Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration
|
|
|
- Bruno Perry
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
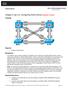
1 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN N/A S2 VLAN N/A S3 VLAN N/A PC1 NIC PC2 NIC PC3 NIC PC4 NIC PC5 NIC PC6 NIC Initial Port Assignments (Switches 2 and 3) Ports Assignment Network Fa0/1 0/ q Trunks (Native VLAN 99) /24 Fa0/6 0/10 VLAN 30 Guest (Default) /24 Fa0/11 0/17 VLAN 10 Faculty/Staff /24 Fa0/18 0/24 VLAN 20 Students /24 All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 7
2 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the topology diagram Erase the startup configuration and reload a switch to the default state Perform basic configuration tasks on a switch Create VLANs Assign switch ports to a VLAN Add, move, and change ports Verify VLAN configuration Enable trunking on inter-switch connections Verify trunk configuration Save the VLAN configuration Task 1: Prepare the Network Step 1: Cable a network that is similar to the one in the topology diagram. You can use any current switch in your lab as long as it has the required interfaces shown in the topology. Note: If you use 2900 or 2950 switches, the outputs may appear different. Also, certain commands may be different or unavailable. Step 2: Clear any existing configurations on the switches, and initialize all ports in the shutdown state. If necessary, refer to Lab 2.5.1, Appendix 1, for the procedure to clear switch configurations. It is a good practice to disable any unused ports on the switches by putting them in shutdown. Disable all ports on the switches: Switch#config term Switch(config)#interface range fa0/1-24 Switch(config-if-range)#shutdown Switch(config-if-range)#interface range gi0/1-2 Switch(config-if-range)#shutdown Task 2: Perform Basic Switch Configurations Step 1: Configure the switches according to the following guidelines. Configure the switch hostname. Disable DNS lookup. Configure an EXEC mode password of class. Configure a password of cisco for console connections. Configure a password of cisco for vty connections. Step 2: Re-enable the user ports on S2 and S3. S2(config)#interface range fa0/6, fa0/11, fa0/18 S2(config-if-range)#switchport mode access All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 7
3 S2(config-if-range)#no shutdown S3(config)#interface range fa0/6, fa0/11, fa0/18 S3(config-if-range)#switchport mode access S3(config-if-range)#no shutdown Task 3: Configure and Activate Ethernet Interfaces Step 1: Configure the PCs. You can complete this lab using only two PCs by simply changing the IP addressing for the two PCs specific to a test you want to conduct. For example, if you want to test connectivity between PC1 and PC2, then configure the IP addresses for those PCs by referring to the addressing table at the beginning of the lab. Alternatively, you can configure all six PCs with the IP addresses and default gateways. Task 4: Configure VLANs on the Switch Step 1: Create VLANs on switch S1. Use the vlan vlan-id command in global configuration mode to add a VLAN to switch S1. There are four VLANS configured for this lab: VLAN 10 (faculty/staff); VLAN 20 (students); VLAN 30 (guest); and VLAN 99 (management). After you create the VLAN, you will be in vlan configuration mode, where you can assign a name to the VLAN with the name vlan name command. S1(config)#vlan 10 S1(config-vlan)#name faculty/staff S1(config-vlan)#vlan 20 S1(config-vlan)#name students S1(config-vlan)#vlan 30 S1(config-vlan)#name guest S1(config-vlan)#vlan 99 S1(config-vlan)#name management S1(config-vlan)#end S1# Step 2: Verify that the VLANs have been created on S1. Use the show vlan brief command to verify that the VLANs have been created. S1#show vlan brief VLAN Name Status Ports default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/4, Fa0/5 Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9 Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13 Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17 Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21 Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1 Gi0/2 10 faculty/staff active 20 students active 30 guest active 99 management active All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 7
4 Step 3: Configure and name VLANs on switches S2 and S3. Create and name VLANs 10, 20, 30, and 99 on S2 and S3 using the commands from Step 1. Verify the correct configuration with the show vlan brief command. What ports are currently assigned to the four VLANs you have created? Step 4: Assign switch ports to VLANs on S2 and S3. Refer to the port assignment table on page 1. Ports are assigned to VLANs in interface configuration mode, using the switchport access vlan vlan-id command. You can assign each port individually or you can use the interface range command to simplify this task, as shown here. The commands are shown for S3 only, but you should configure both S2 and S3 similarly. Save your configuration when done. S3(config)#interface range fa0/6-10 S3(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 30 S3(config-if-range)#interface range fa0/11-17 S3(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 10 S3(config-if-range)#interface range fa0/18-24 S3(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 20 S3(config-if-range)#end S3#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [enter] Building configuration... [OK] Step 4: Determine which ports have been added. Use the show vlan id vlan-number command on S2 to see which ports are assigned to VLAN 10. Which ports are assigned to VLAN 10? Note: The show vlan id vlan-name displays the same output. You can also view VLAN assignment information using the show interfaces interface switchport command. Step 5: Assign the management VLAN. A management VLAN is any VLAN that you configure to access the management capabilities of a switch. VLAN 1 serves as the management VLAN if you did not specifically define another VLAN. You assign the management VLAN an IP address and subnet mask. A switch can be managed via HTTP, Telnet, SSH, or SNMP. Because the out-of-the-box configuration of a Cisco switch has VLAN 1 as the default VLAN, VLAN 1 is a bad choice as the management VLAN. You do not want an arbitrary user who is connecting to a switch to default to the management VLAN. Recall that you configured the management VLAN as VLAN 99 earlier in this lab. From interface configuration mode, use the ip address command to assign the management IP address to the switches. S1(config)#interface vlan 99 S1(config-if)#ip address S1(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config)#interface vlan 99 S2(config-if)#ip address S2(config-if)#no shutdown S3(config)#interface vlan 99 S3(config-if)#ip address All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 7
