A Guide for the Development of ASME B18 Standards for Mechanical Fasteners
|
|
|
- Victoria Warner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FINAL December 20, 2006 A Guide for the Development of ASME B18 Standards for Mechanical Fasteners ASME B Key Words: Guide, B18 Standards FINAL: December 20, 2006 Sponsored and Published By THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS Three Park Avenue New York, N.Y
2 ASME B GUIDE B18 STANDARDS 2
3 GUIDE B18 STANDARDS ASME A GUIDE FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF ASME B18 STANDARDS FOR MECHANICAL FASTENERS 1. Introductory Notes 1.1 Scope This guide covers the elements for the complete development of B18 standards. It should be understood that only those elements applicable to the development of any given standard should be adopted. Clearly, not all may be reasonably applied to any given standard. The discussion of these elements is presented in the order they would normally appear in a given B18 standard and a template is included in Appendix A. 1.2 Comparison to ISO Standards Where ISO standards exist, a detailed comparison to the ASME metric standard, including each geometric characteristic, material, range of size, and performance is suggested to facilitate specification by respective users. The detail of comparison should be included in an appendix while this paragraph in the standard identifies the ISO standards for comparative purposes and refers to the appendix for a detailed summary by applicable characteristic. A good example of this comparison may be found in Appendix IV of ASME B M. Also, an example taken from B M is included in Appendix B of this standard for illustrative purposes. 1.3 Dimensions A statement indicating that: "unless otherwise specified, all dimensions are in inches" or that "all dimensions, unless otherwise specified, are in metric (mm)" should be included. It is recommended that standards be written only in inch or only in metric (mm) and that dual dimensions be avoided. This is intended to provide a basis for possible global acceptance of purely metric documents. All dimensions shall apply before coating and this statement should be included to prevent confusion regarding any dimensional changes that may occur as a result of coating. 1.4 Options This paragraph is intended to offer flexibility to the application of the standard. For example, where special materials, coatings, lubrication, or packaging may be needed by the purchaser, this provision should be included in the standard and specified by the purchaser on the purchase order. 1.5 Terminology This paragraph is intended to reduce the verbiage in each standard and to focus on a single document, namely, ASME B18.12, to provide for consistency in definitions that may have formerly appeared in multiple standards with slight variations. Where terms are not defined in ASME B18.12, they are included and defined in this paragraph Terminology Referenced For definitions of terminology not specifically defined in this standard, refer to ASME B Referenced Standards This paragraph is intended to identify all standards that are specified or referred to in a given stan- 3
4 ASME B GUIDE B18 STANDARDS dard by name, number, and publisher. It should also state that the latest edition of the listed standard is to be used, unless a specific date of issue is included in the list. Specific dates shall not be listed, unless a technical engineering reason has been established necessitating the citing of a specific issue Example of Referenced Standards Standards that are called out should be listed by issuing source. The most current issue of the referenced standard is applicable, unless otherwise specified by the purchaser. Below is an example: Referenced Standards Unless otherwise specified, the standards referenced shall be the most recent at the time of order placement. ASME B1.1, Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN and UNR Thread Form) ASME B18.12, Glossary of Terms for Mechanical Fasteners ASME B , Inspection and Quality Assurance for General Purpose Fasteners ASME B , Inspection and Quality Assurance for High-Volume Machine Assembly Fasteners ASME B18.24, Part Identifying Number (PIN) Code System for B18 Fastener Products Publisher: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME International), Three Park Avenue, New York, NY ; Order Department: 22 Law Drive, Box 2300, Fairfield, NJ ASTM B21, Specification for Naval Brass, Rod, Bar, and Shapes ASTM F1137, Specification for Phosphate/ Oil and Phosphate/Organic Corrosion Protective Coatings for Fasteners ASTM F1941, Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings on Threaded Fasteners [Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN/ UNR)] Publisher: American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA Related Standards This may list standards and their sources that are not referred to in the given document but may cover similar or related products or tests. For example, a spring pin standard may list related standards for other pins such as clevis, cotter, or dowel pins. These would be listed in a similar way as shown in paragraph Part Identifying Number This is a standard "boiler plate" paragraph to refer the specification user to ASME B18.24 and a recommended procedure to establish a part identification number (PIN) applicable to all B18 product standards, typically, paragraph 1.8: For a Part Identifying Number, refer to ASME B General Data This paragraph provides for specification of geometry, materials and heat treatment, dimensional conformance, quality assurance, workmanship, gaging and acceptance procedures, marking requirements, and packaging. A review of the template included in Appendix A of this guide will help to identify, for a given product, which of the features should necessarily be included. 4
5 GUIDE B18 STANDARDS ASME Heads The intention of this paragraph is to describe and identify the head configuration and its dimensions and tolerances. A drawing is usually present and the dimensions are identified by letters which are included with a word description in tables together with stated dimensions and tolerances. These should be specific so that wrench or driver fit is assured. In those products such as pins or studs, which have no head configuration, this paragraph should not be applied. A list of seventeen head characteristics which may be included as appropriate in subparagraphs are listed in Appendix A. The following is an example of typical head characteristics: Top of Head. Top of head shall be full form and chamfered or rounded with the diameter of chamfer circle or start of rounding being equal to the maximum width across flats within a tolerance of minus 15% Width Across Flats. The width across flats of heads shall be the distance, measured perpendicular to the axis of product, overall between two opposite sides of the head Head Taper. Maximum width across flats shall not be exceeded. No transverse section through the head between 25% and 75% of actual head height, as measured from the bearing surface, shall be less than the minimum width across flats Head Height. The head height shall be that overall distance measured parallel to the axis of the product from the top of the head to the bearing surface and shall include the thickness of the washer face. Raised grade and manufacturer's identification are excluded from head height True Position of Head. The axis of the head shall be located at true position with respect to the axis of the body (determined over a distance under the head equal to one diameter) within a tolerance zone having a diameter equivalent to 6% of the maximum width across flats at maximum material condition. 2.2 Product Length This paragraph would normally define the overall product length and tolerances, which are standard, and a procedure for measurement. Additionally, such lengths as the thread length (2.5), grip gaging length, body length, and transition thread length (2.6) are often included as subparagraphs to assist in selection and application. The length of the screw shall be measured parallel to the axis of the screw from the plane of the bearing surface under the head to the plane of the flat of the point. 2.3 Threads Most threads are specified by reference to ASME B1.1 or ASME B1.13M including a given pitch and a class of fit. Methods relating to acceptability are identified as a given system in ASME B1.3, and a separate paragraph (2.4) would be used to specify the thread acceptance system. The following is a typical paragraph for thread specification: 5
