0 0 Q(t) No change 0 0 Q(t) No change Reset Reset Set Set 1 1 Qt () Complement 1 1? Undefined
|
|
|
- Jack Rogers
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T-68 Flip-Flop haracteristic Table (a) JK Flip-Flop (b) Flip-Flop J K (t ) Operation (t ) Operation (t) No change (t) No change eset eset et et t () omplement? Undefined (c) Flip-Flop (d) T Flip-Flop (t ) Operation T (t ) Operation eset (t) No change et t () omplement 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
2 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458 T-69 Present tate Input Next tate Output B B Y tate Table for ircuit of Figure 4-8
3 T-7 Two-dimensional tate Table for the ircuit in Figure 4-8 Present state Next state Output = -= = -= B B B Y Y 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
4 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458 T-7 Present state Input Next state Flip-flop inputs B B J K J B K B tate Table for ircuit with JK Flip-Flops
5 T-72 tate Table for tate iagram in Figure 4-2 Present tate Next tate Output Z B B B 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
6 T-73 tate Table for tate iagram in Table 4-5 Next tate Output Z Present tate 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
7 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458 T-74 Present tate Input Next tate Output B B Y tate Table for esign Example
8 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458 T-75 Present tate Input Next tate B B tate Table for econd esign Example
9 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458 T-76 (a) JK Flip-Flop (b) Flip-Flop (t) (t ) J K (t) (t ) (c) Flip-Flop (d) T Flip-Flop (t) (t ) (t) (t ) T Flip-Flop Excitation Table
10 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458 T-77 Present tate Input Next tate Flip-Flop Inputs B B J K J B K B tate Table with JK Flip-Flop Inputs
11 T-78 Block iagram of a equential ircuit Inputs Outputs ombinational circuit Next state torage elements Present state 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
12 T-79 Logic tructures for toring Information (a) t pd (b) t pd 2 t pd (d) 2 t pd t pd (c) 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
13 T-8 ynchronous locked equential ircuit Inputs ombinational circuit lock pulses Flip-flops Outputs (a) Block diagram (b) Timing diagram of clock pulses 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
14 T-8 Ltch with NO Gates (eset) et state (et) eset state Undefined (a) Logic diagram (b) Function table 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
15 T-82 Logic imulation of Latch Behavior i g i t a l T 5n n 5n Time (econds) 2n 25n 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
16 T-83 Latch with NN Gates (et) et state (eset) eset state Undefined (a) Logic diagram (b) Function table 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
17 T-84 Latch with ontrol Inputs Next state of No change No change = ; eset state = ; et state Undefined (a) Logic diagram (b) Function table 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
18 T-85 Latch (a) Logic diagram Next state of No change = ; eset state = ; et state (b) Function table 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
19 T-86 Latch with Transmission Gates TG TG 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
20 T-87 Mster-lave Flip-Flop Y Y 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
21 T-88 Logic imulation of a Master-lave Flip-Flop i g i t a l Y T 5n n 5n Time (econds) 2n 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
22 T-89 Master-lave JK Flip-Flop J K (a) J K (b) Next tate of 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
23 T-9 -Type Positive Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
24 T-9 Positive Edge-Triggered JK Flip-Flop J K 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
25 T-92 tandard Graphic ymbols for Latch and Flip-Flops with ontrol with ontrol (a) Latches J K J K Triggered Triggered Triggered JK Triggered JK (b) Master-lave Flip-Flops J K J K Triggered Triggered Triggered JK Triggered JK (c) Edge-Triggered Flip-Flops 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
26 T-93 JK Flip-Flop with irect et and eset J K J K Undefined No change omplement (a) Graphic symbols (b) Function table 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
27 T-94 Implementing Input Equations B Y J K lock 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
28 T-95 Example of a equential ircuit B B lock Y 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
29 T-96 Logic iagram and tate Table for = Y Z Y (a) lock Present state Inputs Y Next state (b) tate table Output Z 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
30 T-97 tate iagrams / / / / / /, / / (a), / / (b),, 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
31 T-98 onstruction of a tate iagram / B / B / (a) (b) / B / / / (c) / / / B / / / / (d) / 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
32 T-99 tate iagram for esign Example / / / / / / / / 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany MNO & KIME Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
