Autonomic Drugs -Summaries
|
|
|
- Osborne Carroll
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Autonomic Drugs -Summaries Cholinomimetic Agents Cholinomimetics can mimic some or all of the effects of endogenous acetylcholine (ACh). ACh acts on all of the cholinergic receptor subtypes. Names of agents in bold type may be used on exams. Major effects associated with stimulation of cholinergic receptors are underlined; major implications for dentistry in italics Muscarinic agonists: Act directly on effector tissues on postjunctional receptors (available agents are non-selective for the various subtypes of muscarinic receptors). These agents exert the same effects that are caused by acetylcholine on tissues innervated by parasympathetic nerves; and, in addition, they cause vasodilatation indirectly via release of nitric oxide from vascular endothelial cells. In other words, muscarinic agonists are parasympathomimetics, and will cause all of the peripheral effects coded by the mnemonic, DUMBBELSS except for excitation of skeletal muscle. When administered systemically, they cause many effects other than the desired effect because of the wide distribution of muscarinic receptors. Pilocarpine and cevimeline can be used to stimulate salivary flow in patients with xerostomia. Xerostomia can be caused by irradiation of the neck and face and by Sjögren s syndrome. For a summary of the effects of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems on the various autonomically-innervated tissues/cells, see p. 73 of Yagiela et al., 4 th Ed. ; p. 87 in 5 th Ed. Drugs to know: bethanechol, pilocarpine, cevimeline Indirectly acting cholinomimetics: Inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase will cause buildup of ACh concentrations at all sites where ACh is released from cholinergic nerves. Thus, these agents can stimulate skeletal muscle, stimulate ganglionic transmission (i.e. depolarize postganglionic nerves of both the PNS and SNS; therefore, causing effects associated with both of these systems), cause adrenal release of epinephrine, and also accentuate muscarinic effects due to buildup of ACh at the effector cells (provided that nerve traffic in the postganglionic parasympathetic nerve is not blocked in some manner; ACh levels cannot build up in synapses if it is not released). Central effects of cholinergic nerve stimulation can be caused if the ACh esterase inhibitor is able to get into the brain. A patient being treated for Alzheimer's disease may be taking an ACh esterase inhibitor, donepezil (which can be distributed to the CNS). If skeletal neuromuscular junction blockers (considered in a future lecture) are used along with a general anesthetic during oral surgery, an ACh esterase inhibitor might be used to reverse the effect of the NMJ blocker (if the NMJ blocker is of the competitive-type; see future lecture). Physostigmine has a tertiary nitrogen in its structure and is uncharged at physiological ph (thus it can get into the CNS), unlike neostigmine, which is a quaternary N-containing compound. Physostigmine can be used to treat poisoning by muscarinic antagonists like atropine that are distributed to the CNS. Since atropine acts as a competitive pharmacological antagonist, its effect can be antagonized by ACh, which competes with it for muscarinic receptors. Physostigmine causes a buildup of endogenous ACh levels wherever it is released. Drugs to know: neostigmine, physostigmine, donepezil Cholinergic blocking agents: 1
2 Muscarinic antagonists: Block ACh action on muscarinic receptors at tissues receiving postganglionic parasympathetic nerves and postganglionic sympathetic nerves innervating sweat glands. Result: absence of effects normally associated with tonic (or increased) influence of ACh on these tissues. Drugs to know: atropine, scopolamine, benztropine or trihexyphenydil (used for CNS effect in Tx of Parkinson's disease), ipratropium or tiotropium (used chronically by some patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; i.e. COPD), glycopyrrolate (useful during surgery to decrease secretions), tolterodine (used chronically by some patients with incontinence due to overactive bladder ), diphenhydramine (used in OTC sleep-aid preparations, as antihistamine, to Tx motion sickness, and as an anti-emetic used to help treat cancer chemotherapy-induced vomiting). You might use scopolamine and/or glycopyrrolate acutely in surgery to supplement anesthesia (scopolamine) and to reduce flow of saliva. You might see patients who present with systemic blockade of muscarinic receptors because they are receiving scopolamine for motion sickness, benztropine or trihexyphenydil for Parkinson's disease or tolterodine for Tx of urinary incontinence. Although diphenhydramine is categorized as an antihistamine, it is a potent muscarinic antagonist also. Muscarinic antagonists cause xerostomia, which may account for poor dental health. These patients can be photophobic. Reflex bradycardia (which normally accompanies the effects of injected sympathomimetics that exert pressor effects, i.e. increased arterial pressure) will be blocked (because increased ACh release accounts for reflex bradycardia [ACh acts to cause reflex bradycardia by binding to cardiac M 2 receptors]; therefore, inadvertent injection of sympathomimetic agents is more likely to