6 ASME B GUIDE B18 STANDARDS Threads shall be cut or rolled in accordance with ASME B1.1, Unified Coarse, Class 2A. 2.4 Thread Acceptance Gaging Typically, this paragraph would specify thread dimensional acceptability in accordance with Gaging System 21 as specified in ASME B1.3 or ASME B1.3M for metric product. However, the user may have specified certain thread characteristics which will require a different acceptance procedure and this paragraph will usually state System 21, unless otherwise specified. Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, gaging for screw thread dimensional acceptability shall be in accordance with Gaging System 21 as specified in ASME B1.3M. 2.5 Thread Length Thread length is controlled on many bolts by the so-called grip gaging length maximum. This paragraph will specify this, if applicable, and subparagraphs will specify the method or procedure for measurement. Certain small products, such as machine screws, may specify the thread length in terms of its approach to the bearing surface of the head by the number of thread pitches Machine Screws. Machine screws shall have thread lengths conforming to the following: On screws threaded full length, the distance to first full form thread shall be measured, parallel to the axis of screw, from the bearing surface of the head to the face of a nonchamfered or noncounterbored standard 3A GO thread ring gage assembled by hand as far as the thread will permit. (a) Sizes No. 5 and Smaller. Screws of nominal lengths equal to three diameters and shorter shall have full form threads extending to within one pitch (thread) of the bearing surface of the head, or closer, if practicable. Nominal lengths greater than three diameters, up to and including 1-1/8 in., shall have full form threads extending to within two pitches (threads) of the bearing surface of the head, or closer, if practicable. Screws of longer nominal lengths shall, unless otherwise specified, have a minimum length of full form thread of 1 in. (b) Sizes No. 6 and Larger. Screws of nominal lengths equal to three diameters and shorter shall have full form threads extending to within one pitch (thread) of the bearing surface of the head, or closer, if practicable. Nominal lengths greater than three diameters, up to and including 2 in., shall have full form threads extending to within two pitches (threads) of the bearing surface of the head, or closer, if practicable. Screws of longer nominal lengths shall, unless otherwise specified, have a minimum length of full form thread of 1.50 in Body Length Body length is the distance, as measured parallel to the axis of the fastener, from the underside of the head to the last scratch of thread or top of the extrusion angle Grip Gaging Length This is the distance as measured parallel to the axis of the fastener from the underside of the 6
7 GUIDE B18 STANDARDS ASME head bearing surface to the face of a noncounterbored or noncountersunk standard Go thread ring gage which has been assembled by hand as far as the thread will permit. 2.6 Transition Thread Length A dimension commonly expressed as a reference dimension which accounts for the length of incomplete threads, extrusion angle for rolled threads, and the tolerances on the grip length. It is recommended that both a rolled and cut thread representation be present for each threaded product as may be applicable. Often, the transition thread length may be expressed as the number of pitches for a given thread. 2.7 Point All screws have a point to facilitate starting or to apply pressure (compression). Such points are called out as flat, oval, cup, cone, or half dog. In other cases, points are described as chamfered or rounded from a given diameter below the minor thread diameter, and having a length which is a multiple of the thread pitch. The length of the point measured to the first full formed thread at the major diameter may be specified in the dimensional table for a given screw. Rivets and pins may have sheared ends or may be crowned or chamfered as specified in the applicable product standard. Point features not defined in a given product standard are at the discretion of the manufacturer. 2.8 Body Diameter This is generally the unthreaded portion of a shank whose diameter is the maximum or minimum limit or the basic size with plus and minus tolerances applied. It is often used to "account" for any swell, fin, or die seam under the head from manufacture Reduced Diameter Body These have a body diameter not less than the minimum pitch diameter, and not exceeding the specified minimum full size diameter body. 2.9 True Position of Tapped Hole The axis of a tapped hole in the nut is located at true position with respect to the axis of the nut body within a tolerance zone having a diameter equal to a given percentage of the the maximum width across flats Nut Thickness The nut thickness is the overall distance measured parallel to the axis of the nut, from the top of the nut to the bearing surface. This includes the thickness of the washer face where provided. Raised markings are not included in nut thickness Prongs Cotter pins have a preferred point extended prong having a square or hammered lock design unless otherwise specified Taper Taper pins provide for a taper on the diameter based on a unit of length and for a given tolerance Straightness A rail gage or a sleeve gage is used to assure shank straightness or camber limitations included within respective product standards. At maximum material condition, maximum camber per unit length is generally specified for given product lengths. 7
8 ASME B GUIDE B18 STANDARDS 2.14 Finishes Dimensions for products and dimensional characteristics are usually specified for plain finish. If a coating is specified, it should be in accordance with a class or condition specified in an applicable standard such as an ASTM standard Workmanship A clause which assures that a product will be visually free of irregularities that would impact its fit, form, or function Designation This provides a standard method for call out in communications. Product name, ASME dimensional standard, diameter-pitch, length, mechanical or performance standard, finish type and thickness including applicable standard. Examples: Heavy hex nut, ASME B18.2.6, Unified 1/2-13, ASTM A563 Grade C, Plain Finish Hex cap screw, ASME B18.2.1, Unified 3/8-16 x 4, ASTM A354 Grade BD, type Fe/Zn- 5A, ASTM F1941 Metric hex cap screws, ASME B M, M16 x 2 x 100, ASTM F568M Class 10.9, Plain Finish Metric hex nuts Style 2, ASME B M, M10 x 1.5, ASTM A563M Class 9, Plain Finish 2.17 Grade or Property Class Symbol These marks are mandated by the applicable material and performance specification such as those found in ASTM or SAE. Inch series products are generally related to Grades 2, 5, and 8; while metric series products are related to property classes ranging from 4.6 to A typical callout is as follows: Each bolt shall be marked in accordance with the requirements of ASTM A Manufacturer's or Source Symbol These marks are mandated by the standards that specify material, mechanical, and performance requirements. For fasteners subject to the Fastener Quality Act requirements, the marks used are to be fully traceable and registered by the manufacturer with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. This registration is required by the Fastener Quality Act Inspection and Quality Assurance ASME has seven quality assurance documents (ASME B thru B ) for mechanical fasteners. ASTM has a document (ASTM F1470) to determine sample sizes for mechanical properties using detection or prevention techniques. The standard should be called out in this paragraph, which is the most basic for the given product, with the option for alternative specification left to the purchaser. Unless otherwise specified, products shall be furnished in accordance with ASME B
9 GUIDE B18 STANDARDS ASME Designated Dimensional Conformance This paragraph is intended to designate the characteristics and inspection level established by the technical committee. These are characteristics that have significant impact on the fit, form, and function of the product, should they be found to be nonconforming Dimensional Conformance Example Socket button head cap screws shall have the following designated characteristics inspected to ASME B to the inspection levels shown: Characteristic Threads Head Diameter Socket Size (gaged) Length Fillet Transition Diameter Inspection Level C C C C C 2.21 Materials and Heat Treatment Requirements are usually found in the appropriate ASTM, IFI, or SAE standard Steel. Carbon and alloy steel requirements are defined in such standards as ASTM A307 - Carbon Steel Bolts and Studs, 60,000 PSI Tensile Strength, ASTM A449 - Quench and Tempered Steel Bolts and Studs, and ASTM A563 - Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts, ASTM A563M - Carbon and Alloy Steel Metric Nuts, and ASTM F568M - Carbon and Alloy Steel Externally Threaded Fasteners Corrosion Resistant. A term used to describe a characteristic of the basic material or coating found in or on a fastener. Such standards as ASTM F593 - Stainless Steel Bolts, Hex Cap Screws and Studs and ASTM F594 - Stainless Steel Nuts, ASTM F738M - Stainless Steel Metric Bolts, Screws and Studs, and ASTM F836M - Stainless Steel Metric Nuts define basic material and processing requirements Nonferrous. Includes materials such as brass, titanium, copper, nickel, or aluminum which, with various alloys, are defined in such standards as ASTM F468 - Nonferrous Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, and Studs for General Use or ASTM F468M - Nonferrous Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, and Studs for General Use (Metric) Total Case Depth. Is a distance measured perpendicularly from the surface of a hardened case to a point where differences in chemical or physical properties of the case and core can no longer be distinguished. SAE J423, ASTM F2328, ASTM F2328M, or SAE J121M specify a method to accurately measure the case depth Surface Hardness. The method to measure surface hardness involves the use of an indenter. For routine checks, a Knoop or pyramid indenter may be used. The referee method involves one of these indenters and a given load. See paragraph 3.4 Surface Hardness after Tempering of SAE J Core Hardness. This requires cutting a transverse section through the thread of a bolt, screw, or stud at a distance one diameter from the point or end of the product. Four readings at 90 degree increments are averaged to establish a value. ASTM F606, ASTM F606M, and SAE J1237 describe a procedure for this measurement Microstructure. This examination involves a microscopic look at the metal structure of a polished and etched specimen using magnifications in excess of 10x. Such structures are pictured in the appendix of SAE J78, Self-Drilling Tapping Screws. 9