33 T- Logic iagram for equential ircuit with Flip-Flops B B lock Y 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
34 T- Logic iagram for equential ircuit with JK Flip-Flops Y N Z N O T N Z J J K F F E K N Z K N L K NZ J J K F F E K K N B B 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany MNO & KIME Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
35 T-2 Logic imulation Verification for the ircuit in Figure 4-27 : : : * B: * Y: * * These responses are as asynchronous with the clock and thus do not wait for the next positive clock edge. (a) ircuit test and expected results LK i g i t a l * * * B Y T 5n n 5n Time (econds) 2n 25n 3n (b) imulation results 997 by Prentice-Hall, Inc. LOGI N OMPUTE EIGN FUNMENTL imon & chuster / Viacom ompany Mano & Kime Upper addle iver, New Jersey 7458
7. Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 7 Latches and Flip-Flops Page 1 of 18 7. Latches and Flip-Flops Latches and flip-flops are the basic elements for storing information. One latch or flip-flop can store one bit of information. The
Chapter 7 Latches and Flip-Flops Page 1 of 18 7. Latches and Flip-Flops Latches and flip-flops are the basic elements for storing information. One latch or flip-flop can store one bit of information. The
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits
 Engr354: igital Circuits Chapter 7 Sequential Elements r. Curtis Nelson Sequential Elements In this chapter you will learn about: circuits that can store information; Basic cells, latches, and flip-flops;
Engr354: igital Circuits Chapter 7 Sequential Elements r. Curtis Nelson Sequential Elements In this chapter you will learn about: circuits that can store information; Basic cells, latches, and flip-flops;
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 CE4: Components and esign Techniques for igital ystems Tajana imunic osing ources: Where we are now What we ve covered so far (Chap -5, App. A& B) Number representations Boolean algebra OP and PO Logic
CE4: Components and esign Techniques for igital ystems Tajana imunic osing ources: Where we are now What we ve covered so far (Chap -5, App. A& B) Number representations Boolean algebra OP and PO Logic
ECE380 Digital Logic
 ECE38 igital Logic Flip-Flops, Registers and Counters: Flip-Flops r.. J. Jackson Lecture 25- Flip-flops The gated latch circuits presented are level sensitive and can change states more than once during
ECE38 igital Logic Flip-Flops, Registers and Counters: Flip-Flops r.. J. Jackson Lecture 25- Flip-flops The gated latch circuits presented are level sensitive and can change states more than once during
Set-Reset (SR) Latch
 et-eset () Latch Asynchronous Level sensitive cross-coupled Nor gates active high inputs (only one can be active) + + Function 0 0 0 1 0 1 eset 1 0 1 0 et 1 1 0-? 0-? Indeterminate cross-coupled Nand gates
et-eset () Latch Asynchronous Level sensitive cross-coupled Nor gates active high inputs (only one can be active) + + Function 0 0 0 1 0 1 eset 1 0 1 0 et 1 1 0-? 0-? Indeterminate cross-coupled Nand gates
CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS
 CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Set-Reset Latch 11.3 Gated D Latch 11.4 Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop 11.5 S-R Flip-Flop
CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Set-Reset Latch 11.3 Gated D Latch 11.4 Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop 11.5 S-R Flip-Flop
Theory of Logic Circuits. Laboratory manual. Exercise 3
 Zakład Mikroinformatyki i Teorii Automatów yfrowych Theory of Logic ircuits Laboratory manual Exercise 3 Bistable devices 2008 Krzysztof yran, Piotr zekalski (edt.) 1. lassification of bistable devices
Zakład Mikroinformatyki i Teorii Automatów yfrowych Theory of Logic ircuits Laboratory manual Exercise 3 Bistable devices 2008 Krzysztof yran, Piotr zekalski (edt.) 1. lassification of bistable devices
So far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs.
 equential Logic o far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs. In sequential logic the output of the
equential Logic o far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs. In sequential logic the output of the
Lecture 10 Sequential Circuit Design Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 2010
 EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis Lecture 10 Sequential Circuit esign Zhuo Feng 10.1 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis 2010 Sequencing Outline Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay
EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis Lecture 10 Sequential Circuit esign Zhuo Feng 10.1 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS igital IC esign & Analysis 2010 Sequencing Outline Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems
 Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7. Basic Latch 7.2 Gated SR Latch 7.2. Gated SR
Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7. Basic Latch 7.2 Gated SR Latch 7.2. Gated SR
To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC.
