Modified surface plasmonic waveguide formed by nanometric parallel lines
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Rosalyn Chambers
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
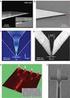
1 Modified surface plasmonic waveguide formed by nanometric parallel lines Xue Wen-Rui( 薛文瑞 ), Guo Ya-Nan( 郭亚楠 ), and Zhang Wen-Mei( 张文梅 ) College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Shanxi University, Taiyuan , China (Received 20 March 2009; revised manuscript received 29 June 2009) In this paper, two kinds of modified surface plasmonic waveguides formed by nanometric parallel lines are proposed. The finite-difference frequency-domain method is used to study propagation properties of the fundamental mode supported by these surface plasmonic waveguide structures. Results show that the transverse magnetic field of the fundamental mode is mainly distributed in the face to face region formed by two rods. With the same geometrical parameters and the same working wavelength of nm, in the case of rods with a triangular cross-section, the degree of localization of field is strong, i.e. the mode area is small, but the fraction of the modal power in the metal increases, so the effective index increases and the propagation length of the mode decreases. With the same geometrical parameters, relative to the case of a working wavelength of nm, when working wavelength is large, the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution is large, i.e. the degree of localization of field is weak, and the interaction of field and silver is weak too, then the effective index decreases, so the propagation length increases. The rounded radii of rods have a great influence on the performance of the surface plasmonic waveguides with rounded triangular cross-sections, but have little influence on the performance of surface plasmonic waveguides with rounded square cross-sections. Since the distribution of transverse magnetic field, effective index, propagation length and the mode area can be adjusted by the geometrical parameters, this kind of modified surface plasmonic waveguide can be applied to the field of photonic device integration and sensors. Keywords: surface plasmon polaritons, optical waveguides PACC: 7320M, 4280L 1. Introduction The interaction of light with matter in nanostructured metallic structures has led to a new branch of photonics called plasmonics. Surface plasmonic waveguides (SPWs) are basic devices in plasmonics. Along the surface of metals, such waveguides guide light in the form of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) with lateral dimensions on the order of subwavelength. Because this kind of waveguide is compatible with existing fabrication technologies, it is believed that these waveguides can be used to overcome the diffraction limit, to offer the possibility of integration of electronics and photonics on the same chip and to fulfil the further miniaturization of photonic devices and high integration density of photonic chips. [1 4] By now, many SPWs have been studied theoretically and experimentally. [5 25] Because wedge SPWs [17,20] can provide relatively long propagation length as well as a strong mode confinement, they have attracted much attention. As suggested by Takahara et al., [5] one can construct a kind of SPW by embedding nanometric parallel lines with circular cross sections in dielectric background. This kind of SPW can be regarded as a combination of two wedge SPWs. Can the cross section of the parallel lines be changed to another wedged one, for example, a triangular or square cross section? What are the influences on their performance with different cross sections of the parallel lines? Up to now, these questions have not been analysed yet and are still open. In this paper, two kinds of modified SPWs formed by nanometric parallel lines are studied. The finitedifference frequency-domain (FDFD) method [26 28] is used to study their propagation properties. Distribution of transverse magnetic field intensity, effective index, propagation length and mode area of the fundamental mode with longer propagation length supported by these SPW structures will be discussed. 2. Structure and simulation method The cross sections of the proposed SPWs formed by nanometric parallel lines in this paper are shown in Figs. 1(a) and 1(b). The first SPW is composed of two Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No ) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, China (Grant No ). Corresponding author. wrxue@sxu.edu.cn c 2010 Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd
2 metal rods with a rounded triangular cross section. The second SPW is composed of two metal rods with a rounded square cross section. For comparison, the third SPW which is composed of two metal rods with a circular cross section, proposed by Takahara et al., [5] is shown in Fig. 1(c). These metal rods are all embedded in dielectric background. In Figs. 1(a), 1(b) and 1(c), 2c is the centric distance of the two rods, a is the radius or the distance from the centre to the vertex of the rod, r is the rounded radius of the rod; ε m is the dielectric constant of metal rods, and ε clad is the dielectric constant of the background. In the calculation, the primary material is chosen to be silver and the dielectric constant ε m is chosen to be j (λ = nm), j (λ = nm), and j (λ = nm). [29] To support the nanometric parallel lines, the background material is chosen to be SiO 2, and its dielectric constant ε clad is Because the value of ε clad is real and about one order smaller than the real part of ε m, we neglected its dispersion here. Fig. 1. Cross sections of the surface plasmonic waveguides formed by (a) triangular, (b) square and (c) circular [5] nanometric parallel lines. Here, 2c is the centric distance of the two rods, a is the radius or the distance from the centre to the vertex of the rod, r is the rounded radius of the rod. ε m is the dielectric constant of metal rods, and ε clad is the dielectric constant of the background. In this paper, the 2D full-vectorial FDFD method [26 28] is used to study the propagation properties of the SPW structures. Given the geometrical parameter, electromagnetic parameter and working wavelength, the propagation constant, effective index and the distribution of magnetic field of each mode at the working wavelength can be obtained by solving the eigenvalue equation using Arnoldi arithmetic. [30] lattices are adopted to discretize the whole computational domain, and 20 layers of them are perfectly matched layer absorbing boundary layers (APML) that are used to truncate the lattices. The spatial discretization distance is x = y = 1.0 nm. The accuracy of the FDFD code adopted in this paper has been validated in our previous work. [22 24] 3. Results and discussions Mode characteristics of the surface plasmonic waveguide with three kinds of cross sections shown in Fig. 1 are investigated first. It is found that there are many modes that can be supported by these kinds of SPWs, but the fundamental mode is more suitable for guiding electromagnetic waves. The distribution of transverse magnetic field intensity H t 2 of the fundamental mode, in the case of a = 75 nm, c = 103 nm, r = 5 nm and λ = nm, is shown in Figs. 2(a), 2(b), and 2(c). Here the transverse magnetic field intensity is defined as H t 2 = H 2 x + H 2 y; H x and H y are components of the magnetic field. It can be seen from Figs. 2(a), 2(b), and 2(c) that the transverse magnetic field of the fundamental mode is mainly distributed in the face to face region which is formed by two rods. In the three cases of rods with triangular, square and circular cross sections when a = 75 nm, c = 103 nm, r = 5 nm and λ = nm, the two corner angles are smallest and the two corner tips are sharpest in the case of rods with triangular cross section, so the degree of localization of field is the largest. Since effective index Re(n eff ), propagation length L prop and mode area A m are the three most important physical quantities that describe the propagation properties of SPWs, we next investigate the dependence of Re(n eff ), L prop and A m of the modes shown
