 101 Unit 04 Practice Exam: Carbohydrates 1. Which is not a monosaccharide? a. lactose b. glucose c. fructose d. galactose 2. Used for immediate energy in the body: a. carbohydrates