10 ASME B GUIDE B18 STANDARDS 3. Performance Requirements and Tests A given B18 standard may specify mechanical or performance characteristics for a product. Additionally, the standard may specify a test procedure to establish that a given fastener meets the applicable mechanical or performance requirements. A listing of the mechanical and performance characteristics generally included in some B18 standards is shown in Appendix A. 3.1 Tensile Strength This is a requirement, usually stated as a minimum, to which a product is processed to meet. Often, for carbon and alloy steel product, it is broadly referred to as property class or strength grade. The exceptions to this rule are found in ASTM A307 and ASTM A490. Both specify a maximum tensile strength in addition to the specified minimum. 3.2 Proof Load Is usually stated to be an absolute value that a product must meet without dimensional change or thread deformation. It is this value that is used with a factor of safety for design purposes. 3.3 Ductility Test A test that is used to assure the integrity of the head to shank junction. It is usually done by applying a load to the head of a screw or bolt by reaching a specified angle between the plane of the head bearing surface and the shank without head separation. 3.4 Drive Test Used to establish that the threads of a screw will, without deformation of its threads, form mating threads in a specified test plate at given rotational speeds. 3.5 Torsional Test In a specified test device, a screw is suitably torqued to failure. The failure torque should meet a given minimum requirement based on thread form. 3.6 Hardness Values may be required at the core, surface, or at the total case depth depending upon the specification requirement. These may be related to tensile strength in screws that are too short to adequately tensile test. 3.7 Hydrogen Embrittlement Products with high hardness and electroplated fasteners often require testing for this failure mode. This paragraph should specify applicable tests and steps to be followed in processing to reduce potential failure. 10
11 GUIDE B18 STANDARDS ASME APPENDIX A STANDARDS TEMPLATE Foreword 1. Introductory Notes 1.1 Scope 1.2 Comparison to ISO Standards 1.3 Dimensions 1.4 Options 1.5 Terminology 1,5.1 terminology referenced 1.6 Referenced Standards example of referenced standards 1.7 Related Standards 1.8 Part Identifying Number 2. General Data 2.1 Heads top of head width across flats head taper head height true position of head width across corners bearing surface chamfer indent corner fill recess depth slot depth feature positional tolerances underhead fillet gaging of head wrenching height head periphery 2.2 Product Length 2.3 Threads 2.4 Thread Acceptance Gaging 2.5 Thread Length machine screws body length grip gaging length 2.6 Transition Thread Length 2.7 Point 2.8 Body Diameter reduced diameter body 2.9 True Position of Tapped Hole 2.10 Nut Thickness 2.11 Prongs preferred points prong alignment 2.12 Taper 2.13 Straightness 2.14 Finishes 2.15 Workmanship 2.16 Designation 2.17 Grade or Property Class Symbol 2.18 Manufacturer s or Source Symbol 2.19 Inspection and Quality Assurance 2.20 Designated Dimensional Conformance dimension conformance examples 2.21 Materials and Heat Treatment steel corrosion-resistant nonferrous total case depth surface hardness core hardness microstructure surface roughness 3. Performance Requirements and Tests 3.1 Tensile Strength 3.2 Proof Load 3.3 Ductility Test 3.4 Drive Test 3.5 Torsional Test 3.6 Hardness 3.7 Hydrogen Embrittlement 11
12 ASME B GUIDE B18 STANDARDS NONMANDATORY APPENDIX B COMPARISON WITH ISO STANDARDS (This Appendix is not an integral part of ASME B M-2001 and is included for information purposes only.) This Appendix describes the technical differences between ASME B M-2001 and ISO 4162: 1990, its draft revision, ISO/DIS : 1998, and related ISO standards. A1 PRODUCT NAMES BOLT AND SCREW Of the products named hex flange screw per ASME B M, those that are threaded full length would be named hexagon screw with flange per ISO 1891, but those that are not threaded full length are named hexagon flange bolt per ISO 4162: 1990, and hexagon bolt with flange per ISO 1891 and ISO/DIS : A2 HEAD HEIGHT AND WRENCHING HEIGHT ASME B M Table 5 specifies maximum head heights for M6, M12, and M16, and minimum wrenching height for M16, in agreement with ISO/DIS ; 1998, which are increased from those specified in ISO 4162: A3 MAXIMUM WIDTH ACROSS COR- NERS ASME B M, Table 5 maximum width across corners is not specified in ISO Instead, ISO/DIS : May 1998 would control the shape of the hexagon by zero positional tolerance at maximum material condition, which is not specified in ASME B M. A4 GAGING OF HEX FLANGE HEAD ISO/DIS would specify a gage C for gaging flange thickness, which is not included in ASME B M. A5 POSITION OF HEAD ASME B M, para. 11 and Table 2 specify positional tolerance at maximum material condition, as in ISO/DIS : May 1998, instead of regardless of feature size, as in ISO 4759/ I ISO/DIS : May 1998 also specifies position of the flange diameter with respect to the shank, which is not specified in ASME B M. A6 BEARING SURFACE ASME B M, para. 13 and Table 5 specify bearing surface concavity of 0.75±0.50 deg, as in ISO/DIS : 1998, which is a draft revision. ISO 4162: 1990 specifies 0 to 1 degrees 30 minimum (0.75±0.75 degrees). ISO/DIS : May 1998 specifies straightness of radial lines on the bearing surface, which is not specified in ASME B M. ASME B M, Table 2 values for circular runout of the bearing circle are greater than those in ISO 4759/I-1978 or ISO/DIS : May A7 FILLETS ASME B M, Table 3 minimum fillet transition diameters and shorter maximum fillet lengths for screws threaded full length are not specified in ISO For Type U fillet, the radius of the fillet extension, r 4 reference in ISO 4162, is not specified in ASME B M. A8 BODY DIAMETER FOR SCREWS THREADED FULL LENGTH ASME B M, Tables 3 and 4 minimum diameters of unthreaded shank for screws threaded full length are not specified in ISO
13 GUIDE B18 STANDARDS ASME A9 REDUCED DIAMETER BODY ASME B M, Table 6 maximum and minimum diameters of reduced body differ from ISO 4162 "d 2 is approximately equal to the pitch diameter (rolling diameter)." The limits specified in ASME B M Table 6 were proposed to ISO/TC2/ WG2 in May 1995, but ISO/TC2/WG2 was not willing to specify limits for the rolling diameter. A10 POINT ASME B M, para. 17 and Table 5 optional rounded point is not in ISO 4162, but Table 8 agrees with ISO A11 STRAIGHTNESS ASME B M specifies straightness at maximum material condition, as in ISO/DIS : May 1998, instead of regardless of feature size, as in ISO 4759/I The formula in ASME B M results in straightness tolerance zone diameters that are smaller for lengths 12 mm and shorter, and larger for lengths 16 mm and longer, than those in ISO 4759/I-1978 or ISO/DIS : May A12 GRIP LENGTH FOR SCREWS THREADED FULL LENGTH ASME B M, Table 10 maximum unthreaded lengths under the head of screws shorter than 2D differ from ISO A13 TRANSITION THREADS ASME B M, para specification on root contour of transition threads is not in ISO A14 POSITION OF BODY-TO-THREAD Coaxiality or position of the body with respect to the thread, specified in ISO 4759/I or ISO/DIS , is not specified in ASME B M. A15 MARKING ASME B M, para. 22 allows markings on the top of the flange but not on the side of the head, as alternatives to markings on the top of the head, while ISO allows markings on the side of the head but not on the top of the flange. ASME B M, para. 22 dimensions of head markings are not specified in ISO 4162 or ISO A16 INSPECTION AND QUALITY ASSURANCE ASME B M, paras. 25 and 26 inspection and quality assurance provisions differ from those in ISO
DESCRIPTION. Stud Bolts for Pressure-Temperature Piping 2-1. General Purpose End-to-End Studs 2-2. Tap End Stud Bolts 2-3. Double End Stud Bolts 2-4
 DESCRIPTION PAGE B7 Studs and Nuts Stud Bolts for Pressure-Temperature Piping 2-1 General Purpose End-to-End Studs 2-2 Tap End Stud Bolts 2-3 Double End Stud Bolts 2-4 Sigma Fasteners, Inc. Section 2 STUD
DESCRIPTION PAGE B7 Studs and Nuts Stud Bolts for Pressure-Temperature Piping 2-1 General Purpose End-to-End Studs 2-2 Tap End Stud Bolts 2-3 Double End Stud Bolts 2-4 Sigma Fasteners, Inc. Section 2 STUD
Fasteners and screw threads
 ISO Standards Handbook: Fasteners and screw threads Volume 2: Product standards Contents Part 3 : Product standards 2001, Ed. 5, 1094 p., ISBN 92-67-10345-8 3.1 External drive hexagon head bolts and screws
ISO Standards Handbook: Fasteners and screw threads Volume 2: Product standards Contents Part 3 : Product standards 2001, Ed. 5, 1094 p., ISBN 92-67-10345-8 3.1 External drive hexagon head bolts and screws
Screw Thread Design. Rev. 3-4-09
 Screw Thread Design Screw Thread Fundamentals A screw thread is defined as a ridge of uniform section in the form of a helix on either the external or internal surface of a cylinder. Internal threads refer
Screw Thread Design Screw Thread Fundamentals A screw thread is defined as a ridge of uniform section in the form of a helix on either the external or internal surface of a cylinder. Internal threads refer
Structural Bolting. Notice the Grade 5 has a much smaller head configuration and a shorter shank then the A325 structural bolt. Rev.
 Structural Bolting ASTM A325 and ASTM A490 are the two U.S. standard structural bolts. When looking at the mechanical requirements of bolts it appears that an ASTM A325 and SAE J429 Grade 5 are identical
Structural Bolting ASTM A325 and ASTM A490 are the two U.S. standard structural bolts. When looking at the mechanical requirements of bolts it appears that an ASTM A325 and SAE J429 Grade 5 are identical
Working Drawing and Assemblies. Chapter 10
 Working Drawing and Assemblies Chapter 10 Objectives 1.Define working drawings. 2. Describe how working drawings are used in industry. 3. List the major components of a complete set of working drawings.
Working Drawing and Assemblies Chapter 10 Objectives 1.Define working drawings. 2. Describe how working drawings are used in industry. 3. List the major components of a complete set of working drawings.