3 in Fig. 2 on the geometrical parameter c. Here Re(n eff ) is defined as Re(β)λ/2π, L prop defined as L prop = 1/Im(β), and the A m defined as the occupied area of the transverse magnetic field intensity H t 2 when its altitude decreases from 100% to 10%. Fig. 2. Distribution of transverse magnetic field intensity of the SPWs with (a) rounded triangular cross section, (b) rounded square cross section and (c) circular cross section for a = 75 nm, c = 103 nm and r = 5 nm at λ = nm. The variations of Re(n eff ), L prop and A m with c in the three cases of a = 50, 75 and 100 nm are shown in Figs. 3(a), 3(b), and 3(c) respectively. It can be seen from these figures that curves can be obviously separated into three groups according to different a. In each group, Re(n eff ) decreases as c increases; however, L prop and A m increase as c increases. The position of curves in each group is influenced by the cross section of rods. We also find that there is a trade-off between the degree of localization of field and the propagation length. [1] In the case of rods with triangular cross section, the degree of localization of field is strong, i.e. the mode area is small, but the fraction of the modal power in the metal increases, the effective index increases and the propagation length of the mode decreases. In the case of rods with circular cross section, the degree of localization of field is weak, i.e. the mode area is large, but the fraction of the modal power in the metal decreases, the effective index decreases and the propagation length of the mode increases. Fig. 3. Dependence of (a) effective index, (b) propagation length and (c) mode area of different SPWs on c when r = 5 nm and λ = nm. Thirdly, in order to find out the dependence of transverse magnetic field distribution of the modes shown in Fig. 2 on the working wavelength, the field intensity distributions for different cross sections of rods with a = 75 nm, c = 103 nm and r = 5 nm at λ = nm and nm are calculated respectively. Here we extend the calculation to a longer wavelength, 800 nm, where vertical-cavity surfaceemitting lasers (VCSELs) are available. The results obtained are shown in Fig. 4. It can be seen from Fig. 4 that the transverse magnetic field distribution is similar to that in Fig. 2. Compared with the case of Figs. 2(a), 2(b), and 2(c), in the case of Figs. 4(a), 4(c), and 4(e), the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution becomes larger. However, in the case of Figs. 4(b), 4(d), and 4(f), the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution becomes smaller. Figures 5(a) 5(c), 5(d) 5(f) and 5(g) 5(i) also show the dependences of Re(n eff ), L prop and A m on c for a = 75 nm, r = 5 nm, λ = nm, nm and nm. It can be seen that the curves of Re(n eff ), L prop and A m could also be separated into three groups according to different cross sections. In each group, Re(n eff ) decreases with the increase of c; however, L prop and A m increase with the increase of c
4 The working wavelength has a great influence on the position of the curves in these figures. We can also see from Figs. 5(d) 5(f) that curves for λ = nm are always at the uppermost of each group of curves. This phenomenon can be explained by the different transverse magnetic field distributions at different wavelengths. Compared to the case of λ = nm, when λ is smaller, the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution is small, i.e. the degree of localization of field is strong, and the interaction of field and silver is strong too, then the effective index increases, and so the propagation length decreases. However, when λ is larger, the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution is larger, i.e. the degree of localization of field is weak, and the interaction of field and silver is weak too, then the effective index decreases, and so the propagation length increases. Fig. 4. Distributions of transverse magnetic field intensity of the SPWs for (a) and (b) rounded triangular cross section, (c) and (d) rounded square cross section, and (e) and (f) circular cross section when a = 75 nm, c = 103 nm and r = 5 nm at λ = nm and nm. Finally, let us investigate the dependence of the distribution of transverse magnetic field intensity, effective index, propagation length and mode area of the proposed SPWs on the rounded radius r. Distributions of transverse magnetic field intensity of SPWs with rounded triangular cross section and with rounded square cross section, for a = 100 nm, c = 128 nm, r = 5 nm or 10 nm and λ = nm, are shown in Fig. 6. It can be seen that the transverse magnetic field distribution of SPWs with the same cross section is similar to each other. Compared to the case of r = 5 nm (Figs. 6(a) and 6(c)), in the case of r = 10 nm (Figs. 6(b) and 6(d)), the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution increases slightly
5 Fig. 5. Dependence of effective index (a) (c), propagation length (d) (f) and mode area (g) (i) of different SPWs on c for a = 75 nm, r = 5 nm, λ = nm, nm and nm. Fig. 6. Distributions of transverse magnetic field intensity of the SPWs with rounded triangular cross section (a) and (b), rounded square cross-section (c) and (d) when a = 100 nm, c = 128 nm, r = 5 nm or 10 nm and λ = nm. Dependence of effective index, propagation length and mode area of SPWs with rounded triangular cross section and with rounded square cross section on c, for the case of a = 100 nm, r = 5 nm or 10 nm and λ = nm, is shown in Fig. 7. For comparison, curves corresponding to the SPW with circular cross section and a = 100 nm are shown also in Fig. 7. It can be seen that the curves could be separated into three groups according to the cross section. In each group, when c increases, effective index decreases, but propagation length and mode area increase. The curve corresponding to the SPW with r = 10 nm takes on a smaller effective index, but larger propagation length and mode area
6 Fig. 7. Dependence of effective index (a), propagation length (b) and mode area (c) of different SPWs on c when a = 100 nm, λ = nm, r = 5 nm and 10 nm. From Figs. 6 and 7, one can find that the rounded radius r has a great influence on propagation properties of the SPW with rounded triangular cross section, but has little influence on the propagation properties of the SPW with rounded square cross section. This phenomenon can be explained by the coupling intensity of the SPPs propagating along the nanometric parallel lines. Because the corner angle of the unrounded triangular cross section is smaller than that of the unrounded squre cross section, the tip of the former is sharper than the latter. When the face to face tip of the nanometric parallel lines are rounded, the change of coupling intensity of the SPPs propagating along the nanometric parallel lines in the case of triangular cross section is larger than that in the case of square cross section, so the rounded radius r has a great influence on the propagation properties of the SPW with rounded triangular cross section than on that with rounded square cross section. 4. Conclusion In this paper, we have designed two modified surface plasmonic waveguides formed by nanometric parallel lines. The numerical calculations show: (i) The transverse magnetic field of the fundamental mode is mainly distributed in the face to face region formed by two rods. This mode is suitable for guiding electromagnetic waves. (ii) With the same geometrical parameters at λ = nm, in the case of rods with triangular cross section, the degree of localization of field is strong, i.e. the mode area is small, but the fraction of the modal power in the metal increases, the effective index increases, and the propagation length of the mode decreases. (iii) With the same geometrical parameters, as compared with the case of λ = nm, when λ is small, the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution is small, i.e. the degree of localization of field is strong, and the interaction of field and silver is strong too, then the effective index increases, and so the propagation length decreases. However, when λ is large, the mode area of transverse magnetic field distribution is large, i.e. the degree of localization of field is weak, and the interaction of field and silver is weak too, then the effective index decreases, and so the propagation length increases. (iv) The rounded radius r has a great influence on the propagation properties of the SPW with rounded triangular cross section, but has little influence on those of the SPW with rounded square cross section. Since distribution of transverse magnetic field, effective index, propagation length and the mode area can be adjusted by the geometrical parameters, this kind of modified SPW can be applied to the field of photonic device integration and sensors. References [1] Barnes W L, Dereux A and Ebbesen T W 2003 Nature [2] Ozbay E 2006 Science [3] Bozhevolnyi S I, Volkov V S, Devaux E, Laluet J Y and Ebbesen T W 2006 Nature [4] Maier S A 2006 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant [5] Takahara J, Yamagishi S, Taki H, Morimoto A and Kobayashi T 1997 Opt. Lett [6] Berini P 1999 Opt. Lett
