Mobile Communication Systems: GSM Global System for Mobile Communication
|
|
|
- Bridget Norman
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comunicações Móveis Licenciatura em Engenharia Electrotécnica e de Computadores Licenciatura em Engenharia Informática e Computação Mobile Communication Systems: GSM Global System for Mobile Communication Mário Jorge Leitão Partially adapted with permission from Mobile Communication: Wireless Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller Overview GSM formerly: Groupe Spéciale Mobile (founded 1982) now: Global System for Mobile Communication Pan-European standard (ETSI, European Telecommunications Standardisation Institute) simultaneous introduction of essential services in three phases by the European telecommunication administrations seamless roaming within Europe possible today many providers all over the world use GSM (more than 180 countries in Asia, Africa, Europe, Australia, America) more than 900 million subscribers more than 70% of all digital mobile phones use GSM Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 2
2 Performance characteristics of GSM Communication mobile, wireless communication; support for voice and data services Total mobility international access, chip-card enables use of access points of different providers Worldwide connectivity one number, the network handles localization High capacity better frequency efficiency, smaller cells, more customers per cell High transmission quality high audio quality and reliability for wireless, uninterrupted phone calls at higher speeds (e.g., from cars, trains) Security functions access control, authentication via chip-card and PIN Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 3 Mobile Services GSM services basic services voice services data services short message service additional services emergency number group 3 fax electronic mail supplementary services identification: forwarding of caller number suppression of number forwarding automatic call-back conferencing with up to 7 participants... Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 4
3 Basic Services Services are supported by traffic channels full rate: 22.8 kbit/s (gross bit rate, unprotected transmission) half rate: 11.4 kbit/s (gross bit rate, unprotected transmission) Voice services (speech coding with protection) full rate: 13 / 12.2 kbit/s (original coder / enhanced full rate coder) half rate: 5.6 kbit/s (enhanced half rate coder) Data services (coding with different levels of protection) full rate: 9.6 / 4.8 / 2.4 kbit/s half rate: 4.8 / 2.4 kbit/s Enhanced data services HSCSD (High Speed Circuit Switched Data) n X 14.4 / n X 9.6 / n X 4.8 kbit/s (n=1, 2, 3, 4) GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) various rates (typically up to 53.6 kbit/s) Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 5 GSM architecture: PLMN - Public Land Mobile Network radio cell BSS radio cell RSS C C NSS VLR HLR VLR GC IWF signaling ISDN, PSTN PDN OSS EIR AuC OMC Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 6
4 GSM architecture: PLMN - Public Land Mobile Network RSS - Radio Subsystem: covers all radio aspects Mobile Station Mobile terminal equipment Base Station Controller Management of several and Base Transceiver Station Transmitter, receiver and antennas BSS Base Station Subsystem Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 7 GSM architecture: PLMN - Public Land Mobile Network NSS - Network Subsystem: switching, mobility management, interconnection to other networks, system control C Mobile Switching Centre Management of all connections HLR Home Location Register Associated to each PLMN VLR Visitor Location Register Associated to each C GC Gateway C C providing interconnection to other networks HLR GC fixed network VLR C C VLR Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 8
5 GSM architecture: PLMN - Public Land Mobile Network OSS - Operation Subsystem: centralized operation, management, and maintenance of all GSM subsystems OMC Operation and Management Control of the radio and network Centre subsystems AuC Authentication Centre Security functions EIR Equipment Identity Register Mobile station registration OMC AuC EIR Network Element HLR C Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 9 GSM architecture: interfaces radio subsystem network and switching subsystem fixed partner networks U m A bis A C SS7 HLR ISDN PSTN Interfaces U m : radio interface A bis : standardized, open interface with 16/64 kbit/s user channels BSS GC IWF VLR ISDN PSTN A: standardized, open interface with 64 kbit/s user channels PDN Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 10