Manufacturing, Supply & Quality Plan for Tower Bolts. SL Tower Bolt Market Penetration
 Manufacturing, Supply & Quality Plan for Tower Bolts Project: SL Tower Bolt Market Penetration Document History Version Date Original Document First Submission Feb 9, 2013 Rev1 Requested Revisions Comments
Manufacturing, Supply & Quality Plan for Tower Bolts Project: SL Tower Bolt Market Penetration Document History Version Date Original Document First Submission Feb 9, 2013 Rev1 Requested Revisions Comments
Metric System & Specifications
 Metric System & Specifications Throughout history, people have been trying to limit the number of measurement systems. Today, only two systems, inch-pound and metric, are predominate in most industrial
Metric System & Specifications Throughout history, people have been trying to limit the number of measurement systems. Today, only two systems, inch-pound and metric, are predominate in most industrial
Two most common lock nut groups: 1-Prevailing Torque Type Lock Nuts:
 Two most common lock nut groups: 1. PREVAILING TORQUE a design feature of the lock nut produces friction between threads of mated components thereby increasing the force needed to tighten as well as loosen
Two most common lock nut groups: 1. PREVAILING TORQUE a design feature of the lock nut produces friction between threads of mated components thereby increasing the force needed to tighten as well as loosen
UNITED STATES CUTTING TOOL INSTITUTE Product Groupings for Standards Activities CUTTING TOOL PRODUCTS
 CUTTING TOOL PRODUCTS 1. BORING ISO 5609 Boring bars for indexable inserts Dimensions ISO 6261 Boring bars (tool holders with cylindrical shank) for indexable inserts Designation JIS B 4128 Boring bars
CUTTING TOOL PRODUCTS 1. BORING ISO 5609 Boring bars for indexable inserts Dimensions ISO 6261 Boring bars (tool holders with cylindrical shank) for indexable inserts Designation JIS B 4128 Boring bars
Fastener Handout. Introduction: Engineering Design Representation 2. Threads 2. Local Notes (callouts) 8. Threaded Mechanical Fasteners 13
 Fastener Handout Introduction: Engineering Design Representation 2 Threads 2 Effect of thread angle on strength: 3 Standardization of Threads: 4 Descriptions of the Thread Series: 4 Class fit: 5 Specification
Fastener Handout Introduction: Engineering Design Representation 2 Threads 2 Effect of thread angle on strength: 3 Standardization of Threads: 4 Descriptions of the Thread Series: 4 Class fit: 5 Specification
Machinery's Handbook 27th Edition TABLE OF CONTENTS FASTENERS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS FASTENERS NAILS, SPIKES, AND WOOD SCREWS 1476 Wire Nails and Spikes 1477 Wood Screws RIVETS AND RIVETED JOINTS 1478 Riveted Joint Design 1478 Classes and Types of Joints 1478 General
TABLE OF CONTENTS FASTENERS NAILS, SPIKES, AND WOOD SCREWS 1476 Wire Nails and Spikes 1477 Wood Screws RIVETS AND RIVETED JOINTS 1478 Riveted Joint Design 1478 Classes and Types of Joints 1478 General
Section. Tolerances. Aluminum Extrusion Manual. 4th Edition
 Section 8 Tolerances Aluminum Extrusion Manual 4th Edition Section 8 How straight is straight enough? How flat is flat enough? How uniform must a wall thickness be in order to be acceptable? These are
Section 8 Tolerances Aluminum Extrusion Manual 4th Edition Section 8 How straight is straight enough? How flat is flat enough? How uniform must a wall thickness be in order to be acceptable? These are
American National, Unified Screw Threads
 C h a p t e r 9 American National, Unified Screw Threads In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards:! Why Use Fasteners! The Text Designation for the Unified National Thread!
C h a p t e r 9 American National, Unified Screw Threads In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards:! Why Use Fasteners! The Text Designation for the Unified National Thread!
Fastener Handout. Introduction: Engineering Design Representation 2. Threads 2. Local Notes (callouts) 8. Threaded Mechanical Fasteners 13
 Fastener Handout Introduction: Engineering Design Representation 2 Threads 2 Effect of thread angle on strength: 3 Standardization of Threads: 4 Descriptions of the Thread Series: 4 Class fit: 5 Specification
Fastener Handout Introduction: Engineering Design Representation 2 Threads 2 Effect of thread angle on strength: 3 Standardization of Threads: 4 Descriptions of the Thread Series: 4 Class fit: 5 Specification
Camcar Socket Screw Technical Manual
 Camcar Socket Screw Technical Manual Camcar Socket Screws Founded on Innovation and Technical Expertise The Camcar brand began in 1943, cold forming a component others said couldn't be made. From that
Camcar Socket Screw Technical Manual Camcar Socket Screws Founded on Innovation and Technical Expertise The Camcar brand began in 1943, cold forming a component others said couldn't be made. From that
C O N V E Y O R C O M P O N E N T S C H A I N S B E L T S B E A R I N G S
 C O N V E Y O R C O M P O N E N T S C H A I N S B E L T S B E A R I N G S January 2009 Issue 6 Valu Guide Brackets The Ultimate in Adjustability and Cost Savings Valu Guide brackets are part of a family
C O N V E Y O R C O M P O N E N T S C H A I N S B E L T S B E A R I N G S January 2009 Issue 6 Valu Guide Brackets The Ultimate in Adjustability and Cost Savings Valu Guide brackets are part of a family
Die casting Figure M2.3.1
 Die casting Die casting is a moulding process in which the molten metal is injected under high pressure and velocity into a split mould die. It is also called pressure die casting. The split mould used
Die casting Die casting is a moulding process in which the molten metal is injected under high pressure and velocity into a split mould die. It is also called pressure die casting. The split mould used
To Use any command in this guide: 1. Select the option from the Design Menu in the Mechanical Eng workspace.
 120 1 ME Mechanical Engineers use a variety of mechanical drawings and computer tools for analysis and design. During the design process, drawings are used throughout to develop and document the design
120 1 ME Mechanical Engineers use a variety of mechanical drawings and computer tools for analysis and design. During the design process, drawings are used throughout to develop and document the design
Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements
 Addendum 1 March 2007 Effective Date: September 1, 2007 Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements ANSI/API SPECIFICATION 7-1 FIRST EDITION, MARCH 2006 EFFECTIVE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2006 ISO 10424-1:2004
Addendum 1 March 2007 Effective Date: September 1, 2007 Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements ANSI/API SPECIFICATION 7-1 FIRST EDITION, MARCH 2006 EFFECTIVE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2006 ISO 10424-1:2004
Thread and End Connection
 www.swagelok.com and End Connection Identification Guide 2 Contents Introduction and End Connection Terminology.. 4 General Terminology... 5 Step-by-Step Identification Procedure for s and End Connections...
www.swagelok.com and End Connection Identification Guide 2 Contents Introduction and End Connection Terminology.. 4 General Terminology... 5 Step-by-Step Identification Procedure for s and End Connections...
DRAFTING. Prepared by:
 GTRI MACHINE SERVICES DRAFTING STANDARDS Prepared by: Machine Services Department Georgia Tech Research Institute December 16, 2011 Copyright 2011 Georgia Tech Research Corporation. Alll rights reserved.
GTRI MACHINE SERVICES DRAFTING STANDARDS Prepared by: Machine Services Department Georgia Tech Research Institute December 16, 2011 Copyright 2011 Georgia Tech Research Corporation. Alll rights reserved.
NEW SIX-SEALS CUTTING RING. INTERNATIONAL INDUSTRIAL PATENT Nr. 864061 of the 10/03/99 FLANKS AND DOES NOT REPLACE THE STANDARD RING CURRENTLY IN USE
 B4 NEW SIX-SEALS CUTTING RING. INTERNATIONAL INDUSTRIAL PATENT Nr. 864061 of the 10/03/99 FLANKS AND DOES NOT REPLACE THE STANDARD RING CURRENTLY IN USE AVAILABLE IN CARBON AND STAINLESS STEEL 23 THEORY
B4 NEW SIX-SEALS CUTTING RING. INTERNATIONAL INDUSTRIAL PATENT Nr. 864061 of the 10/03/99 FLANKS AND DOES NOT REPLACE THE STANDARD RING CURRENTLY IN USE AVAILABLE IN CARBON AND STAINLESS STEEL 23 THEORY
Caps STANDARD WEIGHT Inches / Pounds
 Standard Caps you are here: Home > Weldbend Catalog > Fittings > Caps Caps STANDARD WEIGHT Inches / Pounds For Metric Units >Click Here Nominal Pipe Size Outside Inside Wall Thickness (T) Length (E) Pipe
Standard Caps you are here: Home > Weldbend Catalog > Fittings > Caps Caps STANDARD WEIGHT Inches / Pounds For Metric Units >Click Here Nominal Pipe Size Outside Inside Wall Thickness (T) Length (E) Pipe
This last dimension, the thread pitch diameter, is the most important as it is a reference from which all other thread measurements originate
 Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of the design and use of various thread types and how they are produced.
Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of the design and use of various thread types and how they are produced.
Hilti, Inc. 5400 South 122 nd East Avenue Tulsa, OK 74146. 1-800-879-8000 www.hilti.com
 Attached are page(s) from the 2014 Hilti North American Product Tech Guide. For complete details on this product, including data development, product specifications, general suitability, installation,
Attached are page(s) from the 2014 Hilti North American Product Tech Guide. For complete details on this product, including data development, product specifications, general suitability, installation,
AISI CHEMICAL COMPOSITION LIMITS: Nonresulphurized Carbon Steels
 AISI CHEMICAL COMPOSITION LIMITS: Nonresulphurized Carbon Steels AISI No. 1008 1010 1012 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021 1022 1023 1024 10 1026 1027 1029 10 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 10 1041 1042 1043
AISI CHEMICAL COMPOSITION LIMITS: Nonresulphurized Carbon Steels AISI No. 1008 1010 1012 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021 1022 1023 1024 10 1026 1027 1029 10 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 10 1041 1042 1043
Copper and Copper Alloy Tube, Pipe and Fittings
 Copper and Copper Alloy Tube, Pipe and Fittings COPPER and COPPER ALLOY TUBE and PIPE Seamless Copper Pipe: Copper pipe is almost pure copper manufactured to the requirements of ASTM B 42 - Standard Specification
Copper and Copper Alloy Tube, Pipe and Fittings COPPER and COPPER ALLOY TUBE and PIPE Seamless Copper Pipe: Copper pipe is almost pure copper manufactured to the requirements of ASTM B 42 - Standard Specification
Alternative Steel Materials to BS 5950
 BC 1: 2008 Design Guide on Use of Alternative Steel Materials to BS 5950 BCA Sustainable Construction Series 3 The education and research arm of the Building and Construction Authority 200 Braddell Road
BC 1: 2008 Design Guide on Use of Alternative Steel Materials to BS 5950 BCA Sustainable Construction Series 3 The education and research arm of the Building and Construction Authority 200 Braddell Road
ASME Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Professional Certification
 ASME Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Professional Certification Applicant Information STATEMENT OF POLICY ON THE USE OF ASME GDTP SYMBOLS AND AUTHORIZATION IN ADVERTISING ASME has established procedures
ASME Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Professional Certification Applicant Information STATEMENT OF POLICY ON THE USE OF ASME GDTP SYMBOLS AND AUTHORIZATION IN ADVERTISING ASME has established procedures
EJOT Spiralform. The thread formers for metal. EJOT The Quality Connection
 EJOT Spiralform The thread formers for metal EJOT The Quality Connection Imprint Editor: EJOT GmbH & Co. KG Industrial Fasteners Division D 57319 Bad Berleburg Layout and Realisation: EJOT GmbH & Co. KG
EJOT Spiralform The thread formers for metal EJOT The Quality Connection Imprint Editor: EJOT GmbH & Co. KG Industrial Fasteners Division D 57319 Bad Berleburg Layout and Realisation: EJOT GmbH & Co. KG
Conceptual Design of Buildings (Course unit code 1C2)
 (Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
(Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
DRAFTING MANUAL. Gears (Bevel and Hypoid) Drafting Practice
 Page 1 1.0 General This section provides the basis for uniformity in engineering gears drawings and their technical data for gears with intersecting axes (bevel gears), and nonparallel, nonintersecting
Page 1 1.0 General This section provides the basis for uniformity in engineering gears drawings and their technical data for gears with intersecting axes (bevel gears), and nonparallel, nonintersecting
KIRÁLY TRADING KFT H-1151 Budapest Mogyoród útja 12-14 tel: 061307-3801 Email_pzoli@kiralytrading.hu. Clamps Clamping devices
 04000 Clamps Clamping devices 23000 22000 21000 20000 09000 08000 07000 06000 05000 04000 03000 02000 01000 297 04010 Adjustable straps Tempered steel 1.1191 Black oxide finish nlm 04010-101 Suitable thrust
04000 Clamps Clamping devices 23000 22000 21000 20000 09000 08000 07000 06000 05000 04000 03000 02000 01000 297 04010 Adjustable straps Tempered steel 1.1191 Black oxide finish nlm 04010-101 Suitable thrust
Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes 1
 Designation: A 276 06 Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 276; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Designation: A 276 06 Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 276; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Telescoping Post Indicator Wall Post KENNEDY VALVE ISO 9000 ISO 14001
 Telescoping Post Indicator Wall Post KENNEDY VALVE ISO 9000 ISO 14001 Telescoping Post Indicator 2945 A 1" SQUARE STEM 9" MAX. = 10" MIN. = 7" FIELD ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTIONS 1. Remove the top section from
Telescoping Post Indicator Wall Post KENNEDY VALVE ISO 9000 ISO 14001 Telescoping Post Indicator 2945 A 1" SQUARE STEM 9" MAX. = 10" MIN. = 7" FIELD ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTIONS 1. Remove the top section from
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR HIGH TENSION LINE HARDWARE AND ACCESSORIES FOR ACSR PANTHER & WOLF CONDUCTOR
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR HIGH TENSION LINE HARDWARE AND ACCESSORIES FOR ACSR PANTHER & WOLF CONDUCTOR 1.1.0 SCOPE : This specification covers design, manufacture, testing at manufacture s works before
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR HIGH TENSION LINE HARDWARE AND ACCESSORIES FOR ACSR PANTHER & WOLF CONDUCTOR 1.1.0 SCOPE : This specification covers design, manufacture, testing at manufacture s works before
ASTM A860/A860M-09 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength. Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings. 1. Scope :- 2. Reference Documents :-
 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
Machine Screws, Dowel Pins and Hardware
 Machine Screws, Dowel Pins and Section Contents Plain Socket Head Screws...Page 13-2 Wire Locking Screws...Page 13-3 Captive Screws...Page 13- Ventilation Screws...Page 13- Shoulder Screws...Page 13-
Machine Screws, Dowel Pins and Section Contents Plain Socket Head Screws...Page 13-2 Wire Locking Screws...Page 13-3 Captive Screws...Page 13- Ventilation Screws...Page 13- Shoulder Screws...Page 13-
Machine devices, jig devices
 Machine devices, jig devices 853 K0697 Rolled thread studs DIN 6379 Material: Tempered steel. KIPP Rolled thread studs DIN 6379 Order No. D L B1 B2 Approx. weight g Surface finish: Thread rolled. Class
Machine devices, jig devices 853 K0697 Rolled thread studs DIN 6379 Material: Tempered steel. KIPP Rolled thread studs DIN 6379 Order No. D L B1 B2 Approx. weight g Surface finish: Thread rolled. Class
Standard Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and for General Applications 1
 Designation: A 2/A 2M 04a e1 Standard Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and for General Applications 1 This standard is issued
Designation: A 2/A 2M 04a e1 Standard Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and for General Applications 1 This standard is issued
Pipe Thread Types and Designations
 Pipe Thread Types and Designations Overview: Different types of screw threads have evolved for fastening, and hydraulic systems. Of special concern are plastic-to-metal, taper/parallel threaded joints
Pipe Thread Types and Designations Overview: Different types of screw threads have evolved for fastening, and hydraulic systems. Of special concern are plastic-to-metal, taper/parallel threaded joints
TARIFF CODE and updates standard
 TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
INDICATOR POST STYLE 2945 A TELESCOPING BARREL ASSEMBLY UL AND FM APPROVED
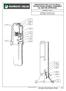 INDICATOR POST STYLE 2945 A TELESCOPING BARREL ASSEMBLY UL AND FM APPROVED Available in Sizes B C D E See Page 6 for Dimensions Kennedy Valve/Indicator Posts 17-1 INDICATOR POST STYLE 2945 A TELESCOPING
INDICATOR POST STYLE 2945 A TELESCOPING BARREL ASSEMBLY UL AND FM APPROVED Available in Sizes B C D E See Page 6 for Dimensions Kennedy Valve/Indicator Posts 17-1 INDICATOR POST STYLE 2945 A TELESCOPING
These features have made Lo Torc valves the choice of high pressure plug value users, worldwide:
 LO TORC Plug Valve The high value, dependable performance, and low maintenance requirements of Halliburton Lo Torc valves can help reduce overall operating costs and help cut downtime. These features have
LO TORC Plug Valve The high value, dependable performance, and low maintenance requirements of Halliburton Lo Torc valves can help reduce overall operating costs and help cut downtime. These features have
Technical Handbook 1
 Technical Handbook IMPORTANT HoloKrome has published this handbook as a guide to dimensional, mechanical, and application data for HoloKrome Socket Screw Products. However, the following limitations must
Technical Handbook IMPORTANT HoloKrome has published this handbook as a guide to dimensional, mechanical, and application data for HoloKrome Socket Screw Products. However, the following limitations must
It's large enough to handle most welding job shop projects, yet small enough to make it a worth while home-workshop tool