7 [7] Maier S A, Kik P G, Atwater H A, Meltzer S, Harel E, Koel B E and Requicha A G 2003 Nat. Mater [8] Pile D F P and Gramotnev D K 2004 Opt. Lett [9] Wang B and Wang G P 2004 Appl. Phys. Lett [10] Pile D F P, Ogawa T, Gramotnev D K, Matsuzaki Y, Vermon K C, Yamaguchi K, Okamoto T, Haraguchi M and Fukui M 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett [11] Liu L, Han Z and He S 2005 Opt. Express [12] Wang G P and Wang B 2006 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B [13] Chen L, Wang B and Wang G P 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett [14] Jung J, Sondergaard T and Bozhevolnyi S I 2007 Phys. Rev. B [15] Lee I, Jung J, Park J, Kim H and Lee B 2007 Opt. Express [16] Wang B and Wang G P 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett [17] Moreno E, Rodrigo S G, Bozhevolnyi S I, Moreno L M and Vidal F J G 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett [18] Zhang H X, Gu Y and Gong Q H 2008 Chin. Phys. B [19] Guo J and Adato R 2008 Opt. Express [20] Arbel D and Orenstein M 2008 Opt. Express [21] Boltasseva A, Volkov V S, Nielsen R B, Moreno E, Rodrigo S G and Bozhevolnyi S I 2008 Opt. Express [22] Xue W R, Guo Y N, Li P and Zhang W M 2008 Opt. Express [23] Xue W R, Guo Y N and Zhang W M 2009 Chin. Phys. B [24] Guo Y N, Xue W R and Zhang W M 2009 Acta Phys. Sin (in Chinese) [25] Dintinger J and Martin J F 2009 Opt. Express [26] Zhu Z and Brown T G 2002 Opt. Express [27] Guo S P, Wu F, Albin S, Tai H and Rogowski R S 2004 Opt. Express [28] Yu C P and Chang H C 2004 Opt. Express [29] Johnson P B and Christy R W 1972 Phys. Rev. B [30] Arnoldi W E 1951 Quart. Appl. Math
Numerical Analysis of Perforated Microring Resonator Based Refractive Index Sensor
 Numerical Analysis of Perforated Microring Resonator Based Refractive Index Sensor M. Gabalis *1, D. Urbonas 1, and R. Petruškevičius 1 1 Institute of Physics of Center for Physical Sciences and Technology,
Numerical Analysis of Perforated Microring Resonator Based Refractive Index Sensor M. Gabalis *1, D. Urbonas 1, and R. Petruškevičius 1 1 Institute of Physics of Center for Physical Sciences and Technology,
Plate waves in phononic crystals slabs
 Acoustics 8 Paris Plate waves in phononic crystals slabs J.-J. Chen and B. Bonello CNRS and Paris VI University, INSP - 14 rue de Lourmel, 7515 Paris, France chen99nju@gmail.com 41 Acoustics 8 Paris We
Acoustics 8 Paris Plate waves in phononic crystals slabs J.-J. Chen and B. Bonello CNRS and Paris VI University, INSP - 14 rue de Lourmel, 7515 Paris, France chen99nju@gmail.com 41 Acoustics 8 Paris We
Plasmonic coaxial waveguide-cavity devices
 Plasmonic coaxial waveguide-cavity devices Amirreza Mahigir, 1,2 Pouya Dastmalchi, 1,2 Wonseok Shin, 3 Shanhui Fan, 3 and Georgios Veronis 1,2, 1 School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,
Plasmonic coaxial waveguide-cavity devices Amirreza Mahigir, 1,2 Pouya Dastmalchi, 1,2 Wonseok Shin, 3 Shanhui Fan, 3 and Georgios Veronis 1,2, 1 School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,
Effects of node buffer and capacity on network traffic
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 21, No. 9 (212) 9892 Effects of node buffer and capacity on network traffic Ling Xiang( 凌 翔 ) a), Hu Mao-Bin( 胡 茂 彬 ) b), and Ding Jian-Xun( 丁 建 勋 ) a) a) School of Transportation Engineering,
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 21, No. 9 (212) 9892 Effects of node buffer and capacity on network traffic Ling Xiang( 凌 翔 ) a), Hu Mao-Bin( 胡 茂 彬 ) b), and Ding Jian-Xun( 丁 建 勋 ) a) a) School of Transportation Engineering,
5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy
 5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy Resolution of optical microscope is limited by diffraction. Light going through an aperture makes diffraction
5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy Resolution of optical microscope is limited by diffraction. Light going through an aperture makes diffraction
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications
 Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
Metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguide devices for manipulating light at the nanoscale
 302 CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS / Vol. 7, No. 4 / April 10, 2009 Metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguide devices for manipulating light at the nanoscale Invited Paper Georgios Veronis 1, Zongfu Yu 2, Şükrü
302 CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS / Vol. 7, No. 4 / April 10, 2009 Metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguide devices for manipulating light at the nanoscale Invited Paper Georgios Veronis 1, Zongfu Yu 2, Şükrü
Axial Sensitivity Of A Cracked Probe Of A Scanning Near- Field Optical Microscope
 Proceedings of the World Congress on New Technologies (NewTech 05) Barcelona, Spain July 5-7, 05 Paper No. 38 Axial Sensitivity Of A Cracked Probe Of A Scanning Near- Field Optical Microscope Yu-Ching
Proceedings of the World Congress on New Technologies (NewTech 05) Barcelona, Spain July 5-7, 05 Paper No. 38 Axial Sensitivity Of A Cracked Probe Of A Scanning Near- Field Optical Microscope Yu-Ching
Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics
 Photonics Technical Note # 21 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric wave-guides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded
Photonics Technical Note # 21 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric wave-guides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded
Surface plasmon nanophotonics: optics below the diffraction limit
 Surface plasmon nanophotonics: optics below the diffraction limit Albert Polman Center for nanophotonics FOM-Institute AMOLF, Amsterdam Jeroen Kalkman Hans Mertens Joan Penninkhof Rene de Waele Teun van
Surface plasmon nanophotonics: optics below the diffraction limit Albert Polman Center for nanophotonics FOM-Institute AMOLF, Amsterdam Jeroen Kalkman Hans Mertens Joan Penninkhof Rene de Waele Teun van
Composite Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Made of Permalloy or Sendust and Effect of Sendust Particle Size on Absorption Characteristics
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 8, 2008 846 Composite Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Made of Permalloy or Sendust and Effect of Sendust Particle Size on Absorption Characteristics K. Sakai, Y. Wada, and S. Yoshikado
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 8, 2008 846 Composite Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Made of Permalloy or Sendust and Effect of Sendust Particle Size on Absorption Characteristics K. Sakai, Y. Wada, and S. Yoshikado
NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY WITH STM AND AFM PROBES
 Vol. 93 (1997) A CTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Scanning Probe Spectroscopy and Related Methods, Poznań 1997 NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY
Vol. 93 (1997) A CTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Scanning Probe Spectroscopy and Related Methods, Poznań 1997 NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY
Electronically Controlled Surface Plasmon Dispersion and Optical Transmission through Metallic Hole Arrays Using Liquid Crystal
