FINANCE FOR LAWYERS. LESSON TWO SUMMARY: TYPES OF CALCULATORS a. Simple b. Financial c. Scientific d. Reverse Polish Notation SYLLABUS
|
|
|
- Domenic French
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FINANCE FOR LAWYERS CLASS ONE: LESSONS ONE AND TWO LESSON ONE PLAN: 1. Read LESSON ONE OBJECTIVES 2. Read COURSE INTRODUCTION (5 pages) 3. Read TEXT pages 1 to 2 4. Read NAVIGATION INSTRUCTIONS 5. Listen to LESSON ONE LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (104 slides; 16 minutes) LESSON ONE SUMMARY: WHY LAWYERS NEED TO KNOW FINANCE a. Tort Law b. Family Law c. Corporate Law d. Real estate and Property Law e. Retirement and Estate Planning f. Tax Law and Tax Planning g. Contracts h. Personal i. Buy a car or house ii. Save for a child s education iii. Pay off a student loan iv. Value a business v. Win the lottery LESSON TWO PLAN: 1. Read LESSON TWO OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 3 to 4 3. Review NAVIGATION INSTRUCTIONS. 4. Examine GLOSSARY and review definitions of new terminology. 5. Listen to LESSON TWO LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (63 slides, 15 minutes) 6. Work LESSON TWO PROBLEMS. LESSON TWO SUMMARY: TYPES OF CALCULATORS a. Simple b. Financial c. Scientific d. Reverse Polish Notation Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 1
2 CLASS TWO: LESSON THREE LESSON THREE PLAN: 1. Read LESSON THREE OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 4 to Listen to LESSON THREE LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (289 slides, 60 minutes) 5. Work LESSON THREE PROBLEMS. LESSON THREE SUMMARY: TYPES OF CALCULATIONS a. Present Value of a Sum b. Future Value of a Sum c. Present Value of an Annuity d. Future Value of an Annuity e. Sinking Fund f. Amortization g. Interest Conversion CLASS THREE: LESSON FOUR AND 5A-1 LESSON FOUR PLAN: 1. Read LESSON FOUR OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 15 to Listen to LESSON FOUR LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (109 slides, 28 minutes) 6. Work LESSON FOUR PROBLEMS. LESSON FOUR SUMMARY: CALCULATOR TERMINOLOGY h. Present Value (PV) i. Future Value (FV) j. Payment (Pmt) k. Nominal Annual Interest (I/yr) l. Number of Periods (N) m. Number of Periods per Year (P/yr) n. Mode (Begin or End) LESSON FIVE: INTEREST TERMINOLOGY: This LESSON divides into four subparts. SUBPART 1. LESSON FIVE A: INTEREST TERMINOLOGY Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 2
3 LESSON FIVE A PLAN: 1. Read LESSON FIVE A OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 15 to Listen to LESSON FIVE A LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (204 slides, 43 minutes) 6. Work LESSON FIVE A PROBLEMS. LESSON FIVE A SUMMARY: INTEREST TERMINOLOGY a. Simple Interest b. Nominal Annual Interest (NAI) c. Periodic Interest Rate d. Compound Interest e. Effective Interest Rate (EFF) CLASS FOUR: CONTINUE LESSON 5A-1; START 5B LESSON FIVE B PLAN: 1. Read LESSON FIVE B OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 3. Examine APR STATUTE 4. Examine APR REGULATIONS 5. Examine GLOSSARY and review definitions of new terminology. 6. Examine ACRONYMS and review definitions of new terminology. 7. Listen to LESSON FIVE B LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (176 slides, 69 minutes) 8. Work LESSON FIVE B PROBLEMS. LESSON FIVE A SUMMARY: APR a. Annual Percentage Rate (APR) b. APR Federal statute c. APR Federal Regulations CLASS FIVE: CONTINUE LESSONS 5A-1 AND 5B; START LESSON 5B-1 LESSON FIVE B-1 PLAN: 1. Read LESSON FIVE B-1 OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 3. Examine APY STATUTE 4. Examine APY REGULATIONS 5. Examine GLOSSARY and review definitions of new terminology. Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 3
4 6. Examine ACRONYMS and review definitions of new terminology. 7. Listen to LESSON FIVE B-1 LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (1 slide) 8. Work LESSON FIVE B PROBLEMS. LESSON FIVE B-1 SUMMARY: APY a. Annual Percentage Yield (APY) b. APY Federal statute c. APY Federal Regulations CLASS SIX: LESSON FIVE C LESSON FIVE C PLAN: 1. Read LESSON FIVE C OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON FIVE C LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (51 slides, 47 minutes) 6. Work LESSON FIVE C PROBLEMS. LESSON FIVE C SUMMARY: YIELD Simple yield a. Yield b. Yield to maturity c. Internal rate of return CLASS SEVEN: COMPLETE LESSON FIVE SERIES AND LESSON FIFTEEN LESSON FIFTEEN PLAN: 1. Read LESSON FIFTEEN OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON FIFTEEN LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (159 slides, 45 minutes) 6. Work LESSON FIFTEEN PROBLEMS. LESSON FIFTEEN SUMMARY: INTEREST RATE CONVERSION i. Nominal to Effective Rate and Periodic Rate. ii. Effective Rate to Nominal Rate and Periodic Rate. Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 4
5 iii. Periodic Rate to Nominal Rate and Effective Rate. CLASS EIGHT: LESSON SIX LESSON SIX PLAN: 1. Read LESSON SIX OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON SIX LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (124 slides, 78 minutes) 6. Work LESSON SIX PROBLEMS. LESSON SIX SUMMARY: WHY PEOPLE CHARGE INTEREST a. Expected Inflation (or Deflation) b. Risk (Market and Individual) c. Liquidity CLASS NINE: CONTINUE LESSON SIX; LESSON SEVEN LESSON SEVEN PLAN: 1. Read LESSON SEVEN OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON SEVEN LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (98 slides, 45 minutes) 6. Work LESSON SEVEN PROBLEMS. LESSON SEVEN SUMMARY: CHOICE OF AN INTEREST RATE d. Buying a House or Car e. Personal Injury Litigation f. Family Law Matters g. Business Valuations h. Retirement or Education Savings CLASS TEN: LESSONS EIGHT AND NINE LESSON EIGHT PLAN: 1. Read LESSON EIGHT OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 5
6 5. Listen to LESSON EIGHT LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (68 slides, 17 minutes) 6. Work LESSON EIGHT PROBLEMS. LESSON EIGHT SUMMARY: AFTER-TAX INTEREST RATE i. Why is it important? j. How to compute it. k. Examples LESSON NINE PLAN: 1. Read LESSON NINE OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON NINE LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (180 slides, 43 minutes) 6. Work LESSON NINE PROBLEMS. LESSON NINE SUMMARY: PRESENT VALUE OF A SUM CLASS TEN: LESSON TEN LESSON TEN PLAN: 1. Read LESSON TEN OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON TEN LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (176 slides, 33 minutes) 6. Work LESSON TEN PROBLEMS. LESSON TEN SUMMARY: FUTURE VALUE OF A SUM Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 6