 It's large enough to handle most welding job shop projects, yet small enough to make it a worth while home-workshop tool H Craft Print Project No. 272 ERE'S a metal bender that will enable you to bend
It's large enough to handle most welding job shop projects, yet small enough to make it a worth while home-workshop tool H Craft Print Project No. 272 ERE'S a metal bender that will enable you to bend
GAS DISTRIBUTION PRODUCTS STEEL SERVICE TEES
 GAS DISTRIBUTION PRODUCTS STEEL SERVICE TEES CONTINENTAL INDUSTRIES ABOUT US THE ULTIMATE CONNECTION Our Company Continental Industries, headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma, was formed in 1958 and is today
GAS DISTRIBUTION PRODUCTS STEEL SERVICE TEES CONTINENTAL INDUSTRIES ABOUT US THE ULTIMATE CONNECTION Our Company Continental Industries, headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma, was formed in 1958 and is today
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SERIES 8000 PRECAST CONCRETE
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SERIES 8000 PRECAST CONCRETE TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION PART 8000 - PRECAST CONCRETE TABLE OF CONTENTS Item Number Page 8100 PRECAST CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION - GENERAL 8-3 8101 General
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SERIES 8000 PRECAST CONCRETE TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION PART 8000 - PRECAST CONCRETE TABLE OF CONTENTS Item Number Page 8100 PRECAST CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION - GENERAL 8-3 8101 General
Bolted Joint Design. Mechanical Properties of Steel Fasteners in Service
 Bolted Joint Design There is no one fastener material that is right for every environment. Selecting the right fastener material from the vast array of those available can be a daunting task. Careful consideration
Bolted Joint Design There is no one fastener material that is right for every environment. Selecting the right fastener material from the vast array of those available can be a daunting task. Careful consideration
ANSI APPROVED 04/11/2014 ANSI APPROVED 08/17/2011. 45 Reaffirmation ANSI APPROVED 02/28/2014. 45 Reaffirmation ANSI APPROVED 05/06/2013
 STANDARDS STATUS REPORT As of November 4, 2015 Note: Dates in RED indicate the last action taken; Highlighted Items Indicate New/Open Items; Grey items have been closed Document TC Status Comments ASME
STANDARDS STATUS REPORT As of November 4, 2015 Note: Dates in RED indicate the last action taken; Highlighted Items Indicate New/Open Items; Grey items have been closed Document TC Status Comments ASME
SERIES NG 1800 STRUCTURAL STEELWORK
 MANUAL OF CONTRACT DOCUMENTS FOR HIGHWAY WORKS VOLUME 2 NOTES FOR GUIDANCE ON THE SPECIFICATION FOR HIGHWAY WORKS SERIES NG 1800 STRUCTURAL STEELWORK Contents Clause Title Page NG 1800 (08/14) General
MANUAL OF CONTRACT DOCUMENTS FOR HIGHWAY WORKS VOLUME 2 NOTES FOR GUIDANCE ON THE SPECIFICATION FOR HIGHWAY WORKS SERIES NG 1800 STRUCTURAL STEELWORK Contents Clause Title Page NG 1800 (08/14) General
James M. Pleasants Company
 James M. Pleasants Company SUBMITTAL DATA GAINESVILLE MECHANICAL DECEMBER 20, 2013 PROJECT: GSU: J-183 HUMANITIES LAW BLDG. QUOTE NO:12116 ENGINEER: STEVENS & WILKINSON GASKETED PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER Tag:
James M. Pleasants Company SUBMITTAL DATA GAINESVILLE MECHANICAL DECEMBER 20, 2013 PROJECT: GSU: J-183 HUMANITIES LAW BLDG. QUOTE NO:12116 ENGINEER: STEVENS & WILKINSON GASKETED PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER Tag:
Ultrasonic Reference Blocks
 Ultrasonic Reference Blocks Custom and Standard Test Blocks for Nondestructive Testing Introduction 3 IIW Type 1 Calibration Block 4 Miniature Angle Beam (ROMPAS) Calibration Block 4 Distance Calibration
Ultrasonic Reference Blocks Custom and Standard Test Blocks for Nondestructive Testing Introduction 3 IIW Type 1 Calibration Block 4 Miniature Angle Beam (ROMPAS) Calibration Block 4 Distance Calibration
Let s look at an example of where grade 5 and grade 8 bolts are subjected to single shear loads (winch plate reference).
 Bolt s I have been on a quite a few online email lists over the last 7 years or so, basically since they first came out. From the original Jeep-L list to the XJ-list to the Rockcrawler.com board, a common
Bolt s I have been on a quite a few online email lists over the last 7 years or so, basically since they first came out. From the original Jeep-L list to the XJ-list to the Rockcrawler.com board, a common
There is no upside to. down time
 EXPANDED and PERFORATED Data and Specifications 30 Similar to Type 302 with excellent mechanical properties, resistance to many corrosive agents. Useful where sanitation and cleanliness are important.
EXPANDED and PERFORATED Data and Specifications 30 Similar to Type 302 with excellent mechanical properties, resistance to many corrosive agents. Useful where sanitation and cleanliness are important.
Standard Specification for Tool Steel High Speed 1
 Designation: A 600 92a (Reapproved 2004) Standard Specification for Tool Steel High Speed This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 600; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Designation: A 600 92a (Reapproved 2004) Standard Specification for Tool Steel High Speed This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 600; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy 1
 Designation: A 68 8 Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 68; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
Designation: A 68 8 Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 68; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
SECTION 02720 SANITARY SEWER AND STORM DRAIN SYSTEMS
 SECTION 02720 SANITARY SEWER AND STORM DRAIN SYSTEMS PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. The requirements for pipe material and installation in sewer and drainage collection systems. All materials
SECTION 02720 SANITARY SEWER AND STORM DRAIN SYSTEMS PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. The requirements for pipe material and installation in sewer and drainage collection systems. All materials
SECTION 15076 CEMENT-MORTAR LINED AND COATED STEEL PIPE
 SECTION 15076 CEMENT-MORTAR LINED AND COATED (CML&C) STEEL PIPE PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 DESCRIPTION This section designates the requirements for steel pipe fabrication, test in shop, installation of steel
SECTION 15076 CEMENT-MORTAR LINED AND COATED (CML&C) STEEL PIPE PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 DESCRIPTION This section designates the requirements for steel pipe fabrication, test in shop, installation of steel
Removing chips is a method for producing plastic threads of small diameters and high batches, which cause frequent failures of thread punches.
 Plastic Threads Technical University of Gabrovo Yordanka Atanasova Threads in plastic products can be produced in three ways: a) by direct moulding with thread punch or die; b) by placing a threaded metal
Plastic Threads Technical University of Gabrovo Yordanka Atanasova Threads in plastic products can be produced in three ways: a) by direct moulding with thread punch or die; b) by placing a threaded metal
Reproduced with the permission of the American Welding Society (AWS), Miami, Florida - 09/15/2011. 7. Stud Welding
 7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
LEGACY REPORT ER-5110. www.icc-es.org. ICC Evaluation Service, Inc. Reissued November 1, 2003. Legacy report on the 1997 Uniform Building Code
 LEGACY REPORT Reissued November 1, 2003 ICC Evaluation Service, Inc. www.icc-es.org Business/Regional Office # 5360 Workman Mill Road, Whittier, California 90601 # (562) 699-0543 Regional Office # 900
LEGACY REPORT Reissued November 1, 2003 ICC Evaluation Service, Inc. www.icc-es.org Business/Regional Office # 5360 Workman Mill Road, Whittier, California 90601 # (562) 699-0543 Regional Office # 900
22 Torque Control. 23 Torque and Turn Control. 25 Stretch Control. 25 Direct Tension Control
 Technical Reference Guide Table of Contents Subject Page # Fastener Material Selection 1 Mechanical Properties Materials 3 Galling 6 Heat Treatment 7 Screw Thread Fundamentals 10 Strength of Threads 12
Technical Reference Guide Table of Contents Subject Page # Fastener Material Selection 1 Mechanical Properties Materials 3 Galling 6 Heat Treatment 7 Screw Thread Fundamentals 10 Strength of Threads 12
Sports and High Mast Lighting Poles Phone: (866) 474-7200 Fax: (817) 924-7049
 Sports and High Mast Lighting Poles 4 High Mast Lighting Poles General American LitePole offers a raising and lowering system that allows for ease of maintaining the lighting system at ground level. Ideal
Sports and High Mast Lighting Poles 4 High Mast Lighting Poles General American LitePole offers a raising and lowering system that allows for ease of maintaining the lighting system at ground level. Ideal
Installation Manual. SKU# 21000 series (Base Rails) SKU# 22000 series (Overhead Racks)
 Installation Manual SKU# 21000 series (Base Rails) SKU# 22000 series (Overhead Racks) Welcome to the world of TracRac! We re delighted that you have chosen TracRac, the ultimate sliding truck rack system.