 Electronically Controlled Surface Plasmon Dispersion and Optical Transmission through Metallic Hole Arrays Using Liquid Crystal NANO LETTERS 2008 Vol. 8, No. 1 281-286 Wayne Dickson,* Gregory A. Wurtz,
Electronically Controlled Surface Plasmon Dispersion and Optical Transmission through Metallic Hole Arrays Using Liquid Crystal NANO LETTERS 2008 Vol. 8, No. 1 281-286 Wayne Dickson,* Gregory A. Wurtz,
Routing of light in arbitrary directions inside a submicrometer-scale
 pubs.acs.org/nanolett Broadband Sharp 90-degree Bends and T Splitters in Plasmonic Coaxial Waveguides Wonseok Shin, Wenshan Cai, Peter B. Catrysse, Georgios Veronis, Mark L. Brongersma, and Shanhui Fan*,
pubs.acs.org/nanolett Broadband Sharp 90-degree Bends and T Splitters in Plasmonic Coaxial Waveguides Wonseok Shin, Wenshan Cai, Peter B. Catrysse, Georgios Veronis, Mark L. Brongersma, and Shanhui Fan*,
P. Lu, Sh. Huang and K. Jiang
 416 Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 33 (2013) 416-422 P. Lu, Sh. Huang and K. Jiang NUMERICAL ANALYSIS FOR THREE-DIMENSIONAL BULK METAL FORMING PROCESSES WITH ARBITRARILY SHAPED DIES USING THE RIGID/VISCO-PLASTIC
416 Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 33 (2013) 416-422 P. Lu, Sh. Huang and K. Jiang NUMERICAL ANALYSIS FOR THREE-DIMENSIONAL BULK METAL FORMING PROCESSES WITH ARBITRARILY SHAPED DIES USING THE RIGID/VISCO-PLASTIC
OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION
 OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Zafar Yasin OUTLINE - Introduction about Optical Fibers. - Main Characteristics of Fiber Optics Communication System. - Light propagation in an Optical Fiber. - Mode Analysis
OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Zafar Yasin OUTLINE - Introduction about Optical Fibers. - Main Characteristics of Fiber Optics Communication System. - Light propagation in an Optical Fiber. - Mode Analysis
Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs)
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 2, 2009 Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs) GRZEGORZ STEPNIAK *, LUKASZ MAKSYMIUK, JERZY SIUZDAK Institute of Telecommunications, Warsaw
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 2, 2009 Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs) GRZEGORZ STEPNIAK *, LUKASZ MAKSYMIUK, JERZY SIUZDAK Institute of Telecommunications, Warsaw
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 138, 647 660, 2013
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 138, 647 660, 2013 FAR-FIELD TUNABLE NANO-FOCUSING BASED ON METALLIC SLITS SURROUNDED WITH NONLINEAR- VARIANT WIDTHS AND LINEAR-VARIANT DEPTHS OF CIRCULAR DIELECTRIC
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 138, 647 660, 2013 FAR-FIELD TUNABLE NANO-FOCUSING BASED ON METALLIC SLITS SURROUNDED WITH NONLINEAR- VARIANT WIDTHS AND LINEAR-VARIANT DEPTHS OF CIRCULAR DIELECTRIC
Nano Optics: Overview of Research Activities. Sergey I. Bozhevolnyi SENSE, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, DENMARK
 Nano Optics: Overview of Research Activities SENSE, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, DENMARK Optical characterization techniques: Leakage Radiation Microscopy Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
Nano Optics: Overview of Research Activities SENSE, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, DENMARK Optical characterization techniques: Leakage Radiation Microscopy Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
A wave lab inside a coaxial cable
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
Modal Propagation Properties of Elliptical Core Optical Fibers Considering Stress-Optic Effects
 Modal Propagation Properties of Elliptical Core Optical Fibers Considering Stress-Optic Effects M. Shah Alam and Sarkar Rahat M. Anwar Abstract The effect of thermally induced stress on the modal properties
Modal Propagation Properties of Elliptical Core Optical Fibers Considering Stress-Optic Effects M. Shah Alam and Sarkar Rahat M. Anwar Abstract The effect of thermally induced stress on the modal properties
GPR Polarization Simulation with 3D HO FDTD
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Xi an, China, March 6, 00 999 GPR Polarization Simulation with 3D HO FDTD Jing Li, Zhao-Fa Zeng,, Ling Huang, and Fengshan Liu College of Geoexploration
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Xi an, China, March 6, 00 999 GPR Polarization Simulation with 3D HO FDTD Jing Li, Zhao-Fa Zeng,, Ling Huang, and Fengshan Liu College of Geoexploration
National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian University Xi an, Shaanxi 710071, China
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 76, 237 242, 2007 A BROADBAND CPW-FED T-SHAPE SLOT ANTENNA J.-J. Jiao, G. Zhao, F.-S. Zhang, H.-W. Yuan, and Y.-C. Jiao National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 76, 237 242, 2007 A BROADBAND CPW-FED T-SHAPE SLOT ANTENNA J.-J. Jiao, G. Zhao, F.-S. Zhang, H.-W. Yuan, and Y.-C. Jiao National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave
Simulation and Design of Printed Circuit Boards Utilizing Novel Embedded Capacitance Material
 Simulation and Design of Printed Circuit Boards Utilizing Novel Embedded Capacitance Material Yu Xuequan, Yan Hang, Zhang Gezi, Wang Haisan Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd Lujiazui Subpark, Pudong Software
Simulation and Design of Printed Circuit Boards Utilizing Novel Embedded Capacitance Material Yu Xuequan, Yan Hang, Zhang Gezi, Wang Haisan Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd Lujiazui Subpark, Pudong Software
NANOFLAM. Projet ANR Blanc 2011 BS0401001. Aide allouée: 337 000, durée 36+8 mois (fin : Mai 2015) Laboratoire H. Curien
 Laboratoire H. Curien Centre de Physique Théorique F. Courvoisier R. Stoian & T. Itina A. Couairon NANOFLAM Projet ANR Blanc 2011 BS0401001 Contrôle de la filamentation et de la génération de plasma avec
Laboratoire H. Curien Centre de Physique Théorique F. Courvoisier R. Stoian & T. Itina A. Couairon NANOFLAM Projet ANR Blanc 2011 BS0401001 Contrôle de la filamentation et de la génération de plasma avec
BROADBAND PHOTOCURRENT ENHANCEMENT IN LONGWAVE INFRARED QUANTUM DOT PHOTODETECTORS BY SUB-WAVELENGTH SURFACE GRATINGS
 Optics and Photonics Letters Vol. 6, No. 1 (2013) 1350002 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S1793528813500020 BROADBAND PHOTOCURRENT ENHANCEMENT IN LONGWAVE INFRARED QUANTUM
Optics and Photonics Letters Vol. 6, No. 1 (2013) 1350002 (6 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S1793528813500020 BROADBAND PHOTOCURRENT ENHANCEMENT IN LONGWAVE INFRARED QUANTUM
GLOBAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY: YSR DIST. Unit VII Fiber Optics Engineering Physics
 Introduction Fiber optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibers. Fiber optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Introduction Fiber optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibers. Fiber optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
All-Optical Logic Gates Based on Nonlinear Slot Waveguide Couplers
 Title All-Optical Logic Gates Based on No Couplers Author(s) Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanor Citation Journal of the Optical Society of A 23(4): 684-691 Issue Date 2006-04-01 DOI Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/8506
Title All-Optical Logic Gates Based on No Couplers Author(s) Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanor Citation Journal of the Optical Society of A 23(4): 684-691 Issue Date 2006-04-01 DOI Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/8506
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02
 104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
Mode Patterns of Parallel plates &Rectangular wave guides Mr.K.Chandrashekhar, Dr.Girish V Attimarad
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 8, August-2012 1 Mode Patterns of Parallel plates &Rectangular wave guides Mr.K.Chandrashekhar, Dr.Girish V Attimarad Abstract-Parallel
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 8, August-2012 1 Mode Patterns of Parallel plates &Rectangular wave guides Mr.K.Chandrashekhar, Dr.Girish V Attimarad Abstract-Parallel
The waveguide adapter consists of a rectangular part smoothly transcending into an elliptical part as seen in Figure 1.