 8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
Sequential Logic. (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements )
 Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Experiment # 9. Clock generator circuits & Counters. Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa
 Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
WEEK 8.1 Registers and Counters. ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1
 WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
Master/Slave Flip Flops
 Master/Slave Flip Flops Page 1 A Master/Slave Flip Flop ( Type) Gated latch(master) Gated latch (slave) 1 Gate Gate GATE Either: The master is loading (the master in on) or The slave is loading (the slave
Master/Slave Flip Flops Page 1 A Master/Slave Flip Flop ( Type) Gated latch(master) Gated latch (slave) 1 Gate Gate GATE Either: The master is loading (the master in on) or The slave is loading (the slave
Memory Elements. Combinational logic cannot remember
 Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Prof. Randy Katz (Unified
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Prof. Randy Katz (Unified
Lecture 10: Sequential Circuits
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Lecture 10: Sequential Circuits avid Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Outline q Sequencing q Sequencing Element esign q Max and Min-elay q Clock Skew q Time Borrowing
Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Lecture 10: Sequential Circuits avid Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Outline q Sequencing q Sequencing Element esign q Max and Min-elay q Clock Skew q Time Borrowing
Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit Design
 Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit esign Outline Sequencing Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay Clock Skew Time Borrowing Two-Phase Clocking 2 Sequencing Combinational logic output depends on current
Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit esign Outline Sequencing Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay Clock Skew Time Borrowing Two-Phase Clocking 2 Sequencing Combinational logic output depends on current
Sequential Circuits. Combinational Circuits Outputs depend on the current inputs
 Principles of VLSI esign Sequential Circuits Sequential Circuits Combinational Circuits Outputs depend on the current inputs Sequential Circuits Outputs depend on current and previous inputs Requires separating
Principles of VLSI esign Sequential Circuits Sequential Circuits Combinational Circuits Outputs depend on the current inputs Sequential Circuits Outputs depend on current and previous inputs Requires separating
Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop.
 Objectives Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop. describe how such a flip-flop can be SET and RESET. describe the disadvantage
Objectives Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop. describe how such a flip-flop can be SET and RESET. describe the disadvantage
Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops
 Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops 1. Overview of a Synchronous Sequential Circuit We saw from last lesson that the level sensitive latches could cause instability in a sequential system. This instability
Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops 1. Overview of a Synchronous Sequential Circuit We saw from last lesson that the level sensitive latches could cause instability in a sequential system. This instability
CDA 3200 Digital Systems. Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012
 CDA 3200 Digital Systems Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012 Outline SR Latch D Latch Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop (FF) S-R Flip-Flop (FF) J-K Flip-Flop (FF) T Flip-Flop
CDA 3200 Digital Systems Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012 Outline SR Latch D Latch Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop (FF) S-R Flip-Flop (FF) J-K Flip-Flop (FF) T Flip-Flop
Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain
 Chapter 3 Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain Counters & Shift Registers Counters, Syllabus Design of Modulo-N ripple counter, Up-Down counter, design of synchronous counters with and without
Chapter 3 Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain Counters & Shift Registers Counters, Syllabus Design of Modulo-N ripple counter, Up-Down counter, design of synchronous counters with and without
DIGITAL COUNTERS. Q B Q A = 00 initially. Q B Q A = 01 after the first clock pulse.