7 CLASS ELEVEN: LESSONS ELEVEN AND TWELVE LESSON ELEVEN PLAN: 1. Read LESSON ELEVEN OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON ELEVEN LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (202 slides, 45 minutes) 6. Work LESSON ELEVEN PROBLEMS. LESSON ELEVEN SUMMARY: PRESENT VALUE OF AN ANNUITY LESSON TWELVE PLAN: 1. Read LESSON TWELVE OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON TWELVE LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (192 slides, 50 minutes) 6. Work LESSON TWELVE PROBLEMS. LESSON TWELVE SUMMARY: FUTURE VALUE OF AN ANNUITY CLASS TWELVE: Continue LESSON TWELVE AND START LESSON THIRTEEN LESSON THIRTEEN PLAN: 1. Read LESSON THIRTEEN OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON THIRTEEN LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (158 slides, 45 minutes) 6. Work LESSON THIRTEEN PROBLEMS. Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 7
8 LESSON THIRTEEN SUMMARY: AMORTIZATION CLASS THIRTEEN: Continue LESSON THIRTEEN AND START LESSON FOURTEEN LESSON FOURTEEN PLAN: 1. Read LESSON FOURTEEN OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON FOURTEEN LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION (252 slides, 55 minutes) 6. Work LESSON FOURTEEN PROBLEMS. LESSON FOURTEEN SUMMARY: SINKING FUNDS CLASS FOURTEEN: LESSON SIXTEEN LESSON SIXTEEN PLAN: 1. Read LESSON SIXTEEN OBJECTIVES and list of new terminology 5. Listen to LESSON SIXTEEN LECTURE and watch accompanying SLIDE PRESENTATION 6. Work LESSON SIXTEEN PROBLEMS. LESSON SIXTEEN SUMMARY: SOLVING FOR AN INTEREST RATE Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved. 8
A Textual Explanation
 NAVIGATION INSTRUCTIONS GLOSSARY FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS FOR LAWYERS LECTURES INDEX INTRODUCTION PRESENT VALUE OF A SUM FUTURE VALUE OF A SUM SINKING FUND AMORTIZATION WITH CHART PRESENT VALUE OF AN ANNUITY
NAVIGATION INSTRUCTIONS GLOSSARY FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS FOR LAWYERS LECTURES INDEX INTRODUCTION PRESENT VALUE OF A SUM FUTURE VALUE OF A SUM SINKING FUND AMORTIZATION WITH CHART PRESENT VALUE OF AN ANNUITY
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation
 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Chapter 5 Key Concepts and Skills Be able to compute the future value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute the present value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Chapter 5 Key Concepts and Skills Be able to compute the future value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute the present value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute
Using Financial Calculators
 Chapter 4 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation 4B-1 Appendix 4B Using Financial Calculators This appendix is intended to help you use your Hewlett-Packard or Texas Instruments BA II Plus financial calculator
Chapter 4 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation 4B-1 Appendix 4B Using Financial Calculators This appendix is intended to help you use your Hewlett-Packard or Texas Instruments BA II Plus financial calculator
CHAPTER 2. Time Value of Money 2-1
 CHAPTER 2 Time Value of Money 2-1 Time Value of Money (TVM) Time Lines Future value & Present value Rates of return Annuities & Perpetuities Uneven cash Flow Streams Amortization 2-2 Time lines 0 1 2 3
CHAPTER 2 Time Value of Money 2-1 Time Value of Money (TVM) Time Lines Future value & Present value Rates of return Annuities & Perpetuities Uneven cash Flow Streams Amortization 2-2 Time lines 0 1 2 3
Fin 5413 CHAPTER FOUR
 Slide 1 Interest Due Slide 2 Fin 5413 CHAPTER FOUR FIXED RATE MORTGAGE LOANS Interest Due is the mirror image of interest earned In previous finance course you learned that interest earned is: Interest
Slide 1 Interest Due Slide 2 Fin 5413 CHAPTER FOUR FIXED RATE MORTGAGE LOANS Interest Due is the mirror image of interest earned In previous finance course you learned that interest earned is: Interest
1. If you wish to accumulate $140,000 in 13 years, how much must you deposit today in an account that pays an annual interest rate of 14%?
 Chapter 2 - Sample Problems 1. If you wish to accumulate $140,000 in 13 years, how much must you deposit today in an account that pays an annual interest rate of 14%? 2. What will $247,000 grow to be in
Chapter 2 - Sample Problems 1. If you wish to accumulate $140,000 in 13 years, how much must you deposit today in an account that pays an annual interest rate of 14%? 2. What will $247,000 grow to be in
Chapter 2 Present Value
 Chapter 2 Present Value Road Map Part A Introduction to finance. Financial decisions and financial markets. Present value. Part B Valuation of assets, given discount rates. Part C Determination of risk-adjusted
Chapter 2 Present Value Road Map Part A Introduction to finance. Financial decisions and financial markets. Present value. Part B Valuation of assets, given discount rates. Part C Determination of risk-adjusted
Time Value of Money Problems
 Time Value of Money Problems 1. What will a deposit of $4,500 at 10% compounded semiannually be worth if left in the bank for six years? a. $8,020.22 b. $7,959.55 c. $8,081.55 d. $8,181.55 2. What will
Time Value of Money Problems 1. What will a deposit of $4,500 at 10% compounded semiannually be worth if left in the bank for six years? a. $8,020.22 b. $7,959.55 c. $8,081.55 d. $8,181.55 2. What will
DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW VALUATION and MULTIPLE CASH FLOWS
 Chapter 5 DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW VALUATION and MULTIPLE CASH FLOWS The basic PV and FV techniques can be extended to handle any number of cash flows. PV with multiple cash flows: Suppose you need $500 one
Chapter 5 DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW VALUATION and MULTIPLE CASH FLOWS The basic PV and FV techniques can be extended to handle any number of cash flows. PV with multiple cash flows: Suppose you need $500 one
FinQuiz Notes 2 0 1 4
 Reading 5 The Time Value of Money Money has a time value because a unit of money received today is worth more than a unit of money to be received tomorrow. Interest rates can be interpreted in three ways.