6 Voice transcoding and rate adaptation Need for transcoding and rate adaptation - 13 kbit/s air-interface (original coder) C - 64 kbit/s ISDN type switching (PCM, A-law) 3 options for Transcoding and Rate Adapter Unit (TRAU) A bis TRAU C 64 kbit/s 64 kbit/s A TRAU C 16 kbit/s 64 kbit/s C TRAU C 16 kbit/s 64 kbit/s (4 x 16 sub-mux) Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 11 Mobile addresses Several mobile numbers are needed II - International Mobile Subscriber Identity Mobile Country Code (MCC) + Mobile Network Code (MNC) + Mobile Subscriber Identification Number (IN) uniquely identifies the user (SIM card) TI - Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity 32 bits local number allocated by VLR, may be changed periodically hides the II over the air interface - transmitted instead of II RN - Mobile Station Roaming Number Visitor Country Code (VCC) + Visitor National destination Code (VNDC) + Current C code + temporary subscriber number generated by VLR for all visiting users helps HLR to determine current location area hides the II inside the network Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 12
7 Mobile station functional groups MT (Mobile Termination) offers common functions used by all services the offers end-point of the radio interface (Um) - equivalent to NT of an ISDN access hides GSM radio specific characteristics TE (Terminal Equipment) peripheral device of the, offers services to a user TA (Terminal Adapter) interfaces MT with different types of terminal TE1 MT U m TE2 TA MT U m Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 13 Mobile station functional groups SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) uniquely associated to a user stores user and location addresses II - International Mobile Subscriber Identity TI - Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity LAI - Location Area Identification supports authentication and encryption mechanisms PIN - Personal Identity Number PUK - PIN Unblocking Key K i - subscriber secret authentication key A3 - authentication algorithm A8 - cipher key generation algorithm contains personal data list of subscribed services RAM for user directory, S Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 14
8 Base transceiver station and base station controller Tasks of a BSS are distributed over and comprises radio specific functions is the switching center for radio channels switch calls from C to correct Functions Management of radio channels X Frequency hopping (FH) X X Management of terrestrial channels X Mapping of terrestrial onto radio channels X Channel coding and decoding X Rate adaptation X Encryption and decryption X X Paging X X Uplink signal measurements X Traffic measurement X Authentication X Location registry, location update X Handover management X Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 15 Mobile switching center The C (mobile switching center) plays a central role in GSM switching functions additional functions for mobility support management of network resources interworking functions via Gateway C (GC) integration of several databases Specific functions of a C switching of 64 kbit/s channels paging and call forwarding termination of SS7 (signaling system no. 7) mobility specific signaling location registration and forwarding of location information support of short message service (S) generation and forwarding of accounting and billing information Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 16
9 Location registers Database requirements scalability high capacity low delay Home Location Register (HLR) central master database data from every user that has subscribed to the operator one database per operator may be replicated subscriber data II - International Mobile Subscriber Identity list of subscribed services with parameters and restrictions location data current C/VLR address Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 17 Location registers Visitor Location Register (VLR) local database data about all users currently in the domain of the VLR includes roamers and non-roamers associated to each C subscriber identity II - International Mobile Subscriber Identity temporary location LAI - Location Area Identification temporary addresses RN - Mobile Station Roaming Number TI - Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 18
10 GSM location / mobile addresses: summary HLR - Home Location Register Permanent Temporary II - International Mobile Subscriber Identity RN - Mobile Station Roaming Number VLR - Visitor Location Register Permanent II - International Mobile Subscriber Identity LAI - Location Area Identification Temporary RN - Mobile Station Roaming Number TI - Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity SIM - Subscriber Identity Module Permanent Temporary II - International Mobile Subscriber Identity LAI - Location Area Identification TI - Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 19 Operation subsystem elements Authentication Center (AuC) associated to HLR search key: II supports authentication and encryption mechanisms K i - subscriber secret authentication key A3 - authentication algorithm A8 - cipher key generation algorithm Equipment Identity Register (EIR) stores mobile stations IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) white list - mobile stations allowed to connect without restrictions black list - mobile stations locked (stolen or not type approved) gray list - mobile stations under observation for possible problems Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC) control capabilities for the radio and the network subsystems Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 20