 Waveguide Adapter Introduction This is a model of an adapter for microwave propagation in the transition between a rectangular and an elliptical waveguide. Such waveguide adapters are designed to keep
Waveguide Adapter Introduction This is a model of an adapter for microwave propagation in the transition between a rectangular and an elliptical waveguide. Such waveguide adapters are designed to keep
Apertureless Near-Field Optical Microscopy
 VI Apertureless Near-Field Optical Microscopy In recent years, several types of apertureless near-field optical microscopes have been developed 1,2,3,4,5,6,7. In such instruments, light scattered from
VI Apertureless Near-Field Optical Microscopy In recent years, several types of apertureless near-field optical microscopes have been developed 1,2,3,4,5,6,7. In such instruments, light scattered from
Tight focus of a radially polarized and amplitudemodulated annular multi-gaussian beam
 Tight focus of a radially polarized and amplitudemodulated annular multi-gaussian beam Chen Jian-Nong( ) a), Xu Qin-Feng( ) a), and Wang Gang( ) b) a) School of Physics, Ludong University, Yantai 26425,
Tight focus of a radially polarized and amplitudemodulated annular multi-gaussian beam Chen Jian-Nong( ) a), Xu Qin-Feng( ) a), and Wang Gang( ) b) a) School of Physics, Ludong University, Yantai 26425,
Ultra-broadband Microwave Metamaterial Absorber
 Ultra-broadband Microwave Metamaterial Absorber Fei Ding 1, Yanxia Cui 1,3, Xiaochen Ge 1, Feng Zhang 1, Yi Jin 1*, and Sailing He 1,2 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory
Ultra-broadband Microwave Metamaterial Absorber Fei Ding 1, Yanxia Cui 1,3, Xiaochen Ge 1, Feng Zhang 1, Yi Jin 1*, and Sailing He 1,2 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory
Terahertz transmission properties of an individual slit in a thin metallic plate
 Terahertz transmission properties of an individual slit in a thin metallic plate J. W. Lee, 1 T. H. Park, 2 Peter Nordlander, 2 and Daniel M. Mittleman 1,* 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Terahertz transmission properties of an individual slit in a thin metallic plate J. W. Lee, 1 T. H. Park, 2 Peter Nordlander, 2 and Daniel M. Mittleman 1,* 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
WHITE PAPER. 50 versus 62.5 micron multimode fiber
 WHITE PAPER 50 versus 62.5 micron multimode fiber www.ixiacom.com 915-6919-01 Rev. A, July 2014 2 Table of Contents What are 50μm fiber and 62.5μm fiber?... 4 Why two standards?... 4 Which technology should
WHITE PAPER 50 versus 62.5 micron multimode fiber www.ixiacom.com 915-6919-01 Rev. A, July 2014 2 Table of Contents What are 50μm fiber and 62.5μm fiber?... 4 Why two standards?... 4 Which technology should
Analysis of Broadband Slot Cut Semi-Circular Microstrip Antennas
 Analysis of Broadband Slot Cut Semi-Circular Microstrip Antennas Amit A. Deshmukh EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Ankita R. Jain EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Apurva A. Joshi EXTC,
Analysis of Broadband Slot Cut Semi-Circular Microstrip Antennas Amit A. Deshmukh EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Ankita R. Jain EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Apurva A. Joshi EXTC,
PHYSICAL METHODS, INSTRUMENTS AND MEASUREMENTS Vol. IV Femtosecond Measurements Combined With Near-Field Optical Microscopy - Artyom A.
 FEMTOSECOND MEASUREMENTS COMBINED WITH NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY Artyom A. Astafiev, Semyonov Institute of Chemical Physics, Moscow, Russian Federation. Keywords: diffraction limit nearfield scanning
FEMTOSECOND MEASUREMENTS COMBINED WITH NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY Artyom A. Astafiev, Semyonov Institute of Chemical Physics, Moscow, Russian Federation. Keywords: diffraction limit nearfield scanning
Copyright 2011 Casa Software Ltd. www.casaxps.com. Centre of Mass
 Centre of Mass A central theme in mathematical modelling is that of reducing complex problems to simpler, and hopefully, equivalent problems for which mathematical analysis is possible. The concept of
Centre of Mass A central theme in mathematical modelling is that of reducing complex problems to simpler, and hopefully, equivalent problems for which mathematical analysis is possible. The concept of
Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment
 Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Axial intensity distribution of lens axicon illuminated by Gaussian-Schell model beam
 46 1, 018003 January 2007 Axial intensity distribution of lens axicon illuminated by Gaussian-Schell model beam Yuan Chen Jixiong Pu Xiaoyun Liu Huaqiao University Department of Electronic Science and
46 1, 018003 January 2007 Axial intensity distribution of lens axicon illuminated by Gaussian-Schell model beam Yuan Chen Jixiong Pu Xiaoyun Liu Huaqiao University Department of Electronic Science and
Fluctuations in airport arrival and departure traffic: A network analysis
 Fluctuations in airport arrival and departure traffic: A network analysis Li Shan-Mei( 李 善 梅 ) a), Xu Xiao-Hao( 徐 肖 豪 ) b), and Meng Ling-Hang( 孟 令 航 ) a) a) School of Computer Science and Technology,
Fluctuations in airport arrival and departure traffic: A network analysis Li Shan-Mei( 李 善 梅 ) a), Xu Xiao-Hao( 徐 肖 豪 ) b), and Meng Ling-Hang( 孟 令 航 ) a) a) School of Computer Science and Technology,
Design of an U-slot Folded Shorted Patch Antenna for RF Energy Harvesting
 Design of an U-slot Folded Shorted Patch Antenna for RF Energy Harvesting Diponkar Kundu, Ahmed Wasif Reza, and Harikrishnan Ramiah Abstract Novel optimized U-slot Folded Shorted Patch Antenna (FSPA) is
Design of an U-slot Folded Shorted Patch Antenna for RF Energy Harvesting Diponkar Kundu, Ahmed Wasif Reza, and Harikrishnan Ramiah Abstract Novel optimized U-slot Folded Shorted Patch Antenna (FSPA) is
SEMICONDUCTOR lasers with optical feedback have
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 34, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1979 Dynamics and Linear Stability Analysis in Semiconductor Lasers with Phase-Conjugate Feedback Atsushi Murakami and Junji Ohtsubo,
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 34, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1979 Dynamics and Linear Stability Analysis in Semiconductor Lasers with Phase-Conjugate Feedback Atsushi Murakami and Junji Ohtsubo,
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
Determination of the relative permittivity of the AlGaN barrier layer in strained AlGaN/GaN heterostructures
 Vol 8 No 9, September 2009 c 2009 Chin. Phys. Soc. 674-056/2009/8(09)/3980-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Determination of the relative permittivity of the AlGaN barrier layer in strained
Vol 8 No 9, September 2009 c 2009 Chin. Phys. Soc. 674-056/2009/8(09)/3980-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Determination of the relative permittivity of the AlGaN barrier layer in strained
Analysis of Electromagnetic Propulsion on a Two-Electric-Dipole System
 Electronics and Communications in Japan, Part 2, Vol. 83, No. 4, 2000 Translated from Denshi Joho Tsushin Gakkai Ronbunshi, Vol. J82-C-I, No. 6, June 1999, pp. 310 317 Analysis of Electromagnetic Propulsion
Electronics and Communications in Japan, Part 2, Vol. 83, No. 4, 2000 Translated from Denshi Joho Tsushin Gakkai Ronbunshi, Vol. J82-C-I, No. 6, June 1999, pp. 310 317 Analysis of Electromagnetic Propulsion
THE INFLUENCE OF SHAPE AND SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF METAL PARTICLES ON THE THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF METAL-POLYMER COMPOSITES
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 6, Issue 12, Dec 2015, pp. 30-35, Article ID: IJMET_06_12_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=6&itype=12