Reading 5 The Time Value of Money Money has a time value because a unit of money received today is worth more than a unit of money to be received tomorrow. Interest rates can be interpreted in three ways.
FinQuiz Notes 2 0 1 5
 Reading 5 The Time Value of Money Money has a time value because a unit of money received today is worth more than a unit of money to be received tomorrow. Interest rates can be interpreted in three ways.
Reading 5 The Time Value of Money Money has a time value because a unit of money received today is worth more than a unit of money to be received tomorrow. Interest rates can be interpreted in three ways.
Future Value of an Annuity Sinking Fund. MATH 1003 Calculus and Linear Algebra (Lecture 3)
 MATH 1003 Calculus and Linear Algebra (Lecture 3) Future Value of an Annuity Definition An annuity is a sequence of equal periodic payments. We call it an ordinary annuity if the payments are made at the
MATH 1003 Calculus and Linear Algebra (Lecture 3) Future Value of an Annuity Definition An annuity is a sequence of equal periodic payments. We call it an ordinary annuity if the payments are made at the
FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS
 FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS 1 Main function is to calculate payments, determine interest rates and to solve for the present or future value of a loan or an annuity 5 common keys on financial calculators: N
FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS 1 Main function is to calculate payments, determine interest rates and to solve for the present or future value of a loan or an annuity 5 common keys on financial calculators: N
Chapter 4: Time Value of Money
 FIN 301 Homework Solution Ch4 Chapter 4: Time Value of Money 1. a. 10,000/(1.10) 10 = 3,855.43 b. 10,000/(1.10) 20 = 1,486.44 c. 10,000/(1.05) 10 = 6,139.13 d. 10,000/(1.05) 20 = 3,768.89 2. a. $100 (1.10)
FIN 301 Homework Solution Ch4 Chapter 4: Time Value of Money 1. a. 10,000/(1.10) 10 = 3,855.43 b. 10,000/(1.10) 20 = 1,486.44 c. 10,000/(1.05) 10 = 6,139.13 d. 10,000/(1.05) 20 = 3,768.89 2. a. $100 (1.10)
TIME VALUE OF MONEY PROBLEM #7: MORTGAGE AMORTIZATION
 TIME VALUE OF MONEY PROBLEM #7: MORTGAGE AMORTIZATION Professor Peter Harris Mathematics by Sharon Petrushka Introduction This problem will focus on calculating mortgage payments. Knowledge of Time Value
TIME VALUE OF MONEY PROBLEM #7: MORTGAGE AMORTIZATION Professor Peter Harris Mathematics by Sharon Petrushka Introduction This problem will focus on calculating mortgage payments. Knowledge of Time Value
CHAPTER 9 Time Value Analysis
 Copyright 2008 by the Foundation of the American College of Healthcare Executives 6/11/07 Version 9-1 CHAPTER 9 Time Value Analysis Future and present values Lump sums Annuities Uneven cash flow streams
Copyright 2008 by the Foundation of the American College of Healthcare Executives 6/11/07 Version 9-1 CHAPTER 9 Time Value Analysis Future and present values Lump sums Annuities Uneven cash flow streams
Ch. 12 FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS 1. 1998 by Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved
 Ch. 12 FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS 1 1998 by Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved CHAPTER TWELVE FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS An understanding of the Internal Revenue Code time value of money sections requires a
Ch. 12 FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS 1 1998 by Steven J. Willis All Rights Reserved CHAPTER TWELVE FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS An understanding of the Internal Revenue Code time value of money sections requires a
Goals. The Time Value of Money. First example. Compounding. Economics 71a Spring 2007 Mayo, Chapter 7 Lecture notes 3.1
 Goals The Time Value of Money Economics 7a Spring 2007 Mayo, Chapter 7 Lecture notes 3. More applications Compounding PV = present or starting value FV = future value R = interest rate n = number of periods
Goals The Time Value of Money Economics 7a Spring 2007 Mayo, Chapter 7 Lecture notes 3. More applications Compounding PV = present or starting value FV = future value R = interest rate n = number of periods
Chapter 5 Time Value of Money 2: Analyzing Annuity Cash Flows
 1. Future Value of Multiple Cash Flows 2. Future Value of an Annuity 3. Present Value of an Annuity 4. Perpetuities 5. Other Compounding Periods 6. Effective Annual Rates (EAR) 7. Amortized Loans Chapter
1. Future Value of Multiple Cash Flows 2. Future Value of an Annuity 3. Present Value of an Annuity 4. Perpetuities 5. Other Compounding Periods 6. Effective Annual Rates (EAR) 7. Amortized Loans Chapter
MAT116 Project 2 Chapters 8 & 9
 MAT116 Project 2 Chapters 8 & 9 1 8-1: The Project In Project 1 we made a loan workout decision based only on data from three banks that had merged into one. We did not consider issues like: What was the
MAT116 Project 2 Chapters 8 & 9 1 8-1: The Project In Project 1 we made a loan workout decision based only on data from three banks that had merged into one. We did not consider issues like: What was the
APPENDIX 3 TIME VALUE OF MONEY. Time Lines and Notation. The Intuitive Basis for Present Value
 1 2 TIME VALUE OF MONEY APPENDIX 3 The simplest tools in finance are often the most powerful. Present value is a concept that is intuitively appealing, simple to compute, and has a wide range of applications.
1 2 TIME VALUE OF MONEY APPENDIX 3 The simplest tools in finance are often the most powerful. Present value is a concept that is intuitively appealing, simple to compute, and has a wide range of applications.