 DIGITAL COUNTERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/digital_counters.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Counter is a sequential circuit. A digital circuit which is used for a counting
DIGITAL COUNTERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/digital_counters.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Counter is a sequential circuit. A digital circuit which is used for a counting
CHAPTER IX REGISTER BLOCKS COUNTERS, SHIFT, AND ROTATE REGISTERS
 CHAPTER IX-1 CHAPTER IX CHAPTER IX COUNTERS, SHIFT, AN ROTATE REGISTERS REA PAGES 249-275 FROM MANO AN KIME CHAPTER IX-2 INTROUCTION -INTROUCTION Like combinational building blocks, we can also develop
CHAPTER IX-1 CHAPTER IX CHAPTER IX COUNTERS, SHIFT, AN ROTATE REGISTERS REA PAGES 249-275 FROM MANO AN KIME CHAPTER IX-2 INTROUCTION -INTROUCTION Like combinational building blocks, we can also develop
Design Example: Counters. Design Example: Counters. 3-Bit Binary Counter. 3-Bit Binary Counter. Other useful counters:
 Design Eample: ers er: a sequential circuit that repeats a specified sequence of output upon clock pulses. A,B,C,, Z. G, O, T, E, R, P, S,!.,,,,,,,7. 7,,,,,,,.,,,,,,,,,,,. Binary counter: follows the binary
Design Eample: ers er: a sequential circuit that repeats a specified sequence of output upon clock pulses. A,B,C,, Z. G, O, T, E, R, P, S,!.,,,,,,,7. 7,,,,,,,.,,,,,,,,,,,. Binary counter: follows the binary
Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor
 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number Page number 349 black chapter 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor 7. Ng f3, h7 h6 349 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number 2 Page number
June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number Page number 349 black chapter 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor 7. Ng f3, h7 h6 349 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number 2 Page number
Sequential Logic: Clocks, Registers, etc.
 ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design
 Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers
 ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
Lecture-3 MEMORY: Development of Memory:
 Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS. Block diagram. Flip Flop. S-R Flip Flop. Block Diagram. Circuit Diagram
 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/sequential_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com The combinational circuit does not use any memory. Hence the previous
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/sequential_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com The combinational circuit does not use any memory. Hence the previous
Memory unit. 2 k words. n bits per word
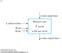 9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
NAND and NOR Implementation
 University of Wisconsin - Madison EE/omp ci 352 Digital ystems Fundamentals harles R. Kime ection 2 Fall 200 hapter 2 ombinational Logic ircuits Part 7 harles Kime & Thomas Kaminski NND and NOR Implementation
University of Wisconsin - Madison EE/omp ci 352 Digital ystems Fundamentals harles R. Kime ection 2 Fall 200 hapter 2 ombinational Logic ircuits Part 7 harles Kime & Thomas Kaminski NND and NOR Implementation
Counters. Present State Next State A B A B 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
 ounter ounters ounters are a specific type of sequential circuit. Like registers, the state, or the flip-flop values themselves, serves as the output. The output value increases by one on each clock cycle.
ounter ounters ounters are a specific type of sequential circuit. Like registers, the state, or the flip-flop values themselves, serves as the output. The output value increases by one on each clock cycle.
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops
 Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Module 3: Floyd, Digital Fundamental
 Module 3: Lecturer : Yongsheng Gao Room : Tech - 3.25 Email : yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au Structure : 6 lectures 1 Tutorial Assessment: 1 Laboratory (5%) 1 Test (20%) Textbook : Floyd, Digital Fundamental
Module 3: Lecturer : Yongsheng Gao Room : Tech - 3.25 Email : yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au Structure : 6 lectures 1 Tutorial Assessment: 1 Laboratory (5%) 1 Test (20%) Textbook : Floyd, Digital Fundamental
Asynchronous counters, except for the first block, work independently from a system clock.
 Counters Some digital circuits are designed for the purpose of counting and this is when counters become useful. Counters are made with flip-flops, they can be asynchronous or synchronous and they can
Counters Some digital circuits are designed for the purpose of counting and this is when counters become useful. Counters are made with flip-flops, they can be asynchronous or synchronous and they can
Digital Fundamentals. Lab 8 Asynchronous Counter Applications
 Richland College Engineering Technology Rev. 0 B. Donham Rev. 1 (7/2003). Horne Rev. 2 (1/2008). Bradbury Digital Fundamentals CETT 1425 Lab 8 Asynchronous Counter Applications Name: Date: Objectives:
Richland College Engineering Technology Rev. 0 B. Donham Rev. 1 (7/2003). Horne Rev. 2 (1/2008). Bradbury Digital Fundamentals CETT 1425 Lab 8 Asynchronous Counter Applications Name: Date: Objectives:
NOTE: The Flatpak version has the same pinouts (Connection Diagram) as the Dual In-Line Package.