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 6, Issue 12, Dec 2015, pp. 30-35, Article ID: IJMET_06_12_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=6&itype=12
Numerical and experimental study on confinement in Y-shaped post wall branching waveguide
 Mobile Information Systems 10 (2014) 217 228 217 DOI 10.3233/MIS-130183 IOS Press Numerical and experimental study on confinement in Y-shaped post wall branching waveguide Hiroshi Maeda a,, Huili Chen
Mobile Information Systems 10 (2014) 217 228 217 DOI 10.3233/MIS-130183 IOS Press Numerical and experimental study on confinement in Y-shaped post wall branching waveguide Hiroshi Maeda a,, Huili Chen
Broadband THz Generation from Photoconductive Antenna
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 331 Broadband THz Generation from Photoconductive Antenna Qing Chang 1, Dongxiao Yang 1,2, and Liang Wang 1 1 Zhejiang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 331 Broadband THz Generation from Photoconductive Antenna Qing Chang 1, Dongxiao Yang 1,2, and Liang Wang 1 1 Zhejiang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 38, 67 78, 2013
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 38, 67 78, 2013 DESIGN AND INVESTIGATION OF A DUAL-BAND ANNULAR RING SLOT ANTENNA FOR AIRCRAFT APPLICATIONS Li Sun *, Bao-Hua Sun, Guan-Xi Zhang, Dan Cao,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 38, 67 78, 2013 DESIGN AND INVESTIGATION OF A DUAL-BAND ANNULAR RING SLOT ANTENNA FOR AIRCRAFT APPLICATIONS Li Sun *, Bao-Hua Sun, Guan-Xi Zhang, Dan Cao,
Nearfield Glass Slip P probe Pro For Neuroly Imaging
 Near-field scanning optical microscopy using a super-resolution cover glass slip Yu-Hsuan Lin 1,2 and Din Ping Tsai 1,3,4,* 1 Instrument Technology Research Center, National Applied Research Laboratories,
Near-field scanning optical microscopy using a super-resolution cover glass slip Yu-Hsuan Lin 1,2 and Din Ping Tsai 1,3,4,* 1 Instrument Technology Research Center, National Applied Research Laboratories,
Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water
 Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
PIPELINE LEAKAGE DETECTION USING FIBER-OPTIC DISTRIBUTED STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSORS WHITE PAPER
 PIPELINE LEAKAGE DETECTION USING FIBER-OPTIC DISTRIBUTED STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSORS WHITE PAPER Lufan Zou and Taha Landolsi OZ Optics Limited, 219 Westbrook Road, Ottawa, ON, Canada, K0A 1L0 E-mail:
PIPELINE LEAKAGE DETECTION USING FIBER-OPTIC DISTRIBUTED STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSORS WHITE PAPER Lufan Zou and Taha Landolsi OZ Optics Limited, 219 Westbrook Road, Ottawa, ON, Canada, K0A 1L0 E-mail:
CREOL, College of Optics & Photonics, University of Central Florida
 OSE6650 - Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Fall 2013 Class 3 slide 1 Challenge: excite and detect the near field Thus far: Nanostructured materials
OSE6650 - Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Fall 2013 Class 3 slide 1 Challenge: excite and detect the near field Thus far: Nanostructured materials
Finite Difference Time Domain and BPM: Flexible Algorithm Selection Technology
 Finite Difference Time Domain and BPM: Flexible Algorithm Selection Technology 1. Introduction This application note shows the use of the Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) module in the calculation
Finite Difference Time Domain and BPM: Flexible Algorithm Selection Technology 1. Introduction This application note shows the use of the Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) module in the calculation
Near-field optics and plasmonics
 Near-field optics and plasmonics Manuel Rodrigues Gonçalves AFM topography 10 Pol. y / (µm) 8 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 x / (µm) 8 10 nm 60 80 100 120 140 Physik M. Sc. Master Advanced Materials Winter semester
Near-field optics and plasmonics Manuel Rodrigues Gonçalves AFM topography 10 Pol. y / (µm) 8 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 x / (µm) 8 10 nm 60 80 100 120 140 Physik M. Sc. Master Advanced Materials Winter semester
Pillbox Antenna for 5.6 GHz Band Dragoslav Dobričić, YU1AW dragan@antennex.com
 Pillbox Antenna for 5.6 GHz Band Dragoslav Dobričić, YU1AW dragan@antennex.com Introduction The pillbox or cheese antenna is made of two parallel plates which are connected to the narrow strip of parabolic
Pillbox Antenna for 5.6 GHz Band Dragoslav Dobričić, YU1AW dragan@antennex.com Introduction The pillbox or cheese antenna is made of two parallel plates which are connected to the narrow strip of parabolic
Tunable fiber polarizing filter based on a single-hole-infiltrated polarization maintaining photonic crystal fiber
 Tunable fiber polarizing filter based on a single-hole-infiltrated polarization maintaining photonic crystal fiber Junqi Guo, 1 Yan-ge Liu, 1,* Zhi Wang, 1 Tingting Han, 2 Wei Huang, 1 and Mingming Luo
Tunable fiber polarizing filter based on a single-hole-infiltrated polarization maintaining photonic crystal fiber Junqi Guo, 1 Yan-ge Liu, 1,* Zhi Wang, 1 Tingting Han, 2 Wei Huang, 1 and Mingming Luo
Algebra 2 Chapter 1 Vocabulary. identity - A statement that equates two equivalent expressions.
 Chapter 1 Vocabulary identity - A statement that equates two equivalent expressions. verbal model- A word equation that represents a real-life problem. algebraic expression - An expression with variables.
Chapter 1 Vocabulary identity - A statement that equates two equivalent expressions. verbal model- A word equation that represents a real-life problem. algebraic expression - An expression with variables.
4.4 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS 4.5 WAVE PROPERTIES HW/Study Packet
 4.4 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS 4.5 WAVE PROPERTIES HW/Study Packet Required: READ Hamper pp 115-134 SL/HL Supplemental: Cutnell and Johnson, pp 473-477, 507-513 Tsokos, pp 216-242 REMEMBER TO. Work through all
4.4 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS 4.5 WAVE PROPERTIES HW/Study Packet Required: READ Hamper pp 115-134 SL/HL Supplemental: Cutnell and Johnson, pp 473-477, 507-513 Tsokos, pp 216-242 REMEMBER TO. Work through all
Mechanical Analysis of Crossbeam in a Gantry Machine Tool and its Deformation Compensation
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 213-218 213 Open Access Mechanical Analysis of Crossbeam in a Gantry Machine Tool and its Deformation
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 213-218 213 Open Access Mechanical Analysis of Crossbeam in a Gantry Machine Tool and its Deformation
Influence of limited-view scanning on depth imaging of photoacoustic tomography
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 1, No. 1 (1) 131 Influence of limited-view scanning on depth imaging of photoacoustic tomography Wu Dan( ) a), Tao Chao( ) a), Liu Xiao-Jun( ) a), and Wang Xue-Ding( ) b) a) Key Laboratory
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 1, No. 1 (1) 131 Influence of limited-view scanning on depth imaging of photoacoustic tomography Wu Dan( ) a), Tao Chao( ) a), Liu Xiao-Jun( ) a), and Wang Xue-Ding( ) b) a) Key Laboratory
Optical Microscopy Beyond the Diffraction Limit: Imaging Guided and Propagating Fields
 Optical Microscopy Beyond the Diffraction Limit: Imaging Guided and Propagating Fields M. Selim Ünlü, Bennett B. Goldberg, and Stephen B. Ippolito Boston University Department of Electrical and Computer
Optical Microscopy Beyond the Diffraction Limit: Imaging Guided and Propagating Fields M. Selim Ünlü, Bennett B. Goldberg, and Stephen B. Ippolito Boston University Department of Electrical and Computer
Simple and scalable fabrication approaches of Nanophotonic structures for PV
 Simple and scalable fabrication approaches of Nanophotonic structures for PV Fabien Sorin Surface du Verre et Interfaces (SVI), UMR 125 CNRS/Saint-Gobain, 39, Quai Lucien Lefranc, 93303 Aubervilliers,