Time Value of Money Practice Questions Irfanullah.co
 1. You are trying to estimate the required rate of return for a particular investment. Which of the following premiums are you least likely to consider? A. Inflation premium B. Maturity premium C. Nominal
1. You are trying to estimate the required rate of return for a particular investment. Which of the following premiums are you least likely to consider? A. Inflation premium B. Maturity premium C. Nominal
Interest Rates and Bond Valuation
 and Bond Valuation 1 Bonds Debt Instrument Bondholders are lending the corporation money for some stated period of time. Liquid Asset Corporate Bonds can be traded in the secondary market. Price at which
and Bond Valuation 1 Bonds Debt Instrument Bondholders are lending the corporation money for some stated period of time. Liquid Asset Corporate Bonds can be traded in the secondary market. Price at which
Sample problems from Chapter 10.1
 Sample problems from Chapter 10.1 This is the annuities sinking funds formula. This formula is used in most cases for annuities. The payments for this formula are made at the end of a period. Your book
Sample problems from Chapter 10.1 This is the annuities sinking funds formula. This formula is used in most cases for annuities. The payments for this formula are made at the end of a period. Your book
Hewlett Packard (HP) 10BII
 Hewlett Packard (HP) 10BII The HP10BII is programmed to perform two basic types of operations: statistical operations and financial operations. Various types of computations are activated by depressing
Hewlett Packard (HP) 10BII The HP10BII is programmed to perform two basic types of operations: statistical operations and financial operations. Various types of computations are activated by depressing
Problem Set: Annuities and Perpetuities (Solutions Below)
 Problem Set: Annuities and Perpetuities (Solutions Below) 1. If you plan to save $300 annually for 10 years and the discount rate is 15%, what is the future value? 2. If you want to buy a boat in 6 years
Problem Set: Annuities and Perpetuities (Solutions Below) 1. If you plan to save $300 annually for 10 years and the discount rate is 15%, what is the future value? 2. If you want to buy a boat in 6 years
CARMEN VENTER COPYRIGHT www.futurefinance.co.za 0828807192 1
 Carmen Venter CFP WORKSHOPS FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS presented by Geoff Brittain Q 5.3.1 Calculate the capital required at retirement to meet Makhensa s retirement goals. (5) 5.3.2 Calculate the capital
Carmen Venter CFP WORKSHOPS FINANCIAL CALCULATIONS presented by Geoff Brittain Q 5.3.1 Calculate the capital required at retirement to meet Makhensa s retirement goals. (5) 5.3.2 Calculate the capital
Ehrhardt Chapter 8 Page 1
 Chapter 2 Time Value of Money 1 Time Value Topics Future value Present value Rates of return Amortization 2 Time lines show timing of cash flows. 0 1 2 3 I% CF 0 CF 1 CF 2 CF 3 Tick marks at ends of periods,
Chapter 2 Time Value of Money 1 Time Value Topics Future value Present value Rates of return Amortization 2 Time lines show timing of cash flows. 0 1 2 3 I% CF 0 CF 1 CF 2 CF 3 Tick marks at ends of periods,
Ch. Ch. 5 Discounted Cash Flows & Valuation In Chapter 5,
 Ch. 5 Discounted Cash Flows & Valuation In Chapter 5, we found the PV & FV of single cash flows--either payments or receipts. In this chapter, we will do the same for multiple cash flows. 2 Multiple Cash
Ch. 5 Discounted Cash Flows & Valuation In Chapter 5, we found the PV & FV of single cash flows--either payments or receipts. In this chapter, we will do the same for multiple cash flows. 2 Multiple Cash
Prepared by: Dalia A. Marafi Version 2.0
 Kuwait University College of Business Administration Department of Finance and Financial Institutions Using )Casio FC-200V( for Fundamentals of Financial Management (220) Prepared by: Dalia A. Marafi Version
Kuwait University College of Business Administration Department of Finance and Financial Institutions Using )Casio FC-200V( for Fundamentals of Financial Management (220) Prepared by: Dalia A. Marafi Version
Integrated Case. 5-42 First National Bank Time Value of Money Analysis
 Integrated Case 5-42 First National Bank Time Value of Money Analysis You have applied for a job with a local bank. As part of its evaluation process, you must take an examination on time value of money
Integrated Case 5-42 First National Bank Time Value of Money Analysis You have applied for a job with a local bank. As part of its evaluation process, you must take an examination on time value of money
Chapter 4 Time Value of Money ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS
 Chapter 4 Time Value of Money ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 4-1 a. PV (present value) is the value today of a future payment, or stream of payments, discounted at the appropriate rate of interest.
Chapter 4 Time Value of Money ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 4-1 a. PV (present value) is the value today of a future payment, or stream of payments, discounted at the appropriate rate of interest.
ANNUITIES. Ordinary Simple Annuities
 An annuity is a series of payments or withdrawals. ANNUITIES An Annuity can be either Simple or General Simple Annuities - Compounding periods and payment periods coincide. General Annuities - Compounding
An annuity is a series of payments or withdrawals. ANNUITIES An Annuity can be either Simple or General Simple Annuities - Compounding periods and payment periods coincide. General Annuities - Compounding
Purpose EL-773A HP-10B BA-II PLUS Clear memory 0 n registers
 D-How to Use a Financial Calculator* Most personal finance decisions involve calculations of the time value of money. Three methods are used to compute this value: time value of money tables (such as those
D-How to Use a Financial Calculator* Most personal finance decisions involve calculations of the time value of money. Three methods are used to compute this value: time value of money tables (such as those
BUSI 121 Foundations of Real Estate Mathematics
 Real Estate Division BUSI 121 Foundations of Real Estate Mathematics SESSION 2 By Graham McIntosh Sauder School of Business University of British Columbia Outline Introduction Cash Flow Problems Cash Flow
Real Estate Division BUSI 121 Foundations of Real Estate Mathematics SESSION 2 By Graham McIntosh Sauder School of Business University of British Columbia Outline Introduction Cash Flow Problems Cash Flow
2 The Mathematics. of Finance. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 The Mathematics of Finance Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.3 Annuities, Loans, and Bonds Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Annuities, Loans, and Bonds A typical defined-contribution
2 The Mathematics of Finance Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.3 Annuities, Loans, and Bonds Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Annuities, Loans, and Bonds A typical defined-contribution
9. Time Value of Money 1: Present and Future Value
 9. Time Value of Money 1: Present and Future Value Introduction The language of finance has unique terms and concepts that are based on mathematics. It is critical that you understand this language, because
9. Time Value of Money 1: Present and Future Value Introduction The language of finance has unique terms and concepts that are based on mathematics. It is critical that you understand this language, because
Understand the relationship between financial plans and statements.