 QUA FLIP-FLOP SN54/LS75 The LSTTL /SI SN54 /LS75 is a high speed Quad Flip-Flop. The device is useful for general flip-flop requirements where clock and clear inputs are common. The information on the
QUA FLIP-FLOP SN54/LS75 The LSTTL /SI SN54 /LS75 is a high speed Quad Flip-Flop. The device is useful for general flip-flop requirements where clock and clear inputs are common. The information on the
IE1204 Digital Design F12: Asynchronous Sequential Circuits (Part 1)
 IE1204 Digital Design F12: Asynchronous Sequential Circuits (Part 1) Elena Dubrova KTH / ICT / ES dubrova@kth.se BV pp. 584-640 This lecture IE1204 Digital Design, HT14 2 Asynchronous Sequential Machines
IE1204 Digital Design F12: Asynchronous Sequential Circuits (Part 1) Elena Dubrova KTH / ICT / ES dubrova@kth.se BV pp. 584-640 This lecture IE1204 Digital Design, HT14 2 Asynchronous Sequential Machines
Combinational Logic Design Process
 Combinational Logic Design Process Create truth table from specification Generate K-maps & obtain logic equations Draw logic diagram (sharing common gates) Simulate circuit for design verification Debug
Combinational Logic Design Process Create truth table from specification Generate K-maps & obtain logic equations Draw logic diagram (sharing common gates) Simulate circuit for design verification Debug
Chapter 5. Sequential Logic
 Chapter 5 Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits (/2) Combinational circuits: a. contain no memory elements b. the outputs depends on the current inputs Sequential circuits: a feedback path outputs depends
Chapter 5 Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits (/2) Combinational circuits: a. contain no memory elements b. the outputs depends on the current inputs Sequential circuits: a feedback path outputs depends
Counters and Decoders
 Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
Digital Fundamentals
 igital Fundamentals with PL Programming Floyd Chapter 9 Floyd, igital Fundamentals, 10 th ed, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Summary Latches (biestables) A latch is a temporary storage
igital Fundamentals with PL Programming Floyd Chapter 9 Floyd, igital Fundamentals, 10 th ed, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Summary Latches (biestables) A latch is a temporary storage
Upon completion of unit 1.1, students will be able to
 Upon completion of unit 1.1, students will be able to 1. Demonstrate safety of the individual, class, and overall environment of the classroom/laboratory, and understand that electricity, even at the nominal
Upon completion of unit 1.1, students will be able to 1. Demonstrate safety of the individual, class, and overall environment of the classroom/laboratory, and understand that electricity, even at the nominal
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
ENEE 244 (01**). Spring 2006. Homework 5. Due back in class on Friday, April 28.
 ENEE 244 (01**). Spring 2006 Homework 5 Due back in class on Friday, April 28. 1. Fill up the function table (truth table) for the following latch. How is this latch related to those described in the lectures
ENEE 244 (01**). Spring 2006 Homework 5 Due back in class on Friday, April 28. 1. Fill up the function table (truth table) for the following latch. How is this latch related to those described in the lectures
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: omputer Organization and Architecture Lecture 8: Registers and ounters Registers A register is a group of flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores one bit of data; n flip-flops are required to store
Systems I: omputer Organization and Architecture Lecture 8: Registers and ounters Registers A register is a group of flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores one bit of data; n flip-flops are required to store
2 : BISTABLES. In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blocks of electronic counting circuits.
