Endoneurium. Perineurium. Epineurium. Parasympathetic division (b) Figure Frontal lobe. Temporal lobe
|
|
|
- Agatha Thornton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
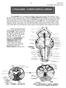
1 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) The Nervous System Cranial and spinal Nerves All neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord Sensory receptors Peripheral and associated ganglia Motor neuron endings Constitutes a pathway between CNS and outlying structures 12 pairs of cranial 31 pairs of spinal Endoneurium Axon Myelin sheath Perineurium Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Epineurium Sensory (afferent) division Motor (efferent) division Somatic nervous Autonomic nervous system system (ANS) Fascicle Blood vessels Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division (b) Figure 13.1 Figure 13.3b Cranial Nerves 12 pairs of Associated with the brain Do not decussate May continue in tracts that do Typically see ipsilateral functional deficits with brain injury Function may be sensory, motor, or both Most are at least partially mixed Each is identified by Number (I through XII) Name Frontal lobe Temporal lobe Infundibulum Facial (VII) Vestibulocochlear (VIII) Glossopharyngeal (IX) Vagus (X) Accessory (XI) Hypoglossal (XII) (a) Filaments of olfactory (I) Olfactory bulb Olfactory tract Optic (II) Optic chiasma Optic tract Oculomotor (III) Trochlear (IV) Trigeminal (V) Abducens (VI) Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Figure 13.5 (a) 1
2 1/17/2016 Cranial I VI Sensory function Motor function PS* fibers I Olfactory (smell) II Optic III Oculomotor (vision) IV Trochlear V Trigeminal (general sensation) VI Abducens Cranial VII XII VII Facial VIII Vestibulocochlear Sensory function Motor function MANY mnemonics to help you remember name, order, and function Google at your own risk A few possibilities PS* fibers (taste) (hearing and balance) Some IX Glossopharyngeal (taste) X Vagus (taste) XI Accessory XII Hypoglossal (b) Cranial Nerves *PS = parasympathetic Figure 13.5 (b) Loss of function casues ptosis, external strabismus ( down and out ) Trochlear Nerve Palsy 2
3 1/17/2016 Testing function Trigeminal neuralgia Loss of function causes internal strabismus Vestibulocochlear Nerve Test 3
4 1/17/2016 Accessory Nerve Testing Functions of the cranial Hypoglossal testing Spinal Nerves Cervical plexus Brachial plexus 31 pairs of mixed named according to their point of issue from the spinal cord 8 cervical (C1 ) 12 thoracic (T1 T12) 5 Lumbar (L1 ) 5 Sacral ( S5) 1 Coccygeal (C0) Cervical enlargement Intercostal Cervical C1 te: only 7 cervical vertebrae Thoracic T1 T12 Lumbar enlargement Lumbar plexus Sacral plexus Cauda equina Lumbar L1 Sacral S5 Coccygeal Co1 Figure
5 Spinal Nerve Organization Spinal connects to the spinal cord via two roots Ventral roots Contain motor (efferent) fibers from the ventral horn motor neurons Fibers innervate skeletal muscles Dorsal roots Contain sensory (afferent) fibers from sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia Conduct impulses from peripheral receptors Dorsal and ventral roots unite to form spinal Emerge from vertebral column via the intervertebral foramina Snack at 1AM Coccygeal (1) Afferent Dorsal root (sensory) Dorsal root ganglion Dorsal horn (interneurons) Somatic sensory neuron Visceral sensory neuron Visceral motor Spinal neuron Ventral horn Ventral root (motor neurons) Somatic (motor) motor neuron Interneurons receiving input from somatic sensory neurons Efferent Interneurons receiving input from visceral sensory neurons Spinal Nerve Organization Rami Each spinal branches into mixed rami Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus Rami communicantes branch off of ventral ramus Involved in ANS signaling pathways Meningeal branch Reenters the vertebral canal and innervates the meninges and blood vessels within Visceral motor (autonomic) neurons Somatic motor neurons Figure Dorsal root ganglion Dorsal ramus of spinal Ventral ramus of spinal Spinal Rami communicantes Sympathetic trunk ganglion Gray matter White matter Ventral root Dorsal root Dorsal and ventral rootlets of spinal Anterior view showing spinal cord, associated, and vertebrae. The dorsal and ventral roots arise medially as rootlets and join laterally to form the spinal. Figure 13.7 (a) 5
6 Spinal Nerve Organization Dorsal ramus Innervates Deep back muscles surface of trunk (skin and muscle) Ventral ramus Innervates Superficial back muscles Limbs Lateral and anterior surfaces of trunk (skin and muscle on side, chest, ribs, abdominal wall) Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus Spinal Rami communicantes Sympathetic trunk ganglion Intercostal Dorsal root ganglion Dorsal root Ventral root Branches of intercostal Lateral Anterior Sternum (b) Cross section of thorax showing the main roots and branches of a spinal. Figure 13.7 (b) Distribution of Spinal Nerves Dermatome Area of skin innervated by the branches of a single spinal All spinal except C 1 participate in dermatomes Most dermatomes overlap T2 L1 L2 L3 C4 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 T10 T11 T12 S2 S3 L1 L2 C2 C3 L3 T2 L2 S2 C2 C3 C4 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 T10 S2 S3 S4 S5 L1 L2 S2 T11 T12 L1 L3 L3 Anterior view (b) view Figure All ventral rami form interlacing networks 4 plexuses Cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral Fibers from the rami branch and become redistributed Each exiting the plexus has fibers from several spinal Advantage? Exception: ventral rami of T 2 T 12 Do not form a plexus Form intercostal Cervical plexus Brachial plexus Cervical enlargement Intercostal Lumbar enlargement Lumbar plexus Sacral plexus Cauda equina Cervical C 1 C 8 Thoracic T 1 T 12 Lumbar L 1 L 5 Sacral S 1 S 5 Coccygeal Co 1 Figure