11 GSM - TDMA/FDMA frequency MHz 124 channels (200 khz) downlink MHz 124 channels (200 khz) uplink FDMA channels time TDMA frame ms time-slot (normal burst) tail user data S training S user data tail 148 bits / ms bits / ms guard space 3 bits 57 bits 1 26 bits 1 57 bits 3 bits 8.25 bits Radio interface bit rate bits/ ms= kbit/s Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 21 Burst structures Normal Burst: normal data transmission TB CD S TS S CD TB GP Trainin Sequence - allows estimation of propagation characteristics (including multipath), in order to set up the equaliser parameters Stealing flags - indicate that a burst normally assigned to traffic is stolen for signalling Guard Period - avoids overlapping between bursts Tail Bits - assist receiver equalisation (set to 0) Coded Data - user data transmission Access Burst: first time access TB SS CD TB GP Synchronisation Sequence - long training sequence Coded Data - channel or handover access request Guard Period - long period since time advance is not yet defined Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 22
12 Burst structures Frequency Correction Burst: frequency synchronisation of the TB FBS TB GP Fixed Bit Sequence - frequency information for local oscilator locking Synchronisation Burst: time synchronisation of the TB CD SS CD TB GP Synchronisation Sequence - long training sequence Coded Data - data used to align the mobile to the base station's time-slot structure Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 23 Frame hierarchy time-slot 15/26 ms = ms frame 8 x 15/26 ms = 60/13 ms = ms frame 0 frame 1 frame 2 traffic multiframe 26 x 60/13 = 120 ms frame 24 frame 25 frame 0 x 51 superframe (*) 6.12 s x 2048 hyperframe (**) 3.5 hours frame 1 frame 2 frame 49 x 26 control multiframe 51 x 60/13 = ms 0 frame 50 (*) - aligns traffic and control multiframes (**) - allows cycle for frame number Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 24
13 Logical channels TCH Traffic Channels CCH Control Channels Full-rate TCH/F Half-rate TCH/H BCH Broadcast Channels CCCH Common Control Channels DCCH Dedicated Control Channels TrafficChannels Full-rate TrafficChannels Half-rate FCCH SCH BCCH Frequency Correction Channel Synchronization Channel Broadcast Control Channel Uplink channel: transmits Downlink channel: transmits RACH Random Access Channel AGCH Access Grant Channel PCH Paging Channel SDCCH Stand-alone Dedicated Control Channel ACCH Associated Control Channels SACCH Slow Associated Control Channel FACCH Fast Associated Control Channel Bi-direccional channel: both transmit Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 25 Logical channels Channel Direction Application Allocation TCH Traffic Channels TCH/H TCH/F User data Allocated by network on demand by BCH Broadcast Channels CCCH Common Control Channels FCCH SCH BCCH RACH AGCH PCH Carrier synchronization Frame synchronisation General network information Cell information (present and adjacent) Request SDCCH for signalling Request TCH for handover Confirmation of SDCCH or TCH request Allert to a call originated in the network Permanent Multiple access with slotted Alhoa contention between Permanent DCCH Dedicated Control Channels SDCCH SACCH FACCH Registration / location updating Call control procedures Control information between and during the progress of a call or call set up Exchange of time critical control information during the progress of a call Allocated by network on demand Associated to a specific TCH or SDCCH Allocated by network or (*) (*) Fast allocation by setting S bit; bits are stolen from TCH Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 26
14 Logical channels Channel TCH Traffic Channels BCH Broadcast Channels CCCH Common Control Channels TCH/H TCH/F FCCH SCH BCCH RACH AGCH PCH Burst type Normal (114 data bits) Frequency correction Synchronisation Normal (114 data bits) Random access Normal (114 data bits) Time-slot Any TS0 - base channel (*) TS0/TS2/TS4/TS6 (**) TS0 - base channel (*) TS2/TS4/TS6 (**) Mulitiframe Bursts / Multiframe Capacity 26 frames x 114 / 120 = 22.8 kbit/s (120 ms) x 114 / 120 = 11.4 kbit/s 51 frames ( ms) 27 minimum 51 typical 51 frames ( ms) 12 minimum x 114 / = 1.94 kbit/s 12 x 114 / = 5.81 kbit/s minimum DCCH Dedicated Control Channels SDCCH SACCH FACCH Normal (114 data bits) TS0 - base channel (*) TS0/TS2/TS4/TS6 (**) Same TS as SDCCH Same TS as TCH Same TS as TCH (bits stolen from TCH) 51 frames ( ms) 26 frames (120 ms) 4 2 (***) 1 Same as TCH 4 x 114 / 120 = 3.8 kbit/s 2 x 114 / 120 = 1.9 kbit/s 1 x 114 / 120 = 0.95 kbit/s Same as TCH (*) Low capacity cells (**) High capacity cells (***) 4 bursts in 2 multiframes equivalent to 2 bursts/ multiframe Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 27 Transmission / reception timing Transmit / receive frame staggering to simplify hardware design, transmitter and receiver never operate at the same time transmission is half-duplex the numbering scheme is staggered by 3 time-slots downlink receive receive uplink transmit transmit Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 28