 2 : BITABLE In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blos of electronic counting circuits. et-reset bistable A bistable circuit, also called a latch, or flip-flop,
2 : BITABLE In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blos of electronic counting circuits. et-reset bistable A bistable circuit, also called a latch, or flip-flop,
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits
 Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: rania.swief@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: rania.swief@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
DIGITAL TECHNICS II. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute. 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013
 DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 1. Counters,
DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 1. Counters,
DIGITAL TECHNICS II. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute
 DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 2. LECTURE: ELEMENTARY SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS: FLIP-FLOPS 1st year BSc course 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1
DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 2. LECTURE: ELEMENTARY SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS: FLIP-FLOPS 1st year BSc course 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1
Digital Electronics Detailed Outline
 Digital Electronics Detailed Outline Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and Digital Electronics (32 Total Days) Lesson 1.1: Foundations and the Board Game Counter (9 days) 1. Safety is an important concept
Digital Electronics Detailed Outline Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and Digital Electronics (32 Total Days) Lesson 1.1: Foundations and the Board Game Counter (9 days) 1. Safety is an important concept
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Napier University. School of Engineering. Electronic Engineering A Module: SE42205 Digital Design
 Napier University School of Engineering Digital Design Clock + U1 out 5V "1" "2" "4" JK-FF D JK-FF C JK-FF B U8 SN7408 signal U4 SN74107 U5 SN74107 U6 SN74107 U3 SN7408 U2 J Q J Q & J Q & K CQ K CQ K CQ
Napier University School of Engineering Digital Design Clock + U1 out 5V "1" "2" "4" JK-FF D JK-FF C JK-FF B U8 SN7408 signal U4 SN74107 U5 SN74107 U6 SN74107 U3 SN7408 U2 J Q J Q & J Q & K CQ K CQ K CQ
CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits
 CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits Last revised 8/15/2007 Objectives: 1. To introduce asynchronous and synchronous flip-flops (latches and pulsetriggered, plus asynchronous preset/clear) 2. To introduce
CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits Last revised 8/15/2007 Objectives: 1. To introduce asynchronous and synchronous flip-flops (latches and pulsetriggered, plus asynchronous preset/clear) 2. To introduce
ASYNCHRONOUS COUNTERS
 LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
Design: a mod-8 Counter
 Design: a mod-8 Counter A mod-8 counter stores a integer value, and increments that value (say) on each clock tick, and wraps around to 0 if the previous stored value was 7. So, the stored value follows
Design: a mod-8 Counter A mod-8 counter stores a integer value, and increments that value (say) on each clock tick, and wraps around to 0 if the previous stored value was 7. So, the stored value follows
Clocking. Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 Clocks 1
 ing Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 s 1 Why s and Storage Elements? Inputs Combinational Logic Outputs Want to reuse combinational logic from cycle to cycle 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05
ing Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 s 1 Why s and Storage Elements? Inputs Combinational Logic Outputs Want to reuse combinational logic from cycle to cycle 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05
Admin. ECE 550: Fundamentals of Computer Systems and Engineering. Last time. VHDL: Behavioral vs Structural. Memory Elements
 Admin C 55: Fundamentals of Computer ystems and ngineering torage and Clocking eading Finish up Chapter ecitation How is it going? VHL questions/issues? Homework Homework ubmissions vis akai C 55 (Hilton):
Admin C 55: Fundamentals of Computer ystems and ngineering torage and Clocking eading Finish up Chapter ecitation How is it going? VHL questions/issues? Homework Homework ubmissions vis akai C 55 (Hilton):
1.1 The 7493 consists of 4 flip-flops with J-K inputs unconnected. In a TTL chip, unconnected inputs
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY LOS ANGELES Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-246 Digital Logic Lab EXPERIMENT 1 COUNTERS AND WAVEFORMS Text: Mano, Digital Design, 3rd & 4th Editions, Sec.
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY LOS ANGELES Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-246 Digital Logic Lab EXPERIMENT 1 COUNTERS AND WAVEFORMS Text: Mano, Digital Design, 3rd & 4th Editions, Sec.