7 Ventral rami Cervical plexus Formed by ventral rami of C 1 C 4 Innervates skin & muscles of the neck, ear, back of head, and shoulders Hypoglossal (XII) Lesser occipital Greater auricular Transverse cervical Ansa cervicalis Accessory (XI) Phrenic Supraclavicular Segmental branches Ventral rami: C 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 Figure 13.8 Phrenic Major motor and sensory of the diaphragm Critical for breathing Receives fibers from C 3 C 5 Therefore receives innervation from both the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus Brachial plexus Formed by ventral rami of C 4 T 1 Gives rise to the that innervate the upper limb Median Ulnar Axillary Radial Musculo Cords Lateral Medial Axillary Musculo Radial Median Ulnar Anterior Dorsal scapular Nerve to subclavius Suprascapular (a) Roots (rami C 5 T 1), trunks,, and cords Trunks Roots Roots (ventral rami): C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 Upper Middle Lower Trunks T 1 Long thoracic Medial pectoral Lateral pectoral Upper subscapular Lower subscapular Thoracodorsal Medial of the arm and forearm Axillary Anterior Humerus Radial Musculo Ulna Radius Ulnar Median Radial (superficial branch) Dorsal branch of ulnar Superficial branch of ulnar Digital branch of ulnar Muscular branch Median Digital branch (c) The major of the upper limb Trunks Roots Figure 13.9 (a) Figure 13.9 (c) 7
8 Injuries Radial damage causes the fingers, wrist, or hand to be in the chronically flexed position Crutch paralysis caused when crutches are improperly adjusted Saturday night paralysis caused by falling asleep with the arm hanging over the armrest of a chair Honeymoon paralysis caused by someone else sleeping on and compressing the arm Injuries Radial damage causes the fingers, wrist, or hand to be in the chronically flexed position Radial is constantly pushed against the humerus, and cannot innervate extensor muscles Improves quickly with therapy Injuries Ulnar is the largest in the body that is not protected by muscle or bone Injury is common Funny bone Weakness in flexion of the hand at wrist, inability to cross fingers Claw hand at rest Injuries Carpal tunnel Caused when the median is compressed as it travels through the wrist Pain, numbness, tingling in the hand, forearm, and shoulder Caused by anything that applies pressure to the median Esp. cumulative trauma caused by repetitive motion If untreated may cause wasting on muscles at the base of the thumb Lumbar plexus Arises from L 1 L 5 (some T 12 ) Innervates thigh, abdominal wall, external genitalia, leg & foot Femoral Innervates quadriceps, skin of anterior thigh & medial surface of leg Functions in extending the knee; sensory function in skin on front and inner sides of thigh, shin, and arch of foot Obturator Passes through obturator foramen Innervates adductor muscles; sensory function in skin on medial aspect of thigh Ventral rami Iliohypogastric Ilioinguinal Genitofemoral Lateral femoral Obturator Ventral rami: Iliohypogastric L 1 Ilioinguinal Femoral L 2 Lateral femoral Obturator L 3 Anterior femoral L 4 Saphenous Femoral L 5 Lumbosacral trunk (a) Ventral rami and major branches of the lumbar plexus (b) Distribution of the major from the lumbar plexus to the lower limb Figure
9 Sacral plexus Arises from L 4 S 4 Serves the buttock, lower limb, pelvic structures & perineum Gives rise to sciatic Longest and thickest of the body Innervates Muscles of the leg and foot Skin on the leg and foot Superior gluteal Lumbosacral trunk Inferior gluteal Common fibular Tibial femoral Pudendal Sciatic Ventral rami Ventral rami: L 4 L 5 S 1 S 2 S 3 S 4 S 5 Co 1 Ventral rami and major branches of the sacral plexus Figure (a) Superior gluteal Inferior gluteal Pudendal Sciatic femoral Common fibular Tibial Sural (cut) Deep fibular Superficial fibular Plantar branches (b) Distribution of the major from the sacral plexus to the lower limb Figure (b) 9
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Lu L m u b m a b r a rta T p a Figure 12.30
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
 Cross section through two fascicles (bundles) of nerve fibers in a nerve CHAPTER 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes CHAPTER OUTLINE The Spinal Cord 482 Functions 482 Gross Anatomy
Cross section through two fascicles (bundles) of nerve fibers in a nerve CHAPTER 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes CHAPTER OUTLINE The Spinal Cord 482 Functions 482 Gross Anatomy