15 Transmission / reception timing Transmit time advance Principle of operation correct timing of uplink bursts at the is required to avoid overlapping different path delays (- distances) must be compensated transmission from the is advanced 0-63 bits under control maximum time advance of 63 bits allows ms round trip delay maximum cell radius is approximately 35 km Initial ranging Access Burst is transmitted without time advance Guard Period of bits allows for a path delay due to 37 km distance measures path delay and sends required time advance on SACCH introduces time advance on all bursts Adaptive control monitors burst and measures delays with specified time advance if path delay varies more than 1 bit period, the new value is signalled on SACCH Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 29 Frequency hopping Application of frequency hoping optional, but usually implemented channels with no frequency hopping: BCH and CCCH Hoping sequence several possible hoping algorithms selected algorithm broadcast on BCCH Slow frequency hopping characteristics in a given time-slot, successive TDMA frame are transmitted on different carriers main hoping parameters period: ms frequency: 217 hops/s number of bits: 1250 bits/hop Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 30
16 Transmission power Mobile station power classes GSM W 39 dbm 5 W 37 dbm 2 W 33 dbm 0.8 W 29 dbm vehicular portable portable portable GSM W 36 dbm 1 W 30 dbm vehicular portable 0.25 W 24 dbm portable usual classes Discontinuous transmission (DTX) for voice no data transmission during periods of silence (approx. 60% of time) Voice Activity Detector (VAD) algorithm suppresses TCH transmission silent frames are sent to synthesise comfort noise at the receiver several advantages reduces interference, on average, by 3 db Increases battery life Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 31 Transmission power Power control implemented on both links objective: lowest power level which provides desired quality (BER) procedure measures power received and BER and sends result on SACCH sends new power level on SACCH, if and when necessary control range GSM dbm GSM dbm Comments effective maxima depend on cell size and capability control steps of 2 db channels with no power control - use maximum power for the cell downlink BCH and CCCH: power set by uplink RACH BCCH broadcasts maximum power level for the cell uses this value to set RACH transmission power Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 32
17 Security in GSM Security services access control/authentication user SIM (Subscriber Identity Module): secret PIN (Personal Identification Number) SIM network: challenge - response method confidentiality voice and signaling encrypted on the wireless link (after successful authentication) anonymity TI - Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity newly assigned at each new location update encrypted transmission 3 algorithms specified in GSM A3 for authentication ( secret, open interface) A5 for encryption (standardized) A8 for encryption key generation ( secret, open interface) secret : A3 and A8 available via the Internet network providers can use stronger mechanisms Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 33 GSM - authentication mobile network SIM K i RAND RAND RAND K i AuC 128 bit 128 bit 128 bit 128 bit A3 SRES* 32 bit SRES A3 32 bit SIM C SRES* =? SRES SRES 32 bit SRES K i : individual subscriber authentication key SRES: signed response Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 34
18 GSM - key generation and encryption mobile network () with SIM K i RAND RAND RAND K i AuC 128 bit 128 bit 128 bit 128 bit SIM A8 A8 cipher key K c 64 bit K c 64 bit data encrypted data SRES data A5 A5 Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 35 GSM protocol layers for signaling U m A bis A C CM CM MM MM RR LAPD m RR LAPD m M LAPD RR M LAPD BSSAP SS7 BSSAP SS7 radio radio PCM PCM PCM PCM 16/64 kbit/s 64 kbit/s / 2048 kbit/s Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 36
19 GSM protocol layers for signaling CM (Connection Management) call control, short message service and supplementary service MM (Mobility Management) registration, authentication, location and handover management RR (Radio Resource Management) setup, maintenance and release of radio channels control of radio transmission quality LAPDm ( Link Access Protocol D-channel modified) modified version of ISDN LAPD protocol M (Base Transceiver Station Management) radio resources control messages between and BSSAP (Base Station System Application Part) control of by C Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 37 Mobile Terminated Call 1: calling a GSM subscriber 2: forwarding call to GC 3: signal call setup to HLR 4, 5: get routing info (RN) from VLR 6: forward routing info to GC calling station PSTN 1 2 7: route call to current C 8, 9: get current status of (LAI + TI) 10, 11: paging of in location area 12, 13: answers paging and authentication request 14, 15: security checks 16, 17: set up connection 4 HLR VLR GC 7 C BSS BSS BSS Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 38