cause cardiac stimulation (provided that the sympathomimetic binds to beta receptors, e.g. epinephrine, norepinephrine) and exaggerated pressor effects. NMJ blocking agents: Blockade of ACh effect on skeletal muscle (to be covered in future lecture). Ganglionic Agents: Drugs to know: nicotine, varenicline, mecamylamine You might see patients taking mecamylamine (which blocks ganglionic transmission) as part of smoking cessation programs. These patients might exhibit photophobia, orthostatic hypotension and xerostomia. Baroreceptor-mediated changes in heart rate will be blocked. (see above: as with muscarinic blockers, because the efferent limb of the reflex arc involves ganglionic transmission). The ganglion-blocked patient will still respond to injected sympathomimetics. In fact, the effect of sympathomimetics will be accentuated in a patient who is taking a ganglionic blocking agent (because baroreceptor reflexes are blocked). You might see patients who are taking varenicline chronically for smoking cessation. Remember that this agent is a partial nicotine receptor agonist (remember from principles that a partial agonist can act as an antagonist). About the only troublesome peripheral effects of varenicline reported to date are nausea and constipation. Sympathomimetic Agents : 2
3 Prototype examples of sympathomimetic amines are: epinephrine - agonist at alpha 1, alpha 2, beta 1 and beta 2 receptors norepinephrine - agonist at alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta 1 receptors isoproterenol - agonist at beta 1 and beta 2 receptors dopamine - agonist at dopamine receptors (DA 1 and DA 2 ), beta 1 and alpha 1 receptors (higher doses) Listed below are prototype sympathomimetics (agonists) with the following information in order: adrenergic receptor subtype activated ; prototype agent ; major effects associated with their stimulation; major implications for dentistry Agents that act primarily via direct-action on adrenergic receptors alpha 1 : phenylephrine (Neosynephrine TM ), a selective agonist at alpha 1 receptors; vasoconstriction, dilation of pupil; employed as vasoconstrictor in local anesthetic solutions, safer for use in cardiac patients than agents with beta activity; powerful alpha agonists can be used for hemostasis, e.g. alpha activity of epinephrine. Is metabolized by MAO, not by COMT, therefore its use should be avoided in patients taking MAO inhibitors (because the vasoconstrictor effect could be potentiated). Patients may be using topical, over-the-counter preparations of this agent as a nasal decongestant. alpha 2 ; clonidine and alphamethyl norepinephrine (levonordefrin); action on receptors in vasomotor center (central nervous system) decreases sympathetic outflow from the vasomotor center to heart and vessels -> hypotension; CNS effect also causes sedation; action on presynaptic membrane of autonomic nerves -> reduced transmitter release; direct action on peripheral blood vessels --> vasoconstriction ; (note: the vasoconstrictor effect is what is exploited in the use of levonordefrin in local anesthetic solutions); patients taking oral clonidine or alpha methyldopa (precursor of the false transmitter alphamethyl norepinephrine) for high blood pressure may show a additive response to sedatives. Also, clonidine causes significant xerostomia. beta 1 ; dobutamine (cardiovascular effects are primarily due to action on beta 1 receptors) stimulation of cardiac tissues, increasing heart rate, conduction velocity and contractility; when using agents with beta 1 agonist activity, use extreme caution in cardiac patients. While this agent is unlikely to be used in the outpatient dentistry arena, you should be aware that agents with beta 1 agonist activity foster cardiac arrhythmias, particularly in the presence of hyperthyroidism, in patients taking digitalis and in the presence of some general anesthetics. beta 2 ; albuterol; relaxation of vascular, bronchiolar and uterine smooth muscle cells, breakdown of glycogen to glucose (if given systemically); For termination of acute attacks of asthma, beta 2 agonists afford the most rapid and efficacious treatment. An inhaler dosage form of this type of sympathomimetic should be available for such patients. Inhalation route of administration restricts the agent s effects primarily to the lung. salmeterol (beta 2 selective agonist); This slow-acting, long-acting compound is used for chronic treatment of asthma, not for termination of acute attacks. Side effects are minimal, may include tachycardia and tremor. 3