5 S3(config-if)#no shutdown Assigning a management address allows IP communication between the switches, and also allows any host connected to a port assigned to VLAN 99 to connect to the switches. Because VLAN 99 is configured as the management VLAN, any ports assigned to this VLAN are considered management ports and should be secured to control which devices can connect to these ports. Step 6: Configure trunking and the native VLAN for the trunking ports on all switches. Trunks are connections between the switches that allow the switches to exchange information for all VLANS. By default, a trunk port belongs to all VLANs, as opposed to an access port, which can only belong to a single VLAN. If the switch supports both ISL and 802.1Q VLAN encapsulation, the trunks must specify which method is being used. Because the 2960 switch only supports 802.1Q trunking, it is not specified in this lab. A native VLAN is assigned to an 802.1Q trunk port. In the topology, the native VLAN is VLAN 99. An 802.1Q trunk port supports traffic coming from many VLANs (tagged traffic) as well as traffic that does not come from a VLAN (untagged traffic). The 802.1Q trunk port places untagged traffic on the native VLAN. Untagged traffic is generated by a computer attached to a switch port that is configured with the native VLAN. One of the IEEE 802.1Q specifications for Native VLANs is to maintain backward compatibility with untagged traffic common to legacy LAN scenarios. For the purposes of this lab, a native VLAN serves as a common identifier on opposing ends of a trunk link. It is a best practice to use a VLAN other than VLAN 1 as the native VLAN. Use the interface range command in global configuration mode to simplify configuring trunking. S1(config)#interface range fa0/1-5 S1(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S1(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1(config-if-range)#no shutdown S1(config-if-range)#end S2(config)# interface range fa0/1-5 S2(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S2(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2(config-if-range)#no shutdown S2(config-if-range)#end S3(config)# interface range fa0/1-5 S3(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S3(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3(config-if-range)#no shutdown S3(config-if-range)#end Verify that the trunks have been configured with the show interface trunk command. S1#show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 99 Fa0/2 on 802.1q trunking 99 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/ Fa0/ Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/1 1,10,20,30,99 Fa0/2 1,10,20,30,99 All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 7
6 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/1 1,10,20,30,99 Fa0/2 1,10,20,30,99 Step 7: Verify that the switches can communicate. From S1, ping the management address on both S2 and S3. S1#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/9 ms S1#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:.!!!! Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms Step 8: Ping several hosts from PC2. Ping from host PC2 to host PC1 ( ). Is the ping attempt successful? Ping from host PC2 to the switch VLAN 99 IP address Is the ping attempt successful? Because these hosts are on different subnets and in different VLANs, they cannot communicate without a Layer 3 device to route between the separate subnetworks. Ping from host PC2 to host PC5. Is the ping attempt successful? Because PC2 is in the same VLAN and the same subnet as PC5, the ping is successful Step 9: Move PC1 into the same VLAN as PC2. The port connected to PC2 (S2 Fa0/18) is assigned to VLAN 20, and the port connected to PC1 (S2 Fa0/11) is assigned to VLAN 10. Reassign the S2 Fa0/11 port to VLAN 20. You do not need to first remove a port from a VLAN to change its VLAN membership. After you reassign a port to a new VLAN, that port is automatically removed from its previous VLAN. S2#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. S2(config)#interface fastethernet 0/11 S2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20 S2(config-if)#end Ping from host PC2 to host PC1. Is the ping attempt successful? Even though the ports used by PC1 and PC2 are in the same VLAN, they are still in different subnetworks, so they cannot communicate directly. Step 10: Change the IP address and network on PC1. Change the IP address on PC1 to The subnet mask and default gateway can remain the same. Once again, ping from host PC2 to host PC1, using the newly assigned IP address. Is the ping attempt successful? Why was this attempt successful? All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 7
7 Task 7: Document the Switch Configurations On each switch, capture the running configuration to a text file and save it for future reference. Task 6: Clean Up Erase the configurations and reload the switches. Disconnect and store the cabling. For PC hosts that are normally connected to other networks (such as the school LAN or to the Internet), reconnect the appropriate cabling and restore the TCP/IP settings. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 7
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
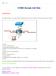
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Basic Wireless Configuration
 Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
What is VLAN Routing?
 Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications
 Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets
 Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging
 Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites
 Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer
 Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router
 Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example
 Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
CCNA Access List Sim
 1 P a g e CCNA Access List Sim Question An administrator is trying to ping and telnet from Switch to Router with the results shown below: Switch> Switch> ping 10.4.4.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending
1 P a g e CCNA Access List Sim Question An administrator is trying to ping and telnet from Switch to Router with the results shown below: Switch> Switch> ping 10.4.4.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending
Enabling Remote Access to the ACE
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to configure remote access to the Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE) module by establishing a remote connection by using the Secure Shell (SSH) or Telnet protocols.
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to configure remote access to the Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE) module by establishing a remote connection by using the Secure Shell (SSH) or Telnet protocols.
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
TotalCloud Phone System
 TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch
 Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Configuring Port Security
 32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide
 Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
- Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP -
 1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
How To Lower Data Rate On A Network On A 2Ghz Network On An Ipnet 2 (Net 2) On A Pnet 2 On A Router On A Gbnet 2.5 (Net 1) On An Uniden Network On
 Lab 8.1.10.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Lab 8.1.10.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Abstract. MEP; Reviewed: GAK 10/17/2005. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2005 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
ANZA Formación en Tecnologías Avanzadas
 INTRODUCING CISCO DATA CENTER NETWORKING (DCICN) Temario This new assoicate level course has been designed to introduce delegates to the three primary technologies that are used in the Cisco Data Center.
INTRODUCING CISCO DATA CENTER NETWORKING (DCICN) Temario This new assoicate level course has been designed to introduce delegates to the three primary technologies that are used in the Cisco Data Center.
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
Fundamentals of Switching
 1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
Cisco Nexus 5548UP. Switch Configuration Guide for Dell PS Series SANs. A Dell Deployment and Configuration Guide
 Cisco Nexus 5548UP Switch Configuration Guide for Dell PS Series SANs Dell Storage Engineering October 2015 A Dell Deployment and Configuration Guide Revisions Date February 2013 October 2013 March 2014
Cisco Nexus 5548UP Switch Configuration Guide for Dell PS Series SANs Dell Storage Engineering October 2015 A Dell Deployment and Configuration Guide Revisions Date February 2013 October 2013 March 2014
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches
 CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
Troubleshooting IP Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
Management Software. Web Browser User s Guide AT-S106. For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch. Version 1.0.0. 613-001339 Rev.
 Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT)
 ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
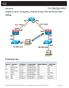 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting
 Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS
 BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Communication analysis provides powerful tool for maintenance, performance monitoring, attack detection, and problems fixing in computer networks. Today networks
BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Communication analysis provides powerful tool for maintenance, performance monitoring, attack detection, and problems fixing in computer networks. Today networks
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH
 Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Brocade to Cisco Comparisons
 1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
CCNA Discovery 4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, In Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, In Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
Cisco Data Centre: Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking
 coursemonster.com/uk Cisco Data Centre: Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking View training dates» Overview In the Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking training course, delegates will learn to:â
coursemonster.com/uk Cisco Data Centre: Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking View training dates» Overview In the Introducing Cisco Data Center Networking training course, delegates will learn to:â
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers
 Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
 Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Study Guide Allan Johnson
 Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Allan Johnson Introduction Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and s is a supplement to your classroom and laboratory experience
Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Allan Johnson Introduction Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and s is a supplement to your classroom and laboratory experience
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Network Detector Setup and Configuration
 339 N. Bernardo Avenue, Suite 200 Mountain View, CA 94043 www.airtightnetworks.net MODE SYST RPS MASTR STAT SPEDUPLX STACK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91 0 11 12 1X 2X 11X 12X 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 2122 23 24 13X
339 N. Bernardo Avenue, Suite 200 Mountain View, CA 94043 www.airtightnetworks.net MODE SYST RPS MASTR STAT SPEDUPLX STACK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91 0 11 12 1X 2X 11X 12X 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 2122 23 24 13X
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R
 VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME. Scenario
 Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Felix Rohrer. PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N. Topology Diagram
 Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0
 Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
LANs and VLANs A Simplified Tutorial
 Application Note LANs and VLANs A Simplified Tutorial Version 3.0 May 2002 COMPAS ID 90947 Avaya Labs 1 Companion document IP Addressing: A Simplified Tutorial COMPAS ID 92962 2 Introduction As the name
Application Note LANs and VLANs A Simplified Tutorial Version 3.0 May 2002 COMPAS ID 90947 Avaya Labs 1 Companion document IP Addressing: A Simplified Tutorial COMPAS ID 92962 2 Introduction As the name
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring Link Aggregation
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