 #2 Budget Development Your Financial Statements and Plans Learning Goals Understand the relationship between financial plans and statements. Prepare a personal balance sheet. Generate a personal income
#2 Budget Development Your Financial Statements and Plans Learning Goals Understand the relationship between financial plans and statements. Prepare a personal balance sheet. Generate a personal income
Chapter F: Finance. Section F.1-F.4
 Chapter F: Finance Section F.1-F.4 F.1 Simple Interest Suppose a sum of money P, called the principal or present value, is invested for t years at an annual simple interest rate of r, where r is given
Chapter F: Finance Section F.1-F.4 F.1 Simple Interest Suppose a sum of money P, called the principal or present value, is invested for t years at an annual simple interest rate of r, where r is given
Chapter 22: Borrowings Models
 October 21, 2013 Last Time The Consumer Price Index Real Growth The Consumer Price index The official measure of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI) which is the determined by the Bureau of Labor
October 21, 2013 Last Time The Consumer Price Index Real Growth The Consumer Price index The official measure of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI) which is the determined by the Bureau of Labor
1. Annuity a sequence of payments, each made at equally spaced time intervals.
 Ordinary Annuities (Young: 6.2) In this Lecture: 1. More Terminology 2. Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity 3. The Ordinary Annuity Formula (Optional) 4. Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity More Terminology
Ordinary Annuities (Young: 6.2) In this Lecture: 1. More Terminology 2. Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity 3. The Ordinary Annuity Formula (Optional) 4. Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity More Terminology
Introduction to the Hewlett-Packard (HP) 10BII Calculator and Review of Mortgage Finance Calculations
 Introduction to the Hewlett-Packard (HP) 10BII Calculator and Review of Mortgage Finance Calculations Real Estate Division Sauder School of Business University of British Columbia Introduction to the Hewlett-Packard
Introduction to the Hewlett-Packard (HP) 10BII Calculator and Review of Mortgage Finance Calculations Real Estate Division Sauder School of Business University of British Columbia Introduction to the Hewlett-Packard
Topics. Chapter 5. Future Value. Future Value - Compounding. Time Value of Money. 0 r = 5% 1
 Chapter 5 Time Value of Money Topics 1. Future Value of a Lump Sum 2. Present Value of a Lump Sum 3. Future Value of Cash Flow Streams 4. Present Value of Cash Flow Streams 5. Perpetuities 6. Uneven Series
Chapter 5 Time Value of Money Topics 1. Future Value of a Lump Sum 2. Present Value of a Lump Sum 3. Future Value of Cash Flow Streams 4. Present Value of Cash Flow Streams 5. Perpetuities 6. Uneven Series
hp calculators HP 12C Loan Amortizations Amortization The HP12C amortization approach Practice amortizing loans
 Amortization The HP12C amortization approach Practice amortizing loans Amortization The word 'amortization' comes from a Latin word meaning "about to die". When a loan earning interest has regular, fixed
Amortization The HP12C amortization approach Practice amortizing loans Amortization The word 'amortization' comes from a Latin word meaning "about to die". When a loan earning interest has regular, fixed
Appendix C- 1. Time Value of Money. Appendix C- 2. Financial Accounting, Fifth Edition
 C- 1 Time Value of Money C- 2 Financial Accounting, Fifth Edition Study Objectives 1. Distinguish between simple and compound interest. 2. Solve for future value of a single amount. 3. Solve for future
C- 1 Time Value of Money C- 2 Financial Accounting, Fifth Edition Study Objectives 1. Distinguish between simple and compound interest. 2. Solve for future value of a single amount. 3. Solve for future
Value of Money Concept$
 Value of Money Concept$ Time, not timing is the key to investing 2 Introduction Time Value of Money Application of TVM in financial planning : - determine capital needs for retirement plan - determine
Value of Money Concept$ Time, not timing is the key to investing 2 Introduction Time Value of Money Application of TVM in financial planning : - determine capital needs for retirement plan - determine
LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE
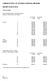 Clinical Staff Staff not holding honorary consultant contracts (lecturers, senior lecturers and readers) 01.04.2012 01.04.2013 scales scales Lecturer 1 33,265 33,597 2 34,799 35,146 3 36,334 36,697 4 37,869
Clinical Staff Staff not holding honorary consultant contracts (lecturers, senior lecturers and readers) 01.04.2012 01.04.2013 scales scales Lecturer 1 33,265 33,597 2 34,799 35,146 3 36,334 36,697 4 37,869
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation
 6 Formulas Discounted Cash Flow Valuation McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Outline Future and Present Values of Multiple Cash Flows Valuing
6 Formulas Discounted Cash Flow Valuation McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Outline Future and Present Values of Multiple Cash Flows Valuing
Dick Schwanke Finite Math 111 Harford Community College Fall 2013
 Annuities and Amortization Finite Mathematics 111 Dick Schwanke Session #3 1 In the Previous Two Sessions Calculating Simple Interest Finding the Amount Owed Computing Discounted Loans Quick Review of
Annuities and Amortization Finite Mathematics 111 Dick Schwanke Session #3 1 In the Previous Two Sessions Calculating Simple Interest Finding the Amount Owed Computing Discounted Loans Quick Review of
Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Principles Used in this Chapter. Simple Interest. Principle 2:
 Learning Objectives Chapter 5 The Time Value of Money Explain the mechanics of compounding, which is how money grows over a time when it is invested. Be able to move money through time using time value
Learning Objectives Chapter 5 The Time Value of Money Explain the mechanics of compounding, which is how money grows over a time when it is invested. Be able to move money through time using time value
Chapter 4. The Time Value of Money
 Chapter 4 The Time Value of Money 1 Learning Outcomes Chapter 4 Identify various types of cash flow patterns Compute the future value and the present value of different cash flow streams Compute the return
Chapter 4 The Time Value of Money 1 Learning Outcomes Chapter 4 Identify various types of cash flow patterns Compute the future value and the present value of different cash flow streams Compute the return
Chapter 3 Present Value
 Chapter 3 Present Value MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following cannot be calculated? a. Present value of an annuity. b. Future value of an annuity. c. Present value of a perpetuity. d. Future value
Chapter 3 Present Value MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following cannot be calculated? a. Present value of an annuity. b. Future value of an annuity. c. Present value of a perpetuity. d. Future value
Key Concepts and Skills
 Chapters 5 and 6 Calculators Time Value of Money and Discounted Cash Flow Valuation McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Key Concepts and Skills Be able
Chapters 5 and 6 Calculators Time Value of Money and Discounted Cash Flow Valuation McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Key Concepts and Skills Be able
Time Value of Money (TVM)
 BUSI Financial Management Time Value of Money 1 Time Value of Money (TVM) Present value and future value how much is $1 now worth in the future? how much is $1 in the future worth now? Business planning
BUSI Financial Management Time Value of Money 1 Time Value of Money (TVM) Present value and future value how much is $1 now worth in the future? how much is $1 in the future worth now? Business planning
Appendix. Time Value of Money. Financial Accounting, IFRS Edition Weygandt Kimmel Kieso. Appendix C- 1
 C Time Value of Money C- 1 Financial Accounting, IFRS Edition Weygandt Kimmel Kieso C- 2 Study Objectives 1. Distinguish between simple and compound interest. 2. Solve for future value of a single amount.
C Time Value of Money C- 1 Financial Accounting, IFRS Edition Weygandt Kimmel Kieso C- 2 Study Objectives 1. Distinguish between simple and compound interest. 2. Solve for future value of a single amount.
Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets
 2 Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets The Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization worksheets are useful in applications where the cash flows are equal, evenly spaced, and either all inflows or
2 Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets The Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization worksheets are useful in applications where the cash flows are equal, evenly spaced, and either all inflows or
Chapter 4. Time Value of Money
 Chapter 4 Time Value of Money Learning Goals 1. Discuss the role of time value in finance, the use of computational aids, and the basic patterns of cash flow. 2. Understand the concept of future value
Chapter 4 Time Value of Money Learning Goals 1. Discuss the role of time value in finance, the use of computational aids, and the basic patterns of cash flow. 2. Understand the concept of future value
CALCULATOR HINTS ANNUITIES
 CALCULATOR HINTS ANNUITIES CALCULATING ANNUITIES WITH THE FINANCE APP: Select APPS and then press ENTER to open the Finance application. SELECT 1: TVM Solver The TVM Solver displays the time-value-of-money
CALCULATOR HINTS ANNUITIES CALCULATING ANNUITIES WITH THE FINANCE APP: Select APPS and then press ENTER to open the Finance application. SELECT 1: TVM Solver The TVM Solver displays the time-value-of-money
2. How would (a) a decrease in the interest rate or (b) an increase in the holding period of a deposit affect its future value? Why?
 CHAPTER 3 CONCEPT REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Will a deposit made into an account paying compound interest (assuming compounding occurs once per year) yield a higher future value after one period than an equal-sized
CHAPTER 3 CONCEPT REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Will a deposit made into an account paying compound interest (assuming compounding occurs once per year) yield a higher future value after one period than an equal-sized
HOW TO CALCULATE PRESENT VALUES
 Chapter 2 HOW TO CALCULATE PRESENT VALUES Brealey, Myers, and Allen Principles of Corporate Finance 11th Edition McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2014 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 2 HOW TO CALCULATE PRESENT VALUES Brealey, Myers, and Allen Principles of Corporate Finance 11th Edition McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2014 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
BEST INTEREST RATE. To convert a nominal rate to an effective rate, press
 FINANCIAL COMPUTATIONS George A. Jahn Chairman, Dept. of Mathematics Palm Beach Community College Palm Beach Gardens Location http://www.pbcc.edu/faculty/jahng/ The TI-83 Plus and TI-84 Plus have a wonderful
FINANCIAL COMPUTATIONS George A. Jahn Chairman, Dept. of Mathematics Palm Beach Community College Palm Beach Gardens Location http://www.pbcc.edu/faculty/jahng/ The TI-83 Plus and TI-84 Plus have a wonderful
Using Financial and Business Calculators. Daniel J. Borgia
 Using Financial and Business Calculators Daniel J. Borgia Table of Contents Texas Instruments (TI) BA-35 SOLAR......................................1 Texas Instruments (TI) BA II PLUS........................................11
Using Financial and Business Calculators Daniel J. Borgia Table of Contents Texas Instruments (TI) BA-35 SOLAR......................................1 Texas Instruments (TI) BA II PLUS........................................11
TIME VALUE OF MONEY. Return of vs. Return on Investment: We EXPECT to get more than we invest!
 TIME VALUE OF MONEY Return of vs. Return on Investment: We EXPECT to get more than we invest! Invest $1,000 it becomes $1,050 $1,000 return of $50 return on Factors to consider when assessing Return on
TIME VALUE OF MONEY Return of vs. Return on Investment: We EXPECT to get more than we invest! Invest $1,000 it becomes $1,050 $1,000 return of $50 return on Factors to consider when assessing Return on
Interest Rates and Bond Valuation
 Interest Rates and Bond Valuation Chapter 6 Key Concepts and Skills Know the important bond features and bond types Understand bond values and why they fluctuate Understand bond ratings and what they mean
Interest Rates and Bond Valuation Chapter 6 Key Concepts and Skills Know the important bond features and bond types Understand bond values and why they fluctuate Understand bond ratings and what they mean
380.760: Corporate Finance. Financial Decision Making
 380.760: Corporate Finance Lecture 2: Time Value of Money and Net Present Value Gordon Bodnar, 2009 Professor Gordon Bodnar 2009 Financial Decision Making Finance decision making is about evaluating costs
380.760: Corporate Finance Lecture 2: Time Value of Money and Net Present Value Gordon Bodnar, 2009 Professor Gordon Bodnar 2009 Financial Decision Making Finance decision making is about evaluating costs
TT03 Financial Calculator Tutorial And Key Time Value of Money Formulas November 6, 2007
 TT03 Financial Calculator Tutorial And Key Time Value of Money Formulas November 6, 2007 The purpose of this tutorial is to help students who use the HP 17BII+, and HP10bll+ calculators understand how
TT03 Financial Calculator Tutorial And Key Time Value of Money Formulas November 6, 2007 The purpose of this tutorial is to help students who use the HP 17BII+, and HP10bll+ calculators understand how
Solutions to Time value of money practice problems
 Solutions to Time value of money practice problems Prepared by Pamela Peterson Drake 1. What is the balance in an account at the end of 10 years if $2,500 is deposited today and the account earns 4% interest,
Solutions to Time value of money practice problems Prepared by Pamela Peterson Drake 1. What is the balance in an account at the end of 10 years if $2,500 is deposited today and the account earns 4% interest,
CHAPTER 5 INTRODUCTION TO VALUATION: THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY
 CHAPTER 5 INTRODUCTION TO VALUATION: THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY 1. The simple interest per year is: $5,000.08 = $400 So after 10 years you will have: $400 10 = $4,000 in interest. The total balance will be
CHAPTER 5 INTRODUCTION TO VALUATION: THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY 1. The simple interest per year is: $5,000.08 = $400 So after 10 years you will have: $400 10 = $4,000 in interest. The total balance will be
10.3 Future Value and Present Value of an Ordinary General Annuity
 360 Chapter 10 Annuities 10.3 Future Value and Present Value of an Ordinary General Annuity 29. In an ordinary general annuity, payments are made at the end of each payment period and the compounding period
360 Chapter 10 Annuities 10.3 Future Value and Present Value of an Ordinary General Annuity 29. In an ordinary general annuity, payments are made at the end of each payment period and the compounding period
Chapter 4. The Time Value of Money
 Chapter 4 The Time Value of Money 4-2 Topics Covered Future Values and Compound Interest Present Values Multiple Cash Flows Perpetuities and Annuities Inflation and Time Value Effective Annual Interest
Chapter 4 The Time Value of Money 4-2 Topics Covered Future Values and Compound Interest Present Values Multiple Cash Flows Perpetuities and Annuities Inflation and Time Value Effective Annual Interest
hp calculators HP 17bII+ Discounting & Discounted Cash Flow Analysis It's About Time The Financial Registers versus Discounted Cash Flow
 HP 17bII+ Discounting & Discounted Cash Flow Analysis It's About Time The Financial Registers versus Discounted Cash Flow Discounting a Single Sum Discounting and Compounding Discounting a Series of Sums
HP 17bII+ Discounting & Discounted Cash Flow Analysis It's About Time The Financial Registers versus Discounted Cash Flow Discounting a Single Sum Discounting and Compounding Discounting a Series of Sums