20 Mobile Terminated Call Channel activity at radio interface BCCH System parameters and other overhead idle updated incoming call successful access PCH AGCH Paging message to specified TI Channel request RACH Assign stand alone dedicated control channel announced TI matches stored value successful paging send RAND calculate SRES / K c SRES confirmed Paging acknowledge SDCCH SDCCH Authentication request Authentication response SDCCH SDCCH Request to transmit in cipher mode Acknowledge cipher mode request SDCCH calculate SRES / K c send SRES switch to cipher mode Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 39 Mobile Terminated Call Channel activity at radio interface (cont.) SDCCH Setup message for incoming call SDCCH Assign traffic channel and release SDCCH Acknowledge channel assignment FACCH FACCH Alerting mobile switch signaling to FACCH using assigned TCH generate ringing sound Connect FACCH mobile off-hook switch to traffic channel FACCH Connect acknowledge switch to traffic channel TCH data flow remote party on-hook FACCH Disconnect Release FACCH FACCH Release complete FACCH Release traffic channel idle updated Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 40
21 Mobile Originated Call 1, 2: connection and authentication request 3, 4: security check HLR 5-8: check resources (free circuit) 9-10: set up call PSTN 6 5 GC C 2 9 BSS Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 41 Mobile Originated Call Channel activity at radio interface BCCH System parameters and other overhead idle updated successful access AGCH Channel request RACH Assign stand alone dedicated control channel number dialed send RAND calculate SRES / K c SRES confirmed Call establishment request SDCCH SDCCH Authentication request Authentication response SDCCH SDCCH Request to transmit in cipher mode Acknowledge cipher mode request SDCCH calculate SRES / K c send SRES switch to cipher mode Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 42
22 Mobile Originated Call Channel activity at radio interface remote party ringing remote party off-hook Setup message for outgoing call SDCCH SDCCH Assign traffic channel and release SDCCH Acknowledge channel assignment FACCH FACCH Alerting remote party FACCH Connect switch signaling to FACCH using assigned TCH ringing tone switch to traffic channel Connect acknowledge FACCH switch to traffic channel TCH data flow Disconnect FACCH mobile on-hook FACCH Release Release complete FACCH FACCH Release traffic channel idle updated Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 43 4 types of handover C C 1 - between different sectors of the same cell 2 - between different cells within the same domain 3 - between different domains within the same C domain 4 - between different C domains Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 44
23 Handover decision receive level old receive level new handover margin HO_MARGIN old new Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 45 Mobile-Assisted Handover (MAHO) scans, measures and reports power received from several RF carrier based on BCCH information OLD C NEW measurement report HO command measurement result HO command clear command clear complete HO decision HO required HO command HO access link establishment clear command clear complete HO request resource allocation ch. activation HO request ack ch. activation ack HO complete HO complete Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 46
24 Location update is aware of location broadcasts Location Area Identification (LAI) on BCCH SIM stores current LAI and TI Events which determine a current location update is switched on and current LAI equals stored LAI a timer set by the network expires and reports position TI may be updated and stored in SIM Events which determine a new location update is switched on and current LAI differs from stored LAI enters a new location area TI and LAI are updated and stored in SIM Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 47 Location update OLD NEW C old HLR VLR C VLR old request II location update request location update request (old LAI/TI sent) send II send II update location request update location cancel location cancel location request update confirmed update confirmed update confirmed cancellation confirmed cancellation confirmed Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 48
25 Location update Channel activity at radio interface successful access BCCH AGCH System parameters and other overhead Channel request RACH Assign stand alone dedicated control channel idle updated send RAND calculate SRES / K c SRES confirmed new TI sent (optional) Location updating request SDCCH SDCCH Authentication request Authentication response SDCCH SDCCH Request to transmit in cipher mode Acknowledge cipher mode request SDCCH SDCCH Location update confirmed Acknowledge new location SDCCH SDCCH Release stand alone dedicated control channel old LAI/TI sent calculate SRES / K c send SRES switch to cipher mode store LAI/TI in SIM idle updated Mário Jorge Leitão GSM 49
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
-The equipment was limited to operate only within the boundaries of each country. -The market for each mo bile equipment was limited.