4 Multiple receptors, not a selective agonist ; dopamine ; vasodilation of kidney arterioles ; dopamine can be used to stimulate cardiac output (via its beta 1 activity) to support the circulation during surgery (while preserving renal blood flow). It will also cause vasoconstriction with higher doses. Use of vasoconstrictors with local anesthetics (LA): rationale- a) such use can reduce the total dose necessasry for the LA to exert its desired effect; LA are potentially toxic ; (vasoconstrictor delays systemic absorption of the LA from the site of injection, thus the local concentration of the LA is kept higher), b) prolongs duration of action of the LA epinephrine - is the most potent sympathomimetic vasoconstrictor, has substantial beta 1 agonist activity; dose should be reduced to 1/5-1/4 normal levels in patients with heart disease. Pressor effect is increased in the presence of non-selective beta receptor blockade (which prevents epi s beta 2 agonist effect, which normally causes vasodilation of skeletal muscle vessels). Also, note that in patients who may be treated systemically with a muscarinic receptor antagonist (e.g. tolterodine, for incontinence), the reflex bradycardia associated with blood pressure elevation will be blocked, thus exaggerating the pressor sympathomimetics. Indirectly acting agents: Act via release of NE from nerve ending stores; therefore their effects are those of norepinephrine; intact neuronal stores of NE are needed in order for these to act. Examples: amphetamine (note: can get into the CNS, unlike injected NE.); tyramine Sympatholytics: Agents acting as pharmacological antagonists: occupy postjunctional receptors, lack efficacy, compete with endogenous NE and EPI for adrenoceptors. Alpha adrenoceptor antagonists: examples: prazosin, tamsulosin - block effects of endogenous NE and EPI that are exerted via alpha receptors: i.e. alpha blockers will decrease arteriolar and venous constriction, decrease load on the heart by decreasing vascular resistance, may cause reflex tachycardia, decrease resistance to urinary outflow. - will block the alpha 1 -mediated vasoconstrictor effect of sympathomimetics included in local anesthetic solutions; can cause orthostatic hypotension. **Note that levonordefrin (alpha 2 agonist) will still be effective in patients treated with alpha 1 blockers. Beta adrenoceptor antagonists: examples: propranolol (non-selective block of beta receptors), metoprolol ("selective" beta 1 blockade), carvedilol (block of α 1 and β receptors) - block cardiac and metabolic effects of sympathomimetics with beta agonist activity, decrease blood pressure (after chronic use); decrease work load on the heart, non-selective beta blockers reduce beta 2 -mediated relaxation of smooth muscle and thus can aggravate asthma (due to loss of the effect of circulating epinephrine on beta 2 receptors on bronchioles) 4
5 - blockade of beta 2 receptors will cause exaggeration of the pressor effect of epinephrine that reaches the blood stream. Agents acting at the sympathetic nerve ending: Note*: These agents can be either sympatholytics or sympathomimetics (e.g. cocaine and, in certain circumstances, MAO inhibitors). guanethidine and bretylium - inhibit nerve action potential- induced release of NE sympatholytic effect; reserpine - inhibits storage of NE in the vesicle depletion of NE stores sympatholytic effect General effects of these agents: global, peripheral decrease/loss of SNS function. Caution: receptor responsiveness to injected sympathomimetics remains and is often enhanced. Reserpine will also have CNS effects (depressant). In tissues with both PNS and SNS innervation, events associated with PNS stimulation will be dominant. Since the SNS support of vasoconstriction is lost (dilating veins as well as arterioles) these agents cause orthostatic hypotension. Use caution with movement of patient from supine to upright position. cocaine - blocks Uptake I (re-uptake of NE into nerve ending) sympathomimetic effect MAO inhibitors (don t need to know individual drug names at this time) can cause decreased NE biosynthesis and formation of a low-efficacy "false transmitter", resulting in decreased sympathetic function, i.e. sympatholytic. Chronic treatment can cause Orthostatic hypotension. However, ingestion of tyramine-containing foods or injection of an indirectly acting sympathomimetic (causing sudden release of remaining, stored NE) can cause a dangerous elevation in blood pressure, i.e. a sympathomimetic effect Use of knowledge practice: Clinical correlation / Case / vignette The patient is a 59 yr. old male. He is being treated chronically with tamsulosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia and also with carvedilol as part of the overall treatment of congestive heart failure (CHF), the latter being complicated by ischemic heart disease (manifest by occasional attacks of angina). The dentist scheduled to treat this patient is concerned that the local anesthetic (LA) to be employed, if absorbed from the injection site, might depress cardiac contractility and/or alter cardiac rhythm in this patient. Pharmacologic implications / questions (assume that the doses of both tamsulosin and carvedilol are sufficient to provide effective plasma levels of these drugs at the time of the dental procedure): 1) What is a pharmacological approach that can be used to reduce/prevent systemic toxicity of the LA? 2) What type of drug is tamsulosin? Carvedilol? These agents bind to receptors? 5
6 3) What side effect(s) might be caused by these agents? What caution(s) must be considered? 4) Would epinephrine be likely to cause cardiac tachyarrhythmias in this patient? Will epinephrine be likely to cause an exaggerated pressor effect in this patient? 5) Considering your answer to question #1, what drug might be used to afford the desired effect? For discussion of the case, after you work on this, see separate file Clinical Case Ans 6
Key Points. Autonomic Nervous System Drugs. Autonomic effects Sympathetic. Drugs can modify ANS activity by: Autonomic Nervous System
 Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION.