Installation Manual SKU# 21000 series (Base Rails) SKU# 22000 series (Overhead Racks) Welcome to the world of TracRac! We re delighted that you have chosen TracRac, the ultimate sliding truck rack system.
DWG 001. Blueprint Reading. Line Standards Drawing Symbols. Instructor Guide
 DWG 001 Blueprint Reading Line Standards Drawing Symbols Instructor Guide Module Purpose Introduction The purpose of the Blueprint Reading modules is to introduce students to production drawings and blueprint
DWG 001 Blueprint Reading Line Standards Drawing Symbols Instructor Guide Module Purpose Introduction The purpose of the Blueprint Reading modules is to introduce students to production drawings and blueprint
SECTION 15105 DUCTILE IRON PIPE AND FITTINGS
 SECTION 15105 DUCTILE IRON PIPE AND FITTINGS PART 1 GENERAL.01 COORDINATION OF WORK Connection to existing pipelines may require shutdown of Owner facilities. Closely coordinate construction work and connections
SECTION 15105 DUCTILE IRON PIPE AND FITTINGS PART 1 GENERAL.01 COORDINATION OF WORK Connection to existing pipelines may require shutdown of Owner facilities. Closely coordinate construction work and connections
FASTENERS - ACCEPTANCE INSPECTION (ISO 3269:2000) IRISH STANDARD I.S. EN ISO 3269:2000. Price Code. Údarás um Chaighdeáin Náisiúnta na héireann
 IRISH STANDARD I.S. EN ISO 3269:2000 ICS 21.060.01 National Standards Authority of Ireland Dublin 9 Ireland Tel: (01) 807 3800 Tel: (01) 807 3838 FASTENERS - ACCEPTANCE INSPECTION (ISO 3269:2000) NSAI
IRISH STANDARD I.S. EN ISO 3269:2000 ICS 21.060.01 National Standards Authority of Ireland Dublin 9 Ireland Tel: (01) 807 3800 Tel: (01) 807 3838 FASTENERS - ACCEPTANCE INSPECTION (ISO 3269:2000) NSAI
OD 1401 9 PRECISION MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
 SUBCOURSE EDITION OD 1401 9 PRECISION MEASURING INSTRUMENTS PRECISION MEASURING INSTRUMENTS SUBCOURSE OD1401 EDITION 9 Unites States Army Combined Arms Support Command Fort Lee, VA 23801-1809 5 CREDIT
SUBCOURSE EDITION OD 1401 9 PRECISION MEASURING INSTRUMENTS PRECISION MEASURING INSTRUMENTS SUBCOURSE OD1401 EDITION 9 Unites States Army Combined Arms Support Command Fort Lee, VA 23801-1809 5 CREDIT
MACHINE DRAWING QUESTION BANK. 2. What are the parts not usually sectioned? (Nov 04)
 MACHINE DRAWING QUESTION BANK UNIT-I 1. Answer the following: Sketch a i. Hexagonal nut convention, ii. Convention of a stud bolt. (Nov 04) 2. What are the parts not usually sectioned? (Nov 04) 3 Answer
MACHINE DRAWING QUESTION BANK UNIT-I 1. Answer the following: Sketch a i. Hexagonal nut convention, ii. Convention of a stud bolt. (Nov 04) 2. What are the parts not usually sectioned? (Nov 04) 3 Answer
Bolting Galvanized Steel
 Bolting Galvanized Steel This chapter gives information on the characteristics, advantages and economics of bolted galvanized structures and zinc coated fasteners, and offers comment on bolting procedures
Bolting Galvanized Steel This chapter gives information on the characteristics, advantages and economics of bolted galvanized structures and zinc coated fasteners, and offers comment on bolting procedures
Milling Chuck Features
 Milling Chuck Features Since its first introduction into the industry in 1963, Nikken has sold over 2,000,000 worldwide and never stopped improving its original design. Featuring multi-roller bearings
Milling Chuck Features Since its first introduction into the industry in 1963, Nikken has sold over 2,000,000 worldwide and never stopped improving its original design. Featuring multi-roller bearings
Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth
 Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth Bulk deformation forming (rolling) Rolling is the process of reducing
Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth Bulk deformation forming (rolling) Rolling is the process of reducing
Lathe Milling Attachment
 Lathe Milling Attachment By L C. MASON BY CLEVERLY stacking cold-rolled flat stock together, T-slots and slide for this lathe milling attachment are made without costly machinery. In fact, only two tools,
Lathe Milling Attachment By L C. MASON BY CLEVERLY stacking cold-rolled flat stock together, T-slots and slide for this lathe milling attachment are made without costly machinery. In fact, only two tools,
CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Texas 77058 REVISION A JULY 6, 1998 REPLACES BASELINE SPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION..............................................
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Texas 77058 REVISION A JULY 6, 1998 REPLACES BASELINE SPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIA FOR PRELOADED BOLTS CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION..............................................
SECTION 33 11 00.15 DUCTILE IRON PIPE AND FITTINGS
 SECTION 33 11 00.15 DUCTILE IRON PIPE AND FITTINGS PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 COORDINATION OF WORK Connection to existing pipelines may require shutdown of AW facilities. Closely coordinate construction work
SECTION 33 11 00.15 DUCTILE IRON PIPE AND FITTINGS PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 COORDINATION OF WORK Connection to existing pipelines may require shutdown of AW facilities. Closely coordinate construction work
Anodes and Misc Equipment
 Anodes and Misc Equipment Application: Platinised Titanium Anodes Platinised titanium anodes are recommended for use in the following electrolytic processes:- Precious metal electroplating - e.g. Au, Pt,
Anodes and Misc Equipment Application: Platinised Titanium Anodes Platinised titanium anodes are recommended for use in the following electrolytic processes:- Precious metal electroplating - e.g. Au, Pt,
C-Plus Softgrip Screwdrivers
 10 C-Plus Softgrip Screwdrivers The multi-purpose screwdrivers with 2K handles From professionals for professionals. Perfect in every detail the C-PLUS series is the result of long-lasting studies into
10 C-Plus Softgrip Screwdrivers The multi-purpose screwdrivers with 2K handles From professionals for professionals. Perfect in every detail the C-PLUS series is the result of long-lasting studies into
BUMAX. REYHER your partner for the BUMAX range
 BUMAX high-tensile stainless steel fasteners REYHER your partner for the BUMAX range Strongest stainless steel fasteners in the world BUMAX 88 and BUMAX ready for delivery from stock Wide range of BUMAX
BUMAX high-tensile stainless steel fasteners REYHER your partner for the BUMAX range Strongest stainless steel fasteners in the world BUMAX 88 and BUMAX ready for delivery from stock Wide range of BUMAX
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes
 Training Objectives After watching the program and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of the stamping process and the die systems used to form sheet metal.
Training Objectives After watching the program and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of the stamping process and the die systems used to form sheet metal.