 1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
Global System for Mobile (GSM) Global System for Mobile (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing
 GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning
 GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3-
 Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure
 GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020502Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020502Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04. Simon Sörman
 Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0
 GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
RELEASE NOTE. Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08. Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90
 ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Using TEMS Pocket. Johan Montelius
 Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Bölüm 8. GSM. 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar!
 Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
The Network Layer Layer 3
 CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
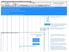 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM
 Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
How To Test Gsm Cell Phone Network On A Cell Phone
 G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing
 Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: solutions@wg.com http://www.wg.com
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: solutions@wg.com http://www.wg.com
Mobile Communication Systems: DECT Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunication
 Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
1. Introduction: The Evolution of Mobile Telephone Systems
 IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks
 Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
PW1 Monitoring a GSM network with a trace mobile
 LPRO WireLess Network and security PW1 Monitoring a GSM network with a trace mobile Module GSM MOBILE LPRO 2012-13 Experimental set-up: 1. SAGEM OT230/OT260 Trace Mobile and charger 2. GSM antenna and
LPRO WireLess Network and security PW1 Monitoring a GSM network with a trace mobile Module GSM MOBILE LPRO 2012-13 Experimental set-up: 1. SAGEM OT230/OT260 Trace Mobile and charger 2. GSM antenna and
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems
 Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Wireless Access of GSM
 Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
GLOSARIO. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Estándar de comunicación celular basado en TDMA.
 GLOSARIO A AC o AuC Ack AGCH A-key AMPS ANSI-136 ó IS-136 ARFCN ASE Authentication Center. Acknowledgement. Access Grant Channel. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Advanced
GLOSARIO A AC o AuC Ack AGCH A-key AMPS ANSI-136 ó IS-136 ARFCN ASE Authentication Center. Acknowledgement. Access Grant Channel. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Advanced
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description
 C1 Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description C1. Parameters included in the modelling In the modelling the number of mobiles and their positioning with respect to the wired device needs to be taken
C1 Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description C1. Parameters included in the modelling In the modelling the number of mobiles and their positioning with respect to the wired device needs to be taken
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
PART 4 GSM Radio Interface
 PRT 4 GSM Radio Interface Lecture 4. Physical channels Frequency [MHz] 960 OWNLINK BS MS 95 95 UPLINK MS BS 890 GSM Radio Spectrum 890.4 890.2 guard band 2 x 25 Mhz band uplex spacing: 45 MHz 24 carriers
PRT 4 GSM Radio Interface Lecture 4. Physical channels Frequency [MHz] 960 OWNLINK BS MS 95 95 UPLINK MS BS 890 GSM Radio Spectrum 890.4 890.2 guard band 2 x 25 Mhz band uplex spacing: 45 MHz 24 carriers
How To Improve Data Rates For Global Evolution (Edge)
 EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
Optimization. Log File Analysis GSM
 Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G
 CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
RADIUS. Brief brochure. Product Purpose
 Product Purpose The Product is designed for searching, intercepting, registering and analyzing of communication sessions as well as service information circulating in cellular GSM networks without encryption
Product Purpose The Product is designed for searching, intercepting, registering and analyzing of communication sessions as well as service information circulating in cellular GSM networks without encryption
Evaluating GSM A5/1 security on hopping channels
 Evaluating GSM A5/1 security on hopping channels Bogdan Diaconescu v1.0 This paper is a practical approach on evaluating A5/1 stream cipher on a GSM hopping network air interface called Um. The end goal
Evaluating GSM A5/1 security on hopping channels Bogdan Diaconescu v1.0 This paper is a practical approach on evaluating A5/1 stream cipher on a GSM hopping network air interface called Um. The end goal
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
Cellular mobile communication is based on the. The Cellular Concept. GSM and PCNs. Moe Rahnema
 GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
Positioning in GSM. Date: 14th March 2003
 Positioning in GSM Date: 14th March 2003 Overview of seminar Potential applications in cellular network Review of localization system and techniques Localization in GSM system Progress of the project with
Positioning in GSM Date: 14th March 2003 Overview of seminar Potential applications in cellular network Review of localization system and techniques Localization in GSM system Progress of the project with
NETWORK AND RF PLANNING
 NETWORK AND RF PLANNING Introduction Achieving maximum capacity while maintaining an acceptable grade of service and good speech quality is the main issue for the network planning. Planning an immature
NETWORK AND RF PLANNING Introduction Achieving maximum capacity while maintaining an acceptable grade of service and good speech quality is the main issue for the network planning. Planning an immature
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
 General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
How To Understand Cellular Communications
 Definition Cellular Communications A cellular mobile communications system uses a large number of low-power wireless transmitters to create cells the basic geographic service area of a wireless communications
Definition Cellular Communications A cellular mobile communications system uses a large number of low-power wireless transmitters to create cells the basic geographic service area of a wireless communications
Frequency Hopping for GSM Base Station Tests with Signal Generators SME
 Frequency Hopping for GSM Base Station Tests with Signal Generators SME Application Note 1GPAN28E A. Winter 07.95 Products: Signal Generator SME Software Package SME-K1 Introduction One of the problems
Frequency Hopping for GSM Base Station Tests with Signal Generators SME Application Note 1GPAN28E A. Winter 07.95 Products: Signal Generator SME Software Package SME-K1 Introduction One of the problems