Multilevel Sequential Logic Circuit Design
 International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Vol., No. 4, December, 4 Multilevel Sequential Logic Circuit Design vni Morgül FSM Vakıf University, iomedical Eng. Dept, Istanbul, Turkey
International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Vol., No. 4, December, 4 Multilevel Sequential Logic Circuit Design vni Morgül FSM Vakıf University, iomedical Eng. Dept, Istanbul, Turkey
Low-Power, High-Speed CMOS Analog Switches
 Low-Power, High-peed MO Analog es G1/3/ -V upply Max Rating 1-V Analog ignal Range On-Resistance r (on) : Low Leakage I (on) : pa Fast ing t ON : ns Ultra Low Power Requirements P :.3 W TTL, MO ompatible
Low-Power, High-peed MO Analog es G1/3/ -V upply Max Rating 1-V Analog ignal Range On-Resistance r (on) : Low Leakage I (on) : pa Fast ing t ON : ns Ultra Low Power Requirements P :.3 W TTL, MO ompatible
74F74 Dual D-Type Positive Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop
 Dual D-Type Positive Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop General Description The F74 is a dual D-type flip-flop with Direct Clear and Set inputs and complementary (Q, Q) outputs. Information at the input is traferred
Dual D-Type Positive Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop General Description The F74 is a dual D-type flip-flop with Direct Clear and Set inputs and complementary (Q, Q) outputs. Information at the input is traferred
Digital Logic Design. Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits. Pu-Jen Cheng
 Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS. Counters. By: Electrical Engineering Department
 Counters By: Electrical Engineering Department 1 Counters Upon completion of the chapter, students should be able to:.1 Understand the basic concepts of asynchronous counter and synchronous counters, and
Counters By: Electrical Engineering Department 1 Counters Upon completion of the chapter, students should be able to:.1 Understand the basic concepts of asynchronous counter and synchronous counters, and
MM74HC4538 Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator
 MM74HC4538 Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator General Description The MM74HC4538 high speed monostable multivibrator (one shots) is implemented in advanced silicon-gate CMOS technology. They feature
MM74HC4538 Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator General Description The MM74HC4538 high speed monostable multivibrator (one shots) is implemented in advanced silicon-gate CMOS technology. They feature
Timing Methodologies (cont d) Registers. Typical timing specifications. Synchronous System Model. Short Paths. System Clock Frequency
 Registers Timing Methodologies (cont d) Sample data using clock Hold data between clock cycles Computation (and delay) occurs between registers efinition of terms setup time: minimum time before the clocking
Registers Timing Methodologies (cont d) Sample data using clock Hold data between clock cycles Computation (and delay) occurs between registers efinition of terms setup time: minimum time before the clocking
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines. Memory elements. Memory element terminology. Clock terminology
 Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Chapter 8. Sequential Circuits for Registers and Counters
 Chapter 8 Sequential Circuits for Registers and Counters Lesson 3 COUNTERS Ch16L3- "Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 Outline Counters T-FF Basic Counting element State
Chapter 8 Sequential Circuits for Registers and Counters Lesson 3 COUNTERS Ch16L3- "Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 Outline Counters T-FF Basic Counting element State
Wiki Lab Book. This week is practice for wiki usage during the project.
 Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
Asynchronous Counters. Asynchronous Counters
 Counters and State Machine Design November 25 Asynchronous Counters ENGI 25 ELEC 24 Asynchronous Counters The term Asynchronous refers to events that do not occur at the same time With respect to counter
Counters and State Machine Design November 25 Asynchronous Counters ENGI 25 ELEC 24 Asynchronous Counters The term Asynchronous refers to events that do not occur at the same time With respect to counter
EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops. Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. For a complete data sheet, please also download:
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC06 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Family Specifications The IC06 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Package Information The IC06 74C/CT/CU/CMOS
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC06 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Family Specifications The IC06 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Package Information The IC06 74C/CT/CU/CMOS
DM74LS112A Dual Negative-Edge-Triggered Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flop with Preset, Clear, and Complementary Outputs
 August 1986 Revised March 2000 DM74LS112A Dual Negative-Edge-Triggered Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flop with Preset, Clear, and Complementary General Description This device contains two independent negative-edge-triggered
August 1986 Revised March 2000 DM74LS112A Dual Negative-Edge-Triggered Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flop with Preset, Clear, and Complementary General Description This device contains two independent negative-edge-triggered
LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters
 LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Introduction to latches and the D type flip-flop 2. Use of actual flip-flops to help you understand sequential
LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Introduction to latches and the D type flip-flop 2. Use of actual flip-flops to help you understand sequential
Verilog: always @ Blocks
 Verilog: always @ Blocks hris Fletcher U Berkeley Version 0.2008.9.4 September 5, 2008 Introduction Sections. to.6 discuss always@ blocks in Verilog, and when to use the two major flavors of always@ block,
Verilog: always @ Blocks hris Fletcher U Berkeley Version 0.2008.9.4 September 5, 2008 Introduction Sections. to.6 discuss always@ blocks in Verilog, and when to use the two major flavors of always@ block,
DATA SHEET. HEF40193B MSI 4-bit up/down binary counter. For a complete data sheet, please also download: INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Family Specifications HEF, HEC The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Package Outlines/Information HEF,
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Family Specifications HEF, HEC The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Package Outlines/Information HEF,
DM74LS169A Synchronous 4-Bit Up/Down Binary Counter
 Synchronous 4-Bit Up/Down Binary Counter General Description This synchronous presettable counter features an internal carry look-ahead for cascading in high-speed counting applications. Synchronous operation
Synchronous 4-Bit Up/Down Binary Counter General Description This synchronous presettable counter features an internal carry look-ahead for cascading in high-speed counting applications. Synchronous operation
Contents COUNTER. Unit III- Counters
 COUNTER Contents COUNTER...1 Frequency Division...2 Divide-by-2 Counter... 3 Toggle Flip-Flop...3 Frequency Division using Toggle Flip-flops...5 Truth Table for a 3-bit Asynchronous Up Counter...6 Modulo
COUNTER Contents COUNTER...1 Frequency Division...2 Divide-by-2 Counter... 3 Toggle Flip-Flop...3 Frequency Division using Toggle Flip-flops...5 Truth Table for a 3-bit Asynchronous Up Counter...6 Modulo
Counters are sequential circuits which "count" through a specific state sequence.
 Counters Counters are sequential circuits which "count" through a specific state sequence. They can count up, count down, or count through other fixed sequences. Two distinct types are in common usage:
Counters Counters are sequential circuits which "count" through a specific state sequence. They can count up, count down, or count through other fixed sequences. Two distinct types are in common usage:
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
[ 4 ] Logic Symbols and Truth Table
![[ 4 ] Logic Symbols and Truth Table [ 4 ] Logic Symbols and Truth Table](/thumbs/40/21640854.jpg) [ 4 ] Logic s and Truth Table 1. How to Read MIL-Type Logic s Table 1.1 shows the MIL-type logic symbols used for high-speed CMO ICs. This logic chart is based on MIL-TD-806. The clocked inverter and transmission
[ 4 ] Logic s and Truth Table 1. How to Read MIL-Type Logic s Table 1.1 shows the MIL-type logic symbols used for high-speed CMO ICs. This logic chart is based on MIL-TD-806. The clocked inverter and transmission
Logic Reference Guide
 Logic eference Guide Advanced Micro evices INTOUCTION Throughout this data book and design guide we have assumed that you have a good working knowledge of logic. Unfortunately, there always comes a time
Logic eference Guide Advanced Micro evices INTOUCTION Throughout this data book and design guide we have assumed that you have a good working knowledge of logic. Unfortunately, there always comes a time
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots
 Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
Decimal Number (base 10) Binary Number (base 2)
 LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. For a complete data sheet, please also download:
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Family Specifications The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Package Information The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Family Specifications The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic Package Information The IC6 74C/CT/CU/CMOS ogic
The enable pin needs to be high for data to be fed to the outputs Q and Q bar.
 of 7 -Type flip-flop (Toggle switch) The -type flip-flops are used in prescalar/divider circuits and frequency phase detectors. Figure shows how the flip-flop (latch) can be made using -input logic circuits
of 7 -Type flip-flop (Toggle switch) The -type flip-flops are used in prescalar/divider circuits and frequency phase detectors. Figure shows how the flip-flop (latch) can be made using -input logic circuits
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D.
 BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits
 EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
COMBINATIONAL and SEQUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design
 PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
74F168*, 74F169 4-bit up/down binary synchronous counter
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 74F168*, * Discontinued part. Please see the Discontinued Product List in Section 1, page 21. 1996 Jan 5 IC15 Data Handbook FEATURES Synchronous counting and loading Up/Down counting
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 74F168*, * Discontinued part. Please see the Discontinued Product List in Section 1, page 21. 1996 Jan 5 IC15 Data Handbook FEATURES Synchronous counting and loading Up/Down counting