TIE ROD END DESIGN TUTORIAL
 TIE ROD END DESIGN TUTORIAL THE FOLLOWING IS A SIMPLIFIED STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE INTENDED TO ILLUSTRATE THE DECISIONS AND COMPROMISES INVOLVED IN DESIGNING A TIE ROD END. THE PROCESS FOR DESIGNING ANY BALL
TIE ROD END DESIGN TUTORIAL THE FOLLOWING IS A SIMPLIFIED STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE INTENDED TO ILLUSTRATE THE DECISIONS AND COMPROMISES INVOLVED IN DESIGNING A TIE ROD END. THE PROCESS FOR DESIGNING ANY BALL
DSM http://www.dsmmfg.com 1 (800) 886-6376
 DESIGN GUIDE FOR BENT SHEET METAL This guide discusses how the bends are made, what thicknesses of sheet metal are commonly used, recommended bend radius to use when modeling the part, some practical limits
DESIGN GUIDE FOR BENT SHEET METAL This guide discusses how the bends are made, what thicknesses of sheet metal are commonly used, recommended bend radius to use when modeling the part, some practical limits
IHSS-N1 WELDED HONEYCOMB CORE SPECIFICATION. Generated: Sergiy Papyshev Engineering. Approved: Don Prysi Manufacturing. Approved: Merzuk Ramic Quality
 IHSS-N1 WELDED HONEYCOMB CORE SPECIFICATION Generated: Sergiy Papyshev Engineering Approved: Don Prysi Manufacturing Approved: Merzuk Ramic Quality Approved: Steven Barnett Administrative DATE DATE DATE
IHSS-N1 WELDED HONEYCOMB CORE SPECIFICATION Generated: Sergiy Papyshev Engineering Approved: Don Prysi Manufacturing Approved: Merzuk Ramic Quality Approved: Steven Barnett Administrative DATE DATE DATE
SECTION 6. Glass Storefront Doors:
 SECTION 6 Glass Storefront Doors: Table of Contents 3070 Storefront Door System Description & Dimensions 6070 Storefront Door System Description & Dimensions Door Leaf Detail Optional 10 Bottom Rail Detail
SECTION 6 Glass Storefront Doors: Table of Contents 3070 Storefront Door System Description & Dimensions 6070 Storefront Door System Description & Dimensions Door Leaf Detail Optional 10 Bottom Rail Detail
LEADER IN CUTTING TECHNOLOGY
 LEADER IN CUTTING TECHNOLOGY FOR OVER 2 YEARS REASONS WHY TRONEX IS THE BEST IN THE WORLD 1 2 SUPERIOR CUTTING PERFORMANCE Cut hundreds of thousands of times before dulling. Cut hundreds of thousands of
LEADER IN CUTTING TECHNOLOGY FOR OVER 2 YEARS REASONS WHY TRONEX IS THE BEST IN THE WORLD 1 2 SUPERIOR CUTTING PERFORMANCE Cut hundreds of thousands of times before dulling. Cut hundreds of thousands of
Technical Product Specification (TPS)
 ISO Standards collection Technical Product Specification (TPS) Contents ISO 1:2002 Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) -- Standard reference temperature for geometrical product specification and verification
ISO Standards collection Technical Product Specification (TPS) Contents ISO 1:2002 Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) -- Standard reference temperature for geometrical product specification and verification
Slide the new steering column shaft through the steering column from the driver compartment.
 Slide the new steering column shaft through the steering column from the driver compartment. Push the column shaft through the steering column until the machined end is out past the column lower bushing.
Slide the new steering column shaft through the steering column from the driver compartment. Push the column shaft through the steering column until the machined end is out past the column lower bushing.
Mechanical Property Changes in Steel during the Pipe Making Process Brent Keil 1
 381 Mechanical Property Changes in Steel during the Pipe Making Process Brent Keil 1 Abstract Welded Steel Pipe (WSP) is arguably the most widely utilized pipe material for the transmission of water throughout
381 Mechanical Property Changes in Steel during the Pipe Making Process Brent Keil 1 Abstract Welded Steel Pipe (WSP) is arguably the most widely utilized pipe material for the transmission of water throughout
Structural Integrity Analysis
 Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
16 April 2012 1032011-F 1994-2002 Dodge Adjustable Track bar with Relocation Bracket 1
 16 April 2012 1032011-F 1994-2002 Dodge Adjustable Track bar with Relocation Bracket 1 BD Adjustable Track Bar w/bracket Dodge 2500-3500 4WD Models 1994-2002 Dodge 1500 4WD Model 1994-2001 P/N# 1032011-F
16 April 2012 1032011-F 1994-2002 Dodge Adjustable Track bar with Relocation Bracket 1 BD Adjustable Track Bar w/bracket Dodge 2500-3500 4WD Models 1994-2002 Dodge 1500 4WD Model 1994-2001 P/N# 1032011-F
Agilent X/P/K281C Adapters
 Agilent X/P/K281C Adapters Including Options 006, 012, 013, 106 Operating and Service Manual Contents 1 Introduction 7 Product Overview 8 Options 8 Instruments Covered by Manual 10 2 Installation 11 Initial
Agilent X/P/K281C Adapters Including Options 006, 012, 013, 106 Operating and Service Manual Contents 1 Introduction 7 Product Overview 8 Options 8 Instruments Covered by Manual 10 2 Installation 11 Initial
SERVICE PARTS LIST PAGE 1 OF 6 BASE ASSEMBLY SPECIFY CATALOG NO. AND SERIAL NO. WHEN ORDERING PARTS 12" DUAL BEVEL COMPOUND MITER SAW B27A
 PAGE 1 OF 6 BASE ASSEMBLY 00 0 EXAMPLE: Component Parts (Small #) Are Included When Ordering The Assembly (Large #). SPECIFY CATALOG NO. AND NO. WHEN ORDERING PARTS 1 02-80-0050 Thrust Bearing (1) 2 05-80-0510
PAGE 1 OF 6 BASE ASSEMBLY 00 0 EXAMPLE: Component Parts (Small #) Are Included When Ordering The Assembly (Large #). SPECIFY CATALOG NO. AND NO. WHEN ORDERING PARTS 1 02-80-0050 Thrust Bearing (1) 2 05-80-0510
Specifications for Programs: 737, 747, 757, 767, 777, 787
 = Performed by GKN BAC 5000 AN General Sealing 6-262, 6-265, 6-267, 6-270 PSD for 787 Only: 6-242, 6-269, 6-271 PSD for 777 Only: 6-261,6-264, 6-266, 6-269, 6-271 BAC 5004 L Installation of Permanent Fasteners
= Performed by GKN BAC 5000 AN General Sealing 6-262, 6-265, 6-267, 6-270 PSD for 787 Only: 6-242, 6-269, 6-271 PSD for 777 Only: 6-261,6-264, 6-266, 6-269, 6-271 BAC 5004 L Installation of Permanent Fasteners
Section 4: NiResist Iron
 Section 4: NiResist Iron Section 4 Ni-Resist Description of Grades...4-2 201 (Type 1) Ni-Resist...4-3 202 (Type 2) Ni-Resist...4-6 Stock Listings...4-8 4-1 Ni-Resist Description of Grades Ni-Resist Dura-Bar
Section 4: NiResist Iron Section 4 Ni-Resist Description of Grades...4-2 201 (Type 1) Ni-Resist...4-3 202 (Type 2) Ni-Resist...4-6 Stock Listings...4-8 4-1 Ni-Resist Description of Grades Ni-Resist Dura-Bar
RIGGING HARDWARE ASME B30.26. Addresses detachable lifting hardware for lifting purposes
 RIGGING HARDWARE ASME B30.26 Addresses detachable lifting hardware for lifting purposes Adjustable Hardware (Turnbuckles, Eye nuts, Swivel Hoist Rings and Eyebolts Compression Hardware (Wire Rope Clips
RIGGING HARDWARE ASME B30.26 Addresses detachable lifting hardware for lifting purposes Adjustable Hardware (Turnbuckles, Eye nuts, Swivel Hoist Rings and Eyebolts Compression Hardware (Wire Rope Clips
1.8 CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALS
 SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL 1.8 CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALS An oil seal is fitted between each end of the crankshaft and the bores of the flywheel housing and gear case cover to retain the lubricating oil in the
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL 1.8 CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALS An oil seal is fitted between each end of the crankshaft and the bores of the flywheel housing and gear case cover to retain the lubricating oil in the
DECIPHERING WELD SYMBOLS
 DECIPHERING WELD SYMBOLS When welds are specified on engineering and fabrication drawings, a cryptic set of symbols issued as a sort of shorthand for describing the type of weld, its size, and other processing
DECIPHERING WELD SYMBOLS When welds are specified on engineering and fabrication drawings, a cryptic set of symbols issued as a sort of shorthand for describing the type of weld, its size, and other processing
AZEK Rail Install Guide
 TRIM MOULDING DECK PORCH RAIL PAVERS AZEK Rail Install Guide Installing AZEK Rail with CableRail by Feeney... 1 Installing CableRail by Feeney for AZEK Rail... 7 Installing AZEK Rail Stairs with CableRail
TRIM MOULDING DECK PORCH RAIL PAVERS AZEK Rail Install Guide Installing AZEK Rail with CableRail by Feeney... 1 Installing CableRail by Feeney for AZEK Rail... 7 Installing AZEK Rail Stairs with CableRail
SCREW THREADS C H A P T E R 17
 C H A P T E R 17 SCREW THREADS Screw threads are of prime importance in machine drawing. It is a functional element used as temporary fasteners such as bolt, stud, nut and screw etc. These are constructed
C H A P T E R 17 SCREW THREADS Screw threads are of prime importance in machine drawing. It is a functional element used as temporary fasteners such as bolt, stud, nut and screw etc. These are constructed
Ensat. Self-tapping inserts SOLID BODIES LINE
 Ensat Self-tapping inserts SOLID BODIES LINE Index DESCRIPTION Page Presentation 3 Materials and Applications 4 Features 5 Preparing the receiving hole 6 Tools Codes 7 Ensat Series 302 Ensat Series 303
Ensat Self-tapping inserts SOLID BODIES LINE Index DESCRIPTION Page Presentation 3 Materials and Applications 4 Features 5 Preparing the receiving hole 6 Tools Codes 7 Ensat Series 302 Ensat Series 303