 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
1. The potential sites of action for sympathomimetics and the difference between a direct and indirect acting agonist.
 1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system. Objectives. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) 12/23/2014
 Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system N231 Nursing Pharmacology Objectives Analyze the implementation of the nursing process in the promotion and maintenance of system stability for individuals
Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system N231 Nursing Pharmacology Objectives Analyze the implementation of the nursing process in the promotion and maintenance of system stability for individuals
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
Adrenergic agonists. R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka
 Adrenergic agonists R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka Outline Recall Introduction to adrenergic agonists Classification of adrenergic
Adrenergic agonists R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka Outline Recall Introduction to adrenergic agonists Classification of adrenergic
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Chapter 13. Sympathetic Nervous System. Basic Functions of the Nervous System. Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System
 Chapter 13 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Basic Functions of the Recognizing changes in Internal environment External environment Processing and integrating changes Reacting to changes Upper Saddle River,
Chapter 13 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Basic Functions of the Recognizing changes in Internal environment External environment Processing and integrating changes Reacting to changes Upper Saddle River,
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers
 Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
The somatic nervous system regulates conscious movements via efferent nerves exit from the CNS to skeletal muscles.
 Lecture 1 Nervous system The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (somatic and autonomic nervous systems; comprised of nerves
Lecture 1 Nervous system The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (somatic and autonomic nervous systems; comprised of nerves
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
PHARMACOLOGY OF VNS VARIANT 1 1) Anti-ChEs: contraindications and precautions. 2) Examples of Cholinesterase reactivators. 3) Cholinoblockers-natural
 VARIANT 1 Anti-ChEs: contraindications and precautions. Examples of Cholinesterase reactivators. Cholinoblockers-natural alkaloids (examples). 4) GIT-effects of Atropine. 5) Pharmacologic characteristic
VARIANT 1 Anti-ChEs: contraindications and precautions. Examples of Cholinesterase reactivators. Cholinoblockers-natural alkaloids (examples). 4) GIT-effects of Atropine. 5) Pharmacologic characteristic
ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Fight or flight response results in: 1. Increased BP 2. Increased blood flow to brain, heart and skeletal muscles
ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Fight or flight response results in: 1. Increased BP 2. Increased blood flow to brain, heart and skeletal muscles
Adrenergic agonists:-
 Adrenergic agonists:- A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream.
Adrenergic agonists:- A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream.
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture. Adrenergic Agents
 PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture Adrenergic Agents Introduction Introduction Adrenergic agents are a broad class of agents employed in the treatment of many disorders. They are those chemical agents that exert
PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture Adrenergic Agents Introduction Introduction Adrenergic agents are a broad class of agents employed in the treatment of many disorders. They are those chemical agents that exert
The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9
 Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2. 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany
 Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Autonomic Receptor Functions
 Part II Autonomic Receptor Functions Summary of ANS overview Pharmacological classification of ANS is based on neurotransmitters: cholinergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic. Major sites for pharmacological
Part II Autonomic Receptor Functions Summary of ANS overview Pharmacological classification of ANS is based on neurotransmitters: cholinergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic. Major sites for pharmacological
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Autonomic (ANS) Pharmacology. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Autonomic (ANS) Pharmacology Sympathetic Nervous System Autonomic and Somatic Innervation Skeletal muscle is innervated by somatic nerves, controlling voluntary actions All other innervated structures
Autonomic (ANS) Pharmacology Sympathetic Nervous System Autonomic and Somatic Innervation Skeletal muscle is innervated by somatic nerves, controlling voluntary actions All other innervated structures
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
Autonomic Nervous System
 MOST FREQUENTLY USED DRUG CATEGORIES FOR AUTONOMIC SYSTEM THERAPY Beta 1 Adrenergic Blockers (Anatgonists) - Work on the Heart Beta 1 Adrenergic receptors are typically found on the heart and is a means
MOST FREQUENTLY USED DRUG CATEGORIES FOR AUTONOMIC SYSTEM THERAPY Beta 1 Adrenergic Blockers (Anatgonists) - Work on the Heart Beta 1 Adrenergic receptors are typically found on the heart and is a means