3. Time value of money. We will review some tools for discounting cash flows.
 1 3. Time value of money We will review some tools for discounting cash flows. Simple interest 2 With simple interest, the amount earned each period is always the same: i = rp o where i = interest earned
1 3. Time value of money We will review some tools for discounting cash flows. Simple interest 2 With simple interest, the amount earned each period is always the same: i = rp o where i = interest earned
USING THE SHARP EL 738 FINANCIAL CALCULATOR
 USING THE SHARP EL 738 FINANCIAL CALCULATOR Basic financial examples with financial calculator steps Prepared by Colin C Smith 2010 Some important things to consider 1. These notes cover basic financial
USING THE SHARP EL 738 FINANCIAL CALCULATOR Basic financial examples with financial calculator steps Prepared by Colin C Smith 2010 Some important things to consider 1. These notes cover basic financial
Chapter 3. Understanding The Time Value of Money. Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1
 Chapter 3 Understanding The Time Value of Money Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1 Time Value of Money A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future. The sooner your money can earn interest,
Chapter 3 Understanding The Time Value of Money Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1 Time Value of Money A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future. The sooner your money can earn interest,
Using Financial And Business Calculators. Daniel J. Borgia
 Using Financial And Business Calculators Daniel J. Borgia August 2000 Table of Contents I. Texas Instruments BA-35 SOLAR II. Texas Instruments BAII PLUS III. Hewlett Packard 12C IV. Hewlett Packard 17BII..
Using Financial And Business Calculators Daniel J. Borgia August 2000 Table of Contents I. Texas Instruments BA-35 SOLAR II. Texas Instruments BAII PLUS III. Hewlett Packard 12C IV. Hewlett Packard 17BII..
CHAPTER 5. Interest Rates. Chapter Synopsis
 CHAPTER 5 Interest Rates Chapter Synopsis 5.1 Interest Rate Quotes and Adjustments Interest rates can compound more than once per year, such as monthly or semiannually. An annual percentage rate (APR)
CHAPTER 5 Interest Rates Chapter Synopsis 5.1 Interest Rate Quotes and Adjustments Interest rates can compound more than once per year, such as monthly or semiannually. An annual percentage rate (APR)
Mathematics. Rosella Castellano. Rome, University of Tor Vergata
 and Loans Mathematics Rome, University of Tor Vergata and Loans Future Value for Simple Interest Present Value for Simple Interest You deposit E. 1,000, called the principal or present value, into a savings
and Loans Mathematics Rome, University of Tor Vergata and Loans Future Value for Simple Interest Present Value for Simple Interest You deposit E. 1,000, called the principal or present value, into a savings
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation
 BUAD 100x Foundations of Finance Discounted Cash Flow Valuation September 28, 2009 Review Introduction to corporate finance What is corporate finance? What is a corporation? What decision do managers make?
BUAD 100x Foundations of Finance Discounted Cash Flow Valuation September 28, 2009 Review Introduction to corporate finance What is corporate finance? What is a corporation? What decision do managers make?
Chapter 6 Contents. Principles Used in Chapter 6 Principle 1: Money Has a Time Value.
 Chapter 6 The Time Value of Money: Annuities and Other Topics Chapter 6 Contents Learning Objectives 1. Distinguish between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due, and calculate present and future values
Chapter 6 The Time Value of Money: Annuities and Other Topics Chapter 6 Contents Learning Objectives 1. Distinguish between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due, and calculate present and future values
T12-1 REVIEW EXERCISES CHAPTER 12 SECTION I
 T12-1 REVIEW EXERCISES CHAPTER 12 SECTION I Use Table 12-1 to calculate the future value of the following ordinary annuities: Annuity Payment Time Nominal Interest Future Value Payment Frequency Period
T12-1 REVIEW EXERCISES CHAPTER 12 SECTION I Use Table 12-1 to calculate the future value of the following ordinary annuities: Annuity Payment Time Nominal Interest Future Value Payment Frequency Period
2. Determine the appropriate discount rate based on the risk of the security
 Fixed Income Instruments III Intro to the Valuation of Debt Securities LOS 64.a Explain the steps in the bond valuation process 1. Estimate the cash flows coupons and return of principal 2. Determine the
Fixed Income Instruments III Intro to the Valuation of Debt Securities LOS 64.a Explain the steps in the bond valuation process 1. Estimate the cash flows coupons and return of principal 2. Determine the
Chapter 4. Time Value of Money. Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4 Time Value of Money Learning Goals 1. Discuss the role of time value in finance, the use of computational aids, and the basic patterns of cash flow. 2. Understand the concept of future value
Chapter 4 Time Value of Money Learning Goals 1. Discuss the role of time value in finance, the use of computational aids, and the basic patterns of cash flow. 2. Understand the concept of future value
Chapter 4. Time Value of Money. Learning Goals. Learning Goals (cont.)
 Chapter 4 Time Value of Money Learning Goals 1. Discuss the role of time value in finance, the use of computational aids, and the basic patterns of cash flow. 2. Understand the concept of future value
Chapter 4 Time Value of Money Learning Goals 1. Discuss the role of time value in finance, the use of computational aids, and the basic patterns of cash flow. 2. Understand the concept of future value
3. If an individual investor buys or sells a currently owned stock through a broker, this is a primary market transaction.
 Spring 2012 Finance 3130 Sample Exam 1A Questions for Review 1. The form of organization for a business is an important issue, as this decision has very significant effect on the income and wealth of the
Spring 2012 Finance 3130 Sample Exam 1A Questions for Review 1. The form of organization for a business is an important issue, as this decision has very significant effect on the income and wealth of the
The values in the TVM Solver are quantities involved in compound interest and annuities.