Simple and scalable fabrication approaches of Nanophotonic structures for PV Fabien Sorin Surface du Verre et Interfaces (SVI), UMR 125 CNRS/Saint-Gobain, 39, Quai Lucien Lefranc, 93303 Aubervilliers,
Vibrations of a Free-Free Beam
 Vibrations of a Free-Free Beam he bending vibrations of a beam are described by the following equation: y EI x y t 4 2 + ρ A 4 2 (1) y x L E, I, ρ, A are respectively the Young Modulus, second moment of
Vibrations of a Free-Free Beam he bending vibrations of a beam are described by the following equation: y EI x y t 4 2 + ρ A 4 2 (1) y x L E, I, ρ, A are respectively the Young Modulus, second moment of
Copyright 1996 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 1996
 Copyright 1996 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 1996 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
Copyright 1996 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 1996 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
From apertureless near-field optical microscopy to infrared near-field night vision
 From apertureless near-field optical microscopy to infrared near-field night vision Yannick DE WILDE ESPCI Laboratoire d Optique Physique UPR A0005-CNRS, PARIS dewilde@optique.espci.fr From apertureless
From apertureless near-field optical microscopy to infrared near-field night vision Yannick DE WILDE ESPCI Laboratoire d Optique Physique UPR A0005-CNRS, PARIS dewilde@optique.espci.fr From apertureless
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope
 Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
Advances in Oxide-Confined Vertical Cavity Lasers. Photonics Research Department. Albuquerque, NM 87 185. (505)844-7287 phone (505)844-8985 FAX
 I Advances in Oxide-Confined Vertical Cavity Lasers Kent D. Choquette, R. P. Schneider, Jr., K. L, Lear, K. M. 6gsC;. H. Q. Hou, H. C. Chui, M. Hagerott Crawford, and W. W. C 7 -. h I4 k#&j Photonics Research
I Advances in Oxide-Confined Vertical Cavity Lasers Kent D. Choquette, R. P. Schneider, Jr., K. L, Lear, K. M. 6gsC;. H. Q. Hou, H. C. Chui, M. Hagerott Crawford, and W. W. C 7 -. h I4 k#&j Photonics Research
Procedure: Geometrical Optics. Theory Refer to your Lab Manual, pages 291 294. Equipment Needed
 Theory Refer to your Lab Manual, pages 291 294. Geometrical Optics Equipment Needed Light Source Ray Table and Base Three-surface Mirror Convex Lens Ruler Optics Bench Cylindrical Lens Concave Lens Rhombus
Theory Refer to your Lab Manual, pages 291 294. Geometrical Optics Equipment Needed Light Source Ray Table and Base Three-surface Mirror Convex Lens Ruler Optics Bench Cylindrical Lens Concave Lens Rhombus
The plasmoelectric effect: optically induced electrochemical potentials in resonant metallic structures
 The plasmoelectric effect: optically induced electrochemical potentials in resonant metallic structures Matthew T. Sheldon and Harry A. Atwater Thomas J. Watson Laboratories of Applied Physics, California
The plasmoelectric effect: optically induced electrochemical potentials in resonant metallic structures Matthew T. Sheldon and Harry A. Atwater Thomas J. Watson Laboratories of Applied Physics, California
Consequence for a dualband application
 rel. bandwidth -6dB [%] DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR INTEGRATED MOBILE PHONE ANTENNAS D. Manteuffel, A. Bahr, D. Heberling, I. Wolff IMST GmbH, Germany, e-mail: manteuffel@imst.de Abstract Based on the investigation
rel. bandwidth -6dB [%] DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR INTEGRATED MOBILE PHONE ANTENNAS D. Manteuffel, A. Bahr, D. Heberling, I. Wolff IMST GmbH, Germany, e-mail: manteuffel@imst.de Abstract Based on the investigation
How To Write An Analysis System For Bridge Test
 Study of Analysis System for Bridge Test Chen Ke, Lu Jian-Ming, Research Institute of Highway, 100088, Beijing, China (chenkezi@163.com, lujianming@263.net) Summary Analysis System for Bridge Test (Chinese
Study of Analysis System for Bridge Test Chen Ke, Lu Jian-Ming, Research Institute of Highway, 100088, Beijing, China (chenkezi@163.com, lujianming@263.net) Summary Analysis System for Bridge Test (Chinese
Refractive Index Measurement Principle
 Refractive Index Measurement Principle Refractive index measurement principle Introduction Detection of liquid concentrations by optical means was already known in antiquity. The law of refraction was
Refractive Index Measurement Principle Refractive index measurement principle Introduction Detection of liquid concentrations by optical means was already known in antiquity. The law of refraction was
Experimental retrieval of the effective parameters of metamaterials based on a waveguide method
 Experimental retrieval of the effective parameters of metamaterials based on a waveguide method Hongsheng Chen 1,3, Jingjing Zhang 1,, Yang Bai 4, Yu Luo 1,, Lixin Ran 1,, Qin Jiang 1, and Jin Au Kong
Experimental retrieval of the effective parameters of metamaterials based on a waveguide method Hongsheng Chen 1,3, Jingjing Zhang 1,, Yang Bai 4, Yu Luo 1,, Lixin Ran 1,, Qin Jiang 1, and Jin Au Kong
Boom Influence on Yagi Antenna Dragoslav Dobričić, YU1AW (Serbia) dragan@antennex.com
 Boom Influence on Yagi Antenna Dragoslav Dobričić, YU1AW (Serbia) dragan@antennex.com Introduction T he boom of the Yagi antenna is an inevitable part of its construction. Theoretically, Yagi antennas
Boom Influence on Yagi Antenna Dragoslav Dobričić, YU1AW (Serbia) dragan@antennex.com Introduction T he boom of the Yagi antenna is an inevitable part of its construction. Theoretically, Yagi antennas
Monochromatic electromagnetic fields with maximum focal energy density
 Moore et al. Vol. 4, No. 10 /October 007 /J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 3115 Monochromatic electromagnetic fields with maximum focal energy density Nicole J. Moore, 1, * Miguel A. Alonso, 1 and Colin J. R. Sheppard,3
Moore et al. Vol. 4, No. 10 /October 007 /J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 3115 Monochromatic electromagnetic fields with maximum focal energy density Nicole J. Moore, 1, * Miguel A. Alonso, 1 and Colin J. R. Sheppard,3
Theremino System Theremino Spectrometer Technology
 Theremino System Theremino Spectrometer Technology theremino System - Theremino Spectrometer Technology - August 15, 2014 - Page 1 Operation principles By placing a digital camera with a diffraction grating
Theremino System Theremino Spectrometer Technology theremino System - Theremino Spectrometer Technology - August 15, 2014 - Page 1 Operation principles By placing a digital camera with a diffraction grating
Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
Experimental realization of a broadband illusion optics device
 Experimental realization of a broadband illusion optics device Chao Li, Xiankun Meng, Xiao Liu, Fang Li, Guangyou Fang Key Laboratory of Microwave and Electromagnetic adiation, Institute of Electronics,
Experimental realization of a broadband illusion optics device Chao Li, Xiankun Meng, Xiao Liu, Fang Li, Guangyou Fang Key Laboratory of Microwave and Electromagnetic adiation, Institute of Electronics,
A Strategy for Teaching Finite Element Analysis to Undergraduate Students
 A Strategy for Teaching Finite Element Analysis to Undergraduate Students Gordon Smyrell, School of Computing and Mathematics, University of Teesside The analytical power and design flexibility offered
A Strategy for Teaching Finite Element Analysis to Undergraduate Students Gordon Smyrell, School of Computing and Mathematics, University of Teesside The analytical power and design flexibility offered
A PRACTICAL MINIATURIZED U-SLOT PATCH ANTENNA WITH ENHANCED BANDWIDTH
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 3, 47 62, 2008 A PRACTICAL MINIATURIZED U-SLOT PATCH ANTENNA WITH ENHANCED BANDWIDTH G. F. Khodaei, J. Nourinia, and C. Ghobadi Electrical Engineering Department