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
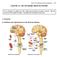 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Case 1: Anticholinesterase
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Dr. Carl Rosow, Dr. David Standaert and Prof. Gary Strichartz Case 1: Anticholinesterase February
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Dr. Carl Rosow, Dr. David Standaert and Prof. Gary Strichartz Case 1: Anticholinesterase February
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. 7-4. Given a group of statements, select the best definition of the term adrenergic (sympathomimetic) drug.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Adrenergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 7-1. Given a group of statements, select the mechanism(s) of action of drugs which stimulate
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Adrenergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 7-1. Given a group of statements, select the mechanism(s) of action of drugs which stimulate
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS
 Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Physiology and Pharmacology
 Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake So what? Vasoactivity
Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake So what? Vasoactivity
The Ideal Local Anesthetic. Pain and Anxiety. Percent Solution. Contents cont: Contents of a dental cartridge
 The Ideal Local Anesthetic Pain and Anxiety University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Ma Ann C. Sabino, DDS PhD Water soluble/stable in solution Non-irritating to nerve Low systemic
The Ideal Local Anesthetic Pain and Anxiety University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Ma Ann C. Sabino, DDS PhD Water soluble/stable in solution Non-irritating to nerve Low systemic
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Milwaukee School of Engineering Gerrits@msoe.edu. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
Pharm Cardiovascular Paragraph
 BEGIN DRUGS OF PARASYMPATHETIC SYSTEM Cholinomimetics Nicotinic Agonists Muscarinic Agonists Anticholinesterase Related Nictotine Succinylcholine Pilocarpine Bethanecol Reversible Irreversible 2 PAM Physostigmine
BEGIN DRUGS OF PARASYMPATHETIC SYSTEM Cholinomimetics Nicotinic Agonists Muscarinic Agonists Anticholinesterase Related Nictotine Succinylcholine Pilocarpine Bethanecol Reversible Irreversible 2 PAM Physostigmine
Pharmacology Drug Chart
 Pharmacology Drug Chart Cholinergic Agonists Acetylcholine Muscarinic HR, CO and BP Salivary Secretions Secretions and Motility in the GIT Bronchiolar Secretions Miosis (Constriction of the Pupil) Pharmacology
Pharmacology Drug Chart Cholinergic Agonists Acetylcholine Muscarinic HR, CO and BP Salivary Secretions Secretions and Motility in the GIT Bronchiolar Secretions Miosis (Constriction of the Pupil) Pharmacology
Vasopressors. Judith Hellman, M.D. Associate Professor Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco
 Vasopressors Judith Hellman, M.D. Associate Professor Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco Overview Define shock states Review drugs commonly used to treat hypotension
Vasopressors Judith Hellman, M.D. Associate Professor Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of California, San Francisco Overview Define shock states Review drugs commonly used to treat hypotension
Dr. RAJENDRAN S INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL EDUCATION
 Page 1 of 7 Dr. RAJENDRAN S INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL EDUCATION AIIMS NOVEMBER 2012 - QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS PHYSIOLOGY This contains only 3 out of 7 questions. For complete questions with explanatory answers,
Page 1 of 7 Dr. RAJENDRAN S INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL EDUCATION AIIMS NOVEMBER 2012 - QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS PHYSIOLOGY This contains only 3 out of 7 questions. For complete questions with explanatory answers,
Anti-Parkinsonism Drugs
 Anti-Parkinsonism Drugs Pharma Team 429 Fahad Alrumaih Ibrahim Alshiddi Sultan Alsalem Ismail Raslan Suhail Asiri Parkinsonism - Could be: primary [idiopathic] or secondary [viral infection or drug induced
Anti-Parkinsonism Drugs Pharma Team 429 Fahad Alrumaih Ibrahim Alshiddi Sultan Alsalem Ismail Raslan Suhail Asiri Parkinsonism - Could be: primary [idiopathic] or secondary [viral infection or drug induced
The Autonomic Nervous System Part II - Basic Pharmacology
 Dr Oliver Pratt, Specialist Registrar Dr Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Hope Hospital, Salford M6 8HD, UK. e mail: carl.gwinnutt@srht.nhs.uk Tutorial Of The Week The Autonomic Nervous
Dr Oliver Pratt, Specialist Registrar Dr Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Hope Hospital, Salford M6 8HD, UK. e mail: carl.gwinnutt@srht.nhs.uk Tutorial Of The Week The Autonomic Nervous
Adrenomimetic Drugs. Tony J.-F. Lee and Robert E. Stitzel MECHANISM OF ACTION CHEMISTRY
 10 Adrenomimetic Drugs Tony J.-F. Lee and Robert E. Stitzel DRUG LIST GENERIC NAME AGE GENERIC NAME AGE Albuterol 105 Amphetamine 106 Dobutamine 105 Dopamine 103 Ephedrine 105 Epinephrine 101 Isoproterenol
10 Adrenomimetic Drugs Tony J.-F. Lee and Robert E. Stitzel DRUG LIST GENERIC NAME AGE GENERIC NAME AGE Albuterol 105 Amphetamine 106 Dobutamine 105 Dopamine 103 Ephedrine 105 Epinephrine 101 Isoproterenol
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to. women, and is a serious condition that can lead to. significant lifestyle changes.
 Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Chapter 28. Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Chapter 28 Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease 1. Introduction Parkinsonism Tremors hands and head develop involuntary movements when at rest; pin rolling sign (finger and thumb) Muscle rigidity arthritis
Chapter 28 Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease 1. Introduction Parkinsonism Tremors hands and head develop involuntary movements when at rest; pin rolling sign (finger and thumb) Muscle rigidity arthritis
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com
 Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com Special thanks to the number #1 internet training site id44.com and also to (NOTE) Please remember
Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com Special thanks to the number #1 internet training site id44.com and also to (NOTE) Please remember
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Adrenergic receptors: Anatomy, physiology, and pharmacological interactions
 Adrenergic receptors: Anatomy, physiology, and pharmacological interactions SANDRA M. MAREE, BS, CRNA Winston-Salem, North Carolina The author presents a review of the peripheral autonomic nervous system
Adrenergic receptors: Anatomy, physiology, and pharmacological interactions SANDRA M. MAREE, BS, CRNA Winston-Salem, North Carolina The author presents a review of the peripheral autonomic nervous system
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Influence of ph Most local anesthetics are weak bases.
 Local anesthetics The agent must depress nerve conduction. The agent must have both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties to be effective by parenteral injection. Structure-activity relationships The typical
Local anesthetics The agent must depress nerve conduction. The agent must have both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties to be effective by parenteral injection. Structure-activity relationships The typical
Autonomic Nervous System Drugs
 adistockshutterstock, Inc. CHAPTER 5 Autonomic Nervous System Drugs William Mark Enlow Sue Greenfield Cliff Roberson KEY TERMS Acetylcholine Acetylcholinesterase Adrenal medulla Adrenergic agonists Adrenergic
adistockshutterstock, Inc. CHAPTER 5 Autonomic Nervous System Drugs William Mark Enlow Sue Greenfield Cliff Roberson KEY TERMS Acetylcholine Acetylcholinesterase Adrenal medulla Adrenergic agonists Adrenergic
Pharmacology 260 Online Course Schedule Spring 2012
 Pharmacology 260 Online Course Spring 2012 The topics listed below do not necessarily correspond to a 1 - hour lecture period. You should cover the topics for each week at some time during that week. Readings
Pharmacology 260 Online Course Spring 2012 The topics listed below do not necessarily correspond to a 1 - hour lecture period. You should cover the topics for each week at some time during that week. Readings
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 ADRENALINE (EPINEPHRINE) ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 226 6 TH JUNE 2011 Prof. John Kinnear Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, UK Correspondence to John.Kinnear@southend.nhs.uk QUESTIONS
ADRENALINE (EPINEPHRINE) ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 226 6 TH JUNE 2011 Prof. John Kinnear Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, UK Correspondence to John.Kinnear@southend.nhs.uk QUESTIONS
DIVISION OF HUMAN NUTRITION
 DIVISION OF HUMAN NUTRITION Example EXAM 2011 - HNE-23306 Nutrition & Pharmacology Date : Place : Explanation : This exam consists of: **** open problems on pharmacokinetics (normally 2-3) *****series
DIVISION OF HUMAN NUTRITION Example EXAM 2011 - HNE-23306 Nutrition & Pharmacology Date : Place : Explanation : This exam consists of: **** open problems on pharmacokinetics (normally 2-3) *****series
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
DIVISION OF HUMAN NUTRITION
 DIVISION OF HUMAN NUTRITION Example EXAM 2013 - HNE-23306 Nutrition & Pharmacology Date : Place : Explanation : This exam consists of: **** open problems on pharmacokinetics (normally 2-3) *****series
DIVISION OF HUMAN NUTRITION Example EXAM 2013 - HNE-23306 Nutrition & Pharmacology Date : Place : Explanation : This exam consists of: **** open problems on pharmacokinetics (normally 2-3) *****series
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 INTRODUCTION TO CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 125 16 TH MARCH 2009 Toby Elkington, Specialist Registrar Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Salford Royal NHS
INTRODUCTION TO CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 125 16 TH MARCH 2009 Toby Elkington, Specialist Registrar Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Salford Royal NHS
Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection Each 1mL contains Glycopyrrolate USP 0.5mg (Glycopyrronium Bromide) and Neostigmine Metilsulfate
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection Each 1mL contains Glycopyrrolate USP 0.5mg (Glycopyrronium Bromide) and Neostigmine Metilsulfate