# DEFINITIONS TERMS. A standard cellular telephone service (CTS) initially placed into operation on Oct. 13, 1983.
 CHAPTER 20 CELLULAR TELEPHONE SYSTEM # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) Stands for Standard Cellular Telephone Service CTS 2) An acronym for Personal Communications System. PCS 3) Stands for Personal Communications
CHAPTER 20 CELLULAR TELEPHONE SYSTEM # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) Stands for Standard Cellular Telephone Service CTS 2) An acronym for Personal Communications System. PCS 3) Stands for Personal Communications
GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper
 GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper Table of contents VAMOS increases your GSM voice capacity at minimum investment / 1 Take the full benefit of VAMOS / 1 Standard aspects / 1
GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper Table of contents VAMOS increases your GSM voice capacity at minimum investment / 1 Take the full benefit of VAMOS / 1 Standard aspects / 1
TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034. Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301. Agenda item: 6.3.3
 TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034 Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301 Source: TSG-RAN WG2 Agenda item: 6.3.3 Doc-1st- Spec CR Rev Subject Cat Version Versio R2-000213 25.301 032 Correction
TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034 Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301 Source: TSG-RAN WG2 Agenda item: 6.3.3 Doc-1st- Spec CR Rev Subject Cat Version Versio R2-000213 25.301 032 Correction
GSM Databases. Virginia Location Area HLR Vienna Cell Virginia BSC. Virginia MSC VLR
 Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
ETSI TS 100 912 V8.4.0 (2000-08)
 TS 100 912 V8.4.0 (2000-08) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Radio subsystem synchronization (GSM 05.10 version 8.4.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TS 100 912 V8.4.0 (2000-08) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Radio subsystem synchronization (GSM 05.10 version 8.4.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
LTE Tutorial GSM Tutorial i
 GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
Revision of Lecture Eighteen
 Revision of Lecture Eighteen Previous lecture has discussed equalisation using Viterbi algorithm: Note similarity with channel decoding using maximum likelihood sequence estimation principle It also discusses
Revision of Lecture Eighteen Previous lecture has discussed equalisation using Viterbi algorithm: Note similarity with channel decoding using maximum likelihood sequence estimation principle It also discusses
Indian Journal of Advances in Computer & Information Engineering Volume.1 Number.1 January-June 2013, pp.1-5 @ Academic Research Journals.
 Cellular System Rajat Chugh, Parag Jasoria, Tushar Arora, Nitin Ginotra and Vivek Anand V Semester, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dronacharya College of Engineering, Khentawas, Farukhnagar,
Cellular System Rajat Chugh, Parag Jasoria, Tushar Arora, Nitin Ginotra and Vivek Anand V Semester, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dronacharya College of Engineering, Khentawas, Farukhnagar,
Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture on cellular telephone systems.
 Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture minus 31 Cellular Telephone Systems Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture
Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture minus 31 Cellular Telephone Systems Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture
How To Understand The Power Of A Cell Phone Network
 TS 25.225 V3.12.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Physical layer Measurements (TDD) (Release 1999) The present
TS 25.225 V3.12.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Physical layer Measurements (TDD) (Release 1999) The present