General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises
 1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
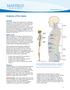 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Anatomicalintroduction
 3rd INTERVENTIONAL HANDS-ON PAIN RELIEF & NEUROMODULATION CADAVER WORKSHOP Anatomicalintroduction Gdansk-Poland Programmeofthelecture Shortintroductionto theanatomyof: 1.Vertebralcolumn 2.Intervertebraldiscs
3rd INTERVENTIONAL HANDS-ON PAIN RELIEF & NEUROMODULATION CADAVER WORKSHOP Anatomicalintroduction Gdansk-Poland Programmeofthelecture Shortintroductionto theanatomyof: 1.Vertebralcolumn 2.Intervertebraldiscs
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011
 Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Body cavities. Body Planes
 Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Spine & Nervous System Trauma
 Spine & Nervous System Trauma Andrea L. Williams PhD, RN Emergency Education Specialist Clinical Associate Professor University of Wisconsin School of Nursing http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g2tdp_7q3n4
Spine & Nervous System Trauma Andrea L. Williams PhD, RN Emergency Education Specialist Clinical Associate Professor University of Wisconsin School of Nursing http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g2tdp_7q3n4
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Central control of the autonomic nervous system
 Central control of the autonomic nervous system John Morris Hypothalamus as an integrative centre regulating the ANS Involved in homeostasis stress responses anticipatory responses Sympathetic and para
Central control of the autonomic nervous system John Morris Hypothalamus as an integrative centre regulating the ANS Involved in homeostasis stress responses anticipatory responses Sympathetic and para
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy. What to do with arm pain? Defining Arm Pain. Arm Pain
 Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Appendix A Partial Pick List of Injury and Sequelae Codes (ICD-10-CA)
 What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): NERVE Blockade for Treatment of Chronic Pain and Neuropathy (L35457) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): NERVE Blockade for Treatment of Chronic Pain and Neuropathy (L35457) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain
 Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Pain Management Top Diagnosis Codes (Crosswalk)
 Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15
 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System 468 Comparison of the Autonomic and Somatic Motor Systems 468 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System 468 Comparison of the Autonomic and Somatic Motor Systems 468 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions *
 ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more
 BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
Chiropractic ICD 9 Code List
 Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
CHAPTER 32 QUIZ. Handout 32-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
 F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
Laser Treatment Policy
 Laser Treatment Policy Pursuant to federal law 21 CFR 812.2(c)7 and 812.3(b), physician(s) at this pain center may advise and use unapproved laser s on patients under one or more of the following conditions:
Laser Treatment Policy Pursuant to federal law 21 CFR 812.2(c)7 and 812.3(b), physician(s) at this pain center may advise and use unapproved laser s on patients under one or more of the following conditions:
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Ventral Surface. The Cranial Nerves 4/5/2010. Review: Spinal Nerves
 The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
III./8.4.2: Spinal trauma. III./8.4.2.1 Injury of the spinal cord
 III./8.4.2: Spinal trauma Introduction Causes: motor vehicle accidents, falls, sport injuries, industrial accidents The prevalence of spinal column trauma is 64/100,000, associated with neurological dysfunction
III./8.4.2: Spinal trauma Introduction Causes: motor vehicle accidents, falls, sport injuries, industrial accidents The prevalence of spinal column trauma is 64/100,000, associated with neurological dysfunction
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Colossus Important Diagnoses. Instructions for How to List Diagnoses
 1 Colossus Important Diagnoses Instructions for How to List Diagnoses 1. Only list diagnoses on HCFA-1500 or CMS-1500 billing forms 2. Use as many billing forms/pages as necessary (4 diagnoses per billing
1 Colossus Important Diagnoses Instructions for How to List Diagnoses 1. Only list diagnoses on HCFA-1500 or CMS-1500 billing forms 2. Use as many billing forms/pages as necessary (4 diagnoses per billing
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28
 The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
MD 2016. Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy. A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