The Neuron and the Synapse. The Neuron. Parts of the Neuron. Functions of the neuron:
 The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Adrenoceptor -activating & other sympathomimetic drugs
 Adrenoceptor -activating & other sympathomimetic drugs Three Neurotransmitters of Sympathetic Nervous System NE, E, DA Adrenoceptor agonists Sympathomimetics : Directly acting Indirectly acting Mixed action
Adrenoceptor -activating & other sympathomimetic drugs Three Neurotransmitters of Sympathetic Nervous System NE, E, DA Adrenoceptor agonists Sympathomimetics : Directly acting Indirectly acting Mixed action
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and asthma
 Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ADRENALIN* Adrenalin* Chloride Solution (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P) 1:1000 (1 mg/ml)
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ADRENALIN* Adrenalin* Chloride Solution (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P) 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Adrenalin* Chloride Injection (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P.) 1:1000, 30
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ADRENALIN* Adrenalin* Chloride Solution (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P) 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Adrenalin* Chloride Injection (Epinephrine Injection U.S.P.) 1:1000, 30
RESPIRATORY VENTILATION Page 1
 Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Norepinephrine Effects On the System
 Norepinephrine Effects On the System NE Conversion to Epinephrine in the Circulation Under stress, the increased norepinephrine produced is transmitted throughout the system. This increased level represents
Norepinephrine Effects On the System NE Conversion to Epinephrine in the Circulation Under stress, the increased norepinephrine produced is transmitted throughout the system. This increased level represents
3. Tunica adventitia is the outermost layer; it is composed of loosely woven connective tissue infiltrated by nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics
 Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP Summary of Product Characteristics
 Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP Summary of Product Characteristics 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP Summary of Product Characteristics 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications. Dr William Dooley
 Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications Dr William Dooley Plan Heart Failure Acute vs. chronic Mx Hypertension Common drugs used Method of action Choice of medications Heart Failure Aims; Short term:
Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications Dr William Dooley Plan Heart Failure Acute vs. chronic Mx Hypertension Common drugs used Method of action Choice of medications Heart Failure Aims; Short term:
The h0rmones of adrenal medulla. University of Debrecen, Department of Physiology
 The h0rmones of adrenal medulla University of Debrecen, Department of Physiology Introduction Adrenal gland (6-10 g) Cortex (5-9 g) Medulla ( 1 g) Chromaffin cells alarm (Selye 1936) flight or fight (Cannon
The h0rmones of adrenal medulla University of Debrecen, Department of Physiology Introduction Adrenal gland (6-10 g) Cortex (5-9 g) Medulla ( 1 g) Chromaffin cells alarm (Selye 1936) flight or fight (Cannon
EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use.
 EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use. R x only DESCRIPTION Epinephrine Injection, USP 1:1000 is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. Each ml contains epinephrine
EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use. R x only DESCRIPTION Epinephrine Injection, USP 1:1000 is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. Each ml contains epinephrine
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
CHAPTER 5 DISCUSSION
 CHAPTER 5 DISCUSSION The present study demonstrated that isolated atria and tracheas from guinea-pigs received chronic pretreatment with cocaine for 14 days, developed supersensitivity to both epinephrine
CHAPTER 5 DISCUSSION The present study demonstrated that isolated atria and tracheas from guinea-pigs received chronic pretreatment with cocaine for 14 days, developed supersensitivity to both epinephrine
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Epinephrine Administration by the EMT
 Epinephrine Administration by the EMT Pilot Project for the Administration of Epinephrine by Washington EMTs Tamara Coulter BS, FF/PM and Captain/MSO Steven Engle North Kitsap Fire & Rescue Objectives
Epinephrine Administration by the EMT Pilot Project for the Administration of Epinephrine by Washington EMTs Tamara Coulter BS, FF/PM and Captain/MSO Steven Engle North Kitsap Fire & Rescue Objectives
Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction When there is an overwhelming threat to the
Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction When there is an overwhelming threat to the