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 3, 47 62, 2008 A PRACTICAL MINIATURIZED U-SLOT PATCH ANTENNA WITH ENHANCED BANDWIDTH G. F. Khodaei, J. Nourinia, and C. Ghobadi Electrical Engineering Department
ME 111: Engineering Drawing
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture # 14 (10/10/2011) Development of Surfaces http://www.iitg.ernet.in/arindam.dey/me111.htm http://www.iitg.ernet.in/rkbc/me111.htm http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~psr/ Indian
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture # 14 (10/10/2011) Development of Surfaces http://www.iitg.ernet.in/arindam.dey/me111.htm http://www.iitg.ernet.in/rkbc/me111.htm http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~psr/ Indian
Energy and material efficient non-circular bore Bitter magnets. A. Akhmeteli 1, A.V. Gavrilin 2
 Energy and material efficient non-circular bore Bitter magnets A. Akhmeteli 1, A.V. Gavrilin 2 Abstract There exist a number of experiments/applications where the second dimension of the bore of Bitter
Energy and material efficient non-circular bore Bitter magnets A. Akhmeteli 1, A.V. Gavrilin 2 Abstract There exist a number of experiments/applications where the second dimension of the bore of Bitter
Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV
 Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Various Technics of Liquids and Solids Level Measurements. (Part 3)
 (Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
(Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
Apertureless Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy Using Heterodyne Detection Method
 Proceedings of the XIth International Congress and Exposition June -5, 8 Orlando, Florida USA 8 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc Apertureless Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy Using Heterodyne
Proceedings of the XIth International Congress and Exposition June -5, 8 Orlando, Florida USA 8 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc Apertureless Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy Using Heterodyne
Theory of probing a photonic crystal with transmission near-field optical microscopy
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 58, NUMBER 4 15 JULY 1998-II Theory of probing a photonic crystal with transmission near-field optical microscopy Garnett W. Bryant, Eric L. Shirley, and Lori S. Goldner National
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 58, NUMBER 4 15 JULY 1998-II Theory of probing a photonic crystal with transmission near-field optical microscopy Garnett W. Bryant, Eric L. Shirley, and Lori S. Goldner National
Instytut Fizyki Doświadczalnej Wydział Matematyki, Fizyki i Informatyki UNIWERSYTET GDAŃSKI
 Instytut Fizyki Doświadczalnej Wydział Matematyki, Fizyki i Informatyki UNIWERSYTET GDAŃSKI I. Background theory. 1. Electromagnetic waves and their properties. 2. Polarisation of light: a) unpolarised
Instytut Fizyki Doświadczalnej Wydział Matematyki, Fizyki i Informatyki UNIWERSYTET GDAŃSKI I. Background theory. 1. Electromagnetic waves and their properties. 2. Polarisation of light: a) unpolarised
Recent developments in high bandwidth optical interconnects. Brian Corbett. www.tyndall.ie
 Recent developments in high bandwidth optical interconnects Brian Corbett Outline Introduction to photonics for interconnections Polymeric waveguides and the Firefly project Silicon on insulator (SOI)
Recent developments in high bandwidth optical interconnects Brian Corbett Outline Introduction to photonics for interconnections Polymeric waveguides and the Firefly project Silicon on insulator (SOI)
EM Noise Mitigation in Circuit Boards and Cavities
 EM Noise Mitigation in Circuit Boards and Cavities Faculty (UMD): Omar M. Ramahi, Neil Goldsman and John Rodgers Visiting Professors (Finland): Fad Seydou Graduate Students (UMD): Xin Wu, Lin Li, Baharak
EM Noise Mitigation in Circuit Boards and Cavities Faculty (UMD): Omar M. Ramahi, Neil Goldsman and John Rodgers Visiting Professors (Finland): Fad Seydou Graduate Students (UMD): Xin Wu, Lin Li, Baharak
Design of 2D waveguide networks for the study of fundamental properties of Quantum Graphs
 Design of 2D waveguide networks for the study of fundamental properties of Quantum Graphs Introduction: what is a quantum graph? Areas of application of quantum graphs Motivation of our experiment Experimental
Design of 2D waveguide networks for the study of fundamental properties of Quantum Graphs Introduction: what is a quantum graph? Areas of application of quantum graphs Motivation of our experiment Experimental
A Simple Fiber Optic displacement Sensor for Measurement of Light Intensity with the Displacement
 A Simple Fiber Optic displacement Sensor for Measurement of Light Intensity with the Displacement Trilochan patra Assistant professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Techno India
A Simple Fiber Optic displacement Sensor for Measurement of Light Intensity with the Displacement Trilochan patra Assistant professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Techno India
Planar Inter Digital Capacitors on Printed Circuit Board
 1 Planar Inter Digital Capacitors on Printed Circuit Board Ajayan K.R., K.J.Vinoy Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India 561 Email {ajayanr jvinoy}
1 Planar Inter Digital Capacitors on Printed Circuit Board Ajayan K.R., K.J.Vinoy Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India 561 Email {ajayanr jvinoy}
The Design and Application of Water Jet Propulsion Boat Weibo Song, Junhai Jiang3, a, Shuping Zhao, Kaiyan Zhu, Qihua Wang
 International Conference on Automation, Mechanical Control and Computational Engineering (AMCCE 2015) The Design and Application of Water Jet Propulsion Boat Weibo Song, Junhai Jiang3, a, Shuping Zhao,
International Conference on Automation, Mechanical Control and Computational Engineering (AMCCE 2015) The Design and Application of Water Jet Propulsion Boat Weibo Song, Junhai Jiang3, a, Shuping Zhao,
CONDENSED MATTER RAPID COMMUNICATIONS
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B CONDENSED MATTER THIRD SERIES, VOLUME 55, NUMBER 14 1 APRIL 1997-II RAPID COMMUNICATIONS Rapid Communications are intended for the accelerated publication of important new results and
PHYSICAL REVIEW B CONDENSED MATTER THIRD SERIES, VOLUME 55, NUMBER 14 1 APRIL 1997-II RAPID COMMUNICATIONS Rapid Communications are intended for the accelerated publication of important new results and
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscope Characterisation of Microstructured Optical Fibre Devices.
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscope Characterisation of Microstructured Optical Fibre Devices. Christopher Wyndham John Hillman Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscope Characterisation of Microstructured Optical Fibre Devices. Christopher Wyndham John Hillman Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Lecture 10: TEM, TE, and TM Modes for Waveguides. Rectangular Waveguide.
 Whites, EE 481/581 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 10: TEM, TE, and TM Modes for Waveguides. Rectangular Waveguide. We will now generalie our discussion of transmission lines by considering EM waveguides.
Whites, EE 481/581 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 10: TEM, TE, and TM Modes for Waveguides. Rectangular Waveguide. We will now generalie our discussion of transmission lines by considering EM waveguides.
A Network Simulation Experiment of WAN Based on OPNET
 A Network Simulation Experiment of WAN Based on OPNET 1 Yao Lin, 2 Zhang Bo, 3 Liu Puyu 1, Modern Education Technology Center, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning, China,yaolin111@sina.com *2
A Network Simulation Experiment of WAN Based on OPNET 1 Yao Lin, 2 Zhang Bo, 3 Liu Puyu 1, Modern Education Technology Center, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning, China,yaolin111@sina.com *2