 Texas Instruments Graphing Calculators have a built in app that may be used to compute quantities involved in compound interest, annuities, and amortization. For the examples below, we ll utilize the screens
Texas Instruments Graphing Calculators have a built in app that may be used to compute quantities involved in compound interest, annuities, and amortization. For the examples below, we ll utilize the screens
Dick Schwanke Finite Math 111 Harford Community College Fall 2015
 Using Technology to Assist in Financial Calculations Calculators: TI-83 and HP-12C Software: Microsoft Excel 2007/2010 Session #4 of Finite Mathematics 1 TI-83 / 84 Graphing Calculator Section 5.5 of textbook
Using Technology to Assist in Financial Calculations Calculators: TI-83 and HP-12C Software: Microsoft Excel 2007/2010 Session #4 of Finite Mathematics 1 TI-83 / 84 Graphing Calculator Section 5.5 of textbook
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Ch. 5 Mathematics of Finance 5.1 Compound Interest SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) What is the effective
Ch. 5 Mathematics of Finance 5.1 Compound Interest SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) What is the effective
THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY
 QUANTITATIVE METHODS THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY Reading 5 http://proschool.imsindia.com/ 1 Learning Objective Statements (LOS) a. Interest Rates as Required rate of return, Discount Rate and Opportunity Cost
QUANTITATIVE METHODS THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY Reading 5 http://proschool.imsindia.com/ 1 Learning Objective Statements (LOS) a. Interest Rates as Required rate of return, Discount Rate and Opportunity Cost
Solutions to Problems: Chapter 5
 Solutions to Problems: Chapter 5 P5-1. Using a time line LG 1; Basic a, b, and c d. Financial managers rely more on present value than future value because they typically make decisions before the start
Solutions to Problems: Chapter 5 P5-1. Using a time line LG 1; Basic a, b, and c d. Financial managers rely more on present value than future value because they typically make decisions before the start
Present Value and Annuities. Chapter 3 Cont d
 Present Value and Annuities Chapter 3 Cont d Present Value Helps us answer the question: What s the value in today s dollars of a sum of money to be received in the future? It lets us strip away the effects
Present Value and Annuities Chapter 3 Cont d Present Value Helps us answer the question: What s the value in today s dollars of a sum of money to be received in the future? It lets us strip away the effects
Time Value of Money PAPER 3A: COST ACCOUNTING CHAPTER 2 BY: CA KAPILESHWAR BHALLA
 Time Value of Money 1 PAPER 3A: COST ACCOUNTING CHAPTER 2 BY: CA KAPILESHWAR BHALLA Learning objectives 2 Understand the Concept of time value of money. Understand the relationship between present and
Time Value of Money 1 PAPER 3A: COST ACCOUNTING CHAPTER 2 BY: CA KAPILESHWAR BHALLA Learning objectives 2 Understand the Concept of time value of money. Understand the relationship between present and
Dick Schwanke Finite Math 111 Harford Community College Fall 2013
 Annuities and Amortization Finite Mathematics 111 Dick Schwanke Session #3 1 In the Previous Two Sessions Calculating Simple Interest Finding the Amount Owed Computing Discounted Loans Quick Review of
Annuities and Amortization Finite Mathematics 111 Dick Schwanke Session #3 1 In the Previous Two Sessions Calculating Simple Interest Finding the Amount Owed Computing Discounted Loans Quick Review of
Standard 5: The student will analyze the costs and benefits of saving and investing.
 TEACHER GUIDE 5.2 SAVING AND INVESTING PAGE 1 Standard 5: The student will analyze the costs and benefits of saving and investing. The Rule of 72 Priority Academic Student Skills Personal Financial Literacy
TEACHER GUIDE 5.2 SAVING AND INVESTING PAGE 1 Standard 5: The student will analyze the costs and benefits of saving and investing. The Rule of 72 Priority Academic Student Skills Personal Financial Literacy
Engineering Economy. Time Value of Money-3
 Engineering Economy Time Value of Money-3 Prof. Kwang-Kyu Seo 1 Chapter 2 Time Value of Money Interest: The Cost of Money Economic Equivalence Interest Formulas Single Cash Flows Equal-Payment Series Dealing
Engineering Economy Time Value of Money-3 Prof. Kwang-Kyu Seo 1 Chapter 2 Time Value of Money Interest: The Cost of Money Economic Equivalence Interest Formulas Single Cash Flows Equal-Payment Series Dealing
LO.a: Interpret interest rates as required rates of return, discount rates, or opportunity costs.
 LO.a: Interpret interest rates as required rates of return, discount rates, or opportunity costs. 1. The minimum rate of return that an investor must receive in order to invest in a project is most likely
LO.a: Interpret interest rates as required rates of return, discount rates, or opportunity costs. 1. The minimum rate of return that an investor must receive in order to invest in a project is most likely
PowerPoint. to accompany. Chapter 5. Interest Rates
 PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 5 Interest Rates 5.1 Interest Rate Quotes and Adjustments To understand interest rates, it s important to think of interest rates as a price the price of using money. When
PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 5 Interest Rates 5.1 Interest Rate Quotes and Adjustments To understand interest rates, it s important to think of interest rates as a price the price of using money. When
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES. For examination purposes, the following amendments shall take effect from 3 June 2011: 1. Chapter 12, Page 329, Chapter Outline
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ChFC01 Fundamentals Of Financial Planning And Investments Date Of Issue : 3 May 2011 [Applicable to 1 st Edition (2003), Re-printed March 2006 version and earlier] The following amendments
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ChFC01 Fundamentals Of Financial Planning And Investments Date Of Issue : 3 May 2011 [Applicable to 1 st Edition (2003), Re-printed March 2006 version and earlier] The following amendments
Chapter 21: Savings Models
 October 16, 2013 Last time Arithmetic Growth Simple Interest Geometric Growth Compound Interest A limit to Compounding Problems Question: I put $1,000 dollars in a savings account with 2% nominal interest
October 16, 2013 Last time Arithmetic Growth Simple Interest Geometric Growth Compound Interest A limit to Compounding Problems Question: I put $1,000 dollars in a savings account with 2% nominal interest
Finance 331 Corporate Financial Management Week 1 Week 3 Note: For formulas, a Texas Instruments BAII Plus calculator was used.
 Chapter 1 Finance 331 What is finance? - Finance has to do with decisions about money and/or cash flows. These decisions have to do with money being raised or used. General parts of finance include: -
Chapter 1 Finance 331 What is finance? - Finance has to do with decisions about money and/or cash flows. These decisions have to do with money being raised or used. General parts of finance include: -
Key Concepts and Skills. Multiple Cash Flows Future Value Example 6.1. Chapter Outline. Multiple Cash Flows Example 2 Continued
 6 Calculators Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Key Concepts and Skills Be able to compute the future value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute the present value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute
6 Calculators Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Key Concepts and Skills Be able to compute the future value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute the present value of multiple cash flows Be able to compute