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
1 What Anapen is and what it is used for?
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Anapen 500 micrograms in 0.3 ml solution for injection (pre-filled syringe) Adrenaline (Epinephrine) Auto-Injector Read all of this leaflet carefully before you
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Anapen 500 micrograms in 0.3 ml solution for injection (pre-filled syringe) Adrenaline (Epinephrine) Auto-Injector Read all of this leaflet carefully before you
How To Understand The Effects Of Drugs On The Brain
 DRUGS AND THE BRAIN Most of the psychological and behavioural effects of psychoactive drugs is due the interaction they have with the nerve cells in the CNS (which includes the brain and peripheral nervous
DRUGS AND THE BRAIN Most of the psychological and behavioural effects of psychoactive drugs is due the interaction they have with the nerve cells in the CNS (which includes the brain and peripheral nervous
DIPHENHYDRAMINE (Benadryl)
 DIPHENHYDRAMINE (Benadryl) Classification: Antihistamine (H1 blocker) Antihistamine; appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells. Therapeutic Relieves effects of histamine
DIPHENHYDRAMINE (Benadryl) Classification: Antihistamine (H1 blocker) Antihistamine; appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells. Therapeutic Relieves effects of histamine
Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD. daniel.dunham@clemc.us
 Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD daniel.dunham@clemc.us Asthma/COPD Narrowing of airways (an H4 histamine response causing inflammation and mucous production), leading to wheezing on inspiration and exhalation.
Protocol in depth Asthma/COPD daniel.dunham@clemc.us Asthma/COPD Narrowing of airways (an H4 histamine response causing inflammation and mucous production), leading to wheezing on inspiration and exhalation.
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER
 Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
BLOCKADE OF THE BIOCHEMICAL CORRELATES OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION IN UTERINE AND INTESTINAL SMOOTH MUSCLE*
 BLOCKADE OF THE BOCHEMCAL CORRELATES OF CONTRACTON AND RELAXATON N UTERNE AND NTESTNAL SMOOTH MUSCLE* Theodore M. Brodyt and Jack Diamond$ Department of Pharmacology, University of Michigan Medical School,
BLOCKADE OF THE BOCHEMCAL CORRELATES OF CONTRACTON AND RELAXATON N UTERNE AND NTESTNAL SMOOTH MUSCLE* Theodore M. Brodyt and Jack Diamond$ Department of Pharmacology, University of Michigan Medical School,
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION. Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology
 PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
Women suffer in silence
 Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Autonomic Pharmacology. Reading: Chapters 6-10 in Katzung are quite good; those in Goodman and Gilman are based on the same fundamental outline.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Dr. Carl Rosow HST-151 1 Autonomic Pharmacology Reading: Chapters 6-10 in Katzung are quite good;
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Dr. Carl Rosow HST-151 1 Autonomic Pharmacology Reading: Chapters 6-10 in Katzung are quite good;
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Hormones & Chemical Signaling
 Hormones & Chemical Signaling Part 2 modulation of signal pathways and hormone classification & function How are these pathways controlled? Receptors are proteins! Subject to Specificity of binding Competition
Hormones & Chemical Signaling Part 2 modulation of signal pathways and hormone classification & function How are these pathways controlled? Receptors are proteins! Subject to Specificity of binding Competition
Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
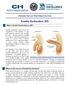 Information from your Patient Aligned Care Team What is Erectile Dysfunction or ED? Erectile dysfunction (also known as impotence) is the inability to get and keep an erection firm enough for sex. Having
Information from your Patient Aligned Care Team What is Erectile Dysfunction or ED? Erectile dysfunction (also known as impotence) is the inability to get and keep an erection firm enough for sex. Having
The Autonomic Nervous System
 Introduction (pp. 526 528) Comparison of the Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems (pp. 526 527) ANS Divisions (pp. 527 528) ANS Anatomy (pp. 528 535) Parasympathetic (Craniosacral) Division (pp. 529 530)
Introduction (pp. 526 528) Comparison of the Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems (pp. 526 527) ANS Divisions (pp. 527 528) ANS Anatomy (pp. 528 535) Parasympathetic (Craniosacral) Division (pp. 529 530)
Drug Excretion. Renal Drug Clearance. Drug Clearance and Half-Life. Glomerular Filtration II. Glomerular Filtration I. Drug Excretion and Clearance
 t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
Chapter 4. The Adrenal Medulla
 Chapter 4 The Adrenal Medulla Introduction Induction of cortisol production requires several minutes, and full elaboration of cortisol action requires several hours. In contrast, the adrenal medullary
Chapter 4 The Adrenal Medulla Introduction Induction of cortisol production requires several minutes, and full elaboration of cortisol action requires several hours. In contrast, the adrenal medullary
Levophed Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP
 Levophed Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP R x only DESCRIPTION Norepinephrine (sometimes referred to as l-arterenol/levarterenol or l-norepinephrine) is a sympathomimetic amine which differs from
Levophed Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP R x only DESCRIPTION Norepinephrine (sometimes referred to as l-arterenol/levarterenol or l-norepinephrine) is a sympathomimetic amine which differs from
